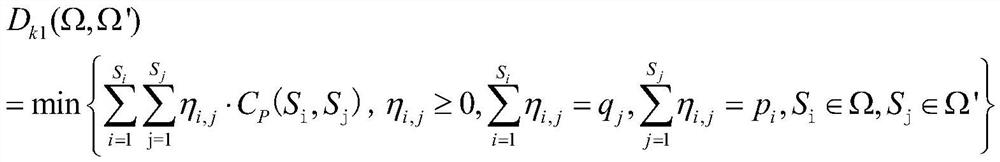Patents
Literature
49 results about "Irrigation scheduling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Irrigation scheduling is the process used by irrigation system managers to determine the correct frequency and duration of watering.
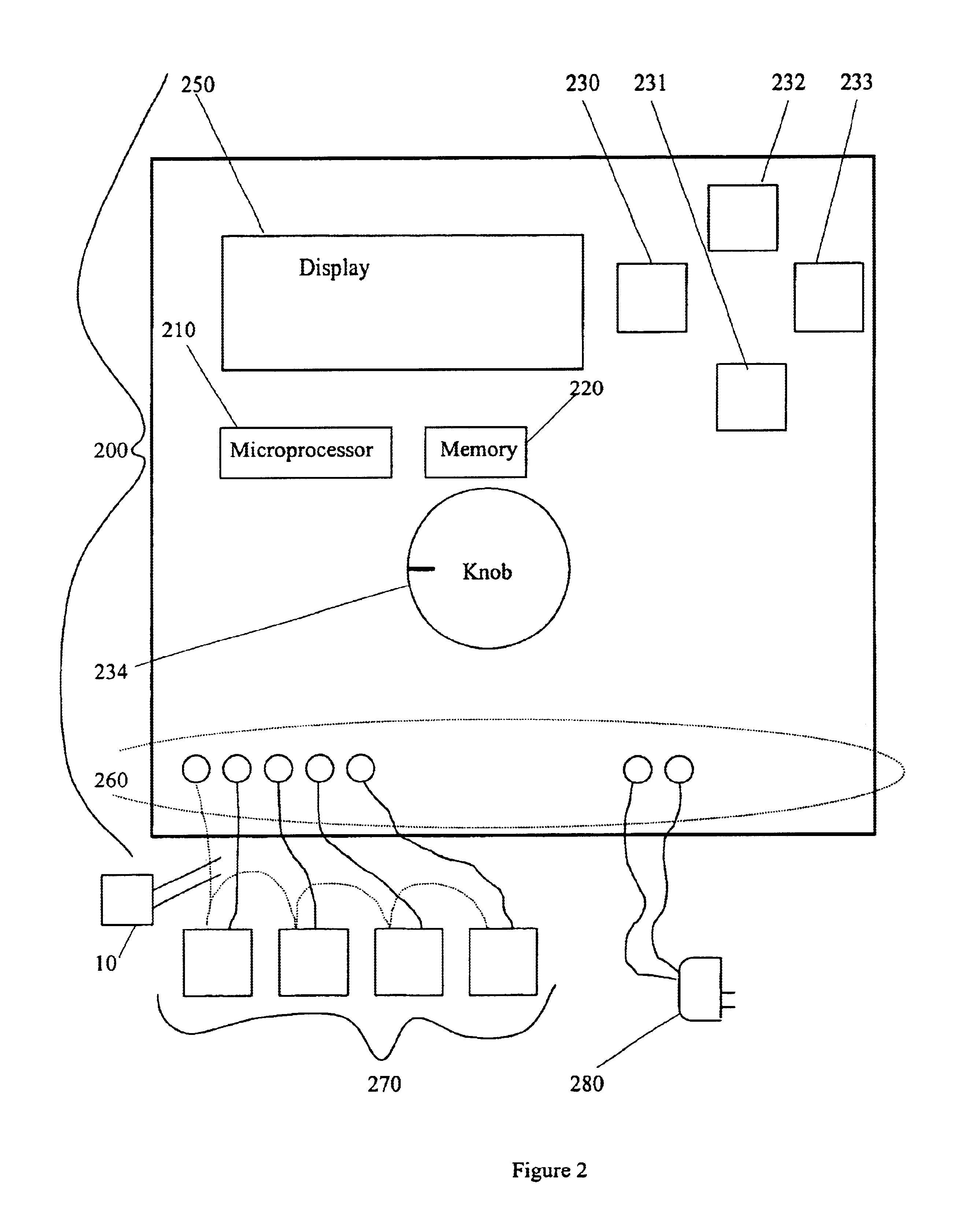
Device that modifies irrigation schedules of existing irrigation controllers
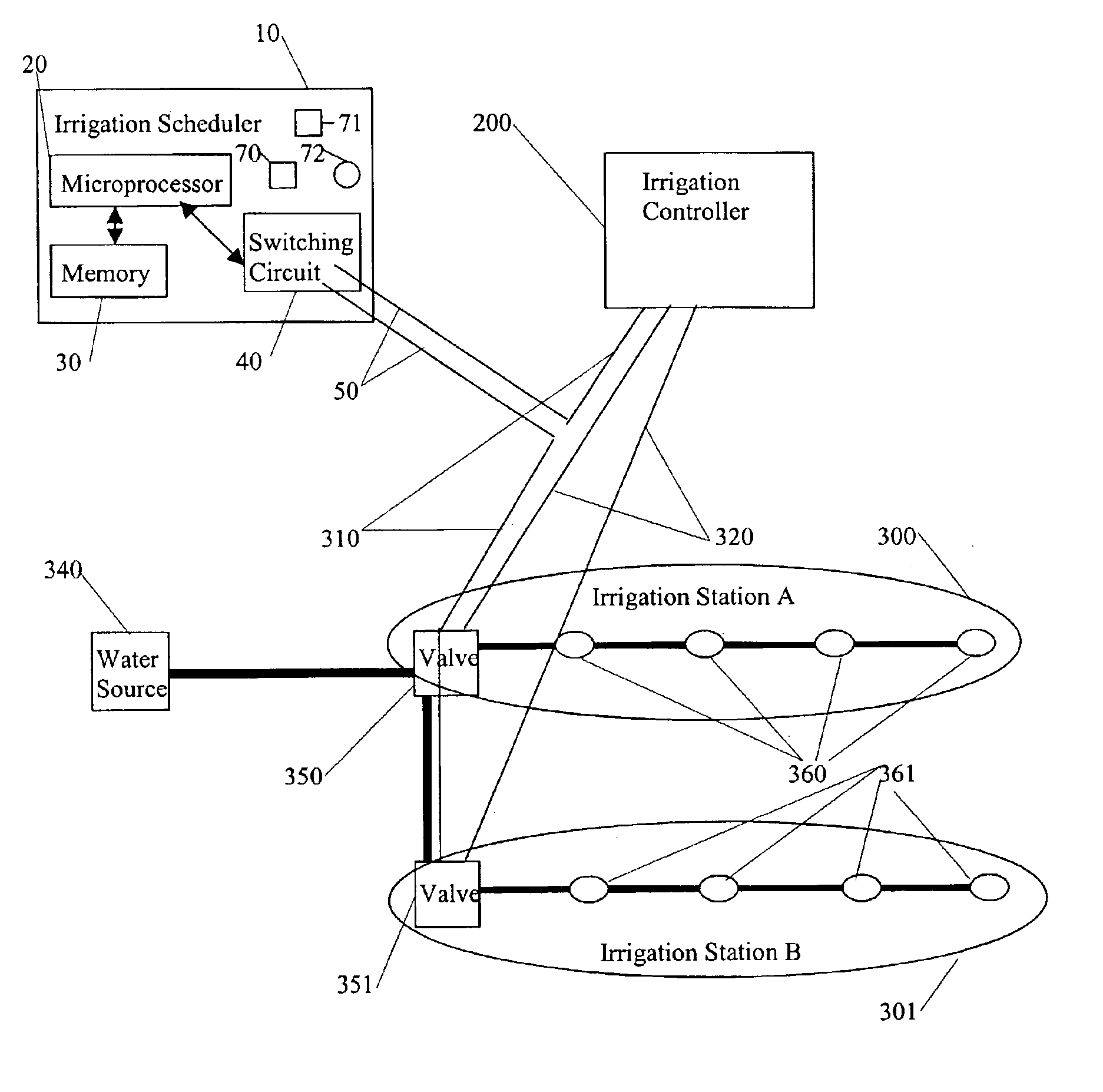
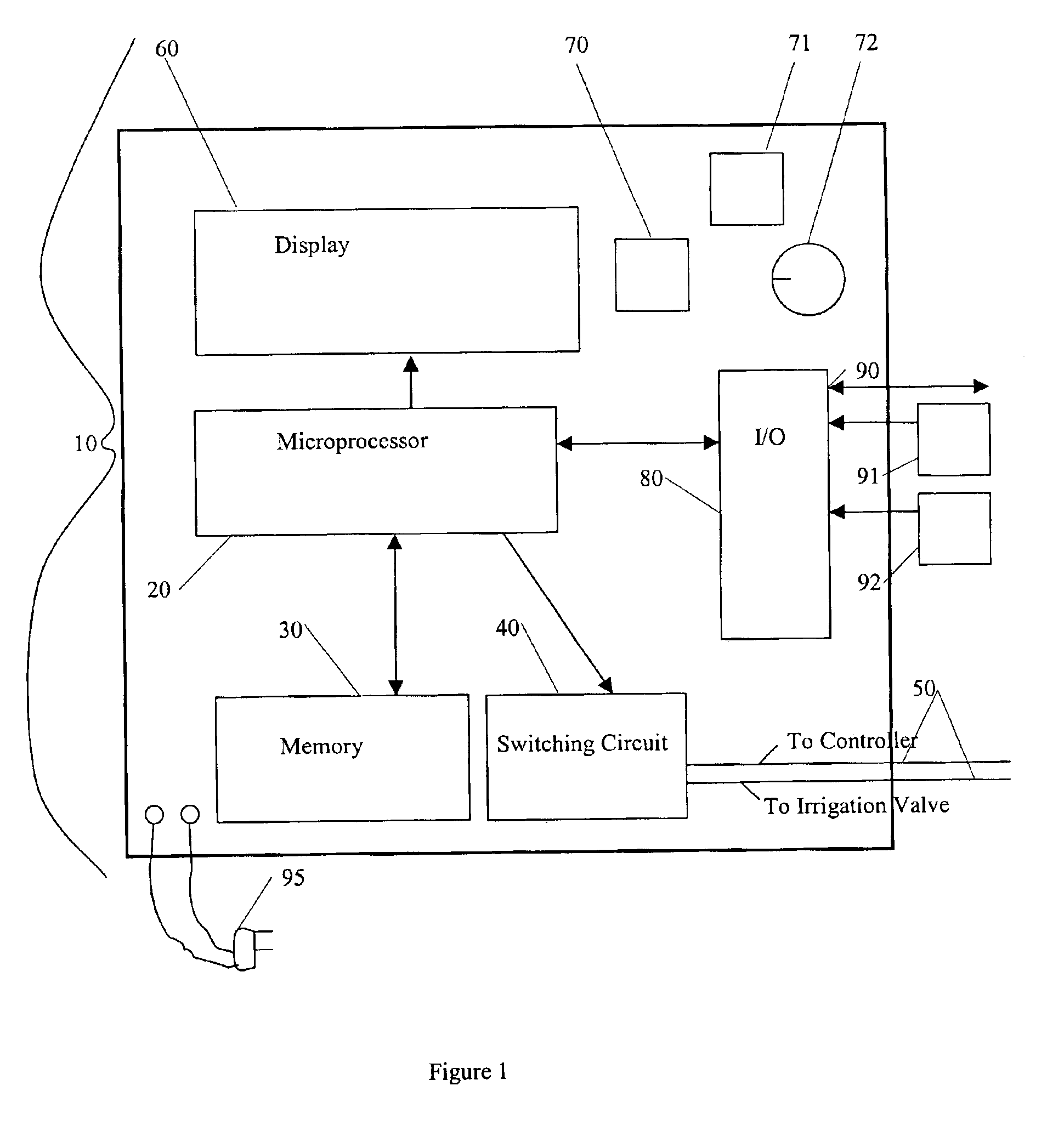
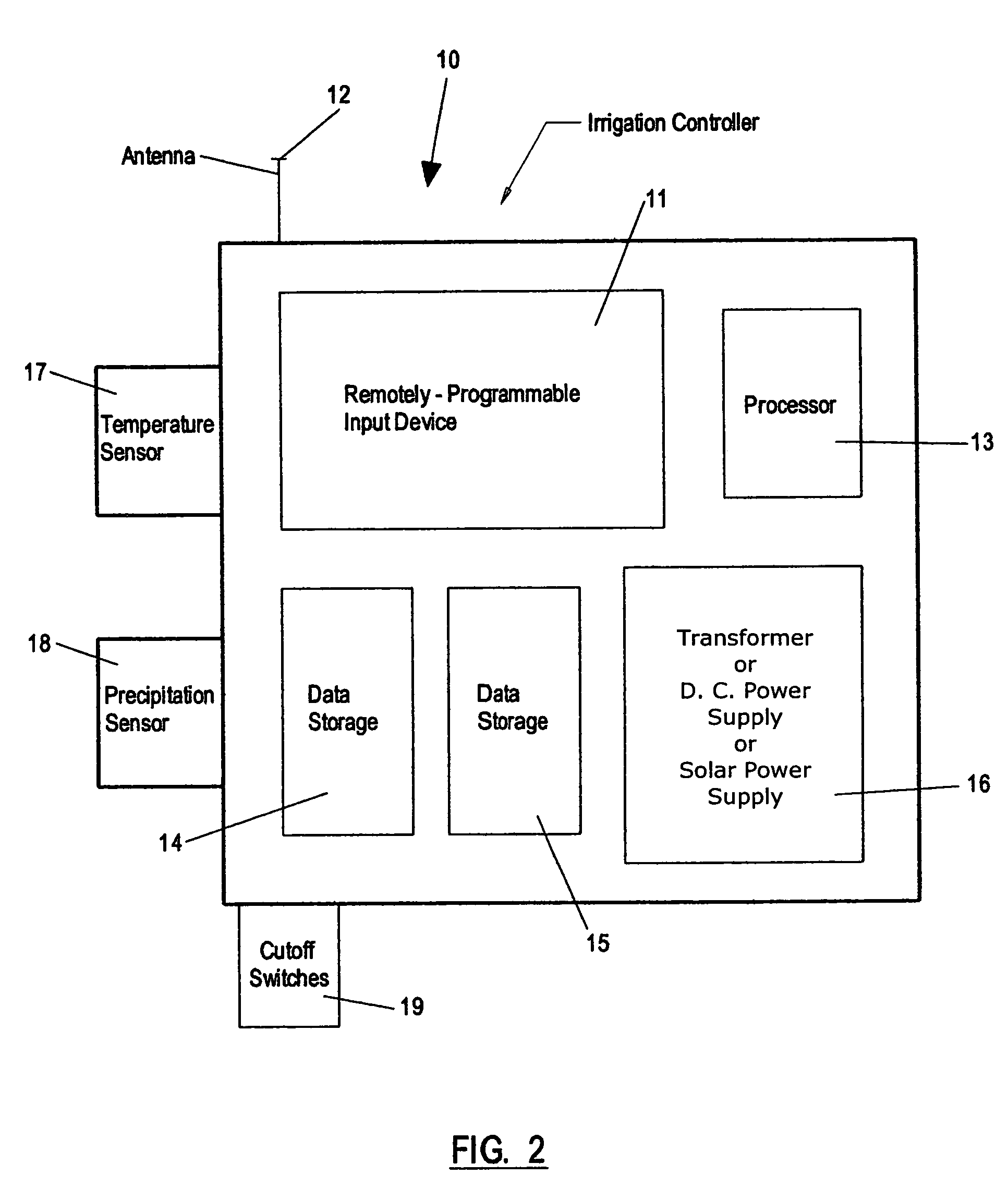
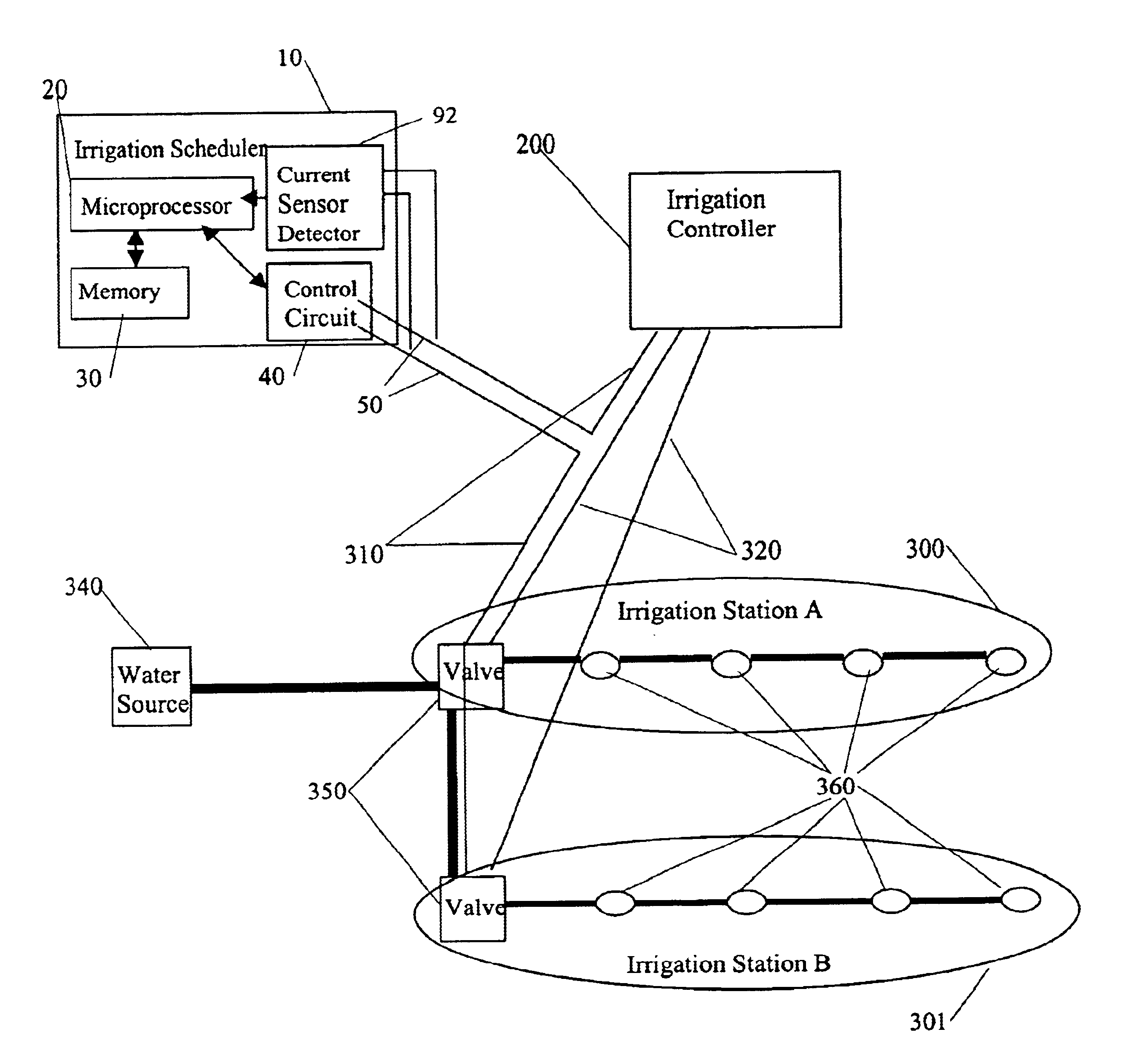
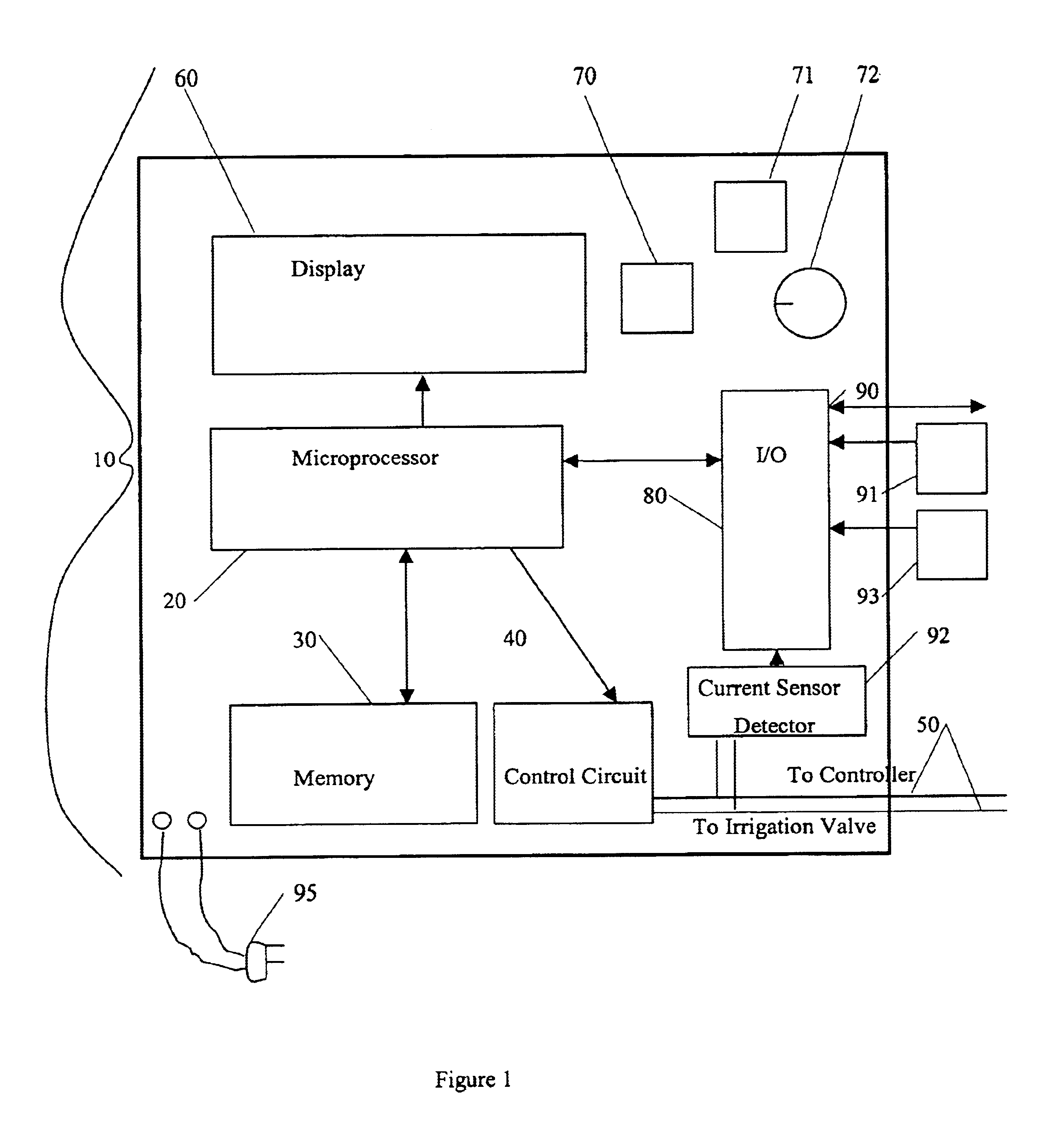
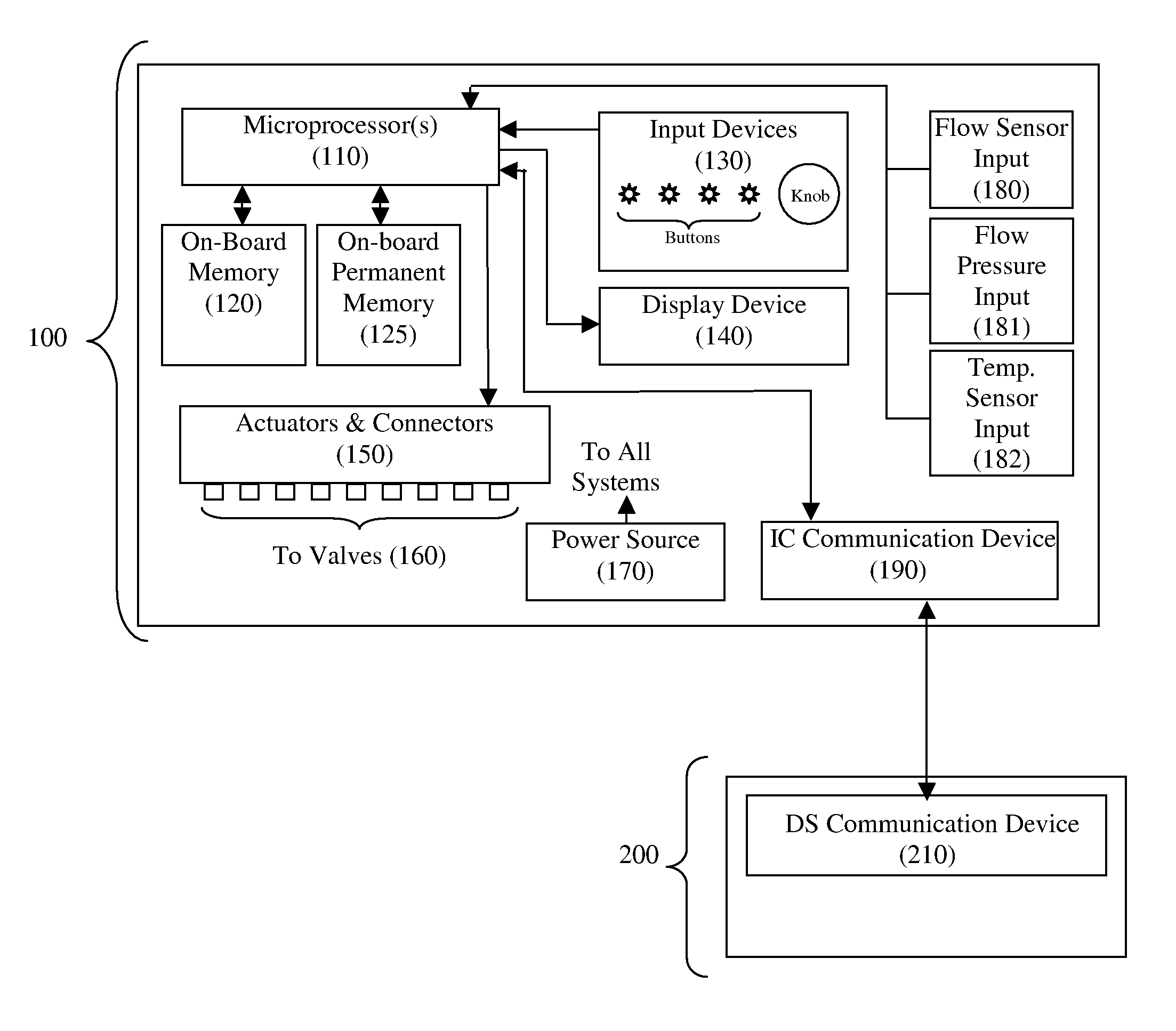
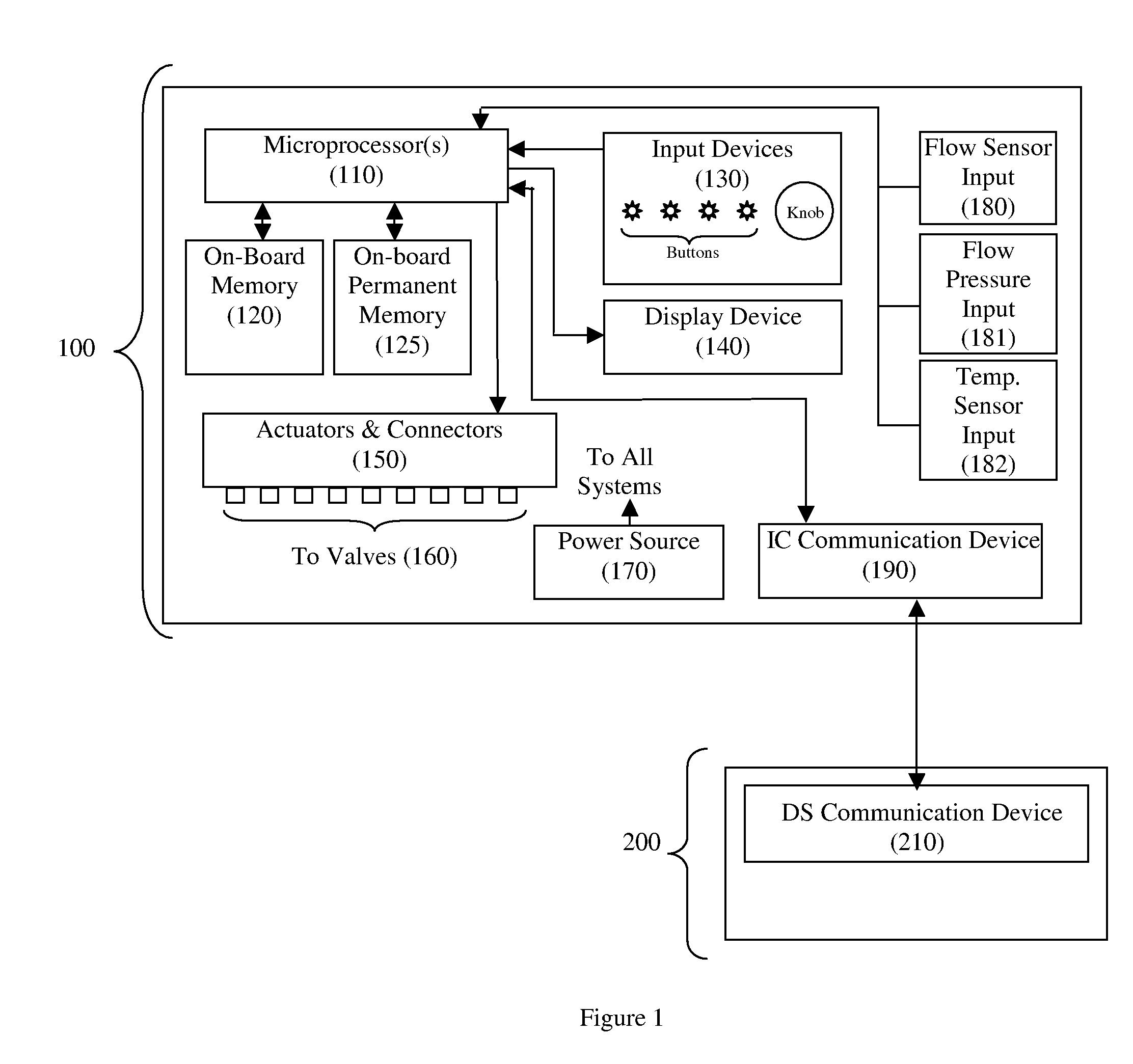
The present invention provides an irrigation control system in which a device (irrigation scheduler) automatically modifies irrigation schedules of installed irrigation controllers to affect irrigating of the landscape based on the water requirements of the landscape plants and comprises: providing an irrigation controller programmed to execute irrigations on watering days by closing an electrical circuit connecting the controller and at least one irrigation valve; providing an irrigation scheduler programmed to execute irrigations on substantially equivalent watering days as the irrigation controller; and the irrigation scheduler selectively interrupting the electrical circuit to control the execution of irrigations on watering days. Preferably the microprocessor uses either an ETo value or weather data used in calculating the ETo value to at least partially derive the improved irrigation schedule.
