In-vitro screening and culturing method for tissue engineering skin seed epidermal keratinocyte high-simulation in-vivo cell extracellular matrix attachment
A technology for tissue engineering skin and extracellular matrix, which is applied in the field of tissue engineering, can solve the problems of low fibroblast adhesion, loss, and short plating cycle, and achieve the effects of high cell purity, simple preparation, and strong specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
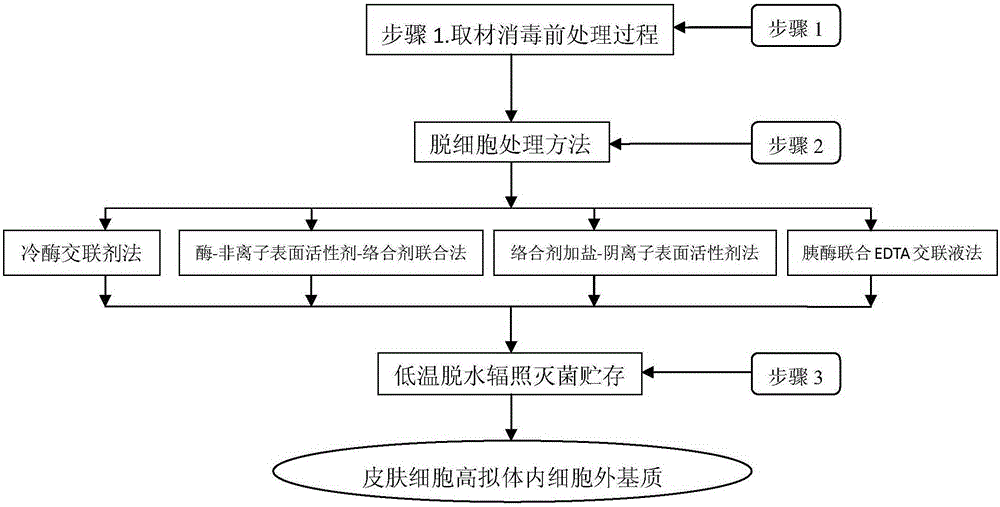
[0082] Embodiment 1 The specific implementation steps and methods of the preparation of the extracellular matrix in the hypermimetic body of the present invention:
[0083] Step 1: Skin disinfection process: take the donor skin including the following (embryonic skin, adult prepuce outer plate, scalp, armpit skin, and trunk skin can all be used) faulty skin with epidermis and dermis structure, cut into tissue pieces and soak in Dilute it in a solution containing 0.05-0.1% benzalkonium bromide with normal saline for 10-15 minutes, disinfect it, and wash the residual benzalkonium bromide repeatedly with sterile normal saline.
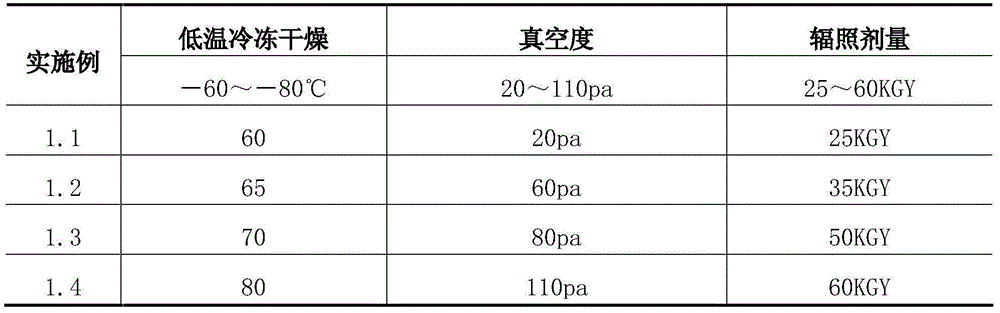
[0084] Step 2: Freeze-dry at low temperature -60-80°C, vacuum up to 20-110pa, remove more than 90-95% of the water in the tissue block, take it out, seal it and pack it in vacuum, and sterilize it by irradiation at a dose of 25-60KGY. The finished product can be stored at room temperature for up to 5 years. To start, you only need to soak at 37°C, recove...
