Extraction method of microcoleus vaginatus intracellular polysaccharide
A technology of Microschamoscapensis and intracellular polysaccharide, which is applied in the field of extraction and purification of intracellular polysaccharide, and can solve the problems such as the extraction process and product of intracellular polysaccharide from desert algae, and the extraction method of intracellular polysaccharide from Microcystheca splendens. , to achieve the effect of easy availability of reagents, good removal effect and good purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
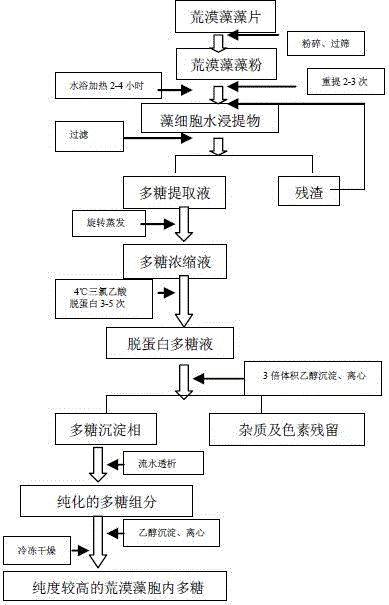
[0034] A method for extracting and purifying intracellular polysaccharides of Microtheca sheaths, the steps of which are:
[0035] A. Preparation of Microcoleena sheath algae powder. The algae powder is derived from the large-scale artificial cultivation of Microcoletheca sheaths. BG-11 liquid medium was used as the culture medium, and its components were as follows (per liter): 1.5 g sodium nitrate, 0.04 g dipotassium hydrogen phosphate trihydrate, 0.07 g magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 0.036 g calcium chloride dihydrate, lemon acid 0.006 g, ferric ammonium citrate 0.006 g, edetate disodium salt 0.001 g, sodium carbonate 0.02 g and 1 mL trace element A5 solution. Among them, the components of A5 solution (per liter) are as follows: 2.86 g of boric acid, 0.039 g of sodium molybdate dihydrate, 0.222 g of zinc sulfate heptahydrate, 0.074 g of copper sulfate pentahydrate, 1.81 g of manganese chloride monohydrate, cobalt nitrate hexahydrate 0.049 g. When preparing 1 liter of BG...
Embodiment 2
[0046] A method for extracting and purifying intracellular polysaccharides of Microtheca sheaths, the steps of which are:
[0047] (1) Grinding the dried Microcolecularis algae flakes (with a fineness of 90 meshes) to obtain Microcoleivoris algae powder;
[0048] (2) Take Microcoletheca sheath algae powder, mix the algal powder and sterile water at a ratio of 1:8, and place it at room temperature for 12 hours; heat it in a water bath (94°C) for 2 hours, filter it with gauze, and take the supernatant; the residue is press The above method was extracted at least 3 times, each time for 2.5 hours, the supernatants were combined, and the polysaccharide extract was stored at 4°C;
[0049] (3) Use a rotary evaporator to concentrate the polysaccharide extract to 1 / 5 of the original volume at 30°C, and store the polysaccharide concentrate at 4°C;
[0050] (4) Precipitate protein with trichloroacetic acid solution at 4°C, so that the content of trichloroacetic acid reaches 4.5% of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] A method for extracting and purifying intracellular polysaccharides of Microtheca sheaths, the steps of which are:
[0057] (1) Grinding the dried Microcolebucus algae flakes (with a fineness of 100 mesh) to obtain Microcoleurotheca algae powder;
[0058] (2) Take Microcoletheca sheath algae powder, mix the algal powder and sterile water at a ratio of 1:9, and place it at room temperature for 18 hours; heat it in a water bath (96°C) for 2.5 hours, filter it with gauze, and take the supernatant; the residue is press The above method was extracted at least 2 times, each time for 2 hours, the supernatants were combined, and the polysaccharide extract was stored at 4°C;
[0059] (3) Use a rotary evaporator to concentrate the polysaccharide extract to 1 / 5 of the original volume at 40°C, and store the polysaccharide concentrate at 4°C;
[0060] (4) Precipitate protein with trichloroacetic acid solution at 4°C, so that the content of trichloroacetic acid reaches 4.5% of the t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com