a co 2 Electrode for electrochemical reduction and its preparation and application
An electrochemical and electrode technology, applied in the field of electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide, can solve the problems of loss of electrode activity, low conversion rate, reduction of electrode reaction area, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
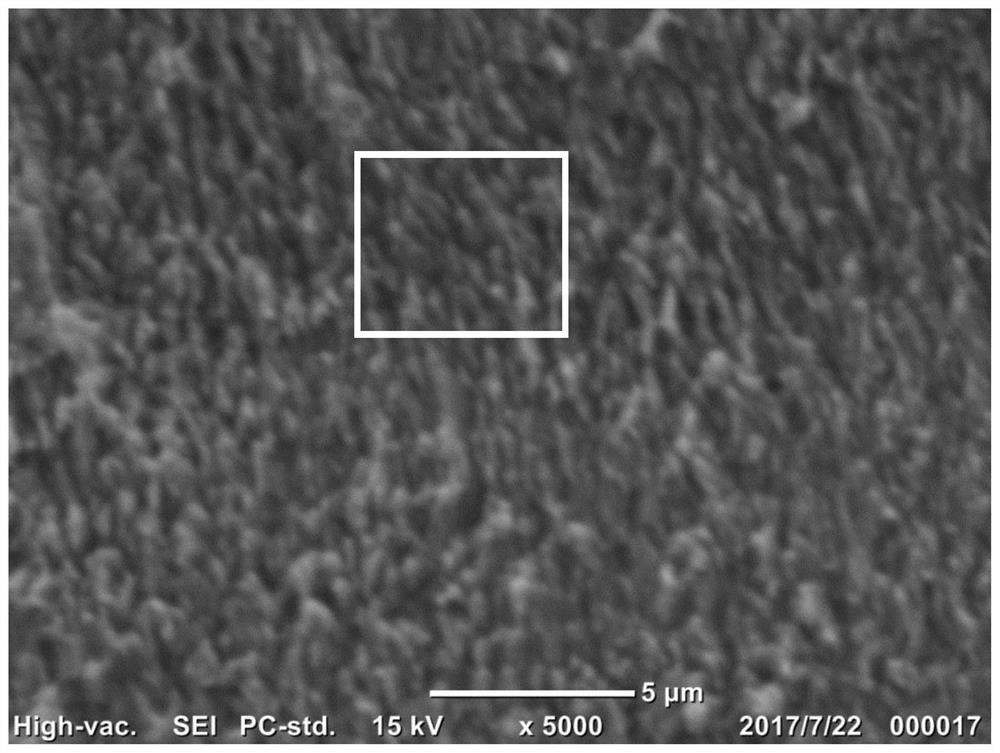
[0027] 1. Base material pretreatment: with a thickness of 100 microns and an area of 10 cm 2 The copper foil is used as the base material. First, it is soaked in concentrated hydrochloric acid with a volume fraction of 36% to 38% for 10 minutes at room temperature to remove impurities such as surface oxide scale, and then rinsed with a large amount of deionized water to neutrality. Dry with high-purity argon;
[0028] 2. Preparation of Cu nanoarray-modified copper electrodes: First, an anodizing solution containing 0.3 M sodium chloride and 5 mM cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) was prepared with deionized water, and 0.8 M NaOH Cathodic auxiliary solution. The two solutions were transferred into the anode compartment and cathode compartment of the H-type electrolytic cell, respectively. The electrolytic cell uses polyimide with a hydroxide ion conductivity of 0.08 Scm as the diaphragm.
[0029] Put the electrolytic cell into a constant temperature water bath with a wa...
Embodiment 2
[0033] 1. Pretreatment of the base material: the In content is 99.9%, the thickness is 200 microns, and the area is 5 cm 2 As the base material, the indium foil was first immersed in absolute ethanol for 50 minutes at room temperature to remove oil stains on the surface, and dried with high-purity Ar; then immersed in 5% hydrochloric acid for 30 minutes , remove impurities such as surface oxide scale, then rinse with a large amount of deionized water to neutrality, and dry with high-purity Ar gas;
[0034] 2. Preparation of In nanoarray-modified indium electrodes: First, an anodizing solution containing 0.2 M potassium chloride and 1 mM cetyltrimethylammonium chloride (CTAC) was prepared with deionized water, and 0.1 M NaOH Cathodic auxiliary solution. The two solutions were transferred into the anode compartment and cathode compartment of the H-type electrolytic cell, respectively. The electrolytic cell uses polyimide with a hydroxide ion conductivity of 0.05 Scm as the dia...
Embodiment 3
[0039] 1. Pretreatment of base material: with Sn content of 99.7%, thickness of 2 mm and area of 5 cm 2 As the base material, the tin sheet was first immersed in acetone at room temperature for 30 minutes to remove oil stains on the surface, and dried with high-purity Ar; then it was immersed in 1% hydrochloric acid for 5 minutes to remove Surface oxide scale and other impurities, then rinse with a large amount of deionized water to neutrality, and dry with high-purity Ar gas;
[0040] 2. Preparation of Sn nanoarray-modified tin sheet electrodes: First, an anodizing solution containing 0.5M rubidium chloride and 0.5mM octadecyltrimethylammonium bromide was prepared with deionized water, and a cathode with 2.0M NaOH was used auxiliary solution. The two solutions were transferred into the anode compartment and cathode compartment of the H-type electrolytic cell, respectively. The electrolytic cell uses polyimide with a hydroxide ion conductivity of 0.02 Scm as the diaphragm....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com