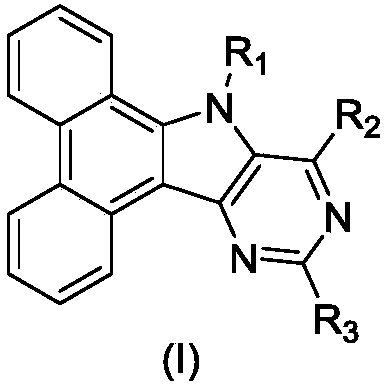
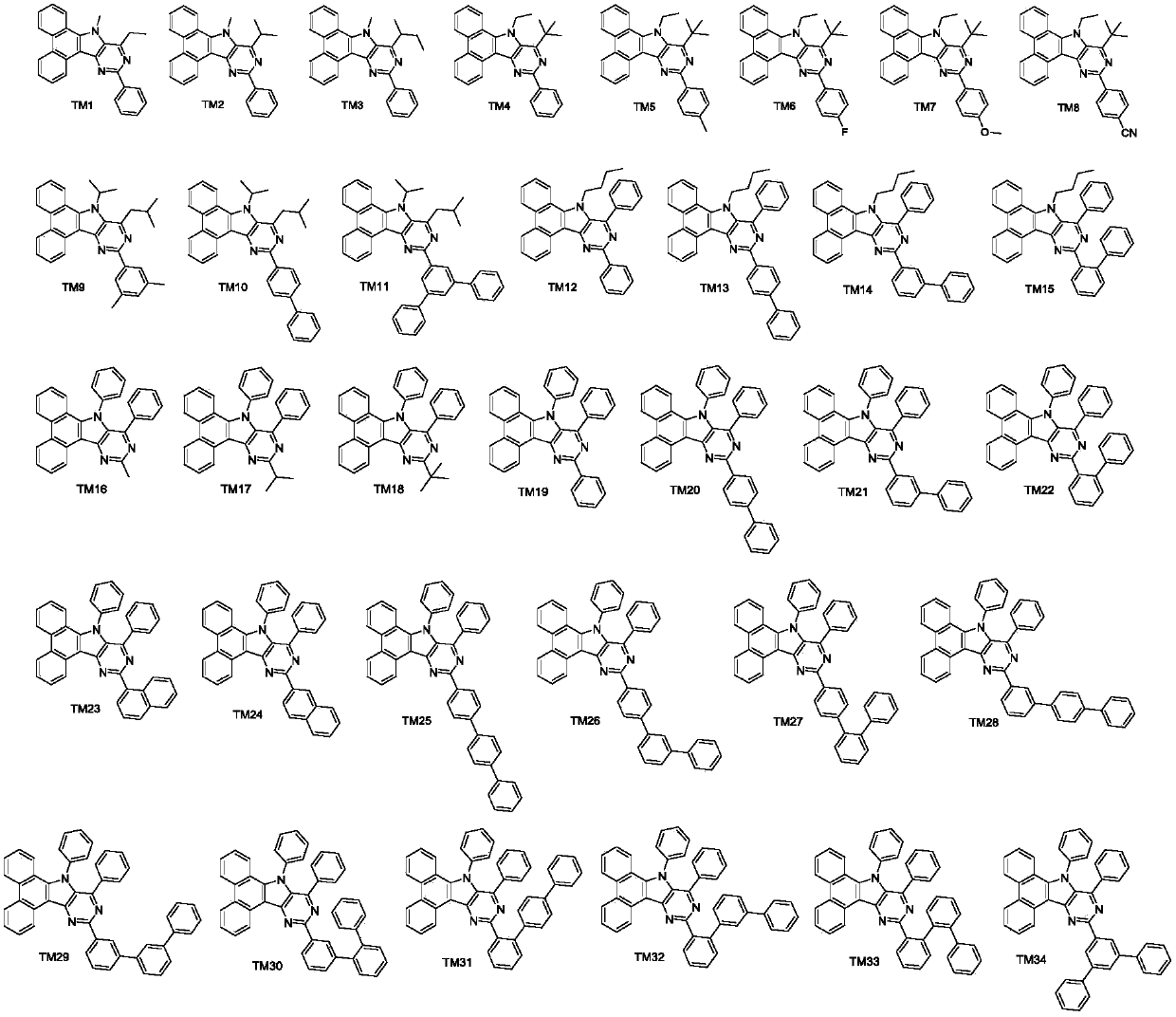
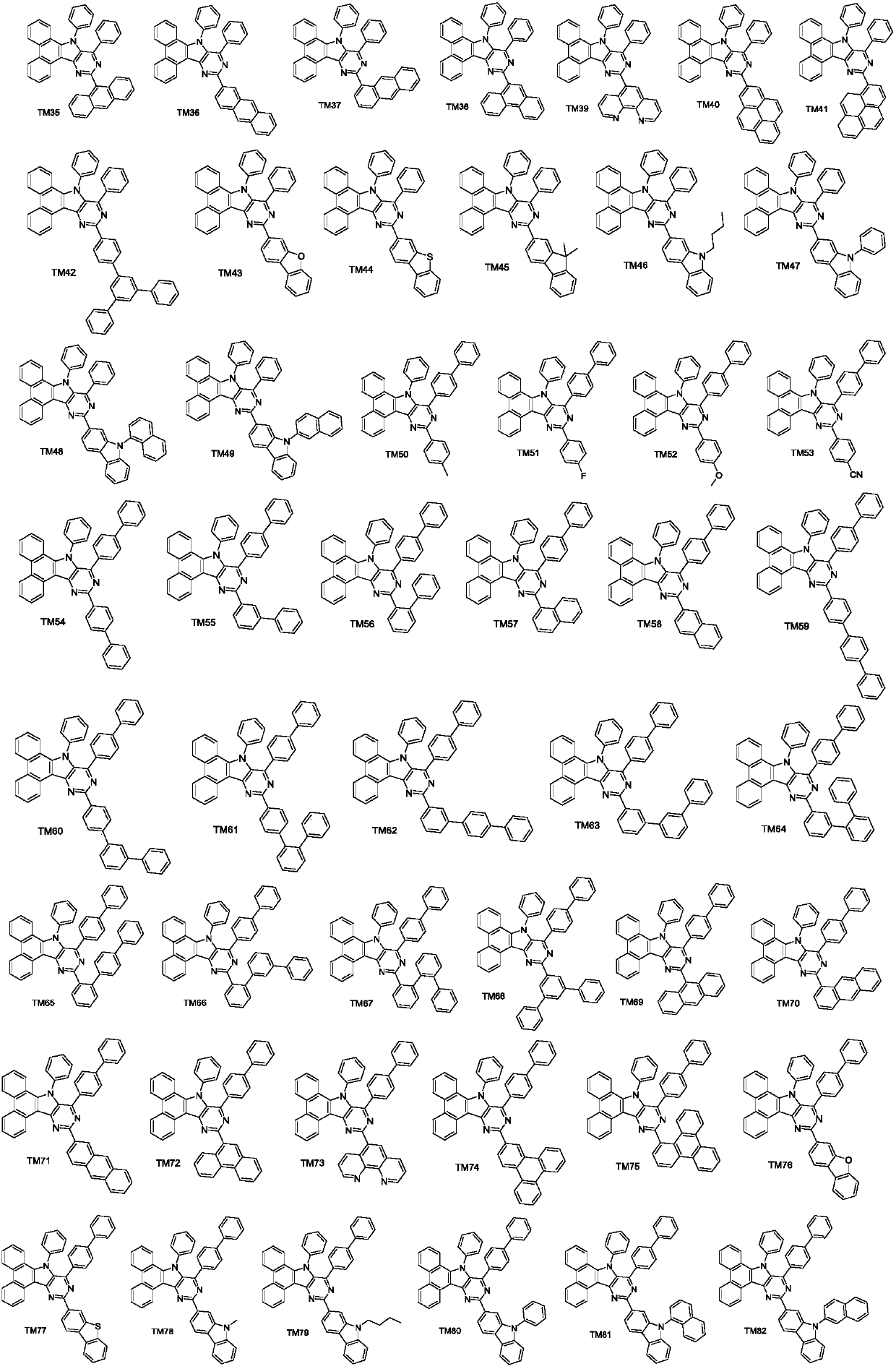
Pyrimidoindole derivative and organic light-emitting diode device thereof
A technology of indole derivatives and pyrimidines, which is applied in the field of pyrimidoindole derivatives and their organic electroluminescence devices, to achieve the effects of improving physical properties, easily obtaining raw materials, and improving luminous efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0042] The preparation method of the pyrimidoindole derivatives of the present invention, the specific synthetic route is as follows:
[0043]
[0044] Using 9-bromo-10-nitrophenanthrene as raw material, react to generate intermediate (BH); intermediate (BH) undergoes Suzuki reaction with 4-bromo-2,6-dichloropyrimidine to obtain intermediate (A); intermediate Body (A) produces ring-forming reaction, obtains intermediate (B); Intermediate (B) and containing R 1 The bromide reaction of group generates intermediate (C); Intermediate (C) and containing R 2 The boronic acid pinacol ester compound of group reacts, generates intermediate (D); Finally, intermediate (D) and containing R 3 The boric acid pinacol ester compound of the group reacts to synthesize the target compound (I).
[0045] The present invention has no special limitation on the reaction conditions of the above-mentioned reactions, and the reaction conditions well-known to those skilled in the art can be adopted....
Embodiment 1
[0050] Embodiment 1: the preparation of intermediate (BH)