Owner:AQUA CONSERVATION SYST +1
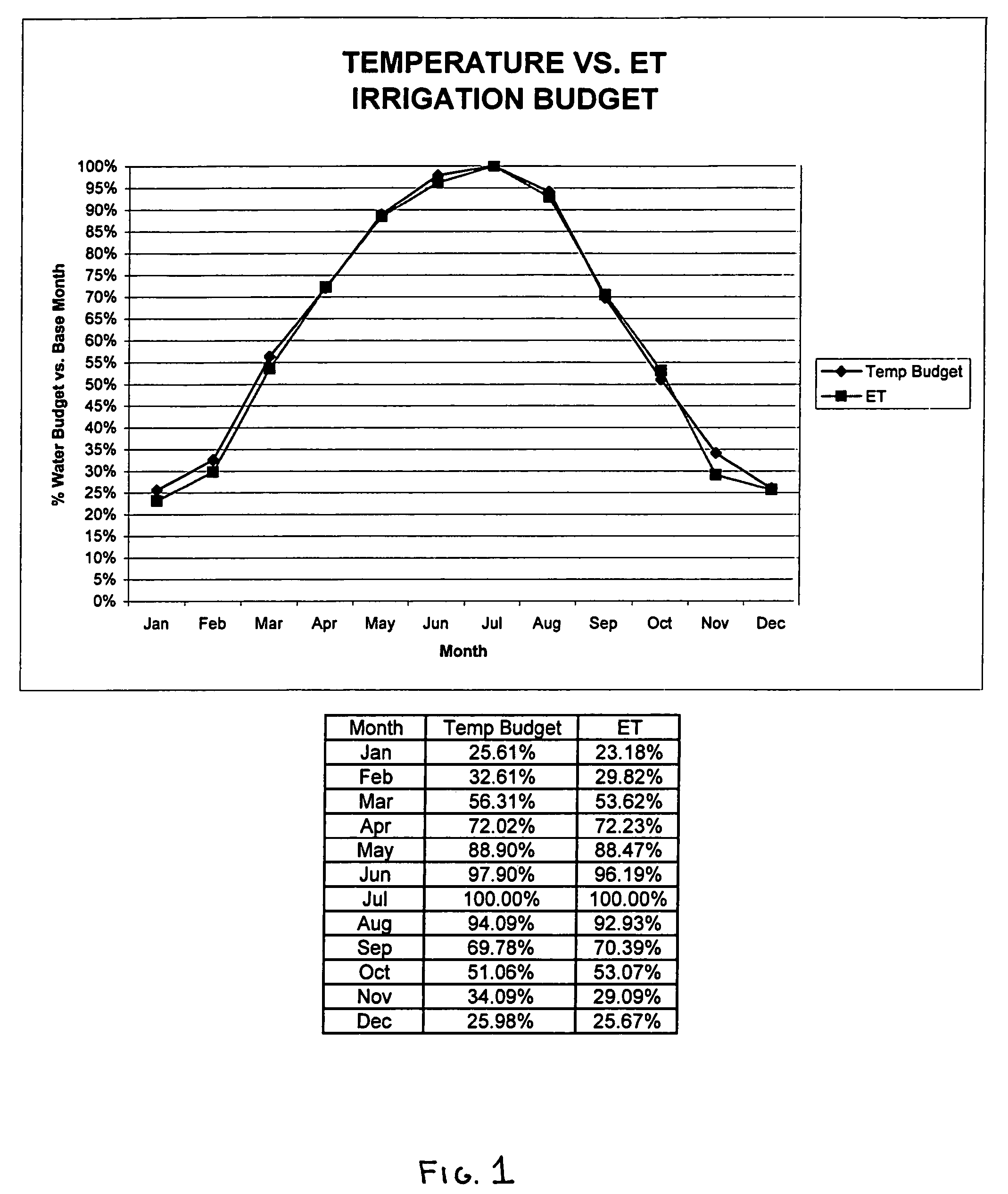
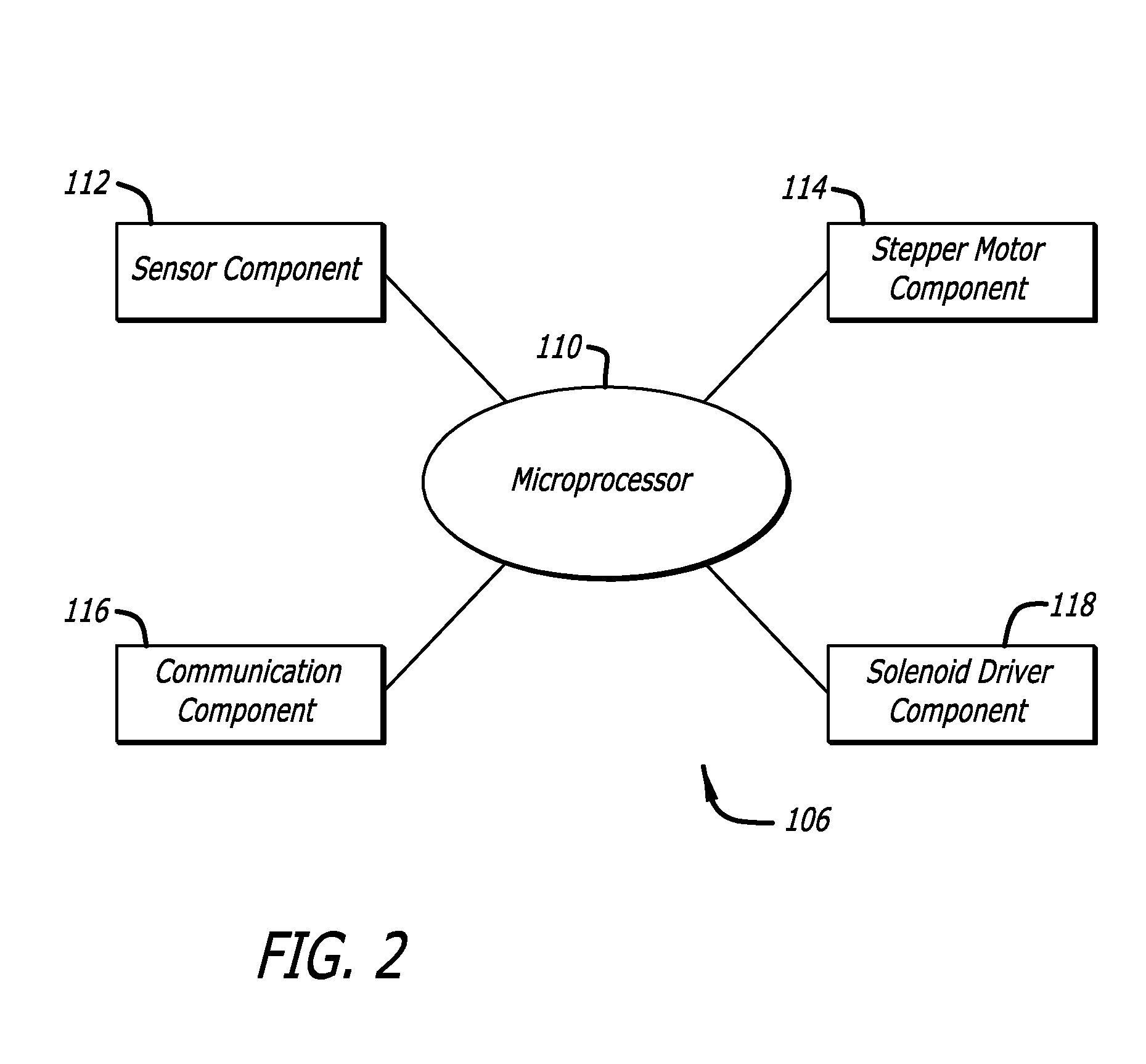
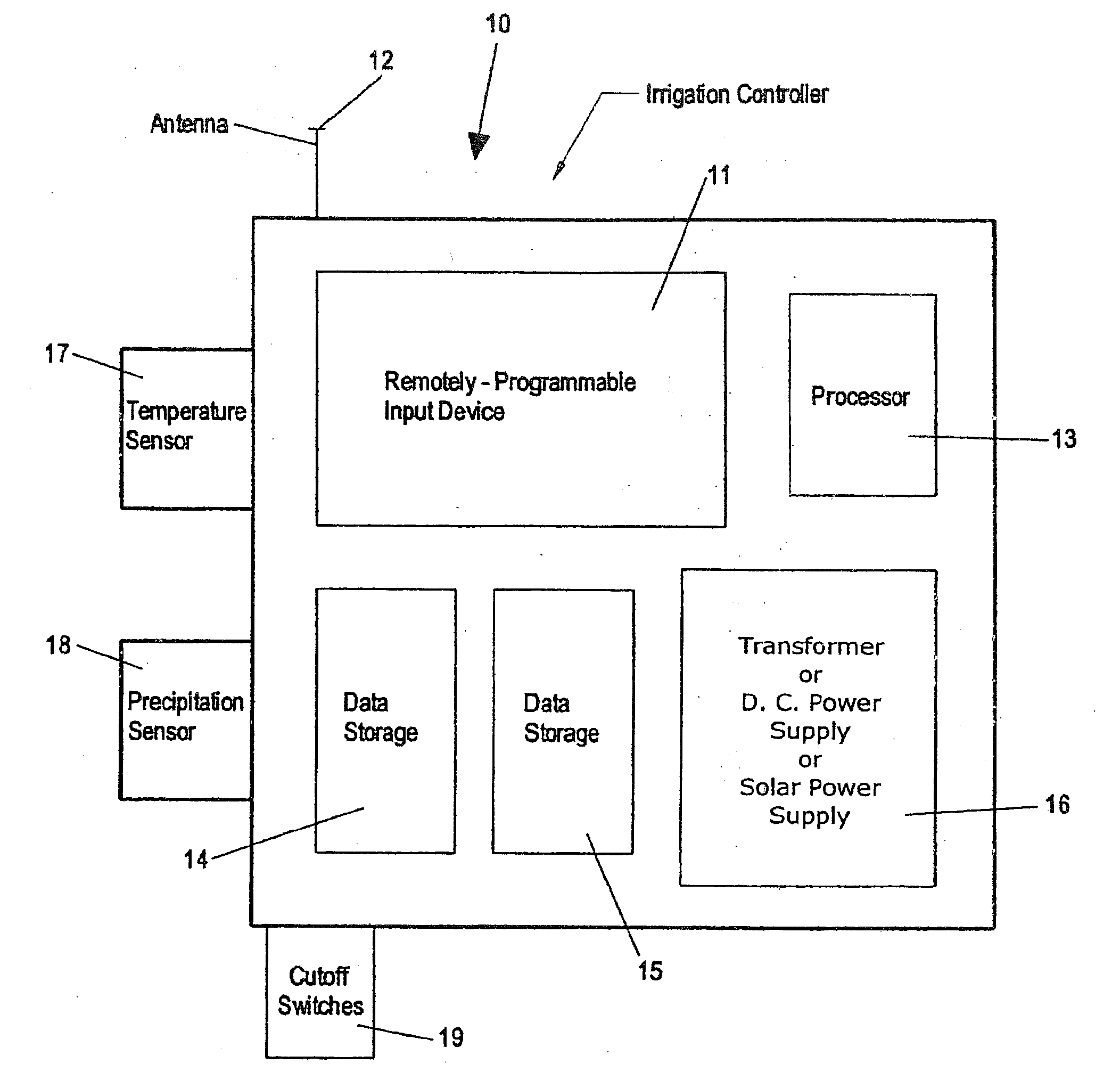
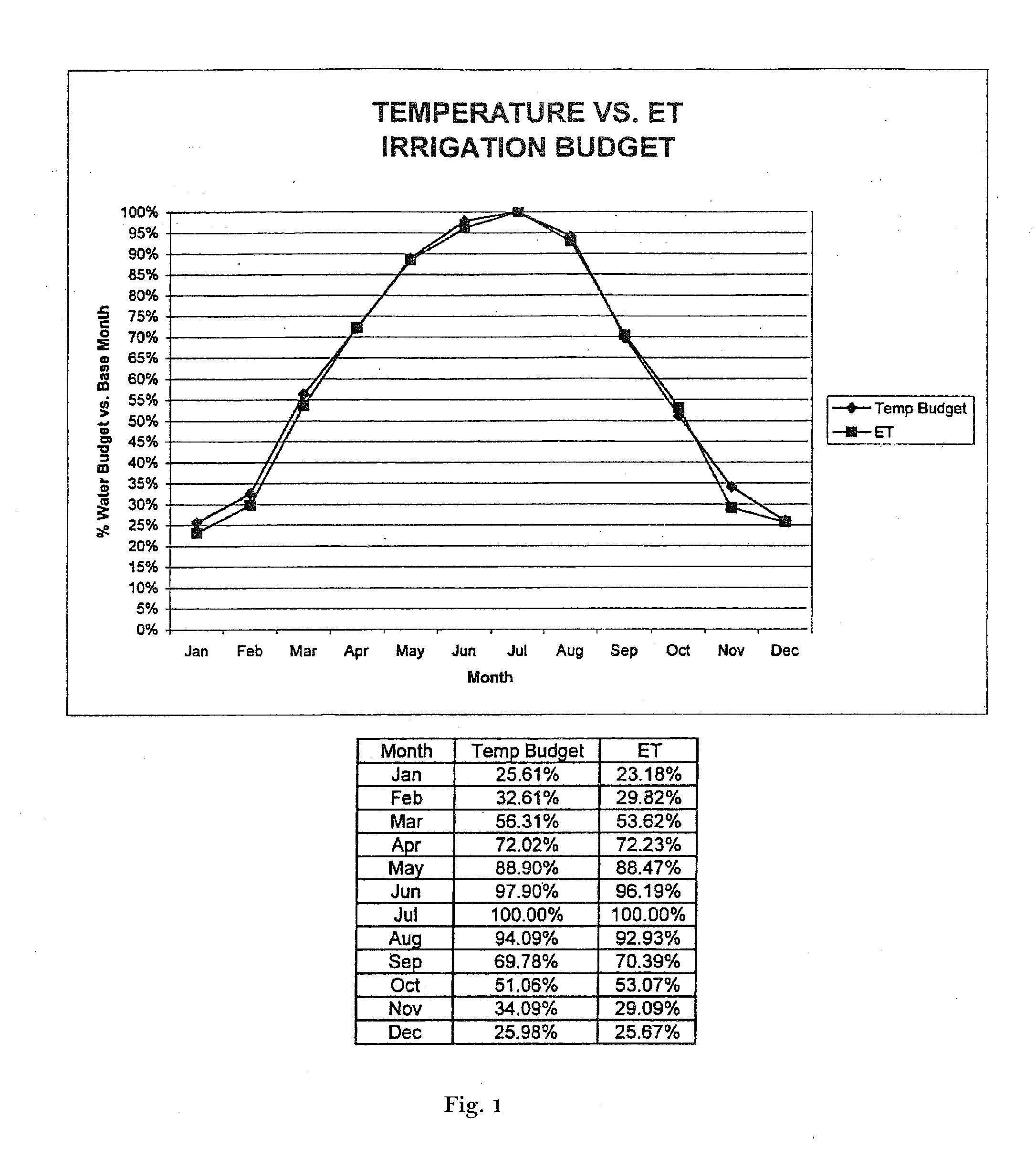
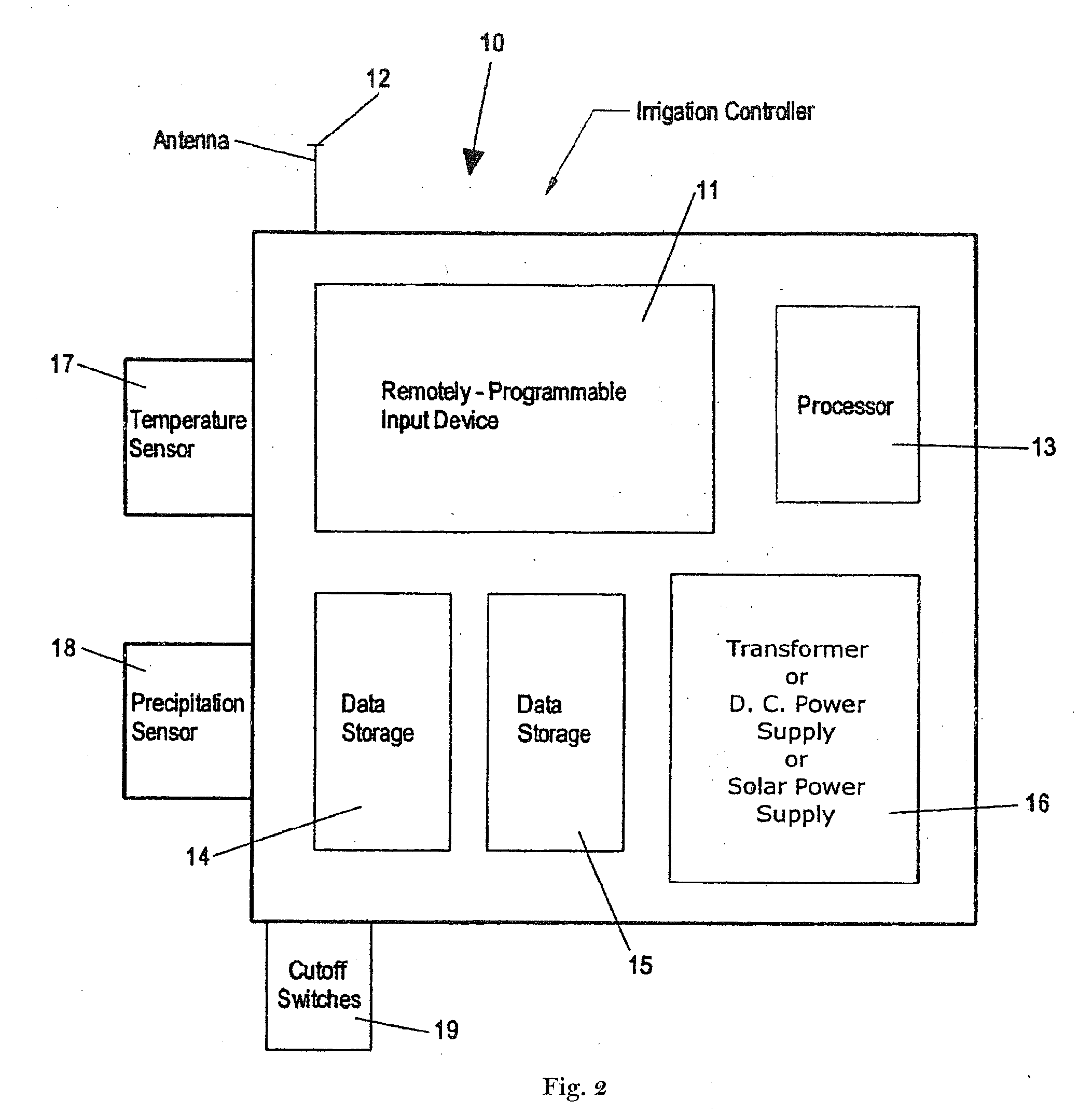
Irrigation controller water management with temperature budgeting
ActiveUS7058478B2Minimizes runoffEasy and less-expensive to installSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationEngineeringEvapotranspiration
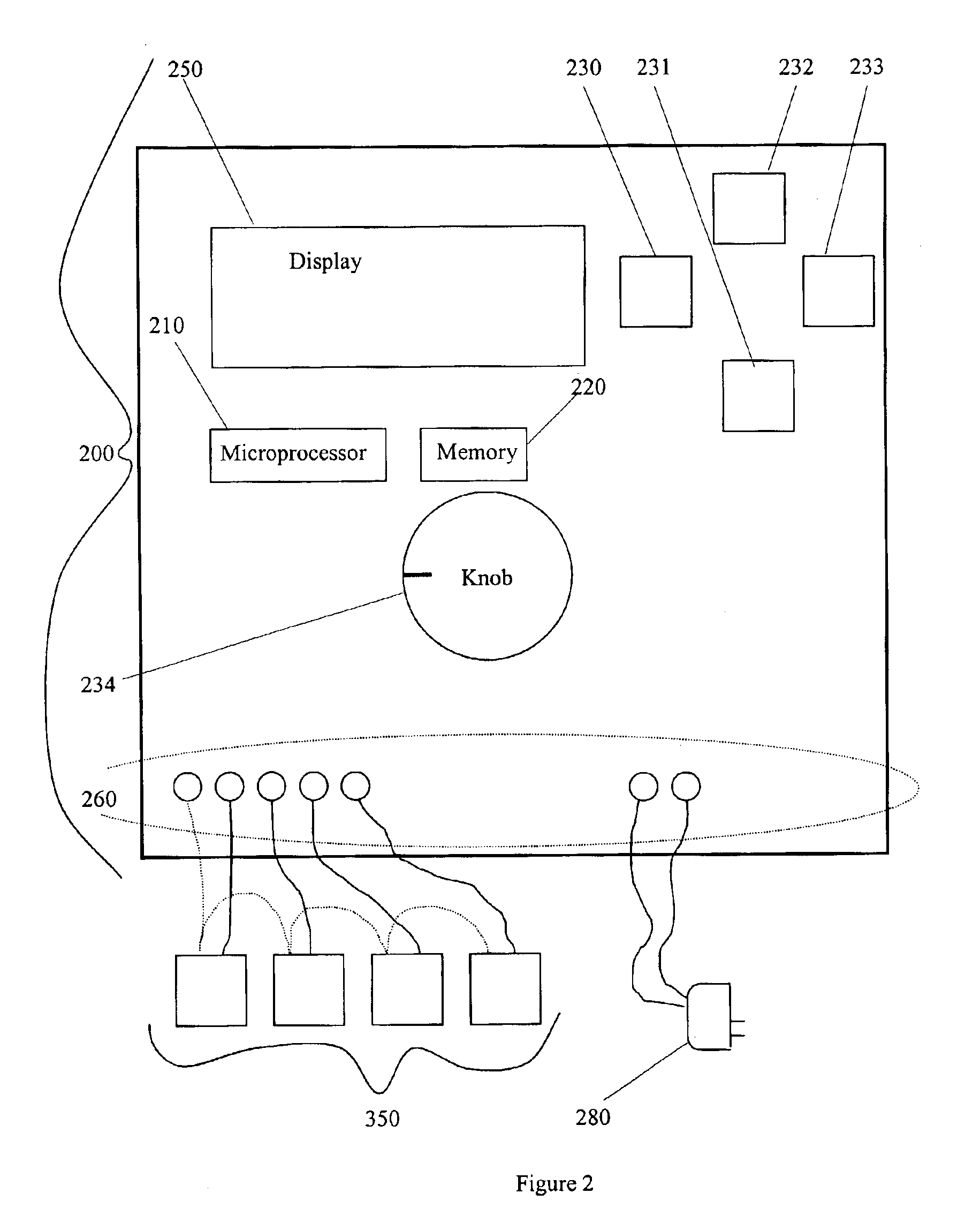
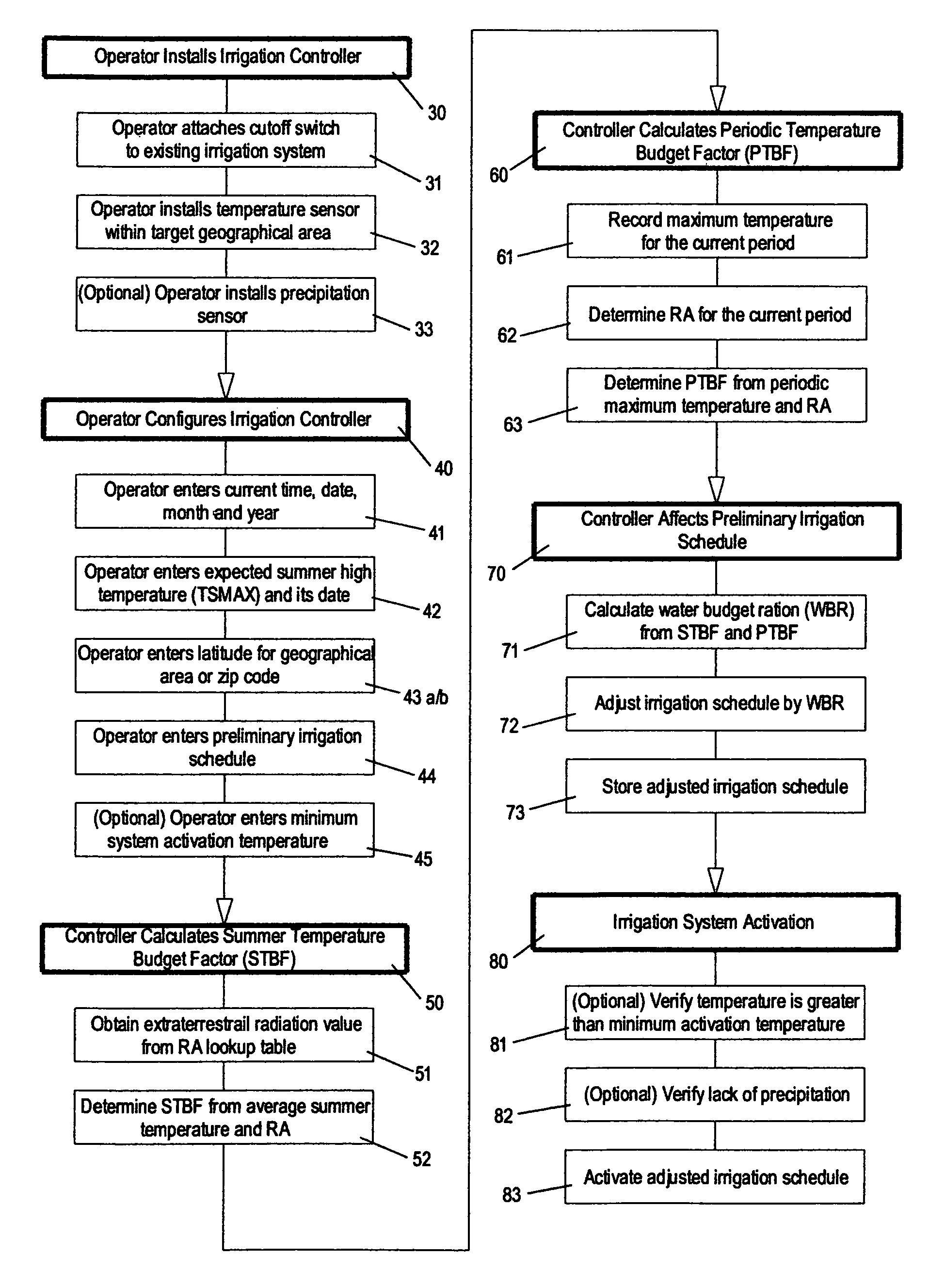
The present invention provides methods for water conservation with irrigation controllers based upon the ambient temperature and extraterrestrial radiation of a particular geographical area. It receives a preliminary irrigation schedule from the operator and computes a water budget ratio by comparing current local geo-environmental data with stored local geo-environmental data, then modifying the preliminary irrigation schedule based upon that ratio. The present invention utilizes fewer variables, is less complex, and is much easier to install and maintain than the current evapotranspiration-based controllers.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Modifying irrigation schedules of existing irrigation controllers
InactiveUS6892114B1Increase irrigationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSelf-acting watering devicesComputer scienceIrrigation control
An irrigation scheduler modifies output of a preprogrammed irrigation schedule of an installed irrigation controller to at least partially improve irrigation of the corresponding landscape. Preferred embodiments accomplish this task using a microprocessor programmed to: (a) derive a first set of information from the output of an irrigation controller used to control an operation of an irrigation valve; (b) receive a second set of information comprising at least one of an environmental factor and a meteorological factor; and (c) use the first set of information and the second set of information to interfere with reception of the output by the valve.
