Endothelial cell selective composite coating material used for cardiovascular stent and preparation method thereof
A composite coating and endothelial cell technology, applied in the interdisciplinary field of disciplines, can solve the problems of reducing the migration and proliferation of endothelial cells, increasing the risk of late thrombosis, and destroying the endothelial layer of blood vessels, so as to achieve efficient and rapid inhibition of growth and endothelialization Insufficient improvement, prevention of restenosis and thrombosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0073] The steps of the preparation method of the base layer are as follows:
[0074] 1) Dissolving the biocompatible monomer of the cell membrane biomimetic structure and the polymerizable monomer containing the hydrophobic functional group with a mass ratio of 1:0.1 to 1:10 in 10 to 100 mL of solvent to obtain solution A, wherein the solvent is Toluene, tetrahydrofuran, dimethyl sulfoxide, chloroform, methylene chloride, isopropanol, ethanol, or methanol;
[0075] 2) adding 0.2% to 2% of the free radical initiator azobisisobutyronitrile of the total mass of the biocompatible monomer of the biomimetic structure of the cell membrane and the polymerizable monomer containing the hydrophobic functional group into the solution A, Obtain solution B;
[0076] 3) Deoxygenate solution B with nitrogen or argon for 5 to 30 minutes, heat to 50 to 90 degrees, and react for 6 to 48 hours;
[0077] 4) removing the solvent under reduced pressure, and precipitating with glacial ether or gla...
Embodiment 1
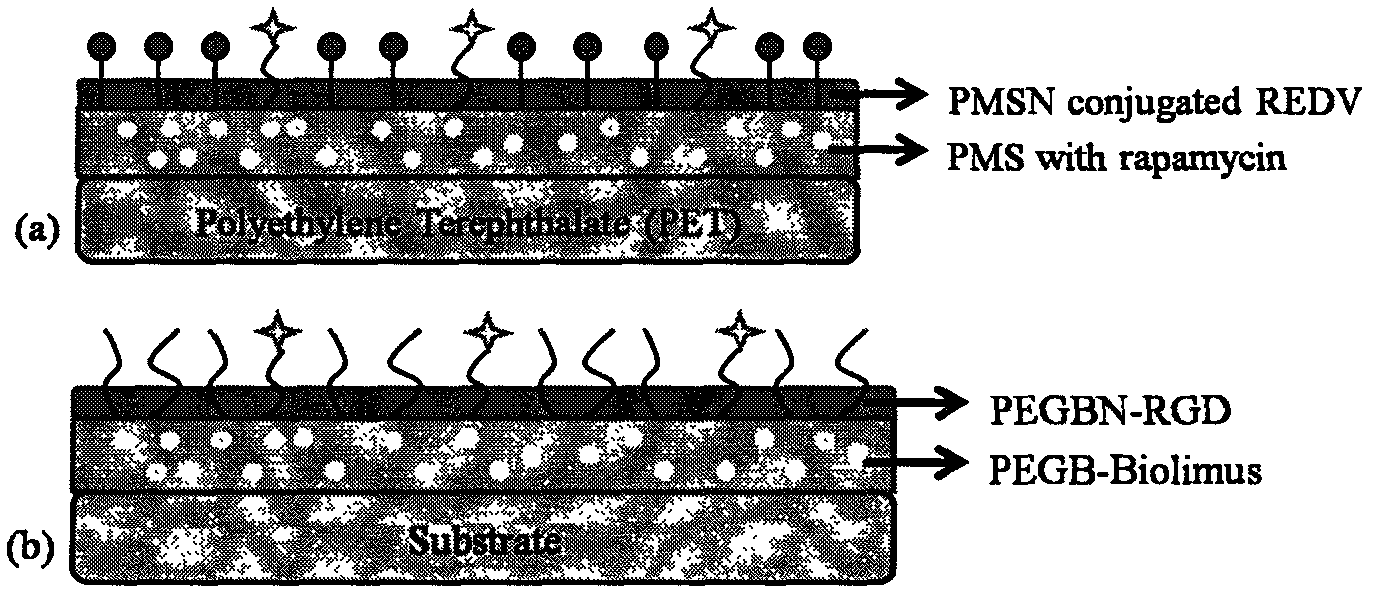
[0090] (1) Prepare the base layer of endothelial cell selective composite coating material
[0091]
[0092] 1) Dissolving 0.5 g of biocompatible monomer MPC with biomimetic structure of cell membrane and 1.5 g of polymerizable monomer SMA with hydrophobic functional group in 30 ml of ethanol to obtain solution A;
[0093] 2) Add 0.04g initiator AIBN to solution A to obtain solution B;
[0094] 3) Deoxygenate solution B with argon for 30 minutes, heat to 60°C, and react for 24 hours;
[0095] 4) removing the solvent under reduced pressure, and precipitating with ice methanol twice to obtain the base layer polymer of the cardiovascular stent;
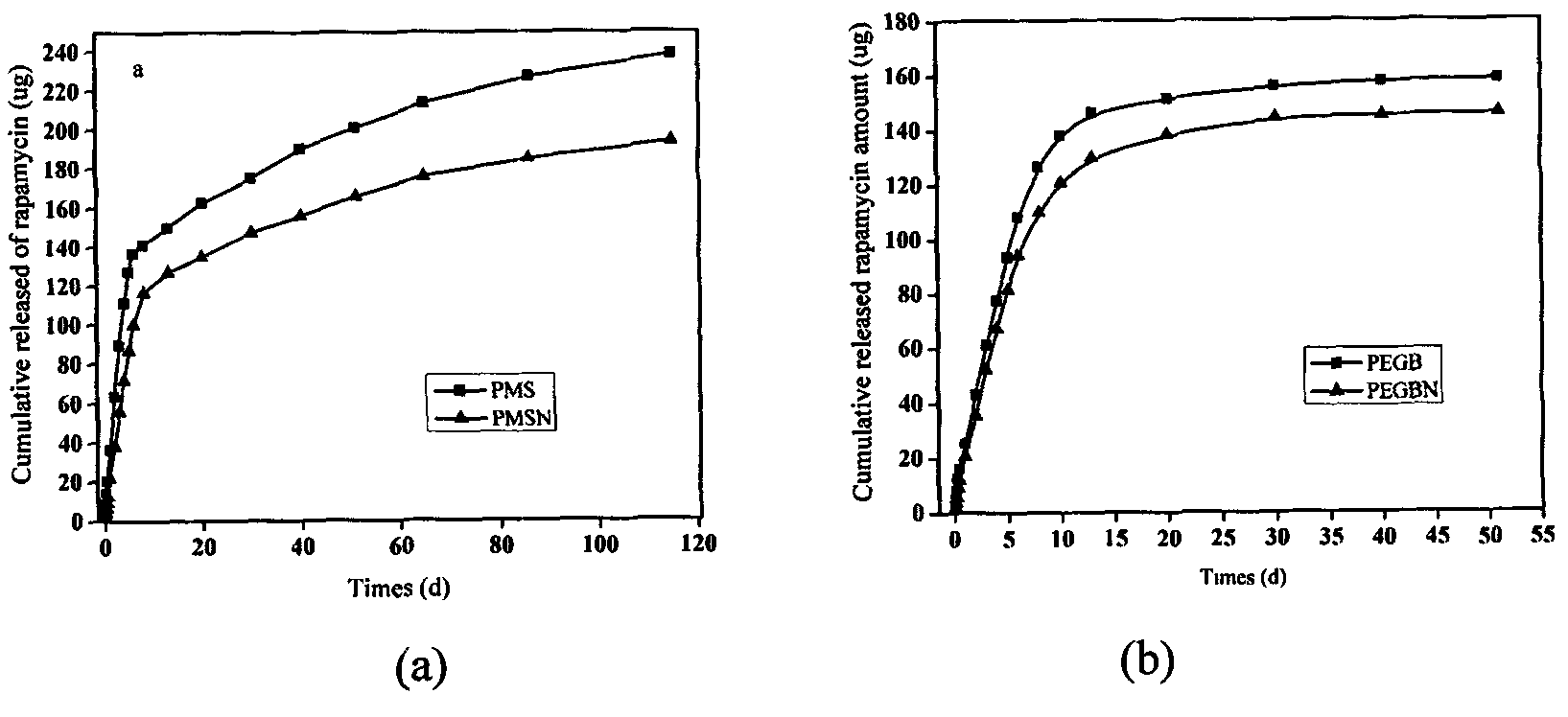
[0096] 5) dissolving the cardiovascular stent basal layer polymer and rapamycin drug in a tetrahydrofuran solvent with a mass ratio of 1:0.5, configuring a solution with a mass percentage concentration of 0.5%, and ultrasonically treating it to obtain a uniformly dissolved solution C;
[0097] 6) The polyethylene terephthalate (PET)...
