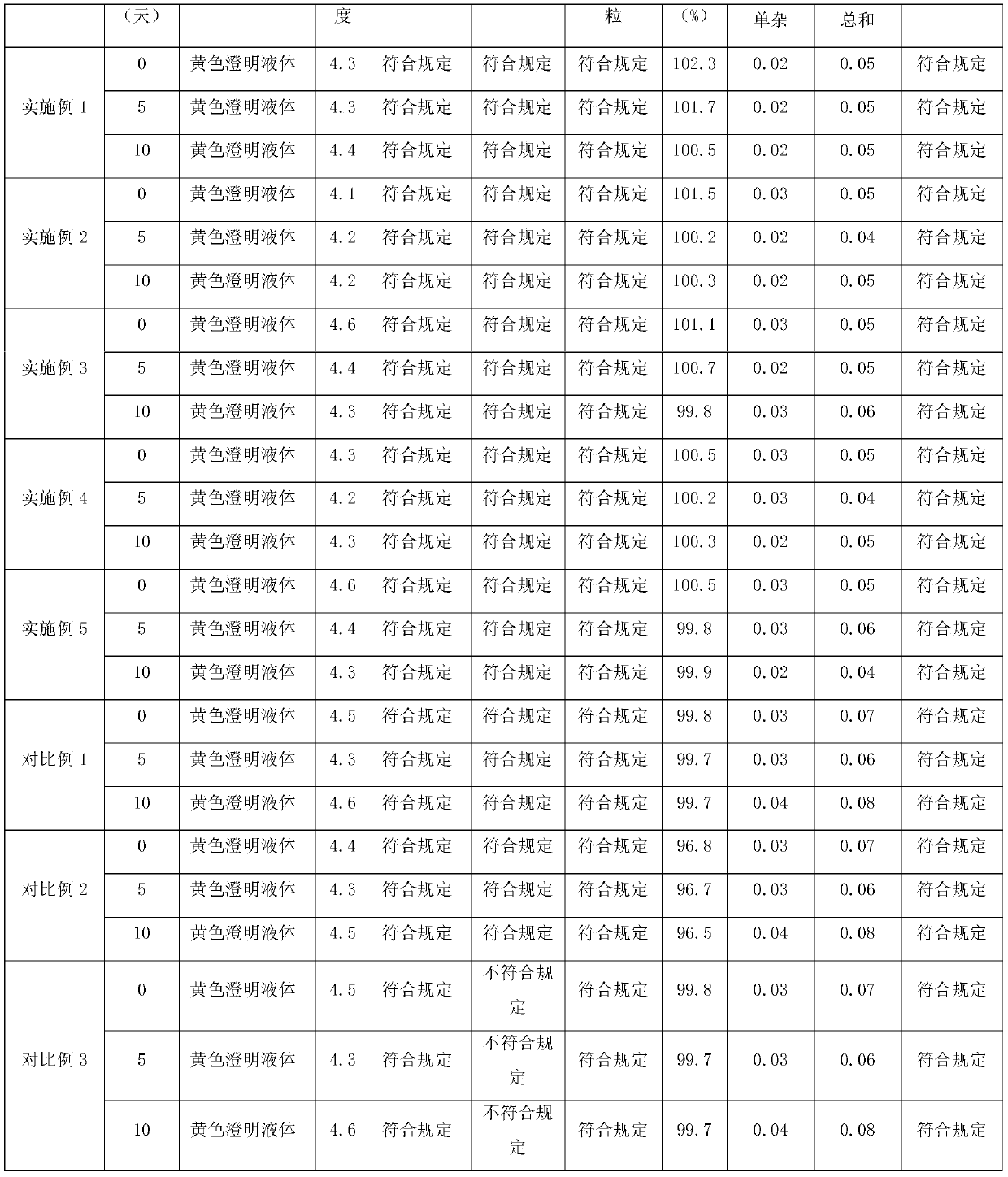
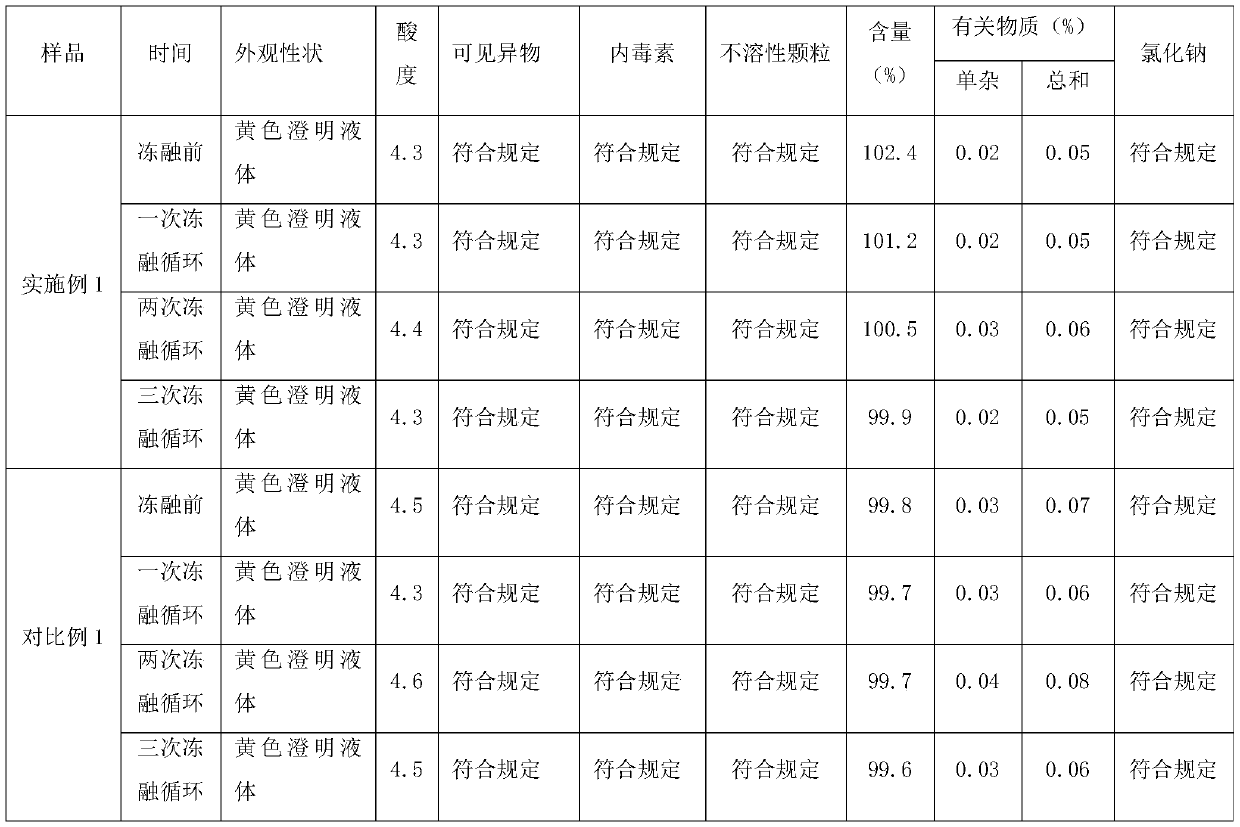
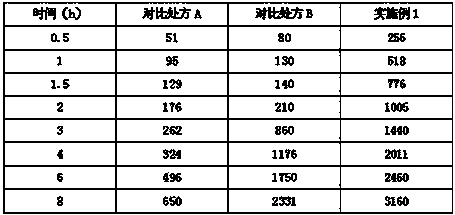
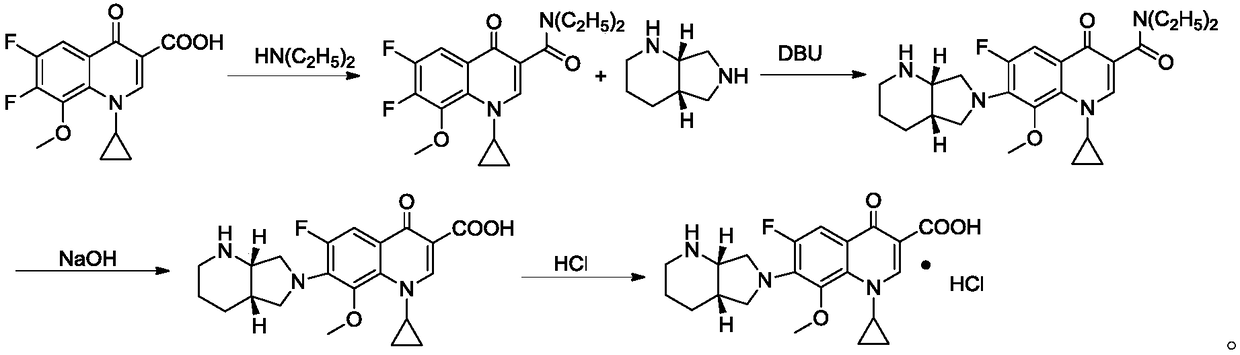
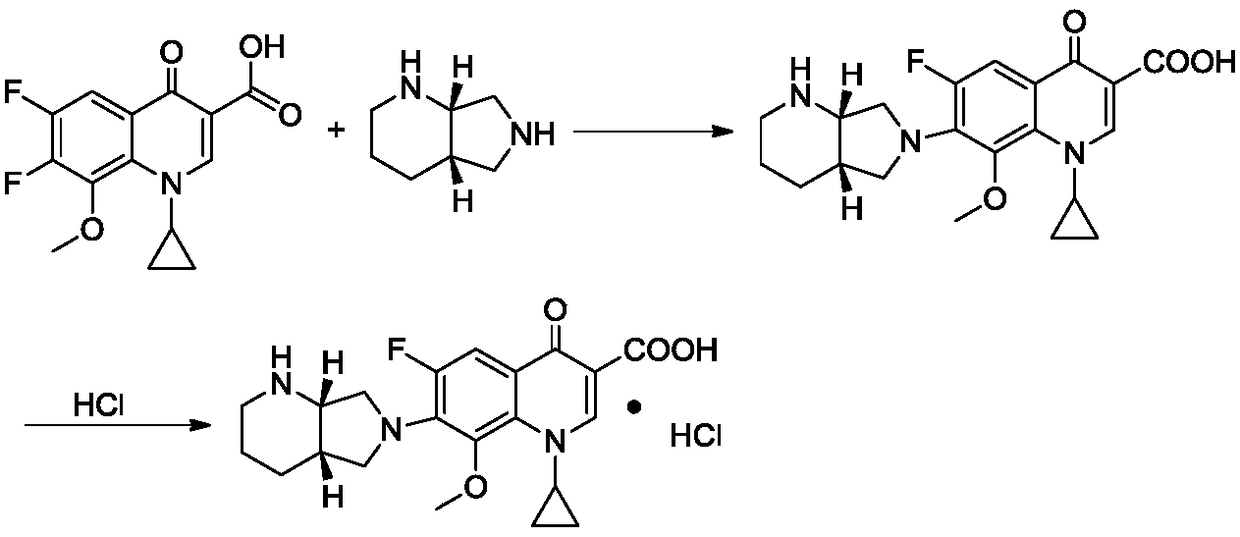
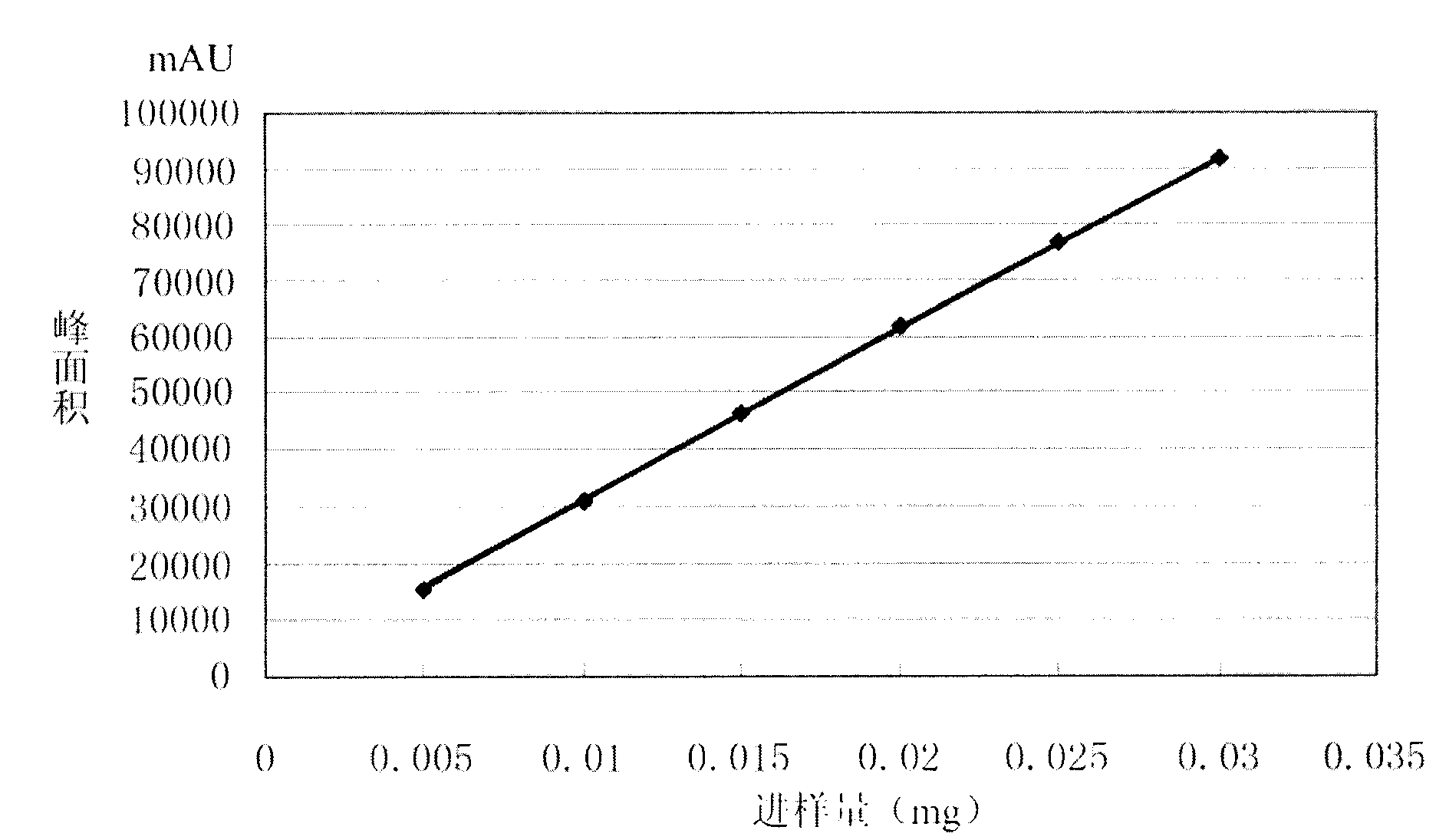Patents
Literature
105 results about "Cinoxacine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
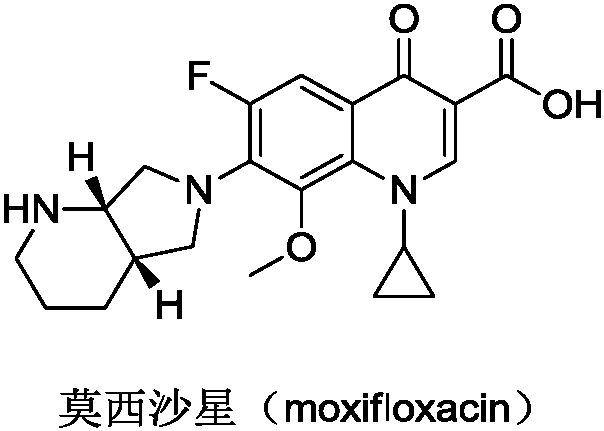
Moxifloxacin aqueous solution type injection
InactiveCN101732246AGood water solubilityImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsO-Phosphoric AcidMedicine
The invention discloses a moxifloxacin aqueous solution type injection which contains moxifloxacin or pharmaceutically acceptable salt, weak acid sodium salt or phosphoric acid sodium salt and water for injection, wherein the content of the moxifloxacin is 0.8-4 percent (g / ml), and the molar concentration of the weak acid sodium salt or the phosphoric acid sodium salt is 0.0002-1mol / L. The moxifloxacin aqueous solution type injection product has strong dissolubility, human body acceptable pH value, easier control of product quality, stability in a storage period, good compatibility with clinical common isotonic solution, low production cost, small volume and convenient transportation and storage.
Owner:SHANDONG BESTCOMM PHARMA CO LTD
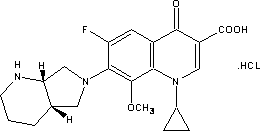
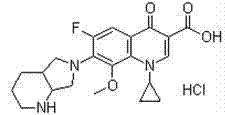
Preparation method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride
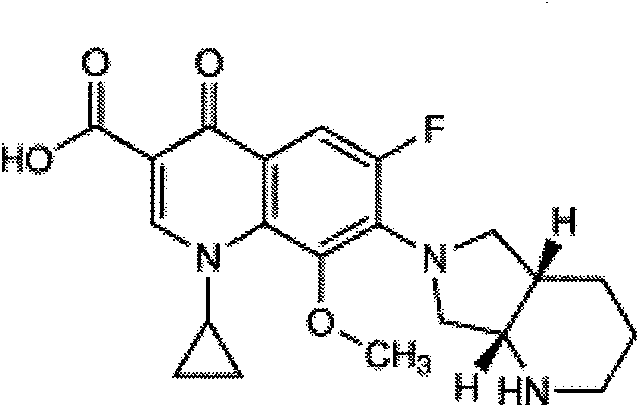
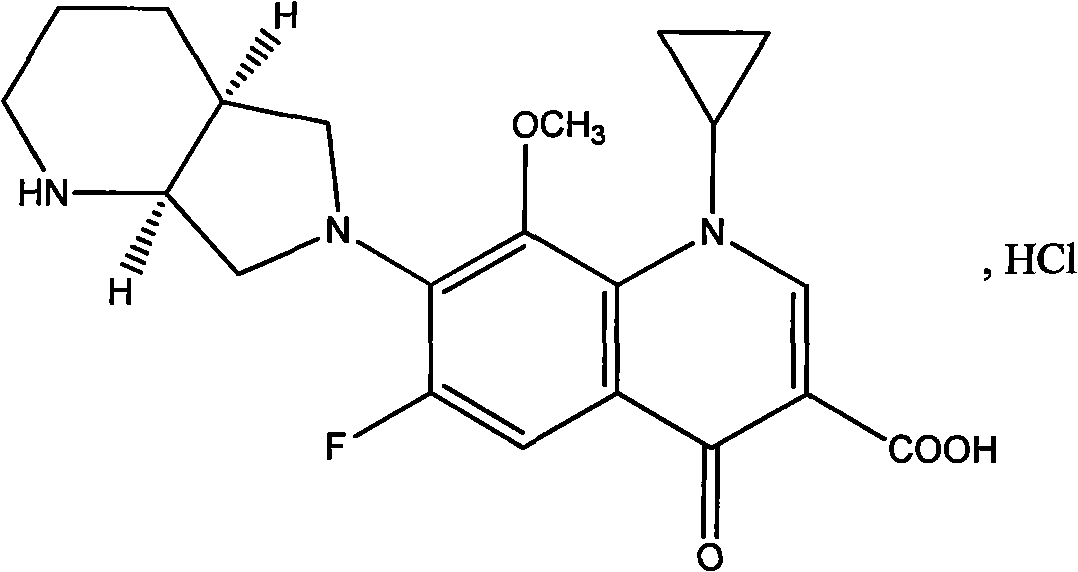
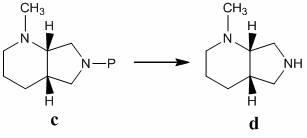
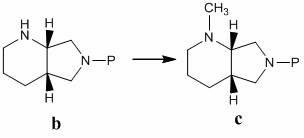
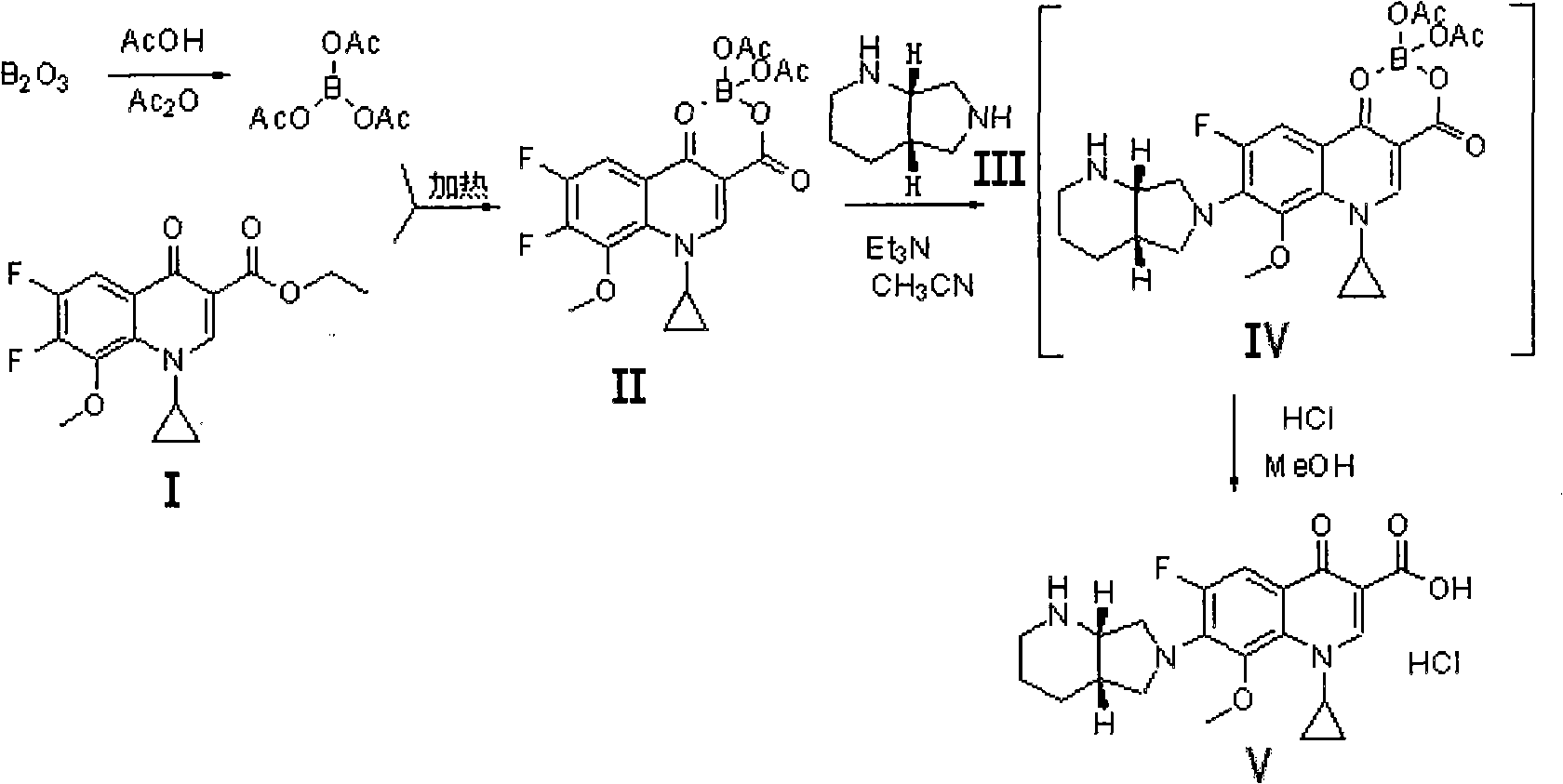
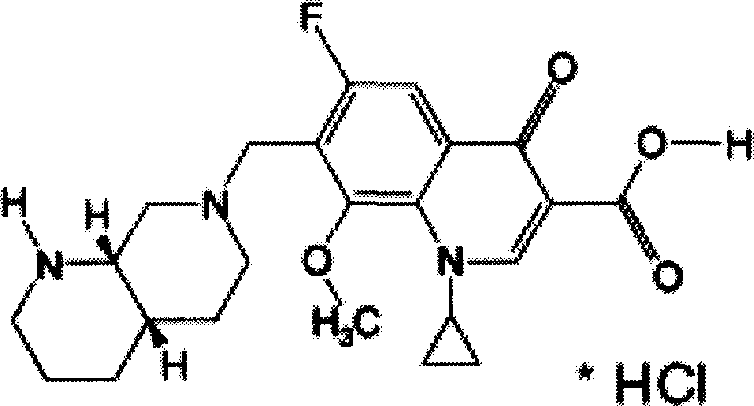
