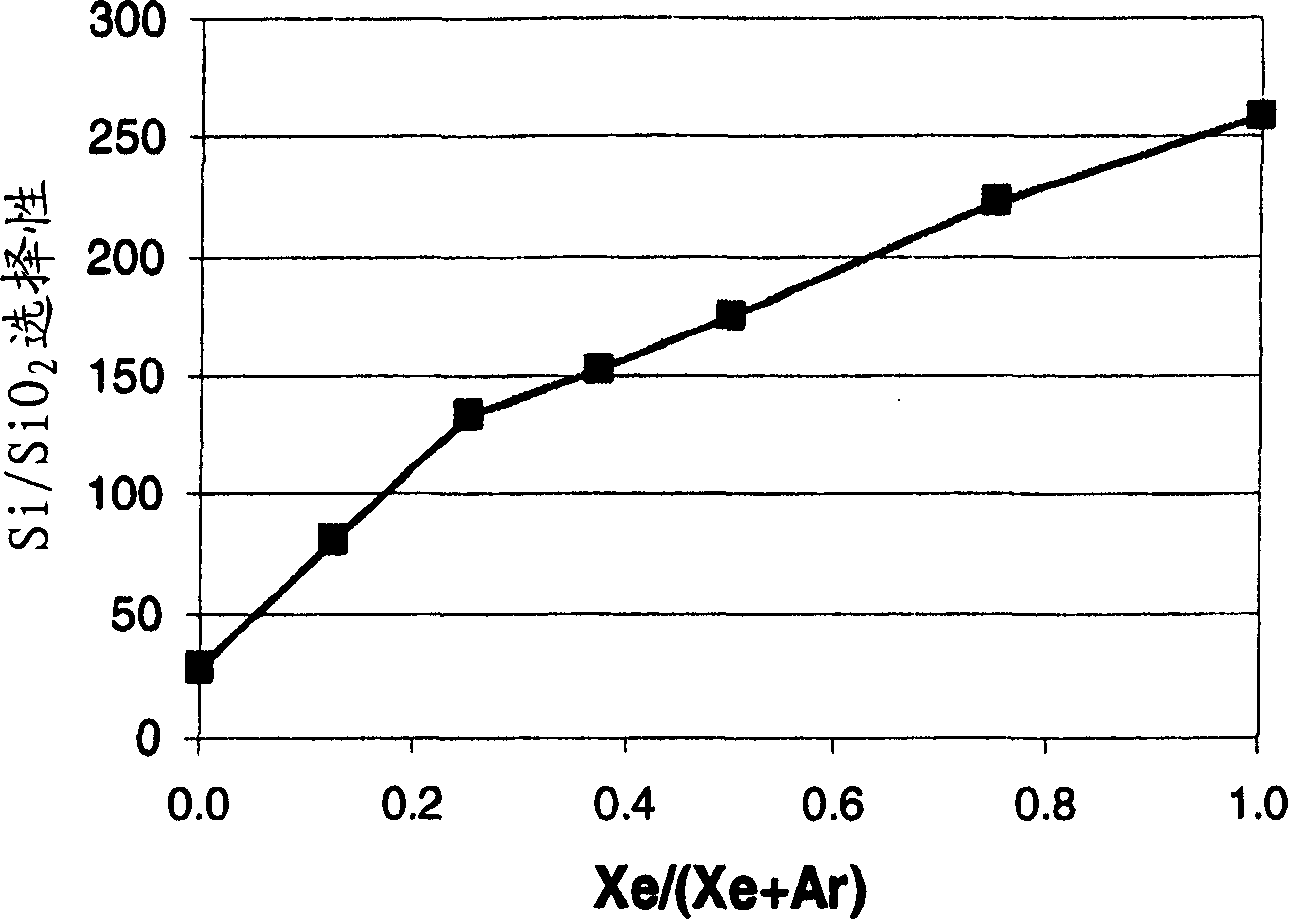
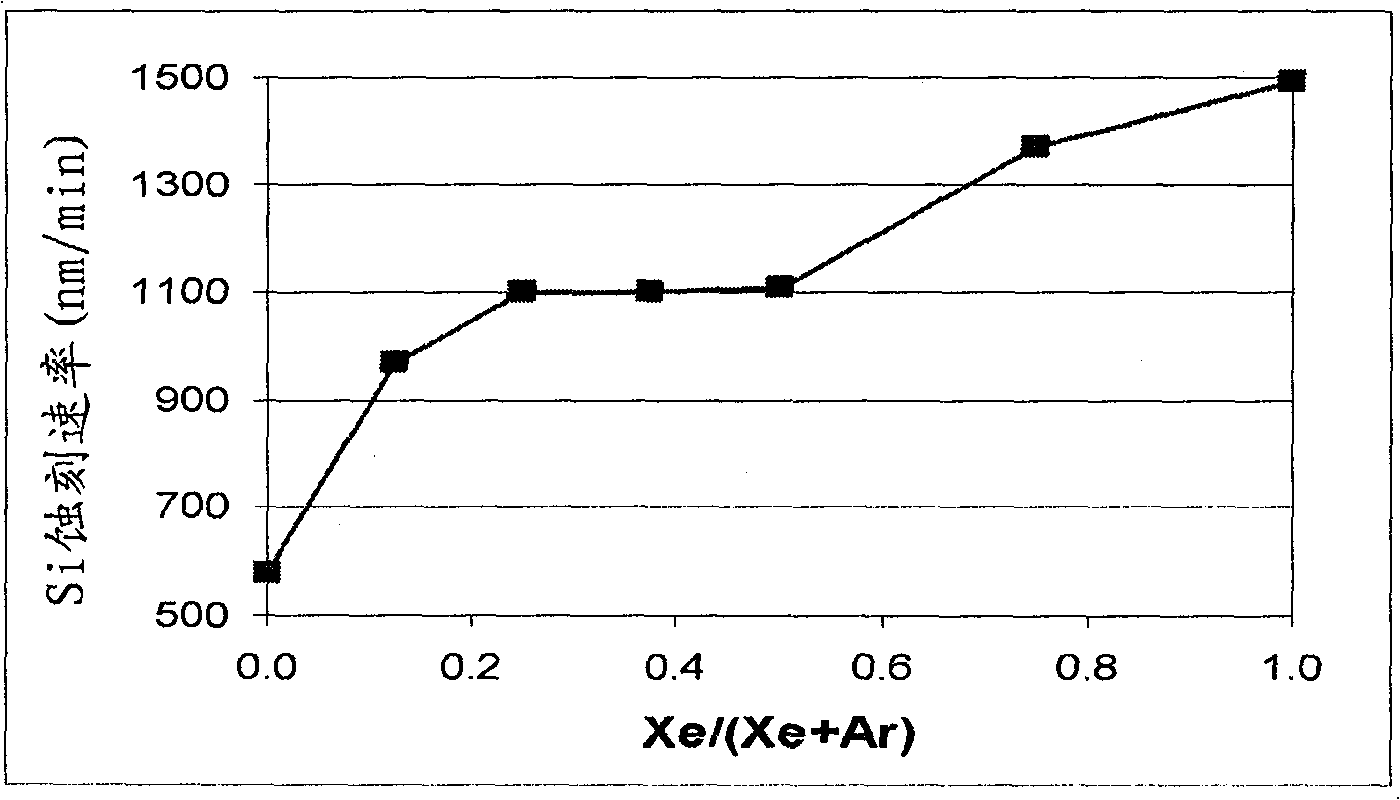
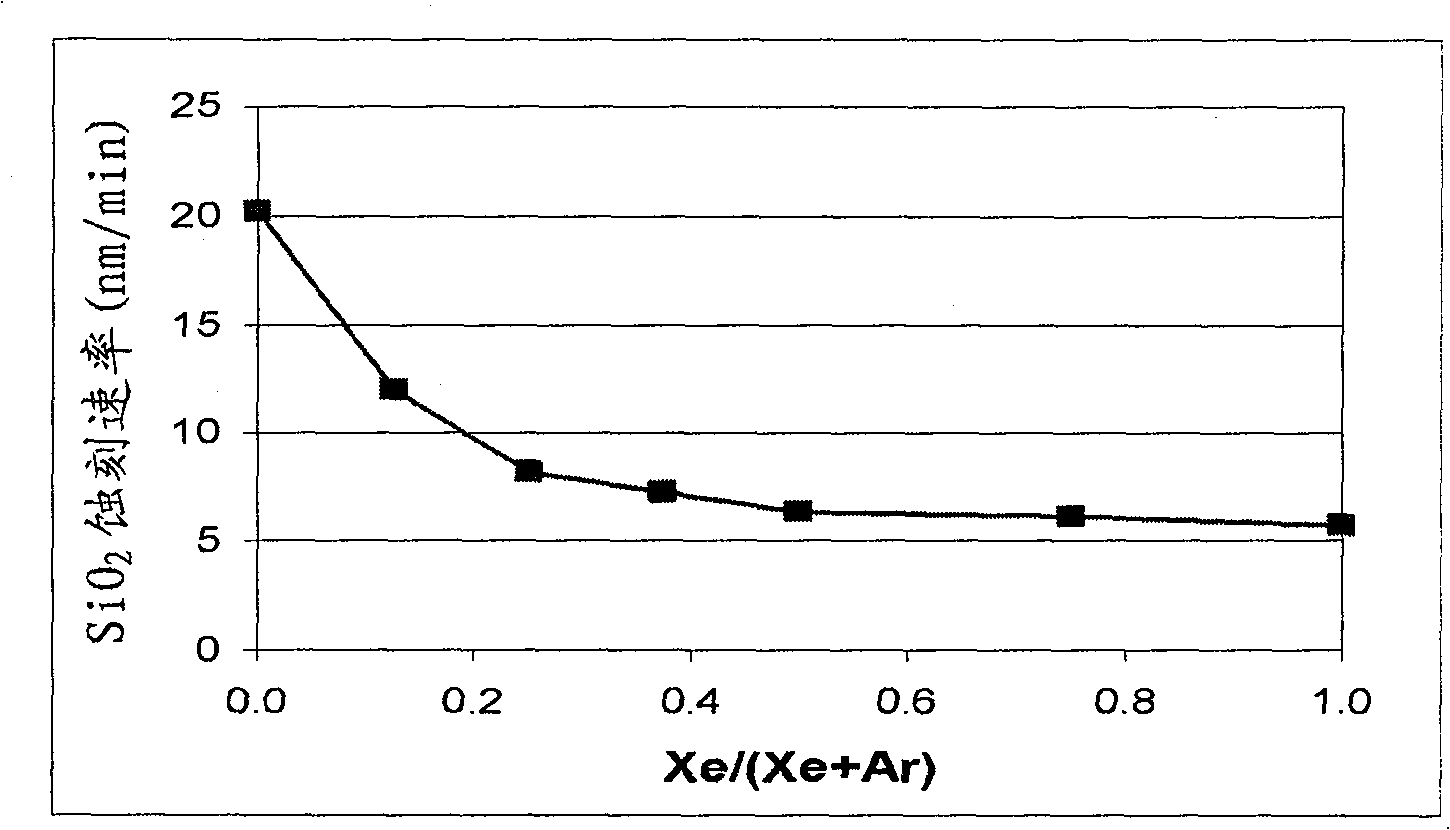
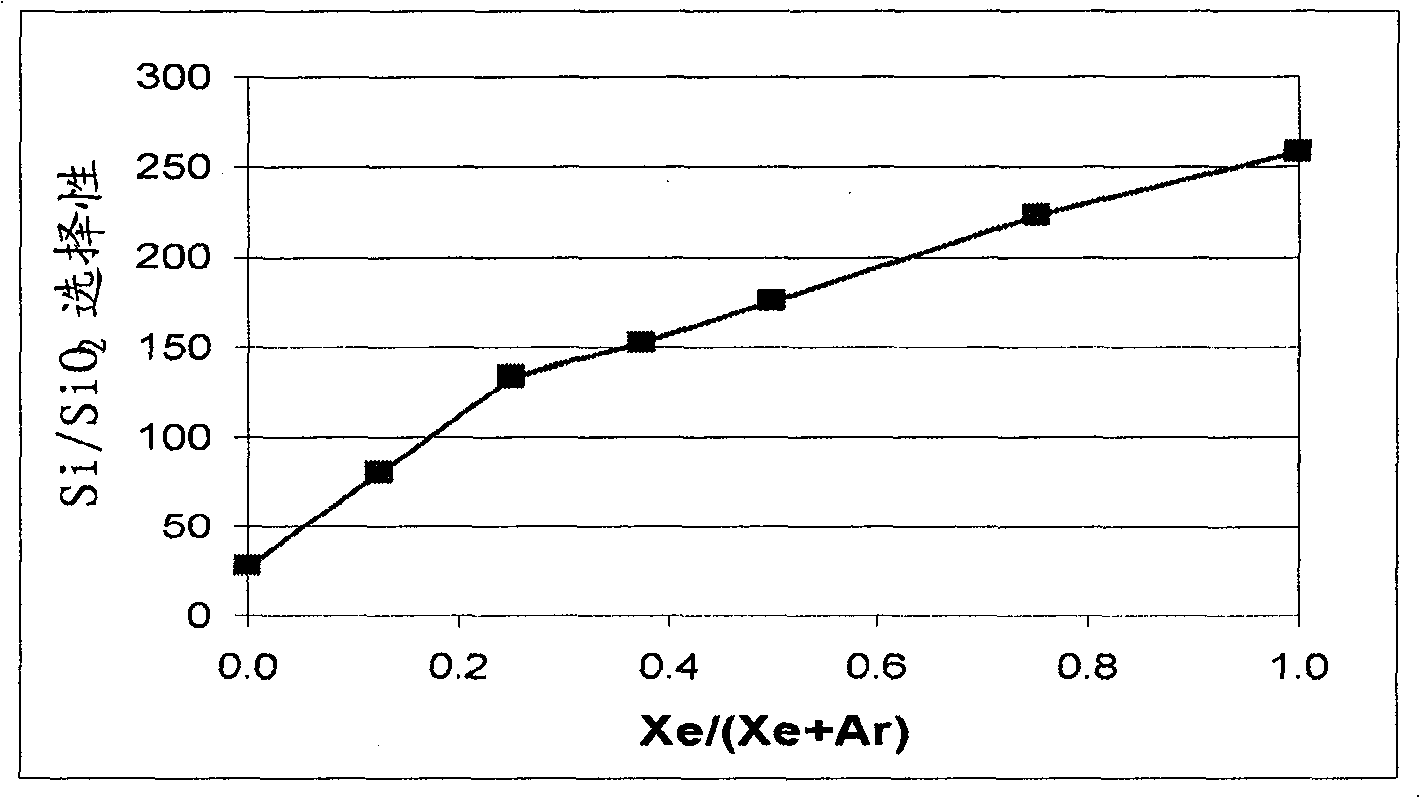
Patents
Literature
59 results about "Xenon difluoride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
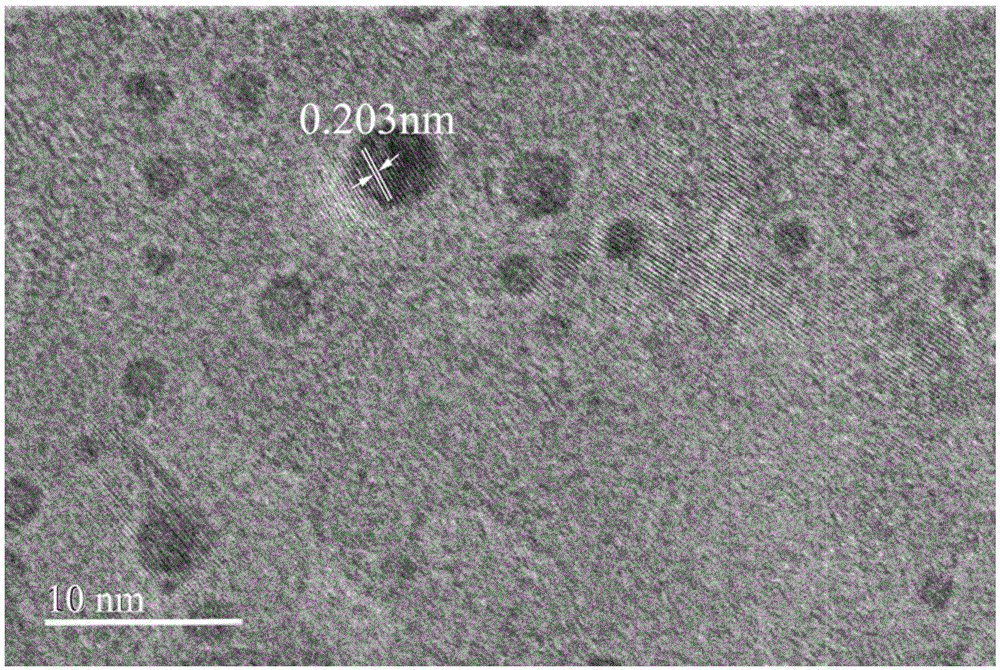
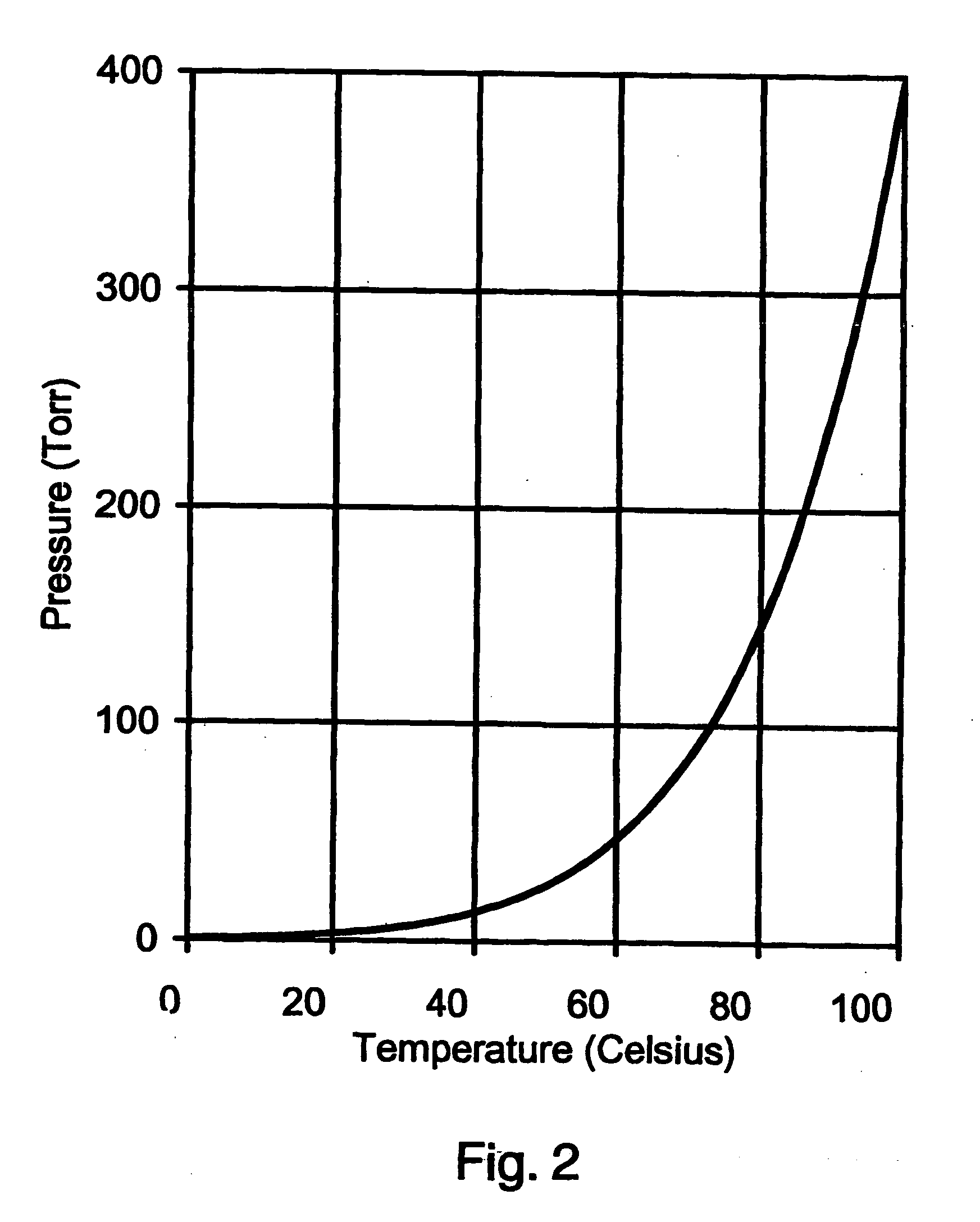
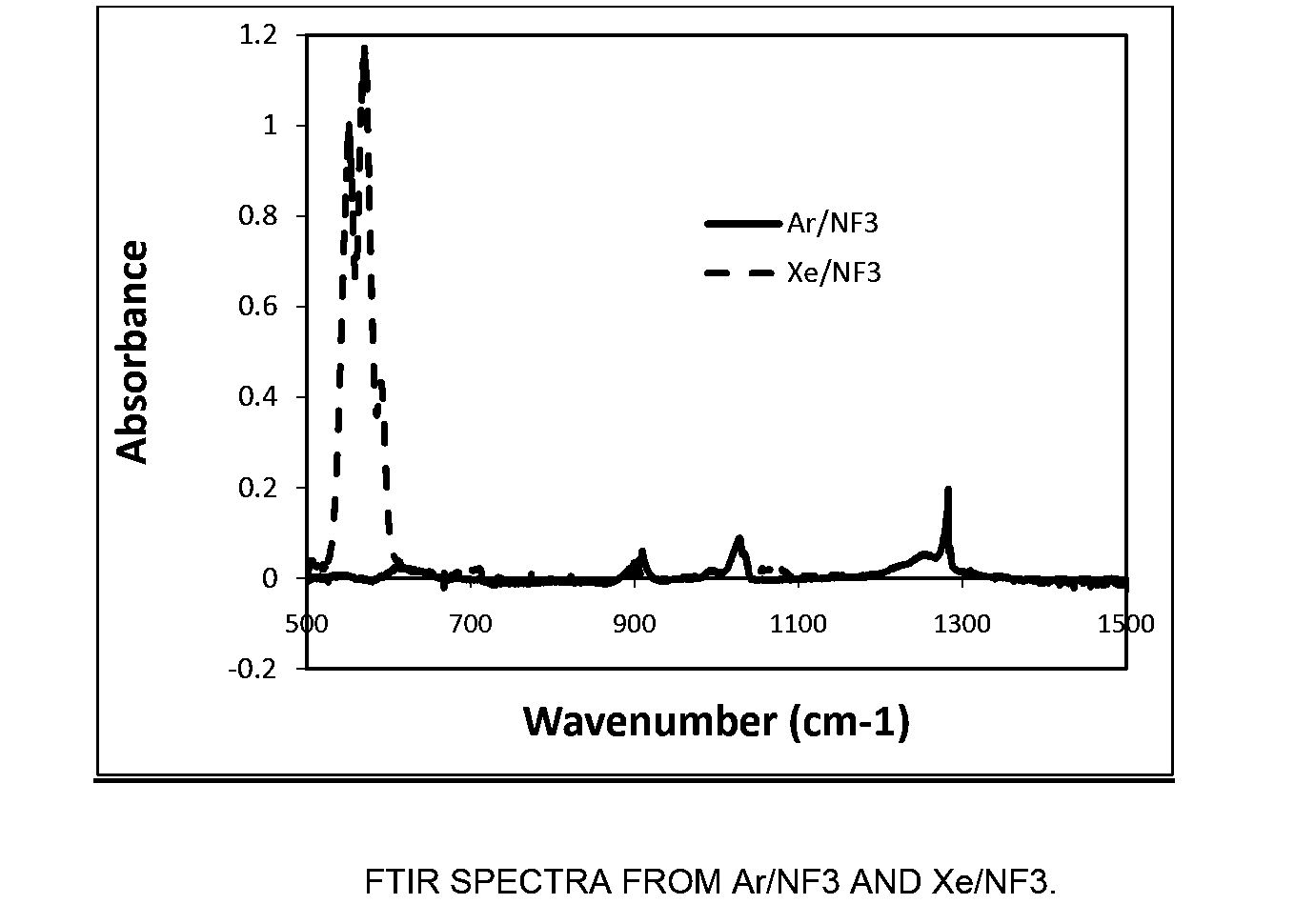
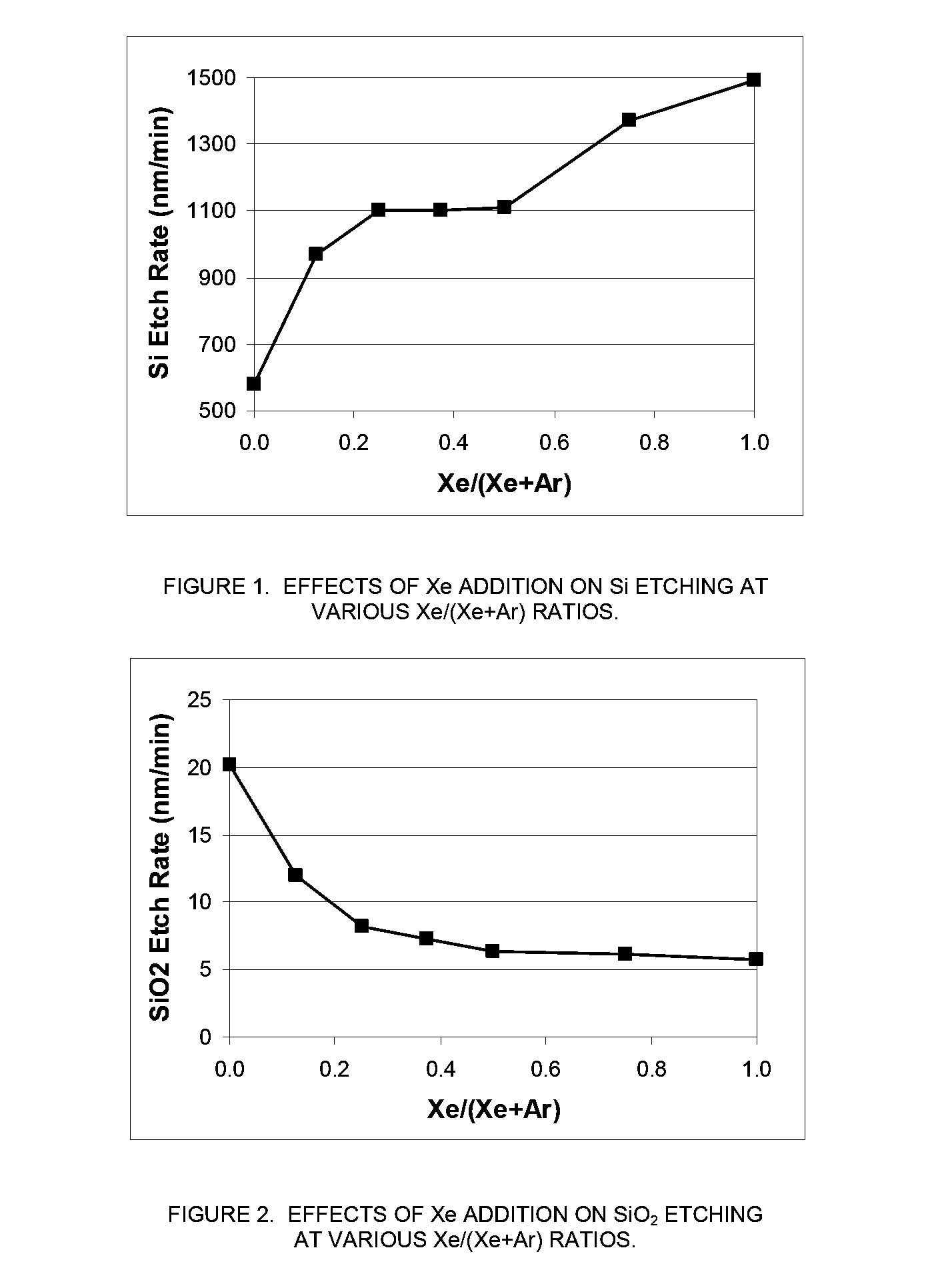
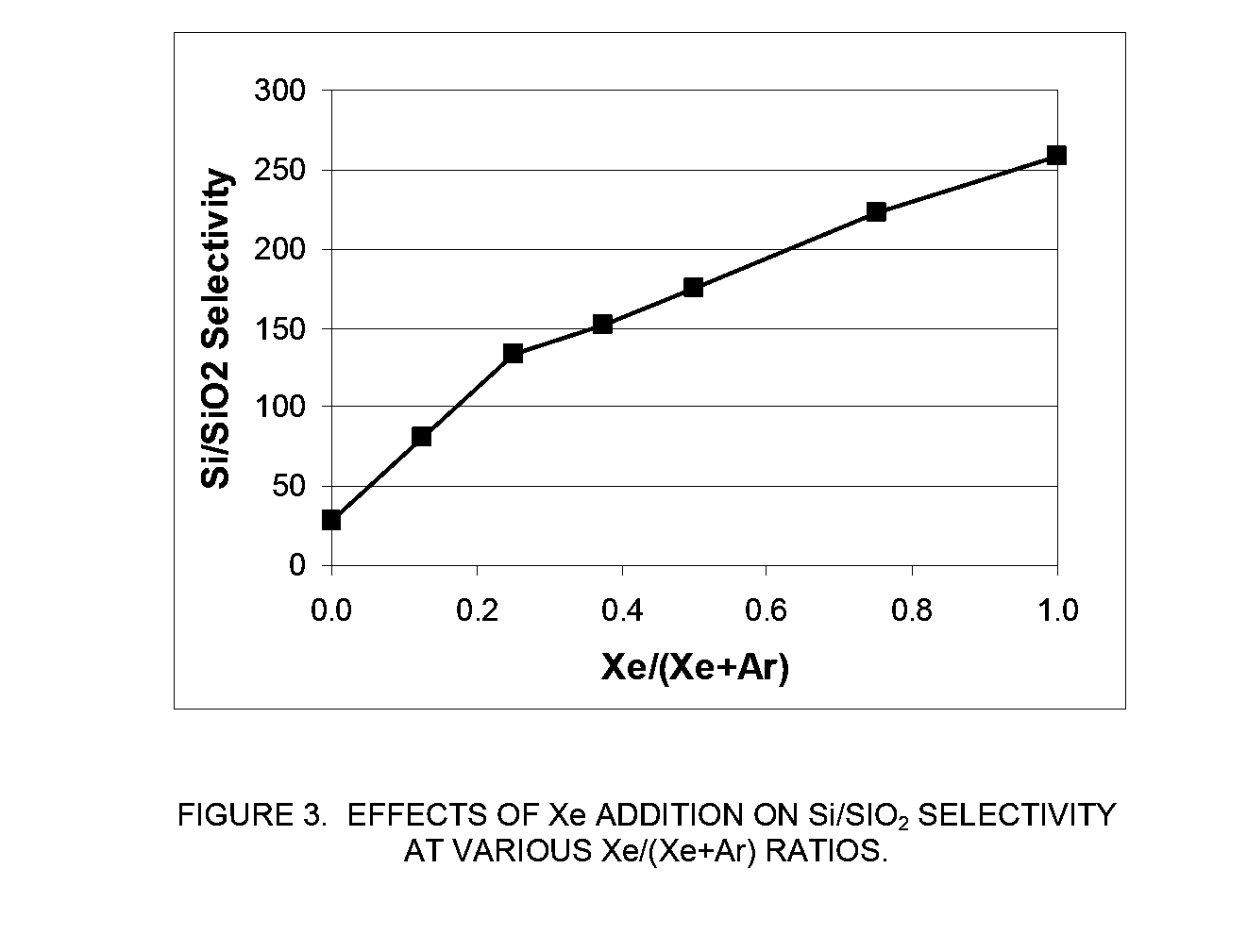
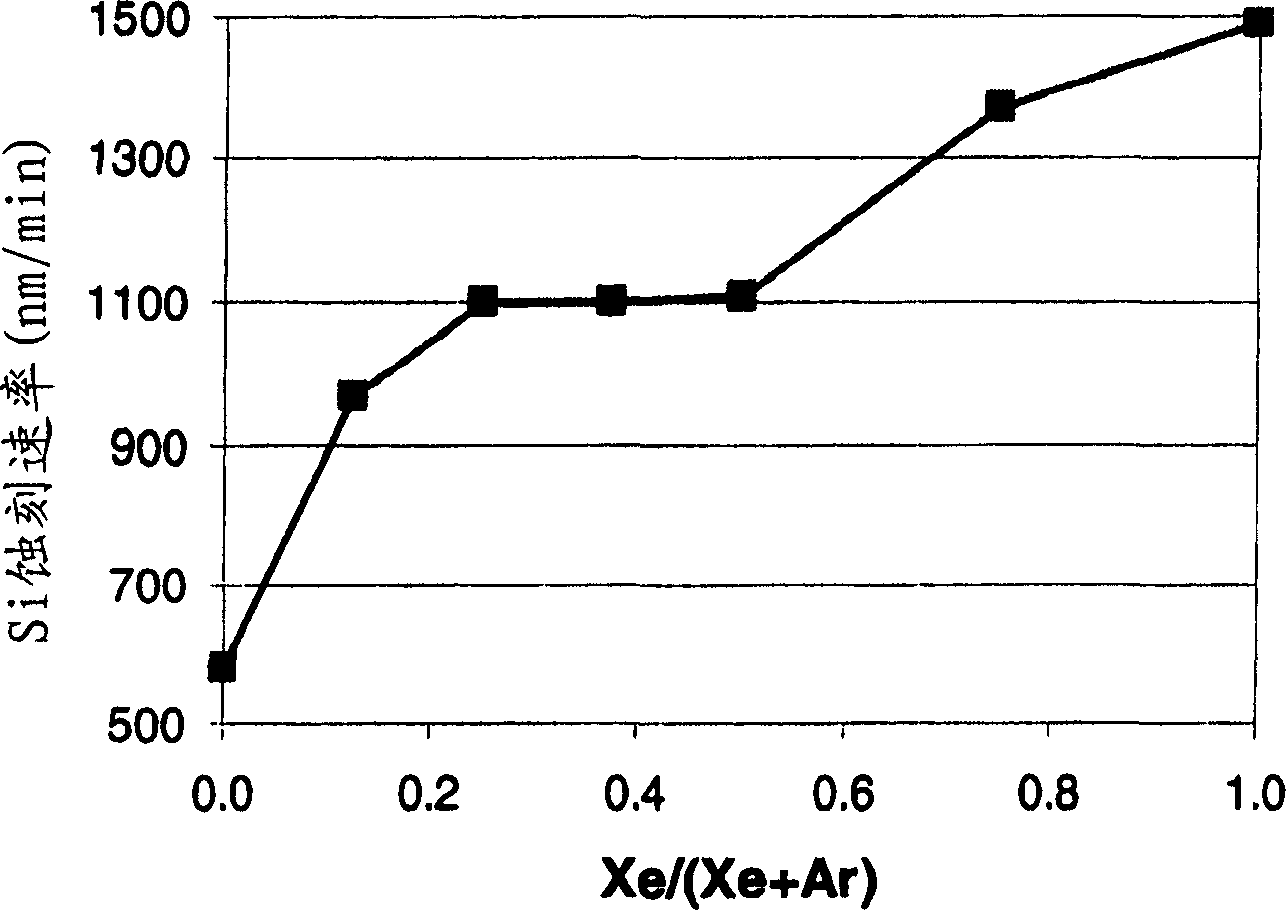
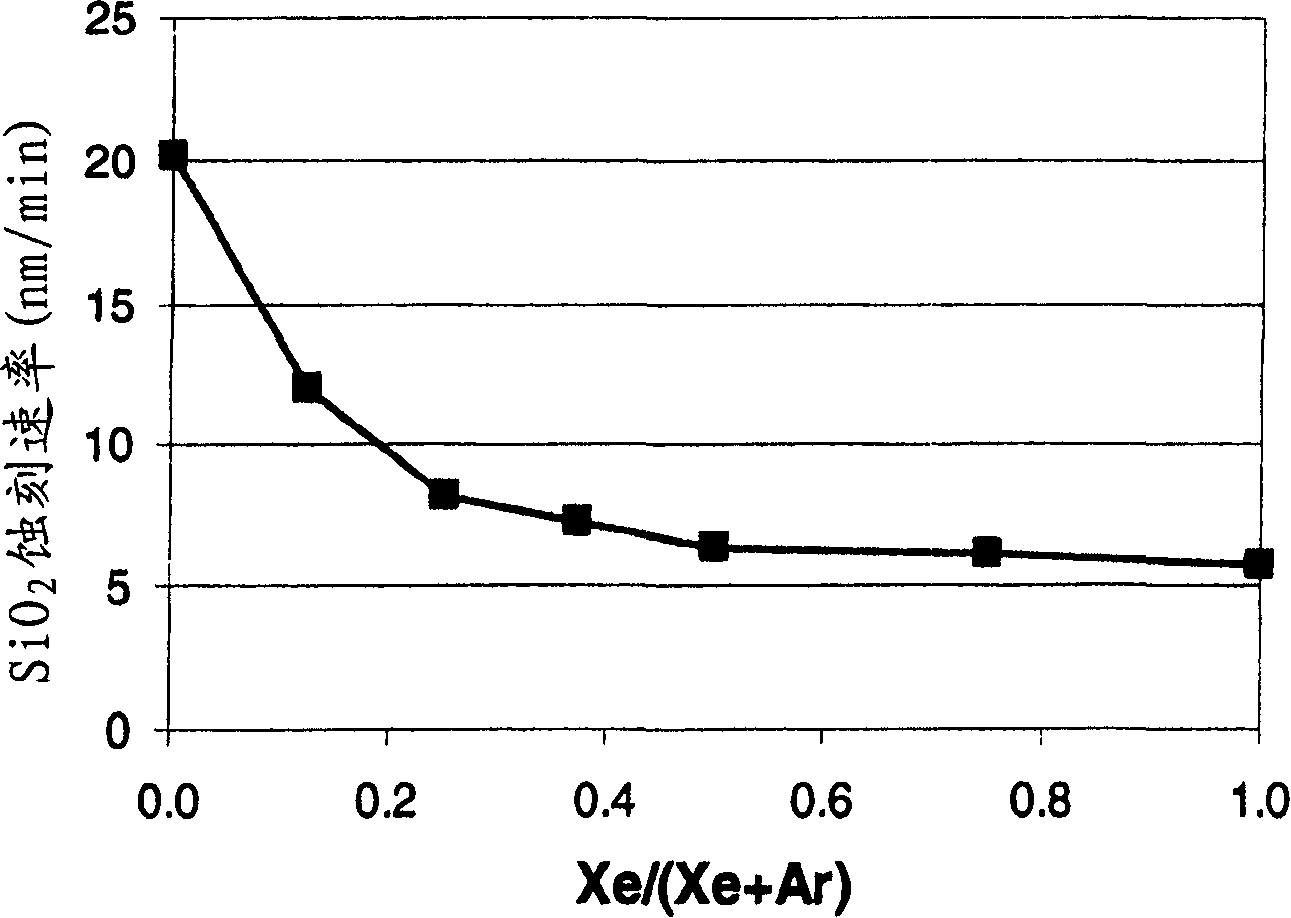
Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula XeF₂, and one of the most stable xenon compounds. Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. It decomposes on contact with light or water vapor but is otherwise stable to storage. Xenon difluoride is a dense, white crystalline solid.
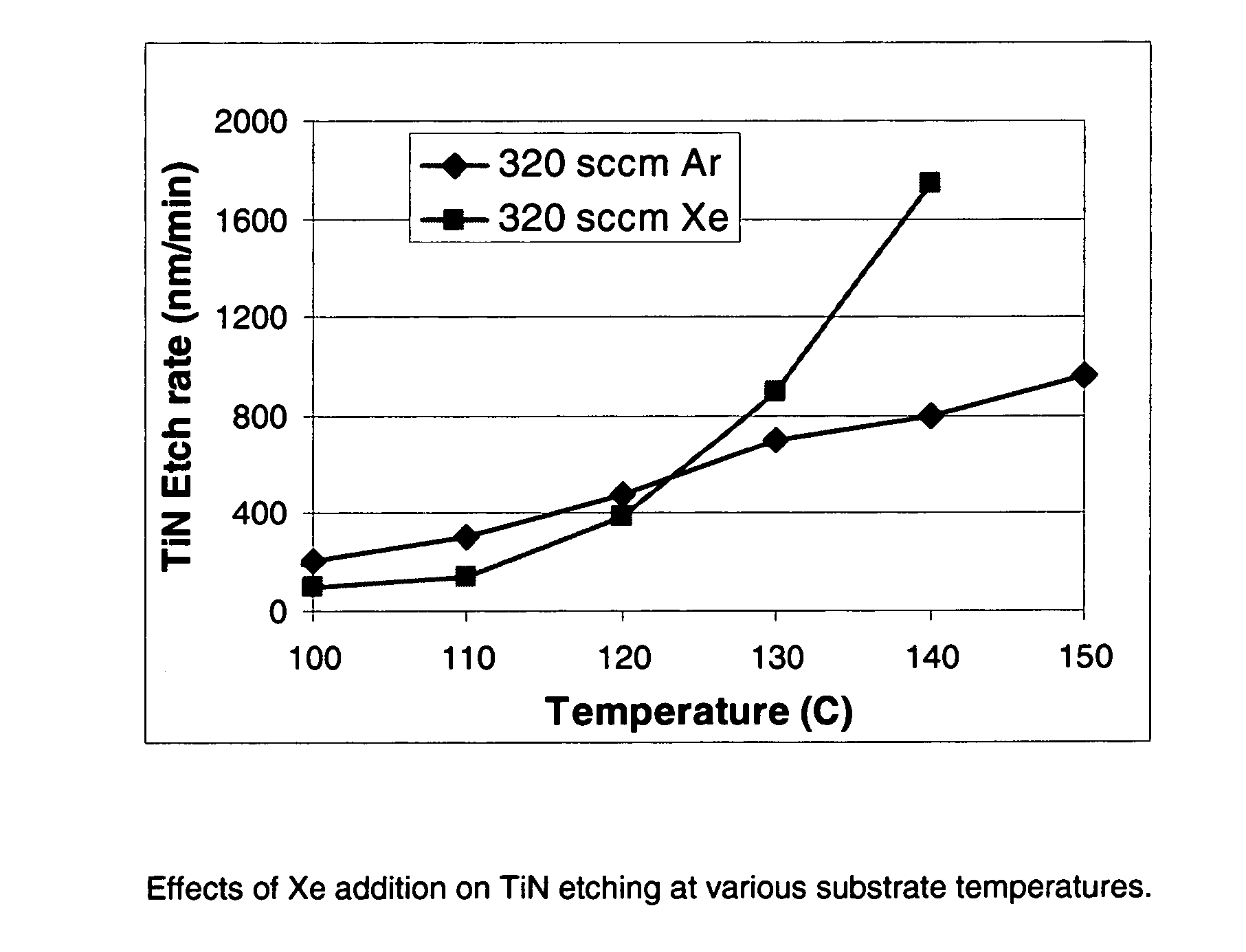
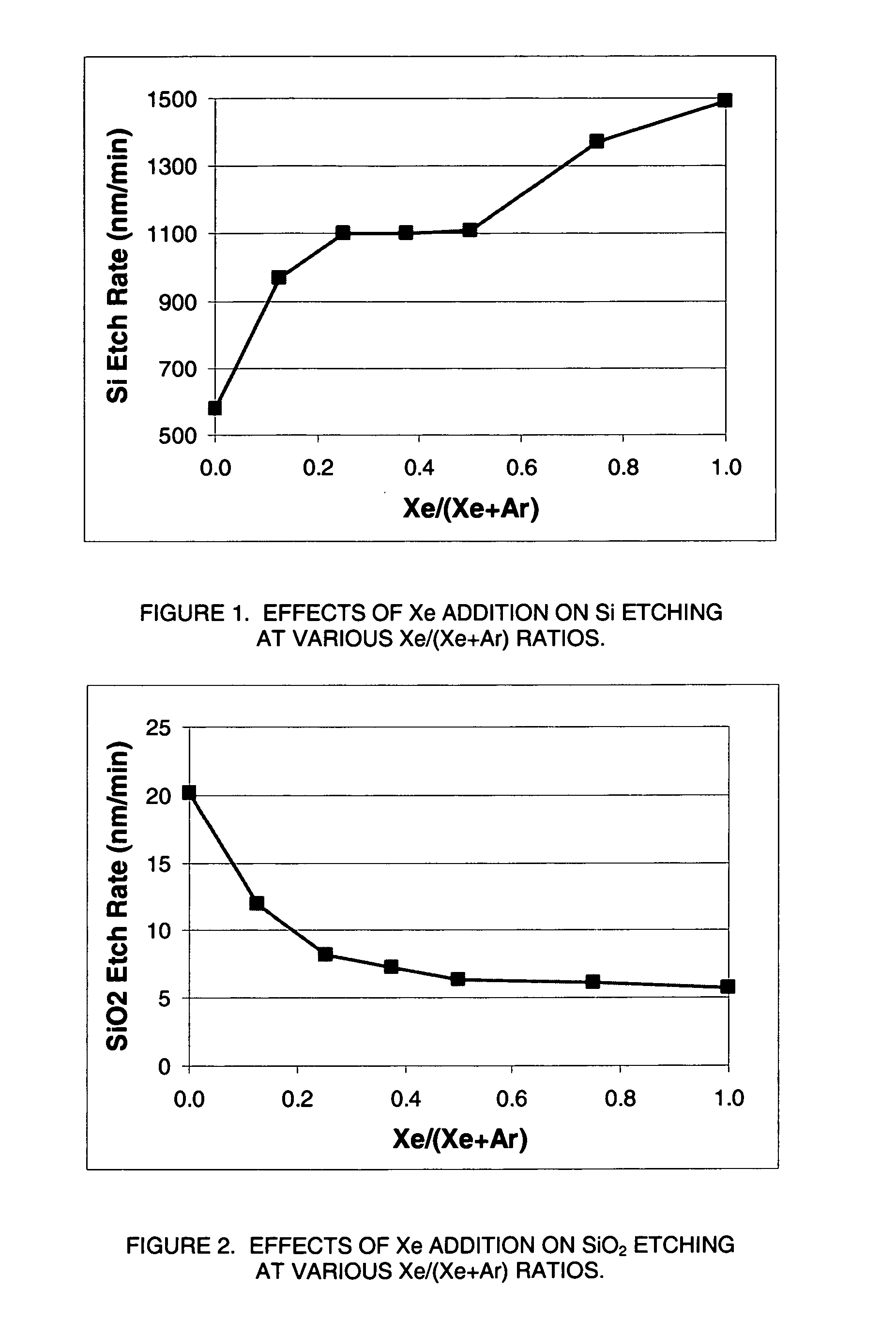
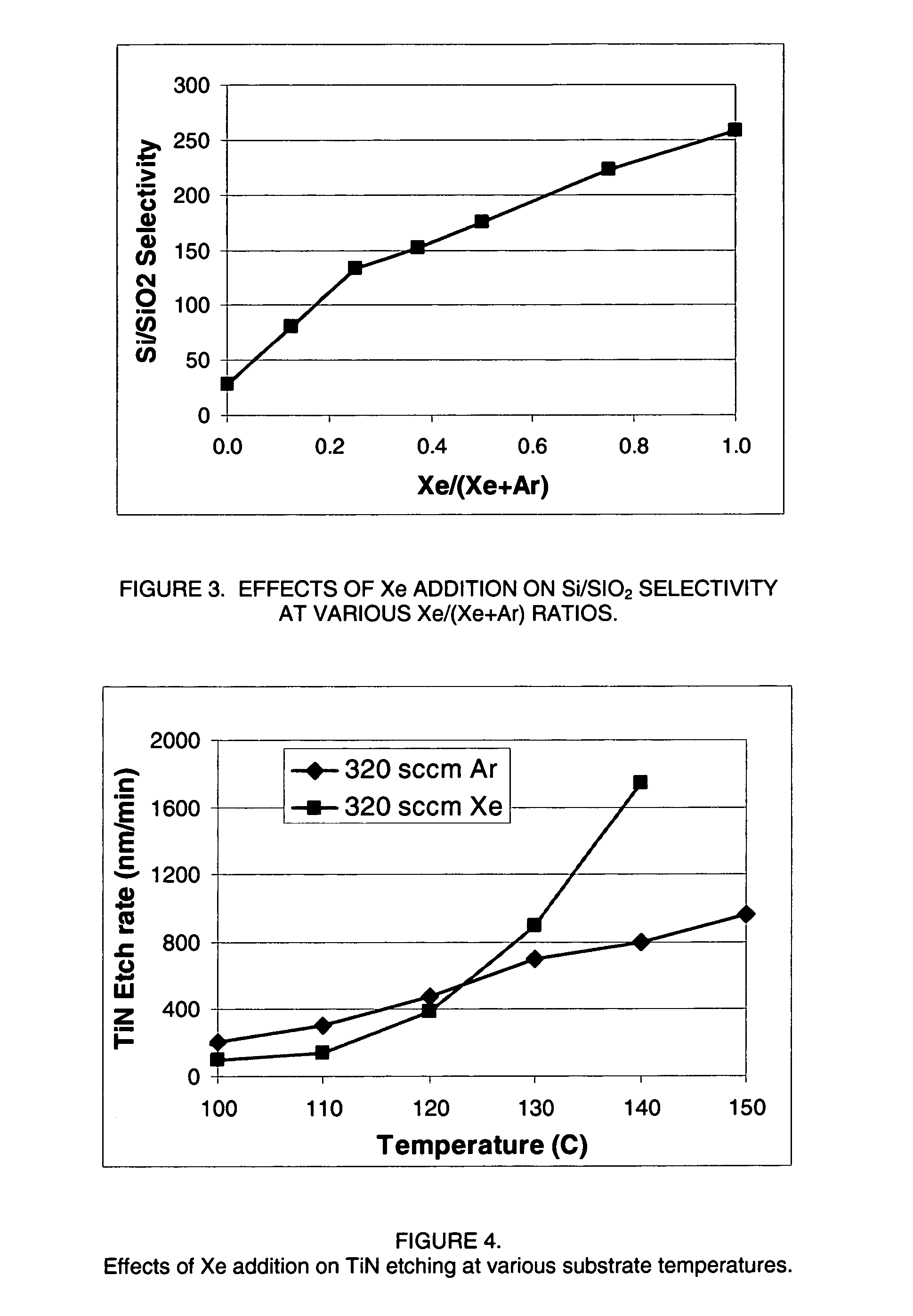
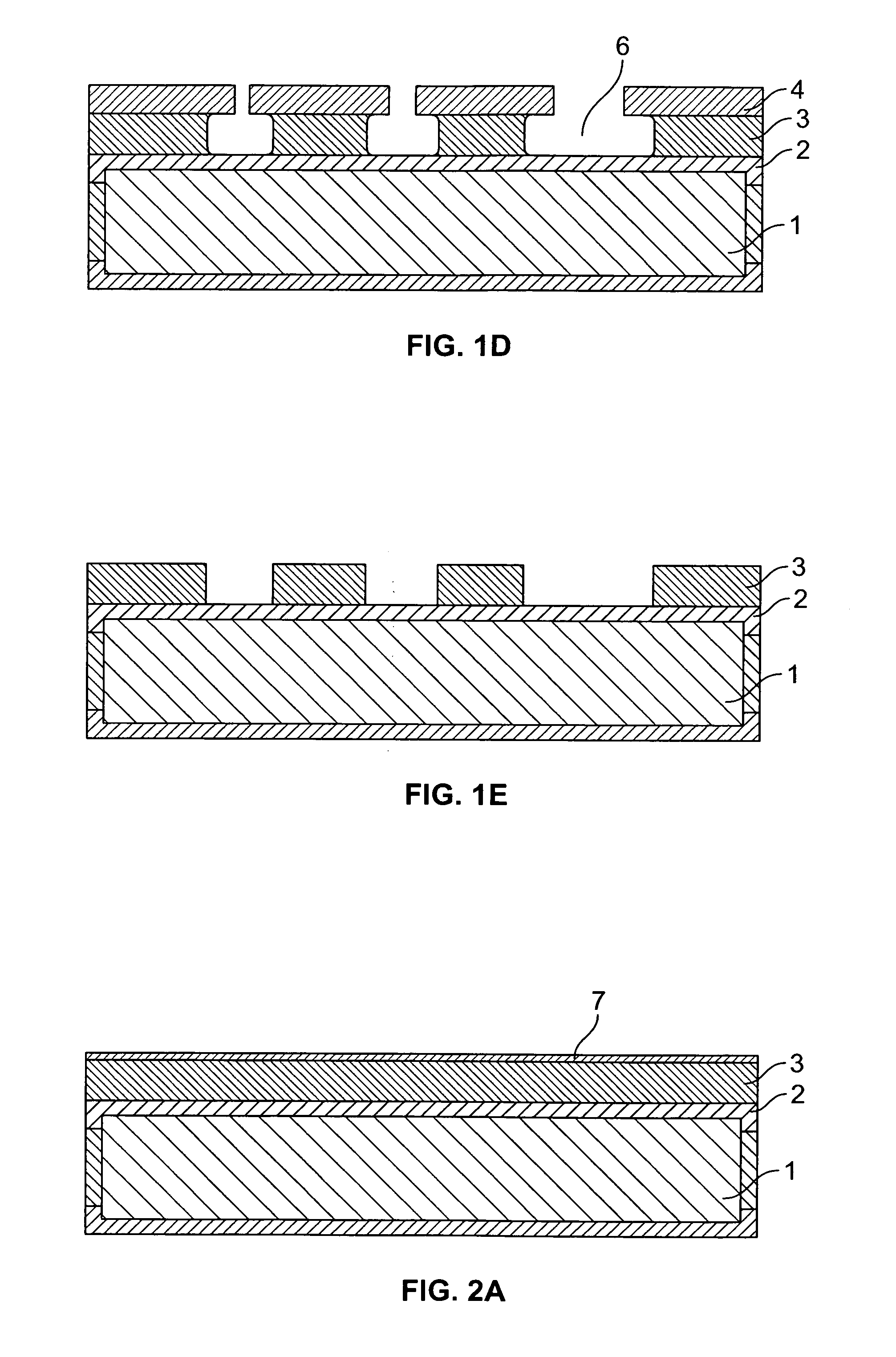
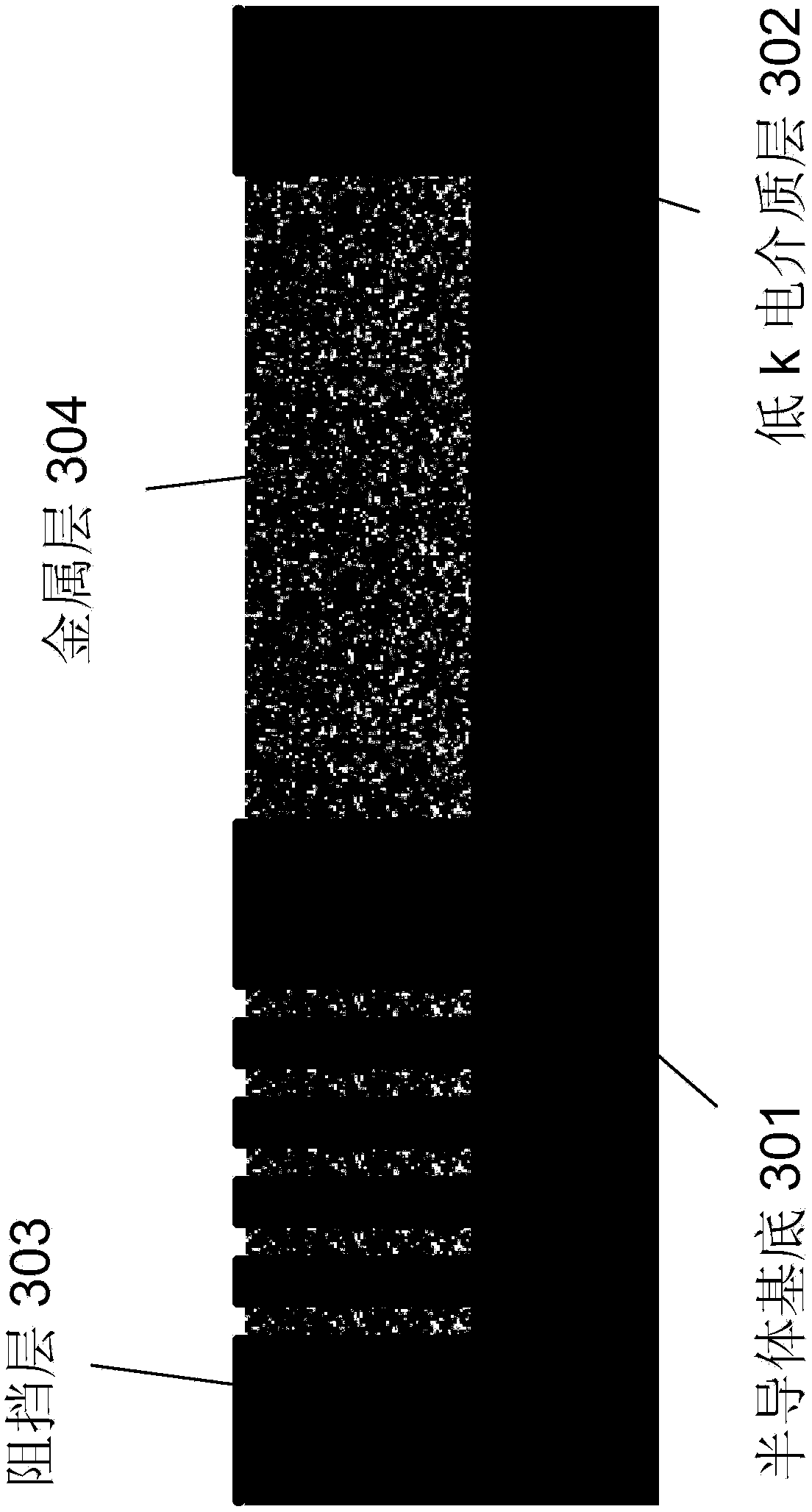
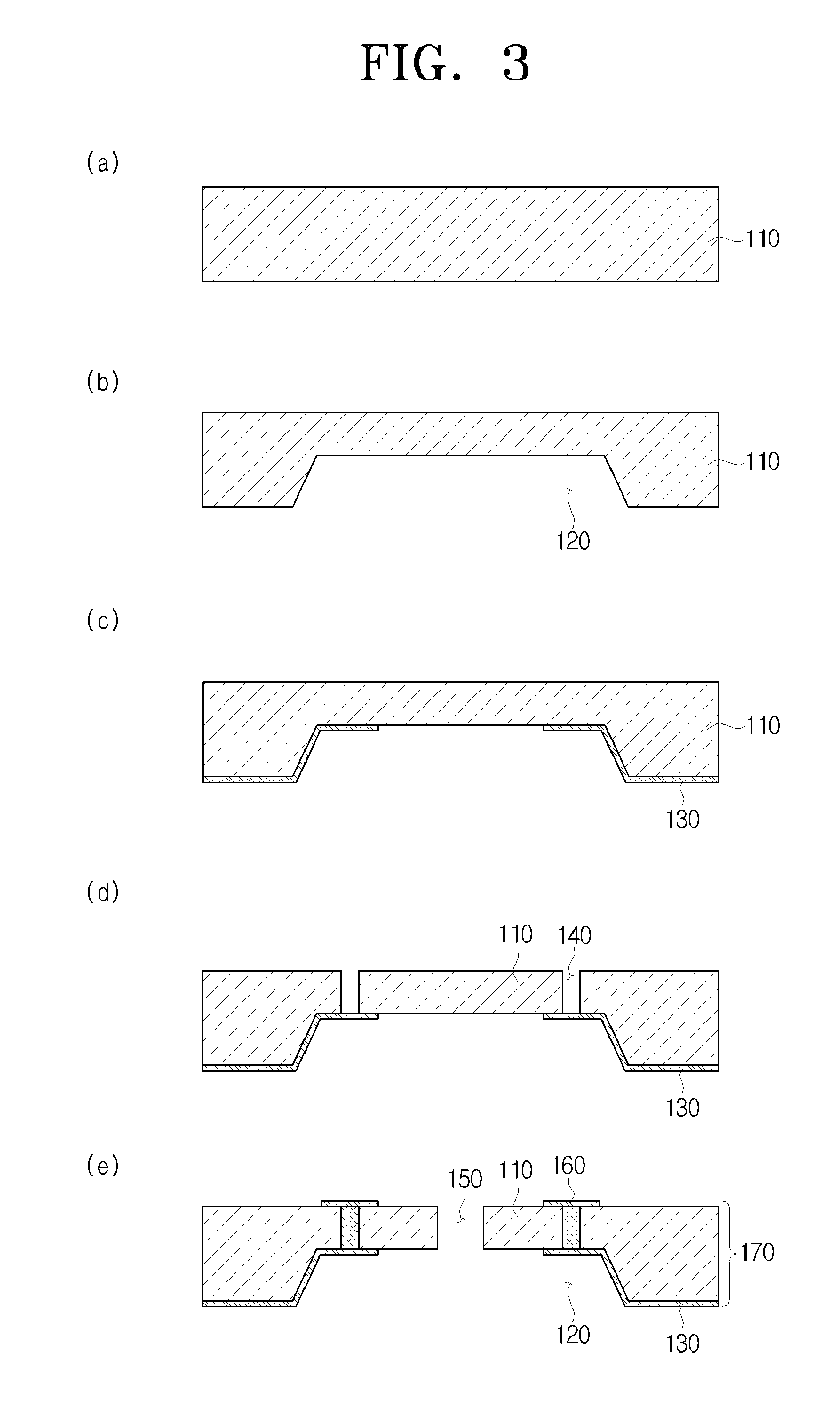
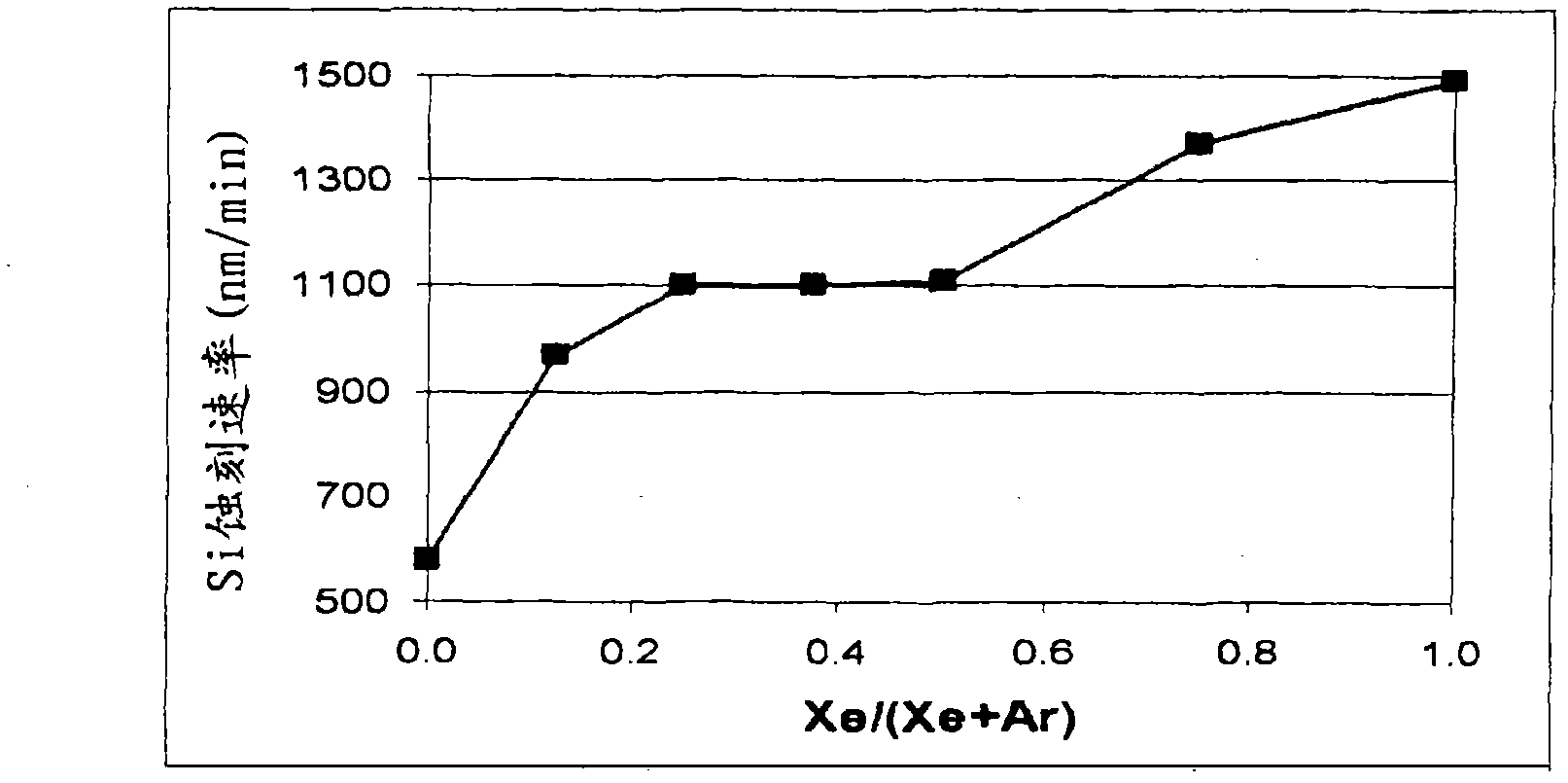
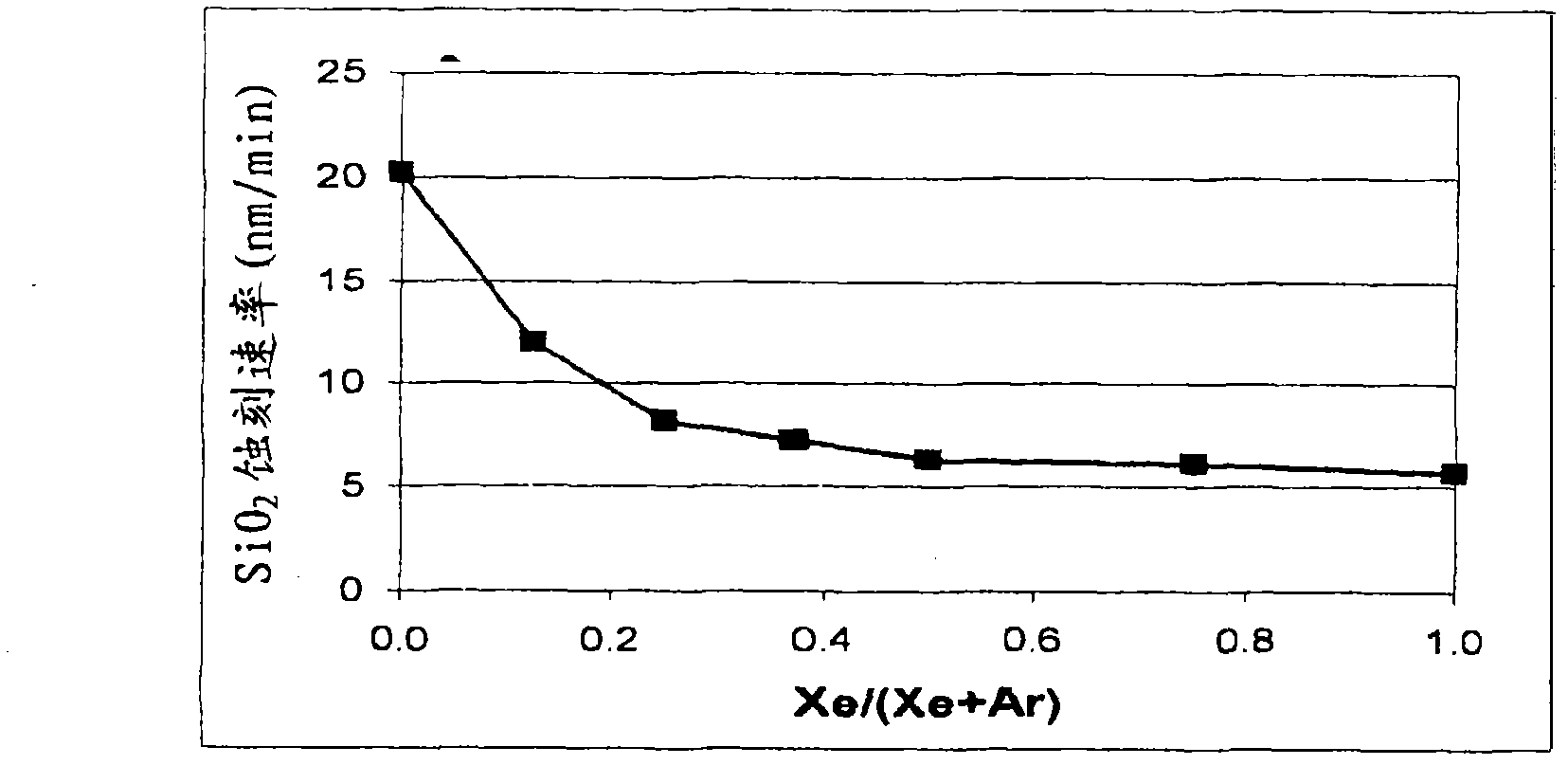
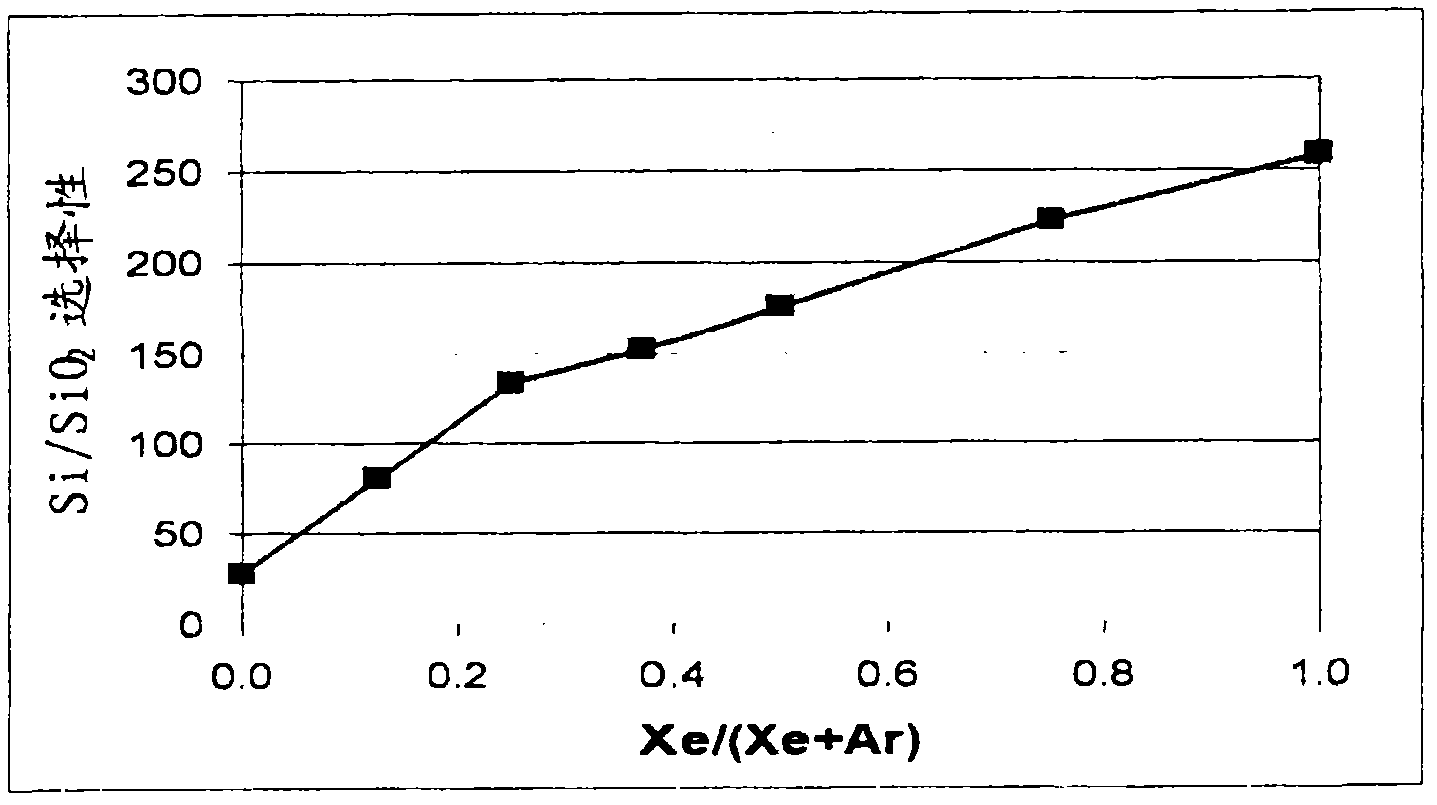
Selective etching of titanium nitride with xenon difluoride
