Multifunctional agricultural microbial agent as well as application method and effects thereof
A microbial inoculant and multi-functional technology, which is applied to the application field of agricultural microorganisms in crop cultivation and organic waste treatment, can solve the problems affecting the enthusiasm of enterprises and farmers, high production cost, low added value, etc., to improve crops. quality, reduce the use of chemical fertilizers, and promote the effect of increasing income
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Preparation of media and strains
[0033] 1. Preparation of culture medium
[0034] 1. Potato and dextrose agar medium (PDA)
[0035] Take 200 grams of peeled potatoes, cut them into small pieces, add 1000ml of water and boil for 30 minutes, filter out the potato pieces, make up the filtrate to 1000ml, add 20 grams of glucose, 15 grams of agar, dissolve and subpackage, sterilize for 30 minutes in 15 pounds , the pH is natural, and no agar is added when preparing the liquid medium.
[0036] 2. Nutrient gravy agar
[0037] It consists of 5g of peptone, 5g of sodium chloride, 3g of beef extract and 1000ml of distilled water. pH7.0 (add 15-20g of agar to the solid medium).
[0038] 3. Fungal solid fermentation medium
[0039] 80g wheat bran, 10g soybean meal, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1.0g, KH 2 PO 4 0.2g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 00.05g, 80mL distilled water.
[0040] 2. Activation of bacteria
[0041] Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis were inoculated on nutrient bou...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Mutual antagonism experiment between strains
[0054] The activated Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, Sporosporium thermophila, Aspergillus oryzae and Trichoderma viride were subjected to mutual antagonism experiments between strains, and they were combined in pairs, divided into 20 combinations in total, and each combination was repeated three times.
[0055] The steel ring method was used for the antibacterial test, and the strain was cultured in the corresponding medium for 2-3 days (190r / min, 28°C) to make a fermentation broth. Take 0.1mL of the fermentation broth of one of the bacteria (A) and spread it on a PDA plate, then place two pre-sterilized steel circles on the solid medium of each plate, and then add 0.25mL to each steel circle For the fermentation broth of any bacteria (B) other than bacteria A, each treatment was repeated three times, and the plate only inoculated with bacteria A was used as a control. Incubate at 28°C and observe the antibac...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Determination of Cellulose and Protein Decomposing Ability of Single Bacteria and Composite Bacteria
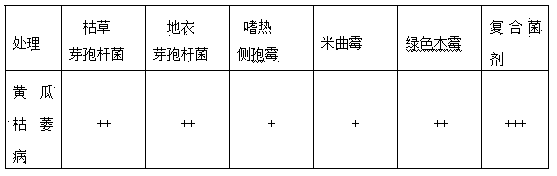
[0064] Bacillus subtilis can synthesize enzymes such as protease, cellulase, α-amylase and lipase by itself, which can effectively degrade organic substances such as cellulose and protein in organic materials; Bacillus licheniformis can produce a variety of active enzymes, Such as protease, cellulase, amylase, lipase, pectinase, glucanase, etc., and can also produce a variety of enzymatic factors; At ~50°C, it can secrete a large amount of cellulase, and quickly decompose organic matter such as straw, livestock and poultry manure, and peat into organic matter; Aspergillus oryzae is a strain that produces complex enzymes. In addition to protease, it can also produce cellulase, Amylase, glucoamylase, phytase, etc. Trichoderma viride is one of the strains with the highest cellulase activity, and the cellulase produced can degrade organic substances, and the effect is ve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com