The invention discloses a preparation method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, comprising the steps of: reacting the 1-cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinoline carboxylic acid and the S,S-2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]nonane to prepare the moxifloxacin in the presence of organic base in organic solvent under the reaction temperature of 60 to 85 DEG C; separating the moxifloxacin, processing the moxifloxacin by concentrated hydrochloric acid in organic solvent under the reaction temperature of 60 to 85 DEG C to obtain the moxifloxacin hydrochloride.
Owner:JIANGSU CHIA TAI FENGHAI PHARMA
Method for performing industrialized production on moxifloxacin hydrochloride
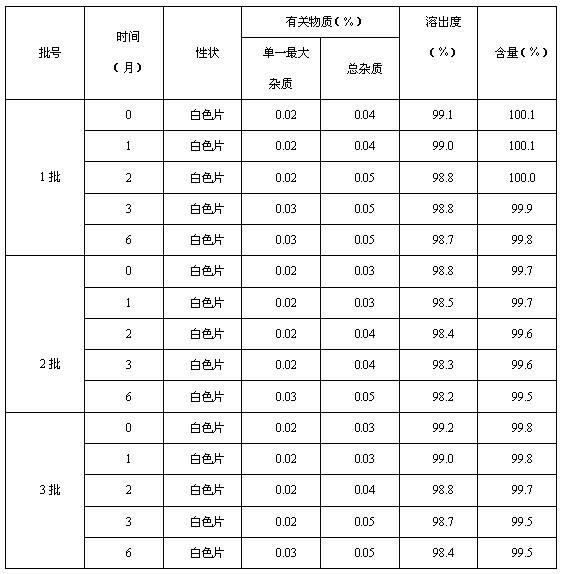
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The method is characterized in that: moxifloxacin hydrochloride is precipitated from solution according to solubility difference of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride in sodium chloride solution with different concentrations so as to fulfill the aim of separation. The method particularly comprises the following steps of: adding sodium chloride into moxifloxacin hydrochloride-containing aqueous solution; stirring to crystallize; filtering; drying; recrystallizing with water; filtering; and drying to obtain the moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The method is simple and convenient in operation; the product has high purity; a single impurity is less than 0.1 percent; the total impurities are less than 0.2 percent; and the method is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:NANJING YOKO PHARMA
Preparation method, detecting method and application of moxifloxacin hydrochloride impurity