InactiveUS20070117396A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEtchingTitanium nitride
This invention relates to an improved process for the selective etching of TiN from silicon dioxide (quartz) and SiN surfaces commonly found in semiconductor deposition chambers equipment and tools. In the process, an SiO2 or SiN surface having TiN thereon is contacted with XeF2 in a contact zone to selectively convert the TiN to a volatile species and then the volatile species is removed from the contact zone. XeF2 can be preformed or formed in situ by reaction between Xe and a fluorine compound.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
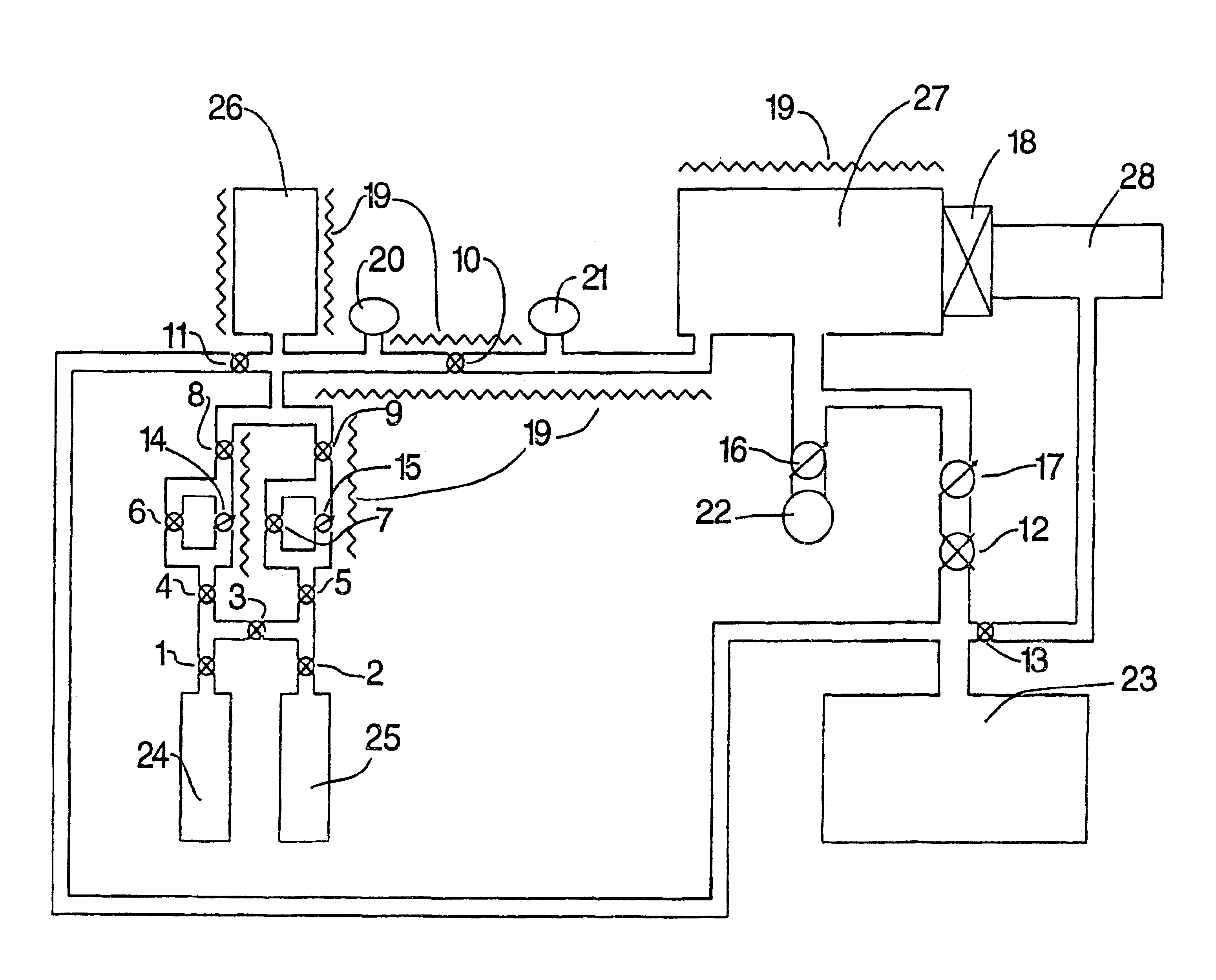
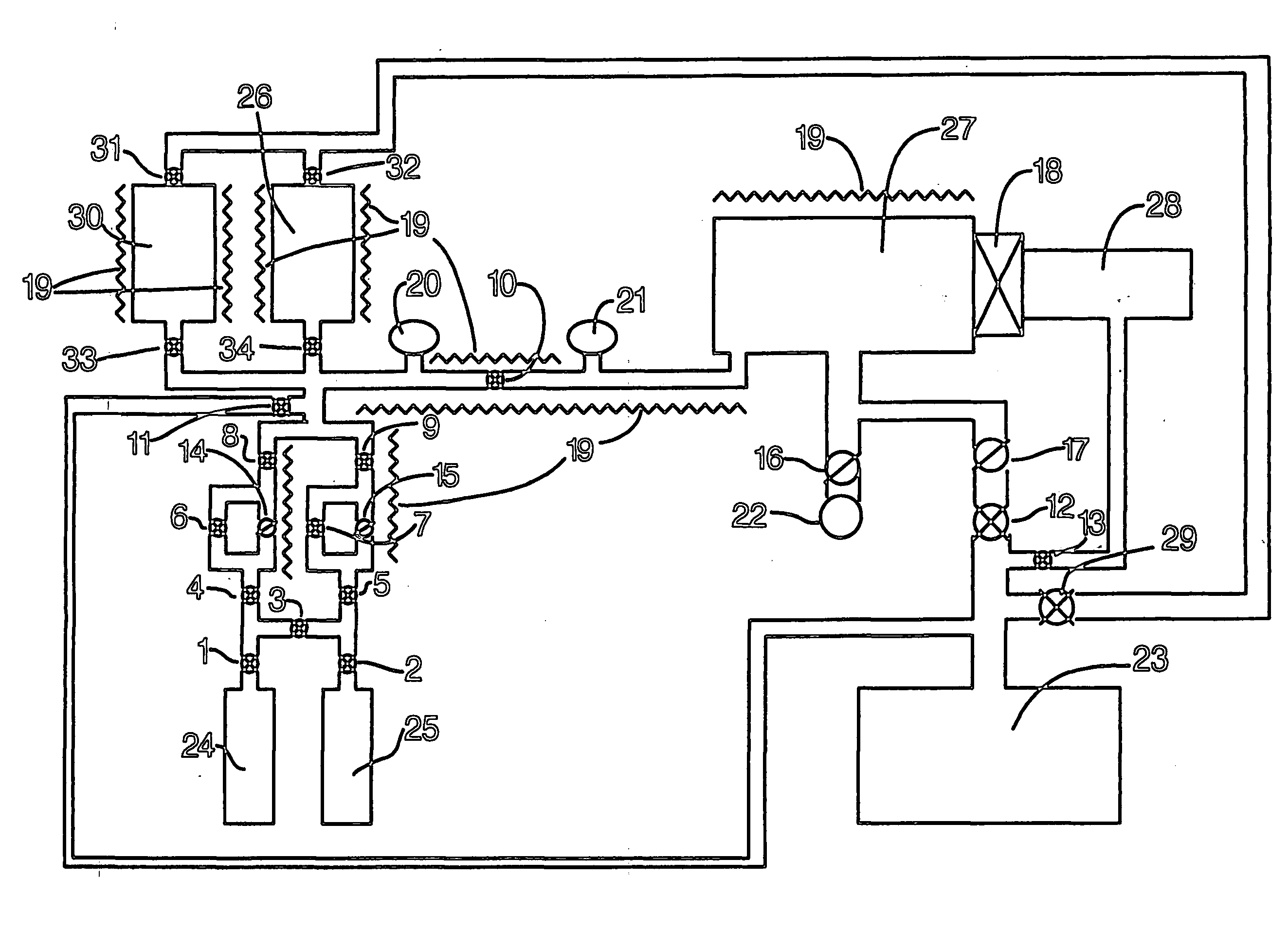
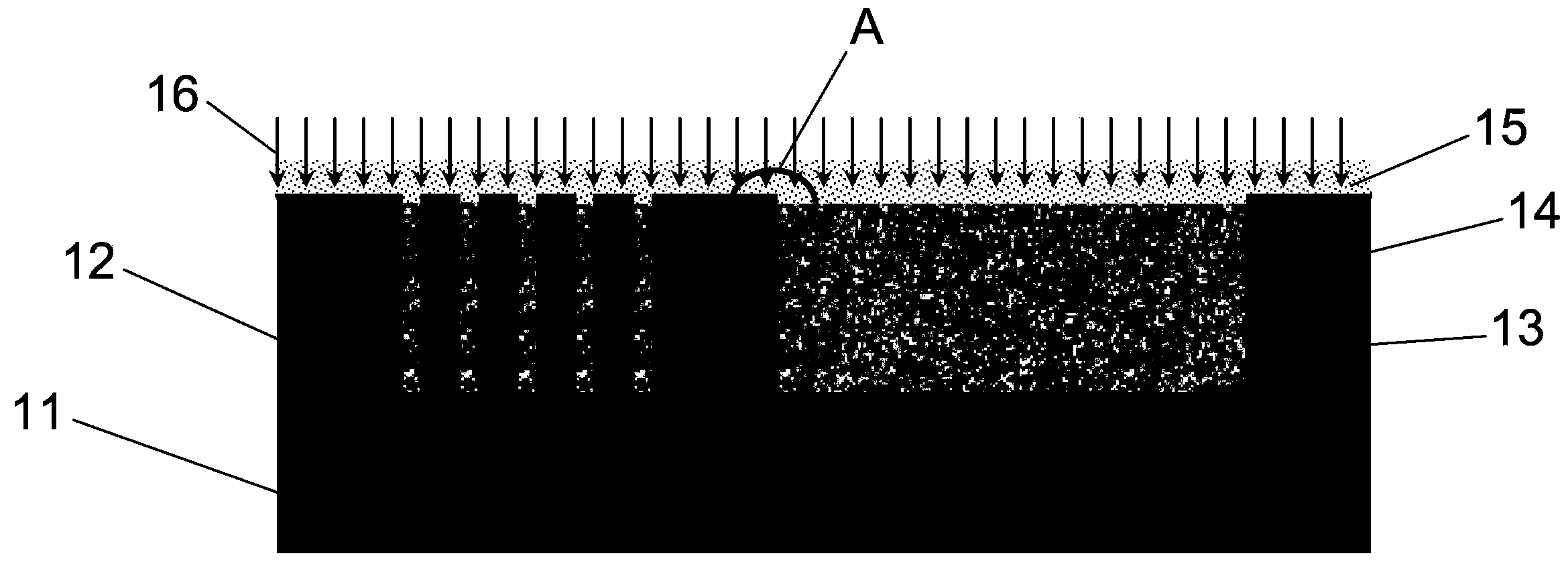
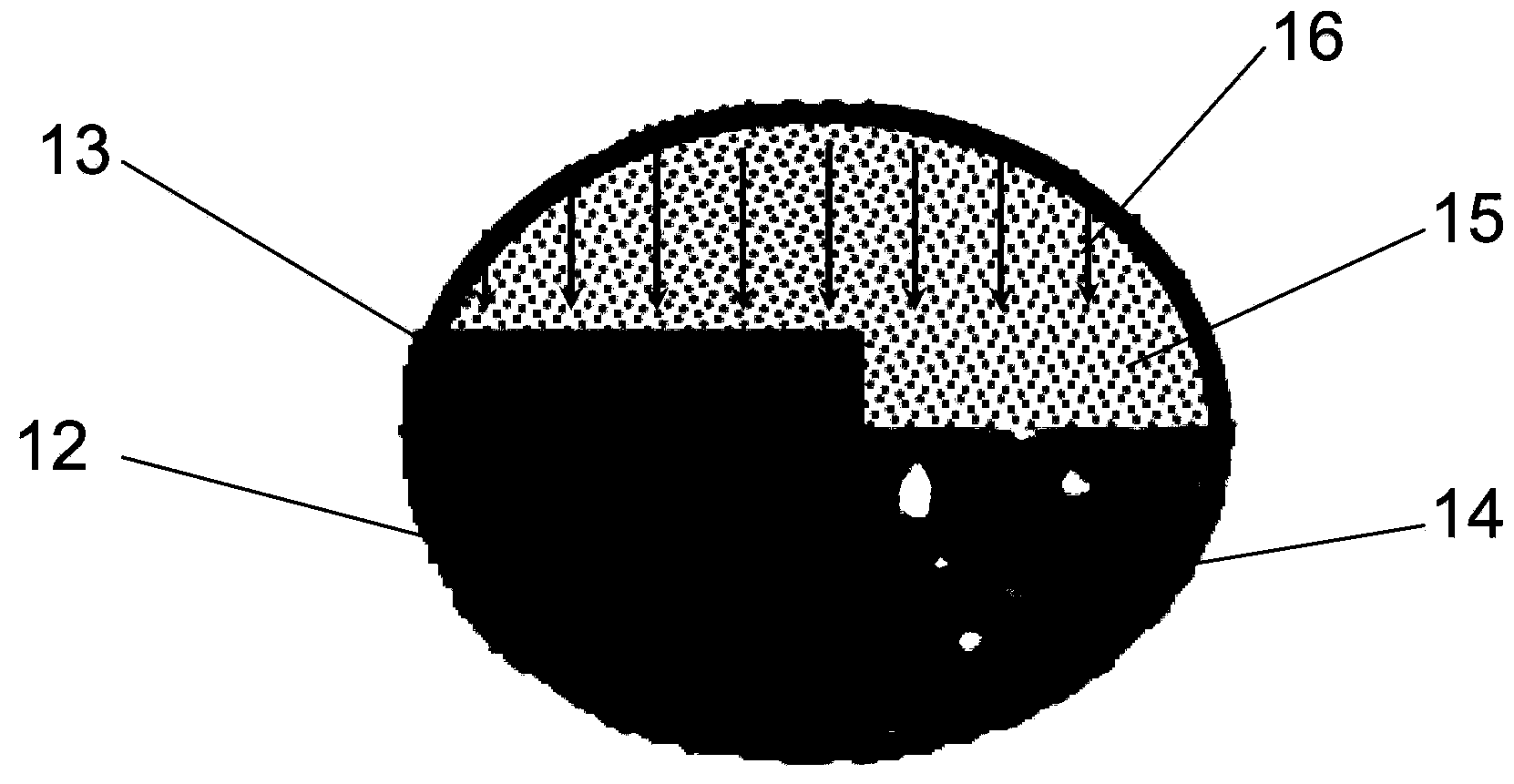
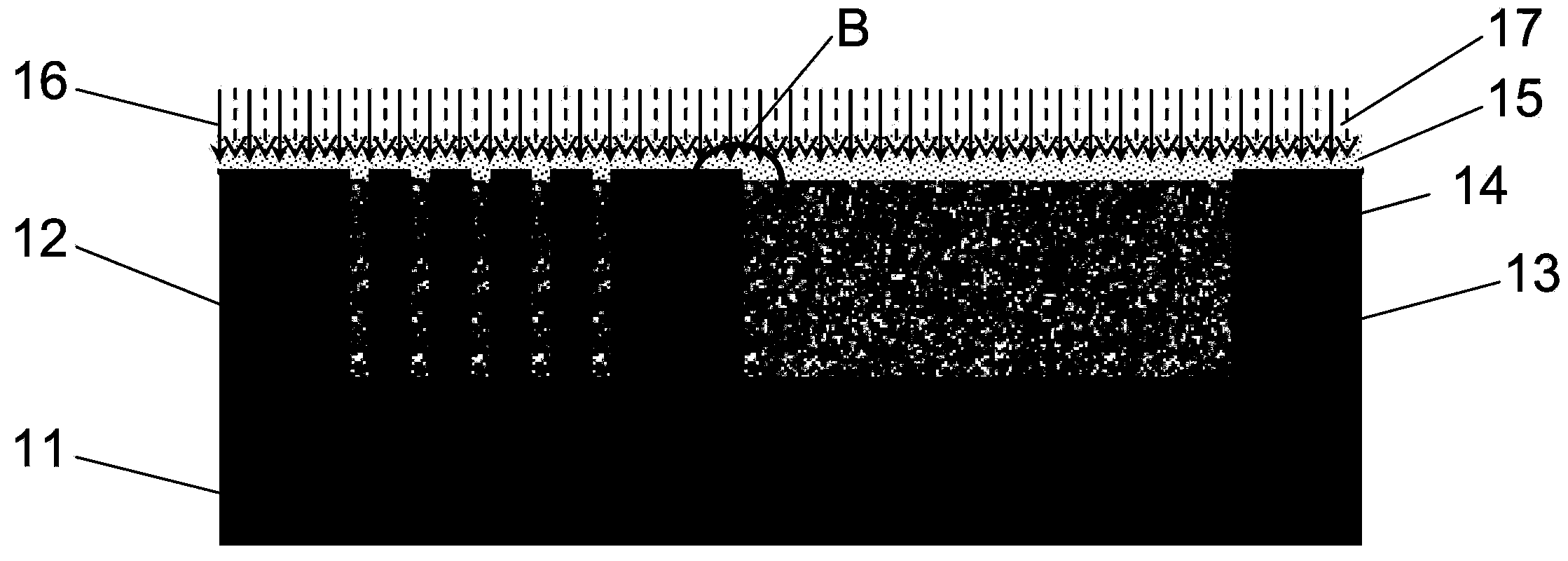
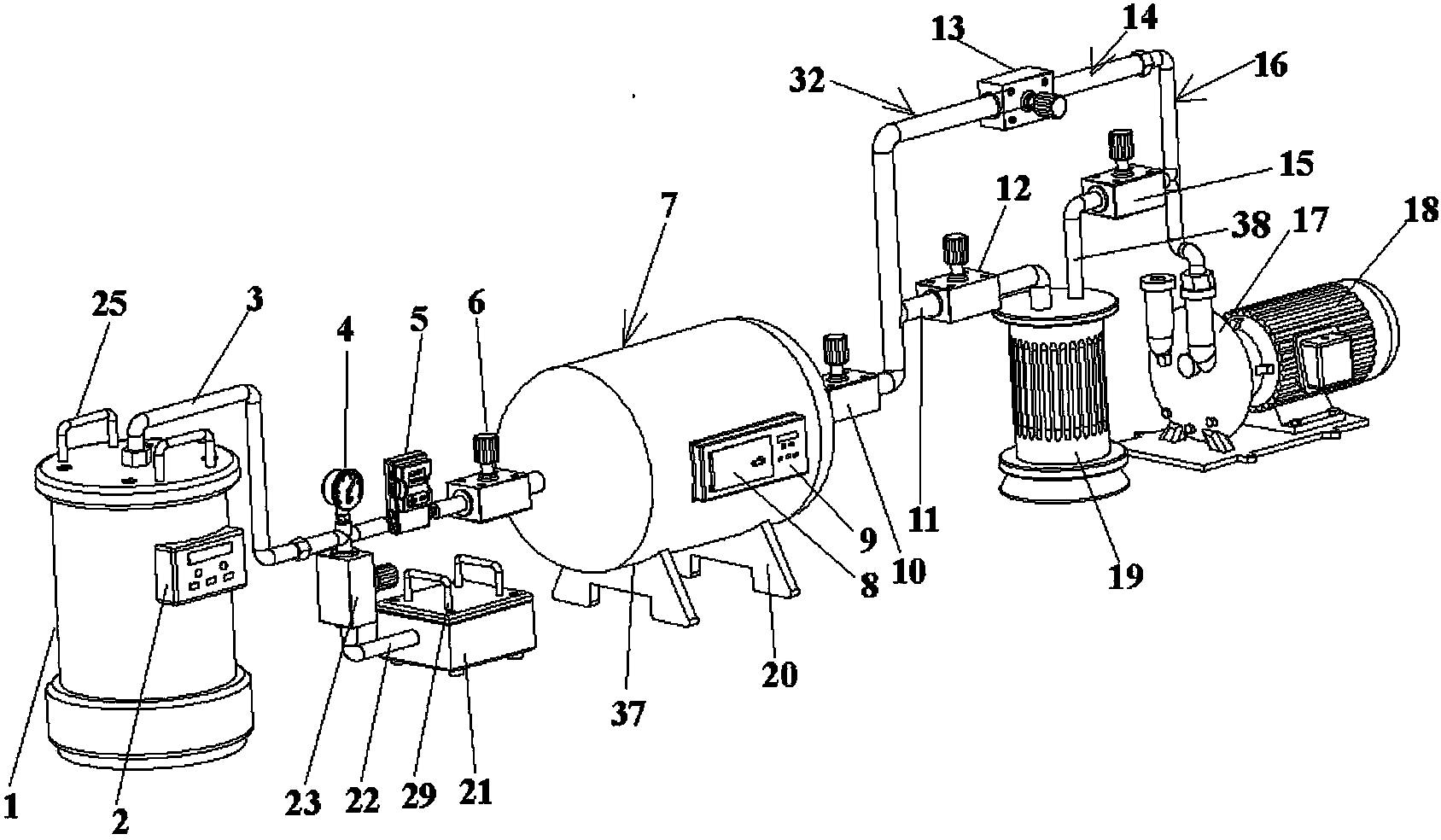
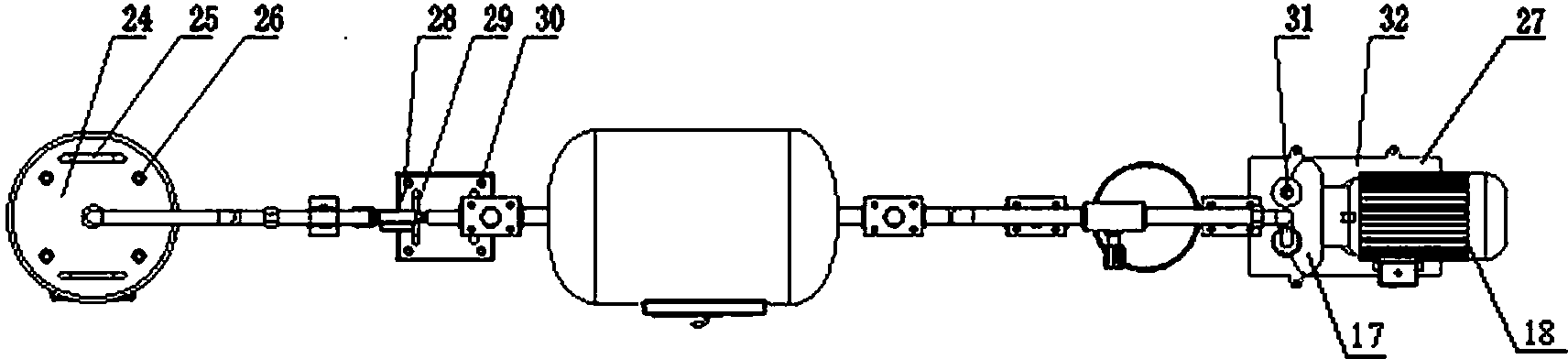
Apparatus for etching semiconductor samples and a source for providing a gas by sublimation thereto
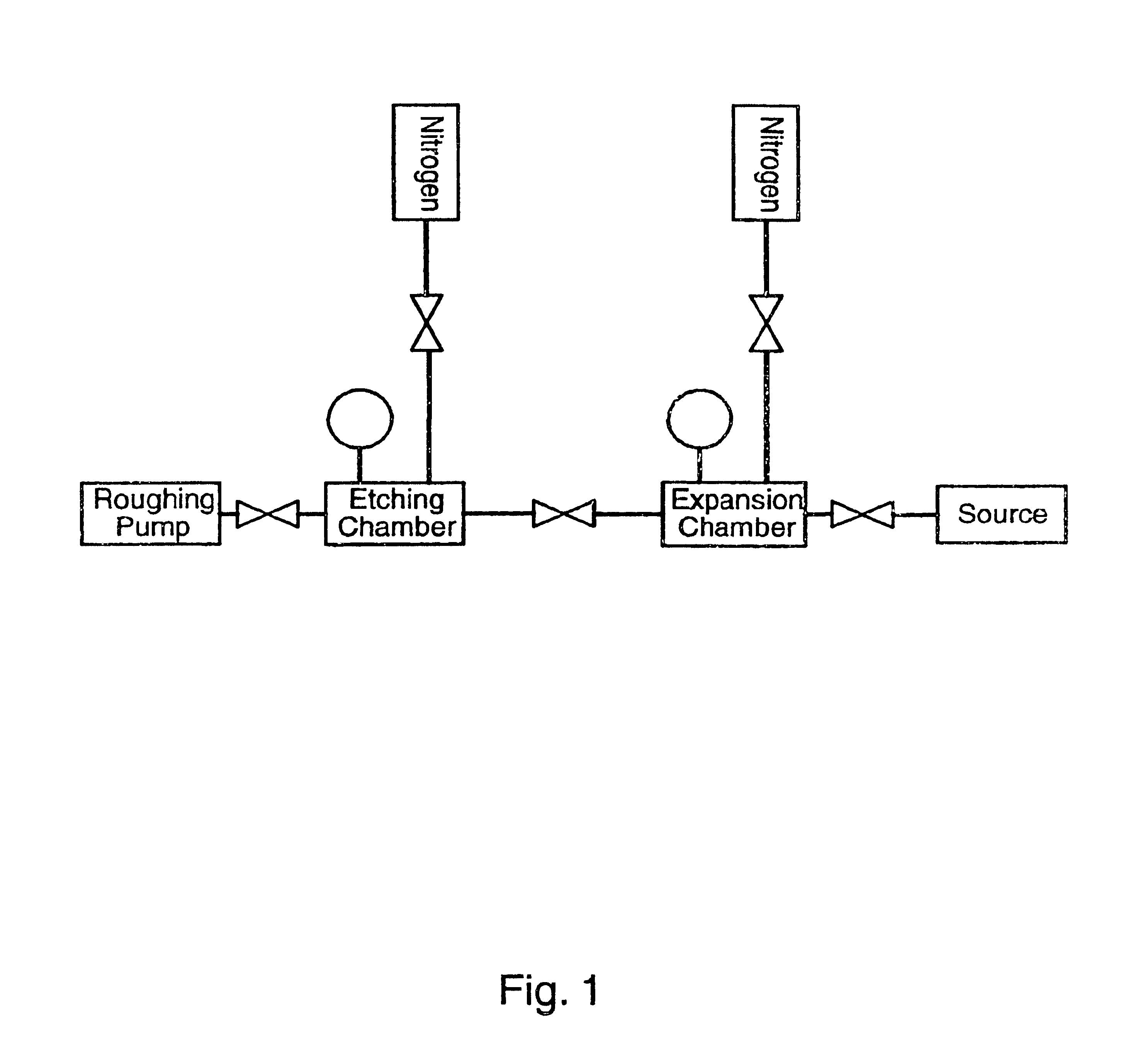
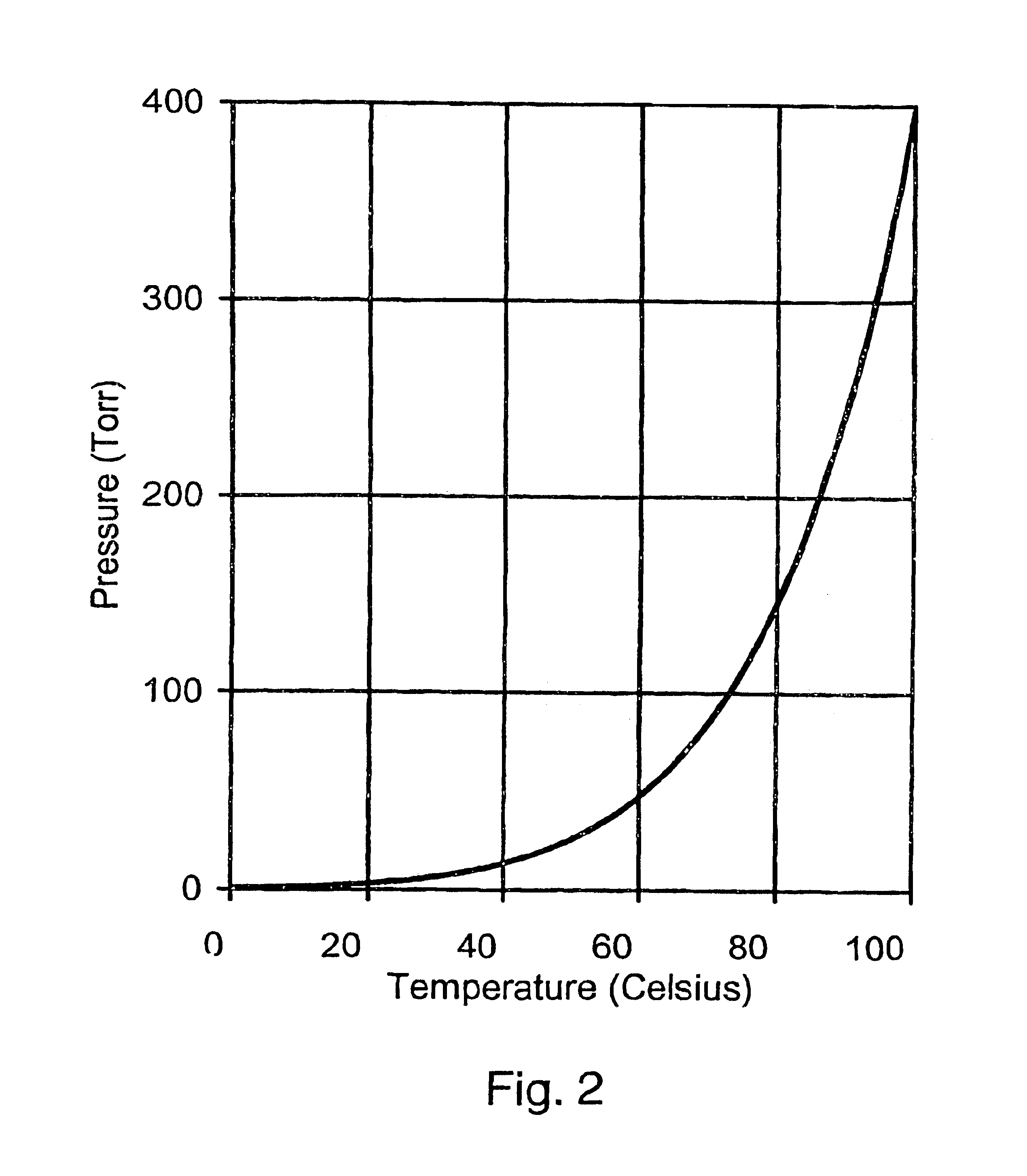
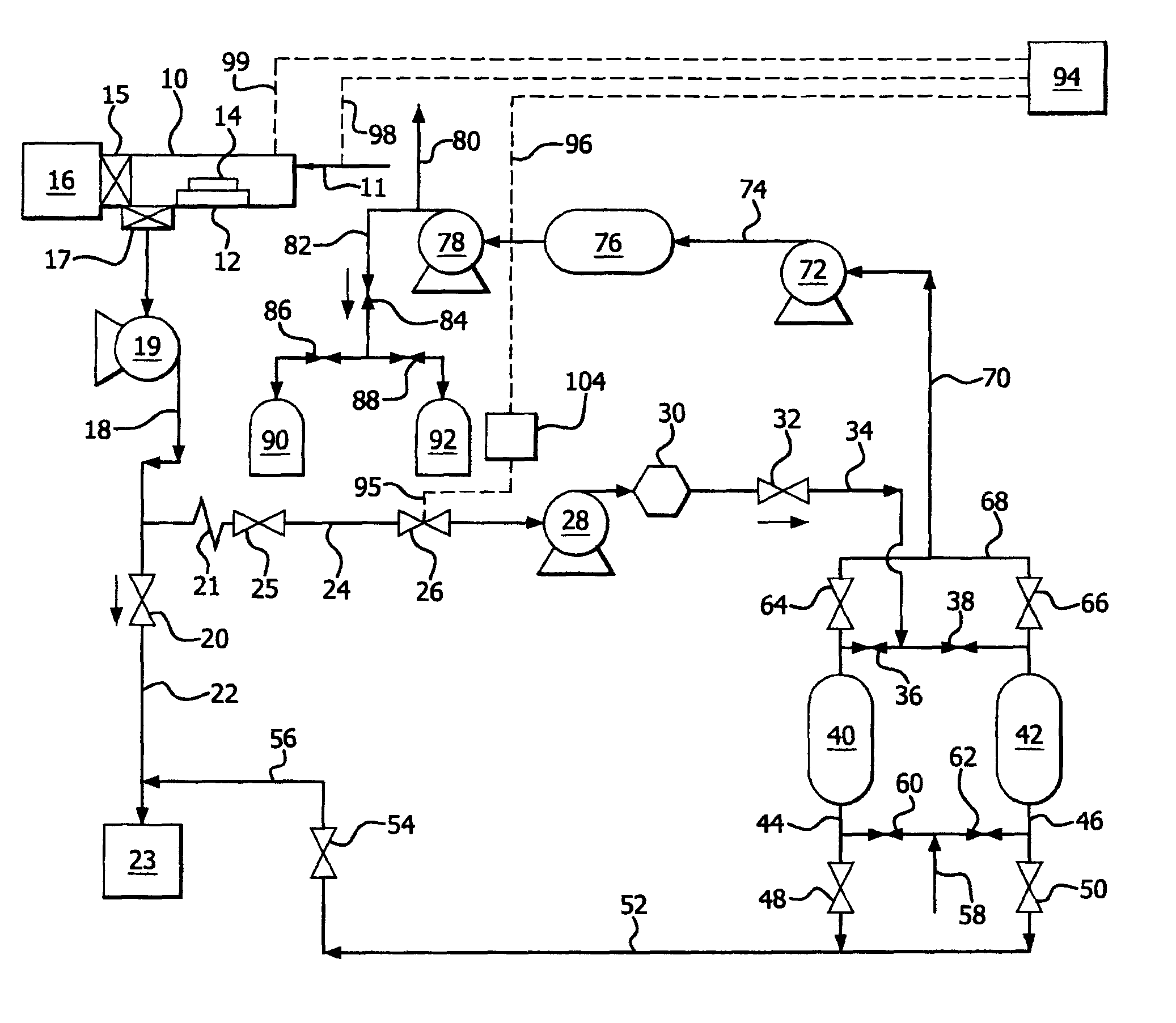
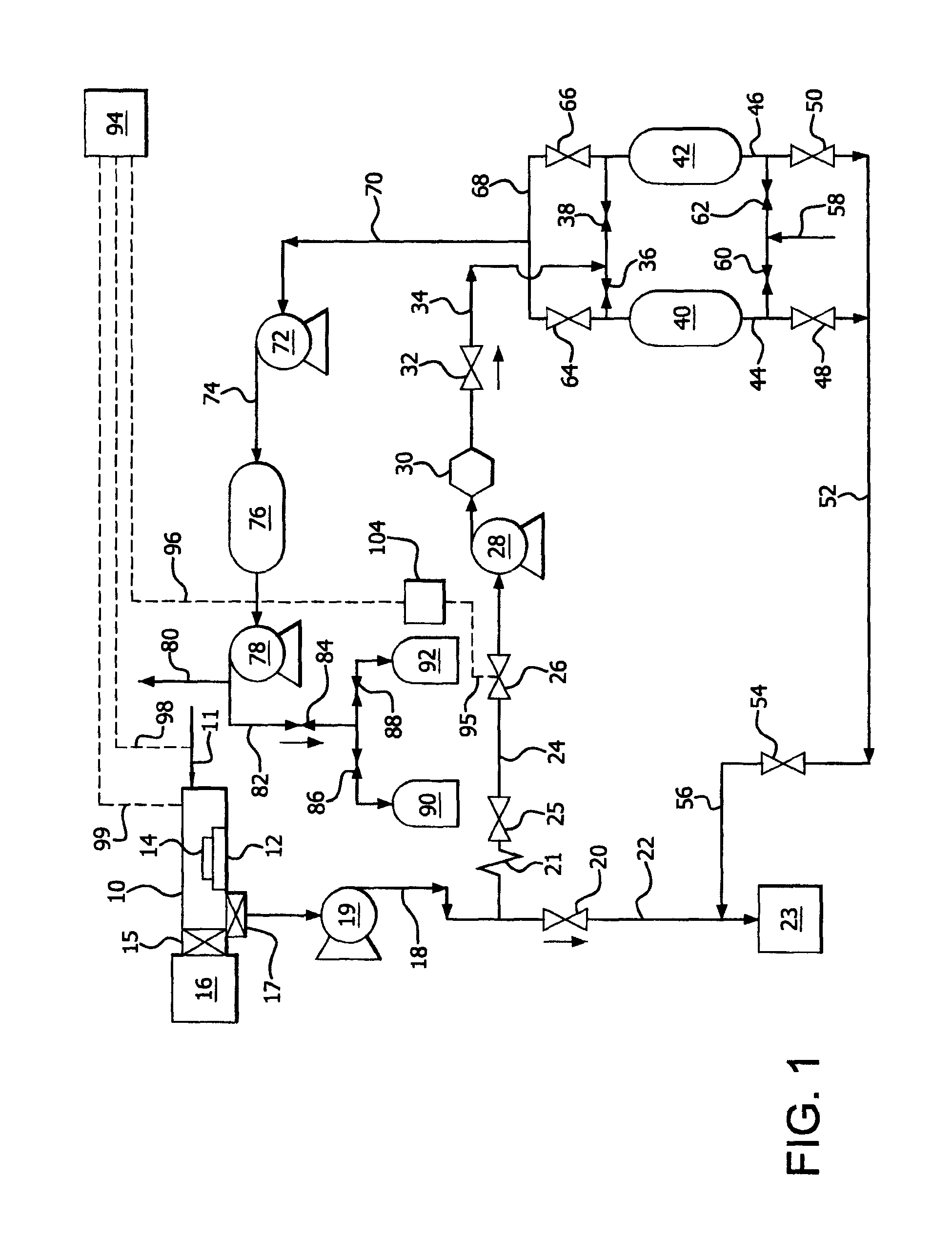
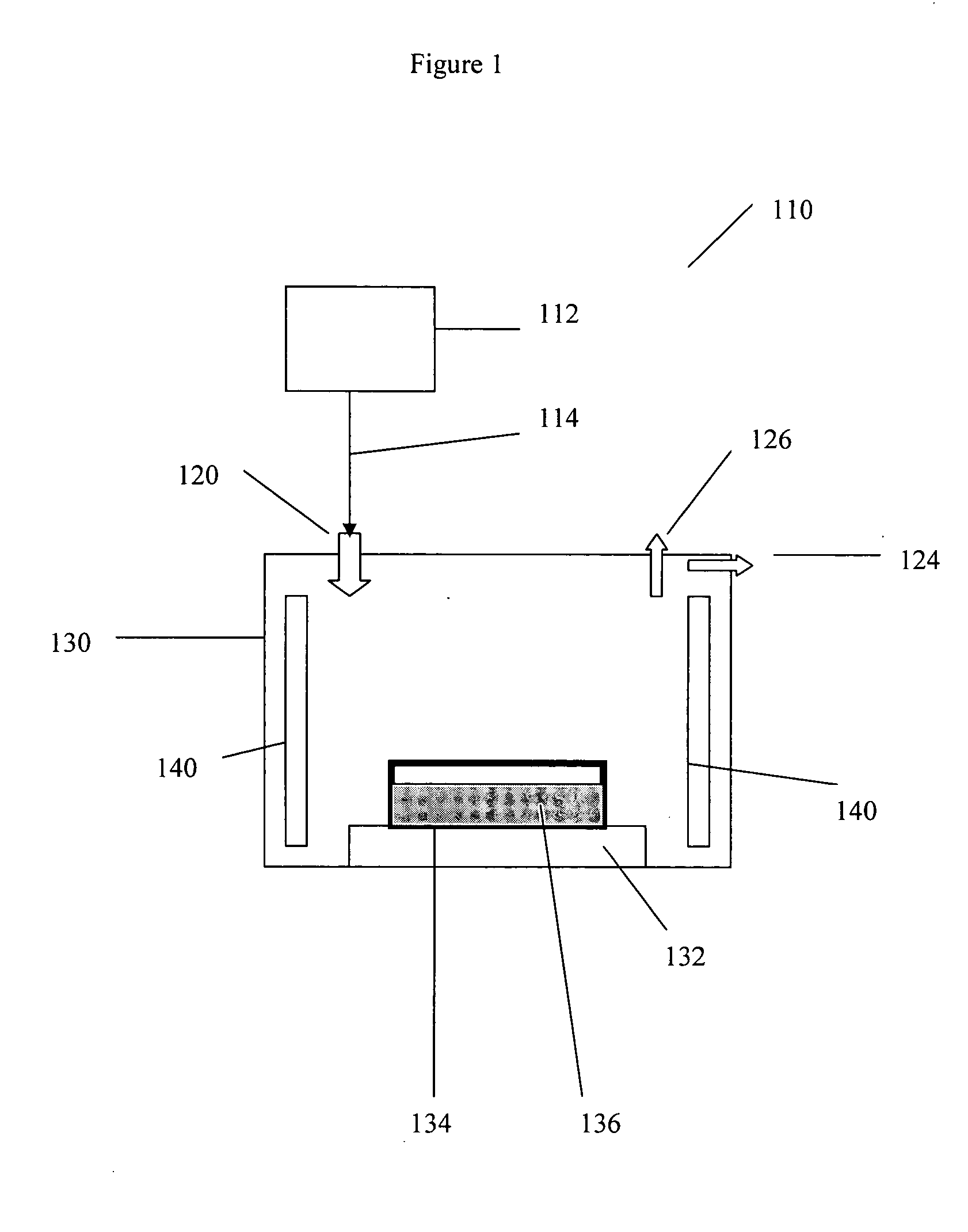
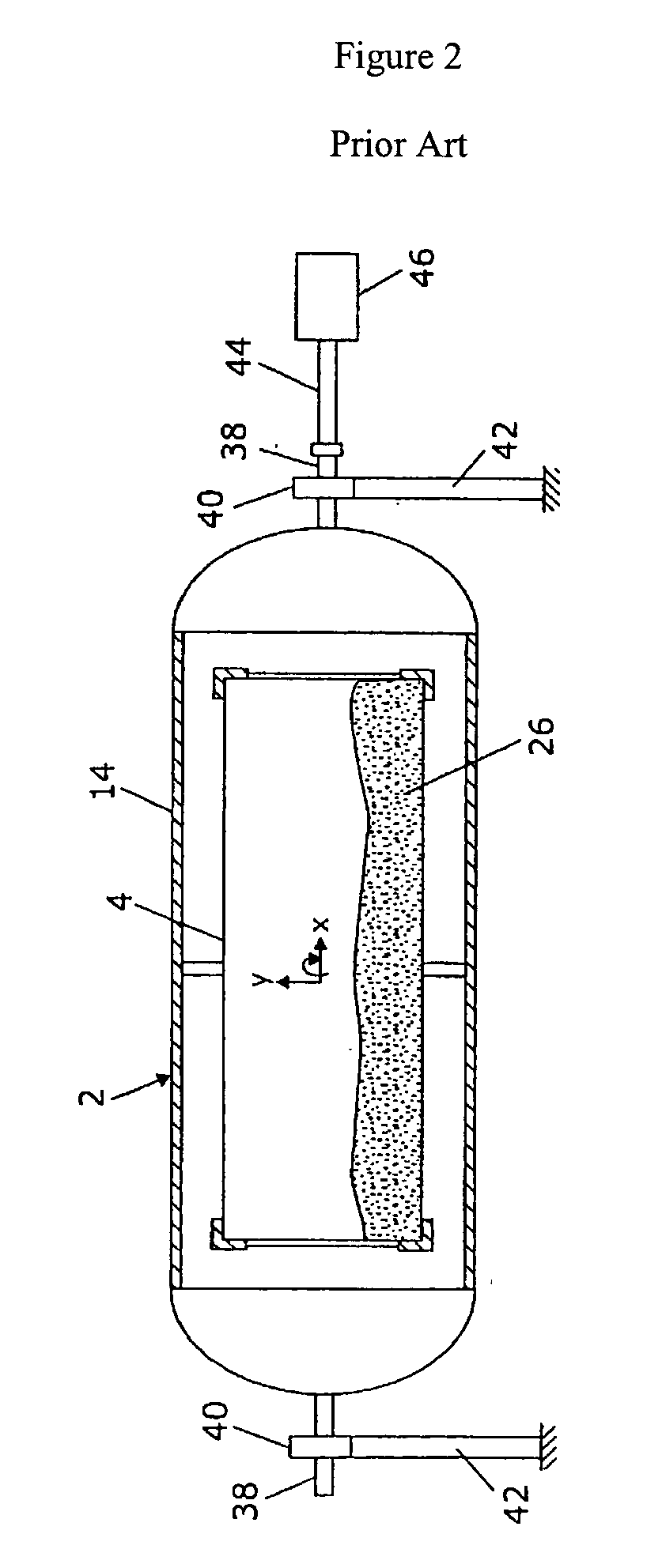
