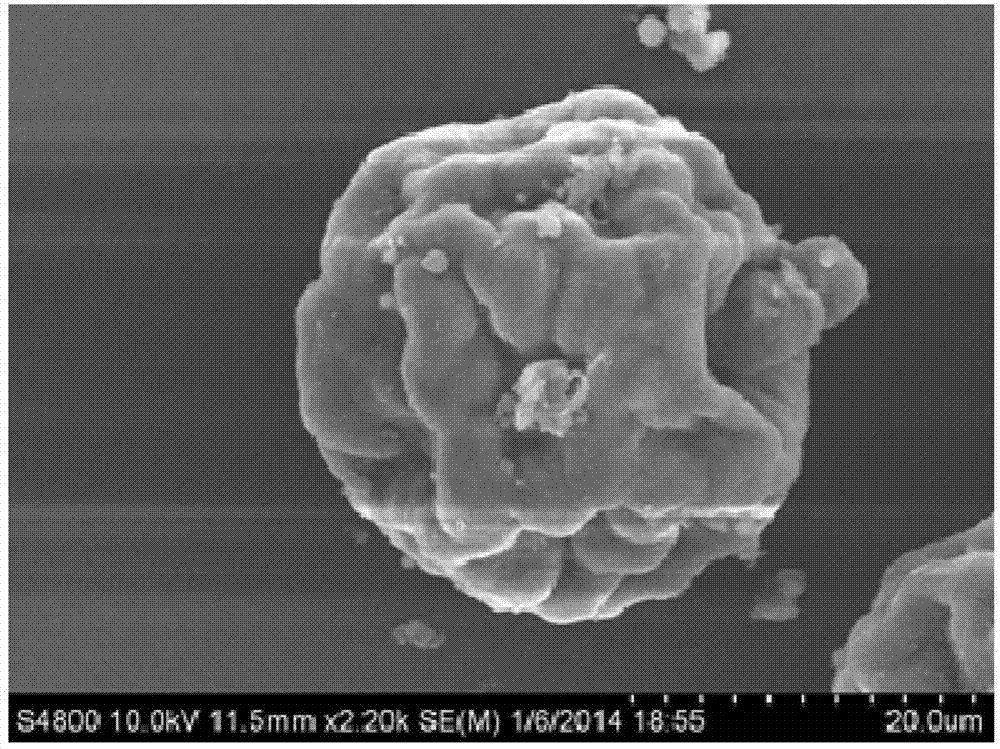
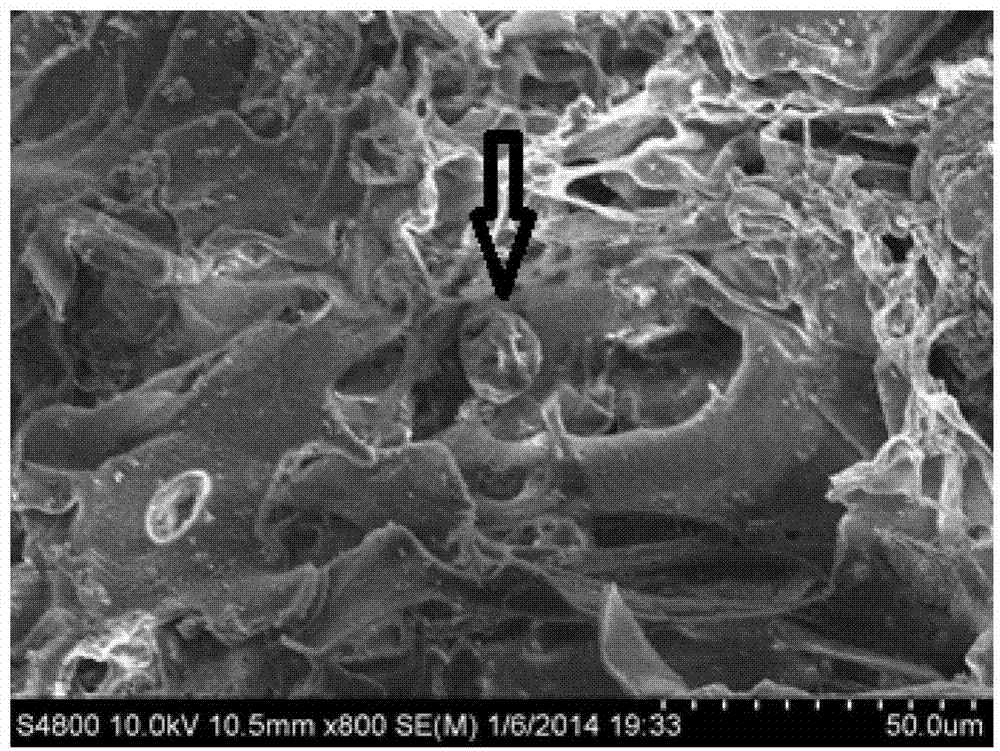
Method for preparing PLGA (polylactic-co-glycolic acid) modified biological factor microsphere supported bone substituted material
A biological factor and bone replacement technology, applied in the field of medical biomaterial preparation, can solve the problems of no cells, affecting the adhesion and growth of osteoblasts and vascular endothelial cells, and limited applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
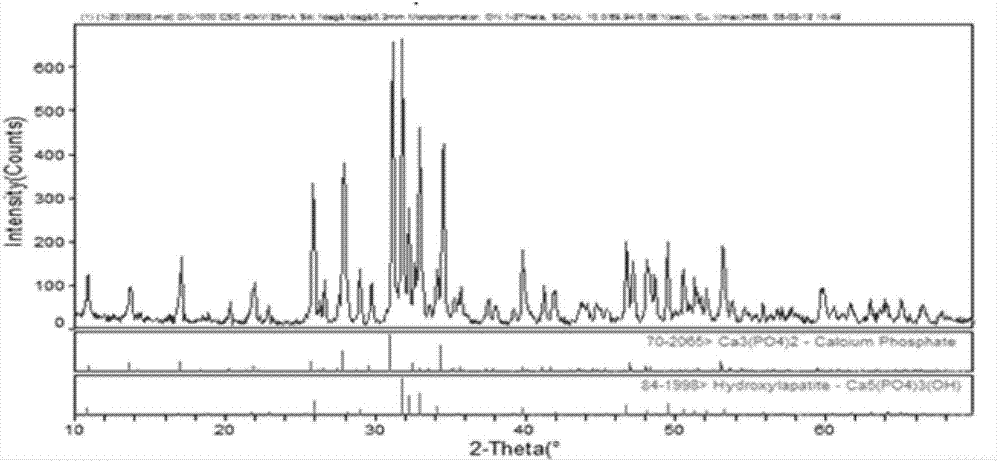
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The preparation method of the modified PLGA biofactor-loaded microsphere bone substitute material comprises the following steps:
[0027] Preparation of drug-loaded chitosan microspheres: 900 mg of carboxymethyl chitosan was dissolved in 29 ml of 2% acetic acid solution by volume to form the first solution; 500 μg of human recombinant adiponectin and 500 μg of human recombinant bone morphogenetic The protein (rhBMP-2 in this example, Genscript Pharmaceuticals, Korea) was dissolved in 1 ml of acetic acid solution with a volume fraction of 2% to form a second solution; the first solution and the second solution were dissolved in 300 ml containing 2 wt% Span- 80 in liquid paraffin, stirred evenly at room temperature to form an emulsion; slowly drop 70mL TPP solution with a mass fraction of 5% into the above emulsion, and fully complete the crosslinking by stirring; The cross-linked product was repeatedly washed and freeze-dried to obtain drug-loaded chitosan microspheres. ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The preparation method of the modified PLGA biofactor-loaded microsphere bone substitute material comprises the following steps:
[0032]Preparation of drug-loaded chitosan microspheres: 1500 mg carboxymethyl chitosan was dissolved in 40 ml of 2% acetic acid solution by volume to form the first solution; 1 mg of human recombinant adiponectin and 1 mg of human recombinant bone morphogenetic The protein (rhBMP-2 in this example, Genscript Pharmaceuticals, Korea) was dissolved in 2ml of acetic acid solution with a volume fraction of 2% to form a second solution; the first solution and the second solution were dissolved in 500ml containing 2wt% Span- 80 in liquid paraffin, stirred evenly at room temperature to form an emulsion; slowly drop the solution containing 5 mg of sodium triphosphate into the above emulsion, and fully complete the crosslinking by stirring; repeatedly wash with petroleum ether, isopropanol and double distilled water in sequence The cross-linked produc...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The preparation method of the modified PLGA biofactor-loaded microsphere bone substitute material comprises the following steps:
[0037] Preparation of drug-loaded chitosan microspheres: 2000 mg carboxymethyl chitosan was dissolved in 50 ml of 2% acetic acid solution by volume to form the first solution; 2 mg of human recombinant adiponectin and 2 mg of human recombinant bone morphogenetic The protein (rhBMP-2 in this example, Genscript Pharmaceuticals, Korea) was dissolved in 5ml of acetic acid solution with a volume fraction of 2% to form a second solution; the first solution and the second solution were dissolved in 600ml containing 2wt% Span- 80 in liquid paraffin, stirred at room temperature to form an emulsion; slowly drop the solution containing 8 mg of sodium triphosphate into the above emulsion, and fully complete the cross-linking by stirring; repeatedly wash with petroleum ether, isopropanol and double distilled water The cross-linked product can be freeze-d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com