ActiveCN104292158AThe preparation method is safeEasy to prepareOrganic chemistryComponent separationCinoxacineBiochemistry
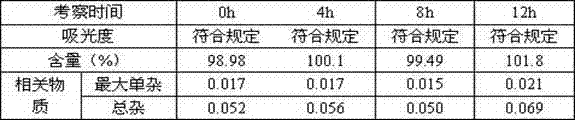
The invention discloses a preparation method and a detecting method of a moxifloxacin hydrochloride photodegraded impurity and an application of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride photodegraded impurity as an impurity reference substance during detection of a moxifloxacin hydrochloride related substance. Through the preparation of the compound, the reference substance is provided for analysis of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride related substance, so as to improve the quality standard of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, and provide important guidance significance for safe medication of moxifloxacin hydrochloride.
Owner:NANJING CHIA TAI TIANQING PHARMA
Preparation method of moxifloxacin impurity F
ActiveCN103396416AHigh purityShort synthetic routeOrganic chemistrySodium bicarbonateAlkaline hydrolysis
The invention discloses a preparation method of moxifloxacin impurity F. The method comprises the following steps of: alkalifying moxifloxacin hydrochloride with sodium bicarbonate solution to get moxifloxacin free alkali, treating the moxifloxacin free alkali with methylation and alkaline hydrolysis reaction, and finally, obtaining high-purity moxifloxacin impurity F by recrystallization. The preparation method has the characteristics that the synthetic routes are simple and short, operations are simple and convenient, the obtained impurity product has higher purity, and the preparation method can be used for moxifloxacin impurity reference substance research, and so on.