An etching apparatus for etching semi combustion samples may include one or more variable volume expansion chambers, two or more fixed volume expansion chambers, or combinations thereof in fluid communication with an etching chamber and a source of etching gas, such as xenon difluoride. The apparatus may further include a source of a mixing gas. An etching apparatus may also include a source of etching gas, an etching chamber in fluid communication with the source of etching gas, a flow controller connected between the source of etching gas and the etching chamber, and a vacuum pump in fluid communication with the etching chamber. A source for providing a gas by sublimation from a solid material is also provided, including a vacuum tight container and a mesh mounted in the interior of the vacuum tight container, wherein the mesh is adapted to receive and restrain the solid material.
Owner:SPTS TECH LTD
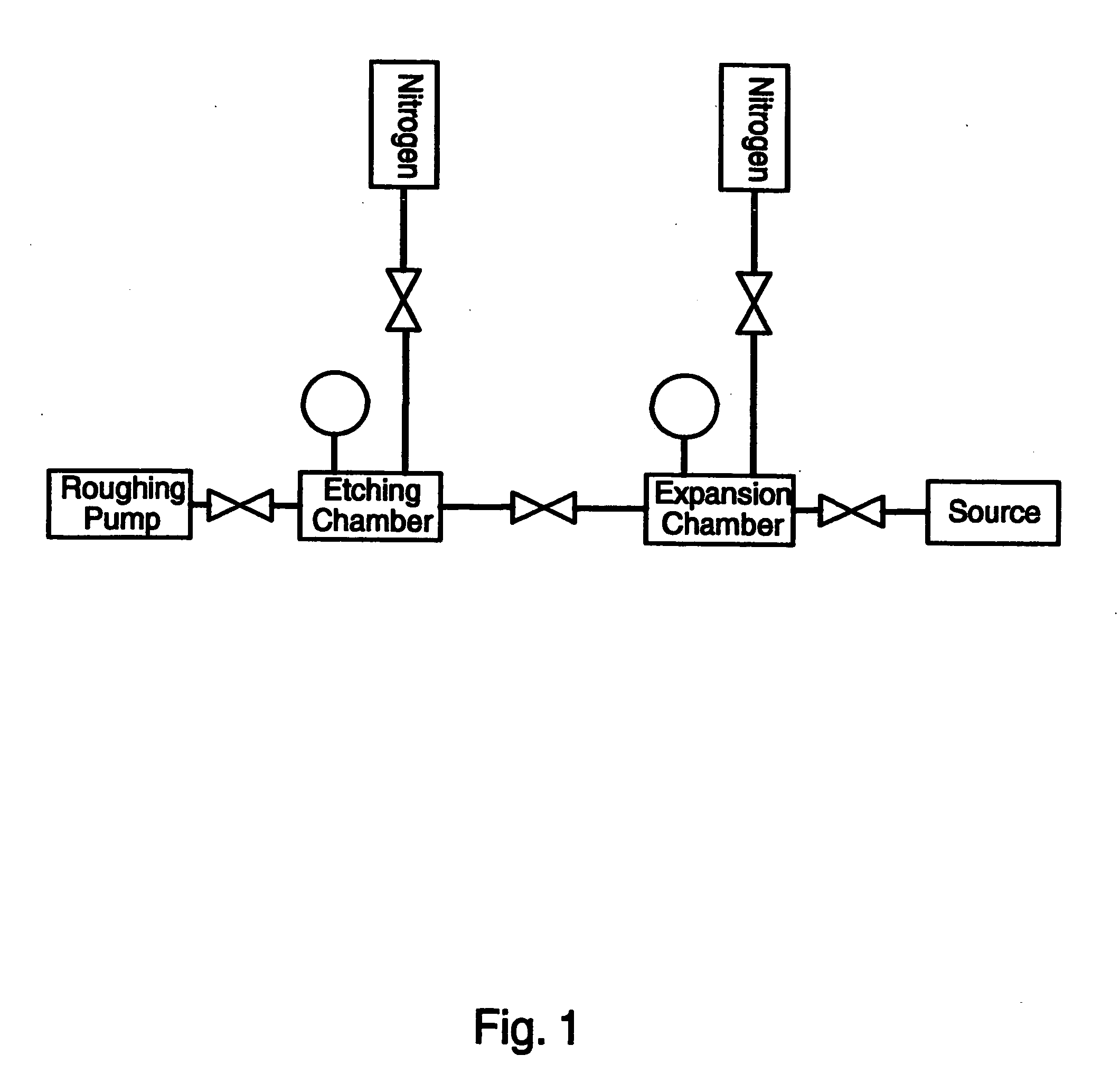
Method and equipment for selectively collecting process effluent
An apparatus and process for recovering a desired gas such as xenon difluoride, xenon, argon, helium or neon, from the effluent of a chemical process reactor that utilizes such gases alone or in a gas mixture or in a molecule that becomes decomposed wherein the chemical