Selective etching and formation of xenon difluoride
A selective, etching technology, applied in the direction of cleaning methods and appliances, chemical instruments and methods, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of unacceptable removal of TiN deposition products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] XeF at various temperatures and pressures 2 Effectiveness in etching of deposited materials
[0070] In this example, using XeF 2 As an etchant, measured for TiN, SiO 2 and SiN etch rate. The test samples were coated with TiN, SiO 2 and SiN thin films on silicon wafers. The etch rate is calculated from the change in film thickness between the initial film thickness and the film thickness after timed exposure to etching or processing conditions.
[0071] For etching, a large amount of XeF 2 Gases were introduced from gas cylinders into the reactor chamber via a never-used remote plasma generator. The XeF 2 The pressure of the gas in the reactor chamber was kept constant by shutting off the gas flow from the cylinder once the desired pressure was reached.
[0072] The test specimens were placed on the surface of a pedestal heater used to maintain different substrate temperatures. The results are shown in Table I below.
[0073] Table I
[0074] Use XeF 2 Etch ...
Embodiment 2
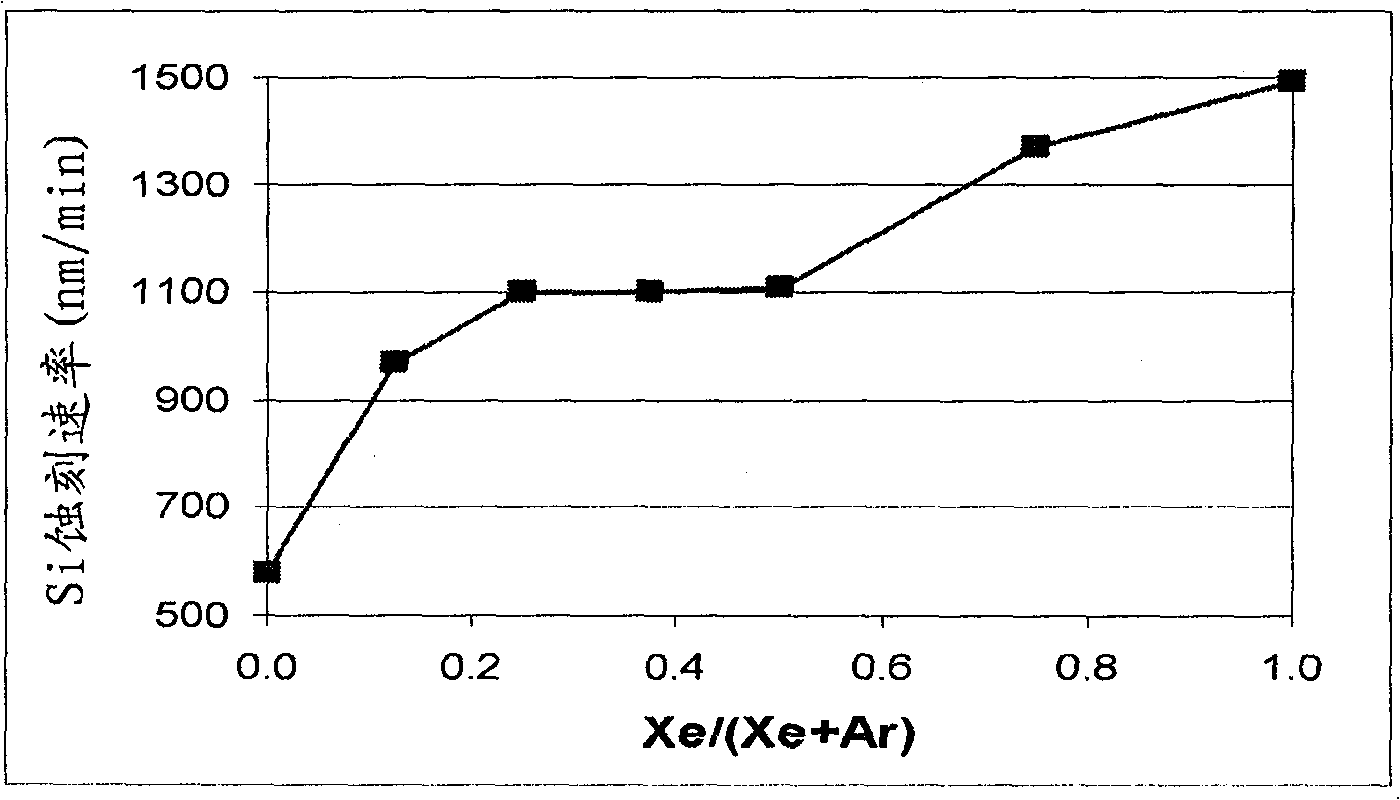
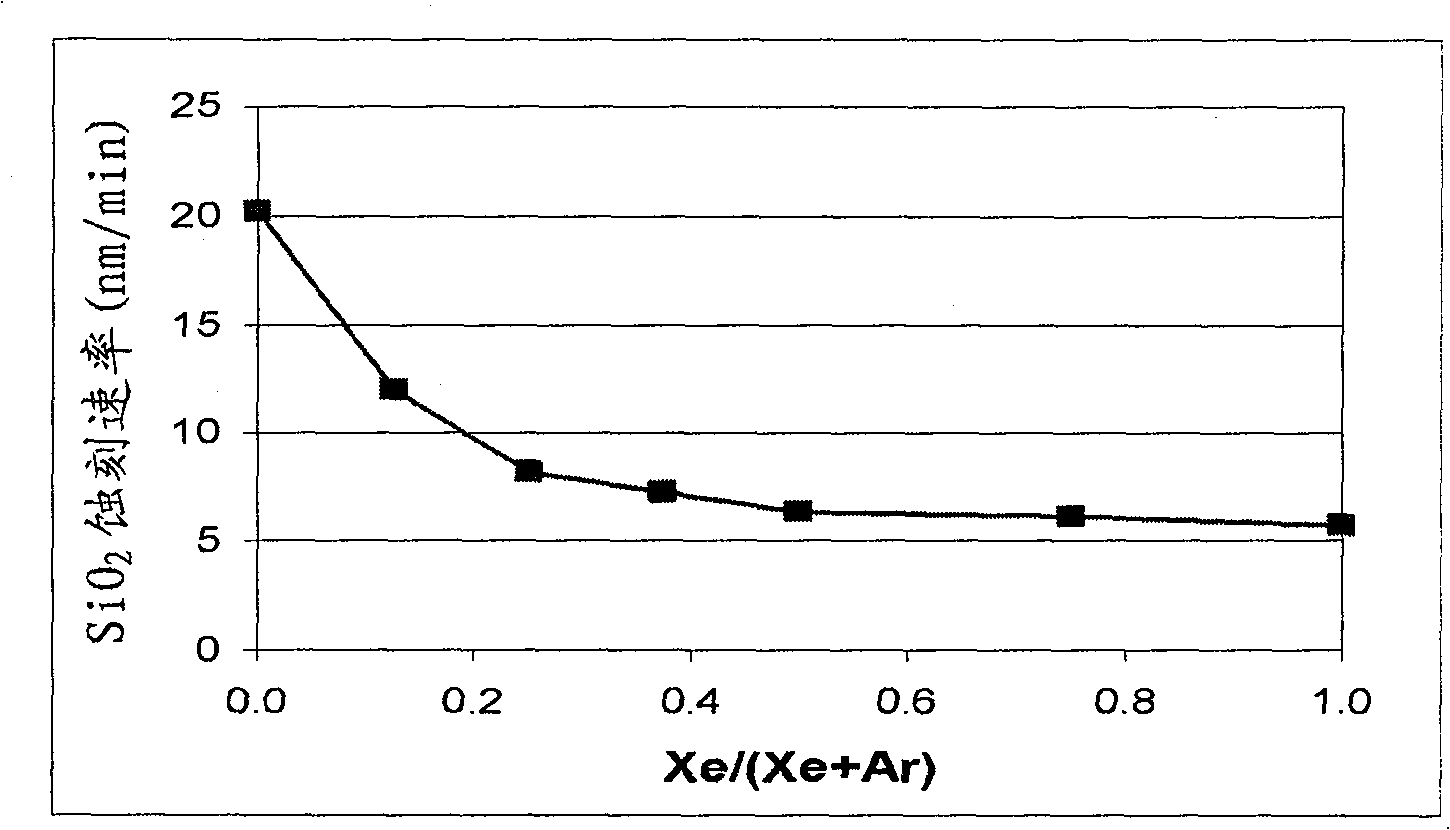
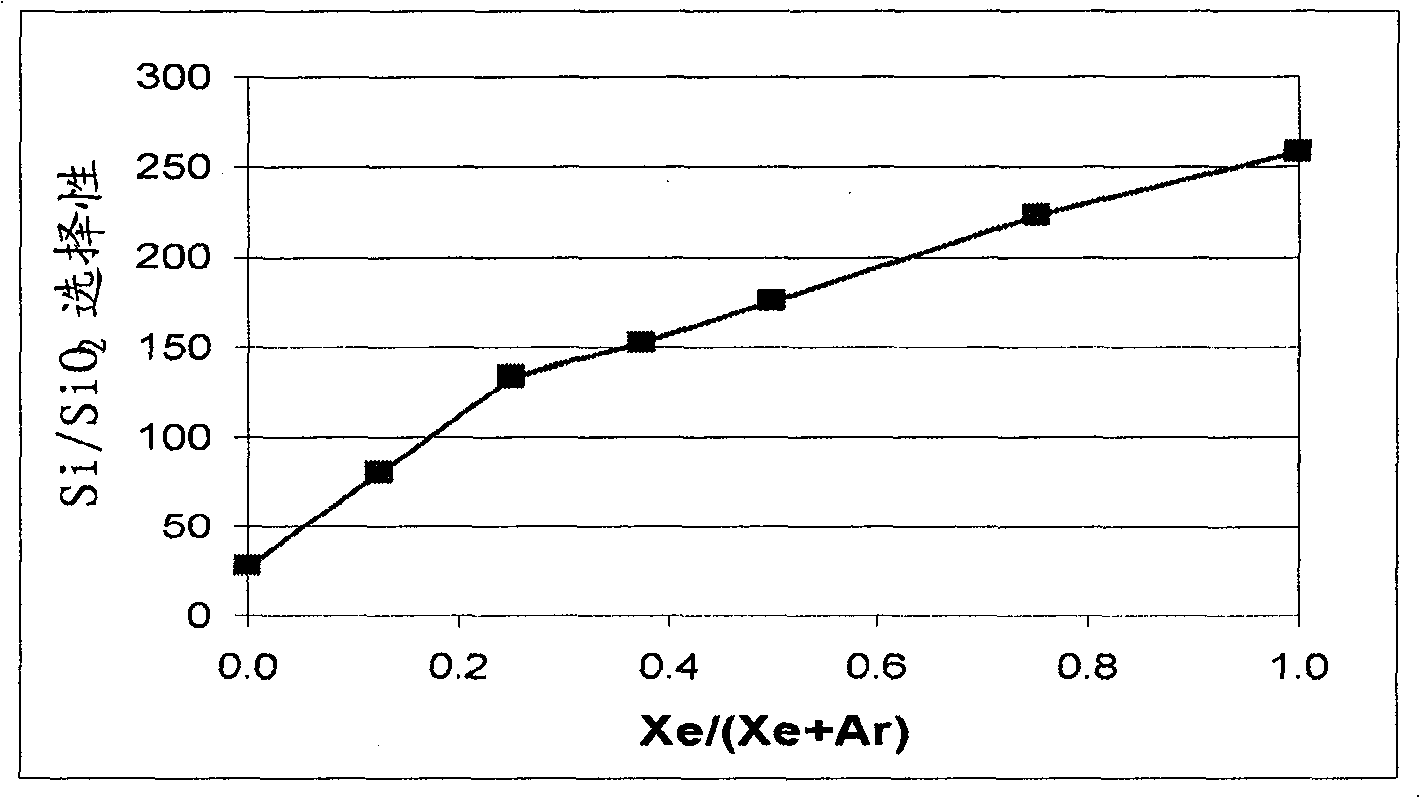
[0079] Silicon vs. SiO 2 selective etching of
[0080] In this example, a MKS Astron remote plasma generator was mounted on top of the reactor chamber. The distance between the outlet of the Astron generator and the sample specimen was approximately six inches. Turn on the remote plasma generator, but turn off the pedestal heater in the reactor chamber. The chamber was kept at room temperature. For Si and SiO using remote plasma 2 The etch rates of both substrates were measured.
[0081] The process gas for the remote plasma is NF 3 , and it is mixed with various amounts of the second gas stream. The second gas stream includes Xe, argon (Ar), or combinations thereof. The total gas flow rate to the reactor chamber was fixed at 400 sccm, and the NF 3 The flow rate was fixed at 80 sccm. While maintaining the total flow rate of the second gas stream at 320 sccm, the ratio of the Xe flow rate to the total flow rate of the second gas stream (Xe / (Ar+Xe)) was at 0 (Ar only as...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Molybdenum (Mo) vs. SiO 2 selective etching of
[0089]A large cylindrical SS etch chamber 2.5 m long and 25 cm in diameter was used to determine the etch rate of another common sacrificial material in MEMS applications: molybdenum (Mo). The remote plasma was generated using a water cooled MKS Astron AX76706 slpm unit. The plasma source was connected to the chamber by a 10 cm long delivery tube with an internal diameter of 4 cm. The sample was placed 2 feet from the load / unload end of the tube.
[0090] At 2.75 Torr, NF 3 At a flow rate of 275 sccm and a Xe or Ar flow rate of 600 sccm, the etch rate of Mo = 1.1 μm / min. SiO 2 The etch rate for NF 3 / Ar gas mixture is 82nm / min, while for NF 3 / Xe mixture at 26 nm / min. Therefore, Xe / NF 3 The selectivity of the mixture is Ar / NF 3 The selectivity of the mixture is at least 3 times. Note that the Mo etch rate is limited by the surface oxide. The etch rate of Mo can be increased to >2.7 microns / minute with surface ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com