Embodiment 2
[0116] (1) Prepare the base layer of endothelial cell selective composite coating material
[0117]
[0118] 1) Dissolving 0.5 g of biocompatible monomer MPC with biomimetic structure of cell membrane and 0.8 ml of polymerizable monomer BMA with hydrophobic functional group in 15 ml of tetrahydrofuran to obtain solution A;
[0119] 2) Add 0.02g initiator AIBN to solution A to obtain solution B;
[0120] 3) Deoxygenate solution B with nitrogen for 30 minutes, heat to 65°C, and react for 30 hours;
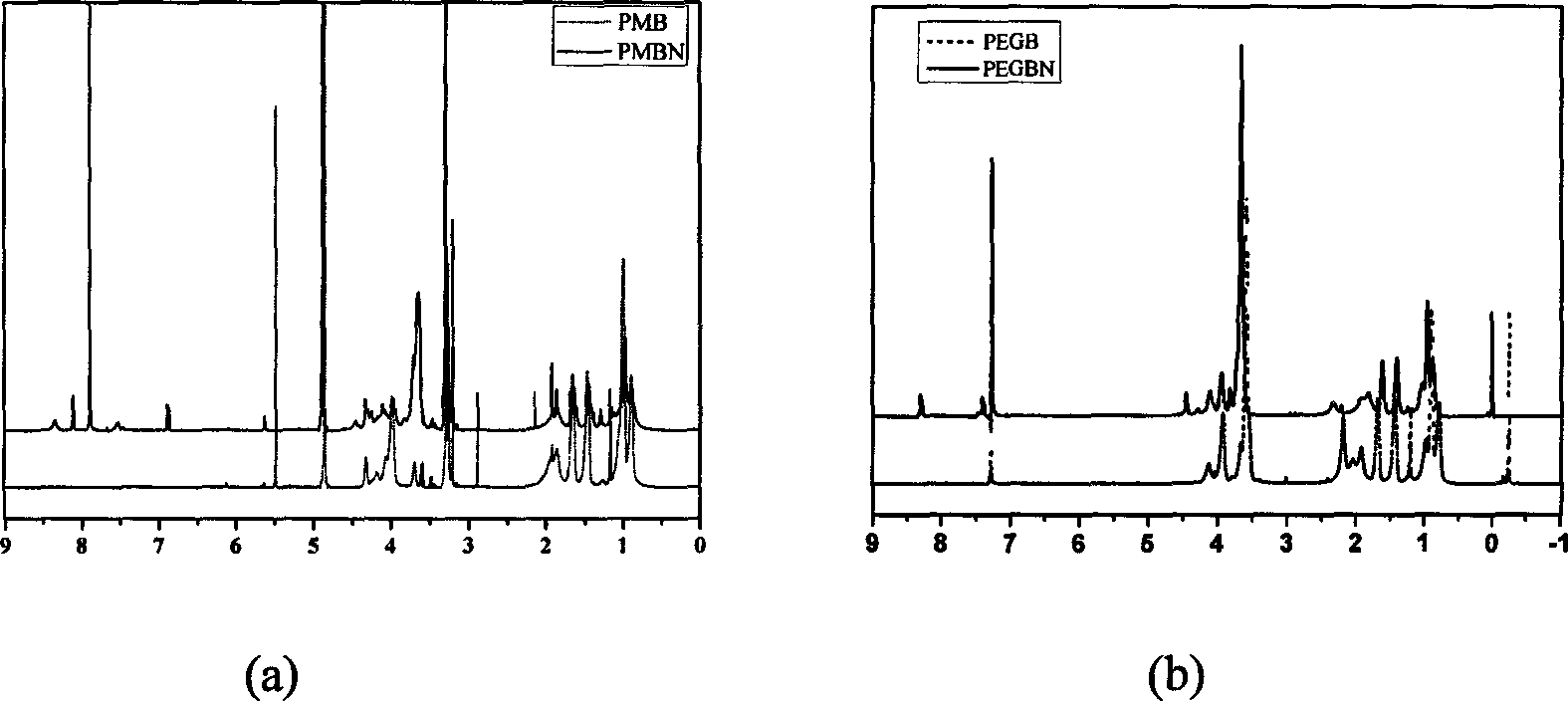
[0121] 4) Desolventization under reduced pressure, precipitation with glacial ether for 2 times, to obtain the base layer polymer of cardiovascular stent; NMR results confirm that the obtained product has the expected structure, such as figure 2 as shown in (a);
[0122] 5) dissolving the cardiovascular stent basal layer polymer and paclitaxel drug (Paclitaxel) with a mass ratio of 1:0.8 in a tetrahydrofuran solvent, configuring a solution with a mass percentage concentration o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com