Nitride catalyst for efficient photocatalytic reduction of nitrate in water and water treatment method thereof
A technology of nitrides and catalysts, which is applied in the field of nitride catalysts for efficient photocatalytic reduction of nitrate in water and its water treatment, can solve problems such as difficulty in meeting the demand for nitrate removal in water, secondary pollution, and easy deactivation of catalysts. Achieve excellent chemical stability, mild reaction conditions, and improve removal performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
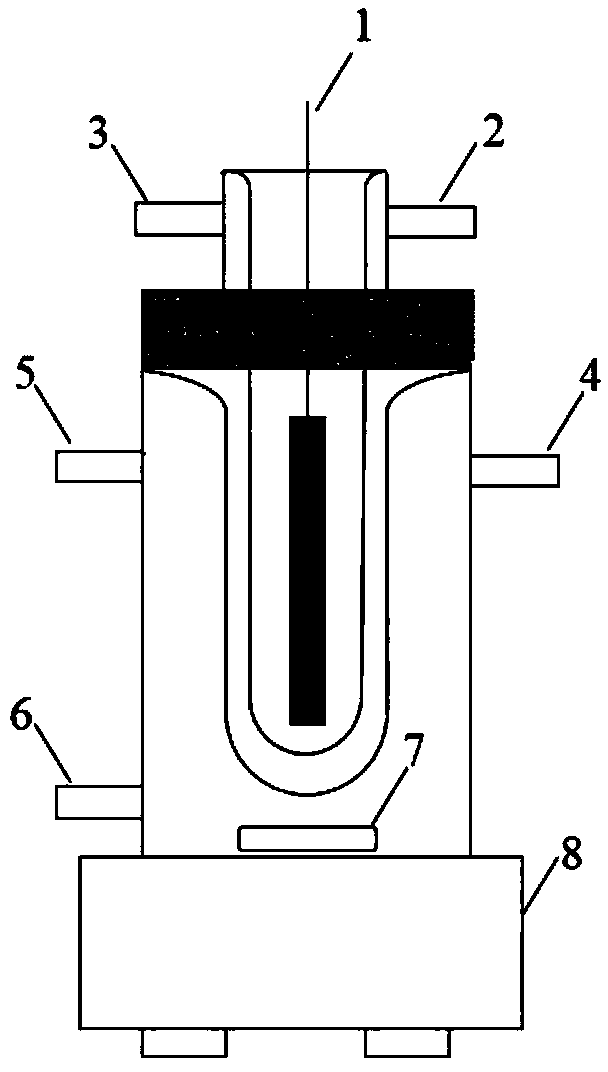
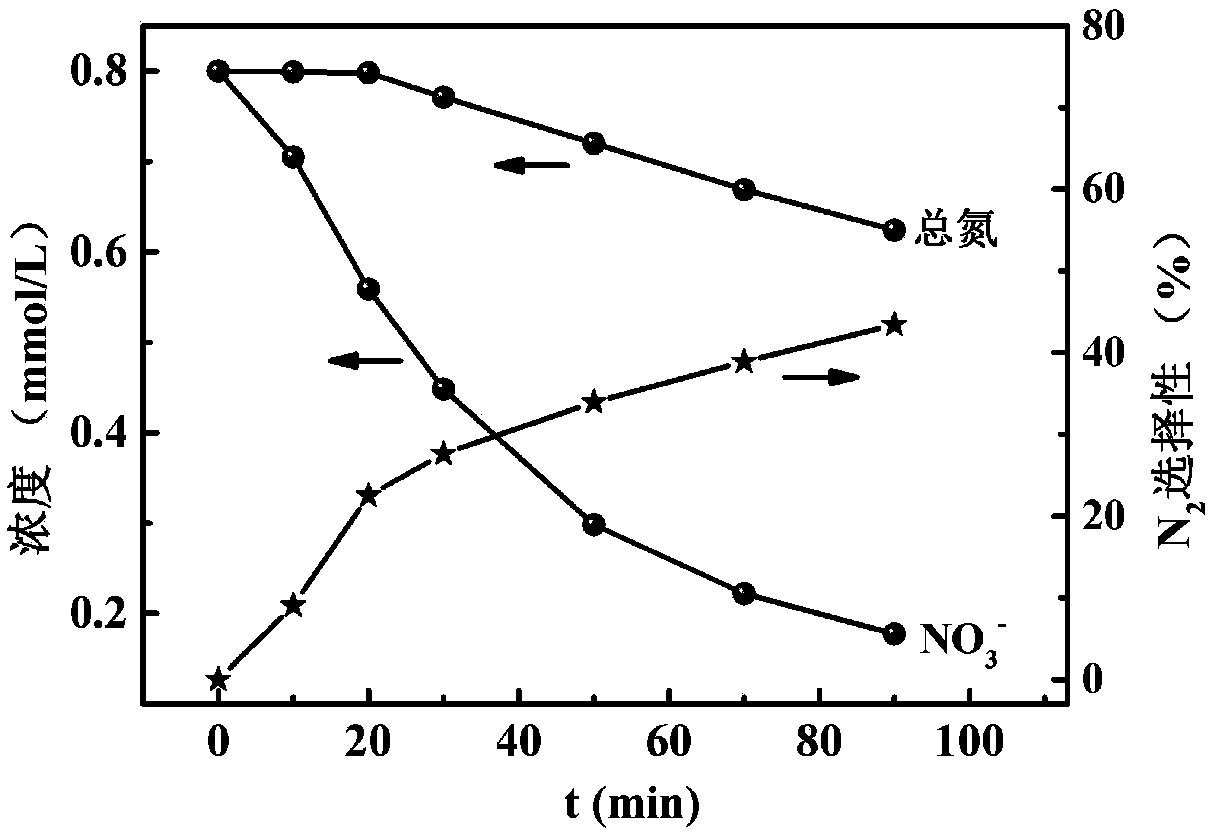
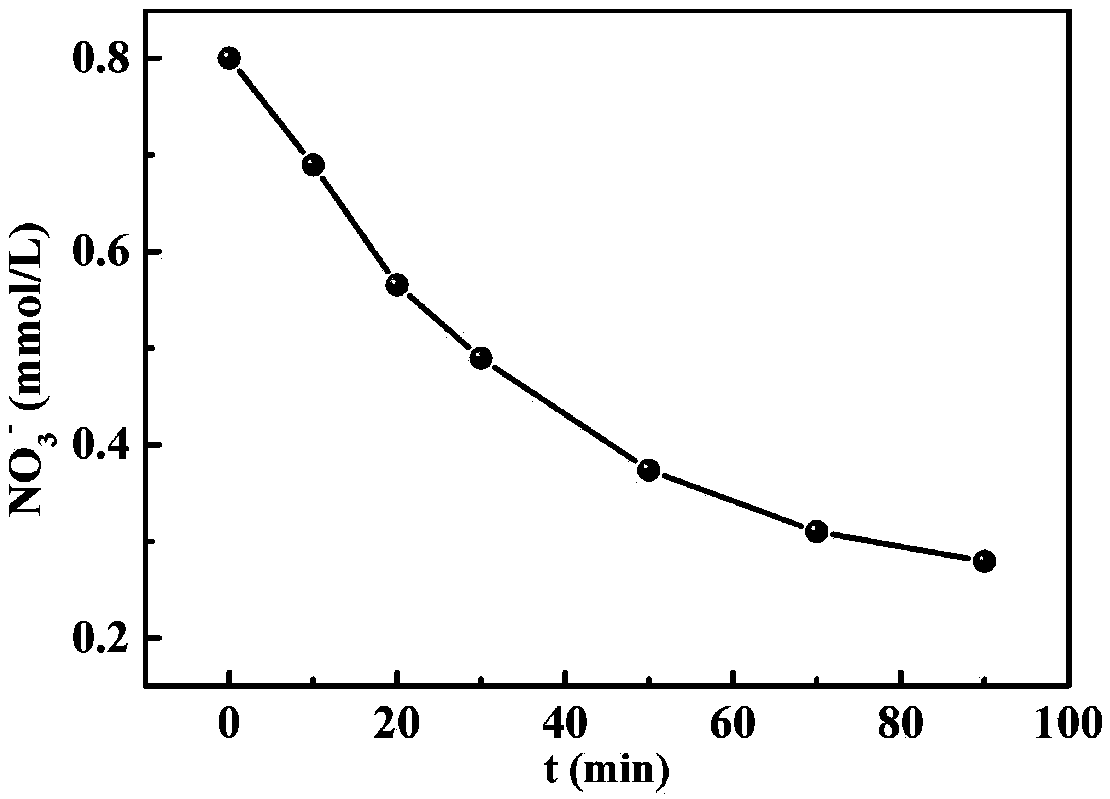
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0025] Step (1): prepare transition type nitride catalyst by alcohol thermal method;
[0026] ① At room temperature, take 1 mL of titanyl sulfate, slowly add it to a solution dissolved in 10 mL of glycerol, 20 mL of ethanol and about 8 mL of ether, and stir for 10 minutes to obtain a clear and uniform solution.
[0027] ② Transfer the mixed solution to a 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene hydrothermal kettle and place it in an oven at 110°C for aging for 1h.
