Method for preparing crosslinkable segmented copolymer by utilizing active free radical soap-free emulsion polymerization and prepared compound thereof
A soap-free emulsion polymerization and compound technology, which is applied in the field of polymer chemistry, can solve the problems that polymers contain metal impurities such as copper, are sensitive to oxygen, and require expensive nitrogen-containing or phosphorus-containing ligands, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 2
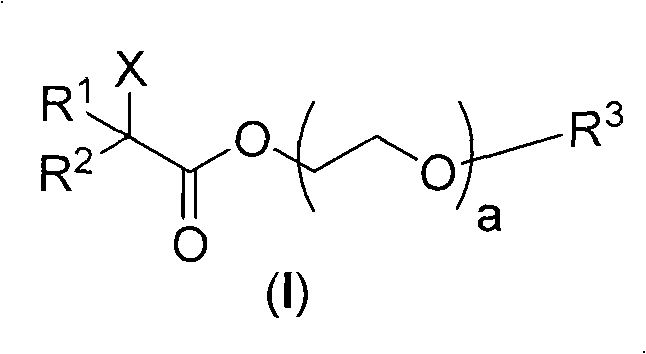
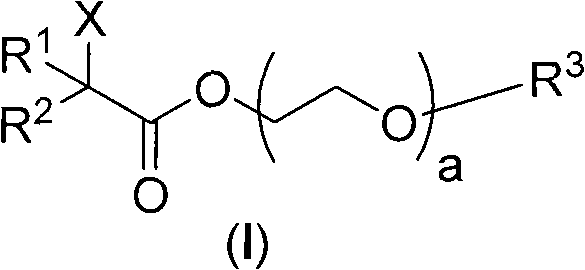
[0058] The preparation of embodiment 1 two (2-bromo-isobutyric acid) polyethylene glycol-2000 diesters (Ia)
[0059] The target compound was prepared from polyethylene glycol-2000, 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide and triethylamine.
[0060] Weigh PEG-2000 (20 g, 10 mmol) into a reaction flask, and then add dry tetrahydrofuran (30 mL). After the dissolution was complete, an excess of dry triethylamine (50 mmol, 5 times that of PEG-2000) was added. Under the protection of argon, 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide (6.9 g, 30 mmol, 3.75 mL) was dissolved in dry tetrahydrofuran (30 mL), and then slowly added dropwise into the reaction flask. The reaction system was reacted at 40°C for 48h. After the reaction was completed, filter, discard the filter cake, and distill the filtrate to remove the solvent under reduced pressure to obtain a light brown viscous liquid. Anhydrous diethyl ether was added to the viscous liquid, mixed well to precipitate solids, filtered, and the resulting filter cake w...
Embodiment 22
[0063] The preparation of embodiment 22-bromopropionic acid polyethylene glycol (800) monomethyl ether ester (Ib)
[0064] The target compound was prepared from polyethylene glycol (800) monomethyl ether, 2-bromopropionic acid, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC), and 4-N,N-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP).
[0065] Weigh PEG-800 (8 g, 10 mmol) and 2-bromopropionic acid (1.53 g, 10 mmol) into a reaction flask, and then add dry tetrahydrofuran (25 mL). After the dissolution was complete, an excess of DCC (5.15 g, 25 mmol) was added, followed by a catalytic amount of DMAP. Under the protection of argon, the system was reacted at 25°C for 48h. After the reaction was completed, filter, discard the filter cake, and distill the filtrate to remove the solvent under reduced pressure to obtain a light brown viscous liquid. Add cold anhydrous diethyl ether to the viscous liquid, mix well to precipitate solids, filter, put the obtained filter cake in a vacuum drying oven, and dry at 40°C until ...
Embodiment 3
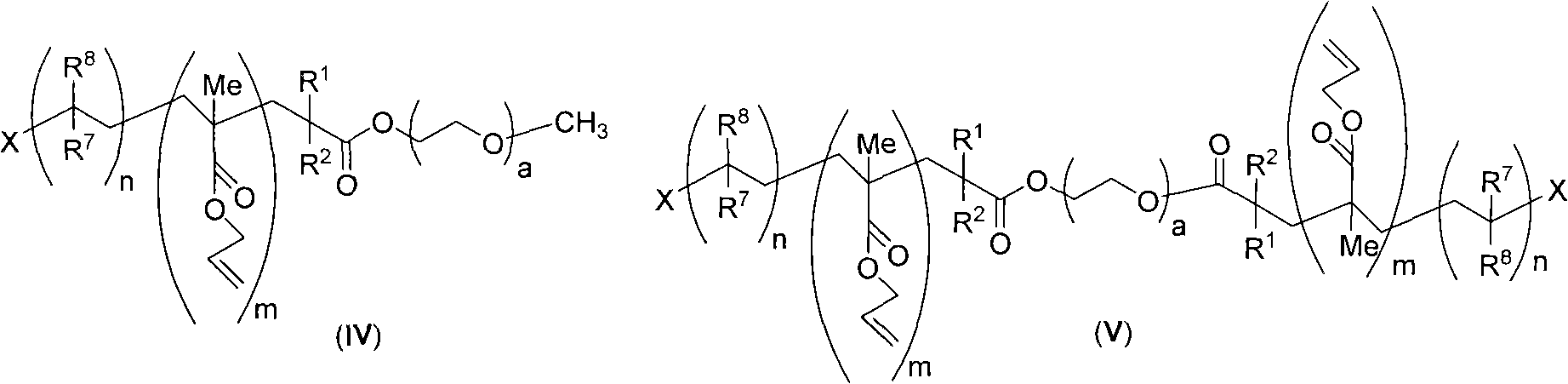
[0067] Example 3 Utilize the two (2-bromo-isobutyric acid) polyethylene glycol-2000 diester (Ia) prepared in Example 1 to carry out atom transfer radical emulsion polymerization of allyl methacrylate (AMA)
[0068] will be pre-treated with glacial acetic acid to remove possible CuBr 2 Impurity CuBr (0.0143g, 0.1mmol) and 2,2'-bipyridine (0.0156g, 0.1mmol) were added to the reaction flask, and an appropriate amount of deionized water (5-10g) was added to dissolve into a blue solution. Under the protection of argon, add bis(2-bromo-isobutyric acid)polyethylene glycol-2000 diester (Ia) (0.3276g, 0.14mmol) and AMA monomer (2.524g, 20mmol), stir at high speed for 30min, Until the system is stable without delamination. The above reaction was moved to a 60°C oil bath and stirred at a medium speed for 5h. During the reaction, samples were taken at regular intervals to track the progress of the reaction.
[0069] After the reaction, use lower alcohol to break the emulsion, and the m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com