Method for removing dihydric alcohol or polyol impurities in glycol and increasing yield of glycol
A technology of ethylene glycol and polyols, applied in chemical instruments and methods, bulk chemical production, and preparation of organic compounds, etc., can solve problems such as high energy consumption of rectification, no involvement, multiple separation devices, etc., and reduce construction Effects of investment, process energy saving, and process simplification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
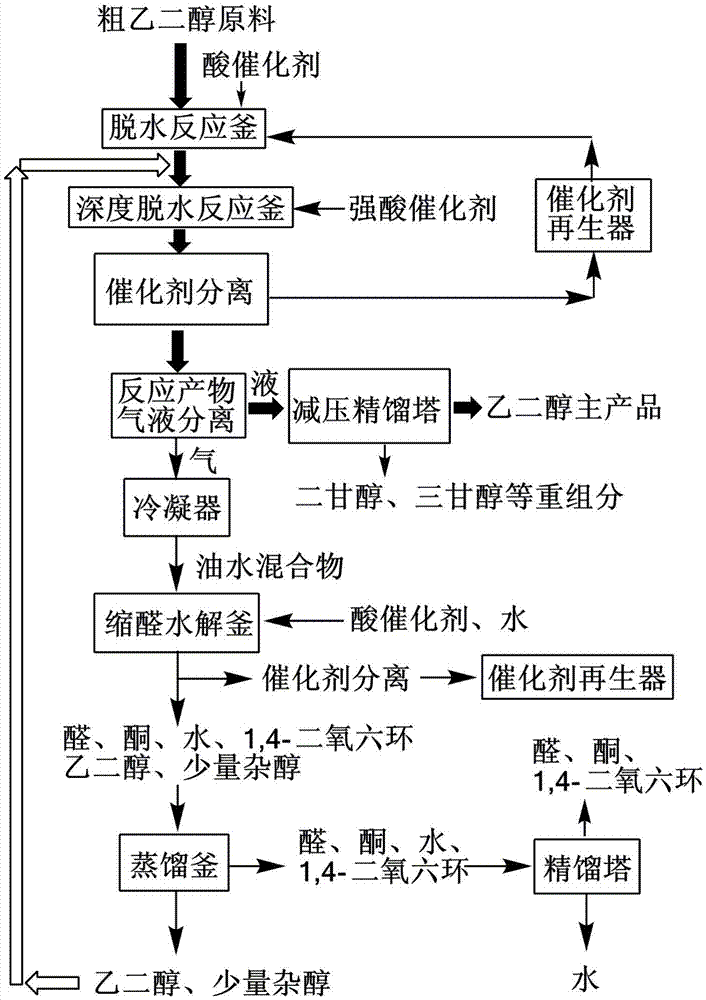
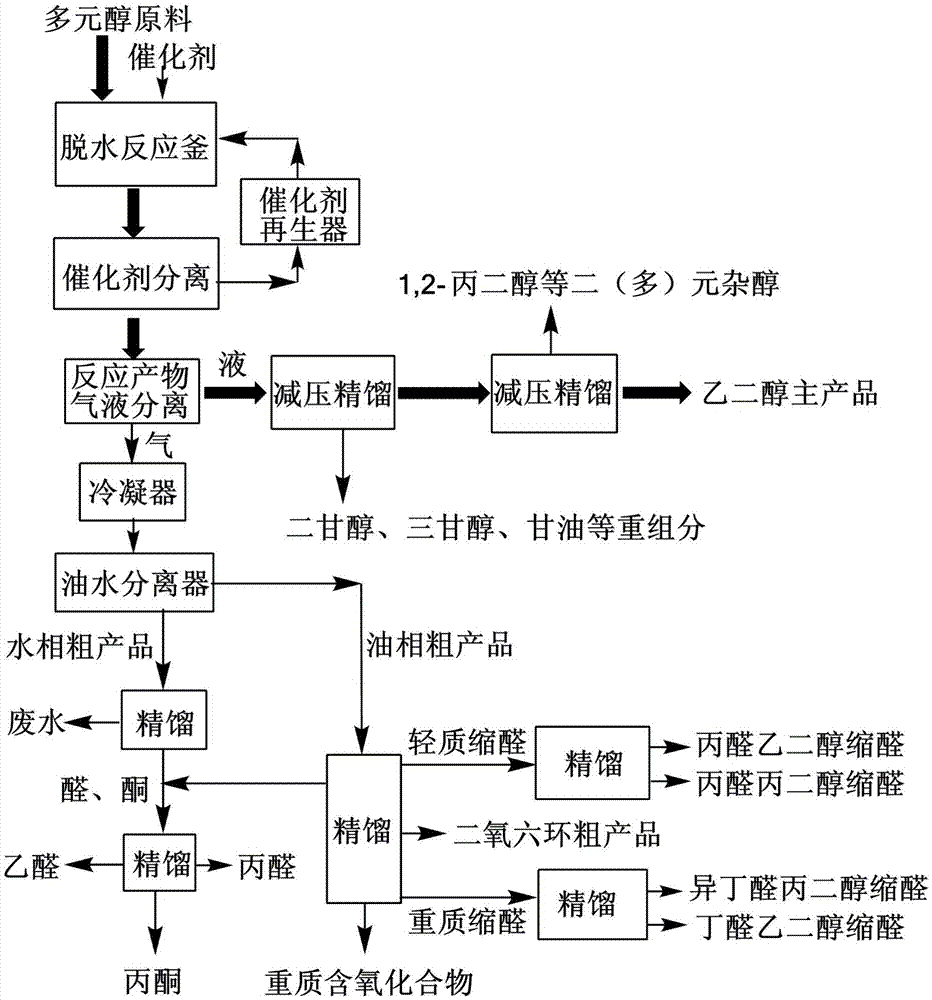
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, under normal pressure, 100 grams of ethylene glycol crude product containing 15% of 1,2-propanediol and 5% of 1,2-butanediol are added to the dehydration reactor, and 2 grams of silicon-aluminum ratio are added. 25 HZSM-5 acid molecular sieve catalyst, heated to 180°C, and reacted for 4 hours. The crude product undergoes dehydration reaction to generate light products such as propionaldehyde, propionaldehyde ethylene glycol acetal, butyraldehyde ethylene glycol acetal, propionaldehyde propylene glycol acetal, 1,4-dioxane, etc. These low boiling point products are all evaporated and mixed with Ethylene glycol separation. The ethylene glycol intermediate in the reactor was sent to the secondary reactor for secondary deep dehydration. The catalyst was 3 grams of HZSM-5 acid molecular sieve with a silicon-aluminum ratio of 80. The reaction temperature was 184°C and the reaction was performed for 2 hours. Secondary deep dehydration completely rem...