Owner:NANJING YOUKE BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL RES +2
Preparation method for moxifloxacin and hydrochloride thereof
ActiveCN103012452AAvoid thermal effectsQuality assuranceGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsAcetic anhydrideIce water
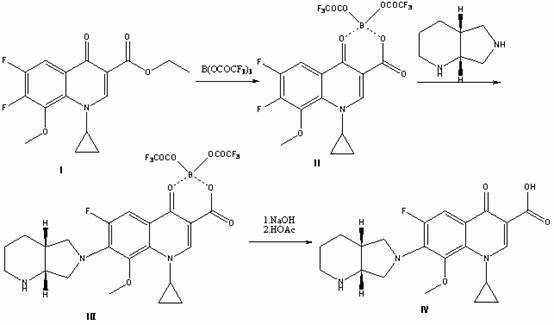
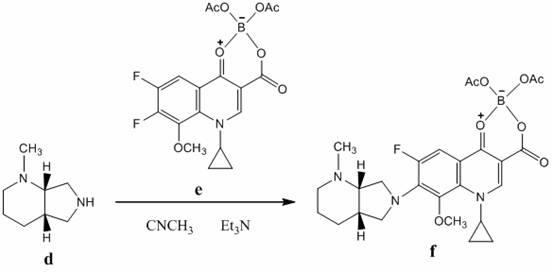
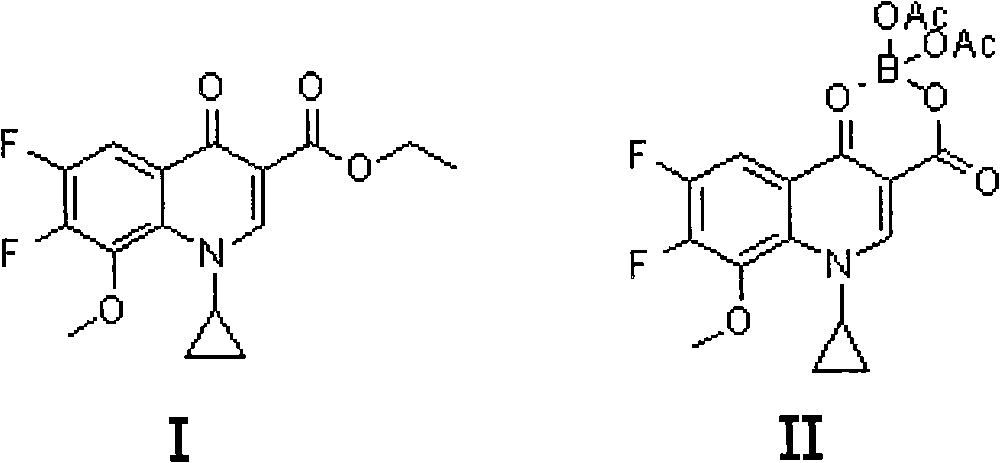
The invention discloses a preparation method for moxifloxacin and hydrochloride thereof. A conventional process has the following defects that a one-pot material addition process has safety hidden troubles such as bumping materials and explosion which are caused by suddenly increased temperature, and a great amount of wastewater is produced because ice water is employed in a separation process of a borane chelate to perform crystallization process to separate the chelate. The method provided by the invention is characterized in that in a chelating reaction, solid boric acid is added in acetic anhydride in a continuous feeding manner to form a chelating agent through reaction, the chelating agent reacts with 1-cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-8-methoxyl-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo quinoline-3-ethyl carboxylate to prepare the borane chelate, and the borane chelate is purified through crystallization and separation by using an organic solvent. The preparation method is simple in process, mild in conditions and safe in the chelating reaction process and solves the problem of the great amount of the wastewater in a preparation process of the chelate. The method has high yield, good selectivity and high product purity and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU CO LTD
Preparation method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride
The invention relates to a preparation method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, which comprises the steps of: making 1-cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-8-methoxyl-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylate-03,04-broron ester acetate and (S,S)-2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0] nonane as raw materials completely react in a solvent, then cooling, adding hydrochloric acid, regulating the pH value to 4-6, stirring and crystallizing for more than 10 minutes, then adding the hydrochloric acid, regulating pH value to 0.5-2, cooling to 0-40 DEG C, crystallizing, leaching, washing, and drying to prepare the moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process, low cost, high yield and high purity, and is more suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:SICHUAN GOWELL PHARMA
Water-soluble salt of aspartic acid carbostyril series antibacterial drugs and injection dosage forms thereof
The invention provides an aspartate quinolone antibiotics water-soluble salt and the injection formulation thereof, including sparfloxacin, gatifloxacin, rufloxacin, pefloxacin, tosufloxacin, moxifloxacin, and so on; the invention improves the water solubility of quinolone antibiotics and enhances the anti-bacterial effect of quinolone antibiotics. Compared with the oral liquid of quinolone drugs of the prior art, the invention has the advantages that: water solubility of the drug is good, as the drug enters the blood directly, the invention can not only achieve treatment function rapidly, but can also be absorbed by the human body fully, and the invention has significant effects in the two aspects of fast onset of action and low consumption. Compared with the injection of the quinolone drugs of the prior art, the invention has the advantages that: due to the existence of the L-aspartate, the antibacterial activity of quinolone drugs can be enhanced.
Owner:SHENYANG WOSEN PHARMA INST
High selectivity method for synthesizing moxifloxacin
ActiveCN102351858AAvoid it happening againSimple processing methodOrganic chemistryAcetic anhydrideIce water
The invention discloses a high selectivity method for synthesizing moxifloxacin. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting boric anhydride with trifluoro acetic anhydride to obtain a chelant; reacting 1-cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester with the chelant, cooling to room temperature, adding ice water, performing suction filtration, and washing a filter cake with water until neutrality to obtain a 1-ethyl-7-chloro-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester trifluoroacetic anhydride boronized chelate; and reacting the 1-ethyl-7-chloro-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester trifluoroacetic anhydride boronized chelate with (S,S)-2,8-diazabicyclo[4,3,0]nonane to obtain a 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-([S,S]-2,8-diazabicyclo[4,3,0]nonane-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester trifluoroacetic anhydride boronized chelate, recycling a solvent under reduced pressure, adding alkali, refluxing, discoloring, filtering, freezing, performing suction filtration, and drying a filter cake. The method is simple, mild in conditions, and high in selectivity, avoids difficultly separated impurities, is high in reaction yield and product purity, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LEPU PHARMA CO LTD
Salt of carbostyril formic acid compound as well as preparation method and application of salt
ActiveCN102584819ARealize determinationEasy to separateOrganic chemistryComponent separationQuinoloneCinoxacine
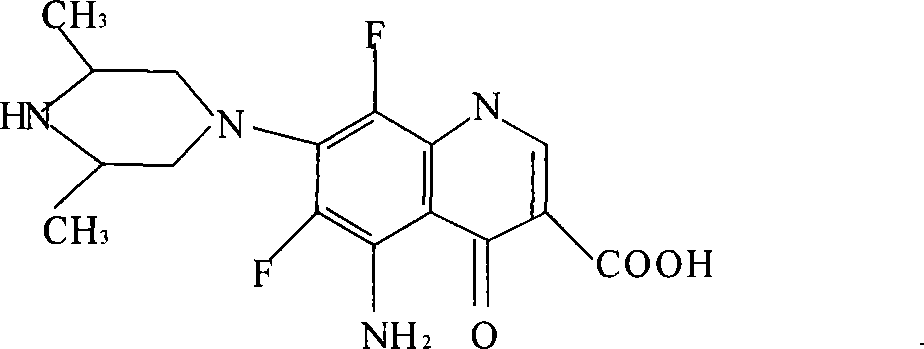
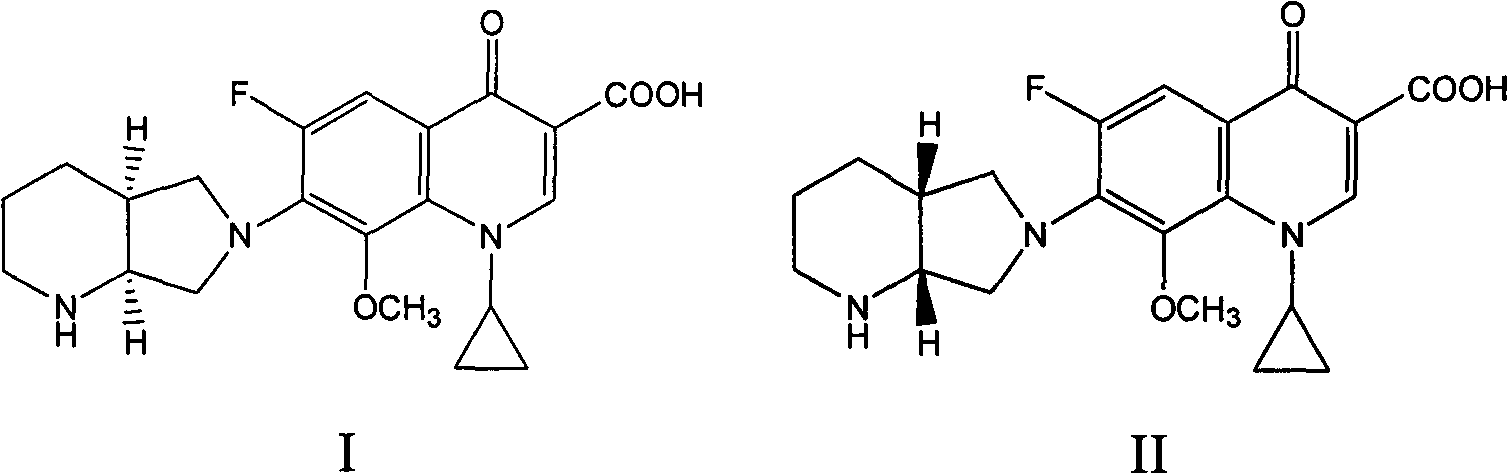
The invention relates to an N-methylated 8-methoxyl carbostyril formic acid compound, acid addition salt or alkali metal salt shown in the formula I, as well as a preparation method and an application in quality detection and analysis of moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The compound or salt thereof is taken as an impurity reference substance, and moxifloxacin hydrochloride is detected and analyzed through an external standard method, so that moxifloxacin hydrochloride raw materials produced industrially and the impurity possibly contained in a preparation can be controlled quantificationally, further the quality of moxifloxacin hydrochloride can be increased, and the security in clinical medication can be improved. The formula I is shown in the description.
Owner:NANJING YOUKE BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL RES +2
Topical ophthalmic or otic solution formulations containing moxifloxacin hydrochloride and dexamethasone phosphate
Topical ophthalmic and otic solution compositions of moxifloxacin and dexamethasone phosphate are disclosed.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method for preparing moxifloxacin or its medicinal salt and its intermediate
ActiveCN102617622AReduce harmLight colorGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsAcetic acidAcetic anhydride
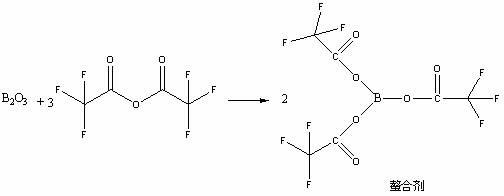
The invention provides a novel method for preparing moxifloxacin or its medicinal salt and its intermediate, which comprises the following steps: dissolving boron trioxide in a certain amount of acetic anhydride and an acetate mixing solution, reacting under the temperature of 90-120 DEG C, cooling a reaction solution; adding cyclized quinolinecarboxylic ester in the reaction solution and reacting at the reaction temperature of 50-80 DEG C, cooling, adding a certain amount of an ether solvent, stirring and then filtering, washing by the ether solvent, drying to obtain the product; reacting with (4aR, 7aR)-octahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine to obtain the moxifloxacin or its medicinal salt. The reaction method of the invention is mild and controllable, the common equipments enable production, the obtained product has the advantages of high purity and good color, boron oxide substitutes boric acid for chelating to reduce the damage of equipments and human body caused by acid mist in the reaction.
