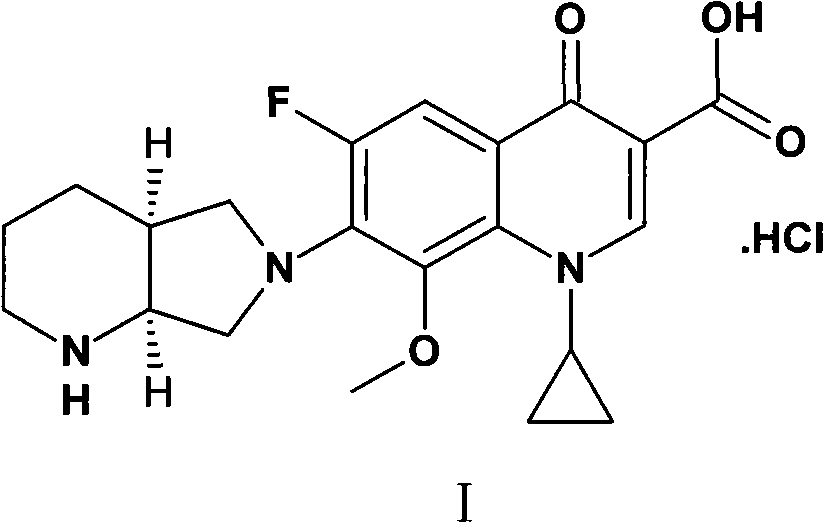
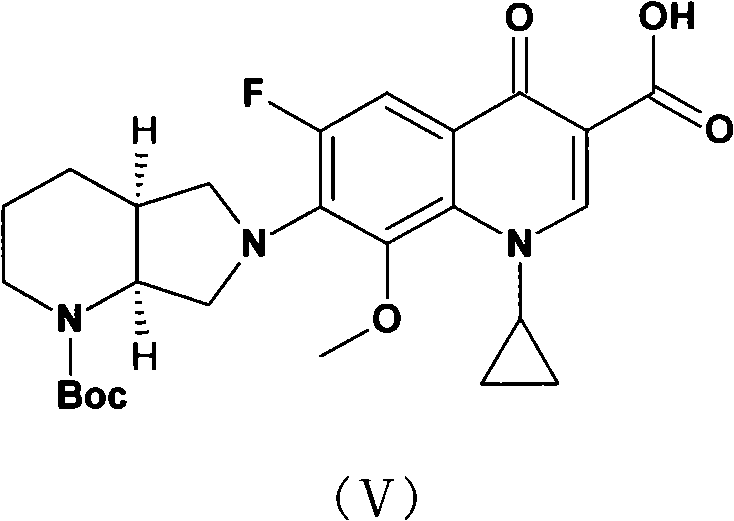