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, under normal pressure, 100 grams of ethylene glycol crude product containing 10% of 2,3-butanediol and 5% of 1,2-pentanediol was added to the dehydration reactor, and 3 grams of silicon The Hβ acid molecular sieve catalyst with an aluminum ratio of 50 was heated to 180°C and reacted for 4 hours. The crude product undergoes dehydration reaction to produce light products such as butanone, butanone glycol ketal, valeraldehyde, pentanone, valeraldehyde glycol acetal, 1,4-dioxane, etc. These low-boiling point products are all evaporated when heated And separated from ethylene glycol. The ethylene glycol intermediate in the reactor is sent to the secondary reactor for secondary deep dehydration. The catalyst is 4 grams of Hβ acid molecular sieve with a silicon-aluminum ratio of 160, and the reaction temperature is 185°C for 2 hours. Secondary deep dehydration completely removes 2,3-butanediol and 1,2-pentanediol. The liquid phase product of the s...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, under normal pressure, the crude product of ethylene glycol containing 5% 1,2-butanediol and 1% glycerol is added to a dehydration reaction with a volume of 8 cubic meters at a flow rate of 1 ton / hour Add 100 kg of HZSM-5 acid molecular sieve catalyst with a silicon-aluminum ratio of 80 to the reactor. The reactor is a fully mixed flow reactor with a stirring rate of 280 rpm and a reaction temperature of 182°C. The crude product undergoes dehydration reaction to produce light products such as butyraldehyde glycol acetal, a small amount of butyraldehyde, 1,4-dioxane, hydroxyacetone, and a small amount of acrolein. These low-boiling point products are all evaporated by heating and separated from ethylene glycol. The ethylene glycol intermediate product discharged from the dehydration reactor is sent to the secondary reactor for secondary deep dehydration. The secondary reactor is a tubular reactor with an inner diameter of 0.3 meters and a lengt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com