Implantable bioartificial liver
A bioartificial and liver technology, applied in the fields of clinical medicine, biomedicine and regenerative medicine, can solve problems such as the inability of implanted cells to eventually replace organ function, the small amount of implanted liver cells, and the problem of blood supply, and achieve the benefit of liver cell specificity. The effect of maintaining sexual function, ensuring survival and functioning, prolonging survival time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
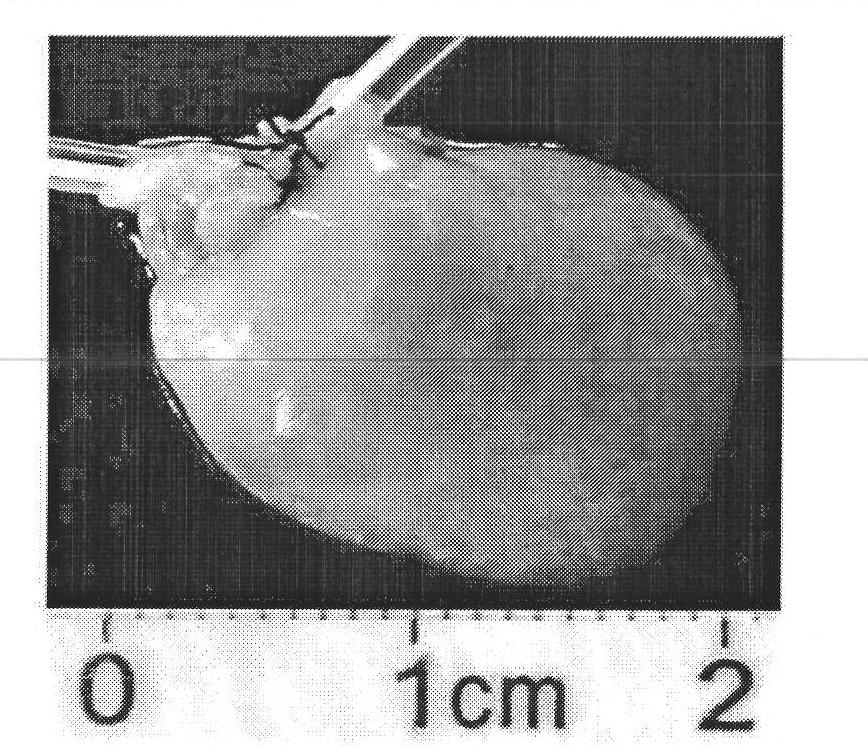
[0033] Example 1 Rat liver decellularization
[0034] 1000ml of ammonia solution with a mass fraction of 0.1% was prepared with distilled water and concentrated ammonia water with a mass fraction of 28%. 100 ml each of SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) with a concentration of 1%, 0.5% and 0.25% was prepared with distilled water. Prepare 50 ml of Triton X-100 solution with a volume fraction of 1% with distilled water.
[0035] The middle lobe of the rat liver with the portal vein and the suprahepatic vena cava was surgically removed from the rat. The portal vein and the suprahepatic vena cava were cannulated separately. Perfuse 0.1% ammonia solution into the middle lobe of the liver at a speed of 1ml / min for 12 hours, at this time the center of the liver turns milky white, and the outflowing perfusate becomes cloudy brown; then perfuse with distilled water at a speed of 1ml / min for 30 minutes; then Perfuse with 1%, 0.5% and 0.25% SDS at a rate of 1ml / min for 1 hour respectively; ...
Embodiment 2
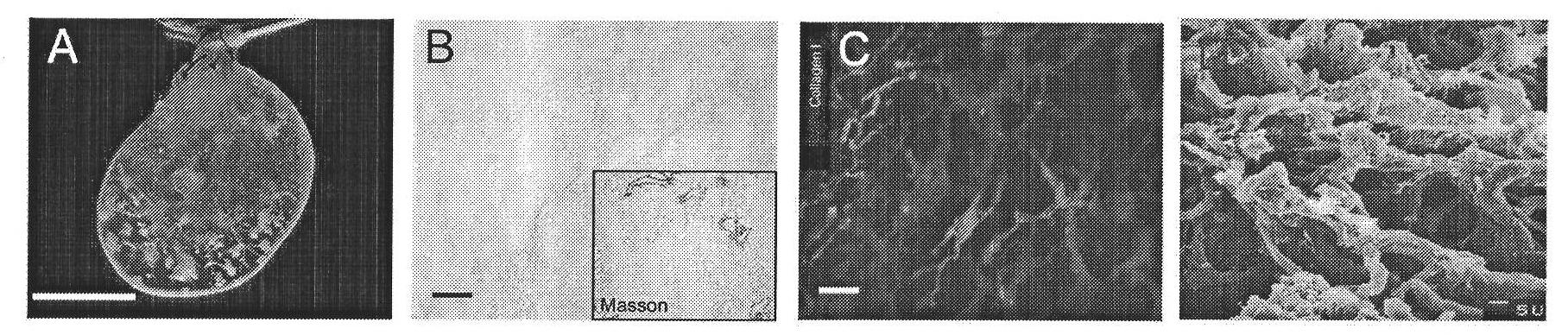
[0039] Example 2 Anticoagulation treatment on the inner surface of the decellularized liver scaffold
[0040] Prepare 1g / L PDADMAC solution and 2g / L heparin solution with sterile distilled water. Perfuse the PDADMAC solution of 1g / L at a speed of 5ml / min for 10 minutes in the portal vein cannula of the decellularized liver stent obtained in Example 1, then leave it to stand for 20 minutes; perfuse with sterile distilled water at a speed of 5ml / min Remove the PDADMAC solution for 10 minutes; then perfuse 2g / L heparin solution at a rate of 5ml / min for 10 minutes, then let stand for 20 minutes; perfuse with sterile distilled water for 10 minutes at a rate of 5ml / min, remove the heparin solution; then repeat The above process was carried out 7 times (8 times in total). After the layer-by-layer self-assembly internal surface anticoagulant modification was completed, antibiotics containing commonly used antibacterial doses such as: penicillin, streptomycin, amphotericin B, fluconazo...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 Portal Vein Implantable Bioartificial Liver Treats Rats with Acute Hepatic Failure
[0044] Rat hepatocytes were routinely isolated, and the activity was detected by trypan blue staining to be greater than 90%. Will 1×10 8 Two freshly isolated rat hepatocytes were suspended in 3 ml of medium, and were cannulated from the portal vein, and injected into the decellularized natural liver scaffold treated with internal surface anticoagulation in Example 2. Then let it stand for 4 hours to allow the liver cells to attach. Then use a cell culture medium such as RPMI1640 or DMEM to perfuse and culture from the portal vein at a rate of 2 ml / min for 2 hours. Finally, perfuse with normal saline at a rate of 2ml / min for 30 minutes to remove the culture medium in the bioartificial liver, and prepare to implant the artificial liver into the portal vein of a rat model of acute liver failure caused by 90% hepatectomy. The rat portal vein was cut off, the original portal ve...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com