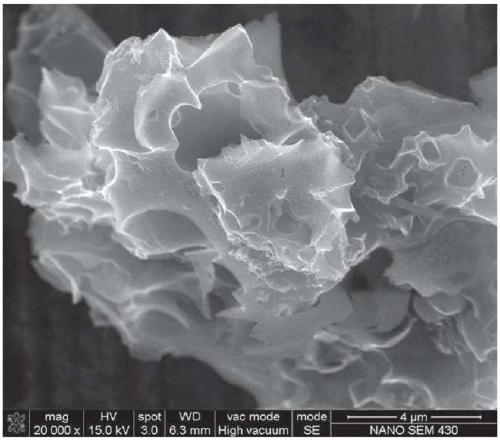
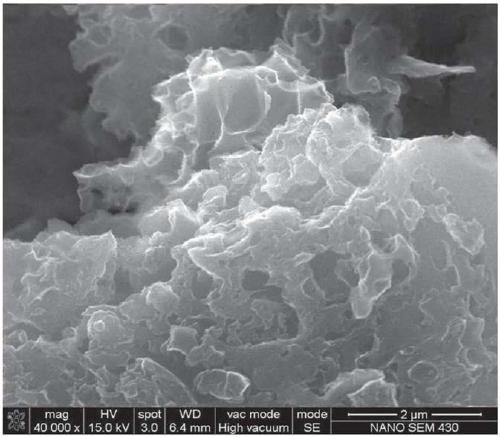
Preparation method of sulfur, nitrogen and phosphorus codoped porous carbon material for supercapacitor
A technology for supercapacitors and porous carbon materials, applied in chemical instruments and methods, hybrid capacitor electrodes, carbon compounds, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable commercial application, cumbersome preparation process, and non-renewable raw materials, and achieve low cost and excellent preparation process. Cumbersome, costly effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] (1) Pre-carbonization treatment of ginkgo leaves: clean the ginkgo leaves, dry them, and pulverize them to obtain powders. Under an argon atmosphere, heat them up to 400°C and keep them warm for 3 hours. Sieve the powders through 200 meshes to obtain pre-carbonized Ginkgo biloba.
[0031] (2) Preparation of sulfur, nitrogen, and phosphorus co-doped porous carbon material: Weigh 3 g of pre-carbonized ginkgo leaves obtained in step (1), put 3.6 g of potassium hydroxide, and 2.4 g of sodium hydroxide into a corundum boat. Place in a tube furnace, in an argon atmosphere, heat up to 200°C, then keep the temperature constant for 0.5h, continue to heat up the tube furnace to the final temperature of 700°C, keep the temperature for 2h, then cool down to room temperature naturally; take out the obtained product, grind After pulverization, add 2mol / L HCl solution to wash, then wash with distilled water until neutral, and dry to obtain: Ginkgo biloba-based porous carbon material f...
Embodiment 2
[0033] (1) Pre-carbonization treatment of ginkgo leaves: clean the ginkgo leaves, dry them, and pulverize them to obtain powders. Under an argon atmosphere, heat them up to 400°C and keep them warm for 3 hours. Sieve the powders through 200 meshes to obtain pre-carbonized Ginkgo biloba.
[0034] (2) Preparation of sulfur, nitrogen, and phosphorus co-doped porous carbon material: Weigh 3 g of pre-carbonized ginkgo leaves obtained in step (1), put 1.8 g of potassium hydroxide, and 1.2 g of sodium hydroxide into a corundum boat, and place the corundum boat Place in a tube furnace, in an argon atmosphere, heat up to 200°C, then keep the temperature constant for 0.5h, continue to heat up the tube furnace to the final temperature of 600°C, keep the temperature for 2h, then cool down to room temperature naturally; take out the obtained product, grind After pulverization, add 2mol / L HCl solution to wash, then wash with distilled water until neutral, and dry to obtain: Ginkgo biloba-ba...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) Pre-carbonization treatment of ginkgo leaves: clean the ginkgo leaves, dry them, and pulverize them to obtain powders. Under an argon atmosphere, heat them up to 400°C and keep them warm for 3 hours. Sieve the powders through 200 meshes to obtain pre-carbonized Ginkgo biloba.
[0037] (2) Preparation of sulfur, nitrogen, and phosphorus co-doped porous carbon material: Weigh 3 g of pre-carbonized ginkgo leaves obtained in step (1), put 3.6 g of potassium hydroxide, and 2.4 g of sodium hydroxide into a corundum boat. Place in a tube furnace, in an argon atmosphere, heat up to 200°C, then keep the temperature constant for 0.5h, continue to heat up the tube furnace to the final temperature of 800°C, keep the temperature for 2h, then cool down to room temperature naturally; take out the obtained product, grind After pulverization, add 2mol / L HCl solution to wash, then wash with distilled water until neutral, and dry to obtain: Ginkgo biloba-based porous carbon material f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com