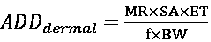Method for measuring contents of harmful organic chloride DCP (1,3-dichloro-2-propanol) of PAE (polyamide epichiorobydrin resin) wet strength agent in paper for daily use, and application of method
A technology of PAE wet strength agent and household paper, which is applied in the detection field, can solve the problems of concealing the actual risk index, high hidden dangers of operation safety, and complicated operation, so as to save the pretreatment operation, avoid the toxicity of the experiment, and the operation is simple and efficient Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
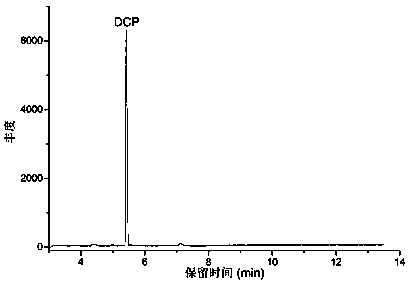
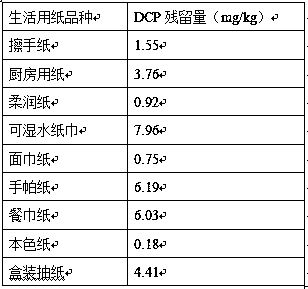
[0073] Example 1 Rapid Detection Method of Residues of Harmful Organic Chlorinated Compound DCP in PAE Wet Strength Agent in Tissue Paper
[0074] 1. Experimental method
[0075] (1) Sample preparation: Weigh 2.0 g of tissue paper, cut into small pieces of 5 mm × 5 mm, keep the sample as loose as possible, put it in a 20 mL headspace bottle, and press the bottle cap tightly.
[0076] (2) Solid-phase microextraction: Place the headspace vial containing the tissue sample prepared in step (1) in a manual extraction device equipped with a solid-phase microextraction needle for equilibrium adsorption. The equilibrium temperature is 45°C and the equilibrium time is 30 minutes. , adsorption for 45min.
[0077] (3) Preparation of standard solution: using water as solvent, dilute DCP standard (1,3-dichloro-2-propanol (DCP) standard, from Aladdin Reagent Co., Ltd.) to 250 mg / kg to prepare mother solution For use, add different volumes of mother liquor in the middle of 2.0g hand-sheets...
Embodiment 2
[0095] Example 2 Rapid detection method for the migratable amount of harmful organic chlorinated substance DCP of PAE wet strength agent in tissue paper
[0096] 1. Experimental method
[0097] (1) Sample preparation: Weigh 2.0g of tissue paper, cut into small pieces of 5mm×5mm, place them in a ground-mouthed conical flask with a stopper, and take 200mL of extraction solvent (distilled water and 0.9% normal saline respectively) in the Erlenmeyer flask. at 40 o C shaking water bath, extraction for 120 minutes. After standing and stratifying, take 4mL of the supernatant as the extract, put it in a 20mL headspace bottle, add 0.8g of analytically pure NaCl and press the bottle cap tightly.
[0098] (2) Solid-phase microextraction: Place the headspace bottle containing the extract prepared in step (1) in a manual extraction device equipped with a solid-phase microextraction needle for equilibrium adsorption. The equilibrium temperature is 45°C and the equilibrium time is 30 minu...
Embodiment 3
[0121] Embodiment 3 precision and accuracy experiment
[0122] The method established in Example 1 and Example 2 is used for standard addition recovery. First, 1.2 mg / kg DCP is added to the PAE-free hand-sheet as the target sample, and the method of Example 1 is used to detect the standard addition recovery of the target sample. The results are shown in Table 4 (the recovery rate of standard addition is 97.11~108.03%); followed by adding 7.5 μg / L DCP to the extract as the target sample, and the method of Example 2 is used to detect the standard recovery rate of the target sample, and the results are shown in the table 5 (the recovery rate of standard addition was 102.75-113.00%).
[0123] Table 4
[0124]
[0125] table 5
[0126]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com