Owner:SHENZHEN SALUBRIS PHARMA CO LTD
Stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride medicinal composition
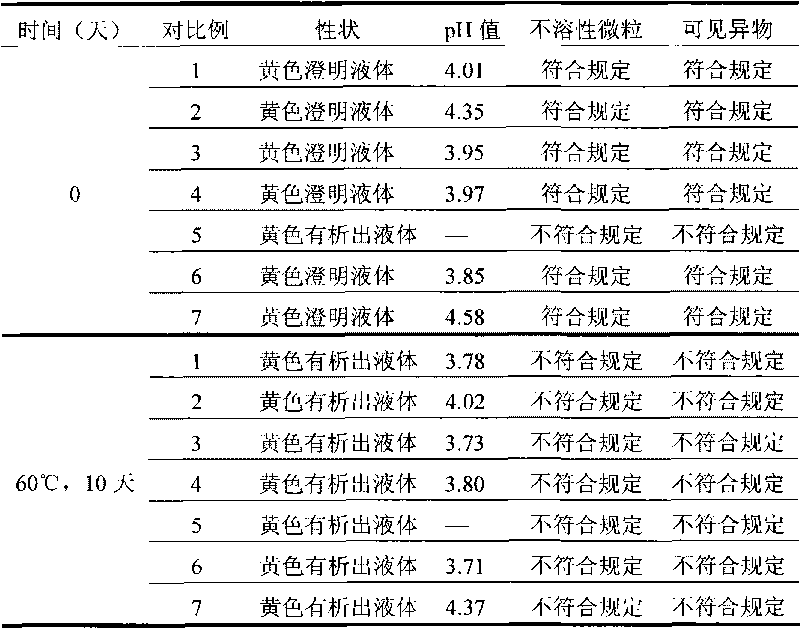
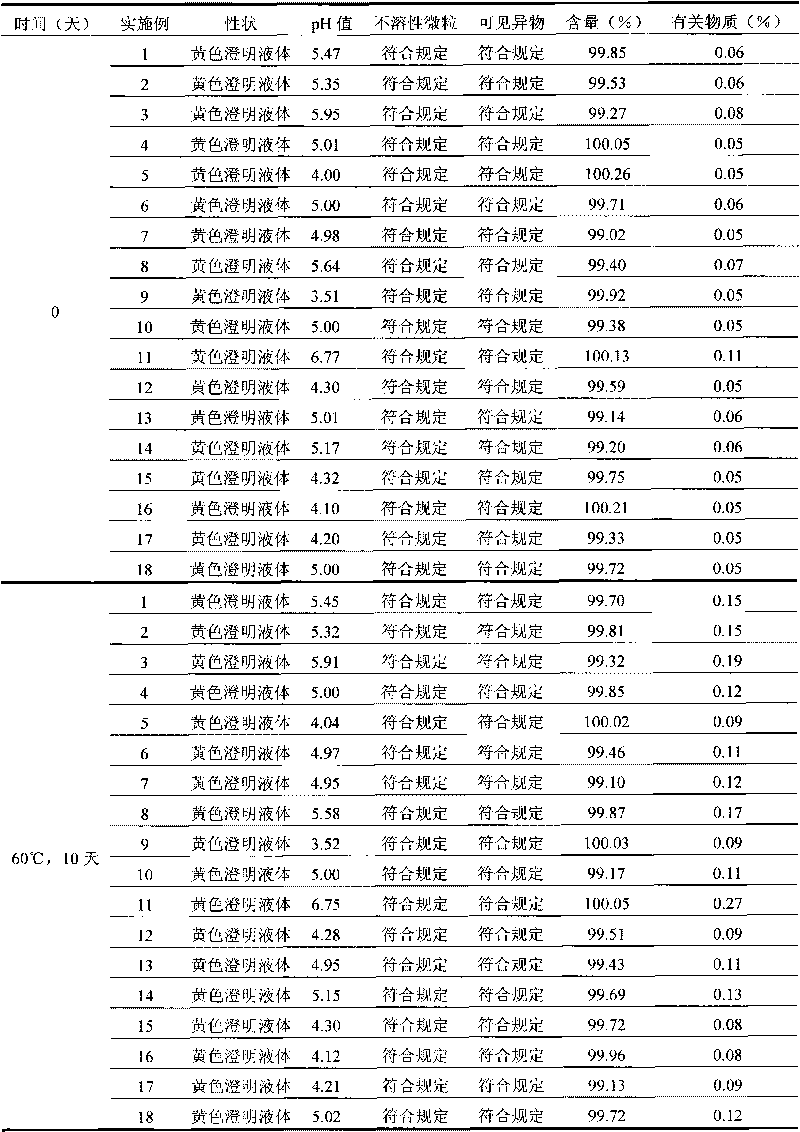
InactiveCN102525982ASolve the problems of poor stability and slow dissolutionHigh yieldAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCinoxacineCyclodextrin
The invention discloses a stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride medicinal composition and a preparation method thereof. The stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride medicinal composition consists of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, hydroxypropyl betacyclodextrin, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose 12 and magnesium stearate. The stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride medicinal composition is high in stability, has the obvious advantages of improving the yield of products, reducing cost and implementing industrialization and is better applied clinically, and preparations of the stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride medicinal composition have high stability.
Owner:TIANJIN HANKANG PHARMA BIOTECH
Moxifloxacin analogue as well as preparation method and application thereof
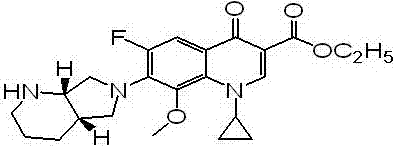
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a moxifloxacin analogue Y shown in a figure. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking moxifloxacin as a raw material, firstly protecting a protection group on a secondary amino group on a 7-position side chain, then performing acyl chlorination and ethyl ester esterification on a 3-bit carboxyl group and removing an amino-group protective agent to obtain the moxifloxacin analogue Y. The preparation of the analogue Y provides a reference substance for moxifloxacin hydrochloride-related substances.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANYISHI PHARMA
Moxifloxacin capsule and its preparation method
ActiveCN1762358AHigh dissolution rateDissolution stabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHydroxypropylmethyl celluloseEthyl cellulose
The invention provides a Moxifloxacin capsule, which comprises Moxifloxacin or its salts and / or hydrate, at least a disintegrating agent and at least a lubricating agent, the shell of the capsule contains hydroxy propyl ethyl cellulose. The invention also discloses the process for preparing the capsule.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANYISHI PHARMA
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride-containing pharmaceutical composition and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103301080AMeet the requirements of bioavailability not limited by dissolutionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCinoxacineMannitol
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing 9%-40% of mannitol moxifloxacin hydrochloride and / or other hydrates, at least one diluent, at least one disintegrating agent and at least one lubricant and a preparation method thereof. Moxifloxacin hydrochloride tablets prepared according to a formula have the advantages of bioavailability without dissolution limitation, satisfied fragility, good liquidity and production feasibility.
Owner:SICHUAN GOWELL PHARMA
Medicinal composition for treating ophthalmic inflammation and application thereof
The invention discloses a Chinese medicinal composition for treating ophthalmic inflammation, which consists of collagen and Chinese medicaments for resisting bacterium and diminishing inflammation, and belongs to the field of pharmacy. Raw material medicaments of effective components of the medicinal composition comprise collagen and medicaments for resisting bacterium and diminishing inflammation such as erythrocin, ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin, levofloxacin and the like which are prepared into various eye preparations by combining the prior art. The technical scheme creatively combines and applies the collagen and the effective components of the medicaments in the eye preparations so as to enlarge the application range of the collagen and achieve remarkable effect in the aspect of treating various ophthalmic inflammations.
Owner:BEIJING HERUN INNOVATION PHARMA TECH DEV
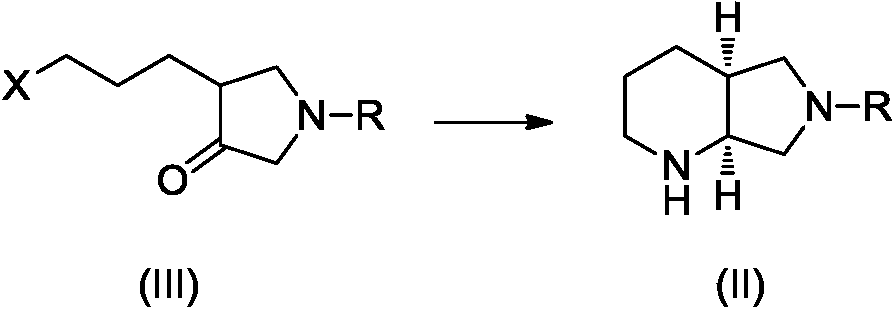
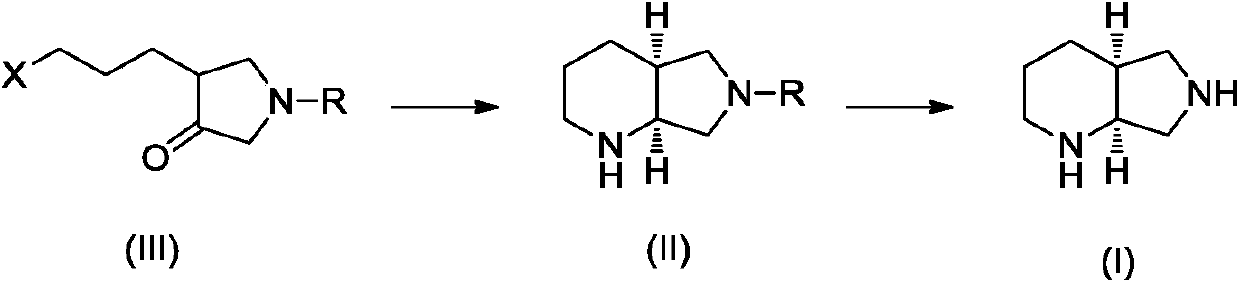
Preparation method of moxifloxacin intermediate compound
The invention discloses a preparation method of a moxifloxacin intermediate compound. The preparation method comprises the following step of under the actions of omega-transaminase and / or immobilizingtype thereof and ammonia donor, performing the following ammonia conversion reaction on a compound shown in a formula (III) in a solvent, so as to prepare a compound shown in a formula (II), whereinan amino acid sequence of the omega-transaminase is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2 or SEQ ID NO.3 in a sequence table; X is chloride, bromine, iodine, methanesulfonate or tosylate; R is C1-4 carbalkoxy, carbobenzoxy or benzyl. The preparation method has the advantage that the cost is low, the fewer steps are required, the operation is simple, the ee value of a product reaches 99% or above, andthe preparation method is more suitable for industrialization production. (The formulas are shown in the attached figures.).