Owner:AQUA CONSERVATION SYST +2
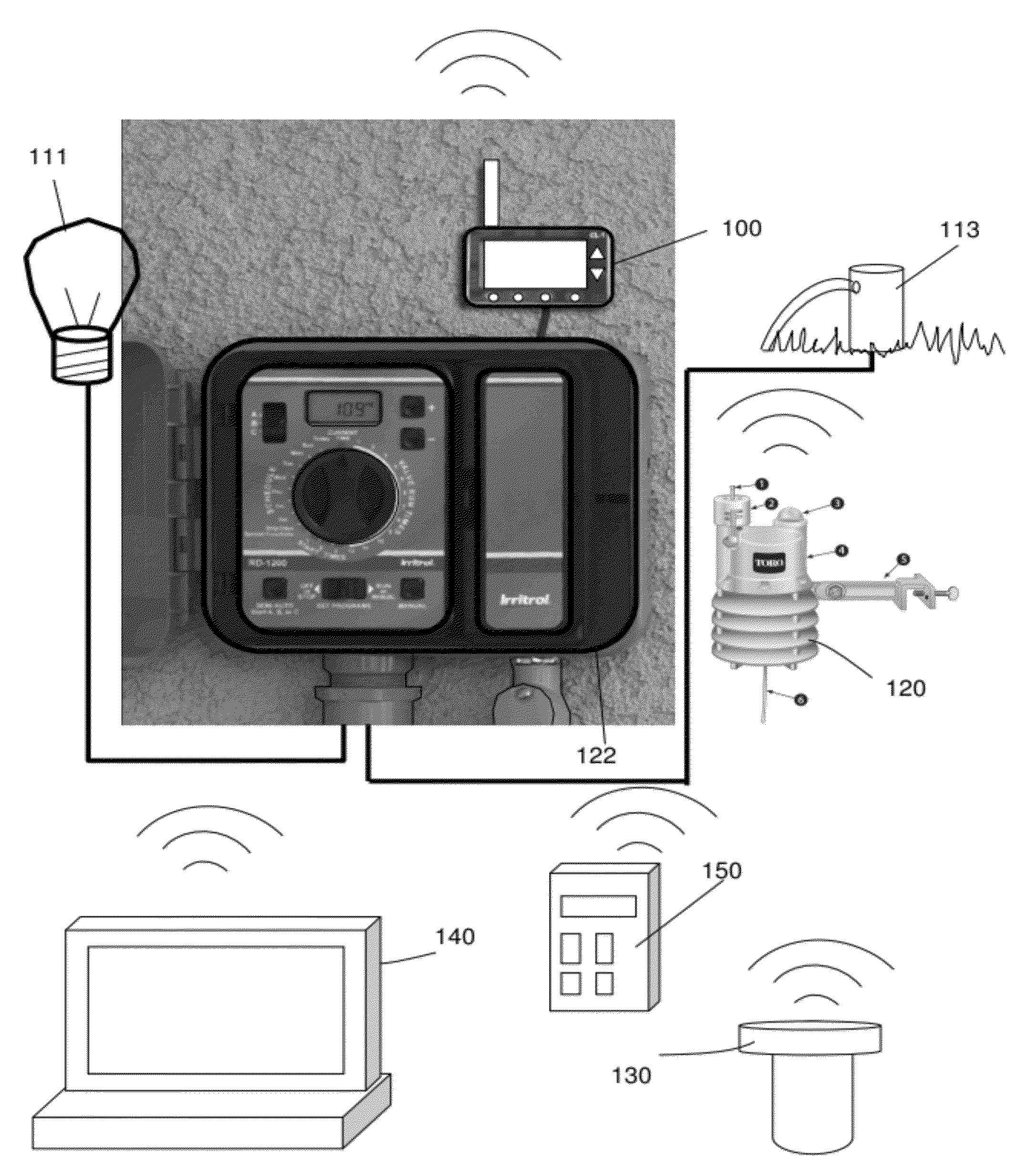
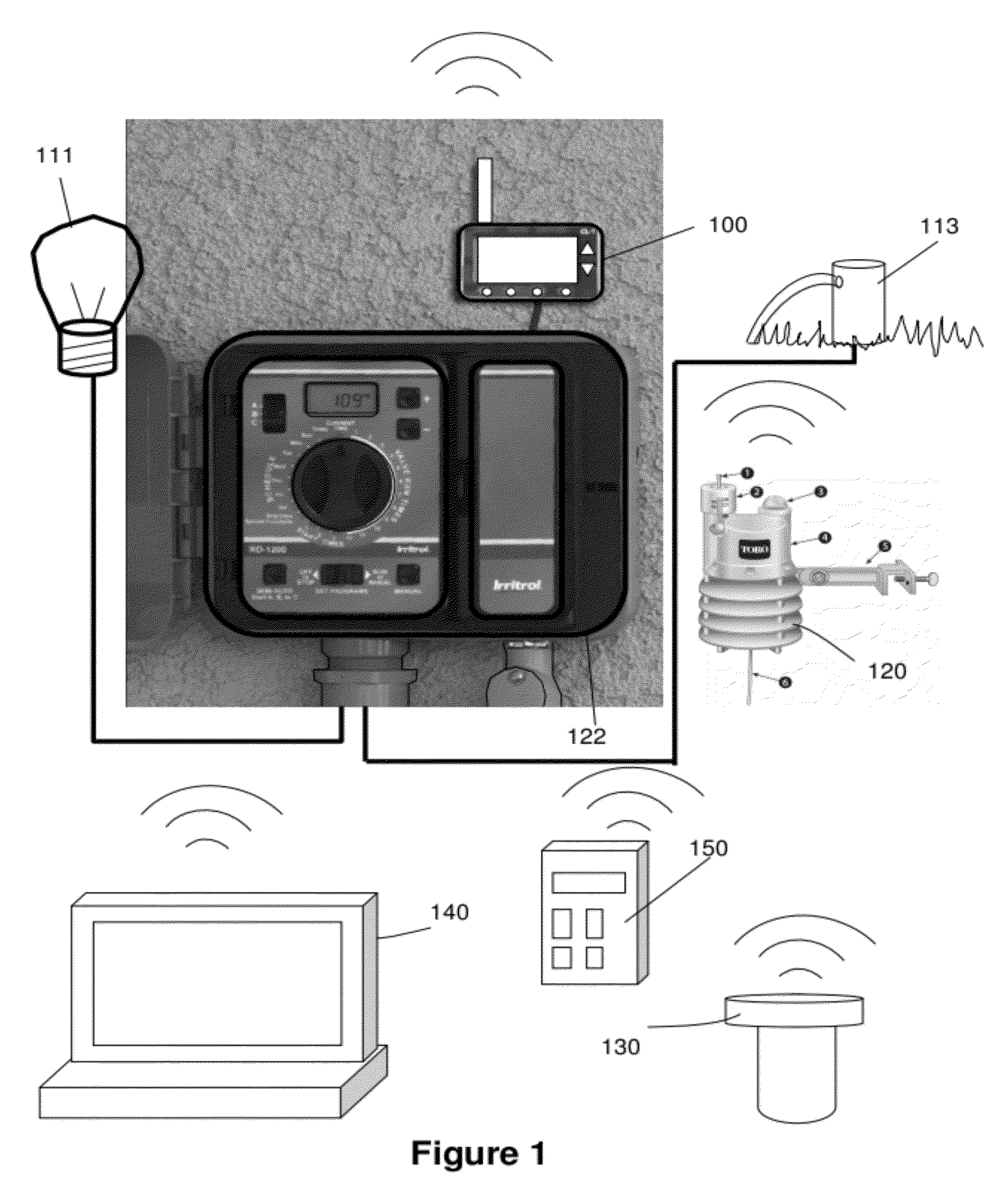
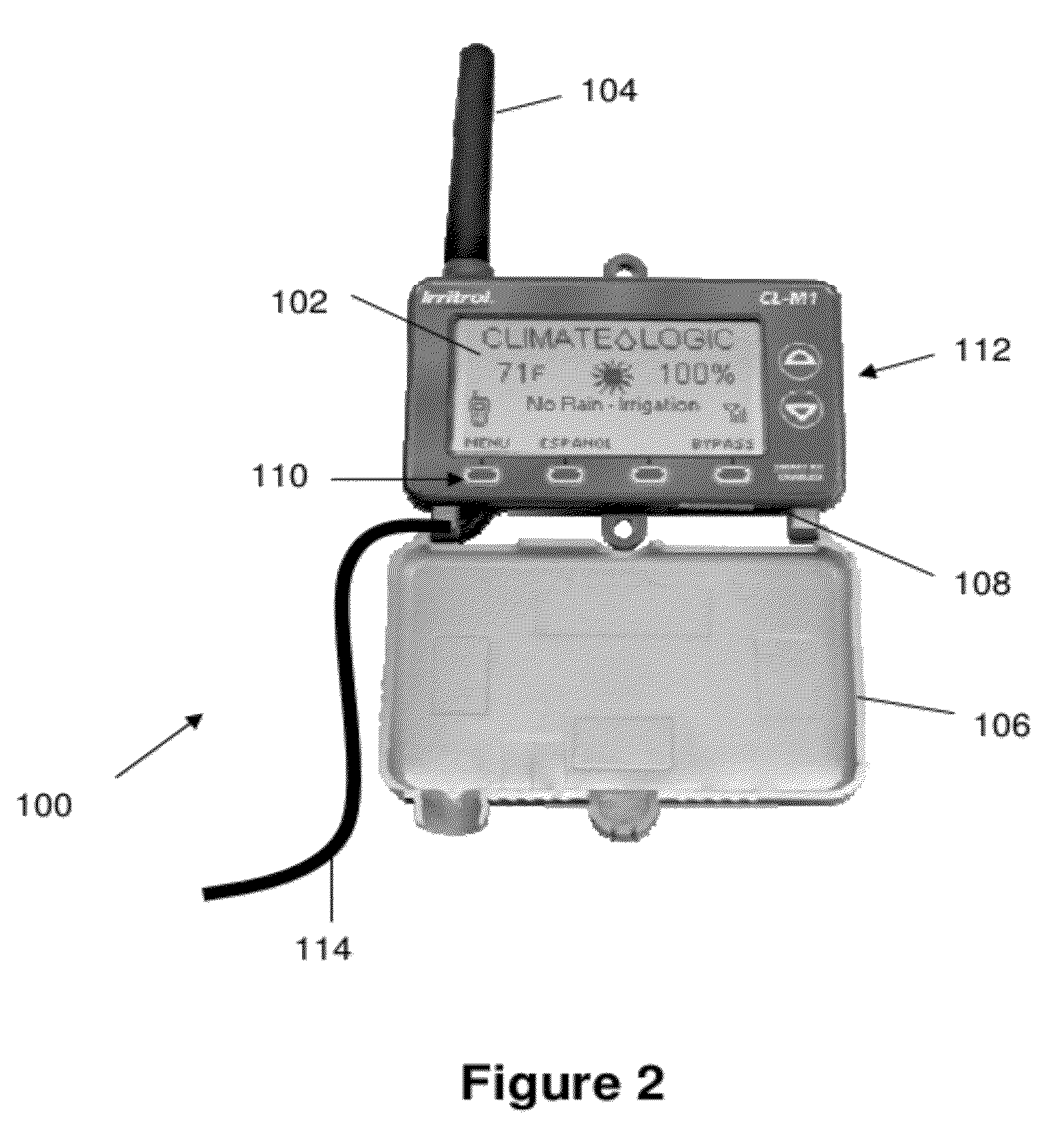
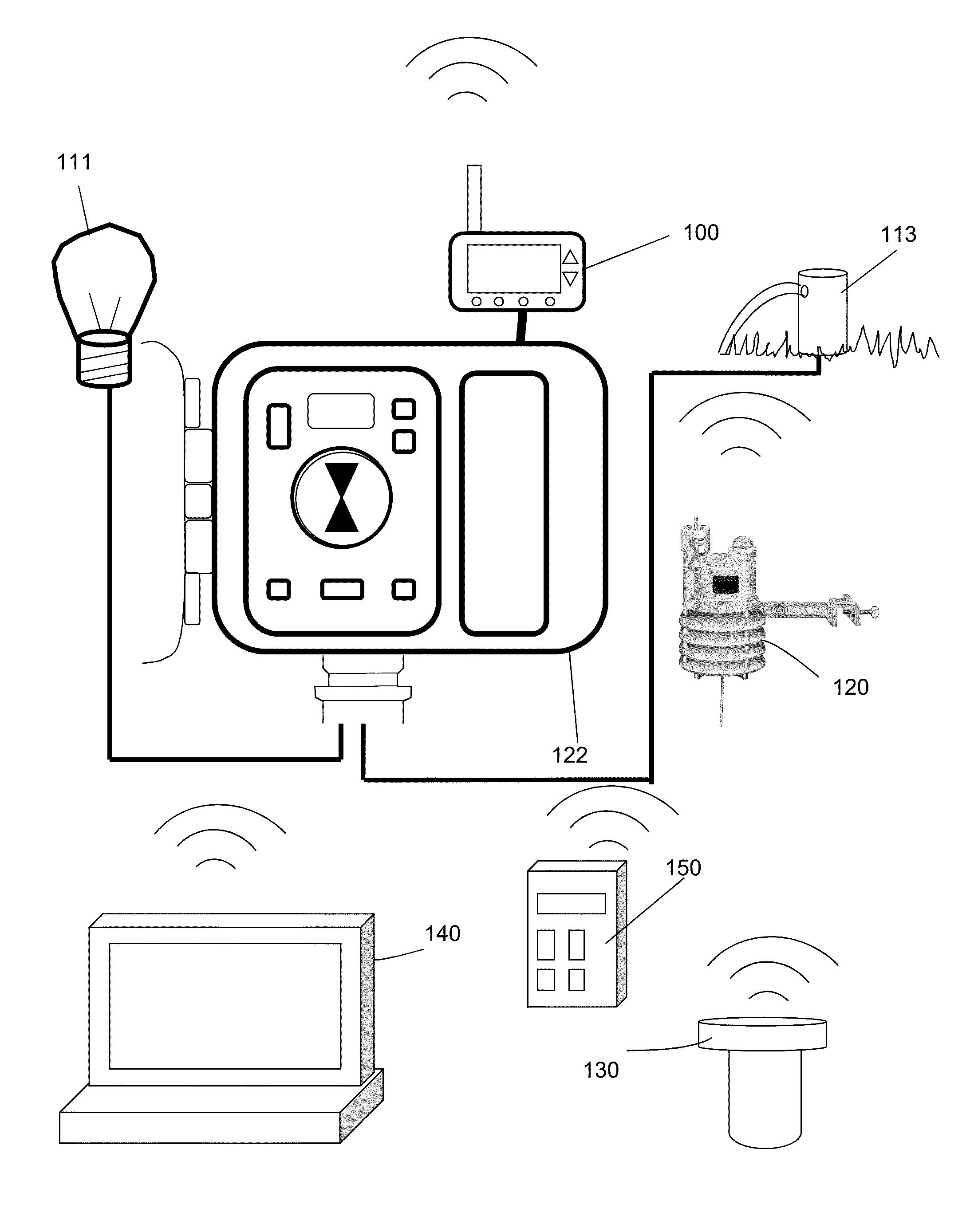
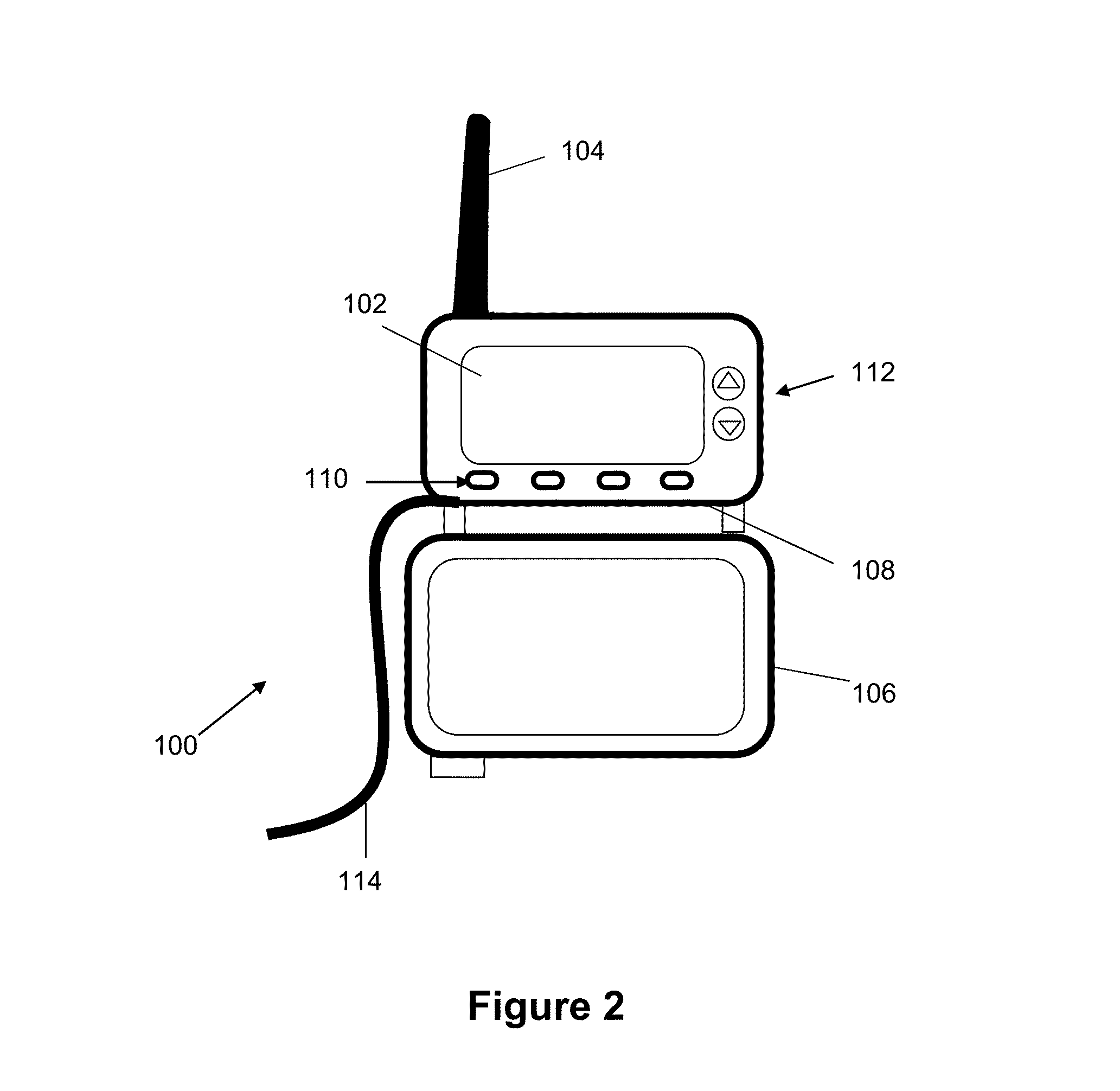
Irrigation Controller With Weather Station
An irrigation control module is described that adjusts a watering schedule for a connected irrigation controller based on weather data provided by a local weather station. The irrigation control module can add additional weather-based irrigation schedule adjustments to an irrigation controller that may otherwise lack the hardware (e.g., wireless transmitter, sufficient memory) and software (e.g., evapotranspiration algorithms) to store and interpret weather data from a weather station.
Owner:TORO CO THE
Irrigation Controller Communication System
An irrigation controller is programmed to automatically initiate communication with a data server to perform at least one of the following functions: (a) exchange irrigation data; (b) receive control data; and (c) receive synchronization data. The irrigation data can be station runtime history, evapotranspiration (ETo) data, rainfall, weather related information, irrigation faults and any other irrigation data. The control data can involve station runtime settings, cycle and soak settings, irrigation scheduling and any other irrigation control data. The synchronization data preferably includes a date and a time, originating from the data server, but can include other data that would be used to synchronize the communication between the irrigation controller and the data server. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention a microprocessor disposed in the irrigation controller is programmed to use the date and time to schedule a future contact with the data server.
Owner:AQUA CONSERVE +2
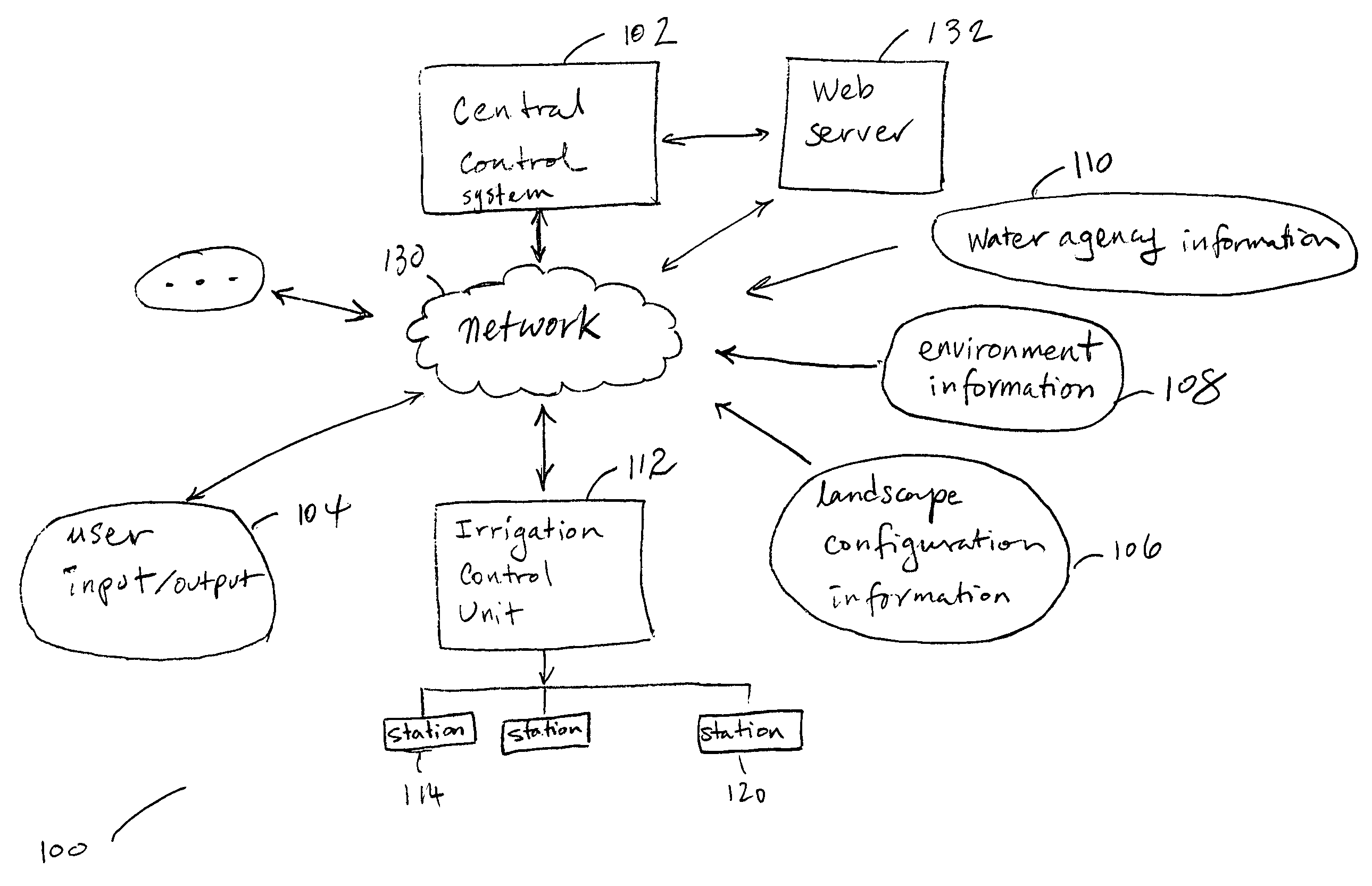
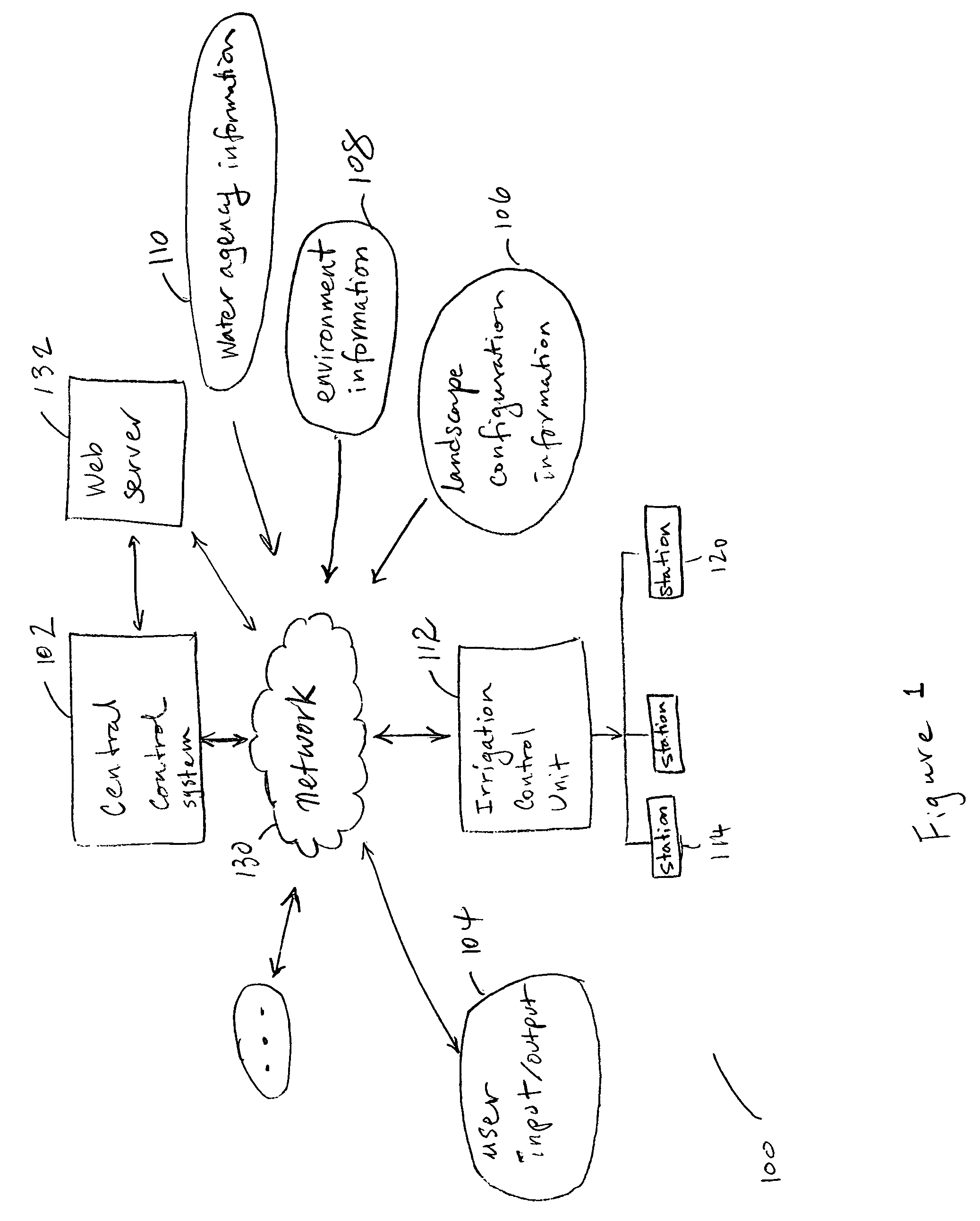
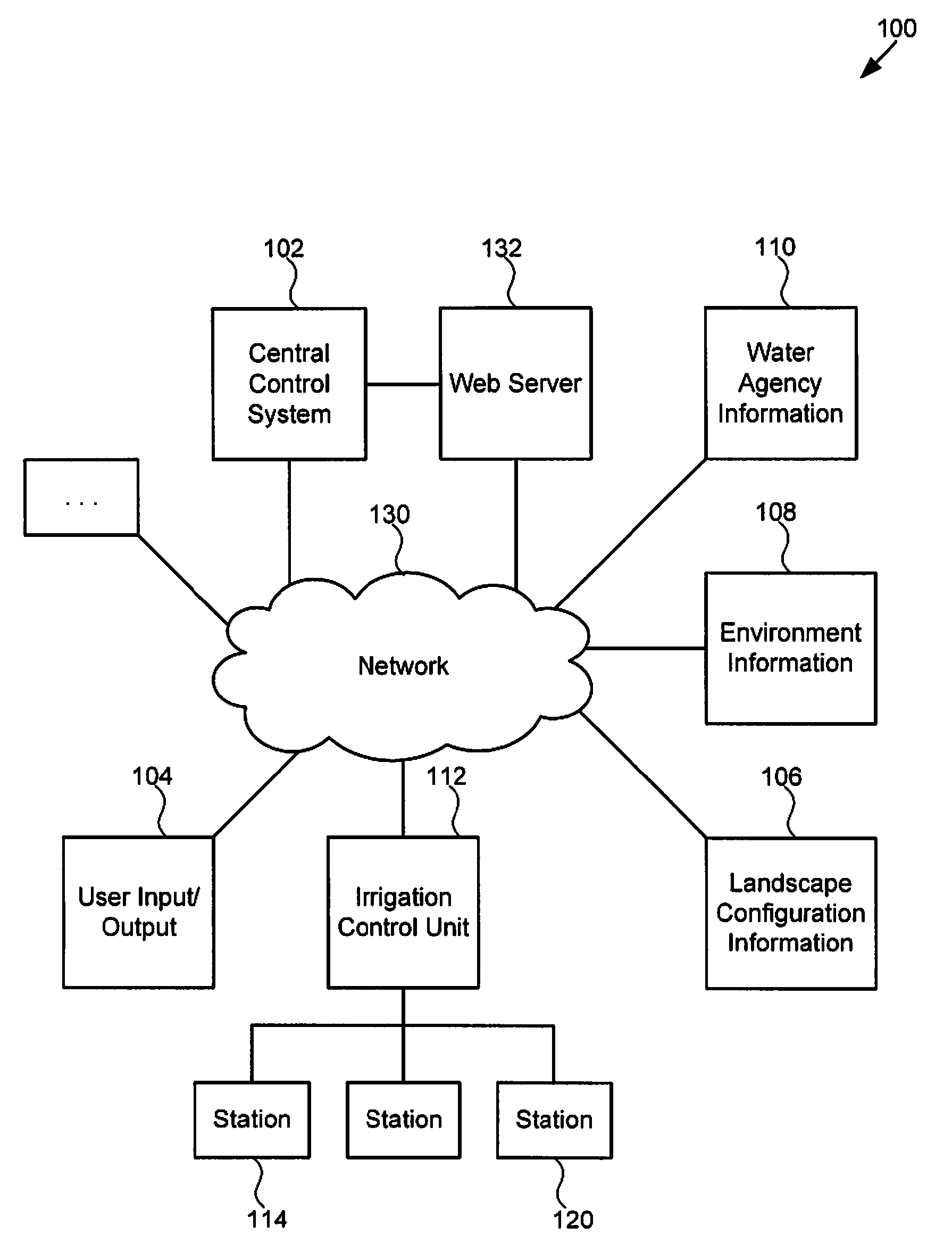
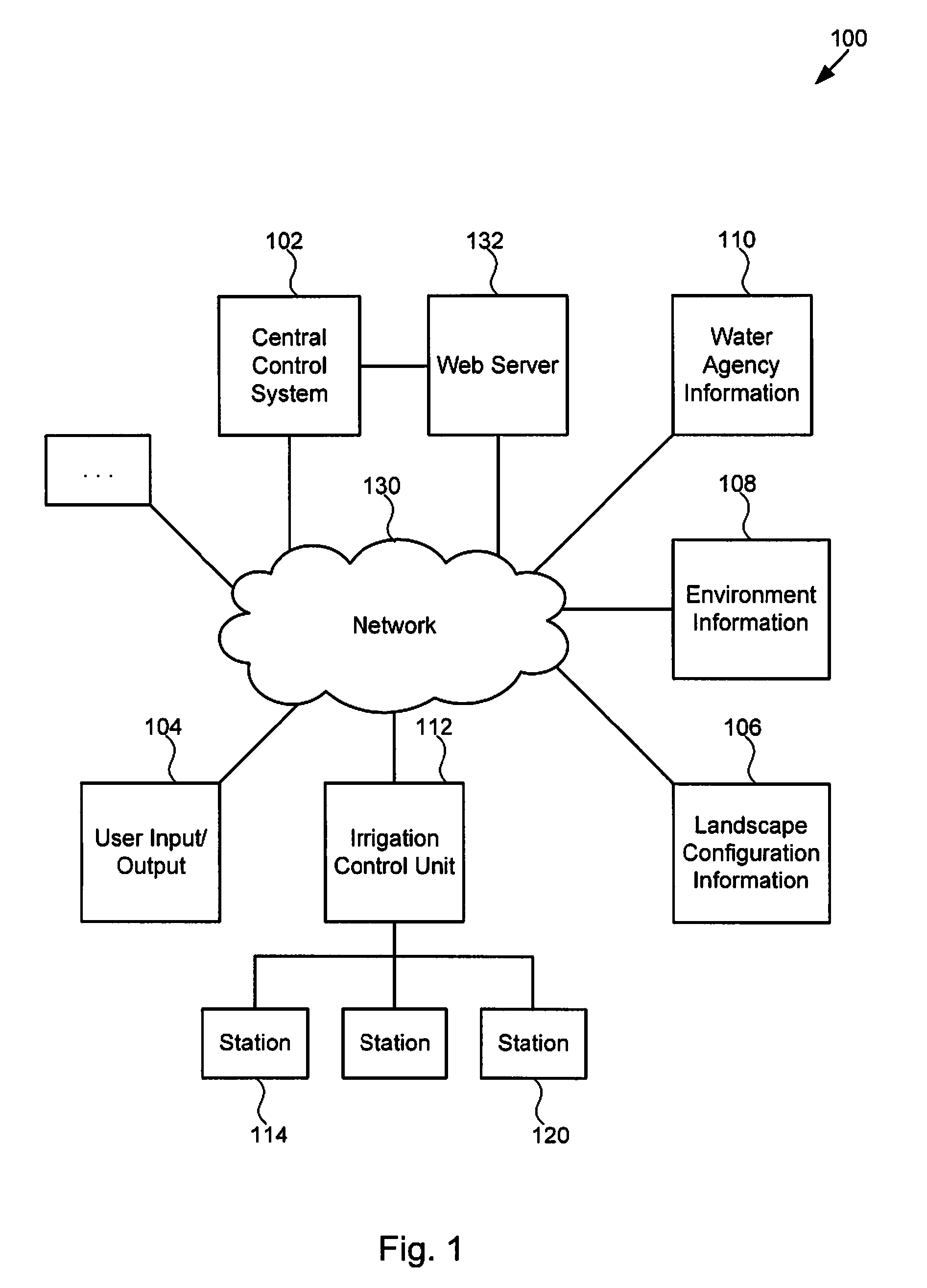
Irrigation system
ActiveUS7596429B2Self-acting watering devicesWatering devicesIrrigation controlIrrigation scheduling
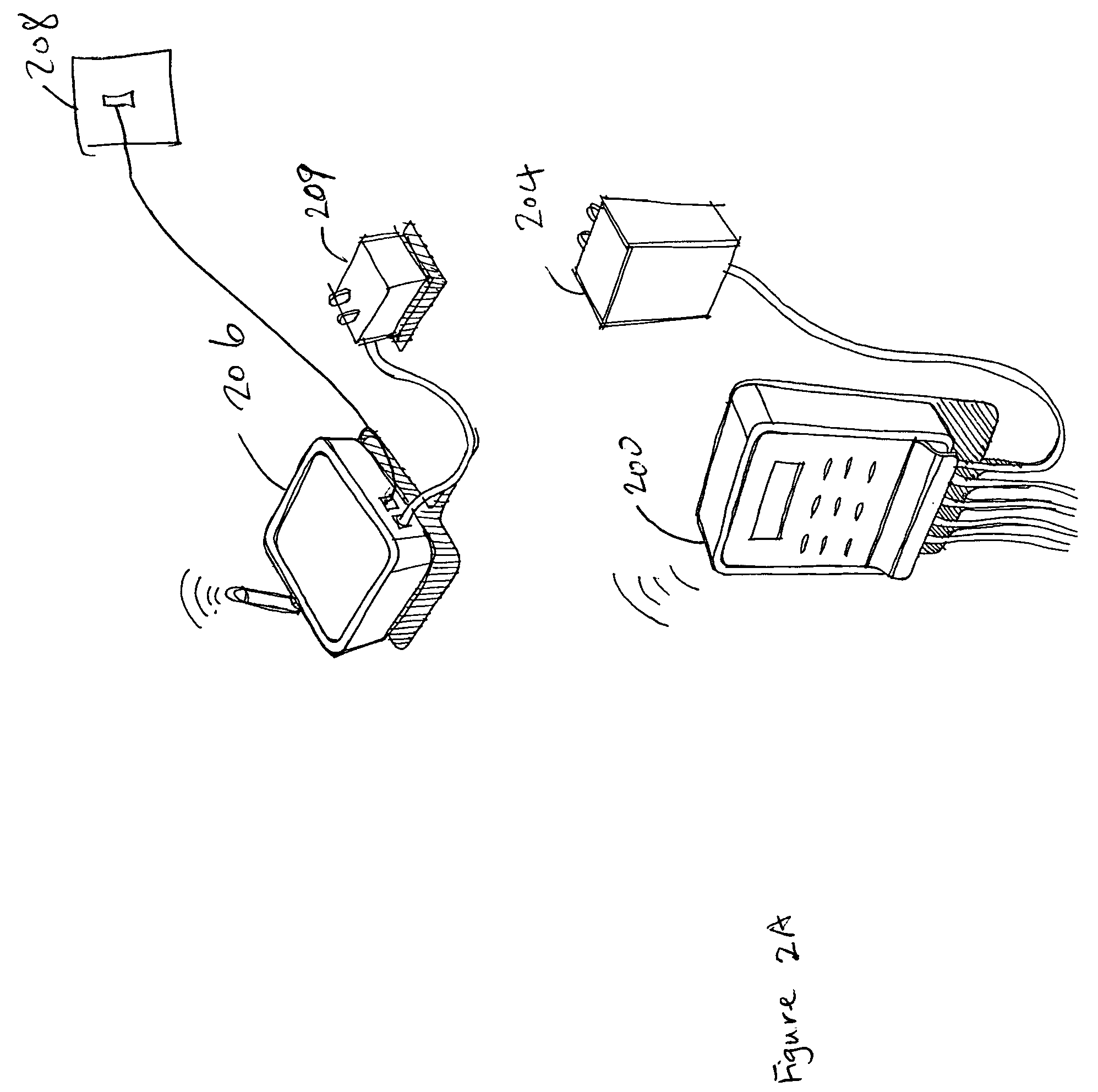
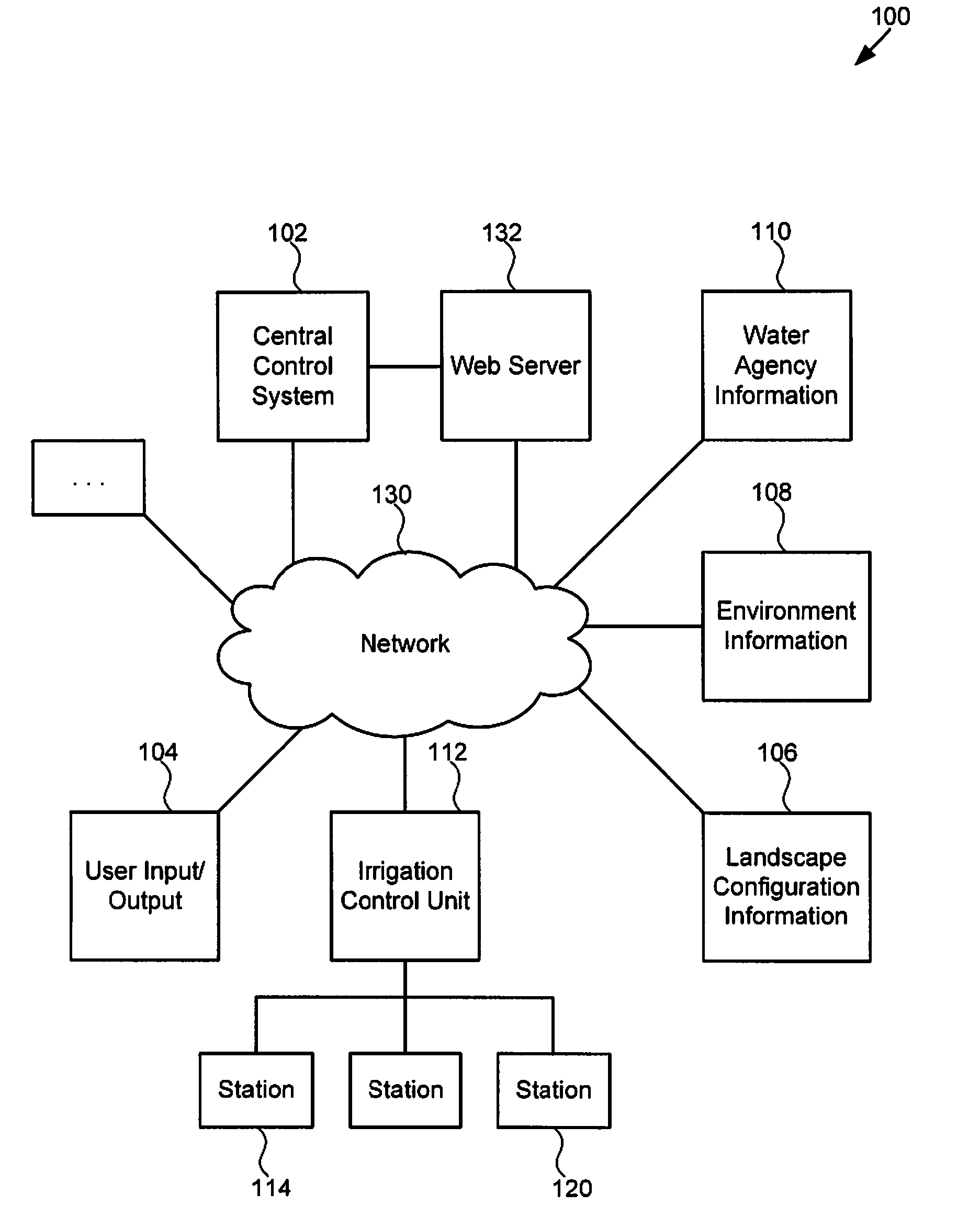
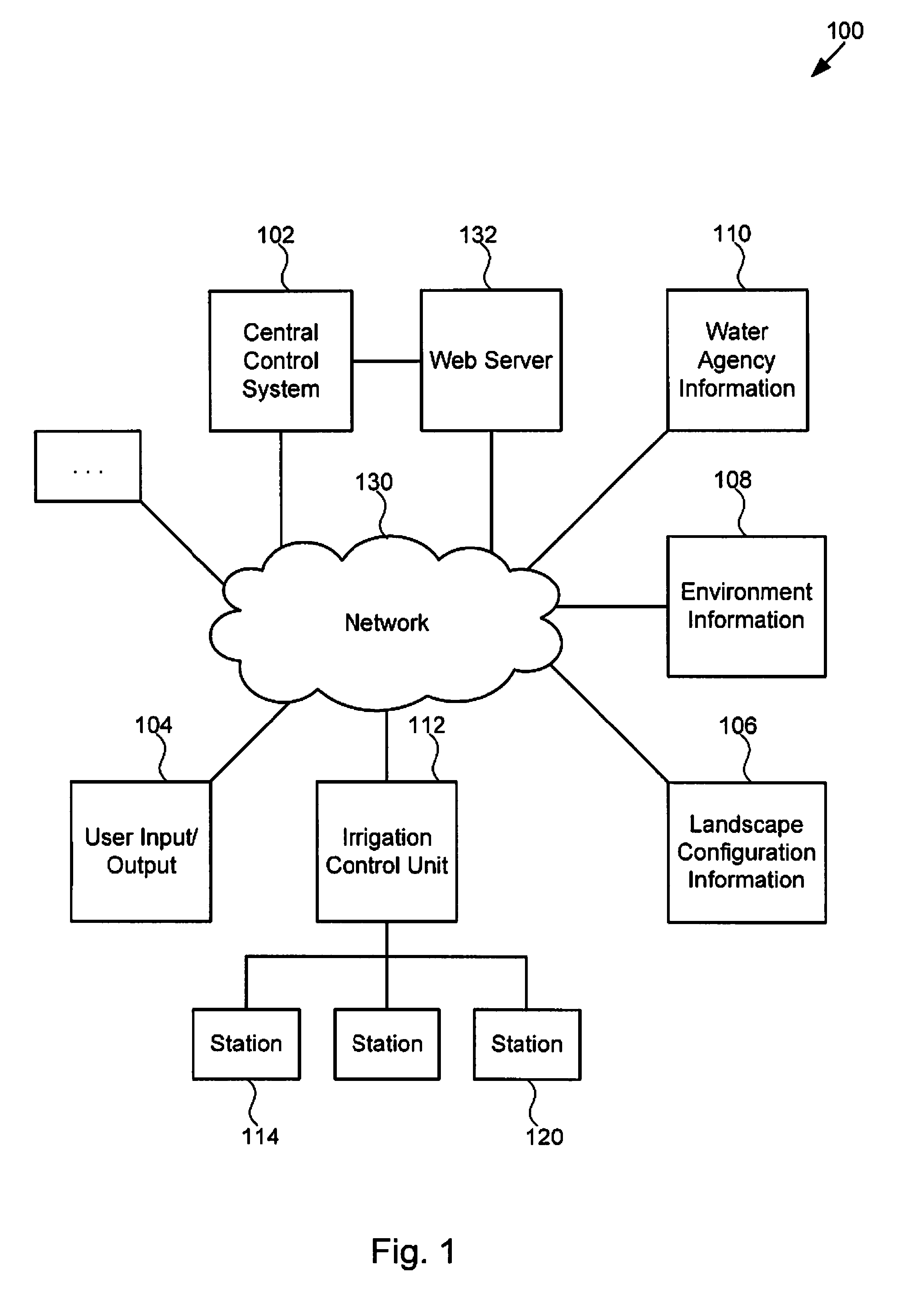