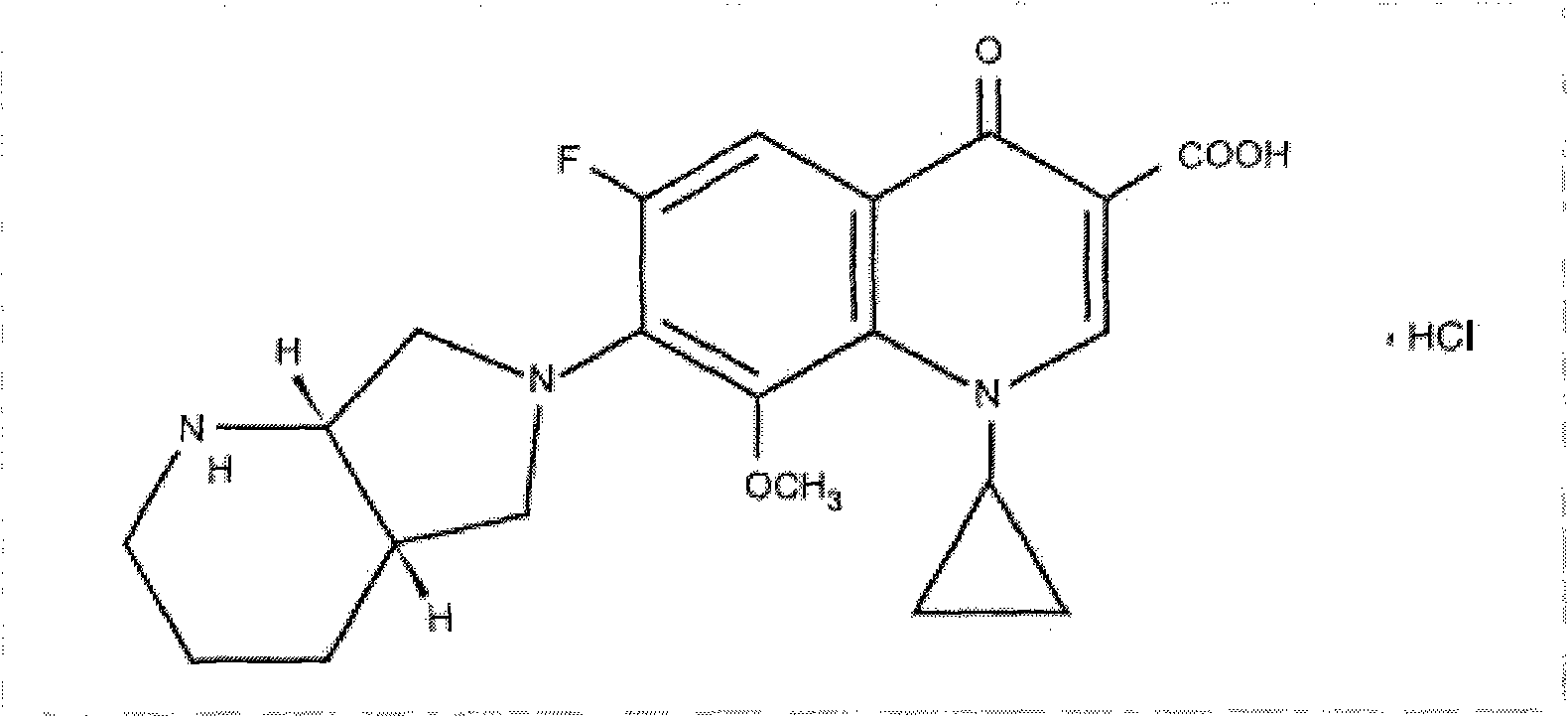
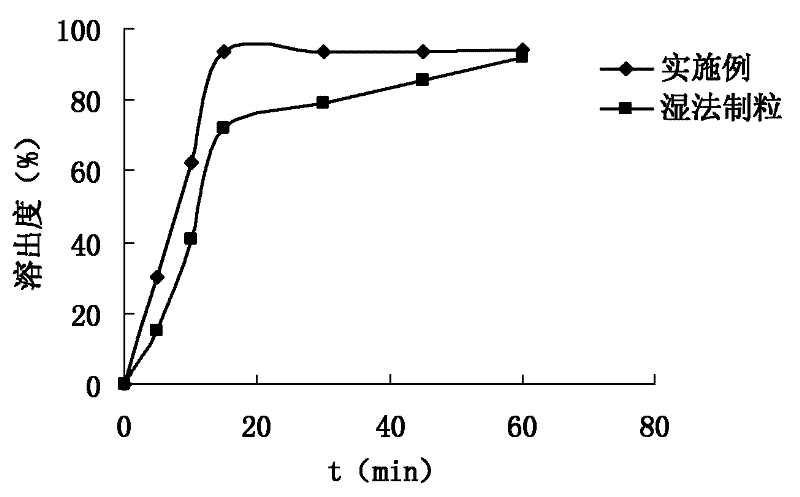