Owner:SHANGHAI PUYI CHEM CO LTD
Strong solution-type moxifloxacin hydrochloride injection and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102895178AImprove solubilitySubstance increaseAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCinoxacinePharmaceutical medicine
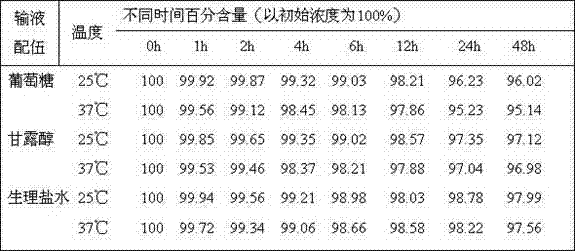
The invention relates to a strong solution-type moxifloxacin hydrochloride injection containing a non-sulfur-containing amino acid or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and preparation method thereof. The solvent used in the strong solution-type moxifloxacin hydrochloride injection is smaller in dosage, with better security, and simultaneously has a more significant effect for improving solubility and stability of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride strong solution; the quality of prepared injections is more stable; and preparation process is simple, and easy to operate.
Owner:CHENGDU GUOHONG PHARMA
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride sodium chloride injection and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111388415AAvoid adsorptionGuaranteed validityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCinoxacineSodium Chloride Injection
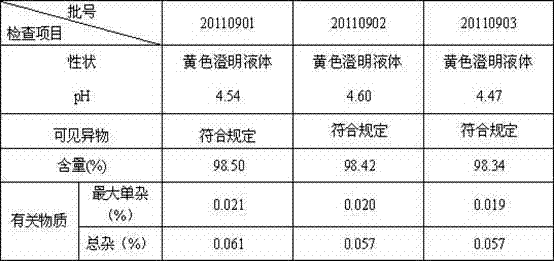
The invention relates to the technical field of pharmaceutical preparations, and particularly discloses a moxifloxacin hydrochloride sodium chloride injection and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding moxifloxacin hydrochloride, sodium chloride and a pH regulator into water for injection, stirring for dissolving, filtering through 3 or 4 groupsof polyether sulfone filter elements with sequentially reduced pore diameters, performing filling, and sterilizing to obtain the moxifloxacin hydrochloride sodium chloride injection. The injection provided by the invention is stable in batch content, low in related substance content, high in effectiveness and safety and good in stability.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG NO 4 PHARMA
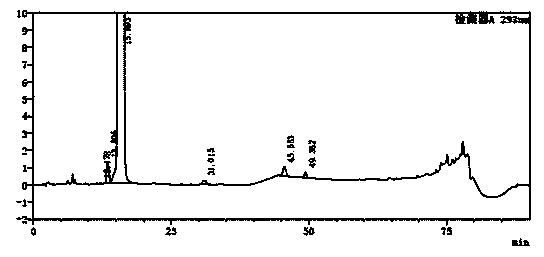
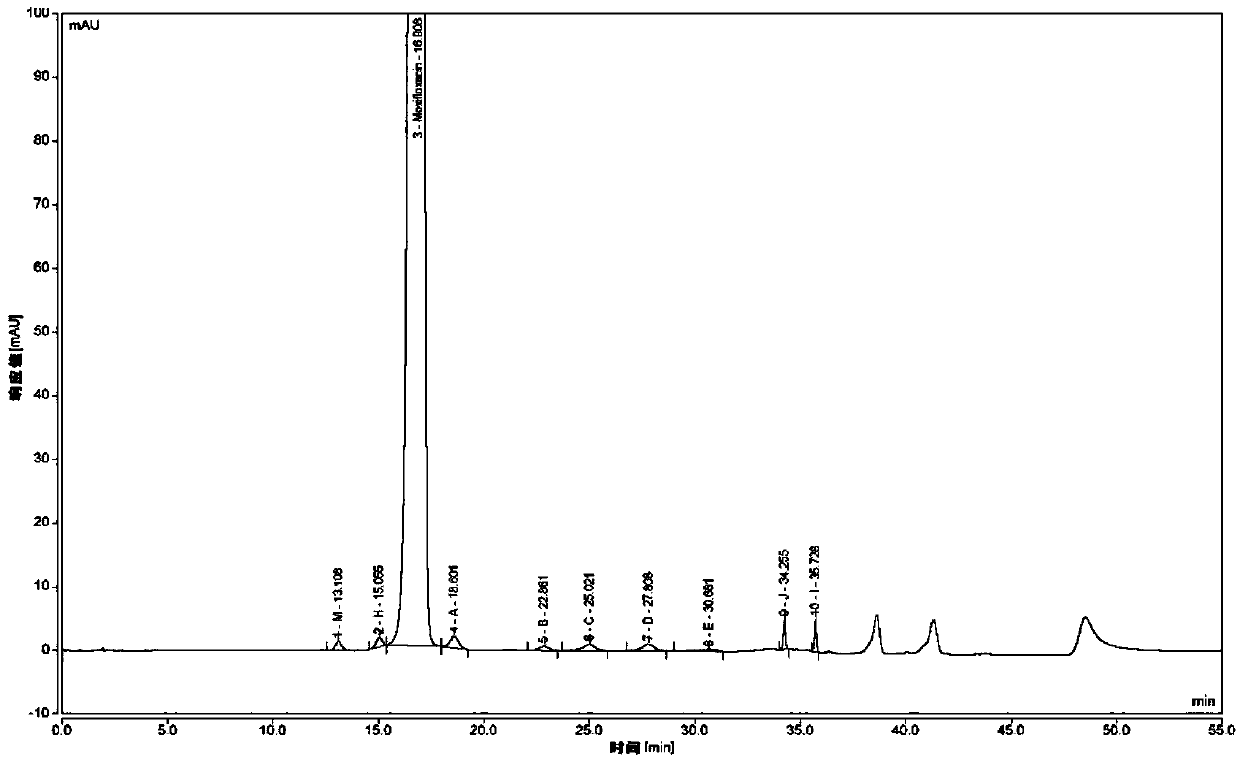
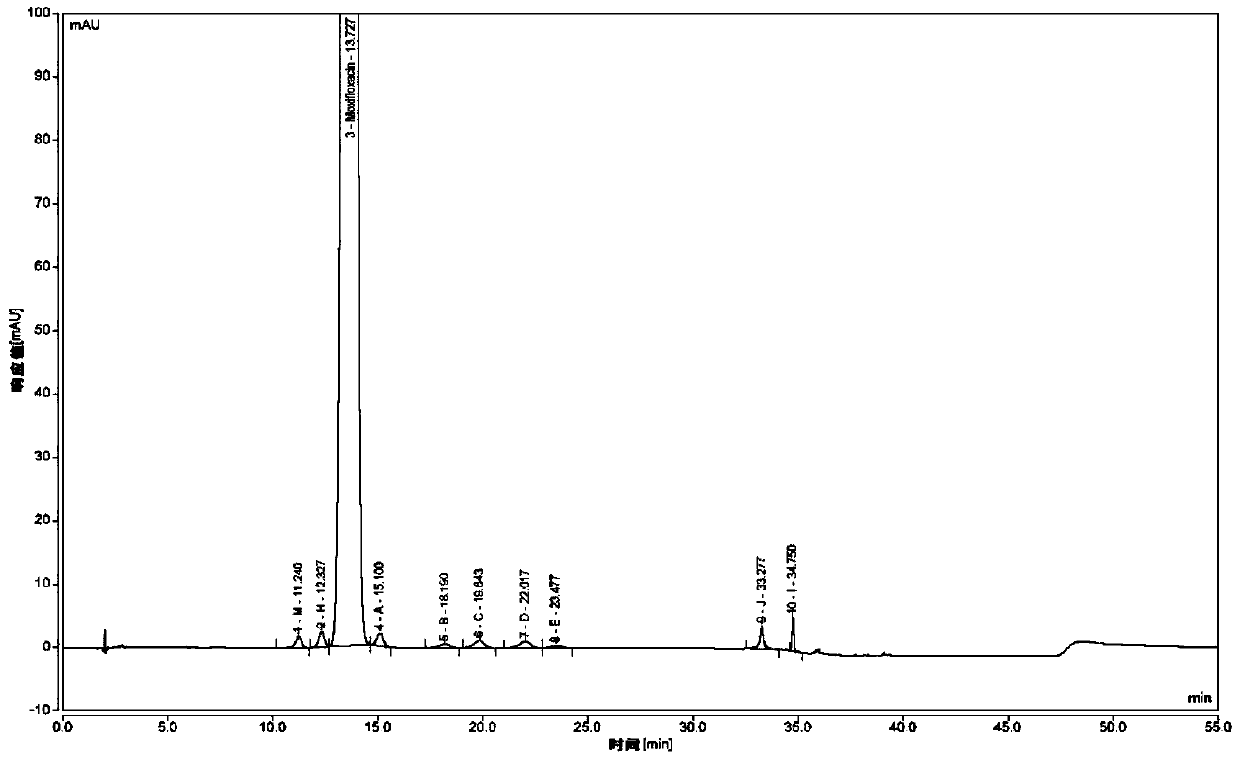
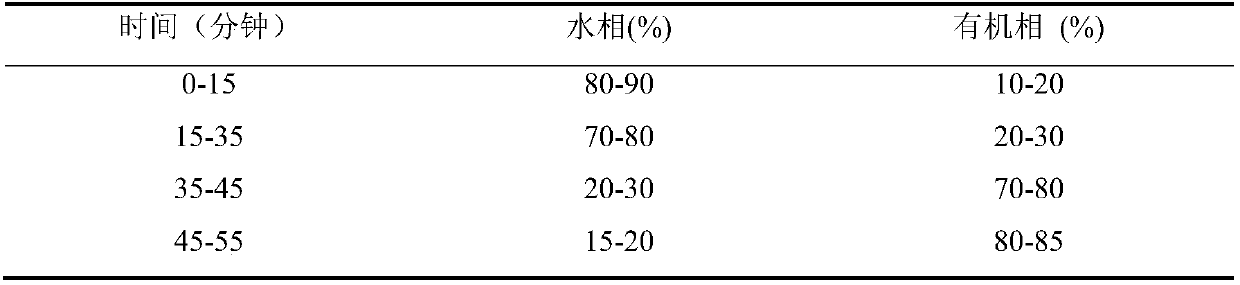
Method for separating moxifloxacin hydrochloride and impurities thereof by high performance liquid chromatography
ActiveCN111024831ASeparation advantageComponent separationAgainst vector-borne diseasesGradient elutionSilica gel
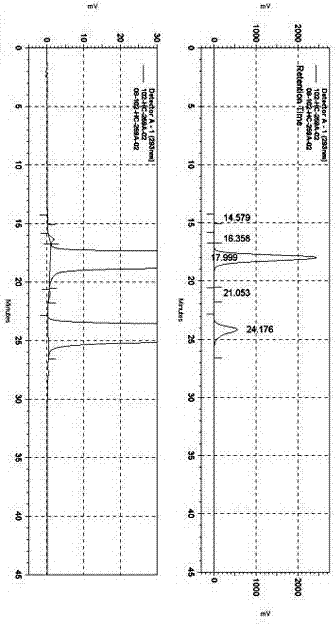
The invention discloses a method for separating moxifloxacin hydrochloride and impurities thereof by high performance liquid chromatography. The method comprises the following steps: taking alkyl bonded silica gel or phenyl bonded silica gel as a filler; wherein a mixed solution of a water phase and an organic phase is used as a mobile phase, the water phase is an aqueous solution of fluorinated organic acid, and the organic phase is methanol or acetonitrile; gradient elution is performed; the method has good specificity, linearity and system durability, can be used for detecting nine impurities including impurities A, B, C, D, E, H, I and J and an impurity M introduced in the moxifloxacin hydrochloride synthesis process, and has certain practicability.
