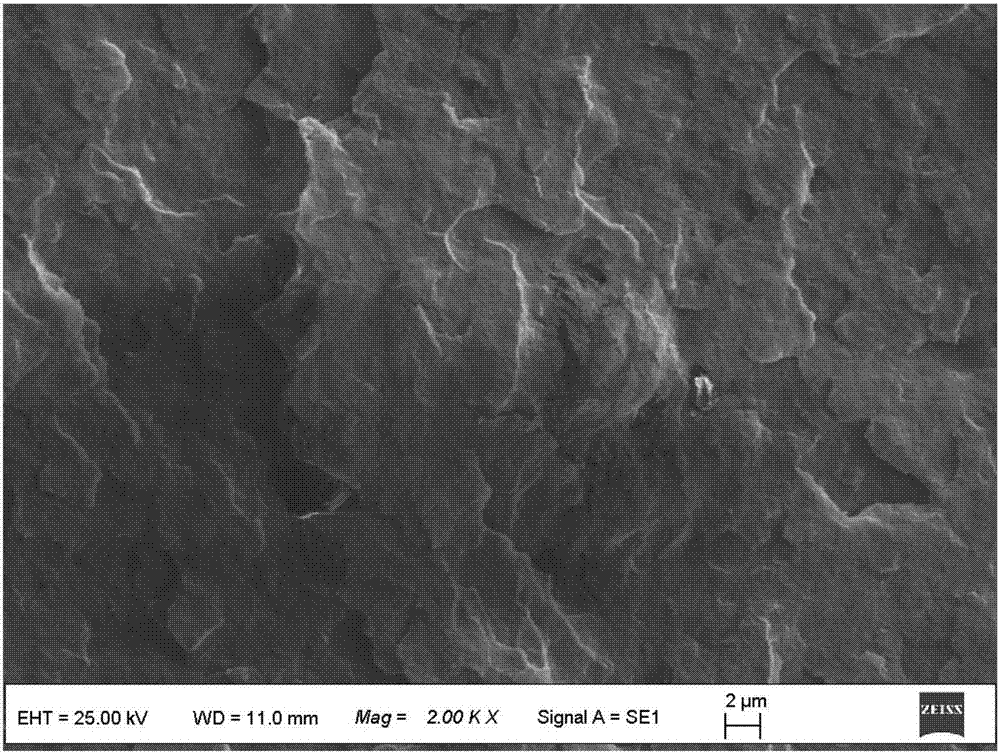
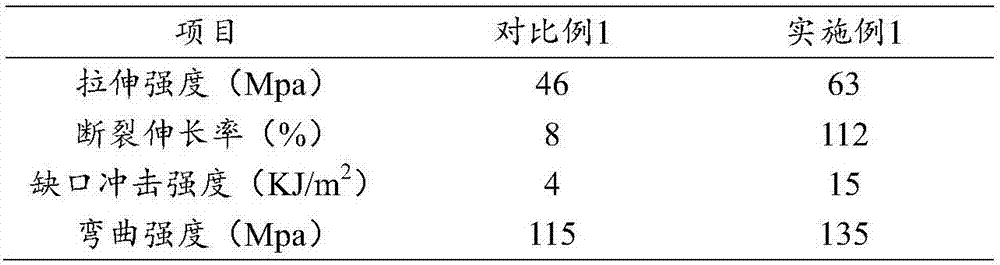
Reinforcing and toughening polylactic acid material and preparation method thereof
A polylactic acid material, reinforcement and toughening technology, applied in the field of reinforced and toughened polylactic acid material and its preparation, can solve the problems that limit the wide application of PLA materials, slow crystallization rate, and decrease in material toughness, so as to improve dimensional stability and processing Effects of fluidity, compatibility improvement, and toughness improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
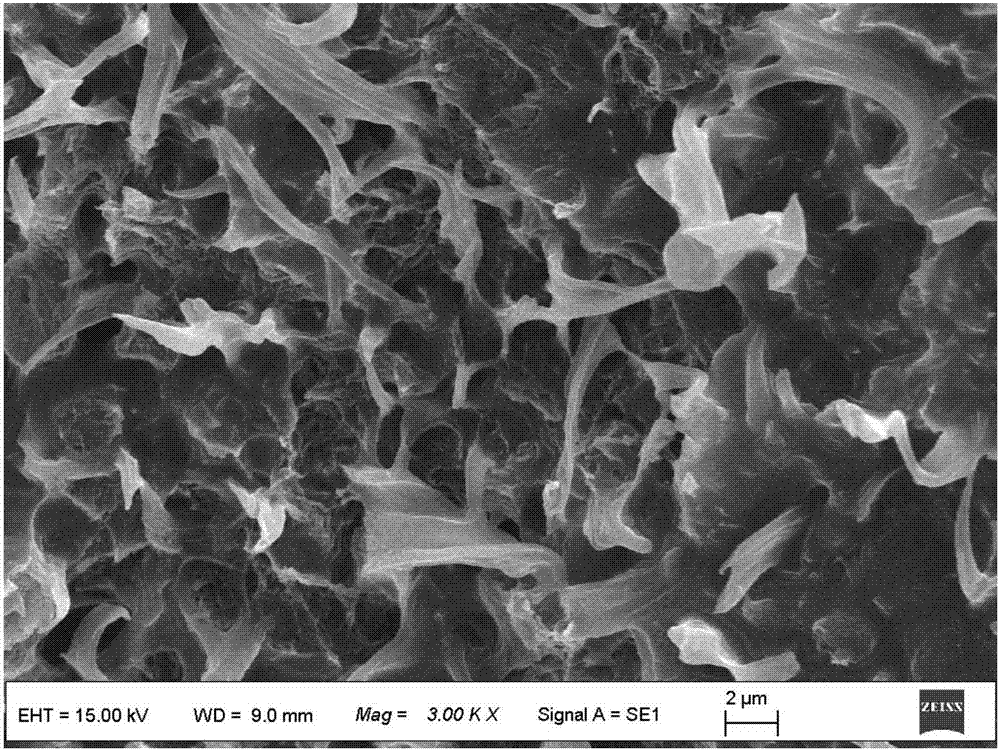
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] (1) Weigh 8g of LDHs and 35g of ε-CL into a three-neck flask, ultrasonicate for 30min, heat up to 110°C, add catalyst stannous octoate, N 2 React under protection for 24 hours. After the reaction is over, dissolve the viscous polymer in dichloromethane, filter and wash to remove impurities, precipitate in glacial hexane, wash to remove unreacted monomers, and vacuum at 40°C. Dry for 24h to get LDHs-g-PCL.
[0049] (2) Add 3 g of LDHs-g-PCL and an organic solvent into a three-necked flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, blow in nitrogen, raise the temperature of the oil bath to 70°C, and after the raw materials are completely dissolved, add 2.2126 g of hydrogenated Add diphenylmethane diisocyanate to the reaction system, add catalyst, react in nitrogen atmosphere for 2h, then adjust the temperature to 75°C, add 0.8g 1,4-butanediol, continue to react for 1.5h, and the reaction product is cooled to room temperature to obtain secondary functionalized LDHs-g-PU.
[005...
Embodiment 2