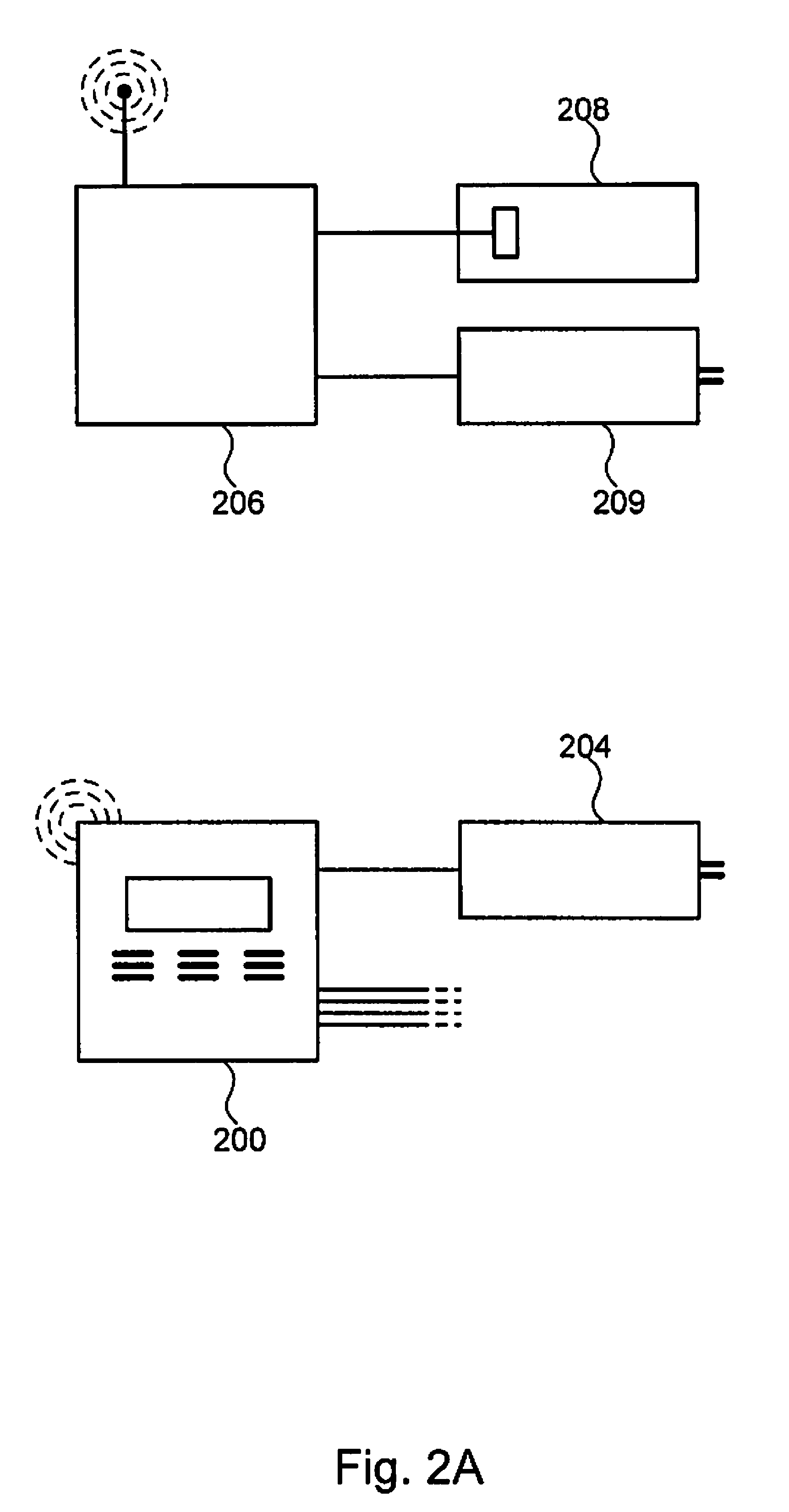
A technique for controlling an irrigation system is disclosed. The technique comprises receiving landscape information, receiving environmental information, deriving an irrigation schedule based on the landscape information and the environmental information, and sending the irrigation schedule to an irrigation control unit.
Owner:ET WATER SYST
Irrigation system
A technique for controlling an irrigation system is disclosed. The technique comprises receiving landscape information, receiving environmental information, deriving an irrigation schedule based on the landscape information and the environmental information, and sending the irrigation schedule to an irrigation control unit.
Owner:ET WATER SYST
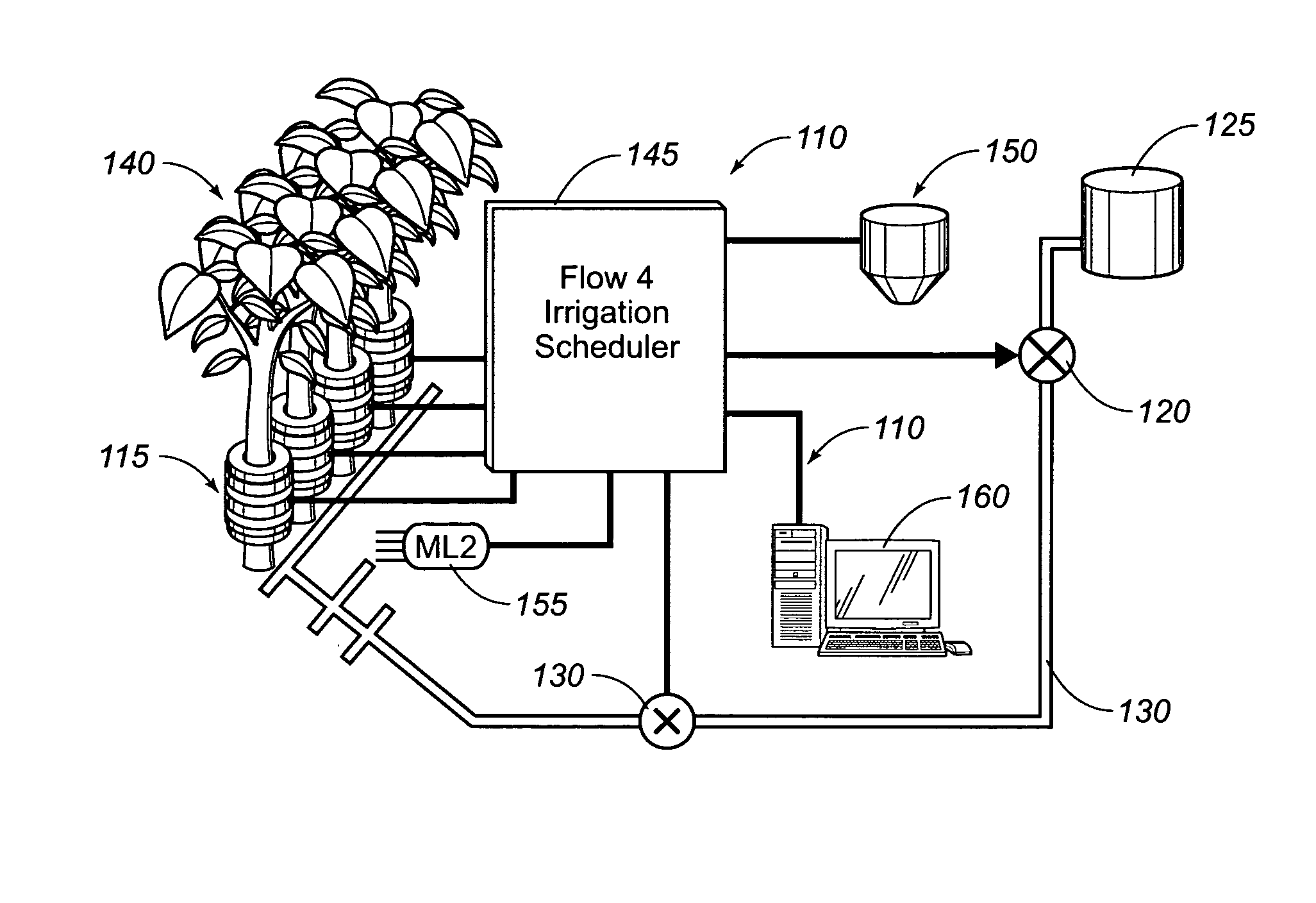
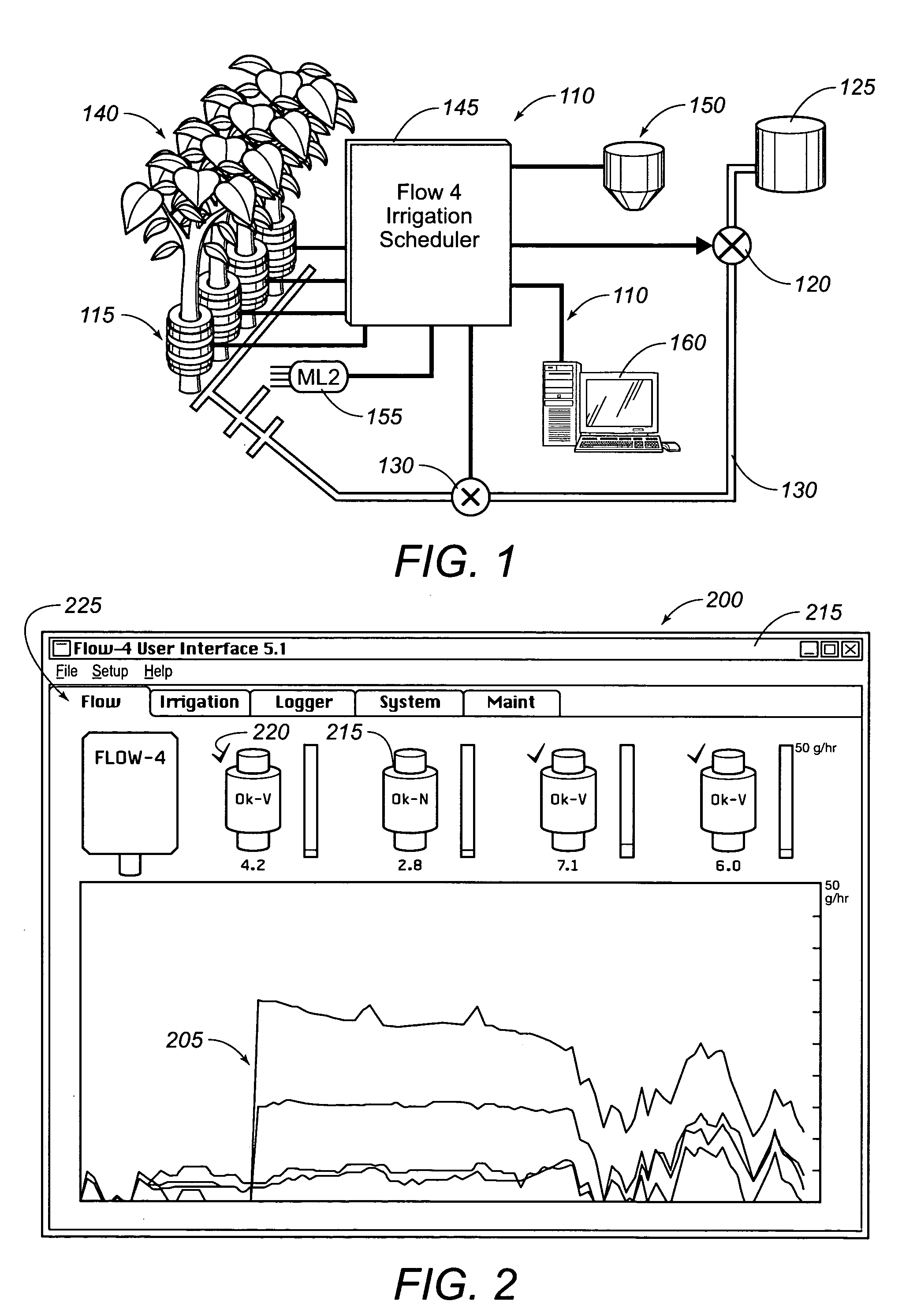
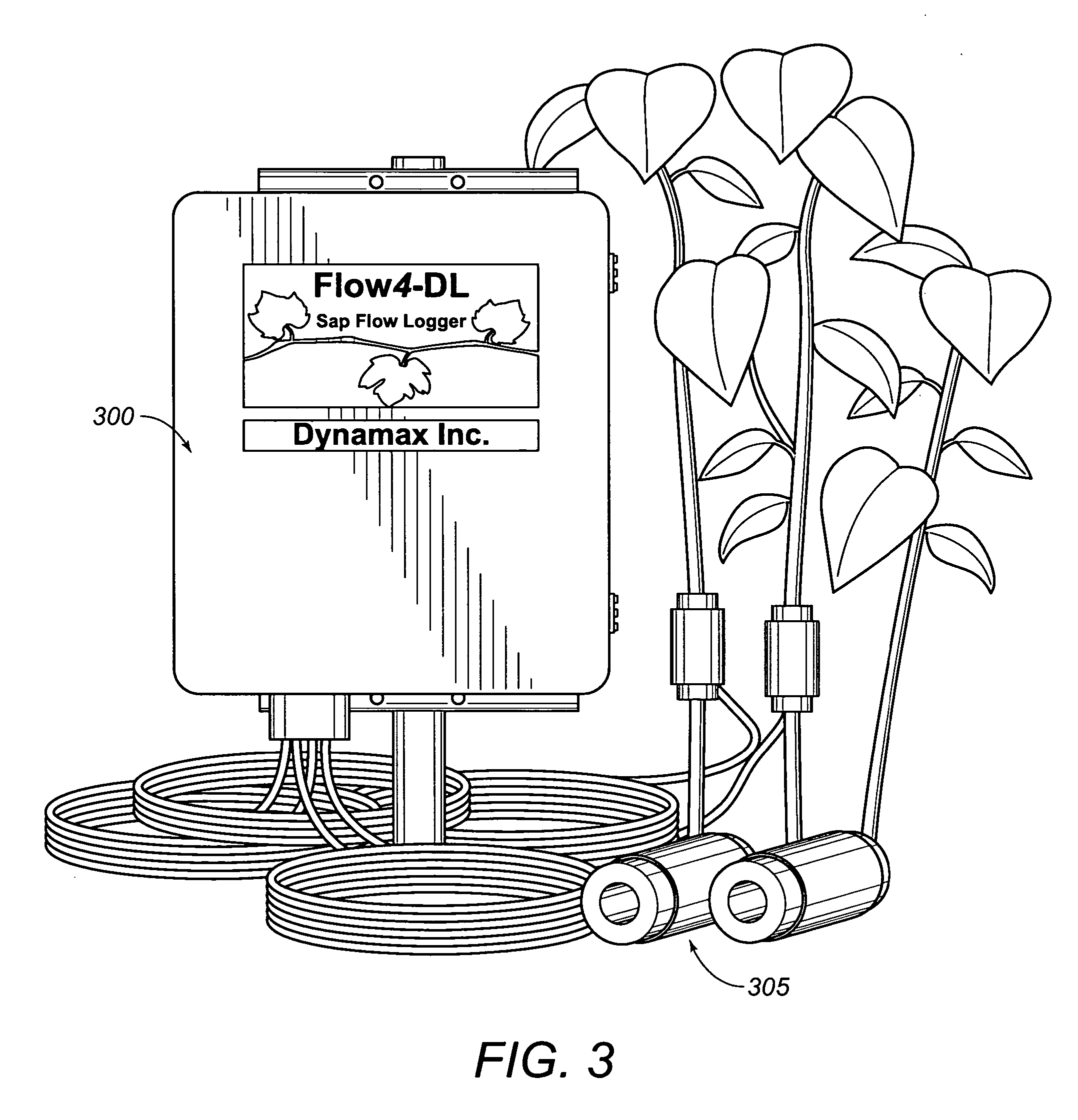
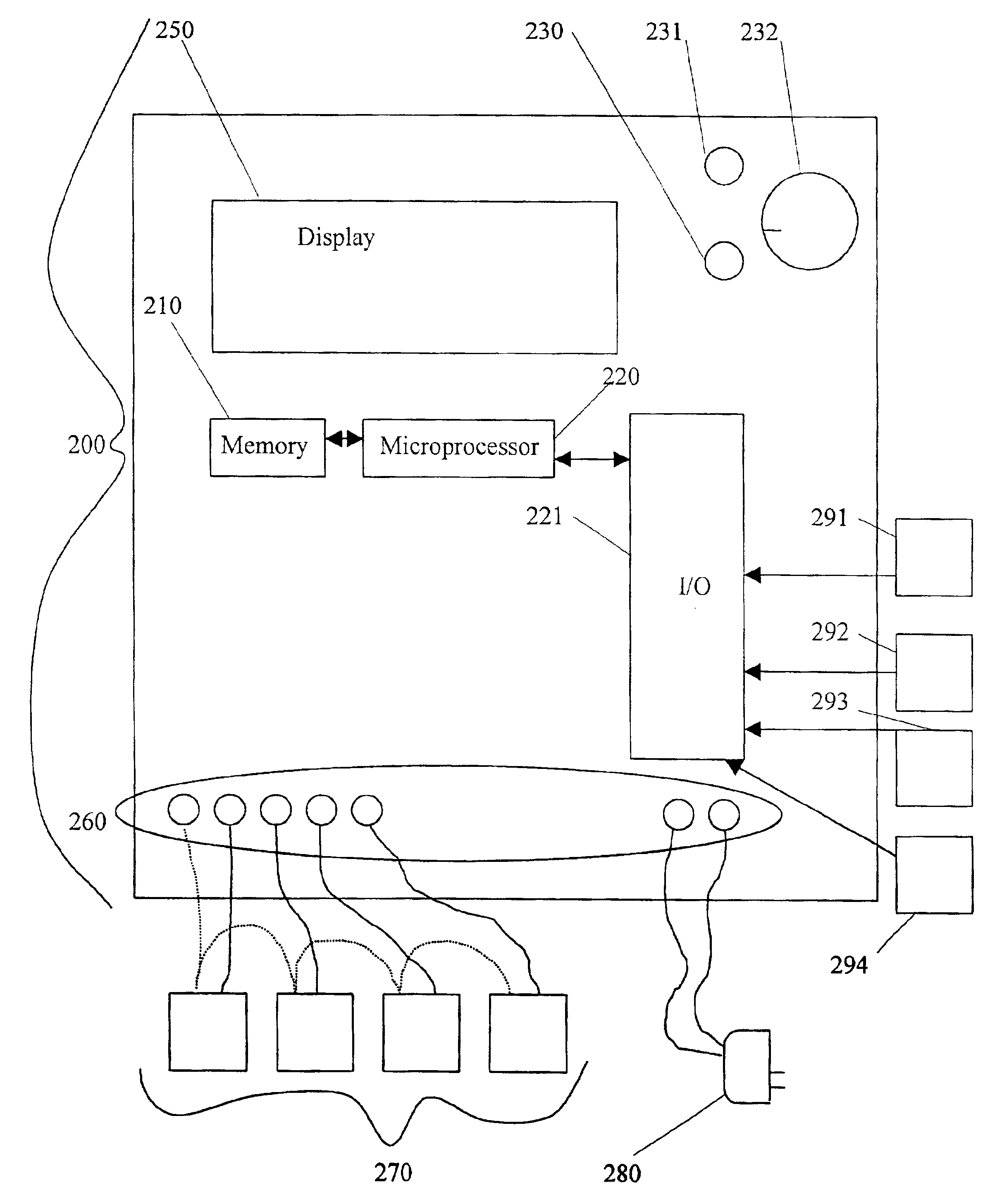
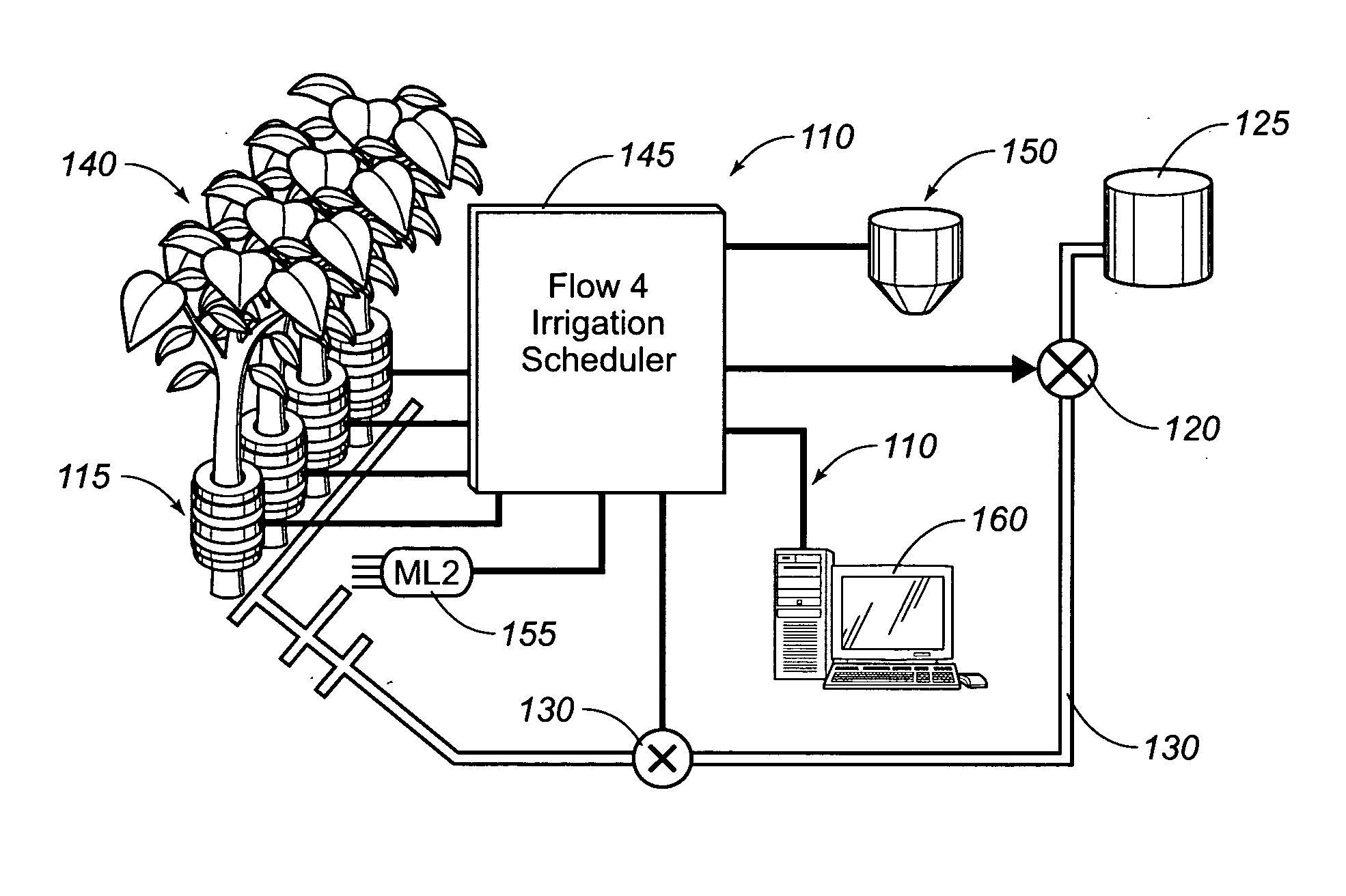
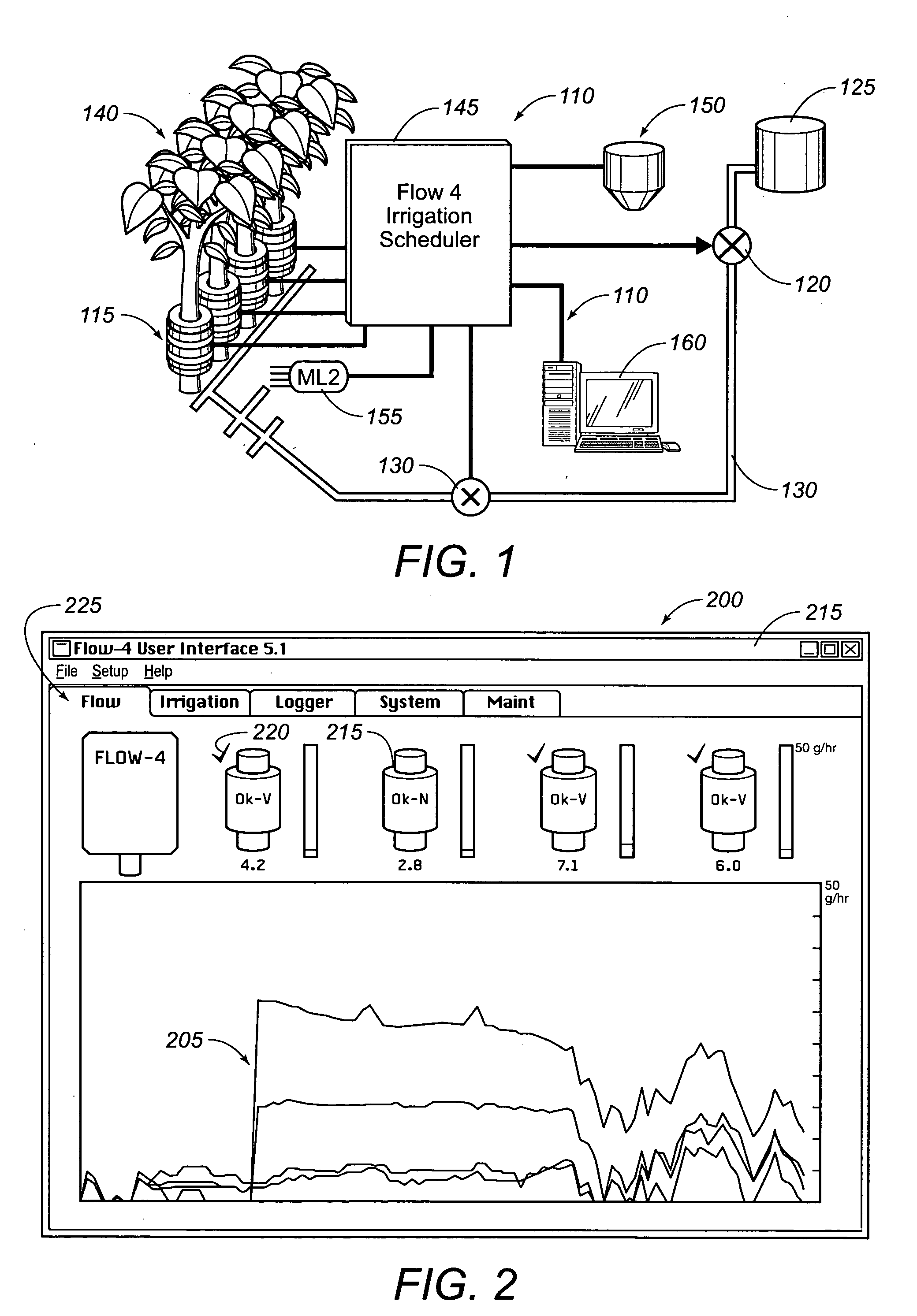
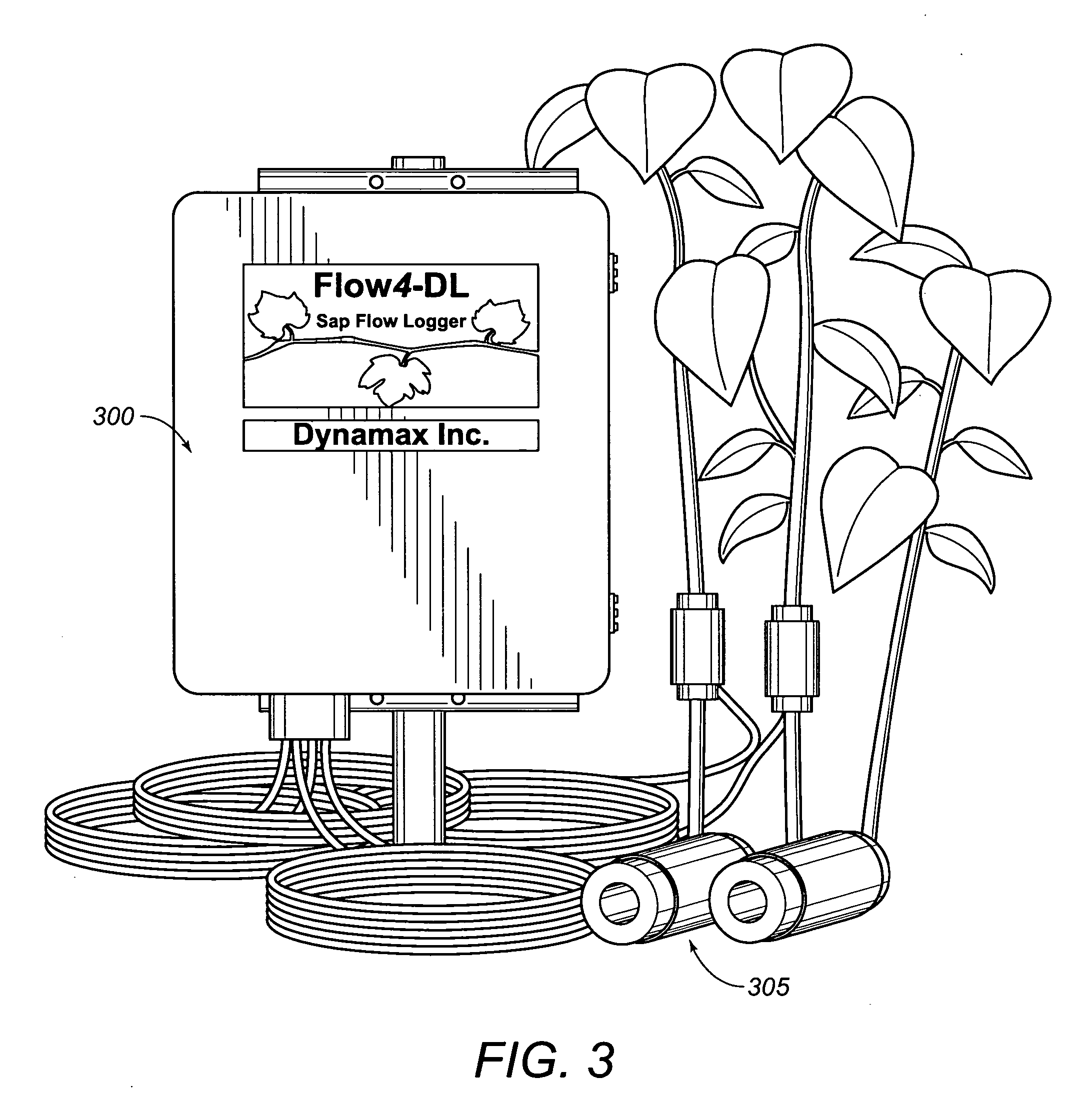
Integrated sap flow monitoring, data logging, automatic irrigation control scheduling system
ActiveUS7280892B2Accurate measurementReduce errorsSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesClosed loopUser interface
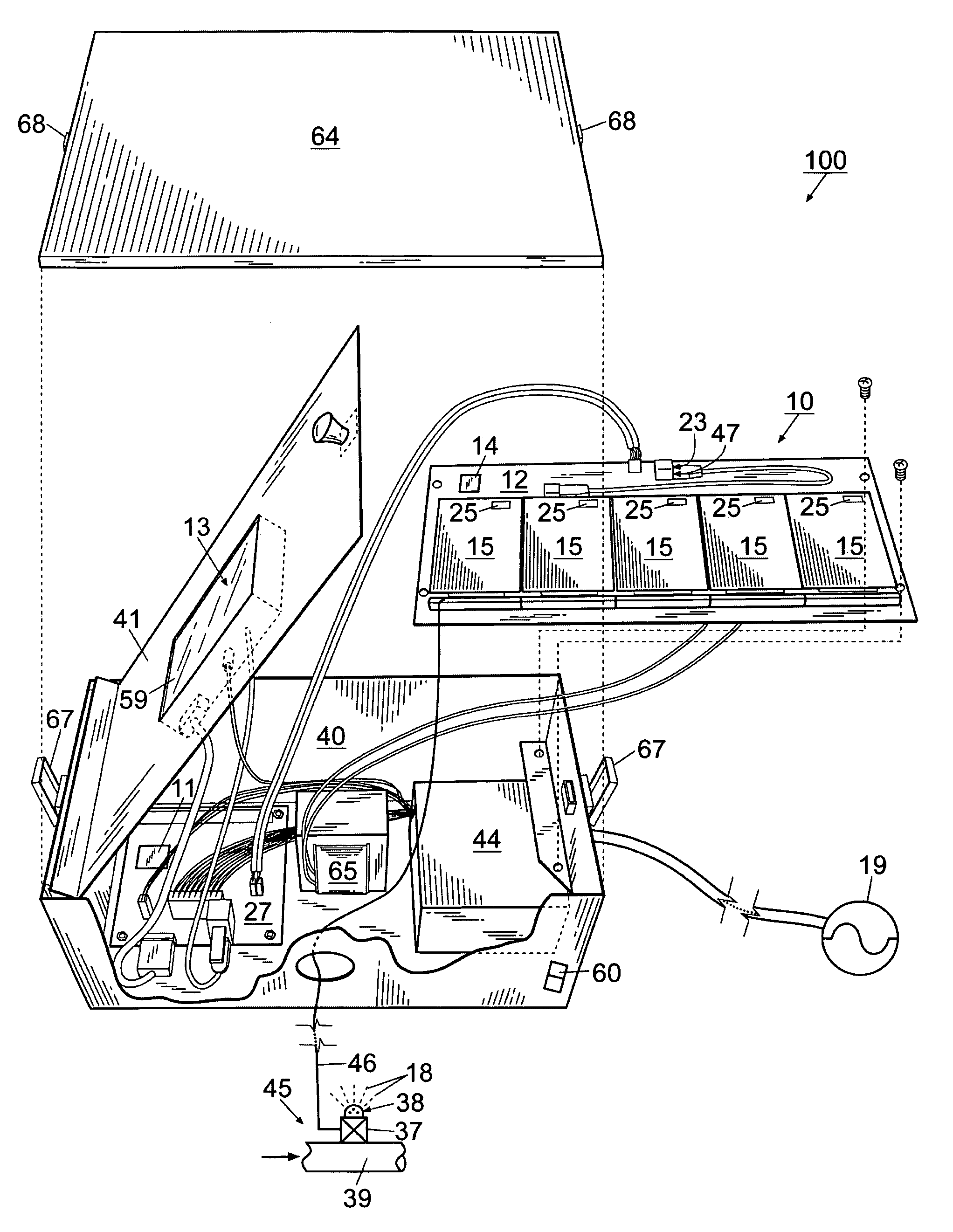
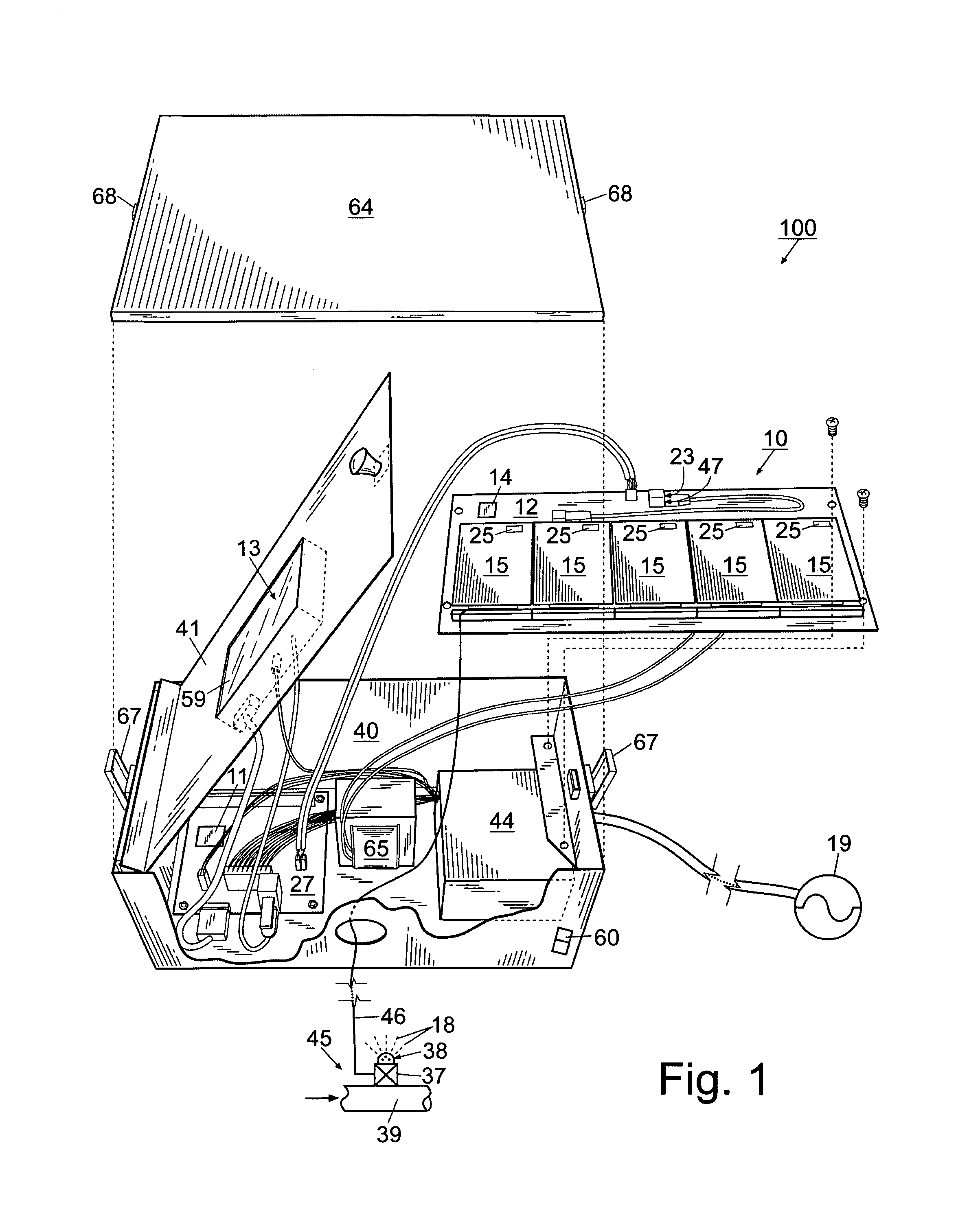
An integrated system for monitoring sap flow and simultaneously performing data-logging and automatically scheduling irrigation in a field; comprising a plurality of in situ sap flow gauges that perform its comprehensive computer-controlled tasks in the field being irrigated. This plurality of sap flow gauge can be detached from and reattached to a like plurality of plant stems as appropriate. A scaling mechanism is used to calculate crop water usage in variously-sized fields. An integrated portable computer apparatus is programmed to perform a plurality of actions including sap flow monitoring via a controller and data-logger; data-logging and automatic irrigation scheduling; a plurality of sap flow gauges; an automatic rain gage; a water meter; an irrigation valve actuator; and any auxiliary and independent weather or soil monitoring sensors. The system is connected to a PC, mounted in a weatherproof