process reactor uses a sequence of different gas composition not all of which contain the desired gas and the desired gas is captured and recovered substantially only during the time the desired gas is in the effluent.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Method and device for removing barrier layer
The invention relates to a method and device for integrating an unstressed electrochemical polishing process for copper interconnection for semiconductor manufacturing, a process for removing a tantalum or titanium oxide film formed in an unstressed polishing process and a process for etching a barrier layer tantalum / tantalum nitride or titanium / titanium nitride by using a xenon difluoride gas phase. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, removing at least part of copper which is plated on a silicon plate by unstressed electrochemical polishing; secondly, removing the tantalum or titanium oxide film formed on the surface of the barrier layer in the copper-removal polishing process; and finally, removing the barrier layer tantalum / tantalum nitride or titanium / titanium nitride by xenon difluoride gas-etching. The device consists of three sub-systems, namely an unstressed electrochemical copper polishing system, a system for removing the tantalum or titanium oxide film on the surface of the barrier layer by using etchant and a xenon difluoride gas-etching system for removing the barrier layer.
Owner:ACM RES SHANGHAI
Apparatus for etching semiconductor samples and a source for providing a gas by sublimation thereto
InactiveUS20050230046A1Electric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsCombustionProduct gas
An etching apparatus for etching semi combustion samples may include one or more variable volume expansion chambers, two or more fixed volume expansion chambers, or combinations thereof in fluid communication with an etching chamber and a source of etching gas, such as xenon difluoride. The apparatus may further include a source of a mixing gas. An etching apparatus may also include a source of etching gas, an etching chamber in fluid communication with the source of etching gas, a flow controller connected between the source of etching gas and the etching chamber, and a vacuum pump in fluid communication with the etching chamber. A source for providing a gas by sublimation from a solid material is also provided, including a vacuum tight container and a mesh mounted in the interior of the vacuum tight container, wherein the mesh is adapted to receive and restrain the solid material.
