Method for improving vitamin C content of tomato quality component by multi-gene polymerization
A technology of gene aggregation and vitamins, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as inability to cultivate high-quality tomatoes and resistance breeding, susceptible to external environmental influences, complex synthesis pathways, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
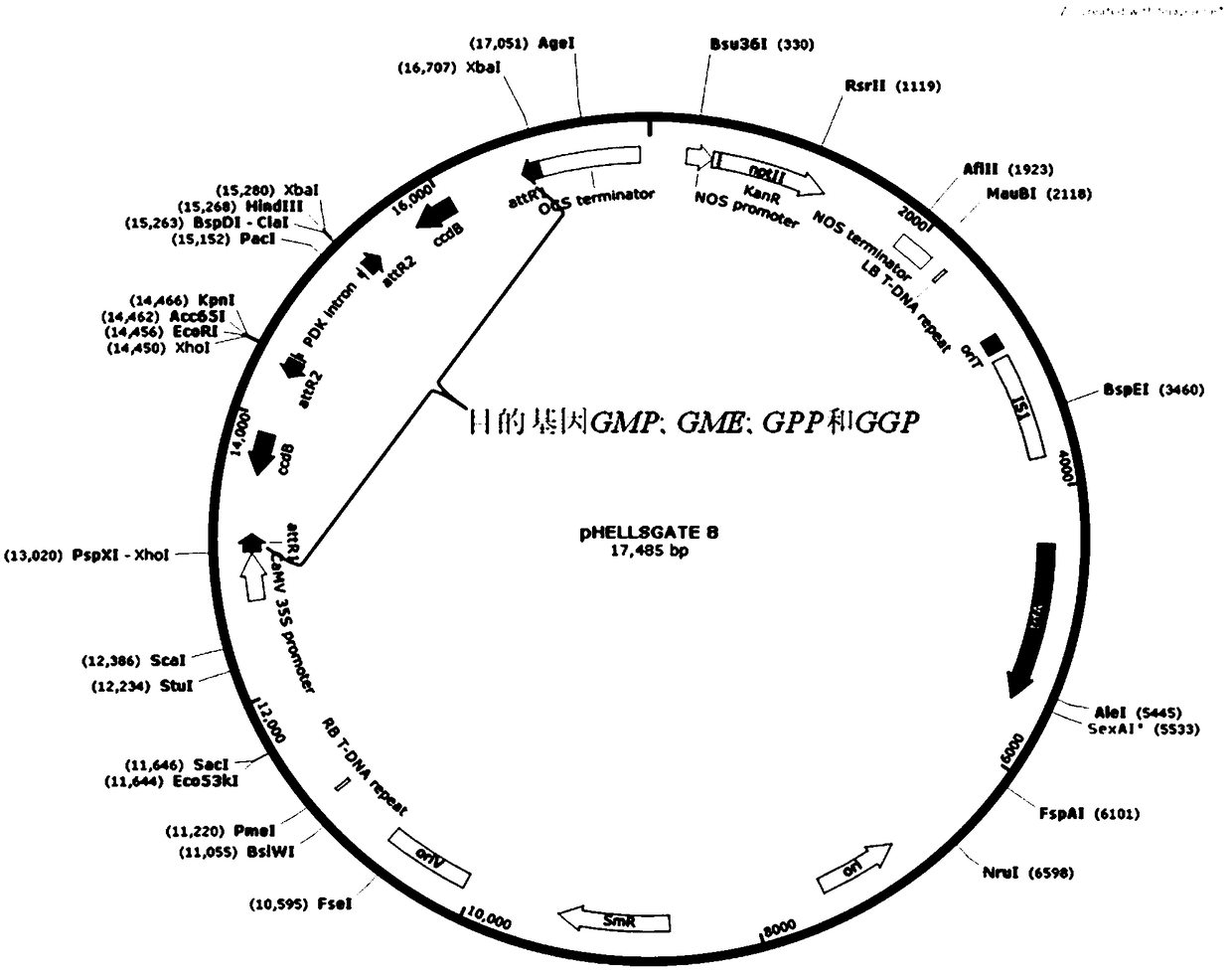
[0062] Embodiment 1: Obtaining of the transgenic polymeric material of the present invention
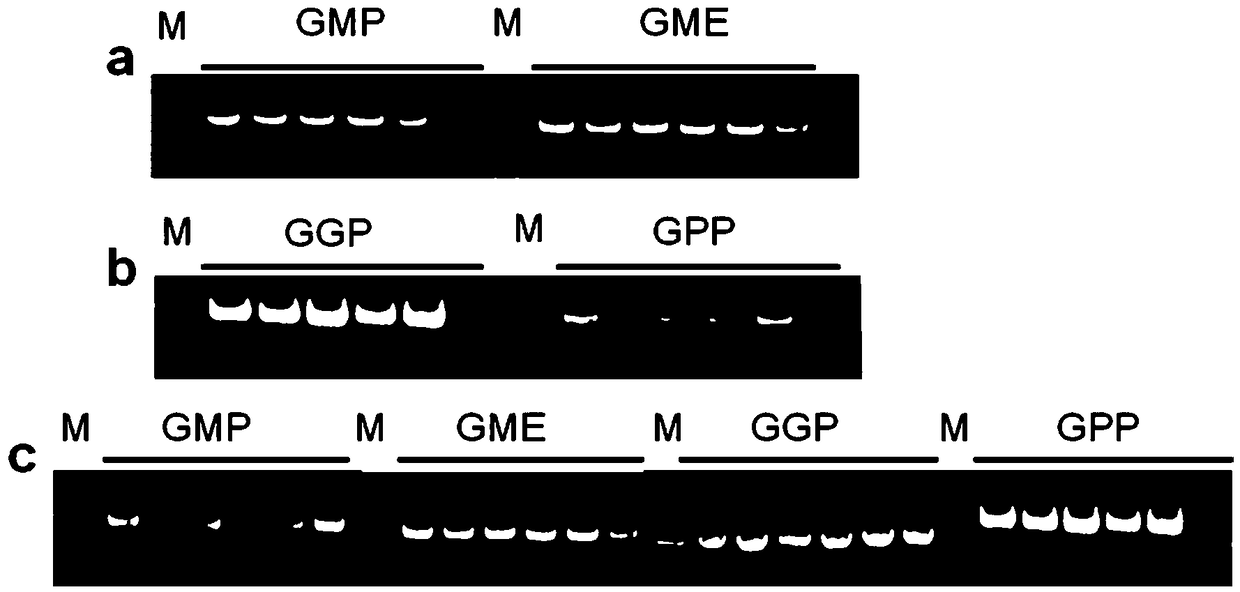
[0063] In the present invention, the aggregated plants are obtained by using the monovalent transgenic lines (SlGMP-OE, SlGME-OE, SlGGP-OE, and SlGPP-OE) preserved in the laboratory by means of conventional hybridization, and tomato conventional lines (Solanum lycopersicumcv. Ailsa Craig (AC) ) as a control to analyze the effect of transgene aggregation on AsA content in tomato. The specific methods for the molecular identification of the hybrid offspring of transgenic materials are as follows:
[0064]1. When the hybridized transgenic aggregated plants and control plants grow to 3-4 true leaves, DNA is extracted by the CTAB method:
[0065] A. Take young leaves (2 to 3 pieces) and place them at the bottom of a 1.5ml centrifuge tube;
[0066] B. Freshly prepare the sample extract and place it at room temperature;
[0067] C. Add 200 μl of sample extract, grind the sample fully wit...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Embodiment 2: Determination of tomato material ascorbic acid of the present invention
[0085] The determination of ascorbic acid includes the determination of reduced ascorbic acid and total ascorbic acid, wherein the total ascorbic acid includes reduced ascorbic acid and oxidized ascorbic acid. The determination method refers to the method of Hu Tixu's doctoral dissertation (2015). The specific steps are as follows: sample preparation. Select the fresh sample of the sample to be tested (the present invention is tomato red ripe fruit), freeze it with liquid nitrogen, and grind it into powder. Weigh about 0.2 g of leaf powder or about 0.4 g of fruit powder in a 2 mL centrifuge tube pre-cooled with liquid nitrogen, and add 1 mL of 6% TCA (trichloroacetic acid, purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.) pre-cooled on ice The solution was mixed well, extracted on ice in the dark for 15 minutes, centrifuged at 12000r / min at 4°C for 15 minutes; sample processing ...