enclosure, and powered by rechargeable battery, solar panel, or AC mains power with battery backup. Computerized monitoring and control procedures are initialized via a custom-developed graphical user interface. At any predetermined interval set by a user, the depth or volume of water required to balance transpiration losses is calculated and irrigation is then automatically triggered. The system affords closed loop control with water flow from soil through plant to atmosphere and from irrigation—and having the benefit of a feedback loop.
Owner:BAVEL MICHAEL VAN
Automatic adjustment of irrigation schedule according to condition of plants
The present invention provides systems and methods in which a microprocessor, disposed in an irrigation controller, is programmed to adjust an irrigation schedule according to a condition of a plant being irrigated. The adjustment to the irrigation schedule may be to the entire irrigated site or only to a portion of the irrigated site. The irrigation schedule may be at least partly derived from ETo data and may be from current ETo data, estimated ETo data or historical ETo data. The condition may be plant establishment, plant maturity or plant health.
Owner:AQUA CONSERVATION SYST
Interactive irrigation system
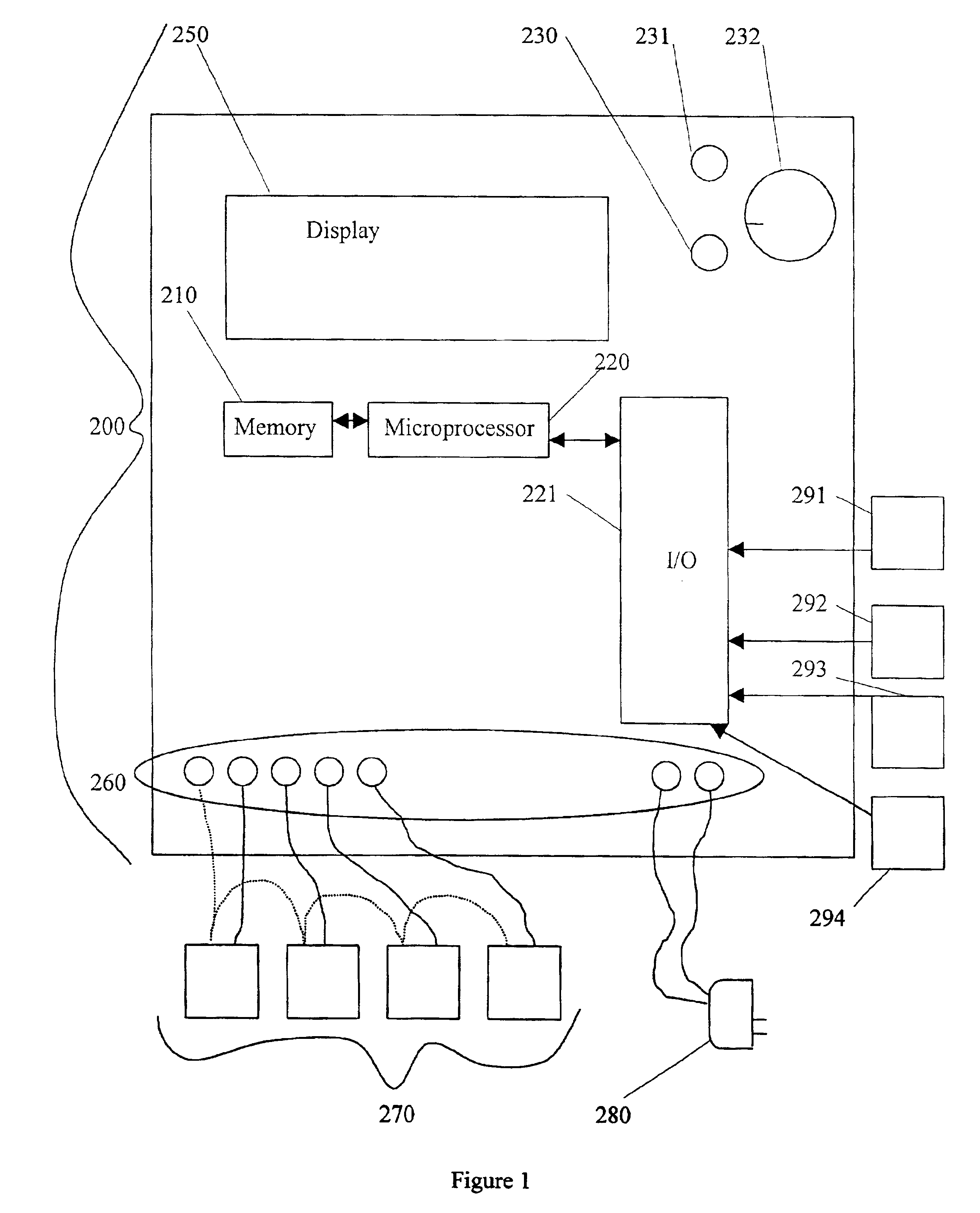
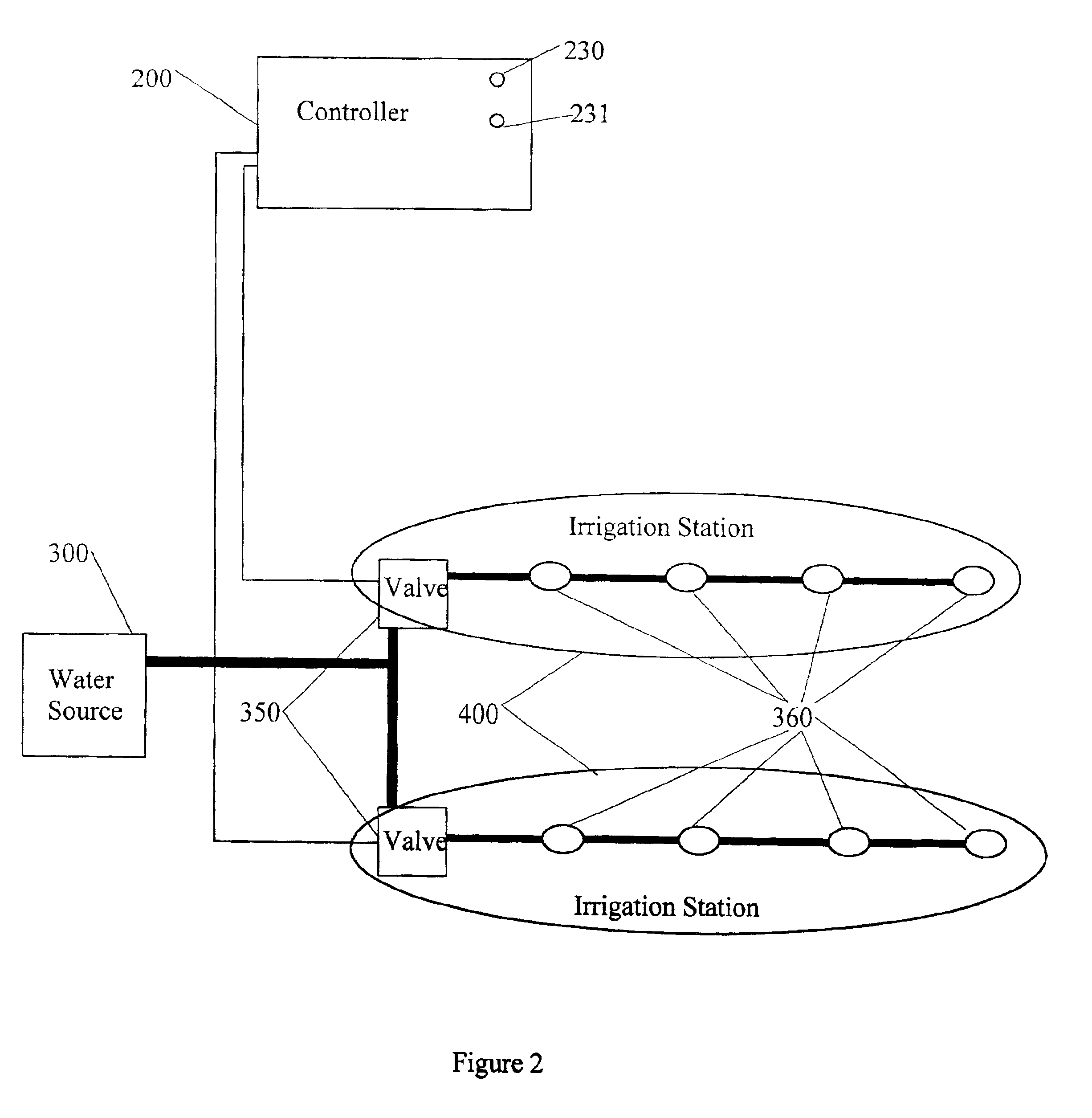
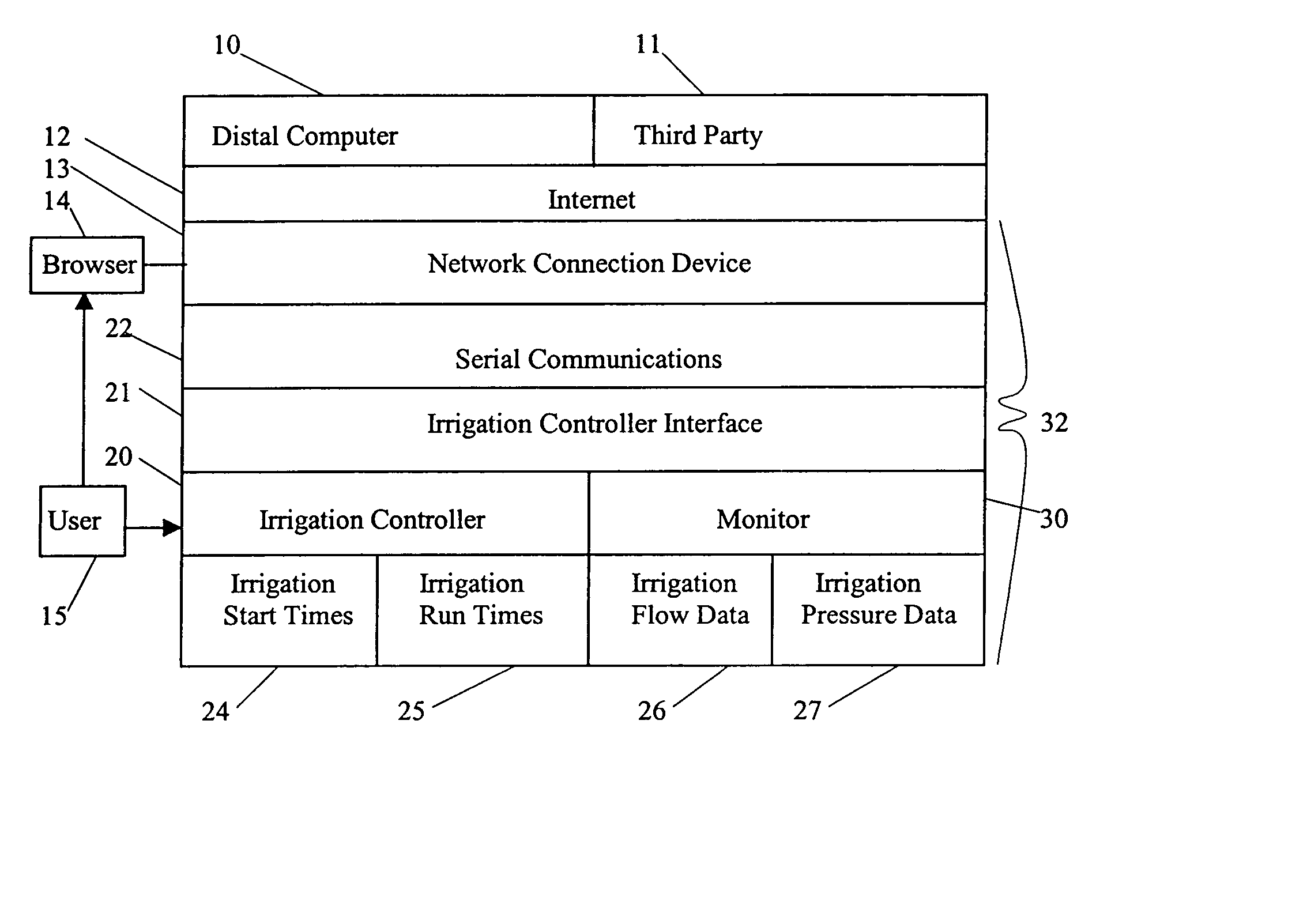
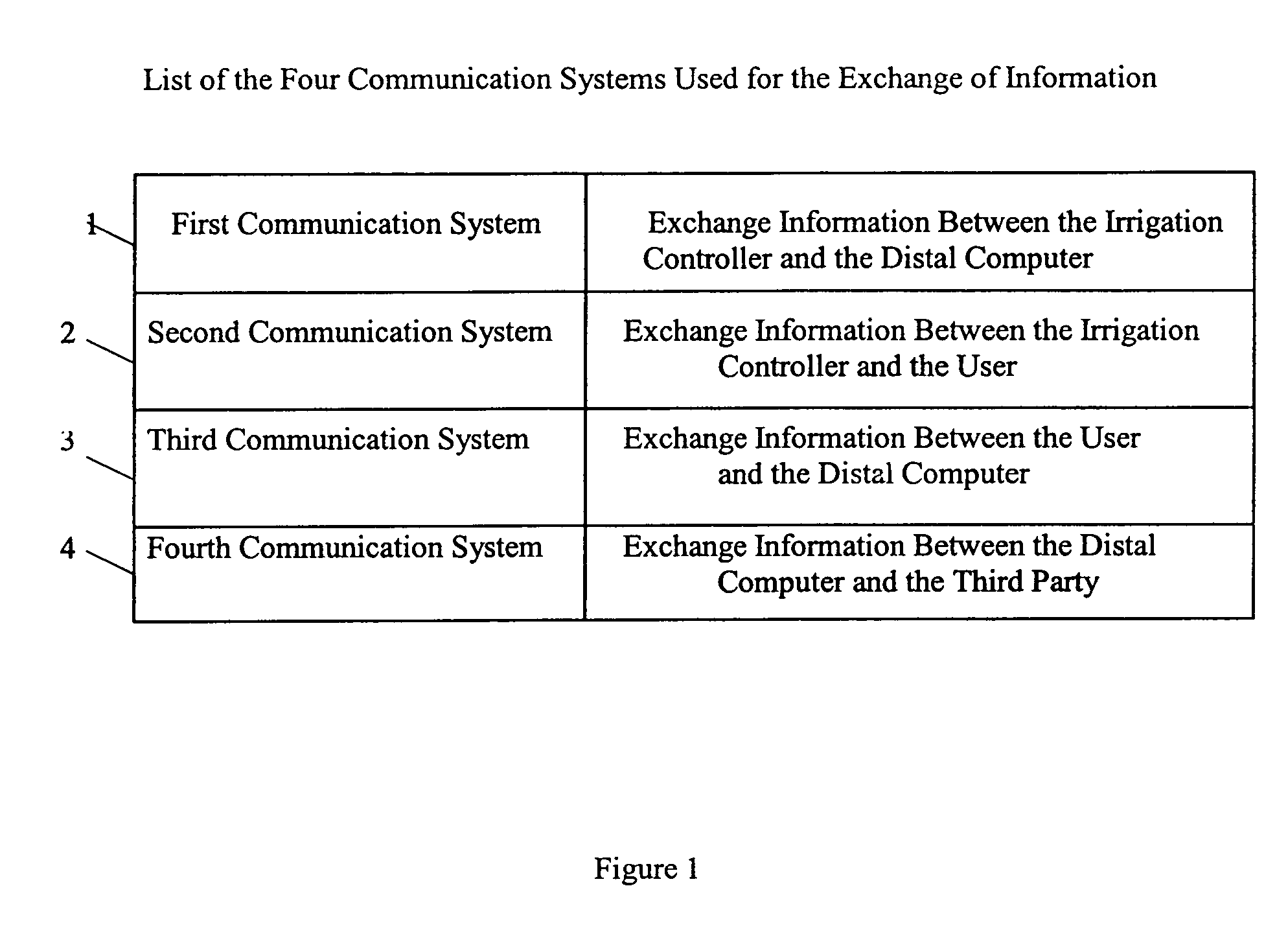
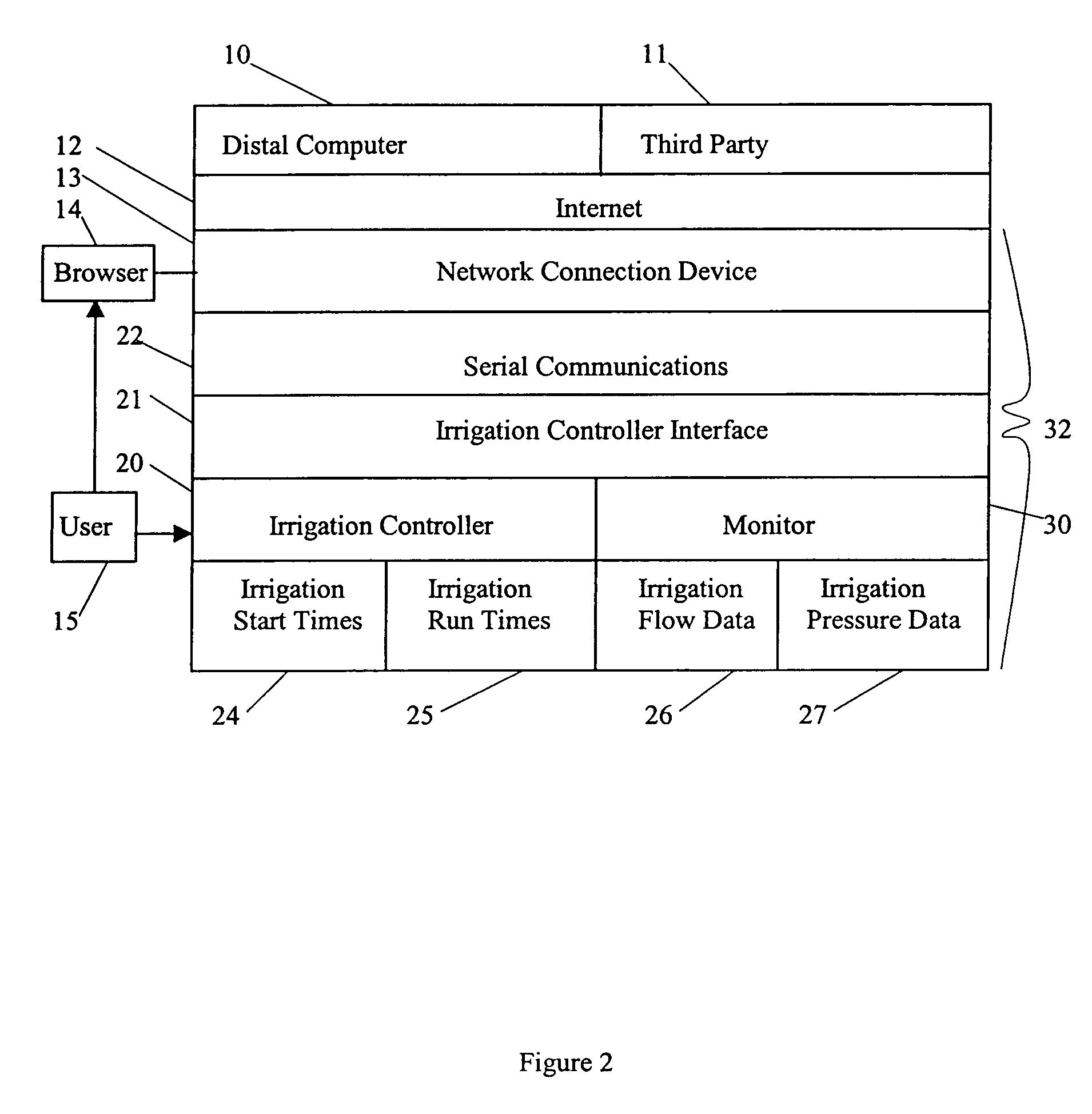
InactiveUS6950728B1Shut downSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesInternet communicationThird party
An interactive irrigation system exchanges information between an irrigation controller and a distal computer, between the irrigation controller and a user, between the user and the distal computer, and between the distal computer and a third party. The information is preferably exchanged over an Internet communication system. The exchanged information includes the following: irrigation scheduling; quantity of water applied to the landscape at the user location, which is compared to ETo values; warnings to users when potential problems with their irrigation systems are detected; and other irrigation information that is useful to the user or a third party.