Owner:JIANGSU CHIA TAI FENGHAI PHARMA
Double-layer moxifloxacin suppository and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102008431AAvoid destructionAvoid side effectsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSide effectIrritation
The invention discloses a double-layer moxifloxacin suppository and a preparation method thereof, which aim to provide a locally-applied suppository with quick response, good curative effect, nonirritant and minimal side effect. The double-layer suppository is divided into an inner layer and an outer layer, wherein the outer layer is a quick-release part which is quickly released to quickly reach optimal blood concentration; and the inner layer is a sustained-release part which is actually an ordinary-release part not subjected to sustained-release treatment. The double-layer moxifloxacin suppository is applied from the vagina so as to avoid the damages of first pass effect of the liver to oral medication and the toxic or side effect of systemic administration, and make the effective medicament concentration of a local lesion greatly exceed levels obtained by oral medication and injection, has long effective duration and the curative effect remarkably better than that of the systemic administration, and is applied to the treatment of vaginitis caused by the infections of staphylococcus aureus, Chlamydia and the like.
Owner:北京化药科创医药科技发展有限公司
Preparation method of moxifloxacin intermediate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a moxifloxacin intermediate 6-benzyl-octahydro-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine (as shown in formula I). The preparation method is to adopt an NaBH4 / H2SO4 reducing system to reduce 6-benzyl-hexahydro-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridine-5,7-dione (as shown in formula II), so as to obtain the target product. The method can be processed at normal temperature and normal pressure to take reaction with high total recovery; the raw material is cheap, easy to get, and easy to store; the operation is simple; the safety is high.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
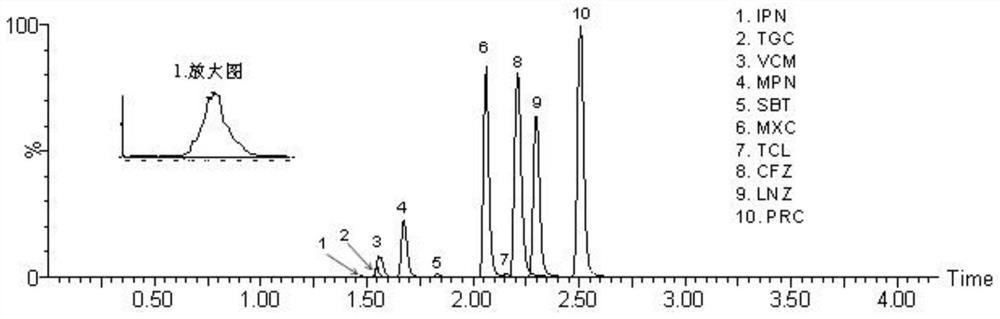
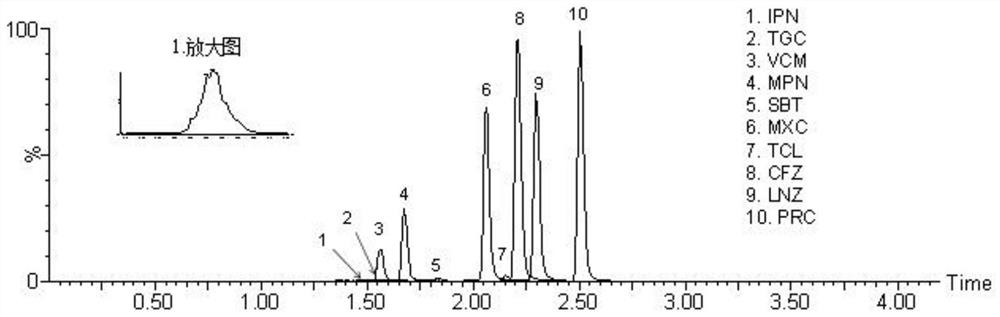
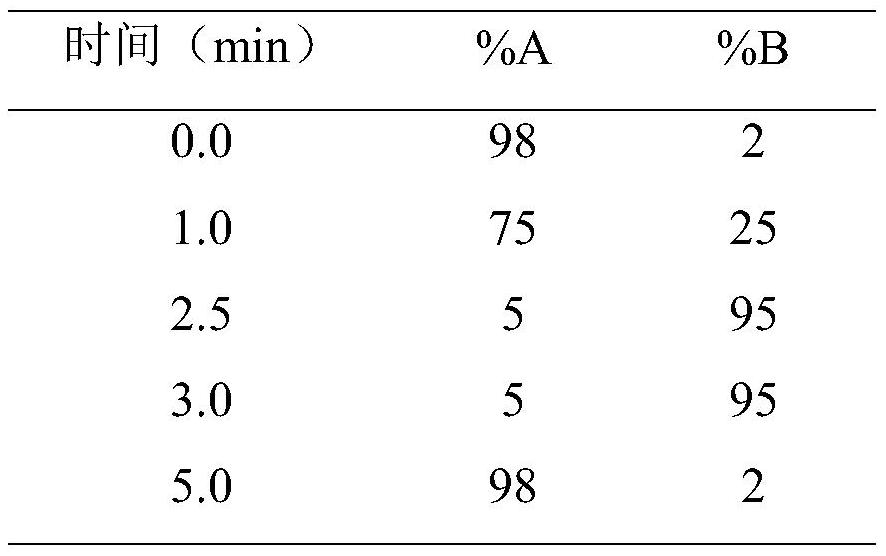
Method for detecting antibacterial agent in serum by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry technology
The invention discloses a method for detecting an antibacterial agent in serum by an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry technology. The antibacterial agent containssulbactam (SBT), imipenem (IPN), linezolid (LNZ), melopenem (MPN), moxifloxacin (MXC), piperacillin (PRC), tigecycline (TGC), cefoperazone (CFZ), vancomycin (VCM) and teicoplanin (TCL). The method comprises the steps: detecting the content of the antibacterial drug in the pretreated serum by adopting an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method, quantifying by utilizing a mass spectrometry isotope internal standard method, establishing a calibration curve by taking the concentration ratio of a standard substance to an internal standard substance as an X axisand the peak area ratio of the standard substance to the internal standard substance as a Y axis, and calculating the concentration of a target drug in the serum. According to the method, the pretreatment process is simple, the sensitivity is high, the specificity is high, separation and detection of the antibacterial agent are completed within 5 min, and a reliable detection method is provided for monitoring the treatment concentration of the antibacterial agent clinically.
Owner:南京品生医学检验实验室有限公司
Stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride compound
The invention discloses a stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride compound. The moxifloxacin hydrochloride compound provided by the invention is prepared through the steps that: moxifloxacin hydrochloride is heated and dissolved in an ethanol-acetonitrile-water solution; proper amounts of potassium nitrate and hydrochloric acid are added to the solution; the pH value is regulated; the solution is stirred, and is washed by using ethanol; the solution is dried, such that the stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride compound is obtained. The stability of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride compound provided by the invention is good, and the compound is convenient to produce, transport, and store. A production technological process is short, the product yield is high, and the production cost is low. Therefore, industrialization can easily be realized.