Embodiment 2
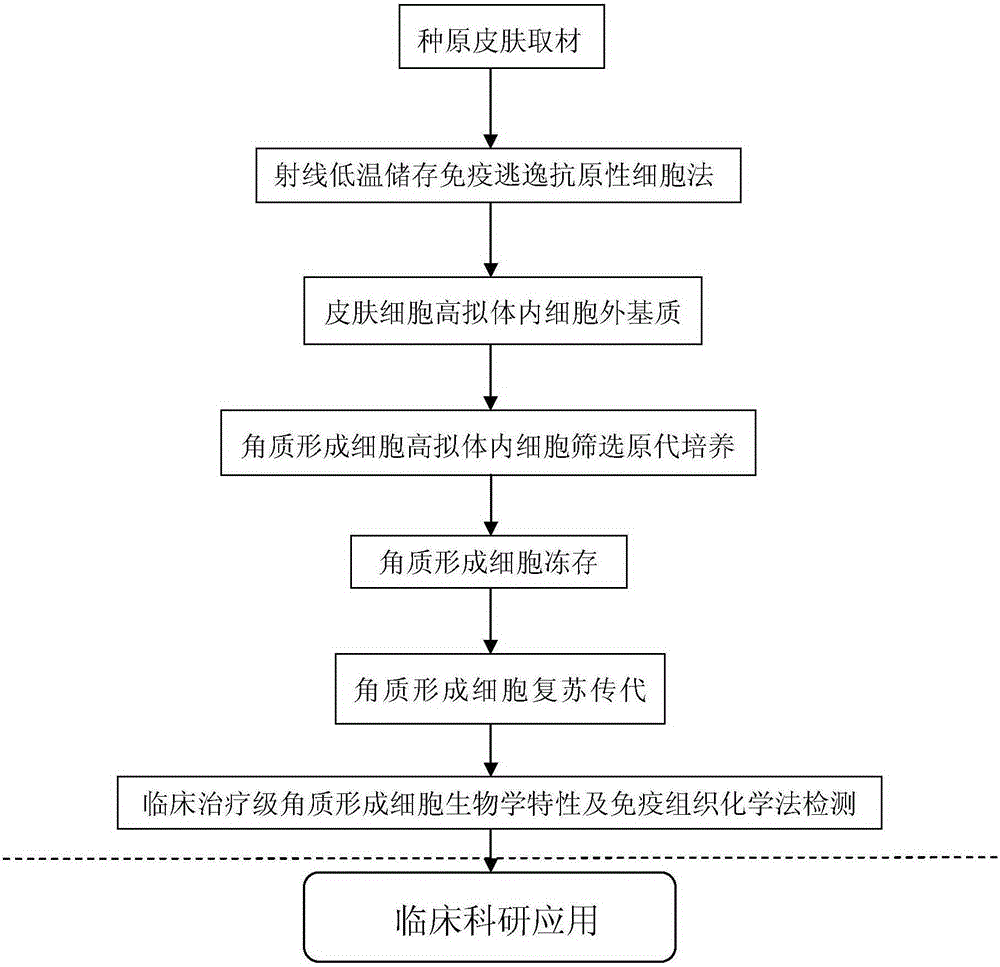
[0109] Embodiment 2 The method for culturing epidermal keratinocytes in a highly mimicked in vivo extracellular matrix of the present invention includes:
[0110] Screening of skin samples:
[0111] Skin cell screening sites include fetal skin, foreskin outer plate, scalp, and armpit skin.
[0112] Highly simulated extracellular matrix parts in the body: fetal skin, foreskin outer plate, scalp, armpit skin, and skin from other parts can be used.
[0113] When receiving it, fully soak it in PBS containing antibiotics (penicillin 80-100u / ml and 80-100μg / ml streptomycin) for 3-5 minutes, and trim the specimen to remove the subcutaneous tissue as much as possible.
[0114] Skin cell screening culture steps:
[0115] Because epidermal keratinocytes have strong adhesion to basement membrane, differential speed of adhesion to extracellular matrix, and habit of growth and expansion of adhesion, this characteristic is used for culture and screening.
[0116] Epidermal keratinocyte s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com