Owner:AQUA CONSERVATION SYST
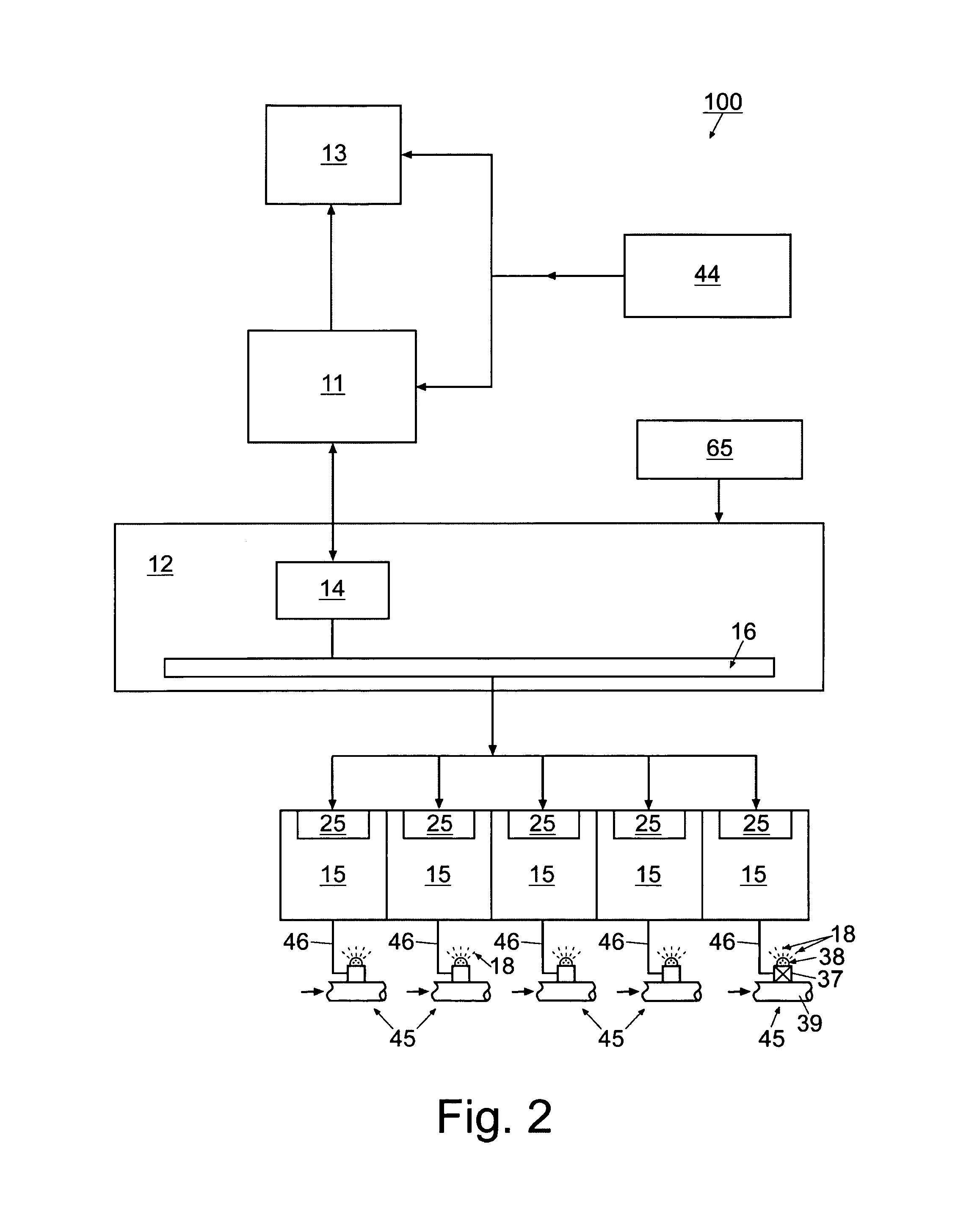
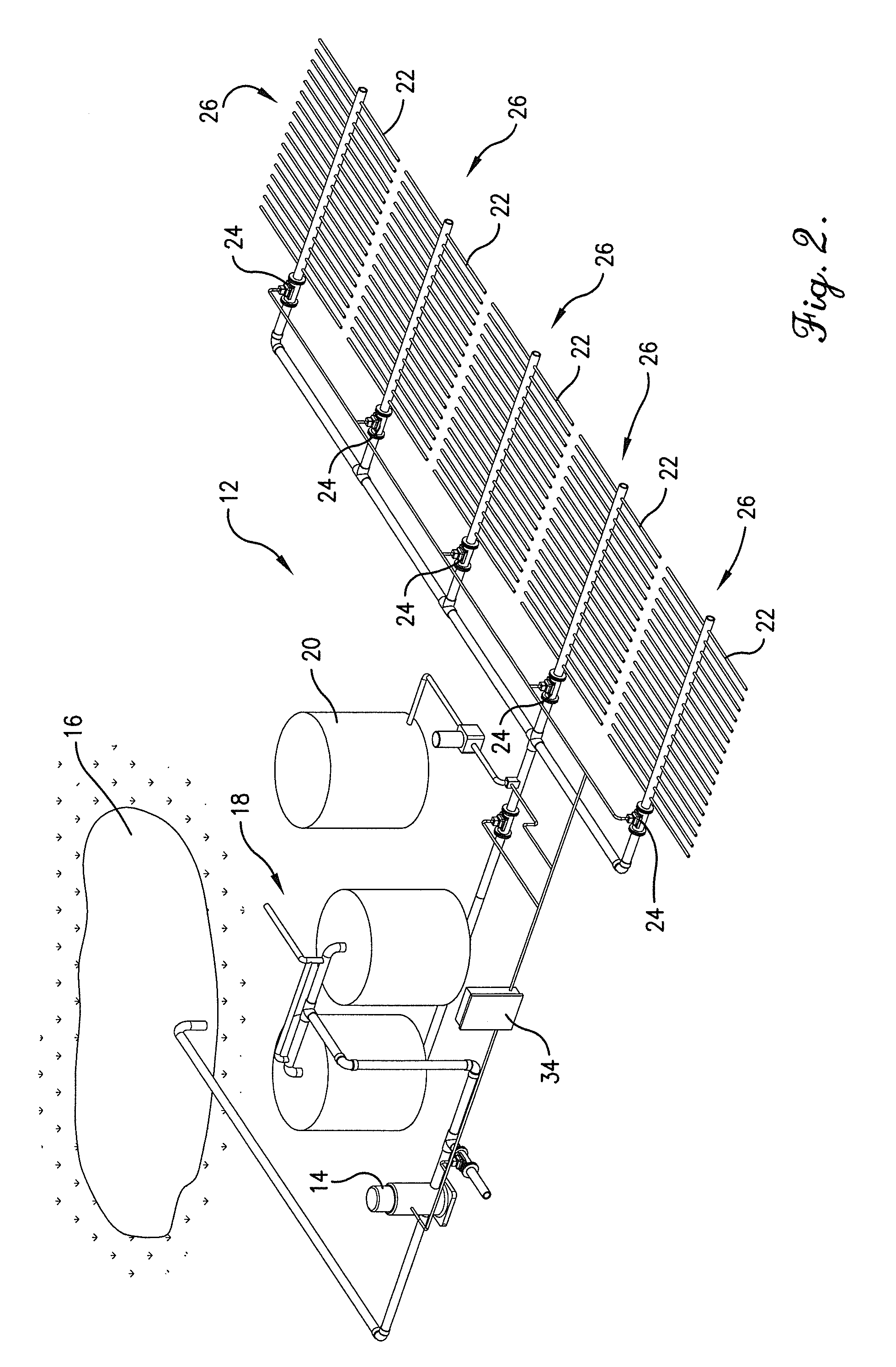
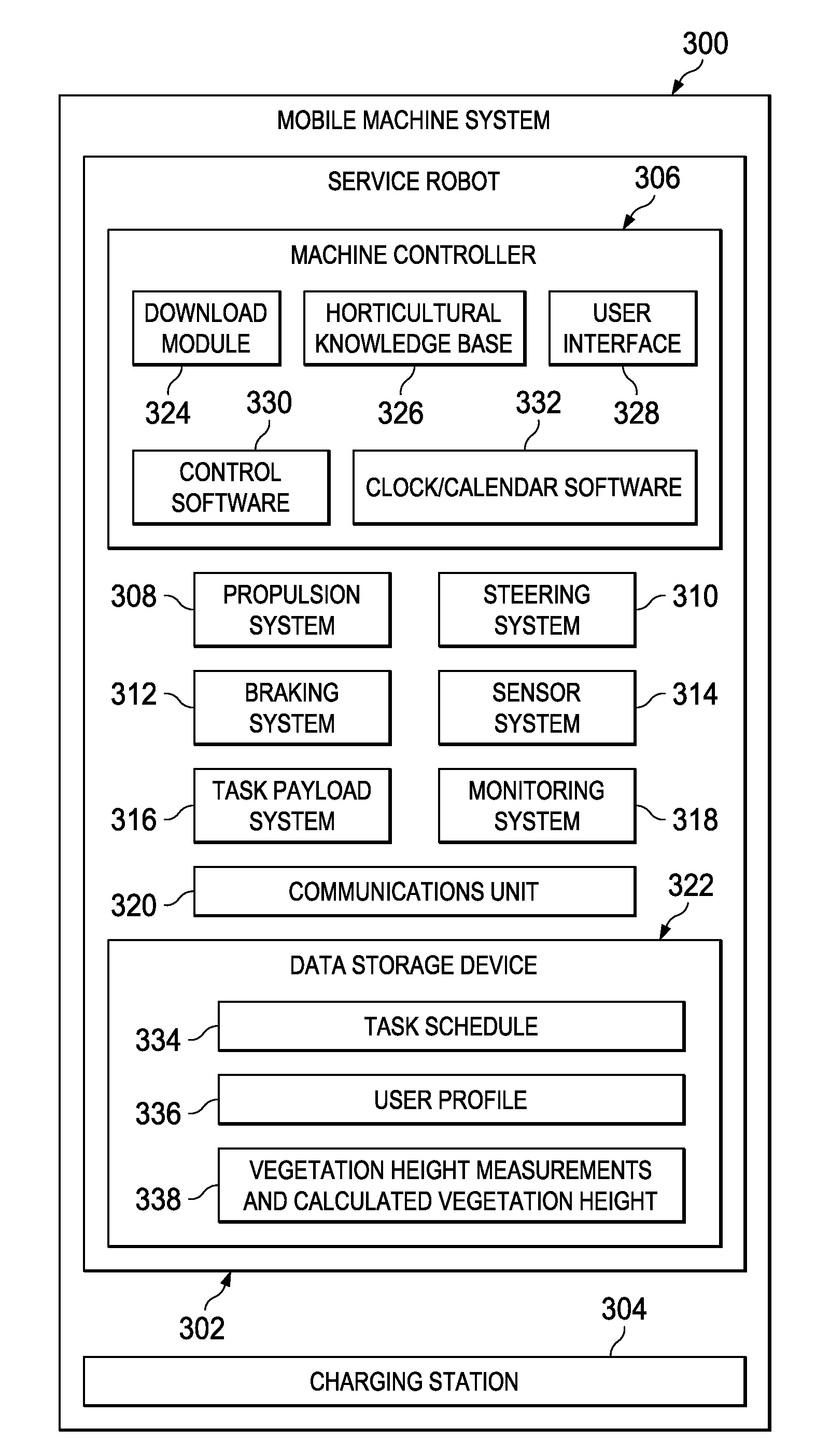
Varying irrigation scheduling based on height of vegetation
A method of controlling application of a substance to vegetation using data obtained via a mobile machine is provided. A height of the vegetation is measured during a scheduled task of the mobile machine. The measured height of the vegetation is compared with a calculated height of the vegetation. Then, an amount of the substance applied by an irrigation system to an area containing the vegetation is adjusted based on a difference between the measured height of the vegetation and the calculated height of the vegetation.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Integrated sap flow monitoring, data logging, automatic irrigation control scheduling system
ActiveUS20050121536A1Accurate measurementReduce errorsSeed and root treatmentSelf-acting watering devicesClosed loopUser interface
An integrated system for monitoring sap flow and simultaneously performing data-logging and automatically scheduling irrigation in a field; comprising a plurality of in situ sap flow gauges that perform its comprehensive computer-controlled tasks in the field being irrigated. This plurality of sap flow gauge can be detached from and reattached to a like plurality of plant stems as appropriate. A scaling mechanism is used to calculate crop water usage in variously-sized fields. An integrated portable computer apparatus is programmed to perform a plurality of actions including sap flow monitoring via a controller and data-logger; data-logging and automatic irrigation scheduling; a plurality of sap flow gauges; an automatic rain gage; a water meter; an irrigation valve actuator; and any auxiliary and independent weather or soil monitoring sensors. The system is connected to a PC, mounted in a weatherproof enclosure, and powered by rechargeable battery, solar panel, or AC mains power with battery backup. Computerized monitoring and control procedures are initialized via a custom-developed graphical user interface. At any predetermined interval set by a user, the depth or volume of water required to balance transpiration losses is calculated and irrigation is then automatically triggered. The system affords closed loop control with water flow from soil through plant to atmosphere and from irrigation—and having the benefit of a feedback loop.
Owner:BAVEL MICHAEL VAN
Irrigation system
A technique for controlling an irrigation system is disclosed. The technique comprises receiving landscape information, receiving environmental information, deriving an irrigation schedule based on the landscape information and the environmental information, and sending the irrigation schedule to an irrigation control unit.
Owner:ET WATER SYST
Electronic Irrigation System Software
InactiveUS20110049260A1Easy to set upAdd featureSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesGraphicsGraphical user interface
In one embodiment, the present invention includes irrigation control software for a computer that interacts with the features of a plurality of advanced sprinklers, environmental sensors, and other available data. The irrigation control software provides a graphical user interface to create a more efficient irrigation scheduling control interface.
Owner:PALMER DOUG +8
Irrigation controller water management with temperature budgeting
ActiveUS20120072037A1Minimizes runoffEasy and less-expensive to installSelf-acting watering devicesClimate change adaptationEngineeringEvapotranspiration
The present invention provides methods for water conservation with irrigation controllers based upon the ambient temperature and extraterrestrial radiation of a particular geographical area. It receives a preliminary irrigation schedule from the operator and computes a water budget ratio by comparing current local geo-environmental data with stored local geo-environmental data, then modifying the preliminary irrigation schedule based upon that ratio. The present invention utilizes fewer variables, is less complex, and is much easier to install and maintain than the current evapotranspiration-based controllers.