Owner:LEBOUITZ KYLE S +1
Selective Etching and Formation of Xenon Difluoride
ActiveUS20100022095A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNoble gas compoundsEtchingPlasma generator
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Method for structuring silicon carbide with the aid of fluorine-containing compounds
InactiveUS20100086463A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCompound aChlorine pentafluoride
A method for etching silicon carbide, a mask being produced on a silicon carbide layer, the unmasked areas of the silicon carbide layer being etched using a fluorine-containing compound, which is selected from the group including interhalogen compounds of fluorine and / or xenon difluoride. The use of chlorine trifluoride, chlorine pentafluoride, and / or xenon difluoride for structuring silicon carbide layers covered with masks containing silicon dioxide and / or silicon oxide carbide; a structured silicon carbide layer obtained by the method, and a microstructured electromechanical component or a microelectronic component including a structured silicon carbide layer obtained by the method.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method for inducing high-nitrogen-doped photo-reduced graphene oxide film through fluorination
The invention discloses a method for inducing high-nitrogen-doped photo-reduced graphene oxide film through fluorination. The method comprises the following steps: by taking graphene oxide prepared by chemical oxidation as a raw material, performing spin coating on graphene oxide sheets on a substrate to form a film, mixing the graphene oxide film with xenon difluoride, fluorinating and illuminating to obtain the high-nitrogen-doped photo-reduced graphene oxide film. According to the method, a fluorinated graphene film is illuminated in an NH3 (flow is 10 torr to 30 torr) atmosphere by using laser or a mercury lamp with energy of 65-75mJ / cm<2> for 5-60 minutes in a selectable region; a defluorination effect is generated during photoreduction, so that vacancy defects are introduced; due to the increment of the vacancy defects, N atom doping is promoted, so that the N-doped content is increased. The high-nitrogen-doped photo-reduced graphene oxide film is convenient to operate and low in cost, and can be prepared on a large scale; the nitrogen-doped content, the conductivity of graphene and the effect of a band gap can be adjusted and controlled through the illumination time, the illumination intensity and the fluorine doping concentration.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Micro-nano fabrication method for auxiliary etch by combining focused ion beam injection and xenon fluoride gas
InactiveCN101456534AImprove structure preparation efficiencyReal-time observation of processing resultsDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingMicro nanoEtching
The invention relates to a micro-nano processing method based on injection of focused ion beams and etching of auxiliary gas, which comprises the following steps: placing a substrate to be processed in a focused ion beam sample chamber; observing appearance of the substrate through an ion beam imaging system; carrying out ion injection and processing on the substrate by using the focused ion beams according to a target processing pattern; and carrying out micro-nano processing on an ion injected area by in situ using a method of auxiliary etching of focused ion beam xenon fluoride gas in the focused ion beam sample chamber. The method is stable and reliable, not only can remarkably improve preparation efficiency, but also improves processing flexibility, can effectively reduce influence of processing re-deposition, and remarkably improves processing accuracy and processing quality.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Selective etching and formation of xenon difluoride
ActiveUS8278222B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEtchingPlasma generator
This invention relates to a process for selective removal of materials, such as: silicon, molybdenum, tungsten, titanium, zirconium, hafnium, vanadium, tantalum, niobium, boron, phosphorus, germanium, arsenic, and mixtures thereof, from silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, nickel, aluminum, TiNi alloy, photoresist, phosphosilicate glass, boron phosphosilicate glass, polyimides, gold, copper, platinum, chromium, aluminum oxide, silicon carbide and mixtures thereof. The process is related to the important applications in the cleaning or etching process for semiconductor deposition chambers and semiconductor tools, devices in a micro electro mechanical system (MEMS), and ion implantation systems. Methods of forming XeF2 by reacting Xe with a fluorine containing chemical are also provided, where the fluorine containing chemical is selected from the group consisting of F2, NF3, C2F6, CF4, C3F8, SF6, a plasma containing F atoms generated from an upstream plasma generator and mixtures thereof.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
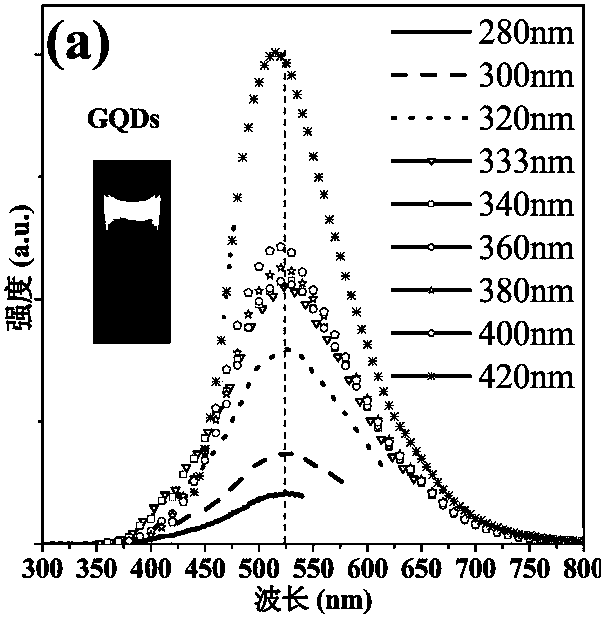
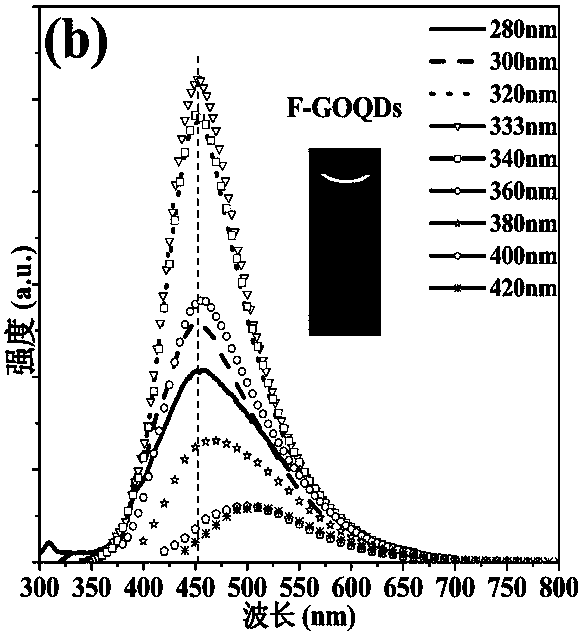
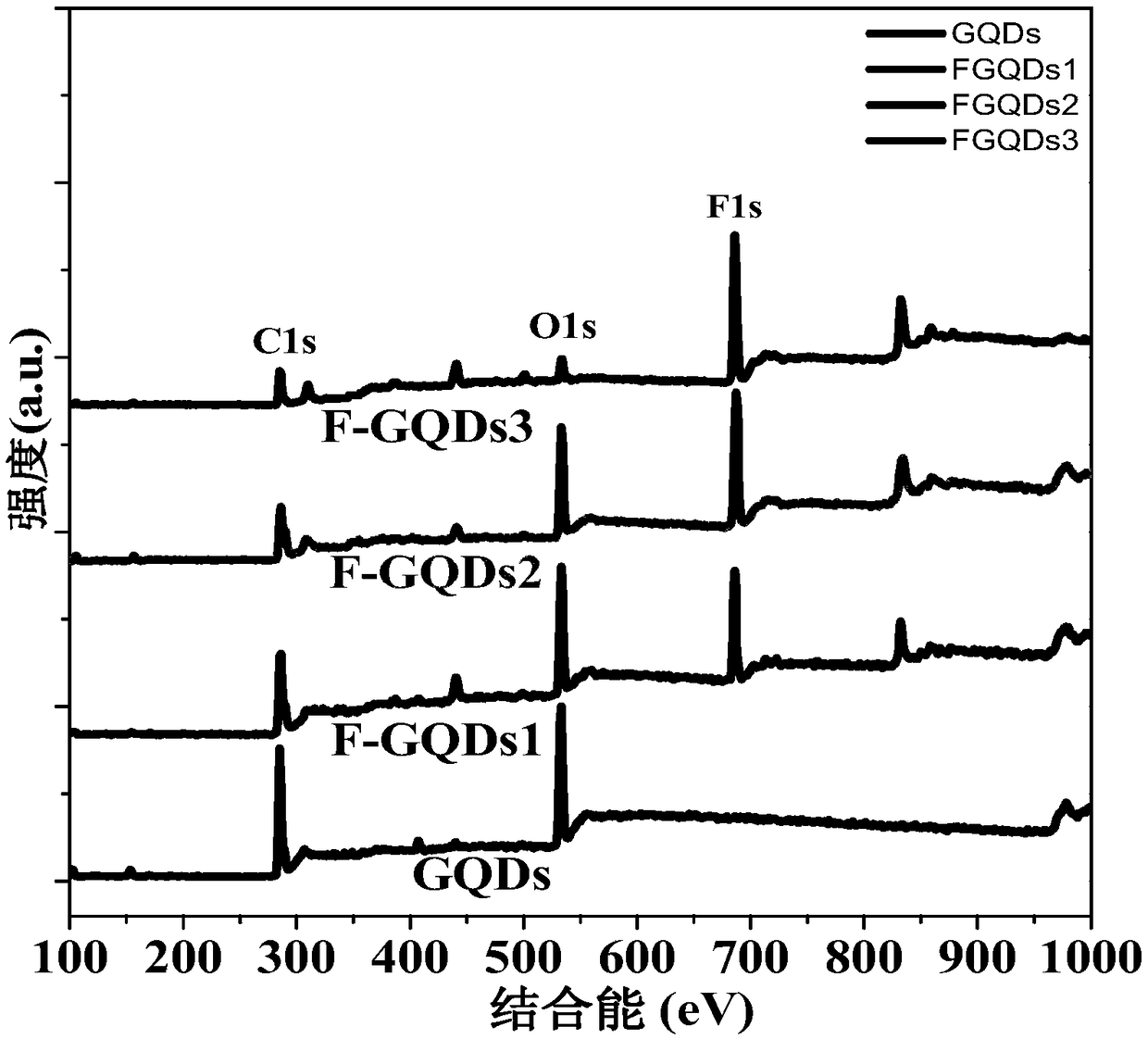
Method for preparing fluorine doped graphene quantum dot with excellent optical properties
InactiveCN105565310AThe production process is simple and easy to controlImprove yieldMaterial nanotechnologyLuminescent compositionsSolubilityDoped graphene
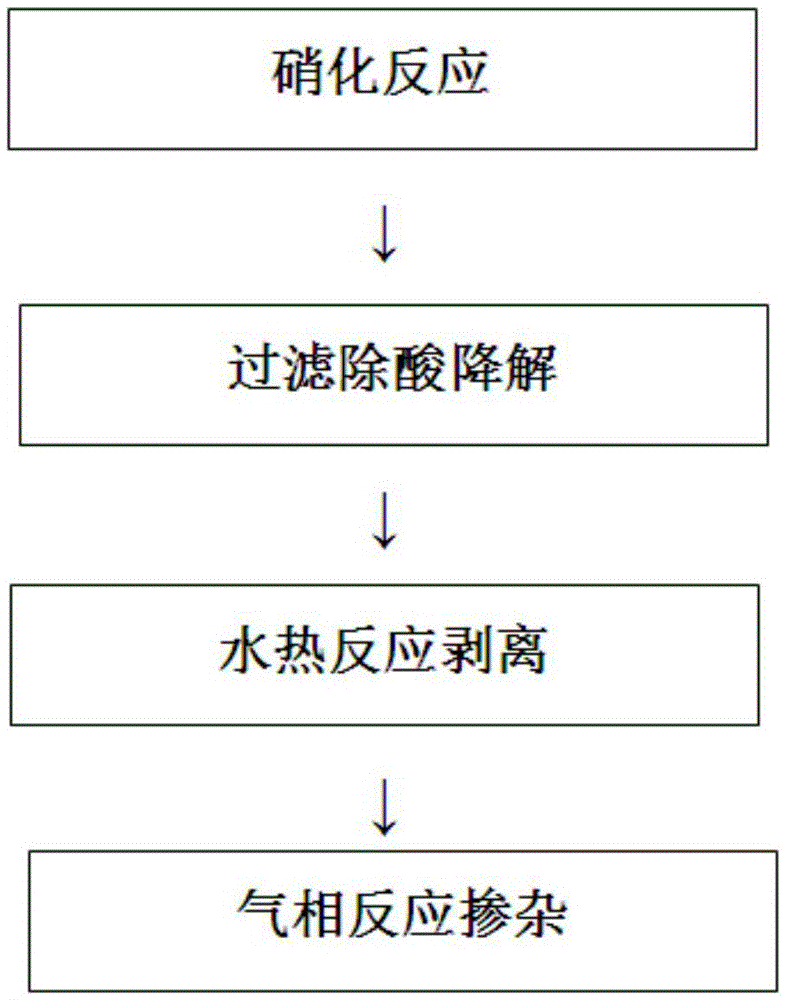
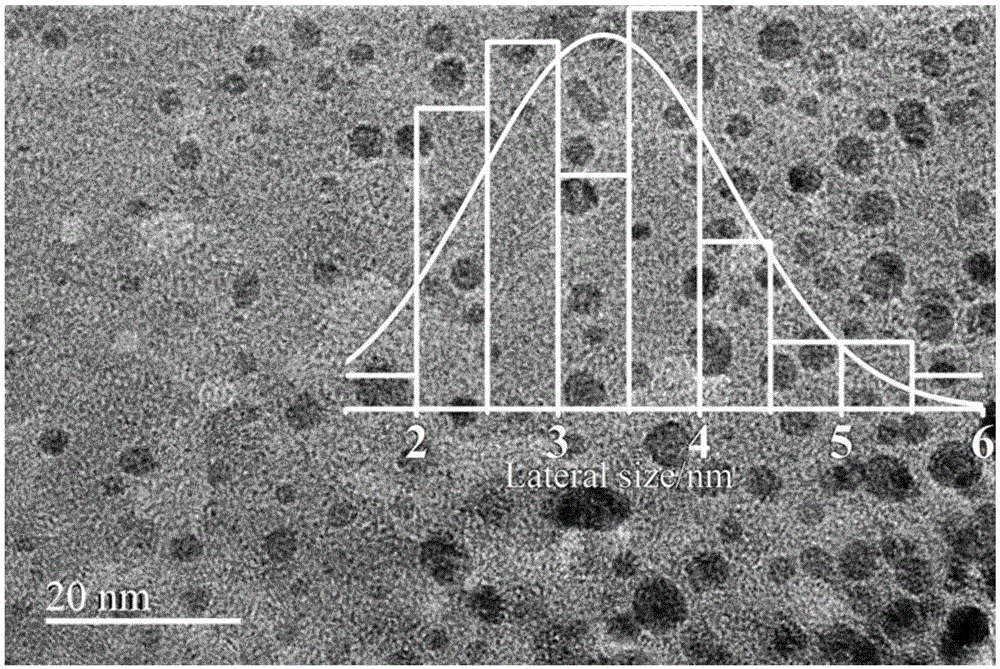
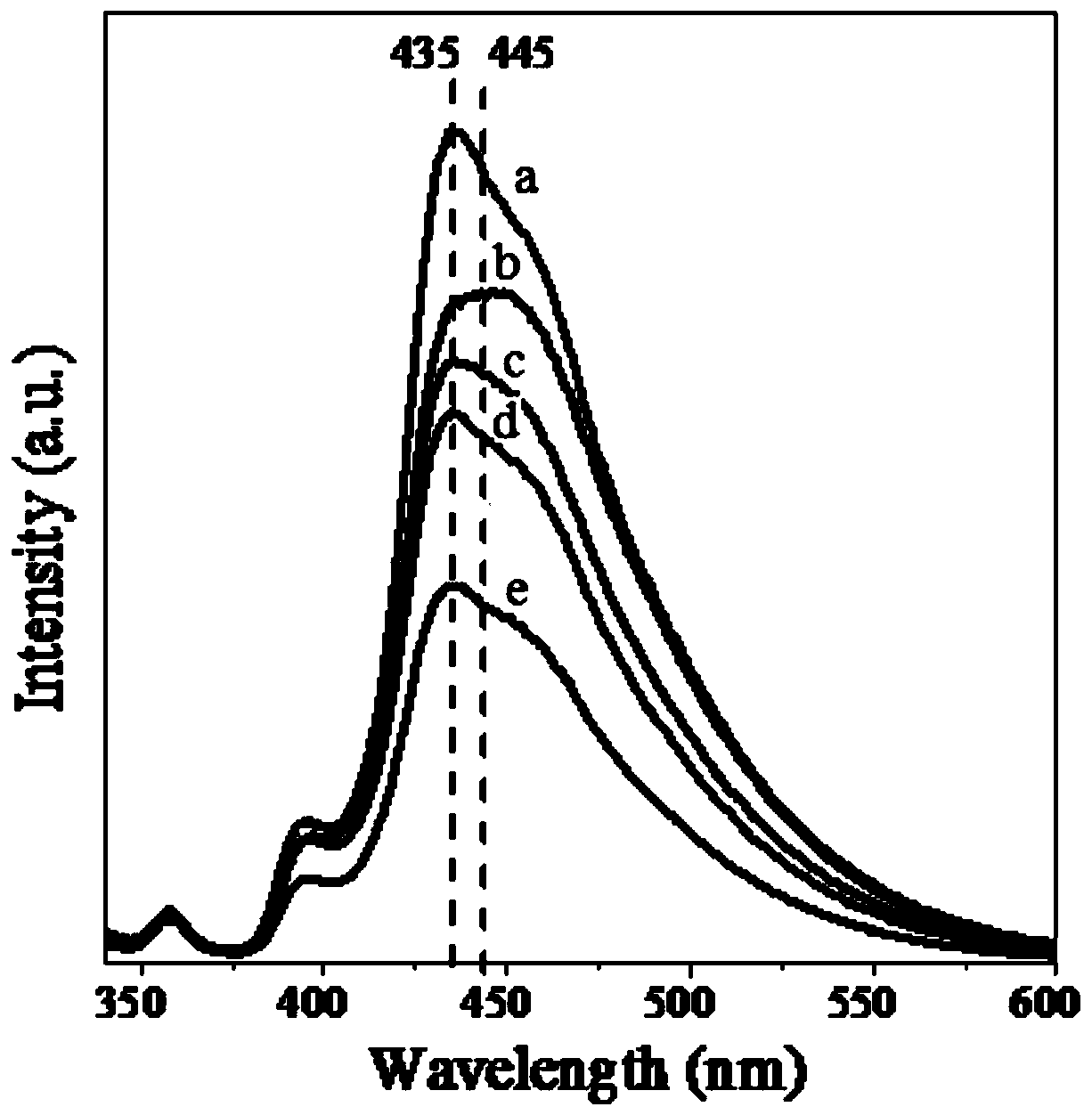
The invention discloses a method for preparing fluorine doped graphene quantum dot with excellent optical properties. The method comprises the steps of using low-cost and industrially produced pyrene as a precursor; performing nitration processing for the surface of pyrene at a low temperature; performing a hydrothermal reaction at a high temperature to remove the nitryl at the surface of the pyrene and then cutting the hexangular cyclic structure of the pyrene, so that graphene quantum dots excellent in water solubility, stable in structure, non-toxic, excellent in photoluminescent characteristics and small in size are prepared; performing a gas-phase reaction for the graphene quantum dots and xenon difluoride (XeF2) at 150 to 200 DEG C to synthesize the fluorine doped graphene quantum dots which are above 34 percent in fluorine content, 3 to 4 nm in crystal particle average particle size, and excellent in optical properties; the fluorine doped graphene quantum dot emits bright green fluorescence under the irradiating of 365 nm ultraviolet light. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, low in requirement on equipment and high in yield; other impurities are not generated.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
System and method for releasing micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) structure by etching silicon sacrificial layer
ActiveCN102115024AEtched thoroughlyImprove surface smoothnessDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingEtchingHigh volume manufacturing
The invention discloses system and method for releasing a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) structure by etching a silicon sacrificial layer. The method adopts xenon difluoride as an etching reactive gas and adopts supercritical carbon dioxide as a carrier gas to release the silicon sacrificial layer. Based on the unique property of carbon dioxide in a supercritical state, silicon is etched more uniformly by xenon difluoride, the smoothness of an etched surface is higher and the etching is more complete. Compared with traditional wet release process and plasma release process, the method prevents devices from being damaged due to stirring or adhesion in the wet release process, improves the uniformity of an entire wafer, increases the reaction speed and the efficiency, shortens the process time, and achieves the effect of feasible large-scale production process of XeF2 etching.
Owner:无锡影速半导体科技有限公司
Method and equipment for selectively collecting process effluent
An apparatus and process for recovering a desired gas such as xenon difluoride, xenon, argon, helium or neon, from the effluent of a chemical process reactor that utilizes such gases alone or in a gas mixture or in a molecule that becomes decomposed wherein the chemical process reactor uses a sequence of different gas composition not all of which contain the desired gas and the desired gas is captured and recovered substantially only during the time the desired gas is in the effluent.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Dehydroxylation and purification of calcium fluoride materials using a halogen containing plasma
InactiveUS20050263064A1Polycrystalline material growthFluoride preparationSingle crystalXenon difluoride
The invention is directed to a process of purifying metal fluoride materials used to make metal fluoride single crystals suitable for making optical elements used in the transmission of wavelengths below 200 nm, and in particular to a process of purifying such materials by the use of a halogen containing plasma to convert metal oxygenates contaminating the feedstocks used in the preparation of the crystals to metal fluorides. The invention also is directed to a process of growing a metal fluoride single crystal using a crystal growth furnace to carry out the foregoing purification procedure followed by the steps of melting the purified material and cooling it using s selected time and temperature cycle to from a metal fluoride single crystal. The plasmas used in practicing the invention can be derived from a variety of halogenated materials including, for example, fluorocarbons, chlorocarbons, boron trihalides, chlorine, fluorine, xenon difluoride and other gaseous or easily volatilized halogenated substances known in the art.
Owner:CORNING INC
Xenon difluoride selective erosion for titanium nitride
InactiveCN101192508ANo side effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEtchingTitanium nitride
The present invention relates to an improved method for selectively etching TiN from silicon dioxide (quartz) and SiN surfaces commonly found in semiconductor deposition chamber equipment and tools. In this method, a SiO2 or SiN surface with TiN thereon is contacted with XeF2 in a contact zone to selectively convert the TiN to a volatile species, which is then removed from the contact zone. XeF2 can be preformed or formed in situ by the reaction of Xe and fluorine compounds.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Selective etching and formation of xenon difluoride
ActiveCN101847570ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning processes and apparatusEtchingPlasma generator
This invention relates to a process for selective removal of materials, such as: silicon, molybdenum, tungsten, titanium, zirconium, hafnium, vanadium, tantalum, niobium, boron, phosphorus, germanium, arsenic, and mixtures thereof, from silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, nickel, aluminum, TiNi alloy, photoresist, phosphosilicate glass, boron phosphosilicate glass, polyimides, gold, copper, platinum, chromium, aluminum oxide, silicon carbide and mixtures thereof. The process is related to the important applications in the cleaning or etching process for semiconductor deposition chambers and semiconductor tools, devices in a micro electro mechanical system (MEMS), and ion implantation systems. Methods of forming XeF2 by reacting Xe with a fluorine containing chemical are also provided, where the fluorine containing chemical is selected from the group consisting of F2, NF3, C2F6, CF4, C3F8, SF6, a plasma containing F atoms generated from an upstream plasma generator and mixtures thereof.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
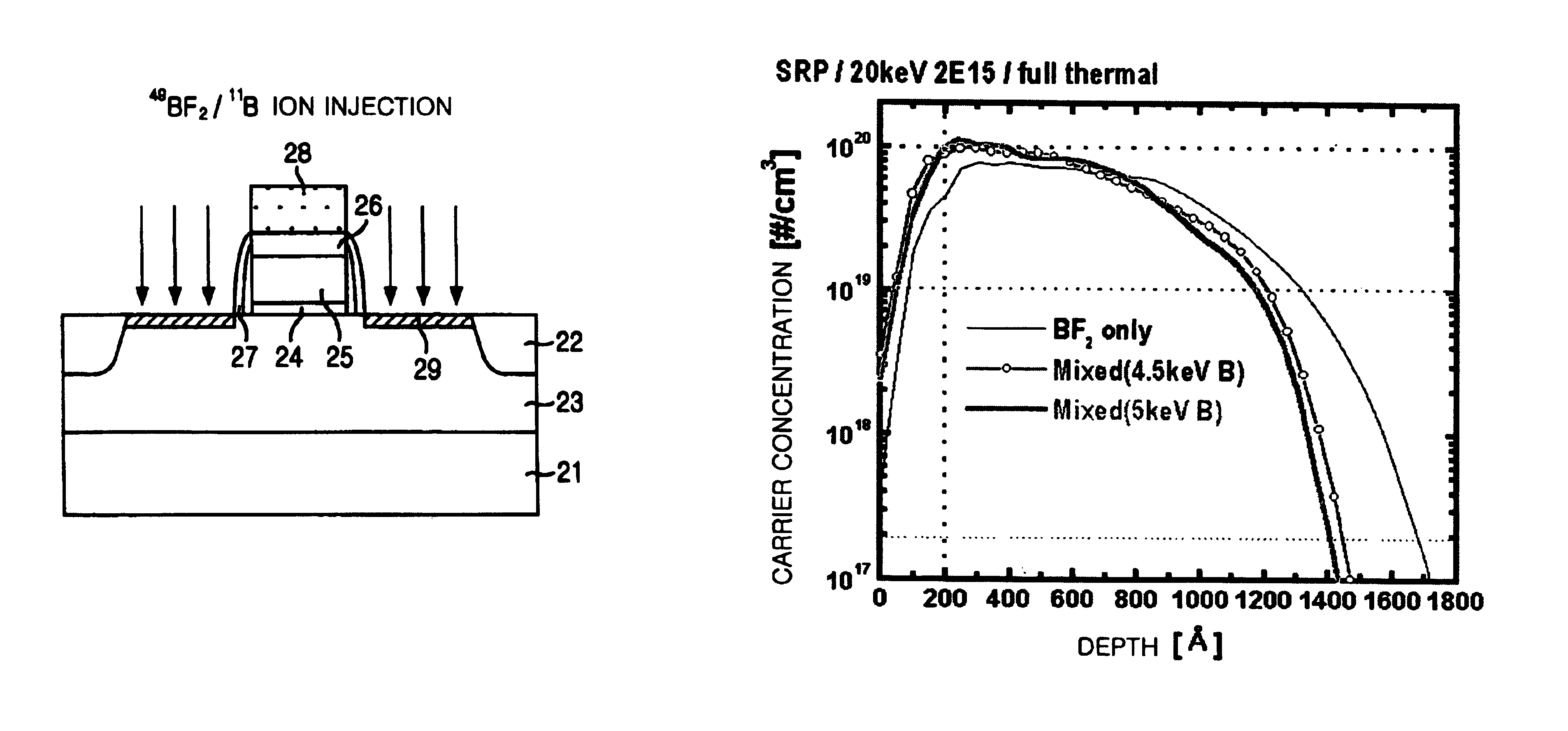
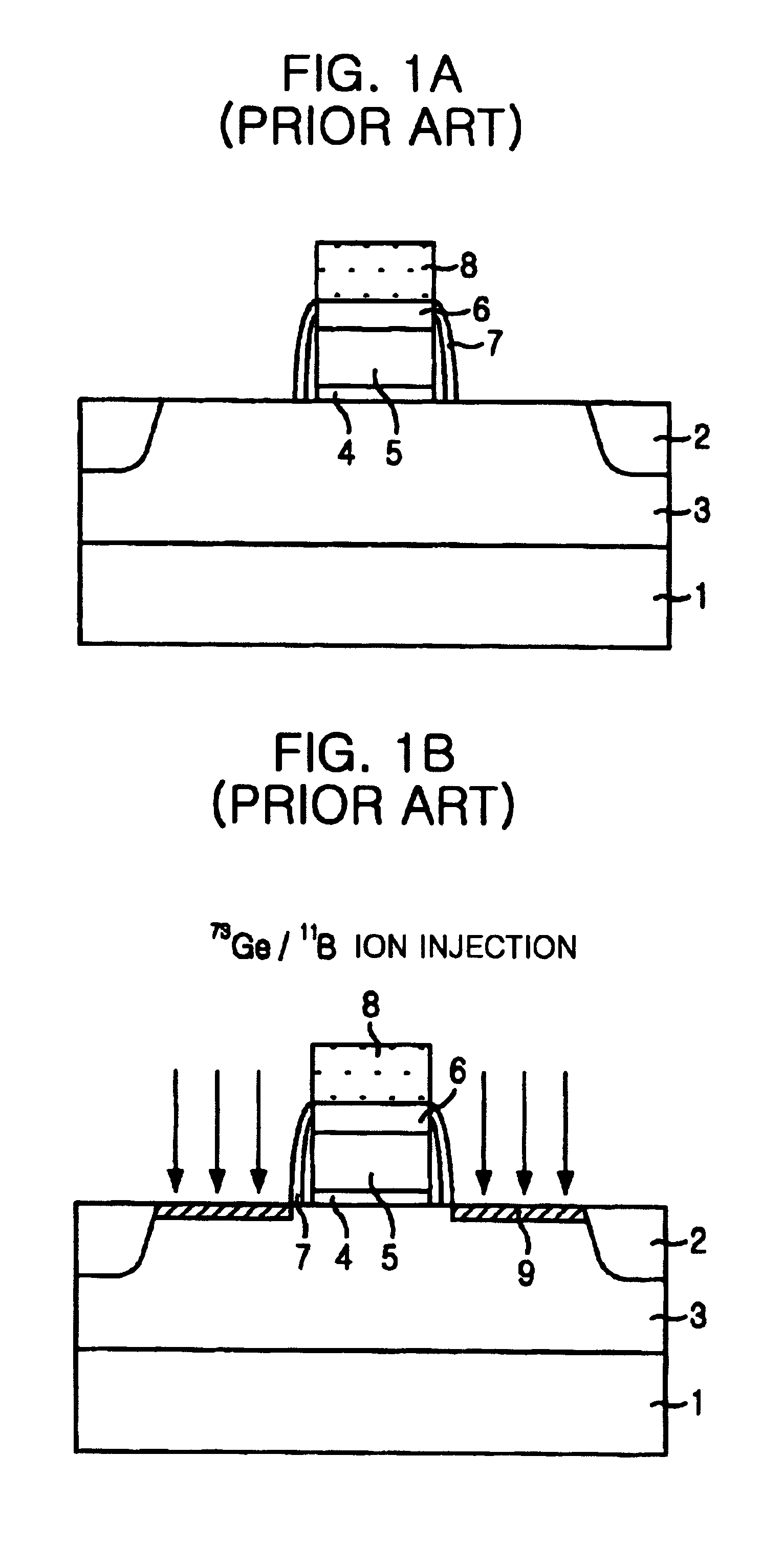
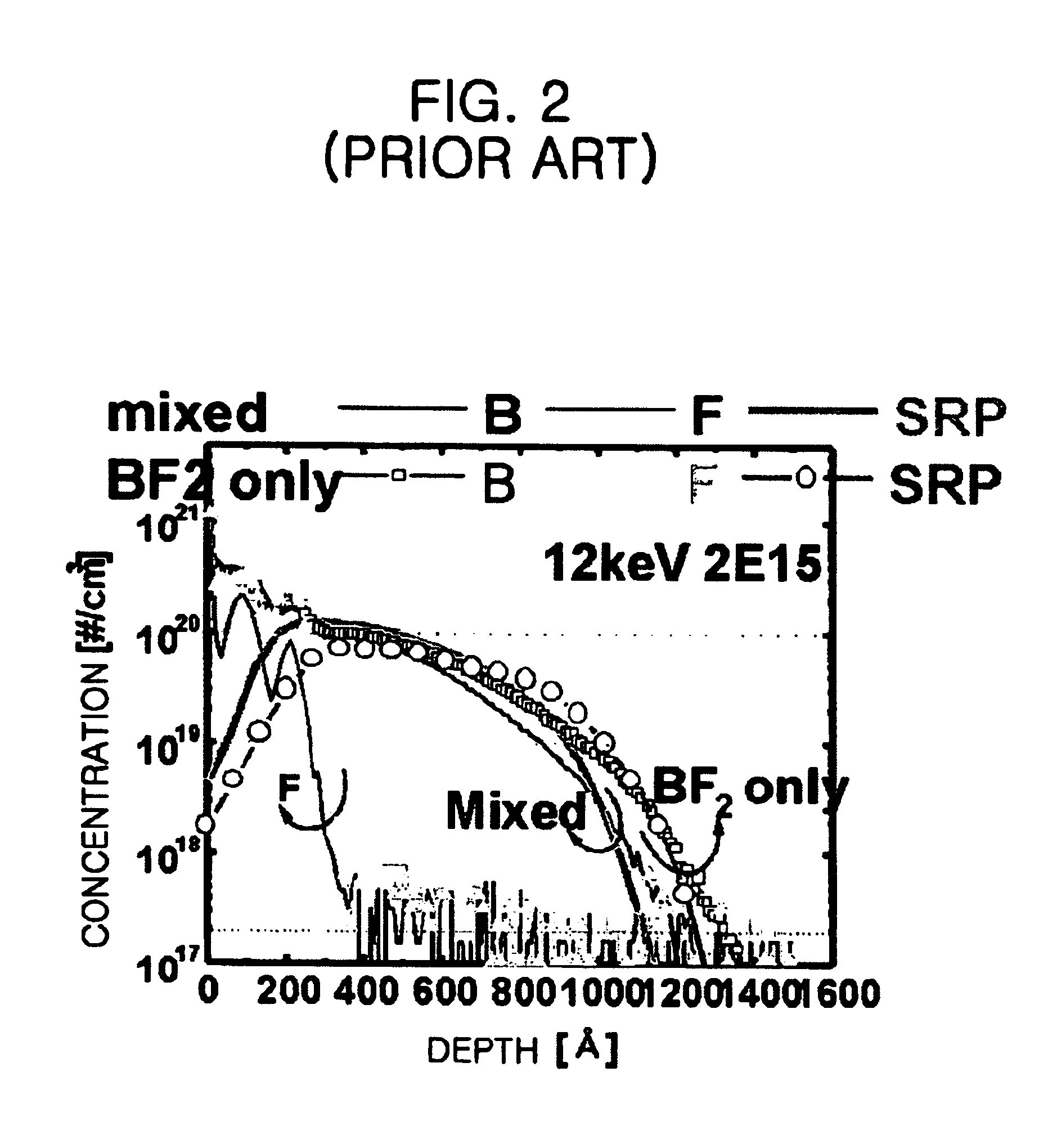
Method for manufacturing a semiconductor device with using double implanting boron and boron difluoride
InactiveUS6939769B2Ion beamImprove productivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesProduction rateThermal treatment
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device capable of acquiring productivity when a p-type source / drain is formed by the implantation of a BF2 and B ions. The method for manufacturing a semiconductor device includes the steps of: implanting a BF2 ion in a p-type source / drain region on a silicon substrate with an ion implantation energy of from about 10 keV to about 20 keV; implanting B ion in the p-type source / drain region with an ion implantation energy of from about 5 keV to about 10 keV; and forming a p-type source / drain by carrying out a thermal treatment.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Barrier layer removal method and barrier layer removal device
ActiveCN103985670ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseTitanium nitride
The invention relates to an integration method and an integration device of an unstressed electrochemical polishing technology of semiconductor manufacturing copper interconnection, a technology of removing a tantalum or titanium oxide thin film formed in an unstressed polishing process and a technology of etching to remove tantalum / tantalum nitride or titanium / titanium nitride on a barrier layer by using a xenon difluoride gas phase. The integration method comprises the following steps: firstly, removing copper plated on at least one part of silicon slices through unstressed electrochemical polishing; secondly, removing the tantalum or titanium oxide thin film formed on the surface of the barrier layer in a copper polishing process; and finally etching for removing tantalum / tantalum nitride or titanium / titanium nitride on the barrier layer by using the xenon difluoride gas phase. The integration device comprises three subsystems which are respectively an unstressed electrochemical copper polishing system, a system for removing tantalum or titanium oxide on the surface of the barrier layer by using an etching agent and a xenon difluoride gas phase etching system for removing the barrier layer.