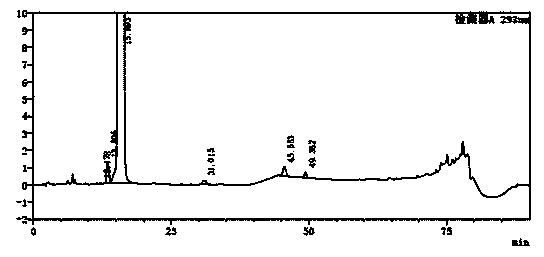
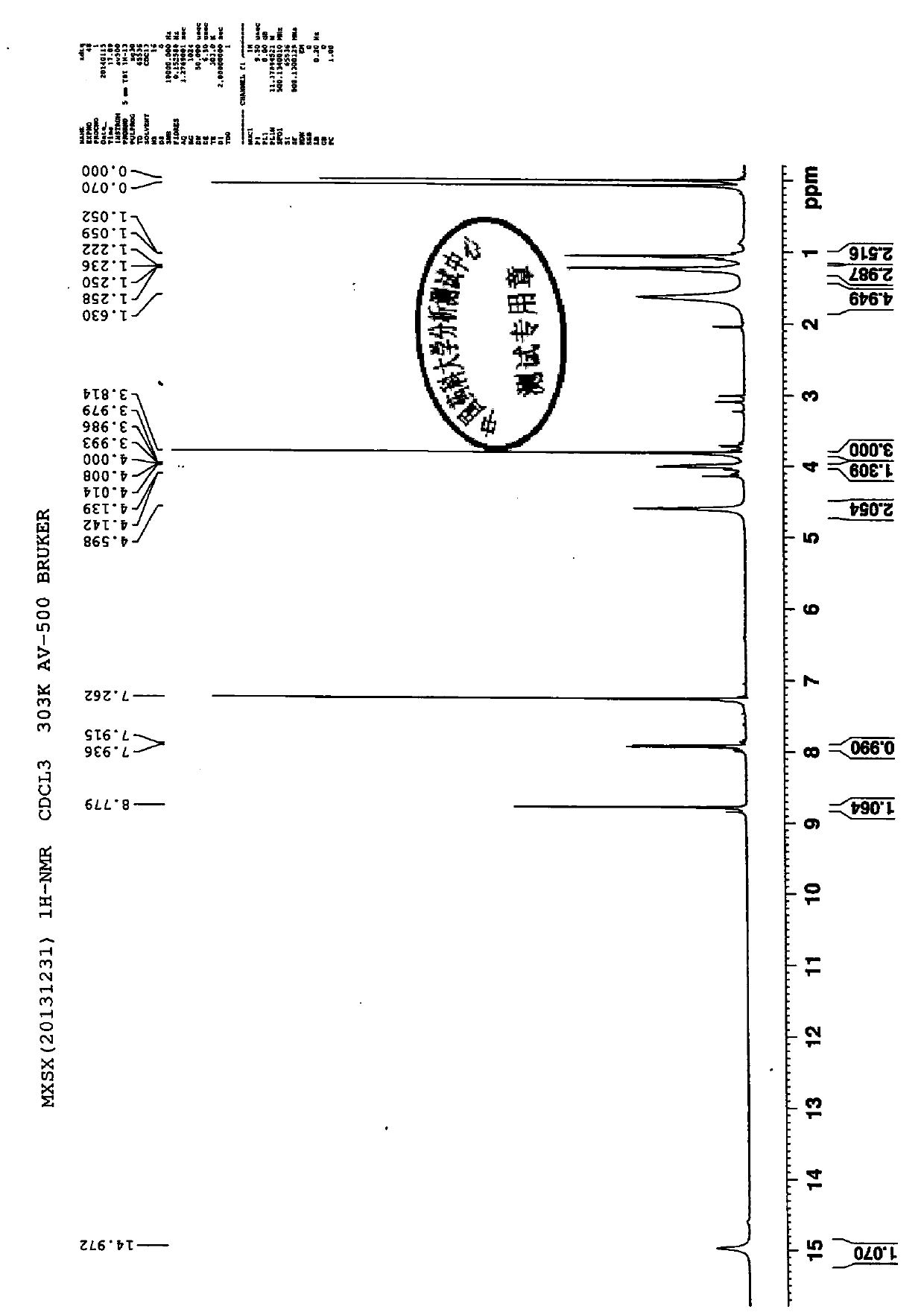
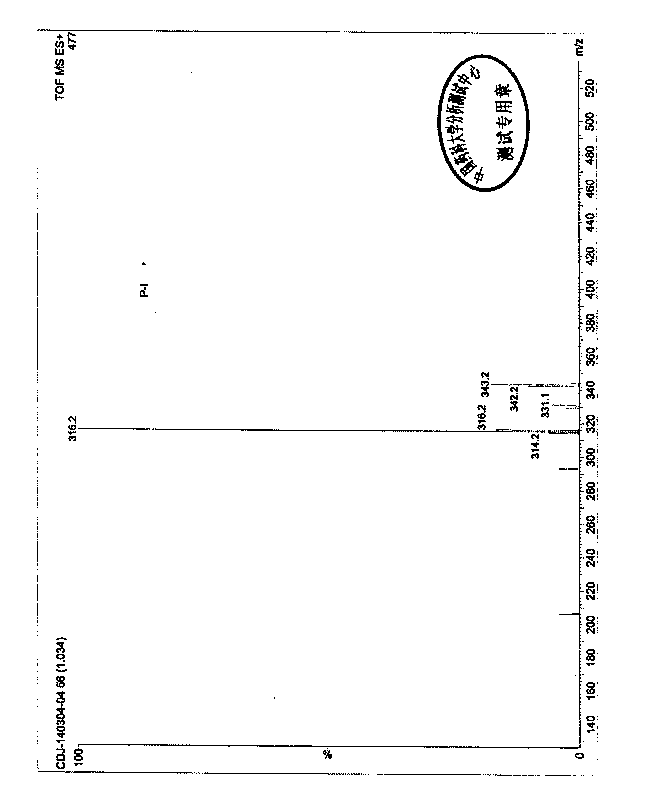