Owner:HUNTER INDUSTRIES
Multi-band photodiode sensor
ActiveUS9451745B1Increased efficiency and cost efficacyReduce irrigationRadiation pyrometryWatering devicesMulti bandEngineering
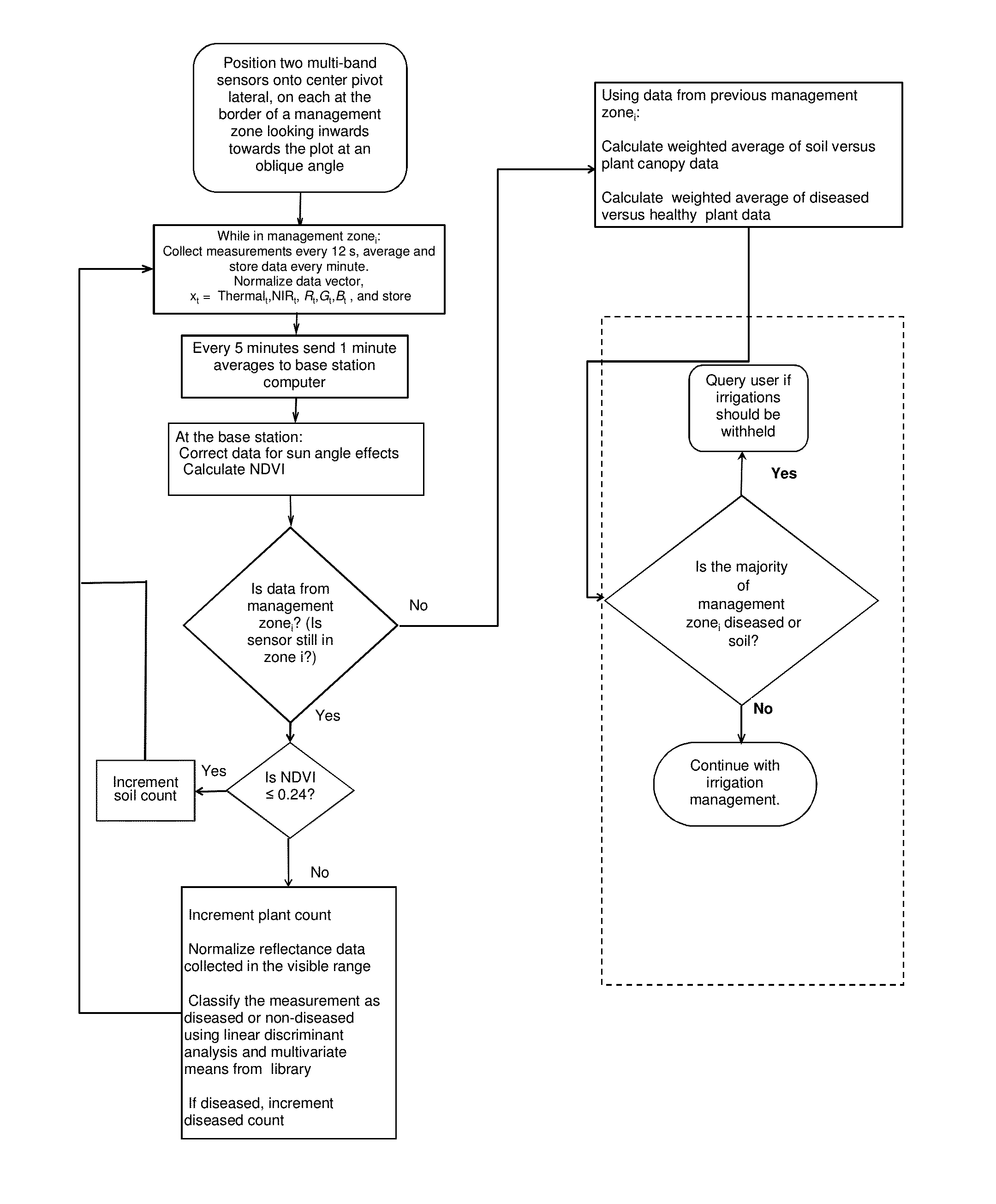
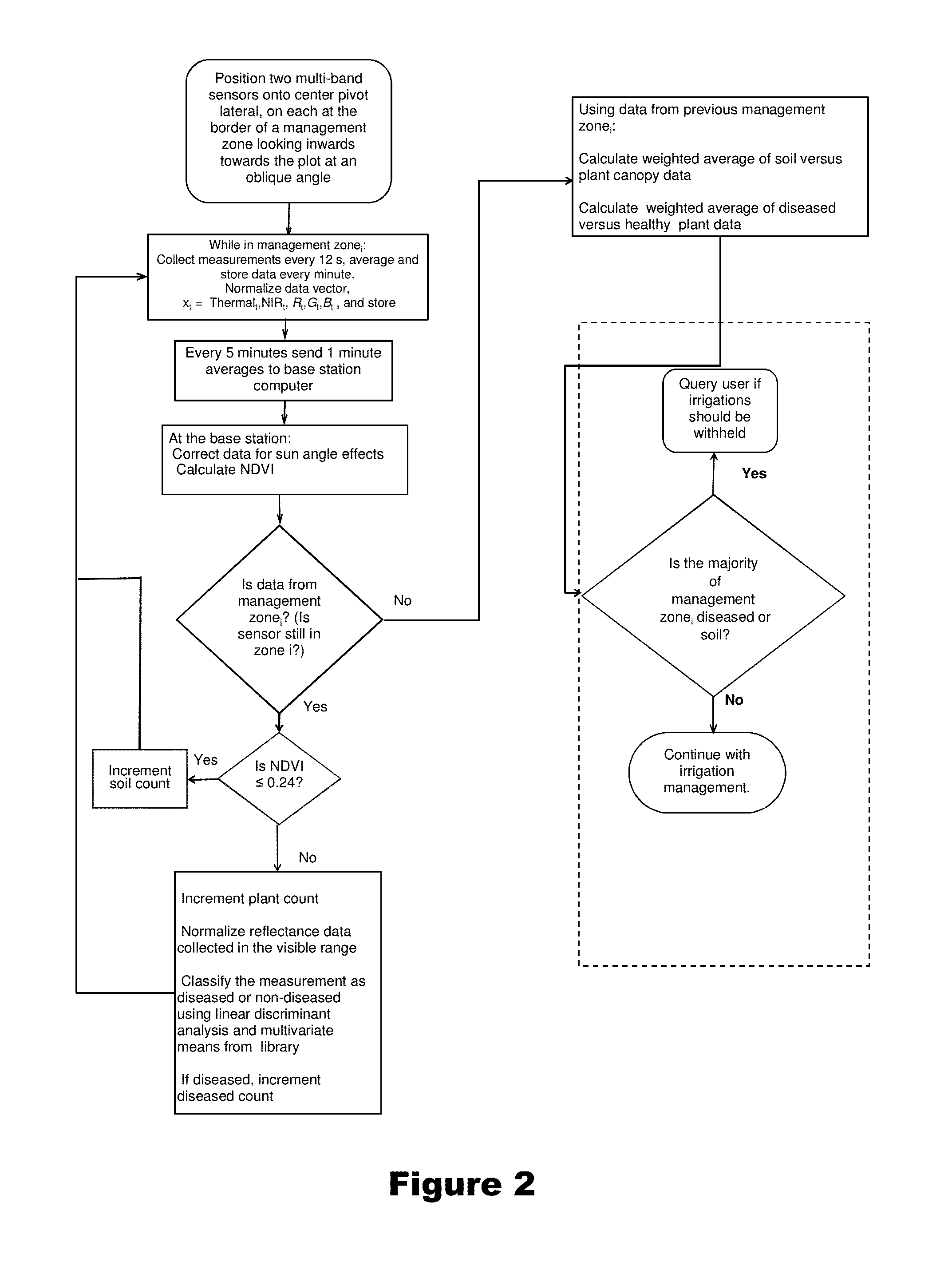
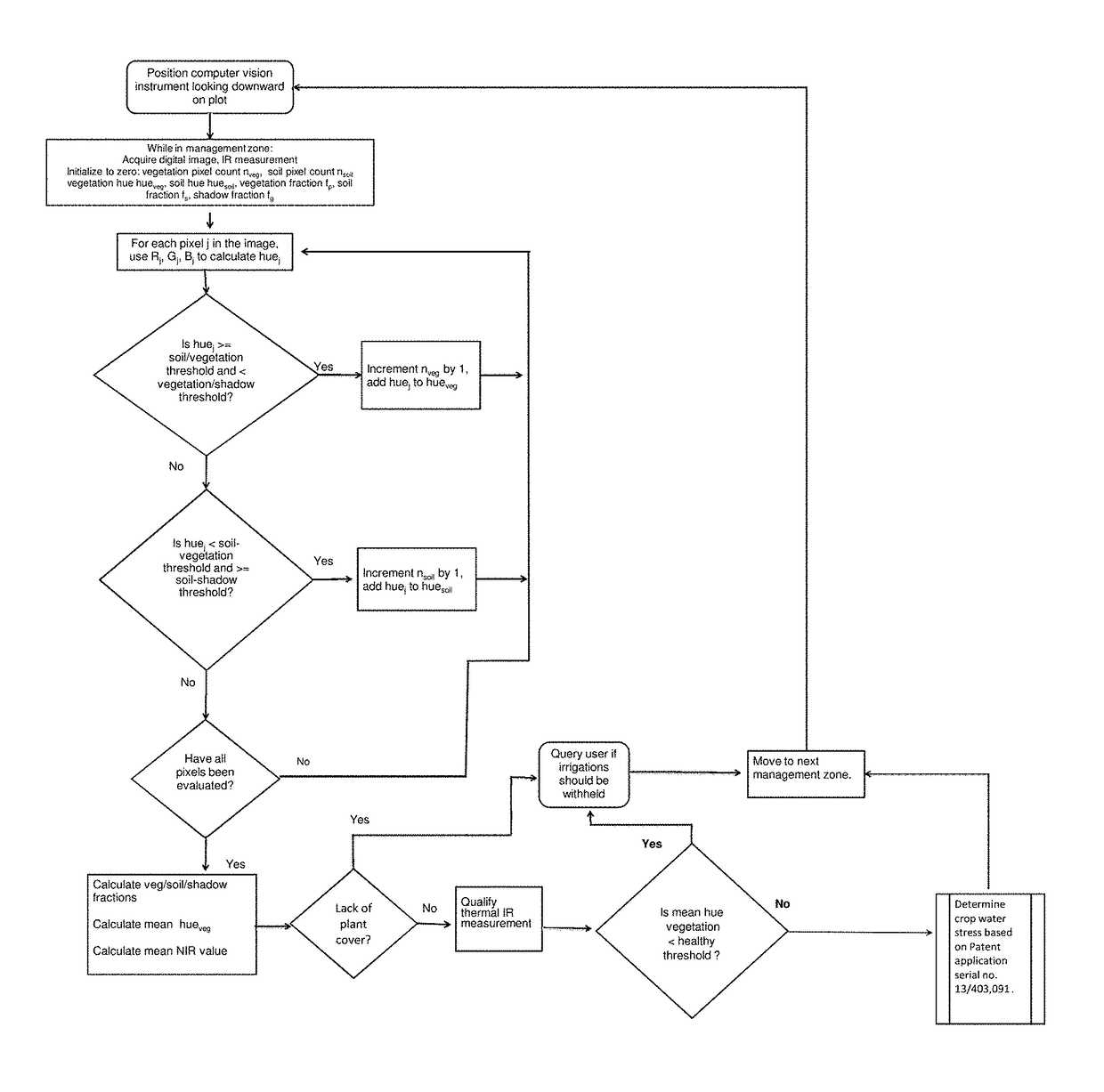
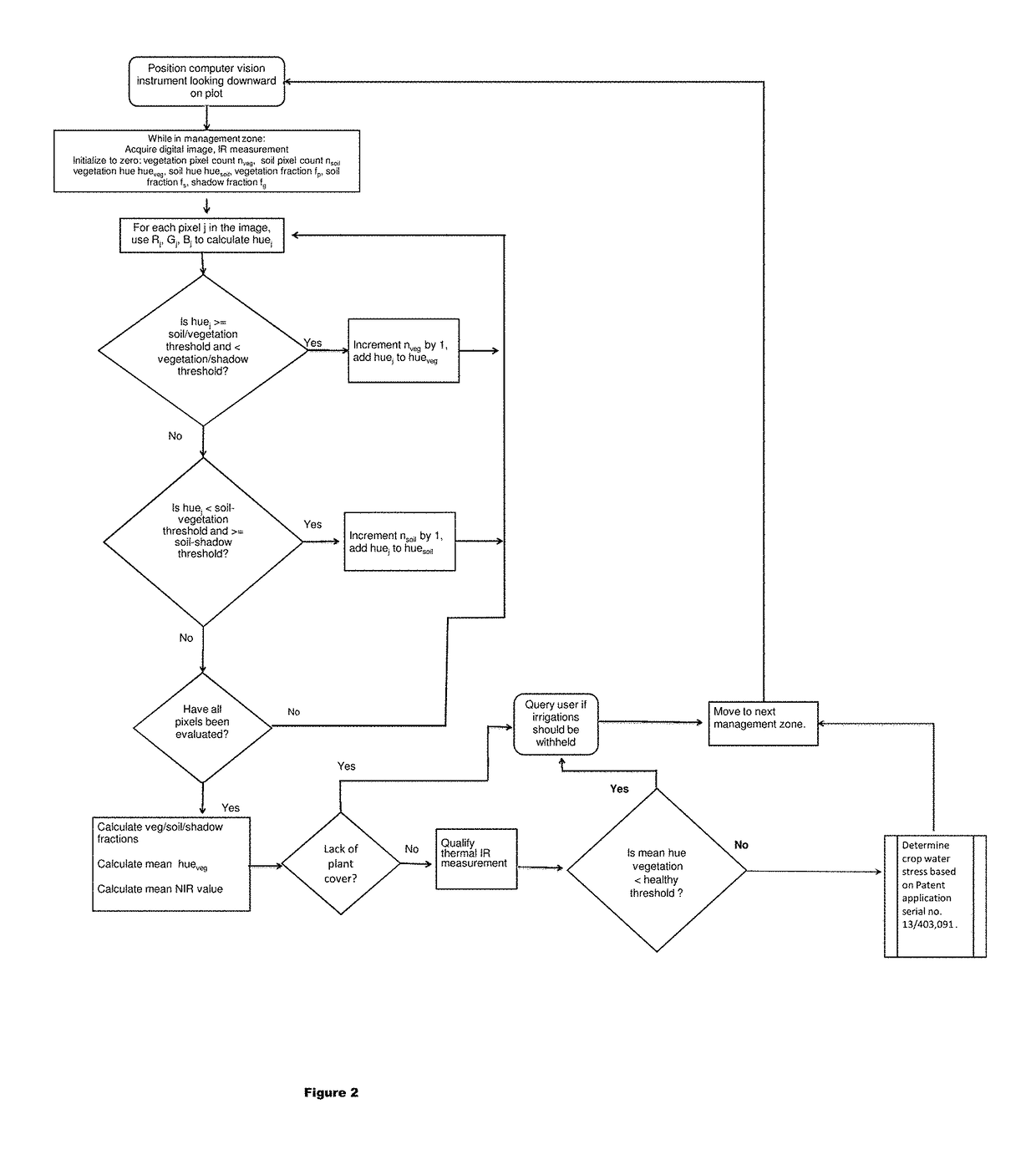
Plant canopy temperature and multi-spectral reflectance are measured with a wireless multi-band sensor, and the temperature data are qualified and the spectral reflectance measurements are classified. The multi-band sensor includes sensors for measuring plant canopy temperature radiation and spectral reflectance over five bands, a microprocessor to receive and store measured data, and a wireless transmitter for transmitting data from the microprocessor to a remote receiver, all enclosed within a single housing. The data are used to detect variations in spectral signature due to plant stress (e.g., disease, water stress) and due to soil background and to qualify temperature data accordingly. The data provide information for decision support algorithms related to the initiation of automatic irrigation scheduling as a function of crop canopy cover, qualification of temperature data used in automatic irrigation scheduling algorithms, and detection of diseased crops for the purpose of withholding irrigations when yield potential is compromised.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY +1
Remote automatic control method and system of water-saving irrigation system
InactiveCN101990840AHigh control precisionHigh Control Hit RateTransmission systemsWatering devicesGeneral Packet Radio ServiceAutomatic control
The invention discloses remote automatic control method and system of a water-saving irrigation system. The method comprises the following steps of utilizing a GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication) / GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) / CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) wireless communication network to transfer a command of a control center to an electromagnetic valve in a remote field, and remotely controlling opening and closing of the electromagnetic valve to enable the irrigation system to automatically carry out irrigation, thereby reaching an unattended state; and feeding back opening and closing signals of the electromagnetic valve in the remote field to the control center through the GSM / GPRS / CDMA wireless communication network so that an operator of the control center can know whether the electromagnetic valve in the remote field receives the command signal. The invention has the advantages of high control accuracy, high control hit rate, rapid sending command response, high automation degree and the like. The operator can preset an irrigation plan of a whole irrigation period, and the system can automatically carry out irrigation according to the irrigation plan and can reach the unattended state.
Owner:遵义群建塑胶制品有限公司
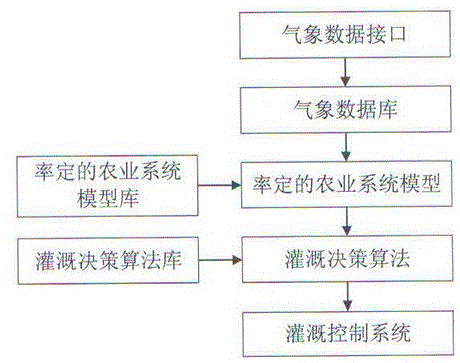
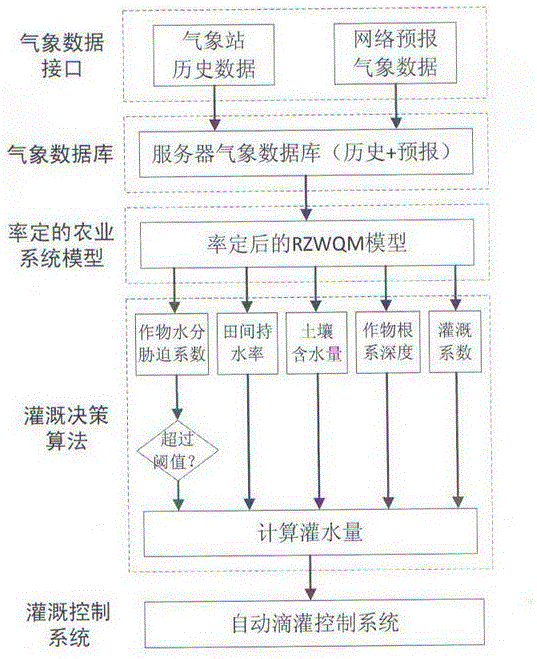
Irrigation decision-making system and method based on agricultural system model
ActiveCN106688827AAccurate Irrigation ScheduleData processing applicationsClimate change adaptationAgricultural irrigationProgram planning
The invention provides an irrigation decision-making system and method based on an agricultural system model, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural irrigation decision-making. The system comprises a meteorological data interface, a meteorological database, the calibrated agricultural system model, a calibrated agricultural system model base, an irrigation decision-making algorithm, an irrigation decision-making algorithm base and an irrigation control system, wherein the meteorological data interface is used for providing meteorological data needed for calculation for the calibrated agricultural system model, the calibrated agricultural system model is used for conducting calculation according to meteorological conditions to obtain crop growth information and soil and crop moisture conditions, the irrigation decision-making algorithm is used for judging whether irrigation is conducted or not and calculating the irrigation amount according to the model calculation result, and the irrigation control system is used for conducting irrigation according to the irrigation amount calculated by the irrigation decision-making algorithm. The irrigation decision-making system and method based on the agricultural system model overcome the defects of an existing irrigation decision-making system and method, an accurate irrigation plan is made without installing field sensors, and a future irrigation plan and the corresponding irrigation effect can be predicted.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Irrigation controller with weather station
An irrigation control module is described that adjusts a watering schedule for a connected irrigation controller based on weather data provided by a local weather station. The irrigation control module can add additional weather-based irrigation schedule adjustments to an irrigation controller that may otherwise lack the hardware (e.g., wireless transmitter, sufficient memory) and software (e.g., evapotranspiration algorithms) to store and interpret weather data from a weather station.
Owner:TORO CO THE
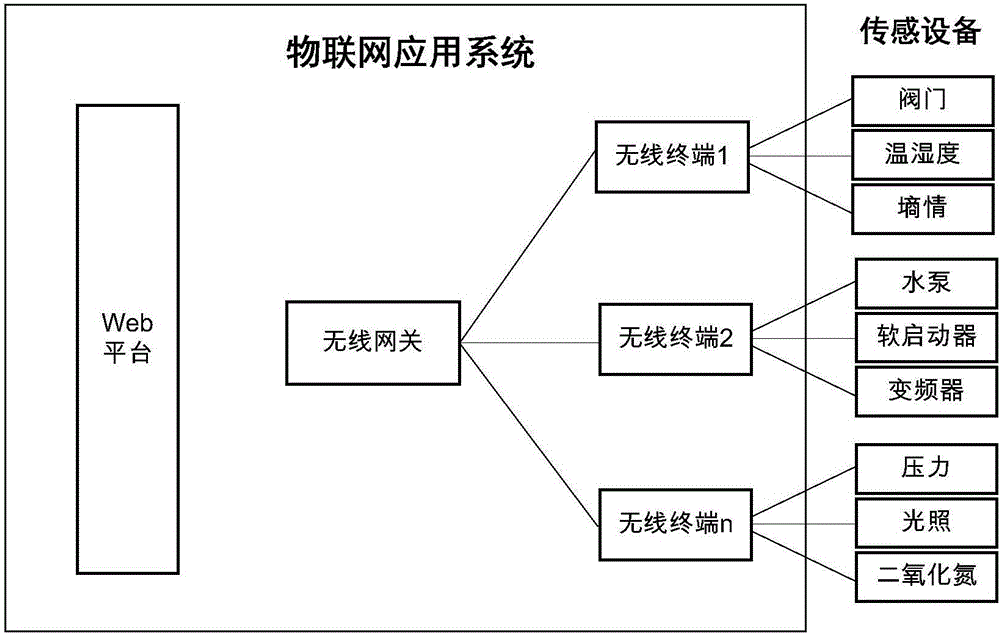
Agricultural irrigation water saving system
InactiveCN106258858ARealize automatic irrigationReal-time monitoring of regional environmentWatering devicesCultivating equipmentsWireless gatewaySoil moisture content
The invention relates to an agricultural irrigation water saving system. The system comprises a Web platform, a wireless gateway and wireless terminal equipment, wherein a mobile communication network is adopted for communication between the Web platform and the wireless gateway, and a short-range wireless communication network is adopted for communication between the wireless gateway and the wireless terminal equipment. The Web platform issues a control instruction to the wireless gateway, the wireless gateway forwards the instruction to the wireless terminal equipment, and then the wireless terminal equipment carries out corresponding operation and returns a result. The Web platform comprises an irrigation planning module used for making irrigation strategies according to different crops, different environmental attributes, real-time soil moisture content data, pipeline pressure and the like. The system intelligently makes the irrigation strategies in a pointed mode, can monitor region environment in real time and remotely control equipment to achieve automatic irrigation and improves water-saving capacity and accuracy of irrigation.
Owner:北京慧图科技(集团)股份有限公司
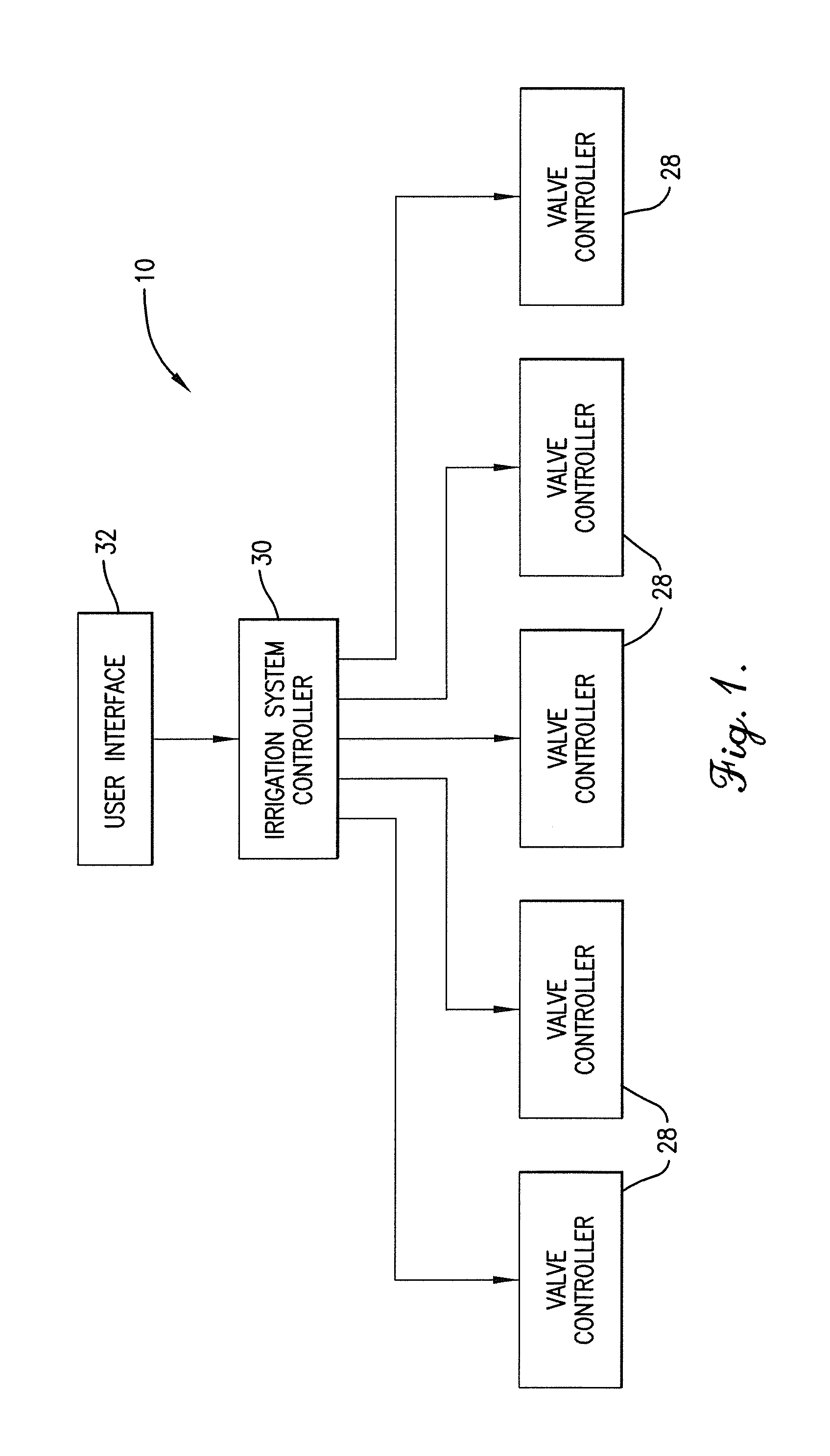
Irrigation control system and method
An irrigation control system with a programmable controller having a high speed central processor and a touch screen monitor for independent and simultaneous operation of multiple watering stations and schedules. The touch screen monitor allows for quick entry of changes to irrigation schedules that can be made while the system is in use, thus preventing service interruption. The irrigation control system will accommodate multiple watering stations with precise accuracy and allows for independent start times for each station. Multiple output terminals permit connection to various watering stations as a pre-programmed, removable thumb drive containing the operating system and application software is connected through a USB port to a high speed central processor. The irrigation method describes using the controller for optimum plant growth and health.
Owner:ECO PRECISE IRRIGATION CONTROLS
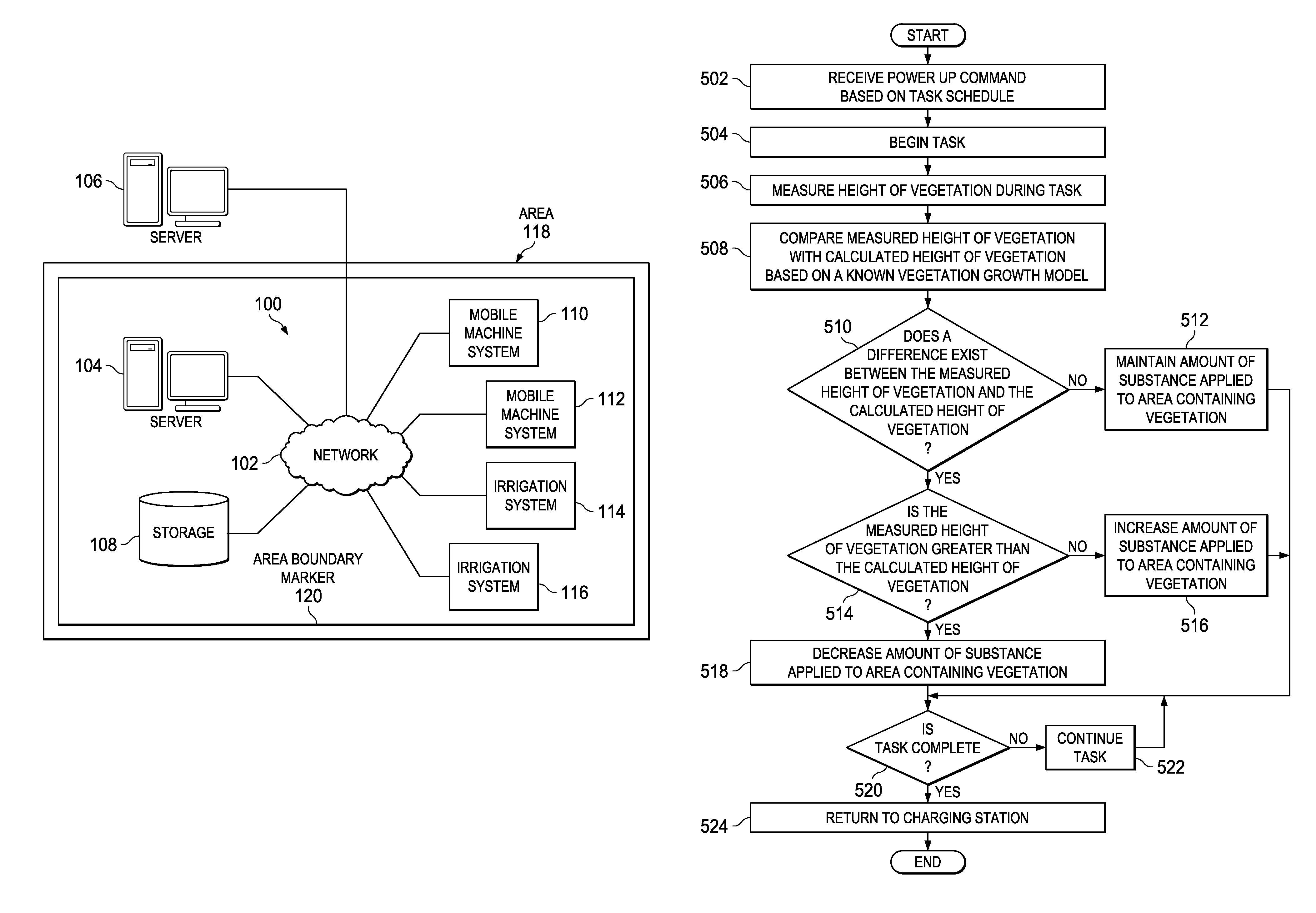
Varying irrigation scheduling based on height of vegetation
A method of controlling application of a substance to vegetation using data obtained via a mobile machine is provided. A height of the vegetation is measured during a scheduled task of the mobile machine. The measured height of the vegetation is compared with a calculated height of the vegetation. Then, an amount of the substance applied by an irrigation system to an area containing the vegetation is adjusted based on a difference between the measured height of the vegetation and the calculated height of the vegetation.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Irrigation control method and device
InactiveCN108094370ARealize monitoringAccurately determine irrigation conditionsWatering devicesResourcesBiologyMoisture
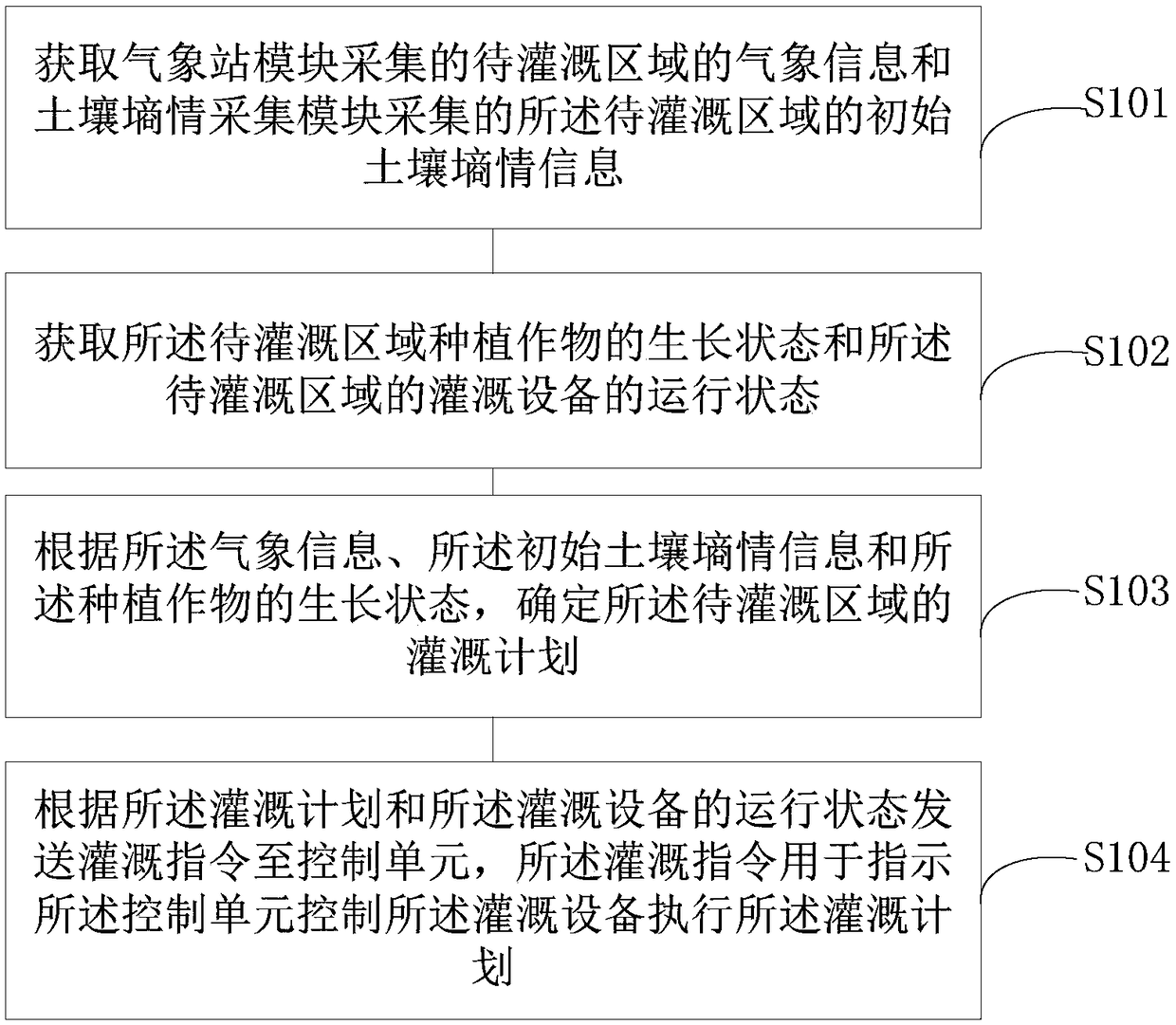
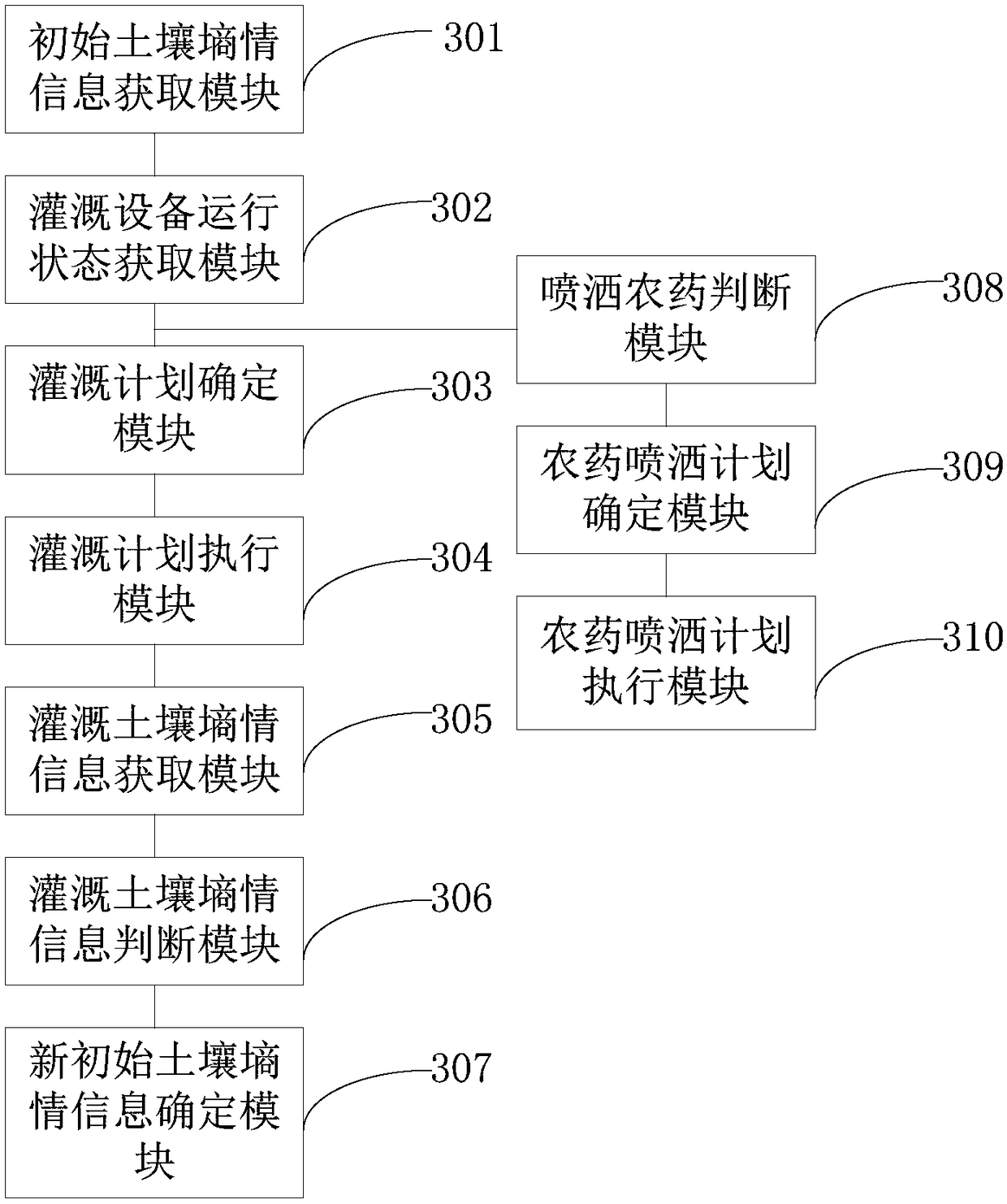
The invention is applicable to the technical field of farmland irrigation, and provides an irrigation control method and device. The method includes the following steps that weather information, collected by a meteorological station module, of a to-be-irrigated region and initial soil moisture information, collected by a soil moisture acquisition module, of the to-be-irrigated region are obtained;the growth state of planting crops in the to-be-irrigated region and the running state of an irrigation device in the to-be-irrigated region are obtained; according to the weather information, the initial soil moisture information and the growth state of the planting crops, an irrigation plan of the to-be-irrigated region is determined; according to the irrigation plan and the running state of the irrigation device, an irrigation command is sent to a control unit, and the irrigation command is used for instructing a control unit to control the irrigation device to carry out the irrigation plan. After adopting the above scheme, the irrigation condition of a farmland can be determined, and the soil moisture is maintained in the optimal range of crop growth.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED MATHEMATICS HEBEI ACADEMY OF SCI
Electronic Irrigation System Software
InactiveUS20130099022A9Easy to set upAdd featureSelf-acting watering devicesWatering devicesGraphicsGraphical user interface
In one embodiment, the present invention includes irrigation control software for a computer that interacts with the features of a plurality of advanced sprinklers, environmental sensors, and other available data. The irrigation control software provides a graphical user interface to create a more efficient irrigation scheduling control interface.