Owner:天津汉嘉医药科技有限公司
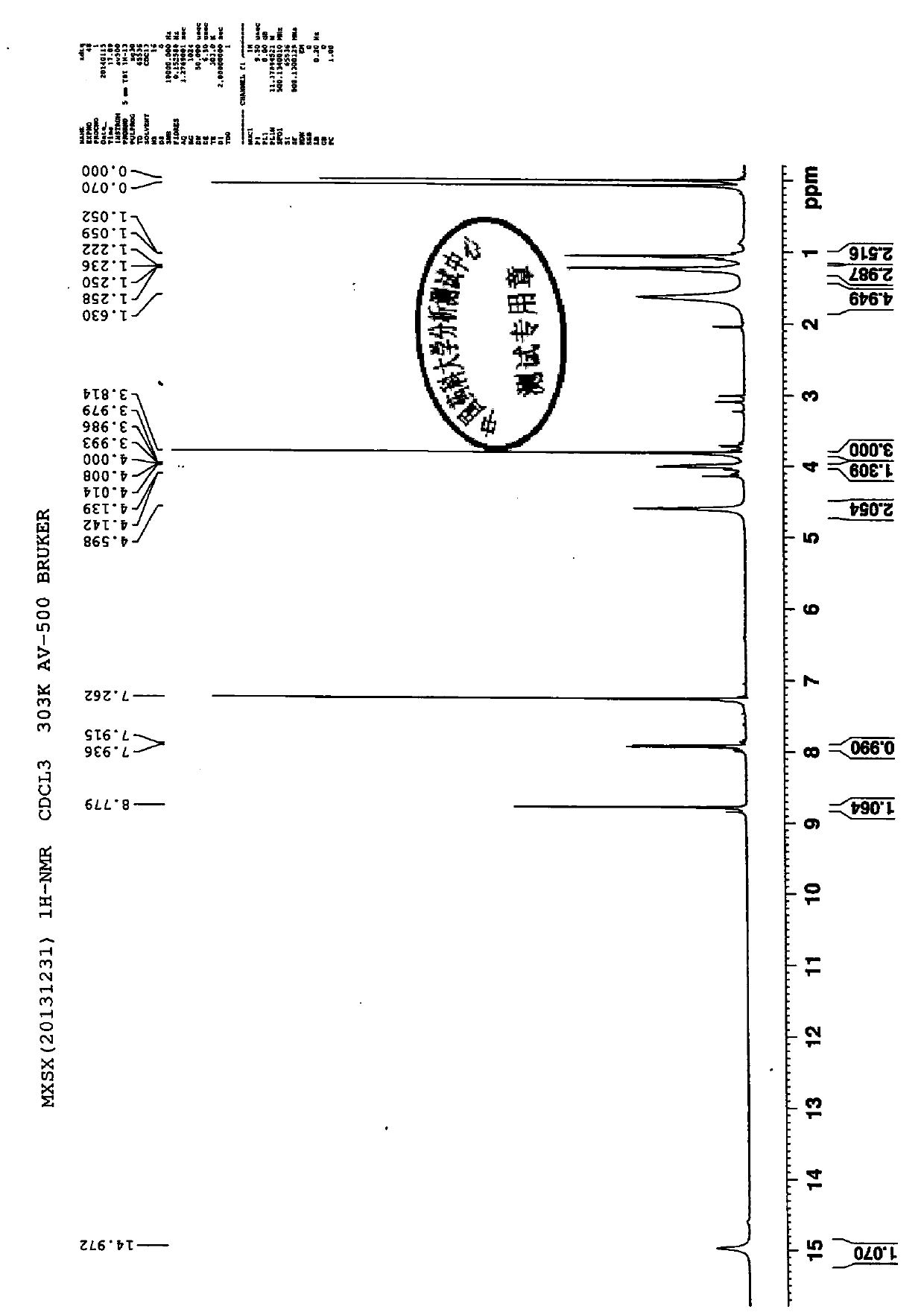
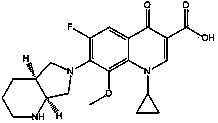
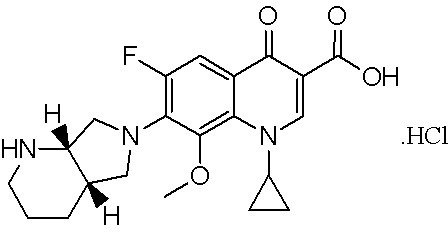
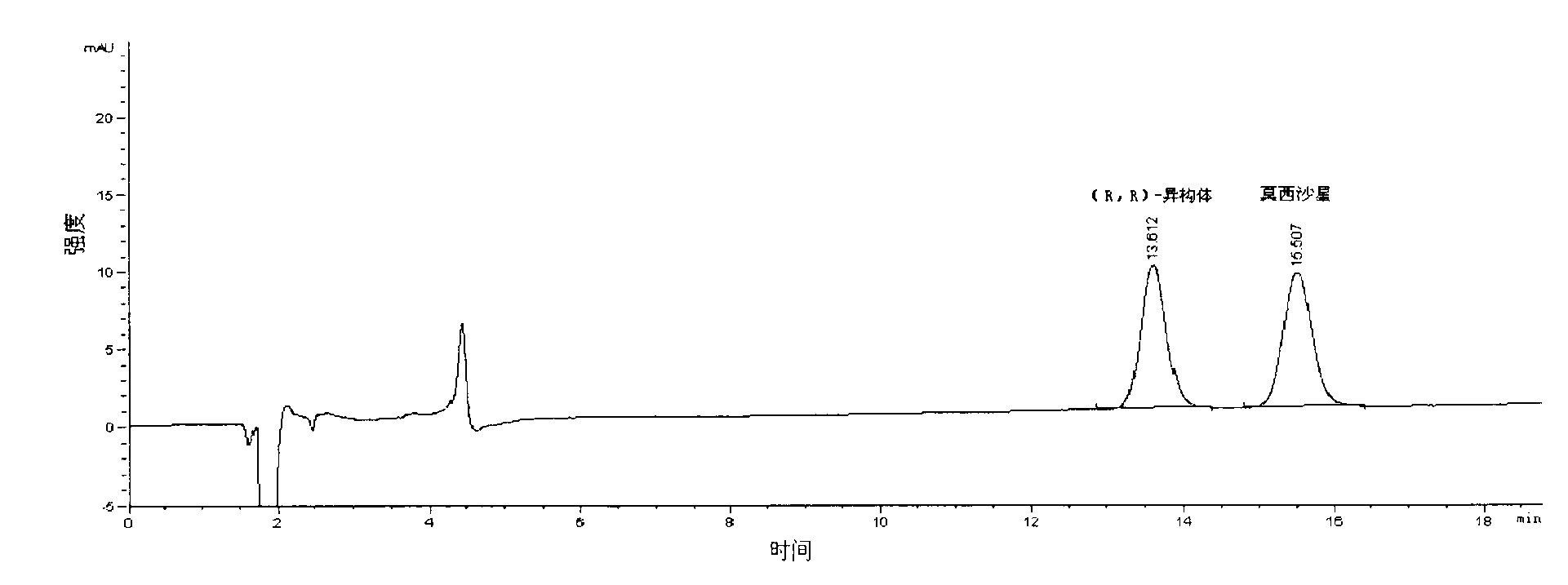
Detection method of moxifloxacin (R, R) isomer and application thereof
The present invention provides a detection method of a moxifloxacin (R, R) isomer. According to the detection method, high performance liquid chromatograph is used for detecting, wherein the conditions are that: the chromatographic column is an octadecyl silane bonded silica gel chromatographic column, and the mobile phase is a solvent containing L-leucine and metal ions, wherein the metal ions are Cu<2+>, Zn<2+> or a mixture thereof, the solvent comprises water and an organic solvent, and the volume ratio of water and the organic solvent is 77-82:23-18. The detection method provided by the present invention has high sensitivity and specificity, is simple to operate, can fast and accurately detect the moxifloxacin (R, R) isomer, can be used for quality control of moxifloxacin, lays a foundation for research and development and quality testing of the compounds, and has a practical significance.
Owner:天津康鸿医药科技发展有限公司 +1
Small-volume moxifloxacin hydrochloride injection and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103239394AReduce energy consumptionLow costAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsActivated carbonCinoxacine
The invention relates to a small-volume moxifloxacin hydrochloride injection and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: regulating the PH value of 0.01-0.04 / ml of moxifloxacin hydrochloride water solution for injection to 4.2-4.7, adding activated carbon for absorption, treating by a filter membrane of 0.22mu m, filling nitrogen, encapsulating and sterilizing to prepare 10ml of small-volume injection. The injection product does not have sub-visible particles, is good in clarity and safe in medication, can be conveniently mixed with injections such as glucose, mannitol and the like, and is not restricted to a sodium chloride injection. The invention solves the problem that the sodium chloride injection can not be used for some patients having specific physiques.
Owner:北京赛盟医药科技发展有限公司
Method for synthesizing moxifloxacin degradation impurity
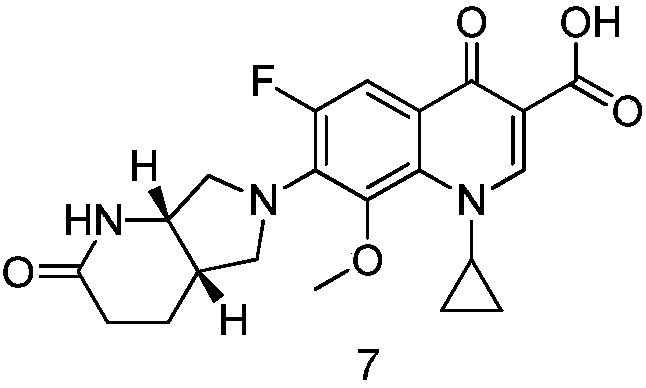
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a moxifloxacin degradation impurity. The method comprises the following steps: (1) enabling a compound of a formula 1 shown in the description to contact with p-methyl benzene sulfonic chloride so as to otbain a compound of a formula 2 shown in the description; (2) performing an oxidation on the compound of the formula 2 shown in the descrption soas to obtain a compound of a formula 3 shown in the description; (3) removing p-methyl benzene sulfonic chloride from the compound of the formula 3 shown in the description so as to obtain a compoundof a formula 4 shown in the description; (4) performing a substitution reaction on the compound of the formula 4 shown in the description and a compound of a formula 5 shown in the description so as to obtain a compound of a formula 6 shown in the description; and (5) performing acidic hydrolysis on the compound of the formula 6 shown in the description, so as to obtain a compound of a formula 7 shown in the description. The invention provides a method for orientated synthesis of the compound of the formula 7 shown in the description, by using the method, the compound of the formula 7 shown inthe description can be prepared, and meanwhile, the compound of the formula 7 shown in the description can be used as an impurity reference product for detecting related substances of the moxifloxacin degradation impurity.
Owner:YANGTZE RIVER PHARM GRP CO LTD
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride external preparation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104224691ASmooth appearanceEasy to carry and useAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsFenamic acidIrritation
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical preparations and particularly relates to a moxifloxacin hydrochloride external preparation and a preparation method thereof. The external preparation specifically refers to a cream and comprises a combination of a skin penetration enhancer comprising N-trimethyl chitosan, menthol and isopropyl myristate, the external preparation can be directly acted on an infection part, the gastric and intestinal irritation caused by oral administration is avoided, and the skin is not irritated either. The cream further greatly improves the skin penetration rate of a medicine, so that the local absorption is fast, and the treatment effect is remarkable. To further enhance the anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, namely butyl flufenamate, is further added in the cream. The preparation process of the cream is simple and feasible, is high in reproducibility, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:NANJING YOUKE BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL RES +2
Preparation method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride and intermediate thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride and an intermediate thereof. The preparation method of the intermediate III of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride includes the following steps: making an intermediate II of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride and (S,S)-2,8-diazabicyclo[4,3,0]nonane have condensation reaction in an organic solvent in the presence of alkali to obtainthe intermediate III of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The preparation method is simple and safe in operation, does not require special equipment and avoids use of highly toxic materials and mild inreaction conditions. The obtained the moxifloxacin hydrochloride I has high purity and low production cost, and is suitable for industrial production. (img file='DDA0001750656940000011.TIF' wi='700' he='192' / ).
Owner:上海新礼泰药业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com