Owner:ACM RES SHANGHAI
Xenon difluoride gas-phase etching method for barrier layer
ActiveCN103700615AIncrease etch rateAvoid over etchingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseLight beam
The invention discloses a xenon difluoride gas-phase etching method for a barrier layer. The method comprises the following steps: (1) spraying xenon difluoride to the surface of an exposed barrier layer; (2) only irradiating the barrier layer on the upper surface of a dielectric layer to increase the etching rate of the barrier layer on the upper surface of the dielectric layer to be higher than that of the barrier layer on the sidewalls of grooves and connecting holes by adopting light beams. According to the method, the barrier layer on the upper surface of the dielectric layer is irradiated by the light beams to increase the etching rate of the barrier layer on the upper surface of the dielectric layer to be higher than that of the barrier layer on the sidewalls of the grooves and the connecting holes, so that the barrier layer on the sidewalls of the grooves and the connecting holes is prevented from being excessively etched, the microcosmic etching uniformity is improved, and better process effects are achieved.
Owner:ACM RES SHANGHAI
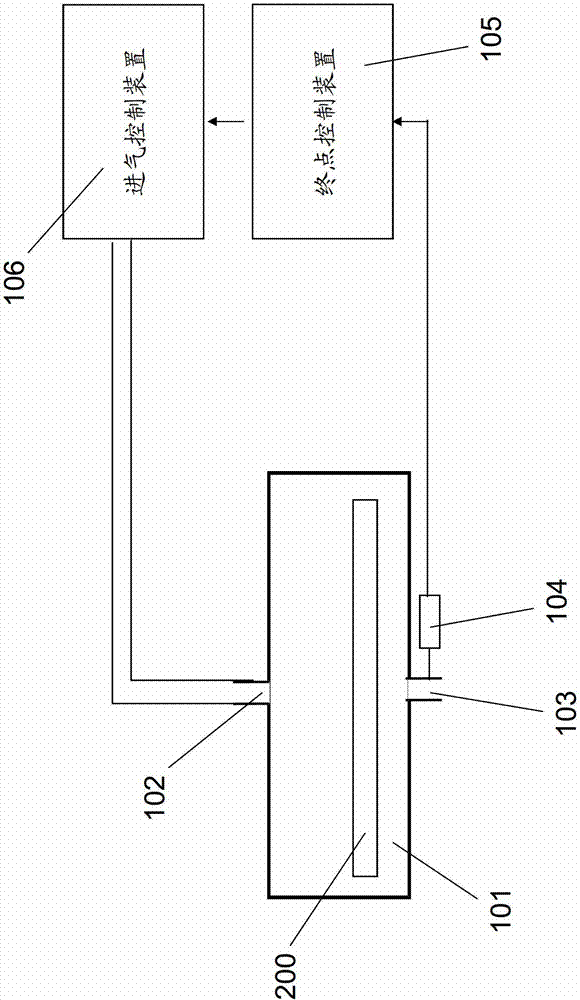
End point detection device and end point detection method
ActiveCN103594390AAccurate detectionQuality assuranceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementGas phaseControl signal
The invention discloses an end point detection device used for detecting an end point of a xenon difluoride gas phase etching process. The end point detection device comprises a process cavity, a gas concentration detection device, an end point control device and a gas intake control device, wherein the process cavity is provided with a gas inlet and a gas outlet; the gas concentration detection device is provided at the gas outlet of the process cavity and detects the concentration of a xenon difluoride gas discharged from the process cavity; the end point control device is connected with the gas concentration detection device, calculates the concentration of the discharged xenon difluoride gas according to a detection result of the gas concentration detection device, and compares the concentration with a preset concentration value, and the end point control device generates and sends a control signal if the concentration of the discharged xenon difluoride gas is equal to or greater than the preset concentration value; and the gas intake control device is connected with the gas inlet of the process cavity, constant quantity of the xenon difluoride gas is filled in the process cavity through the gas inlet of the process cavity, and the gas intake device stops filling the xenon difluoride gas into the process cavity after receiving the control signal sent by the end point control device. The invention further discloses an end point detection method.
Owner:ACM RES SHANGHAI
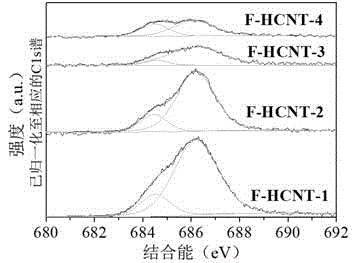
Method for preparing fluorine-doped helical carbon nanotube
ActiveCN104528686AFill in the gapWide variety of sourcesMaterial nanotechnologyLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor materialsPtru catalyst
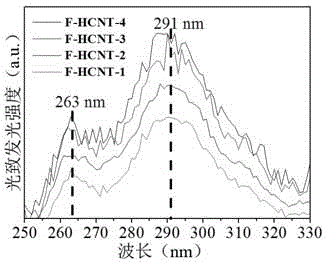
The invention discloses a method for preparing a fluorine-doped helical carbon nanotube. The method comprises the following steps: at first, preparing oxide nanoparticles of nickel by utilizing the sol-gel method reduce the oxide nanoparticles of nickel with hydrogen into nickel nanoparticles to serve as a catalyst to realize high-temperature pyrolysis of acetylene and reacting the product with xenon difluoride to obtain a fluorinated helical carbon nanotube. The raw materials of the sol-gel method include nickel nitrate hexahydrate and citric acid monohydrate, and a solvent is anhydrous ethanol. According to the invention, the photoluminescence of the fluorine-doped helical carbon nanotube is increased to 263 nm and 291 nm deep UV regions, so that the shortcomings of a conventional semi-conductor material in the region are greatly avoided, and the fluorine-doped helical carbon nanotube can serve as base materials of ultraviolet fluorescence and ultraviolet detectors and is used in the fields of photoetching technique, optical information storage and pharmaceutical analysis.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method of forming a floating metal structure in an integrated circuit
InactiveUS7227212B1Reduce capacitanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricNoble gas
In one embodiment, a sacrificial layer is deposited over a base layer. The sacrificial layer is used to define a subsequently formed floating metal structure. The floating metal structure may be anchored into the base layer. Once the floating metal structure is formed, the sacrificial layer surrounding the floating metal structure is etched to create a unity-k dielectric region separating the floating metal structure from the base layer. The unity-k dielectric region also separates the floating metal structure from another floating metal structure. In one embodiment, a noble gas fluoride such as xenon difluoride is used to etch a sacrificial layer of polycrystalline silicon.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Method for preparing fluorine-doped graphene quantum dots
ActiveCN108706579AHigh purityOvercoming Difficulty Incorporating Graphene Quantum DotsGrapheneNanotechnologySimple Organic CompoundsDoped graphene
The invention provides a method for preparing fluorine-doped graphene quantum dots, relating to the field of production and preparation of graphene quantum dots. According to the method disclosed by the invention, by utilizing a photochemical principle, fluorine is directly doped into graphene quantum dot powder by utilizing a photochemical method, and the fluorine doping concentration can be controlled by controlling a mass ratio of xenon difluoride to the graphene quantum dots. The method is simple and easy to operate, doping can be completed within a few minutes to more than ten minutes, and the defect that other impurities are easily introduced in the traditional method for taking fluorine-containing organic compounds as a fluorine source can be overcome.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
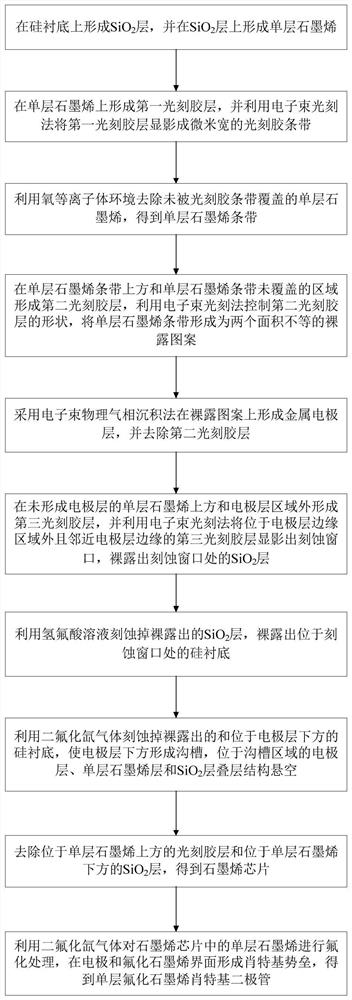
Single-layer fluorinated graphene Schottky diode and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113192835AIncrease migration rateStrong adhesionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSchottky barrierMetallic electrode
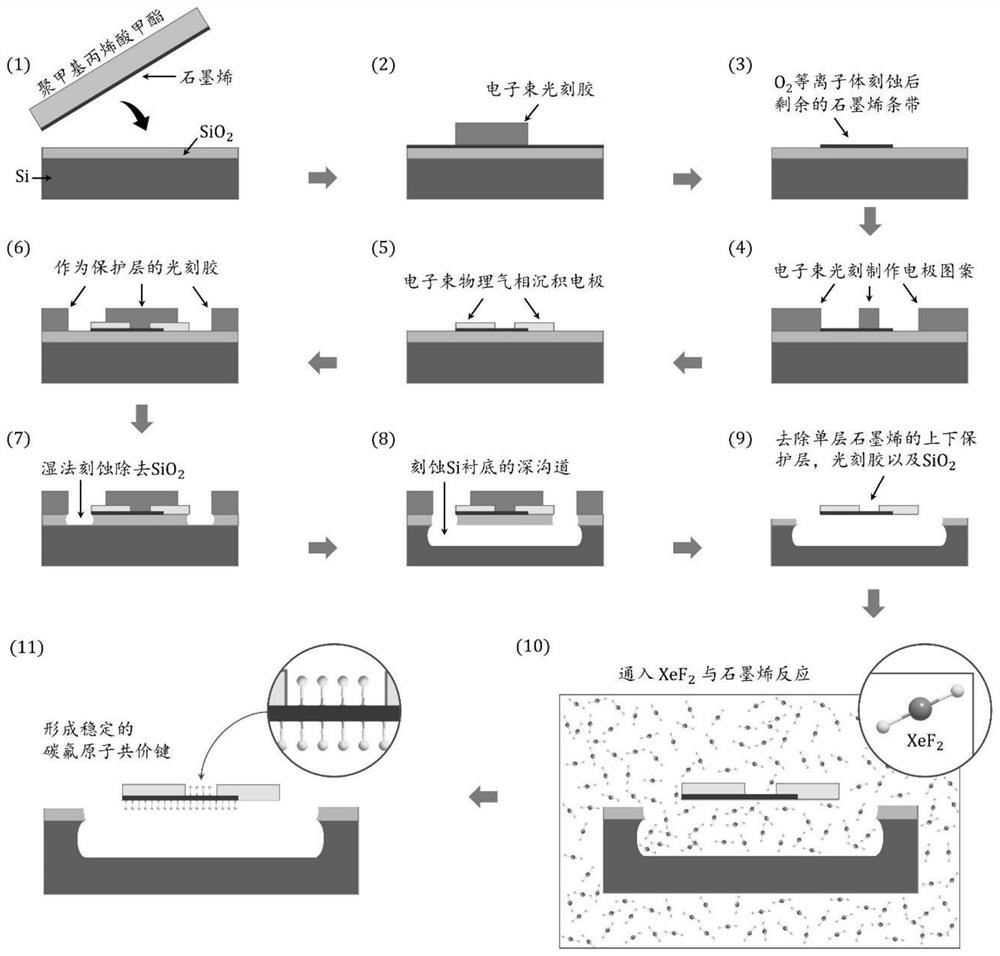
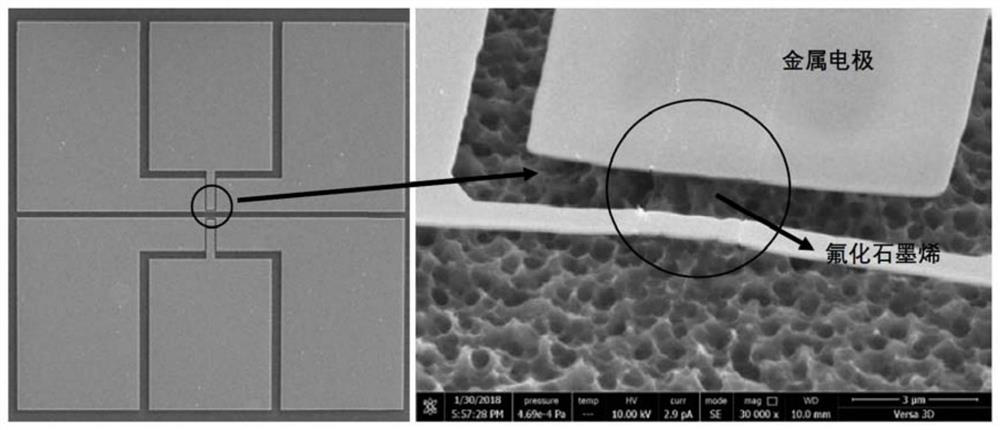
The invention discloses a single-layer fluorinated graphene Schottky diode and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the method, a composite etching process is adopted, a deep groove is formed in a silicon substrate, the whole single-layer graphene diode device is made to suspend on the groove, and meanwhile a metal electrode is prepared on the single-layer graphene diode device; moreover, the graphene is fluorinated through xenon difluoride (XeF2) gas, an electron energy band gap is opened, a stable fluorocarbon atom covalent bond is formed in a suspended part, and a Schottky barrier is formed on an interface of a metal electrode and the fluorinated graphene to trigger a diode effect. By adopting the method, the influence of the semiconductor substrate on the thickness of the Schottky diode device and the negative influence of doping / impurities or defects of the semiconductor substrate on the performance of the Schottky diode device can be avoided, and the Schottky diode has the advantages of high response frequency, high electron migration rate and the like; and the method is of great significance to the development of integrated circuits under the micro-nano scale.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
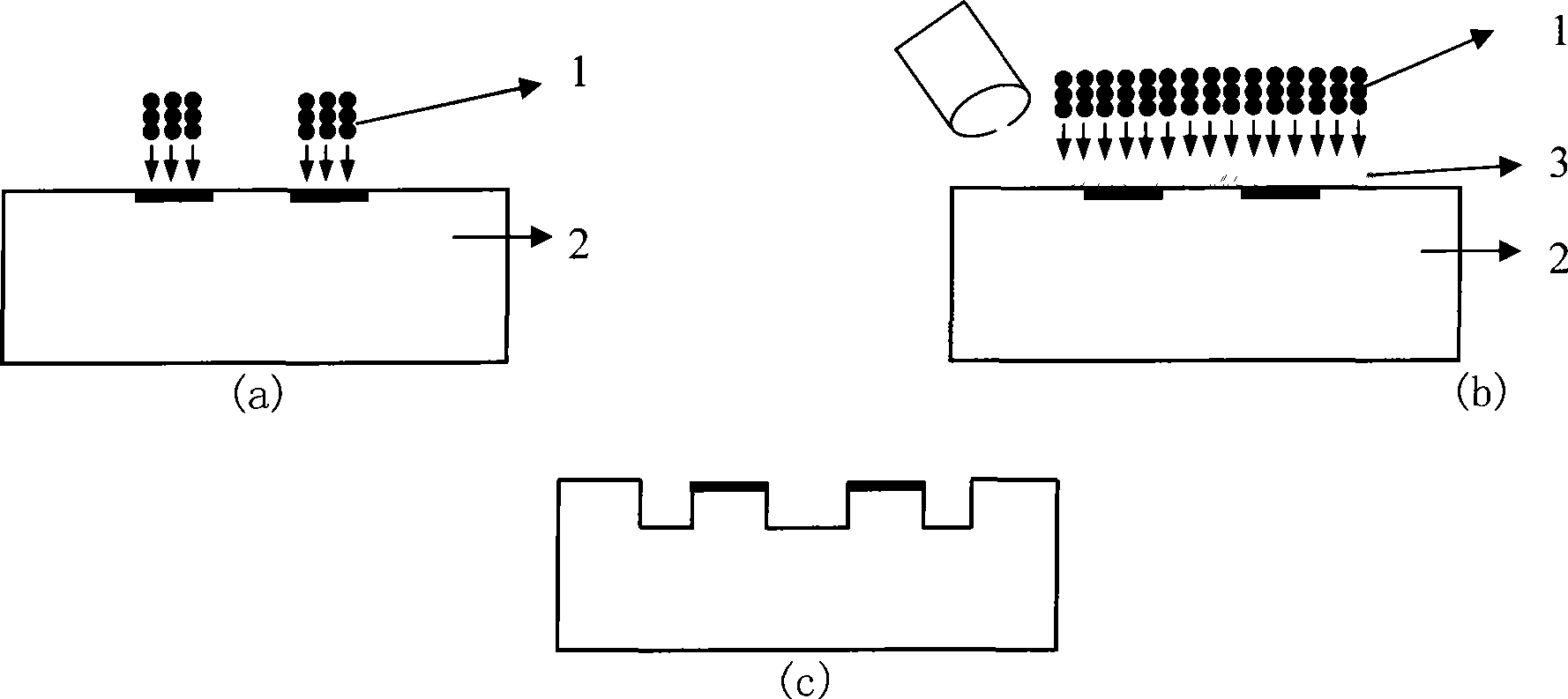
Method for fabricating micro speaker and micro speaker fabricated by the same