Embodiment 3
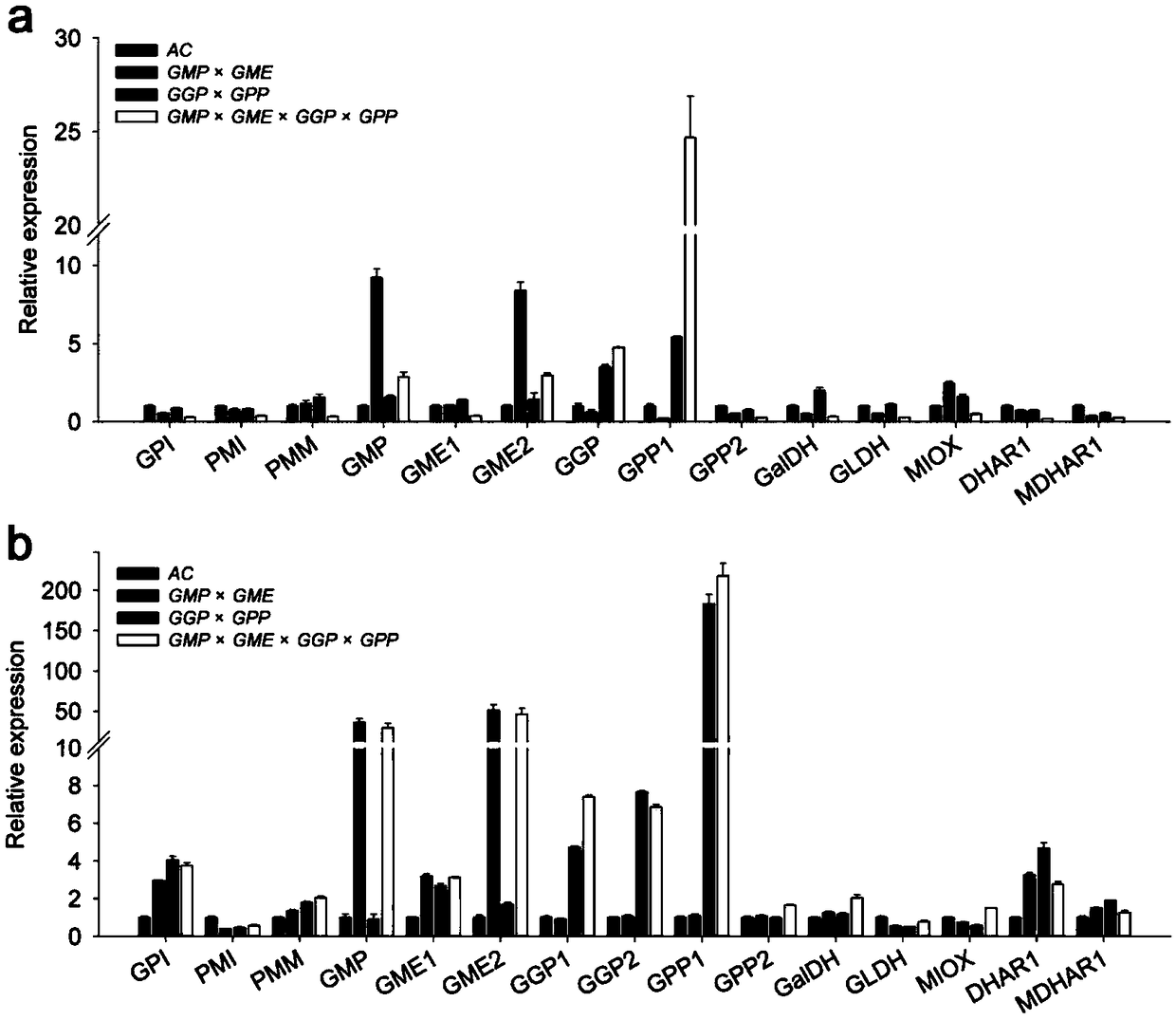
[0089] Example 3: Analysis of gene expression in leaves and fruits of tomato material of the present invention
[0090] The total RNA of leaves and fruits of related materials was extracted (Trizol method, the kit was purchased from Invitrogen), and the RNA was reverse-transcribed into cDNA using the reverse transcription kit HiScript 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (purchased from Novizyme Biotechnology Co., Ltd.). Using LightCycler480SYBR Green I Master Kit (Roche, http: / / www.roche.com / ), perform fluorescence quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) according to the kit steps to detect the relative expression of ascorbic acid anabolic genes. The qRT-PCR primers used in the experiment are shown in Table 1 (the primers were synthesized by Beijing Tianyi Huiyuan Biotechnology Co., Ltd.):
[0091] Table 1 qRT-PCR primers used in experiments
[0092]
[0093] The qRT-PCR reaction system is SYBR-Green Mix 5 μL, forward primer + reverse primer 0.5 μL + 0.5 μL, cDNA 4 μL. The qPCR reacti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com