[0053] (1) Weigh 8g of LDHs and 45g of ε-CL into a three-neck flask, ultrasonicate for 40min, heat up to 100°C, add catalyst stannous octoate, N 2 React under protection for 20 hours. After the reaction is over, dissolve the viscous polymer in dichloromethane, filter and wash to remove impurities, precipitate in glacial hexane, wash to remove unreacted monomers, and vacuum at 35°C. Dry for 30h to get LDHs-g-PCL.
[0054] (2) Add 3 g of LDHs-g-PCL and an organic solvent into a three-necked flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, feed nitrogen, raise the temperature of the oil bath to 60°C, and press LDHs-g-PCL after the raw materials are completely dissolved. The molar ratio of PCL to diisocyanate is 1:2.3. Add diphenylmethane diisocyanate to the reaction system, add catalyst, react in nitrogen atmosphere for 1h, then adjust the temperature to 70°C, according to the molar ratio of diisocyanate to chain extender After adding ethylene glycol at a ratio of 0.14:1, the reaction ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] (1) Weigh 8g of LDHs and 19g of ε-CL into a three-neck flask, ultrasonicate for 50min, heat up to 120°C, add catalyst dibutyltin, N 2 React under protection for 30 hours. After the reaction is over, dissolve the viscous polymer in dichloromethane, filter and wash to remove impurities, precipitate in glacial hexane, wash to remove unreacted monomers, and vacuum at 45°C. Dry for 20h to get LDHs-g-PCL.
[0059] (2) Add 3g of LDHs-g-PCL and organic solvent into a three-necked flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, feed nitrogen gas, raise the temperature of the oil bath to 70°C, and press LDHs-g-PCL after the raw materials are completely dissolved. The molar ratio of PCL to diisocyanate is 1:5. Add 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate and toluene diisocyanate to the reaction system, add catalyst, react in nitrogen atmosphere for 2 hours, then adjust the temperature to 80°C, The molar ratio of the chain agent was 0.75:1. After adding 1,2-propanediol, the reaction was continued...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com