Method of preparing metal by electrolyzing solid metal sulfide in aqueous solution
A metal sulfide and aqueous solution technology, applied in the electrolysis process, electrolysis components, electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of volatilization of toxic substances, high reaction temperature, complex equipment and process, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding emissions, high electrolysis efficiency, and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A method for preparing a metal by electrolysis of a solid metal sulfide in an aqueous solution is carried out in the following steps:
[0047] Step 1: Press
[0048] After the copper sulfide raw material is ground into copper sulfide powder with a particle size of 20 μm, it is pressed under a pressure of 40 MPa for 2 minutes to obtain a porous sheet;
[0049] Step 2: Preparation for Electrolysis
[0050] (1) Place the porous sheet in a copper crucible, make the porous sheet closely contact with the copper crucible, then connect the copper crucible with a copper wire collector with a diameter of 0.2±0.01mm to make a cathode, and place a 13±0.1mm high-purity graphite The rod is connected with a copper wire collector with a diameter of 0.2±0.01mm to make an anode;
[0051](2) The sodium hydroxide of equal mass and deionized water are mixed to obtain 50wt% sodium hydroxide solution, and as electrolyte solution, electrolyte solution is put into the container of tetrahydrof...
Embodiment 2
[0057] A method for preparing a metal by electrolysis of a solid metal sulfide in an aqueous solution, the same as in Example 1, the difference lies in:
[0058] (1) the sulfide of step 1 adopts lead sulfide;
[0059] (2) Apply 2.5±0.1V between the two electrodes in step 3;
[0060] (3) In step 2, a platinum wire with a diameter of 0.5 ± 0.01mm and a purity of 99.95% is connected to a current collector of a copper wire with a diameter of 0.2 ± 0.01mm to make an anode;
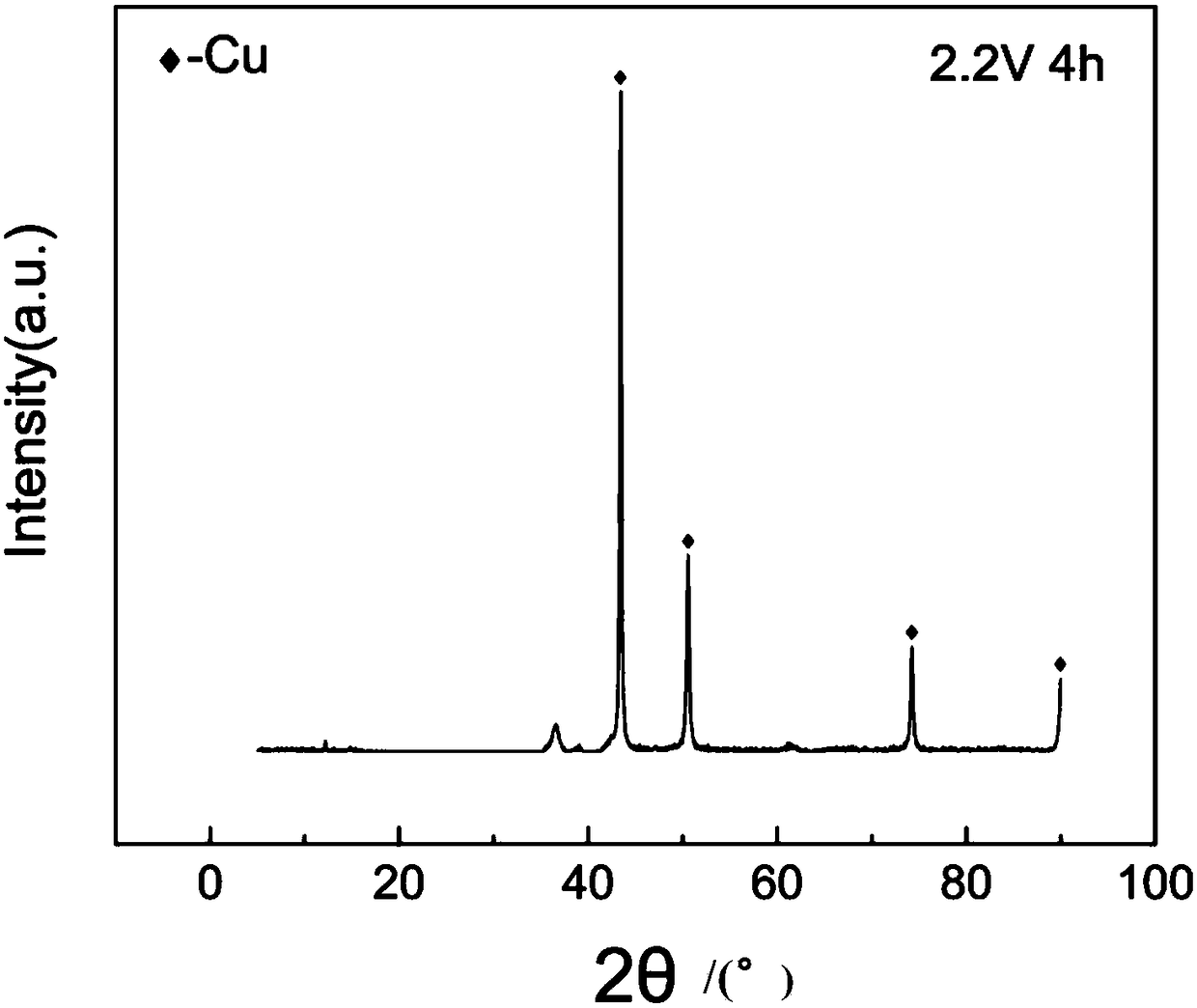
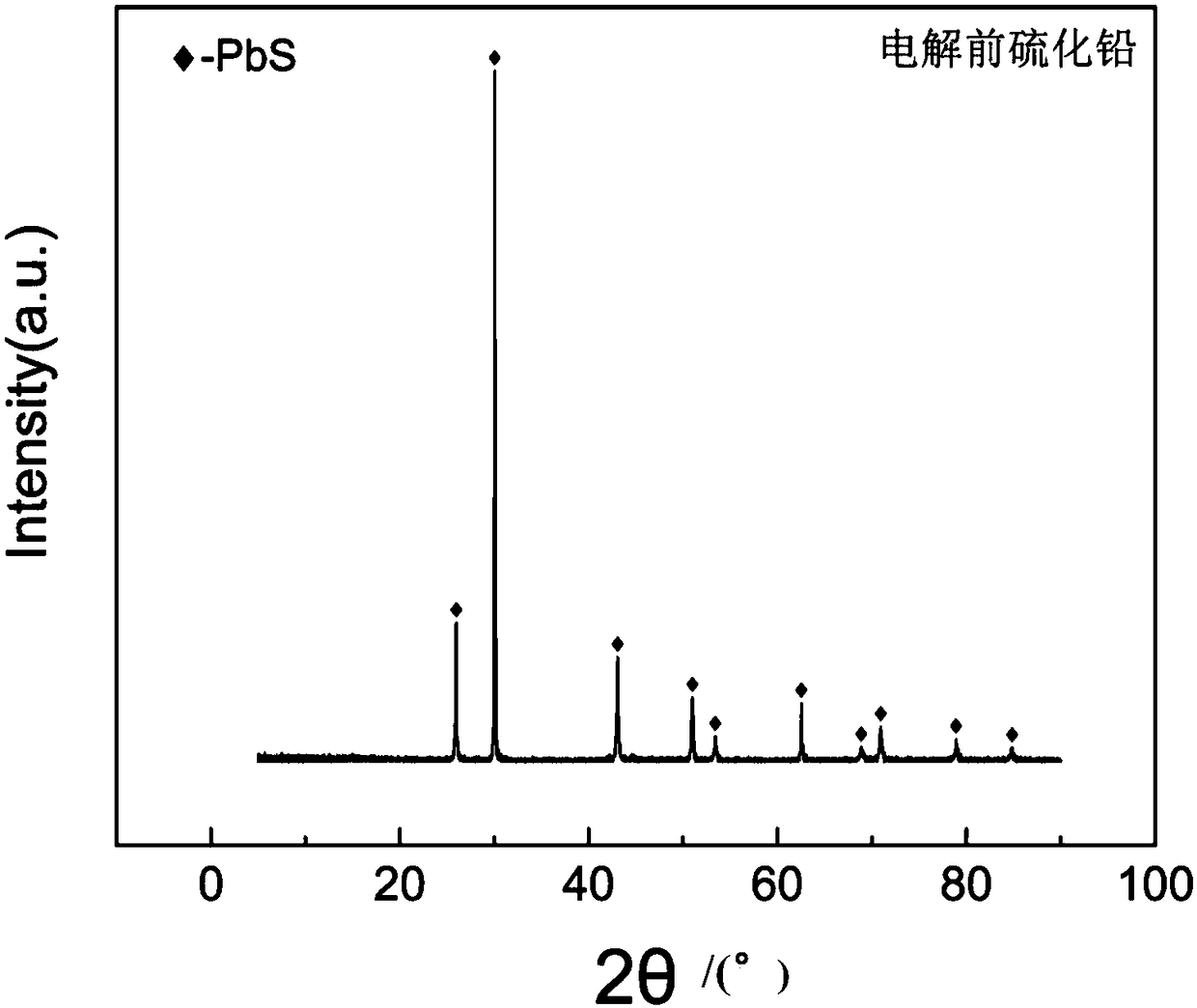
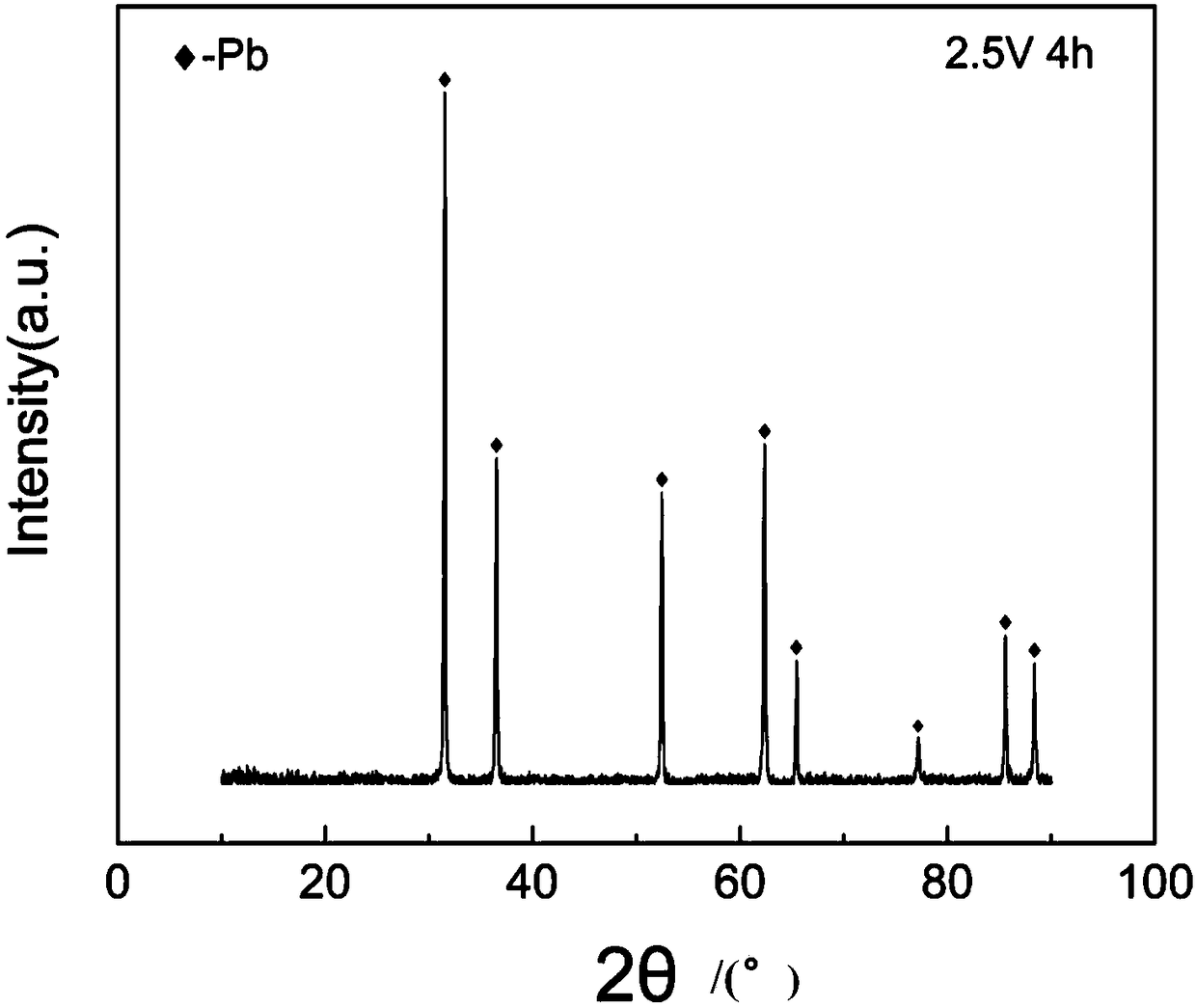
[0061] (4) figure 2 It is the XRD analysis figure of the lead sulfide sample before the electrolysis of the present embodiment, image 3 It is the lead XRD analysis figure obtained after the electrolysis of the present embodiment. It can be seen from the figure that after electrolysis, lead sulfide is completely converted into metallic lead.
[0062] Other methods are the same.
Embodiment 3
[0064] A method for preparing a metal by electrolysis of a solid metal sulfide in an aqueous solution, the same as in Example 1, the difference lies in:
[0065] (1) the sulfide of step 1 adopts antimony sulfide;
[0066] (2) Figure 4 It is the XRD analysis figure of the sample of antimony sulfide before the electrolysis of the present embodiment, Figure 5 It is the XRD analysis figure of the antimony obtained after the electrolysis of the present embodiment. It can be seen from the figure that after the electrolysis, the antimony sulfide is completely converted into metal antimony simple substance;
[0067] Other methods are the same.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com