[0051] Under an argon atmosphere, 400 ml of dehydrated tetrahydrofuran was added to 30.21 g (100 mmol) of 9-bromo-10-nitrophenanthrene, and cooled to -40°C. Slowly add 63ml of 1.6M n-butyllithium hexane solution, heat to 0°C, stir for 1 hour, then cool to -78°C, add dropwise 50ml of dehydrated tetrahydrofuran solution containing 26.0g (250mmol) trimethyl borate , stirred at room temperature for 5 hours. 200 ml of 1N hydrochloric acid was added dropwise, and after stirring for 1 hour, the aqueous layer was removed. The organic layer was dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, the organic solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure, and washed with toluene to obtain 18.43 g (69 mmol) of intermediate (BH) with a yield of 69%.
Embodiment 2
[0052] Embodiment 2: the preparation of intermediate (A)
[0053] 13.35g (50mmol) intermediate (BH), 11.39g (50mmol) 4-bromo-2,6-dichloropyrimidine, 1.73g (1.5mmol) tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium, 6g (150mmol) hydroxide Sodium was dissolved in a mixed solution of 250ml of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran and 125ml of water, and the reaction was refluxed for 24 hours. After the reaction, the system was cooled to room temperature, extracted with dichloromethane, and washed with water. It was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the organic solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was purified by column chromatography to obtain 16.29 g (44 mmol) of Intermediate (A), with a yield of 88%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com