A method for fabricating a micro speaker is provided, including forming a package wafer and a device wafer by batch processing, bonding the package wafer and the device wafer to each other, and forming a diaphragm by isotropic-etching a back surface of the device wafer using a xenon difluoride (XeF2). As a result, a micro-electronic-mechanic system (MEMS) technology-based piezoelectric micro speaker having a wide frequency response range is realized, by batch processing, thereby providing simplified structure and processing and reducing fabricating cost.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
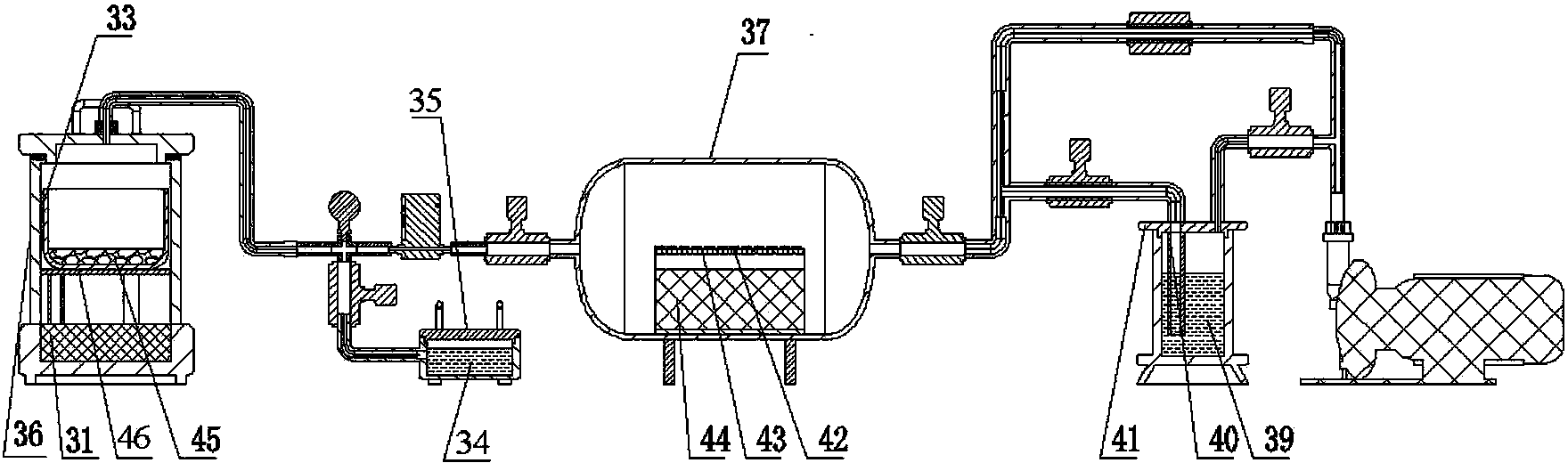
Rubber surface fluorination modification testing device
InactiveCN103630676ASolve the problem of surface fluorination modificationEfficient recyclingMaterial testing goodsTemperature controlEngineering
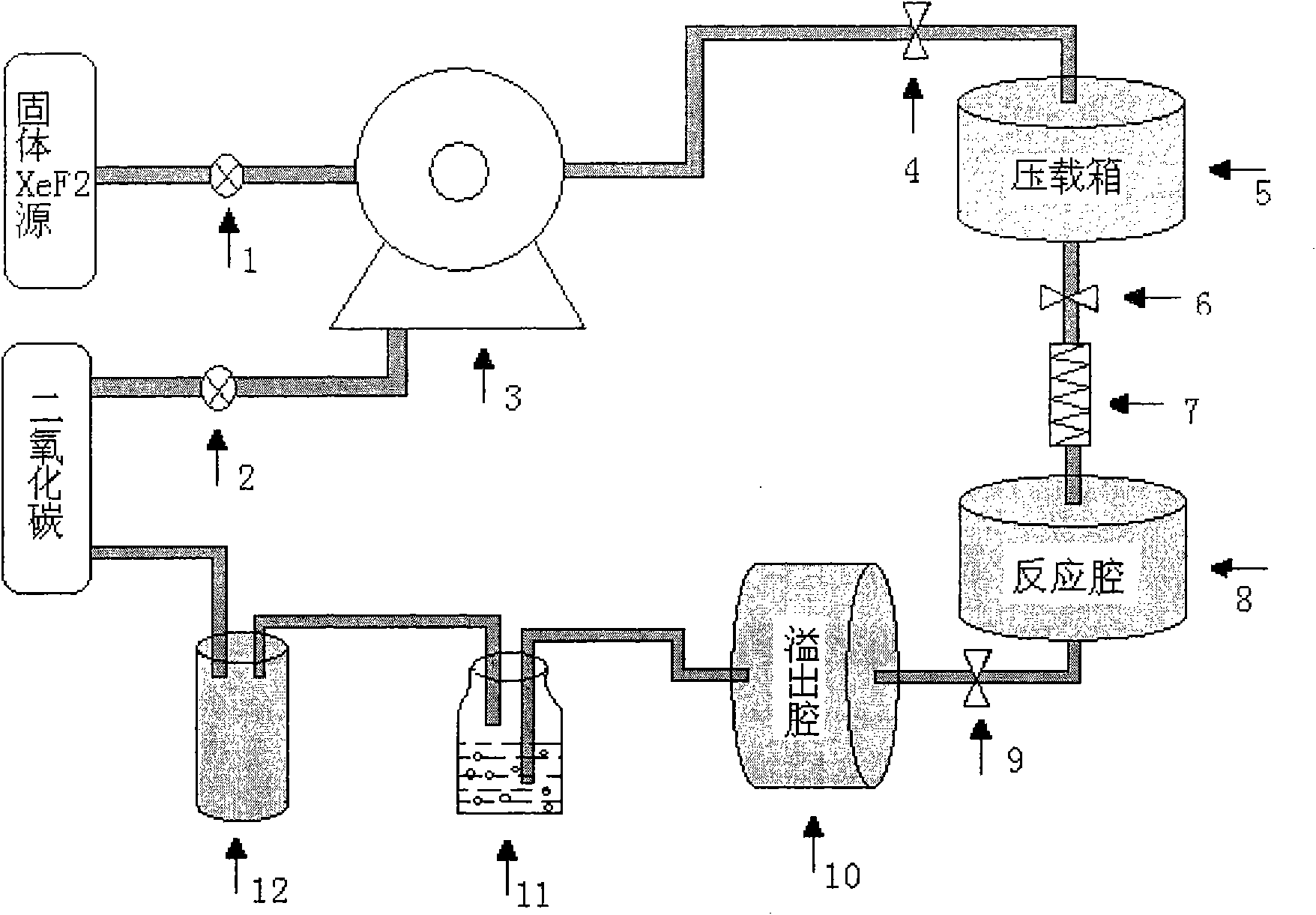
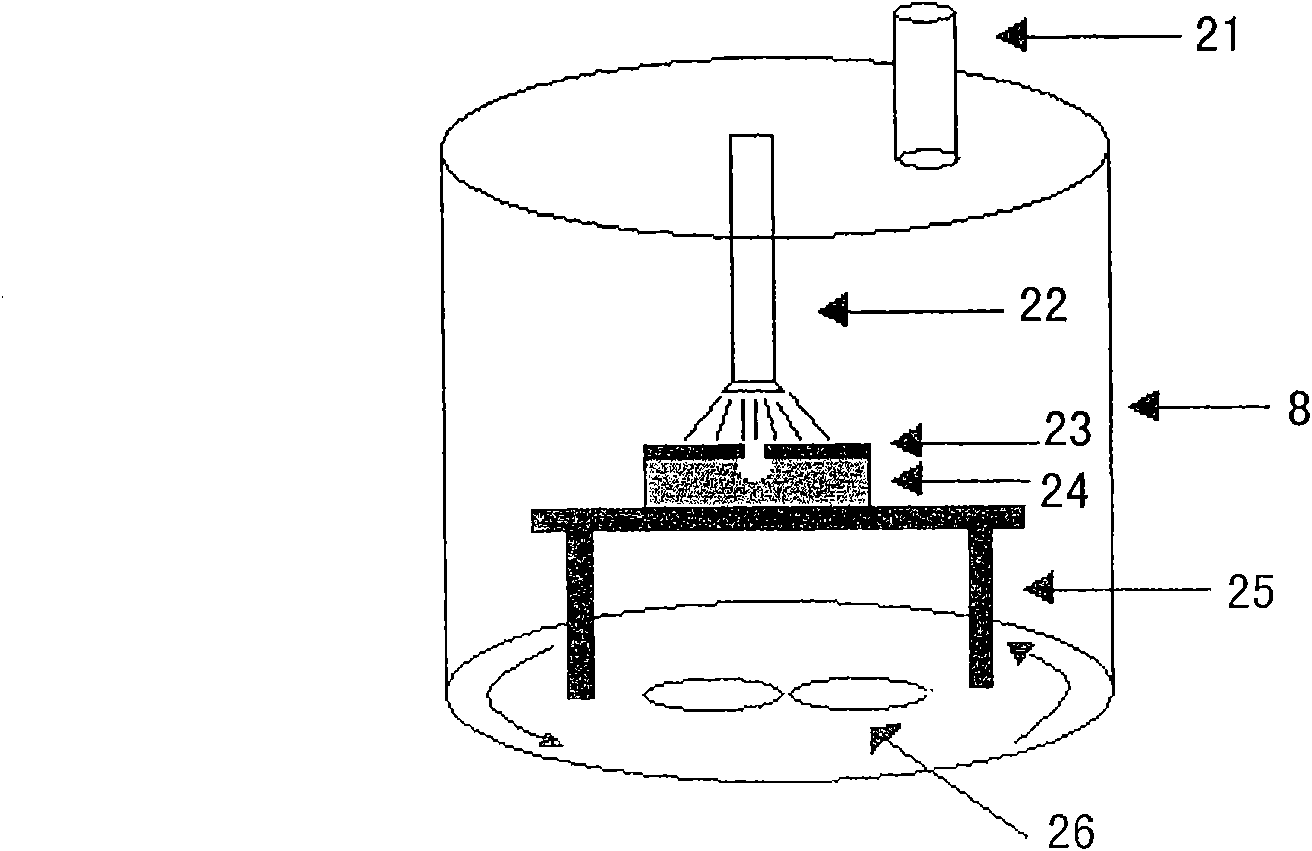
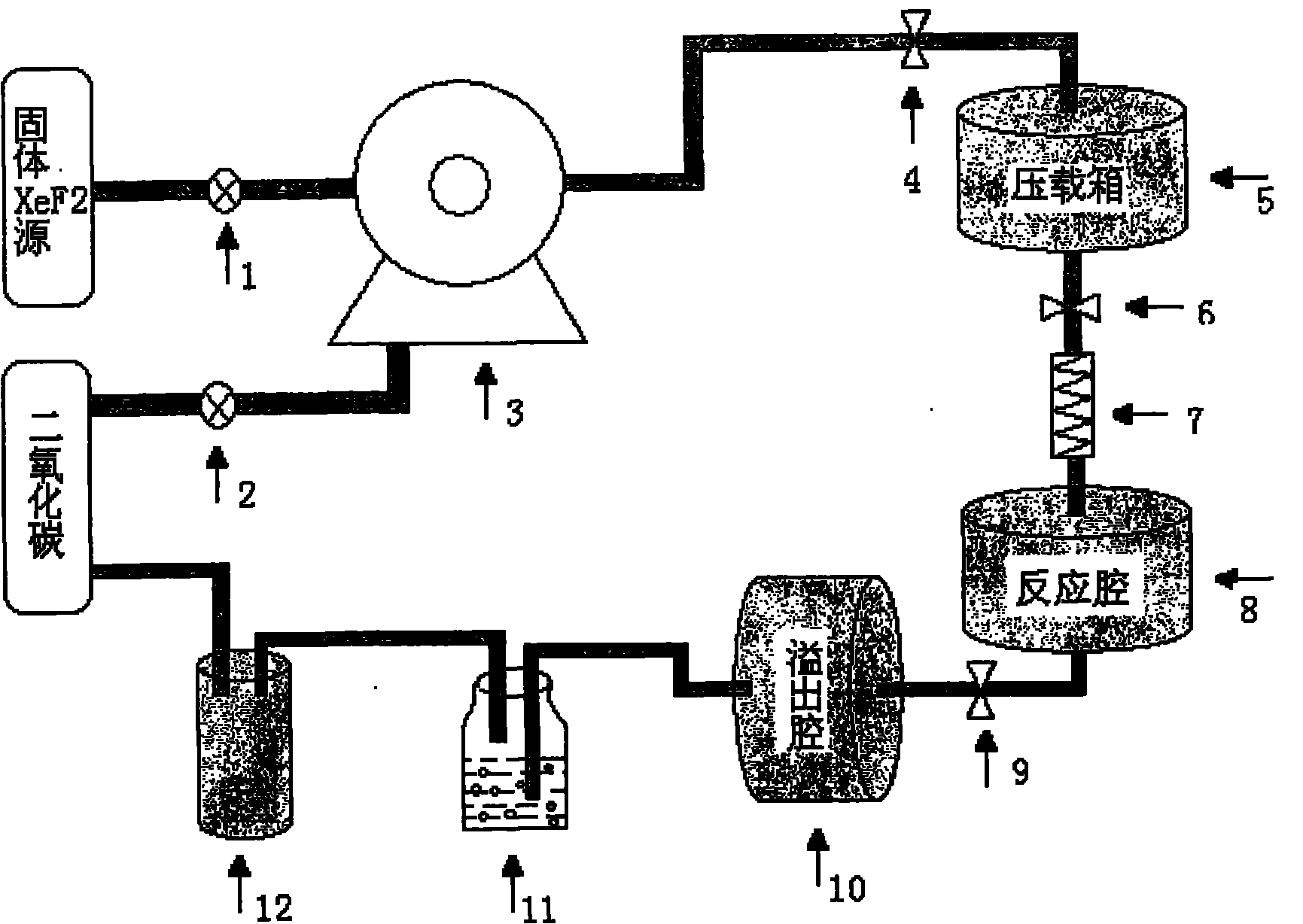
The invention discloses a rubber surface fluorination modification testing device which mainly comprises an xenon difluoride generating device, a gas flow meter, a pressure meter, a rubber surface fluorination device, a tail gas recovering device, a vacuum pump, a motor, an xenon difluoride recovering device, a throttle valve, a stainless steel pipe, a temperature control panel, a heating plate, a sealing ring, a rubber sample placing frame and other parts. A rubber sample is placed on the rubber sample placing frame and is positioned in the rubber fluorination device, and a defined mount of xenon difluoride gas is introduced to carry out surface fluorination modification on the rubber sample. The rubber fluorination device is vacuumized through the vacuum pump, the throttle valve and the stainless steel pipeline, and an xenon difluoride crystal is heated at certain temperature by using the heating device so as to be sublimated into a gaseous state, the gaseous xenon difluoride enters the rubber fluorination device under the action of a pressure difference, and the rubber sample is subjected to surface fluorination modification. By adopting the rubber surface fluorination modification testing device, rubber is subjected to surface fluorination modification testing under the condition of different temperatures and pressure intensities.
Owner:SHENYANG LIGONG UNIV
Microelectronic mechanical system structure forming method
InactiveCN104627949AImprove removal rateNo stickingDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingMetallurgyRoom temperature
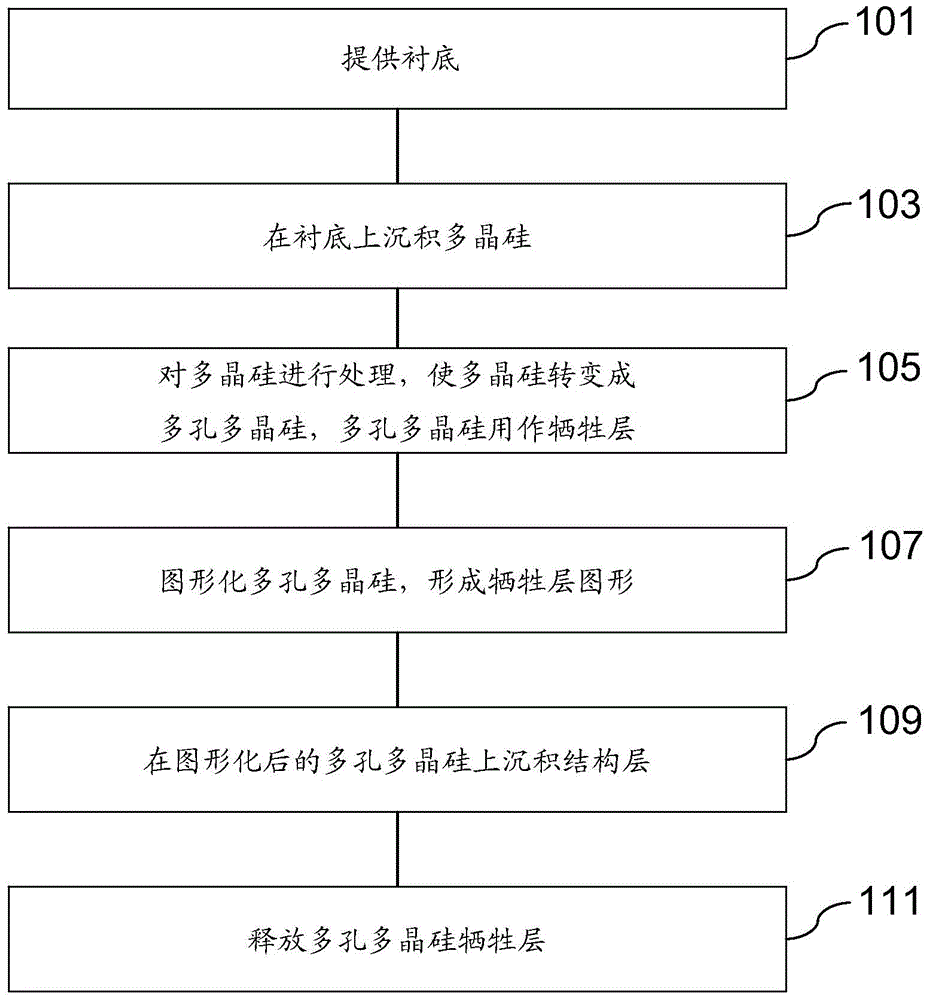
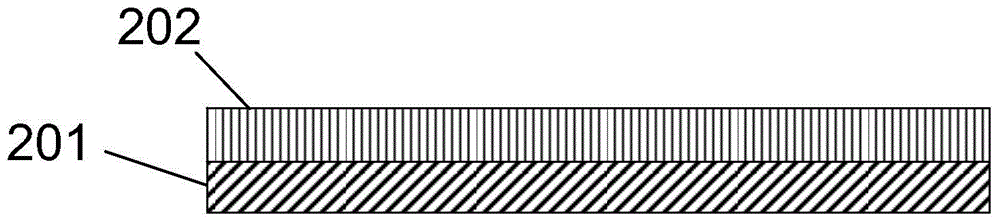
The invention discloses a microelectronic mechanical system structure forming method, which comprises the following steps: providing a substrate; depositing polycrystalline silicon on the substrate; treating the polycrystalline silicon, so that the polycrystalline silicon is transformed into porous polycrystalline silicon, wherein the porous polycrystalline silicon is used as a sacrificial layer; imaging the porous polycrystalline silicon to form a sacrificial layer pattern; depositing a structure layer on the imaged porous polycrystalline silicon; and releasing the porous polycrystalline silicon sacrificial layer. The porous polycrystalline silicon is adopted as the sacrificial layer; and the sacrificial layer is in a pore form so that the removal rate of the sacrificial layer is improved. In addition, the porous polycrystalline silicon sacrificial layer can be released by adopting xenon difluoride; and a production product is in a gaseous state at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, so that the adhesion phenomenon is avoided; and the reliability of microelectronic mechanical system structure formation is improved.
Owner:ACM RES SHANGHAI
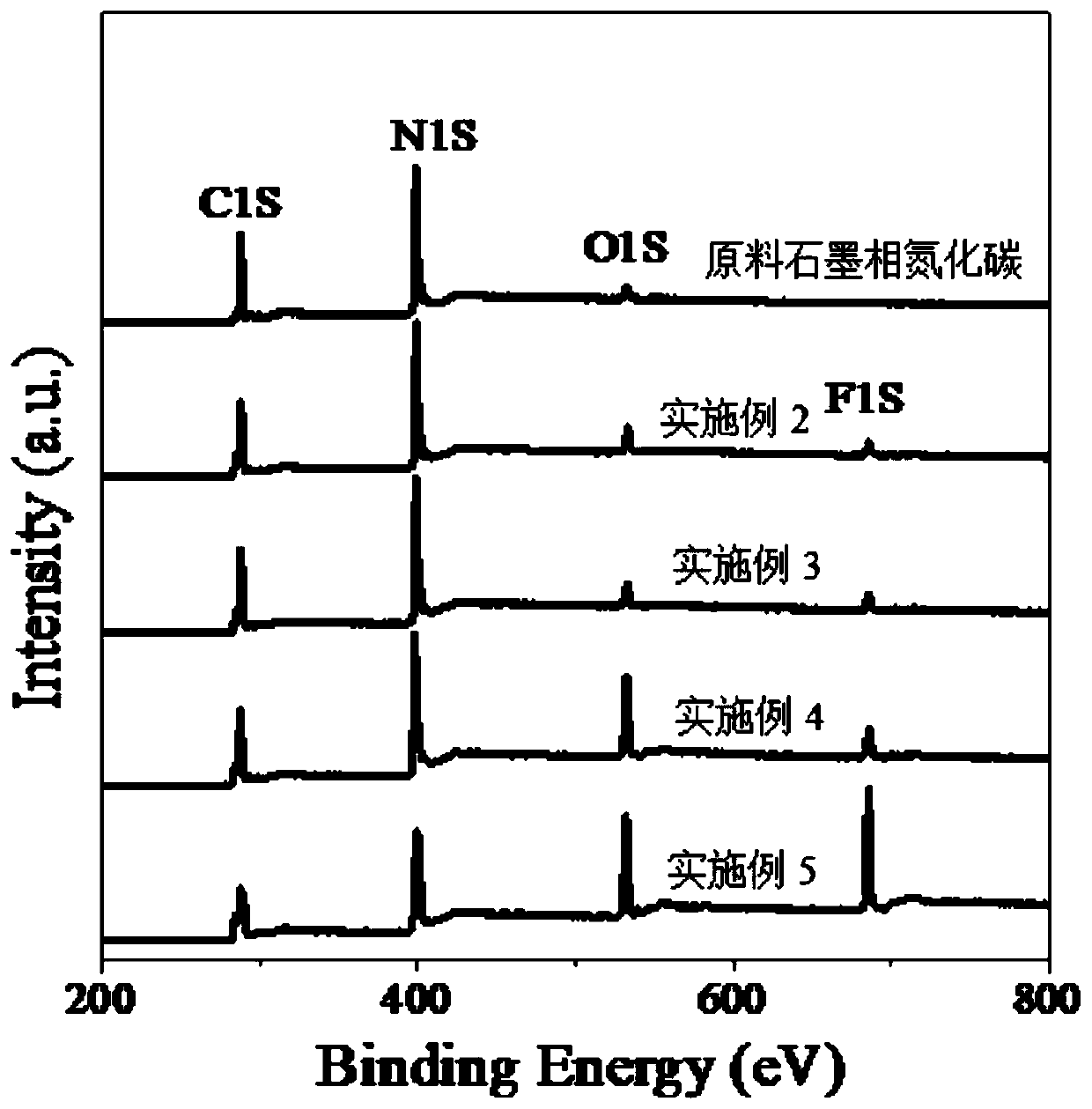
Preparation method of fluorinated carbon nitride with high fluorine content
PendingCN111298823AMild fluorinationFluorinated stablePhysical/chemical process catalystsNitrogen and non-metal compoundsPhysical chemistryCarbon nitride
The invention discloses a preparation method of fluorinated carbon nitride with high fluorine content, which comprises the following steps: by using graphite-phase carbon nitride as a raw material, xenon difluoride as a fluorine source and a high-pressure digestion tank as a reaction chamber, carrying out constant-temperature reaction at 200+ / -20 DEG C under the condition that the graphite-phase carbon nitride and xenon difluoride are not in contact with each other, thereby obtaining the fluorinated carbon nitride, wherein the mass ratio of xenon difluoride to graphite-phase carbon nitride isgreater than or equal to 10. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention takes xenon difluoride as a fluorine source, and compared with fluorine gas, the method is mild in fluorination, relatively stable and safer to operate, xenon difluoride is used as a fluorine source, an existing conventional high-pressure digestion tank can be used as reaction equipment, special customization is not needed, and the production cost is effectively reduced. In addition, xenon difluoride is used as a fluorine source and is matched with a high-pressure digestion tank to be used as reaction equipment to react at the constant temperature of 200+ / -20 DEG C, so that the high-fluorine-content doped graphite-phase carbon nitride can be obtained.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Selective etching and formation of xenon difluoride
InactiveCN102592994ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEtchingPlasma generator
This invention relates to a selective etching and formation of xenon difluoride, and in particular relates to a process for selective removal of materials, such as: silicon, molybdenum, tungsten, titanium, zirconium, hafnium, vanadium, tantalum, niobium, boron, phosphorus, germanium, arsenic, and mixtures thereof, from silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, nickel, aluminum, TiNi alloy, photoresist, phosphosilicate glass, boron phosphosilicate glass, polyimides, gold, copper, platinum, chromium, aluminum oxide, silicon carbide and mixtures thereof. The process is related to the important applications in the cleaning or etching process for semiconductor deposition chambers and semiconductor tools, devices in a micro electro mechanical system (MEMS), and ion implantation systems. Methods of forming XeF2 by reacting Xe with a fluorine containing chemical are also provided, where the fluorine containing chemical is selected from the group consisting of F2, NF3, C2F6, CF4, C3F8, SF6, a plasma containing F atoms generated from an upstream plasma generator and mixtures thereof.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Silicon etching solution for removing abrasive grains
ActiveCN112251233AIncrease viscosityImprove solubilitySurface treatment compositionsPolyethylene glycolPyrrolidinones
The invention relates to a silicon etching solution for removing abrasive grains. The etching solution is composed of nitric acid, hydroxylamine nitrate, fluorosulfonic acid, ammonium bifluoride, xenon difluoride, sulfuric acid, a thickening agent and deionized water. The thickening agent can be any one of polyacrylamide, hexanol, octanol, polyethylene glycol, polyvinylpyrrolidone and the like. Hydroxylamine nitrate and fluorosulfonic acid react to generate hydrofluoric acid, xenon difluoride is slowly decomposed in an acid environment to generate hydrofluoric acid, the concentration of hydrofluoric acid in the etching liquid composition is increased, the time-dependent change of the etching liquid composition can be inhibited, and the stable etching rate is maintained. The abrasive grainremoving etching solution can be directly used for the back roughening process of an abrasive disc, deep mechanical abrasive grains are etched, the polishing and abrasive grain removing procedure is omitted, the cost is saved, the production efficiency is improved, and meanwhile the stable etching service life can be maintained.
Owner:湖北兴福电子材料股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com