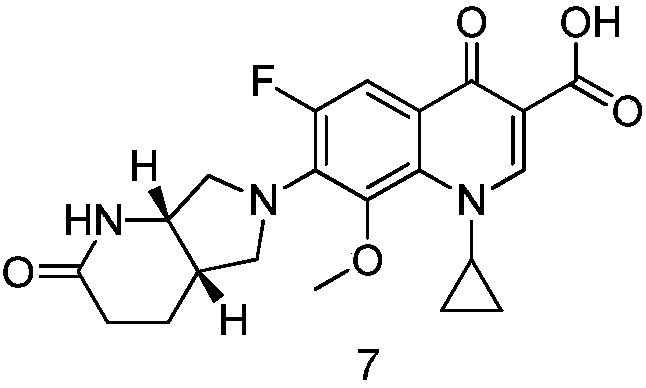
Method for synthesizing moxifloxacin degradation impurity
A synthesis method and impurity technology are applied in the field of synthesis of moxifloxacin degrading impurities, which can solve the problems of complex reaction product components, unsuitable for directional preparation, and no mention of synthesis methods, so as to meet the requirements of quality research and the starting materials Inexpensive and easy to obtain, easy to control the effect of process operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
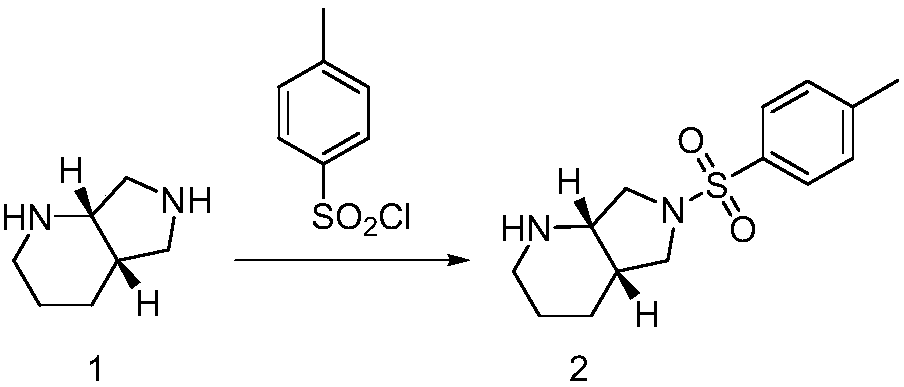
[0055] The preparation of embodiment 1 compound 2
[0056] Add 12.6g of (S,S)-2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]nonane (moxifloxacin intermediate, 1.0 equivalent) into 126ml of acetonitrile, then lower the temperature to 0°C~10°C, Add 9.8g (0.5 equivalents) p-toluenesulfonyl chloride in batches, add and keep warm for 2 hours, take a sample, and monitor by thin-layer chromatography (ethyl acetate:petroleum ether=1:3, volume ratio) shows that the raw materials have been reacted, Add 100 mL of water to quench, and extract with 100 mL of dichloromethane, wash the organic layer with water, wash with saturated brine, and concentrate to obtain a residual solid. 60 milliliters (ethyl acetate:petroleum ether=1:1, volume ratio) of mixed solvent was stirred and heated to 50-60°C to dissolve, then cooled and crystallized, suction filtered, and the filter cake was washed with 20mL petroleum ether to obtain 10.7 grams of white Solid, yield 75.3%. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 )δ=7.75-7.73(d,2H,Ph-H),7.33-7.32(d,...
Embodiment 2
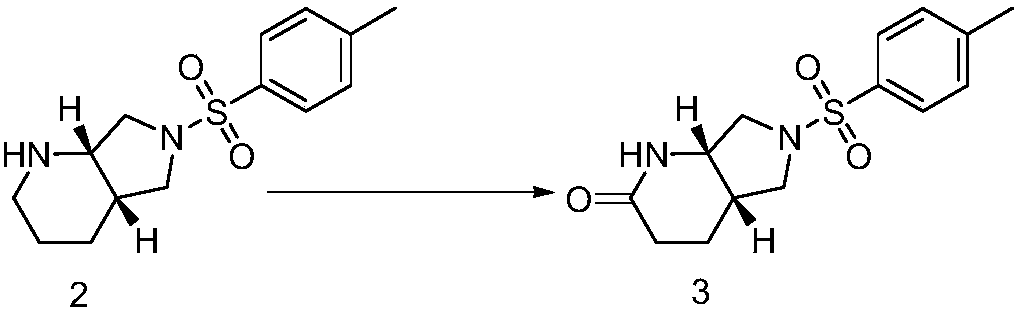
[0057] The preparation of embodiment 2 compound 3
[0058] Add 7g of compound 2 to 700mL of tetrahydrofuran, then add 350mL of purified water, add 21g of sodium bicarbonate, stir to dissolve, slowly add 47.4g of iodine, continue to stir at 25°C for 6 hours, then take a sample, add ethyl acetate and sodium thiosulfate Aqueous solution, organic phase thin-layer chromatography (ethyl acetate) to monitor the reaction, the raw materials disappeared, the reaction solution was concentrated at 40 ° C to remove the solvent, added 1.0 liter of ethyl acetate for extraction and 500 mL of sodium thiosulfate aqueous solution, separated, and the organic layer was washed with water , washed with saturated brine, and concentrated to obtain a residue that was pulped in a mixed solvent of 30 ml (ethyl acetate:petroleum ether=1:1, volume ratio) for 30 minutes to obtain 6.1 g of off-white solid with a yield of 72.2%. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 )δ=7.73-7.71(d,2H,Ph-H),7.35-7.37(d,2H,Ph-H),6.38(s,1H,NH),3.93-...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The preparation of embodiment 3 compound 4
[0060] Add 6g of compound 3 (6.0g, 0.042mol) to 40% hydrobromic acid (60ml), add acetic acid (15ml) and phenol (6.0g) under stirring, heat to 90°C and reflux for 8h, TLC [developer: chloroform -methanol (1:2, volume ratio), iodine color] shows that the reaction is completed and then cooled, followed by extraction with ethyl acetate (50ml×2). Add 40% sodium hydroxide solution to the water phase to adjust the pH to about 7, concentrate under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, and the residue is beaten with 60 mL of a mixed solvent of chloroform-methanol (1:2, volume ratio) for 30 minutes, then suction filtered and washed. After the filtrate was concentrated, the residue obtained was purified by silica gel column chromatography, methanol:dichloromethane=1:15 to 1:5 (volume ratio) was rinsed, and the target components were collected and concentrated to obtain 1.43g of a light yellow oil, which was collected. rate 50%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com