New genetic engineering subunit vaccine for transmissible gastroenteritis virus of swine
An infectious and gastroenteritis technology, applied in genetic engineering, viruses, viral peptides, etc., can solve the problems of lack of glycosylation modification of antigenic proteins, strong virulence of virus strains, and weak immune protection, etc., to achieve protein immunity Good originality, batch-to-batch stability, and good immunogenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] Embodiment 1 Construction of recombinant eukaryotic expression vector pCI-S1-GS
[0103] 1. The codon-optimized S1 gene was obtained from Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd., and cloned into the pUC-57 vector to construct the pUC-S1 plasmid vector. The optimized S1 gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1.
[0104] 2. S1 gene amplification uses pUC-S1 as a template, and S1-F and S1-R as primers for PCR amplification (the gene sequences of S1-F and S1-R are shown in SEQ ID NO.3 and 4), and the amplified See Table 1 for the augmentation system. The reaction conditions were: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 minutes; denaturation at 95°C for 45 seconds, renaturation at 60°C for 45 seconds, extension at 72°C for 2 minutes, 30 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10 minutes, and storage at 4°C.
[0105] Table 1 S1 gene amplification system
[0106]
[0107]
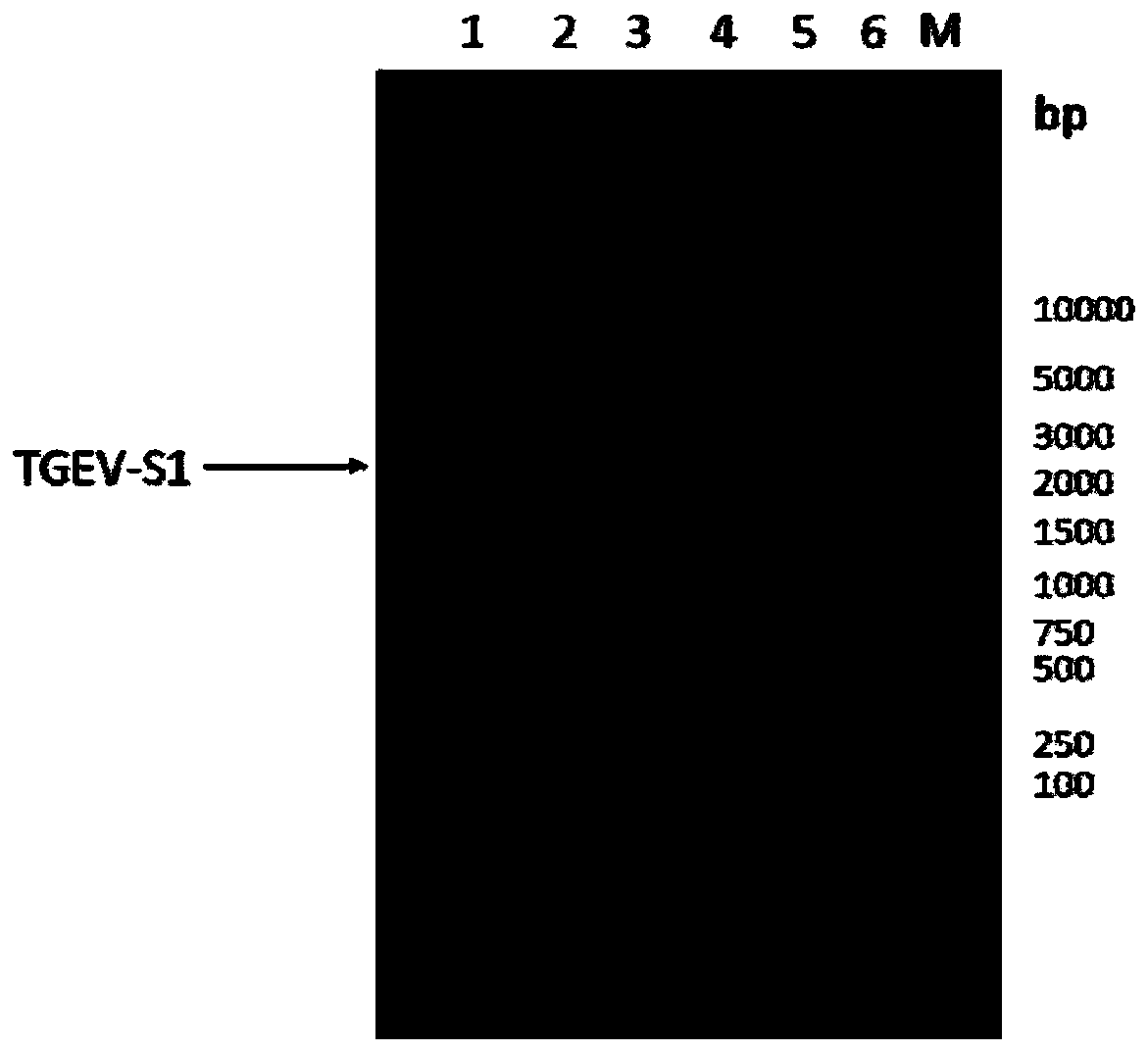
[0108] Perform gel electrophoresis on the PCR product to identify the size of the target gene, such as figure 1 As...
Embodiment 2
[0119] Example 2: Construction and screening of recombinant CHO cells
[0120] 1. Cell Transfection
[0121] 1.1 Prepare cells Take CHO cells in the logarithmic growth phase, sample and count, and use 1×10 6 The cell density of cells / ml continues to be subcultured, maintain the seeds, centrifuge the remaining cells, centrifuge at 1000rpm for 4 minutes, discard the supernatant, resuspend with about 20ml of fresh CHO-WM medium, centrifuge again, centrifuge at 1000rpm for 4 minutes, discard the supernatant After resuspending with a small amount of medium for counting, the final cell density was adjusted to 1.43×10 7 cells / ml.
[0122] 1.2 Plasmid and cell mixing Take 5ug of the pCI-S1-GS plasmid vector in Example 1, add it to the EP tube, add 0.7ml cells, mix well, and let stand for 15 minutes.
[0123] 1.3 Electric transfer to 280V 20ms for 2 pulses. After the electric shock is completed, immediately transfer the cells to a shaker flask for suspension culture. After 48 hours,...
Embodiment 3
[0133] Example 3 SDS-PAGE detection
[0134] The cell culture supernatant harvested in Example 2 was subjected to SDS-PAGE detection, and empty CHO cells were used as a negative control. The specific operation is as follows: take 40 μl of harvested cell culture, add 10 μl of 5×loading buffer, bathe in boiling water for 5 minutes, centrifuge at 12000 r / min for 1 minute, take the supernatant and carry out SDS-PAGE gel (12% concentration gel) electrophoresis, After electrophoresis, the gel was stained and decolorized to observe the target band. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the target band appears around the molecular weight of about 150kDa. Because the S1 protein has more glycosylation modifications, its molecular weight is about 66kDa higher than the molecular weight calculated by amino acid sequence theory. The negative control has no band at the corresponding position.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com