Owner:PALMER DOUG +8
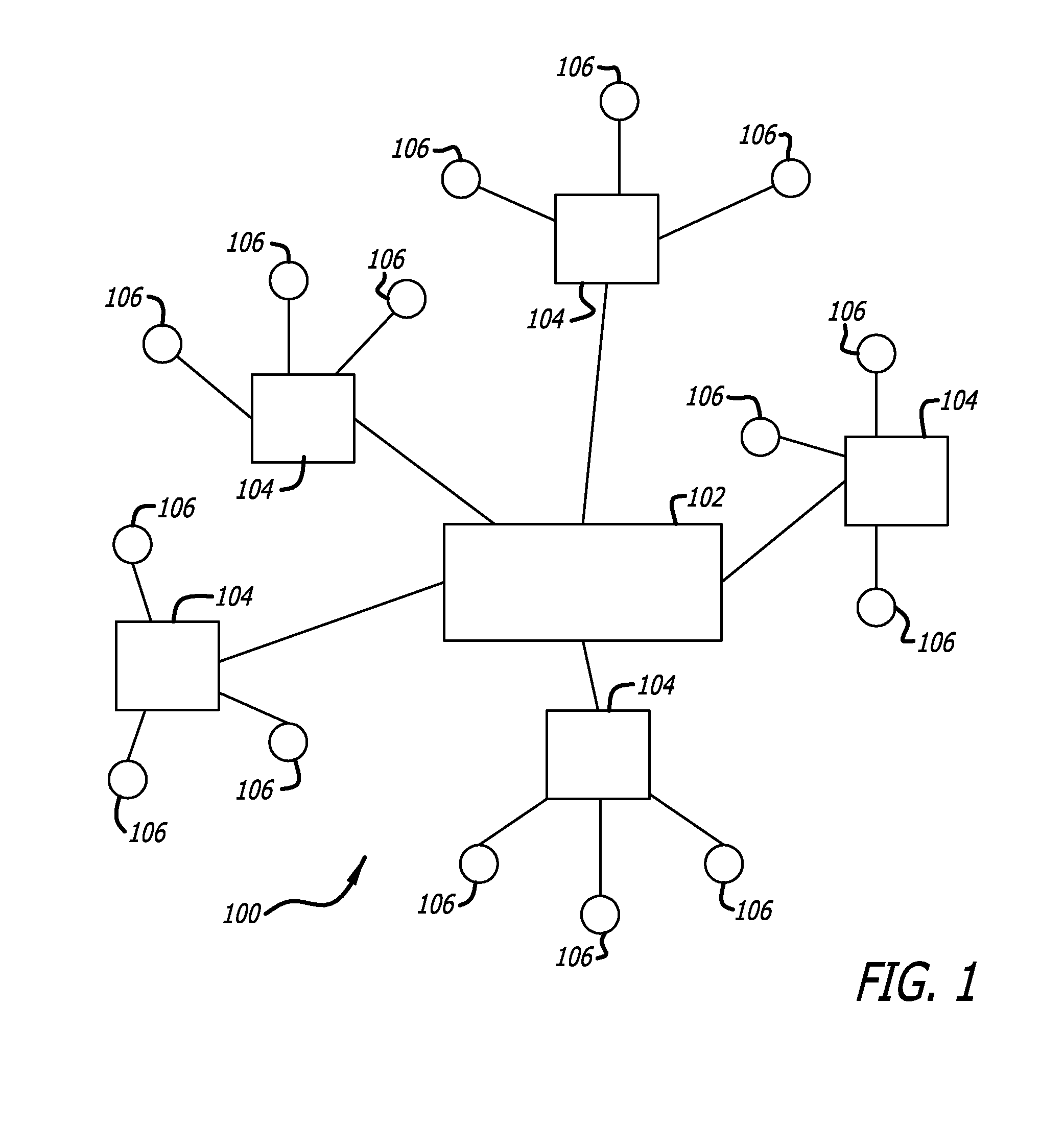
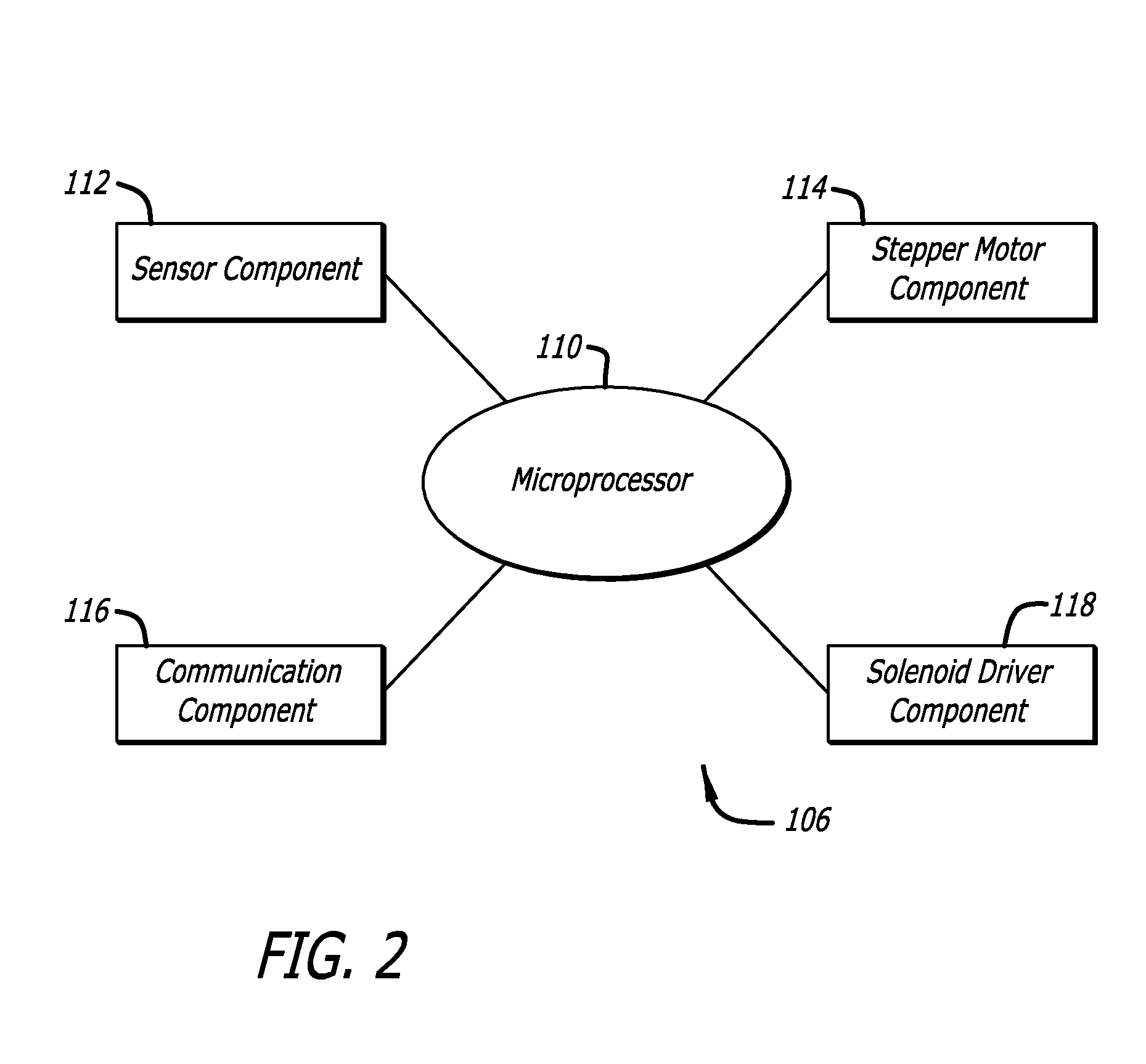
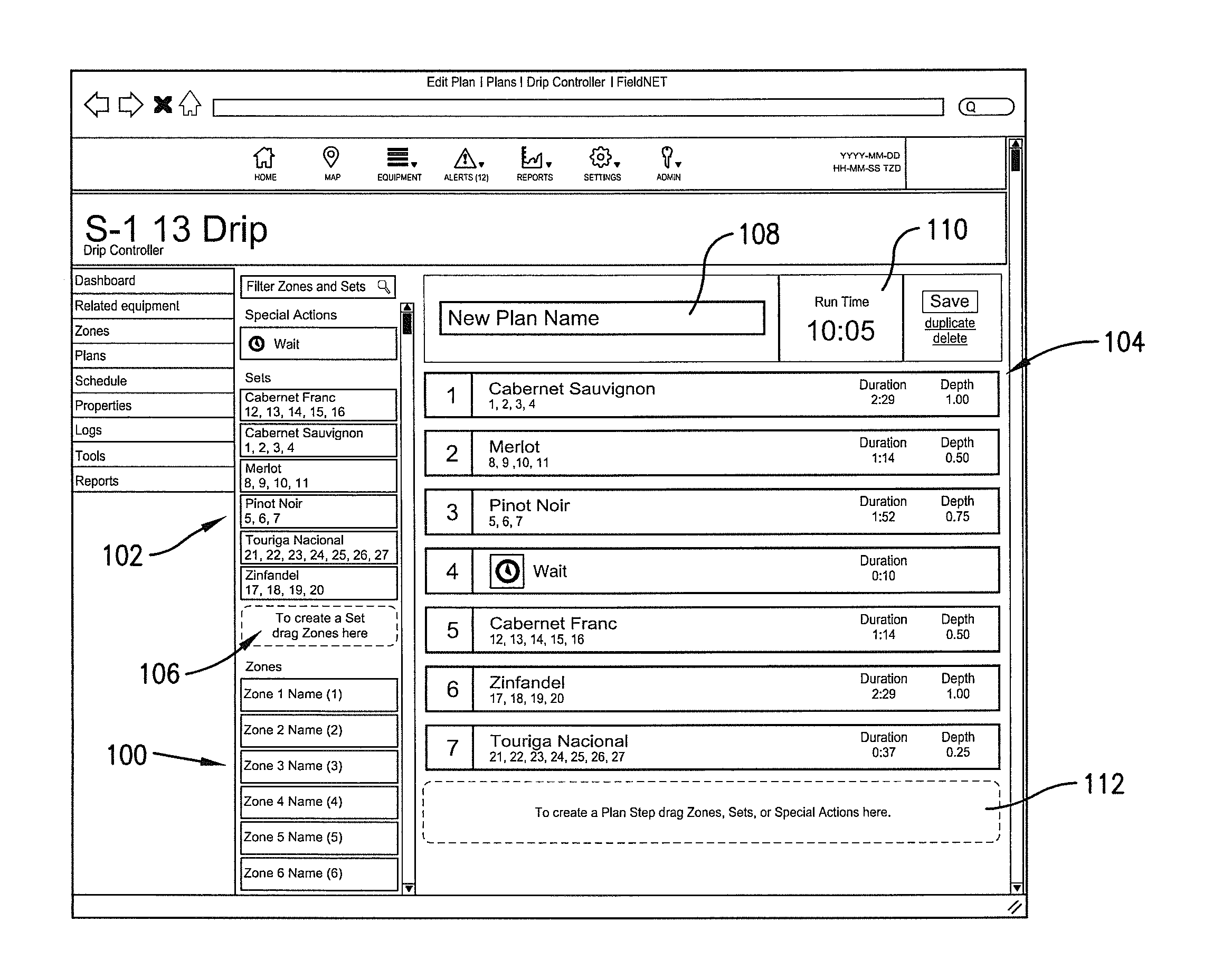
Control system for an irrigation system
InactiveUS9408353B2Simplifies creation and modification and implementationQuickly and easily create newComputer controlClimate change adaptationDrag and dropGraphical user interface
A control system for a low-volume irrigation system includes a plurality of valve controllers for opening and closing valves; an irrigation system controller for controlling the valve controllers in accordance with an irrigation plan; and a graphical user interface for allowing a user to interact with the irrigation controller and to create the irrigation plan. The graphical user interface displays an irrigation zone list, an irrigation set list, and an irrigation plan field. The user interface has drag and drop functionality that permits an irrigation zone listing from the irrigation zone list to be dragged and dropped into any of the irrigation set listings in the irrigation set list and that permits an irrigation zone listing or an irrigation set listing to be dragged and dropped into the irrigation plan to create irrigation steps within the irrigation plan.
Owner:LINDSAY CORP
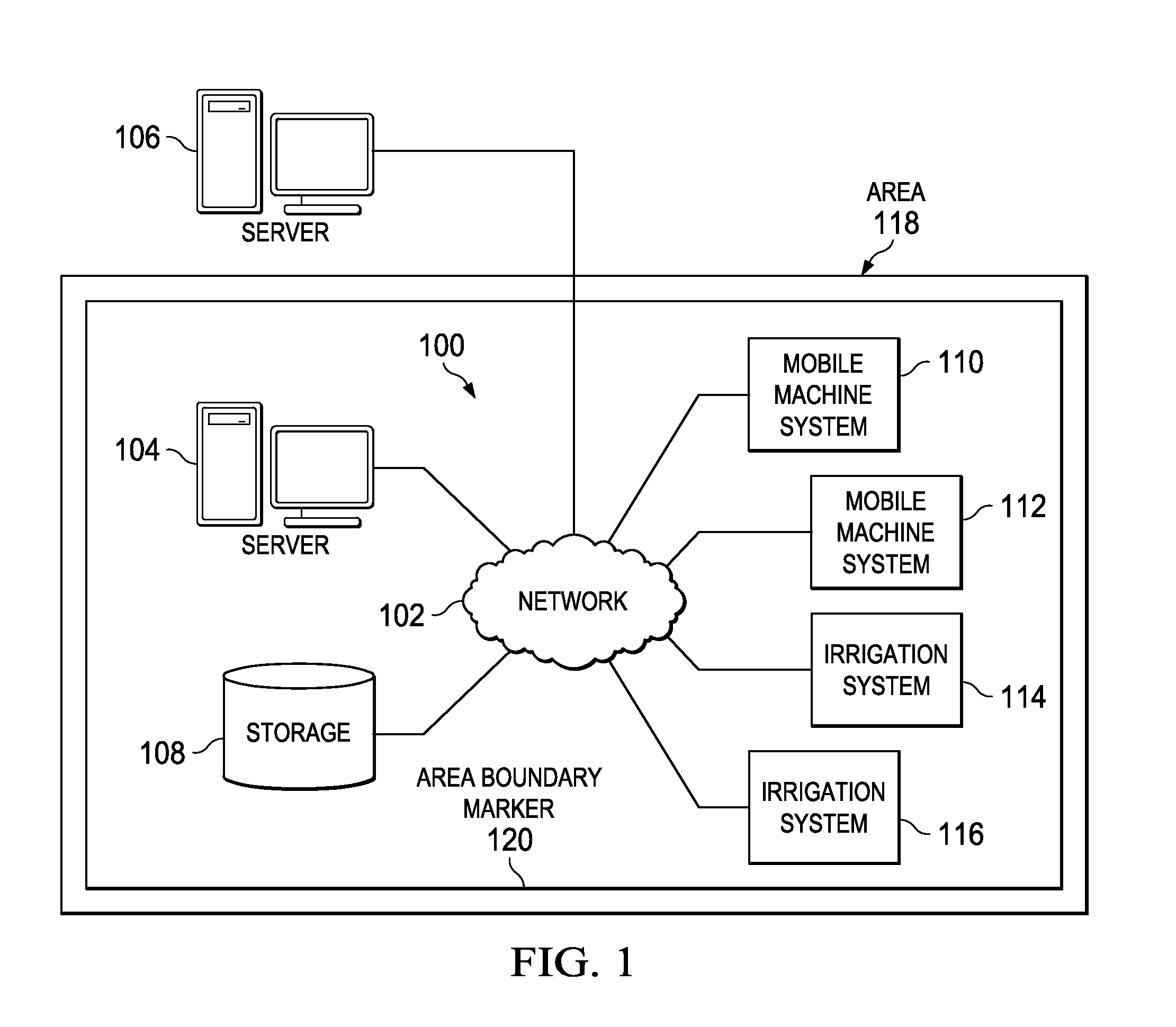
Varying Irrigation Scheduling Based on Height of Vegetation
A method of controlling application of a substance to vegetation using data obtained via a mobile machine is provided. A height of the vegetation is measured during a scheduled task of the mobile machine. The measured height of the vegetation is compared with a calculated height of the vegetation. Then, an amount of the substance applied by an irrigation system to an area containing the vegetation is adjusted based on a difference between the measured height of the vegetation and the calculated height of the vegetation.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Computer vision qualified infrared temperature sensor
ActiveUS9866768B1Reduced false positive irrigation schedulingImprove efficiencyTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryProcess MeasuresVisual perception
Plant canopy images and temperature are acquired with a wireless computer vision instrument, and the temperature data are qualified and pixels within the image are classified. The instrument includes sensors for measuring plant radiation due to canopy temperature and an imaging sensor which collects data over four bands, a microprocessor to receive and store and process measured data from the sensors, and a wireless transmitter for transmitting data from the microprocessor to a remote receiver. The data are used to detect plant stress and canopy cover percentage and to qualify temperature data accordingly. The data from the sensors provide information for decision support algorithms related to the initiation of automatic irrigation scheduling as a function of crop canopy cover and water stress, the qualification of temperature data used in automatic irrigation scheduling algorithms, and the detection of diseased crops for the purpose of withholding irrigations when yield potential is compromised.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
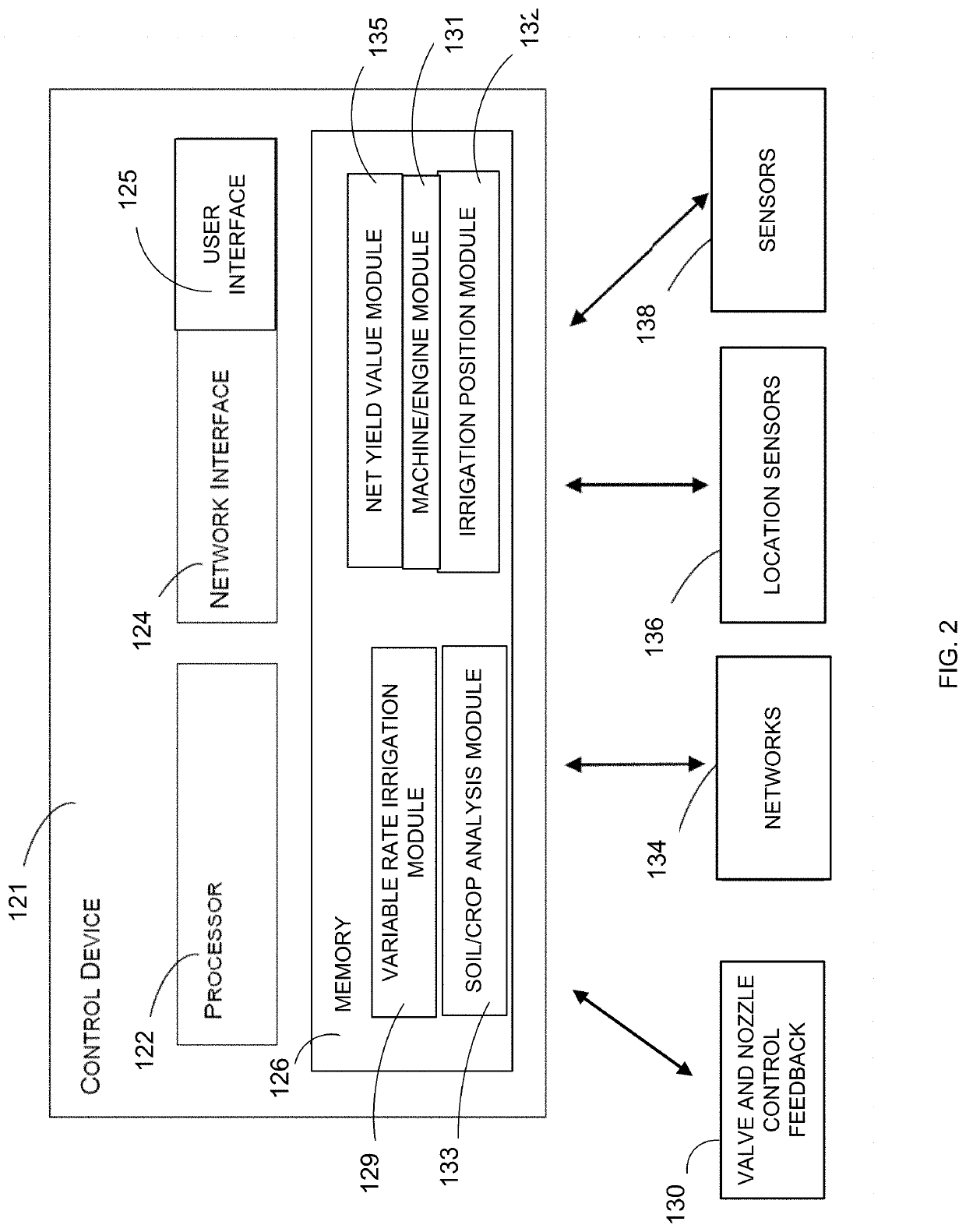
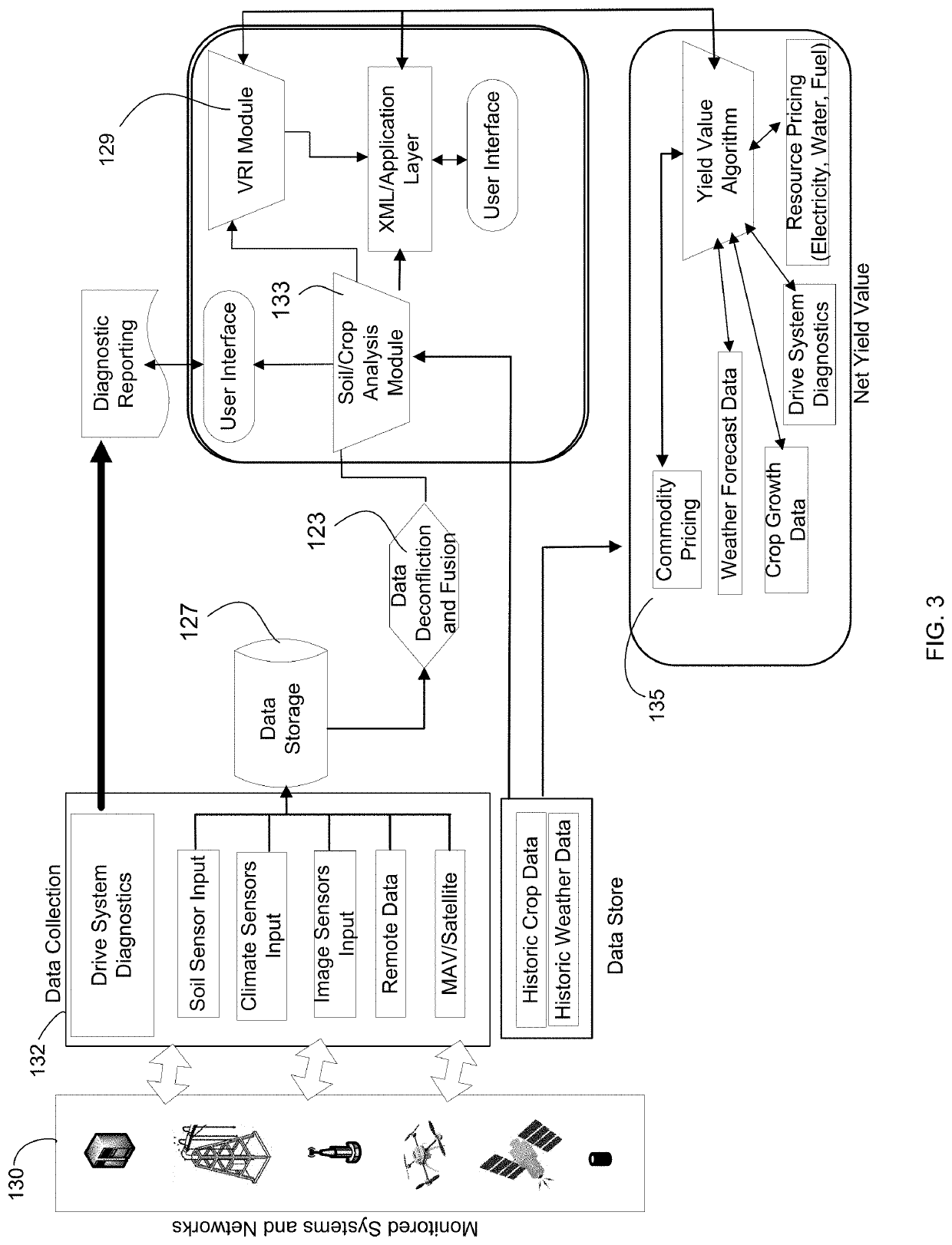
System, method and apparatus for integration of field, crop and irrigation equipment data for irrigation management
ActiveUS20210169025A1Programme controlImage enhancementEnvironmental resource managementGraphical user interface
The present invention provides a system, method and apparatus for providing an irrigation scheduling module including a graphical user interface for providing irrigation scheduling data for a given field location. According to a preferred embodiment, the irrigation scheduling module is configured to calculate and display an irrigation recommendation for a given set of forecast data. According to a further preferred embodiment, the irrigation recommendation includes a representative shape in the form of a circle which changes from a full circle to a crescent-shaped percentage of the full circle based on the field moisture status.
Owner:VALMONT INDUSTIES INC
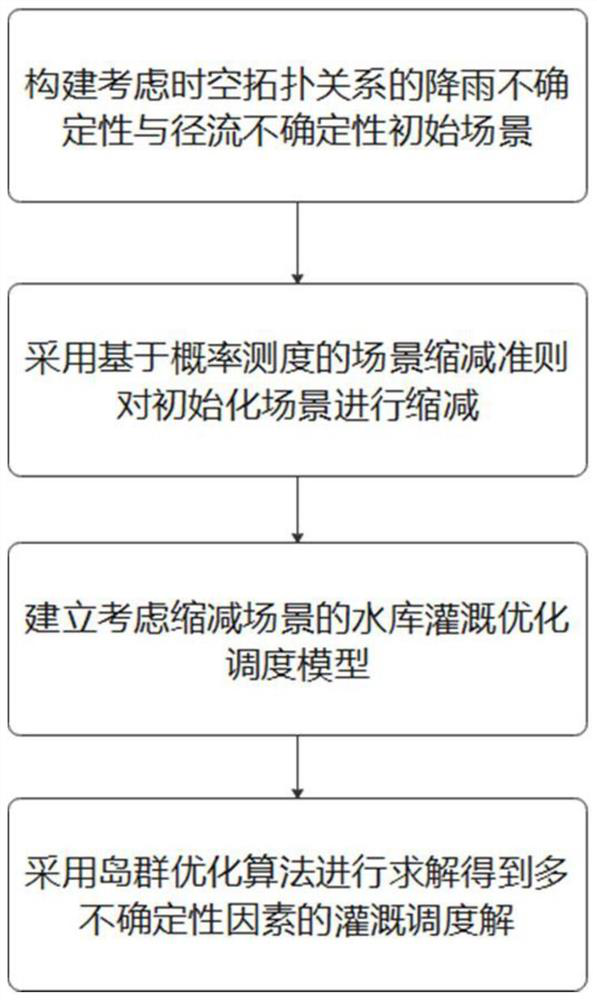
Reservoir irrigation optimal scheduling method considering multiple uncertainties
ActiveCN112613720AImprove irrigation schedulingImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionResourcesOptimal schedulingSpacetime topology
The invention provides a reservoir irrigation optimal scheduling method considering multiple uncertainties. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an initial scene considering rainfall uncertainty and runoff uncertainty of a space-time topological relation; reducing the initialized scene by adopting a scene reduction criterion based on probability measurement; establishing a reservoir irrigation optimal scheduling model considering the reduction scene; and solving the model in the step 3 by adopting an island group optimization algorithm, and scheduling irrigation water supply according to a calculation result. The reservoir irrigation optimal scheduling model influenced by multiple uncertain factors is established by adopting chaotic scene planning, and the scheduling result is solved by adopting the island group optimization algorithm, so that a good reference is provided for the reservoir irrigation scheduling water quantity, the problems caused by the uncertain factors are effectively solved, and the reservoir irrigation scheduling efficiency is improved. And the reservoir irrigation scheduling level and scheduling accuracy are greatly improved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Precise crop irrigation algorithm and control system
PendingCN113179923AFunctionalClimate change adaptationWatering devicesAgricultural scienceControl system
The invention discloses a precise crop irrigation algorithm and a control system. The precise crop irrigation algorithm comprises crop water demand calculation and irrigation schedule calculation; crop water demand calculation adopts a Penman method; a irrigation schedule comprises a watering quota and an irrigation quota; the irrigation schedule is classified according to dry crops and paddy field crops, and different irrigation schedules are executed for different crop types. The irrigation amount is determined according to the irrigation schedules, the irrigation schedules are calculated every ten days by adopting lists and diagrams or computer programming calculation, the control system can collect basic agrometeorology and soil moisture content information, and a new irrigation algorithm is utilized, different irrigation schemes are provided for different farmlands, real-time scheme operation instructions are provided, and meanwhile, the system also has the functions of fertilization management and pest and disease damage management.
Owner:湖北良顷农业科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com