[0028] ③ After the hydrothermal kettle is cooled, the sample is centrifuged, washed several times with ethanol, dried under vacuum at 80°C and collected for later use.
[0029] ④The above-mentioned titanium nitride precursor was calcined at 1300°C for 15 hours at a heating rate of 5°C / min in nitrogen. A transition type nitride titanium nitride is obtained.
[0030] Step (2): photocatalytic reduction of nitrate in water;
[0031] Potassium nitrate was used as the source of nitrate. Weigh 0.08g of the catalyst with an electr...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0033] The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is: the catalyst for photocatalytic reduction of nitrate in water in step (1) is covalent nitride B prepared by roasting method x N y (x=0, y=0).
[0034] ①Weigh a certain amount of boric acid and melamine in a beaker, dissolve in 250mL deionized water, heat and stir in a water bath at 90°C, crystallize by evaporation or cooling for 12 hours, and obtain a white gel-like substance.
[0035] ② Filter with a Buchner funnel and wash with deionized water for 3-5 times.
[0036] ③The obtained white solid was dried in a constant temperature drying oven at 60°C for 6-8 hours, and then ground to obtain a white powdery precursor.
[0037] ④Put the ground precursor in an alumina crucible and put it into a tube furnace for two-stage calcination: the first stage is to increase the temperature from room temperature to 600°C at a rate of 4°C / min, and keep it for 2 hours; In the second stage, the temperature is raised ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0040]The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the catalyst for the photocatalytic reduction of nitrate in water in step (1) is a nitride with a different shape.
[0041] ① At room temperature, take 1 mL of titanyl sulfate, slowly add it to a solution dissolved in 10 mL of glycerol, 20 mL of ethanol and about 8 mL of ether, and stir for 10 minutes to obtain a clear and uniform solution.
[0042] ② Transfer the mixed solution to a 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene hydrothermal kettle, and place it in an oven at 110°C for aging for 1h, 2d, and 7d (1h is a spherical structure, 2d is a core-shell structure, and 7d is an empty-shell structure).
[0043] ③ After the hydrothermal kettle is cooled, the sample is centrifuged, washed several times with ethanol, dried under vacuum at 80°C and collected for later use.
[0044] ④The above-mentioned titanium nitride precursor was calcined at 1300°C for 15 hours at a heating rate of 5°C / min in nitrogen. TiNs with d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com