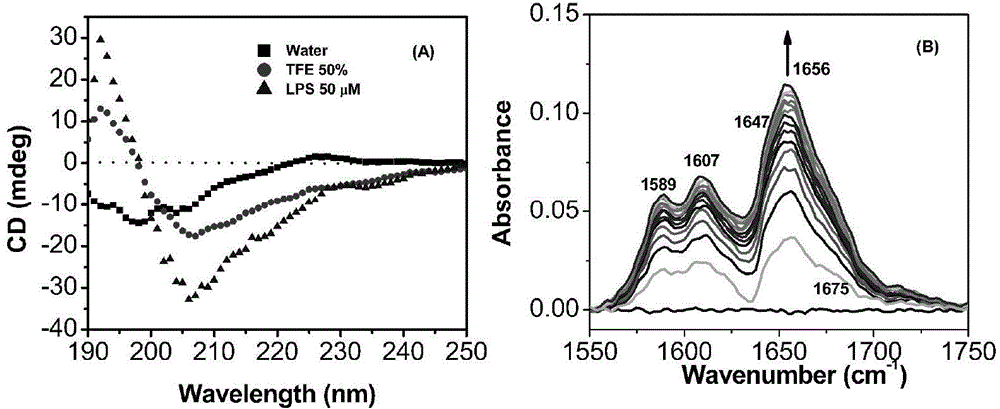
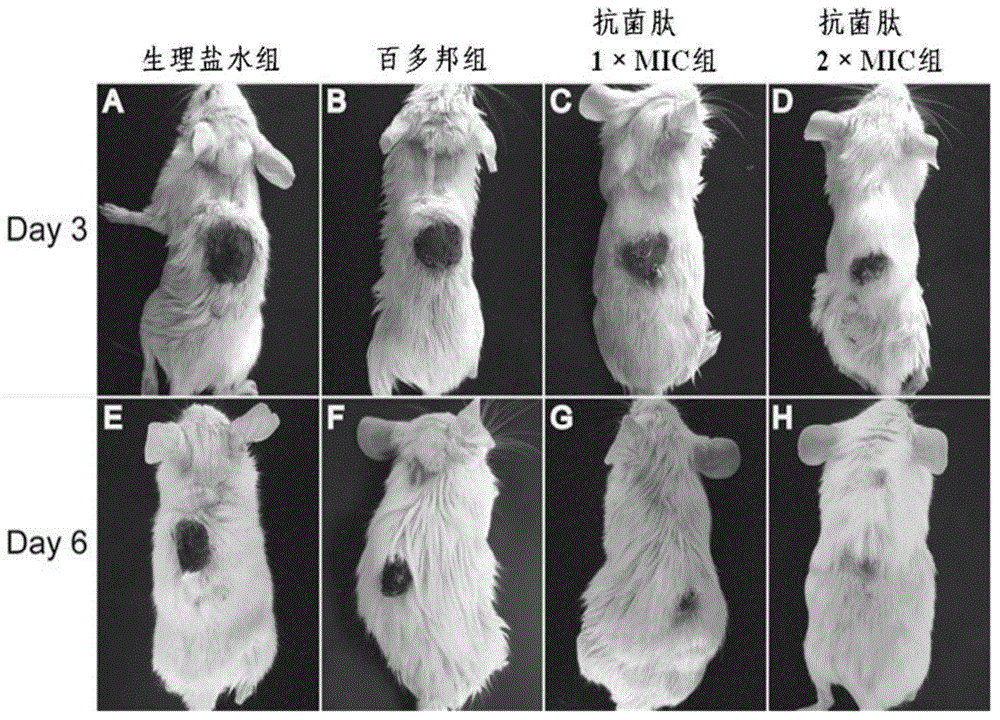
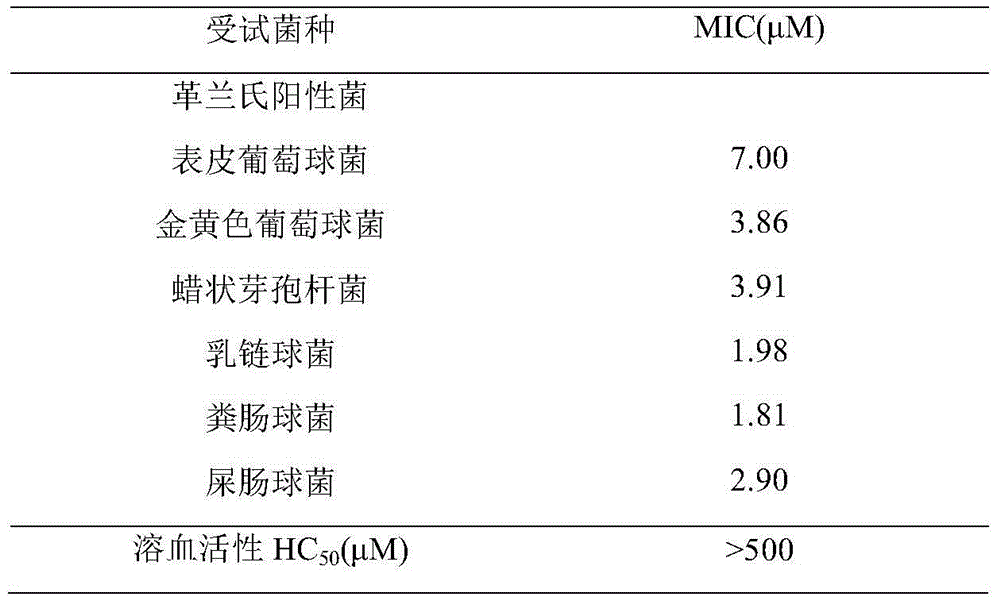
Antibacterial peptide derivative from forest frog and application thereof
A technology of antimicrobial peptides and derivatives, which is applied in the field of preparation of antibacterial drugs and antimicrobial peptide derivatives. It can solve the problems of low antibacterial and anticancer activity, limited popularization and application, and cytotoxicity of host cells, so as to promote skin wound healing, The effect of broad-spectrum antibacterial activity and simple and convenient preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Preparation of Antimicrobial Peptide Derivatives
[0023] 1. Chemical synthesis method of antimicrobial peptide derivatives: According to the amino acid sequence described in the summary of the invention, an automatic peptide synthesizer is used to synthesize according to the standard Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis procedure. The synthetic peptide was purified by reverse HPLC (Vydac218TP1022 column); 2. The molecular weight was determined by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF);
[0024] 3. The purity of the purified antimicrobial peptide derivatives is identified by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and the purity used in the test is 95%. Determine the amino acid sequence structure with an automatic amino acid sequencer;
[0025] 4. Antimicrobial peptide derivatives contain a total of 18 amino acid residues, with a molecular weight of 2542.9 Da and an isoelectric point of 12.6. The full amino acid se...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Antibacterial experiments of antimicrobial peptide derivatives against Gram-positive bacteria:
[0029] The pathogenic bacteria in the following examples all come from the General Microbiology Center (CGMCC) of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee and the China Industrial Microbiological Culture Collection Management Center (CICC), wherein: Staphylococcus aureus (AS 1.72), Bacillus cereus Bacillus (AS 1.126), Streptococcus lactis (AS 1.1690), Enterococcus faecalis (CGMCC 1.595), Enterococcus faecium (CGMCC 1.2334), Staphylococcus epidermidis (CICC 23664).
[0030] Minimum inhibitory concentration (minimal inhibitory concentration, MIC): the lowest concentration of the sample at which no bacterial growth can be detected. The two-fold dilution method was used. The specific method is as follows:
[0031] Bacteria were inoculated on LB solid medium and cultured upside down in a 37°C incubator. After the colonies grow out, use an inoculation loop ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Antibacterial experiments of antimicrobial peptide derivatives against Gram-negative bacteria:
[0038] The pathogenic bacteria in the following examples all come from the General Microbiology Center (CGMCC) of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee and the China Industrial Microbiological Culture Collection Management Center (CICC), wherein: Escherichia coli (AS 1.349), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (CGMCC1.860), Enterobacter aerogenes (CGMCC 1.876), Enterobacter cloacae (CGMCC 1.58), Klebsiella pneumoniae subspecies (CGMCC1.716), Acinetobacter baumannii (CICC 22934). The bacterial culture method and MIC determination method are consistent with the method described in Example 2, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0039] The minimum inhibitory concentration of table 2 antimicrobial peptide derivatives to Gram-negative bacteria
[0040]
[0041] It can be seen from the test results that the antimicrobial peptide derivatives showed a strong selectiv...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com