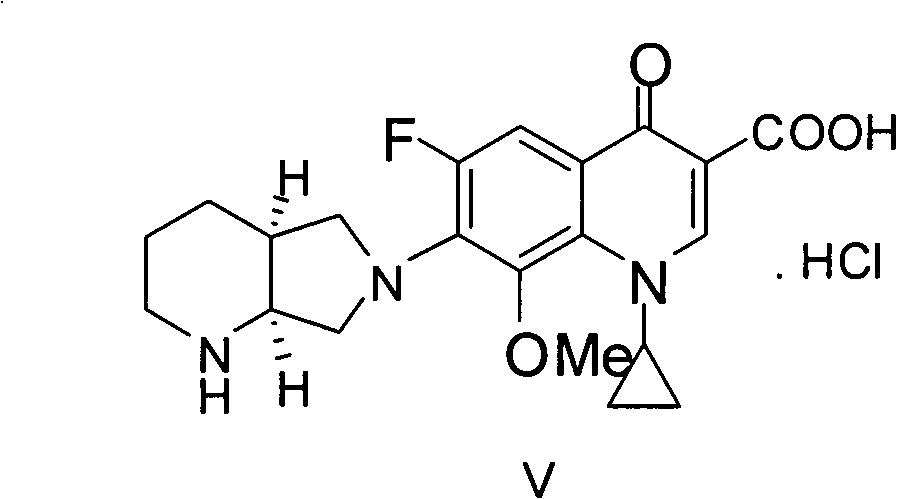
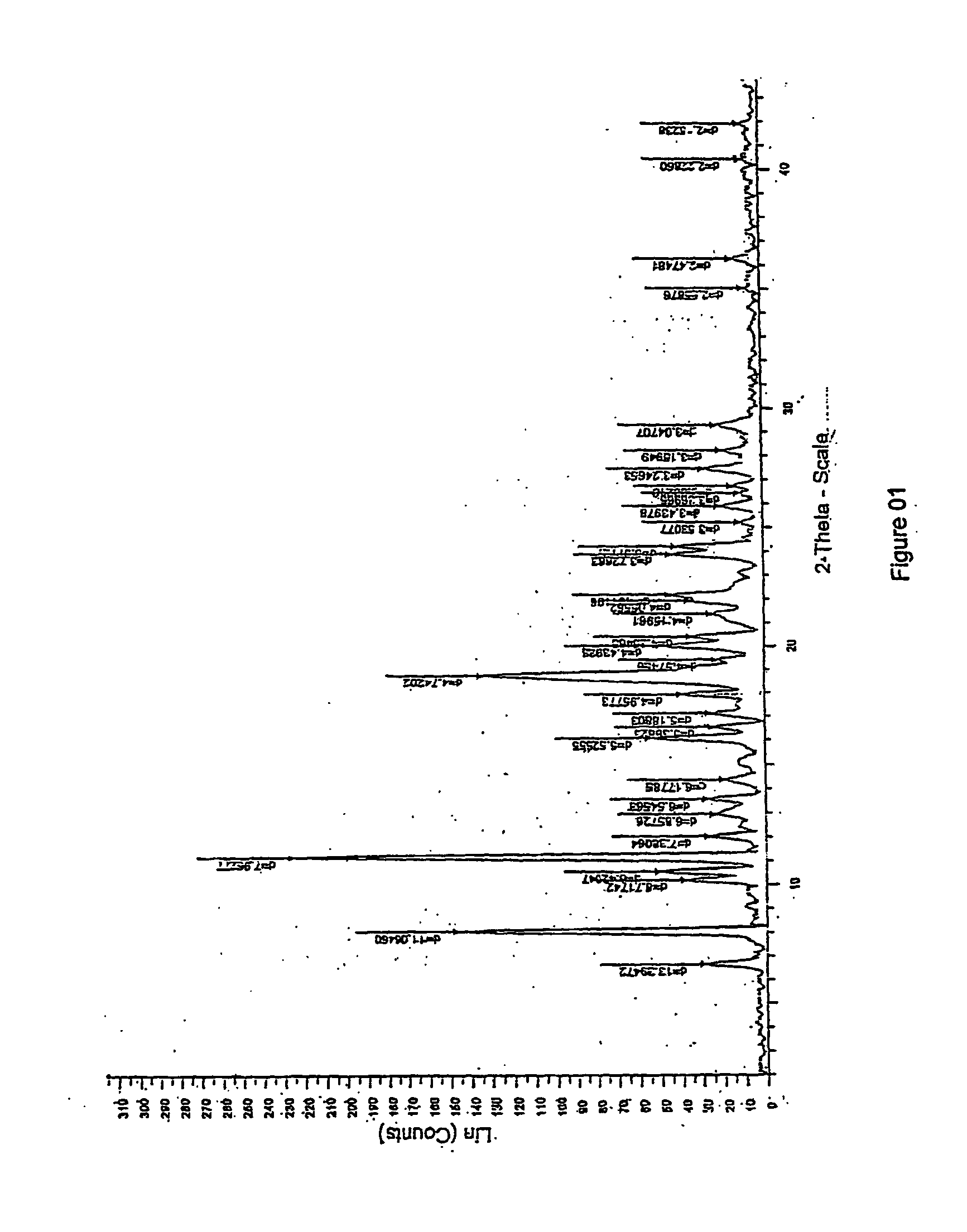
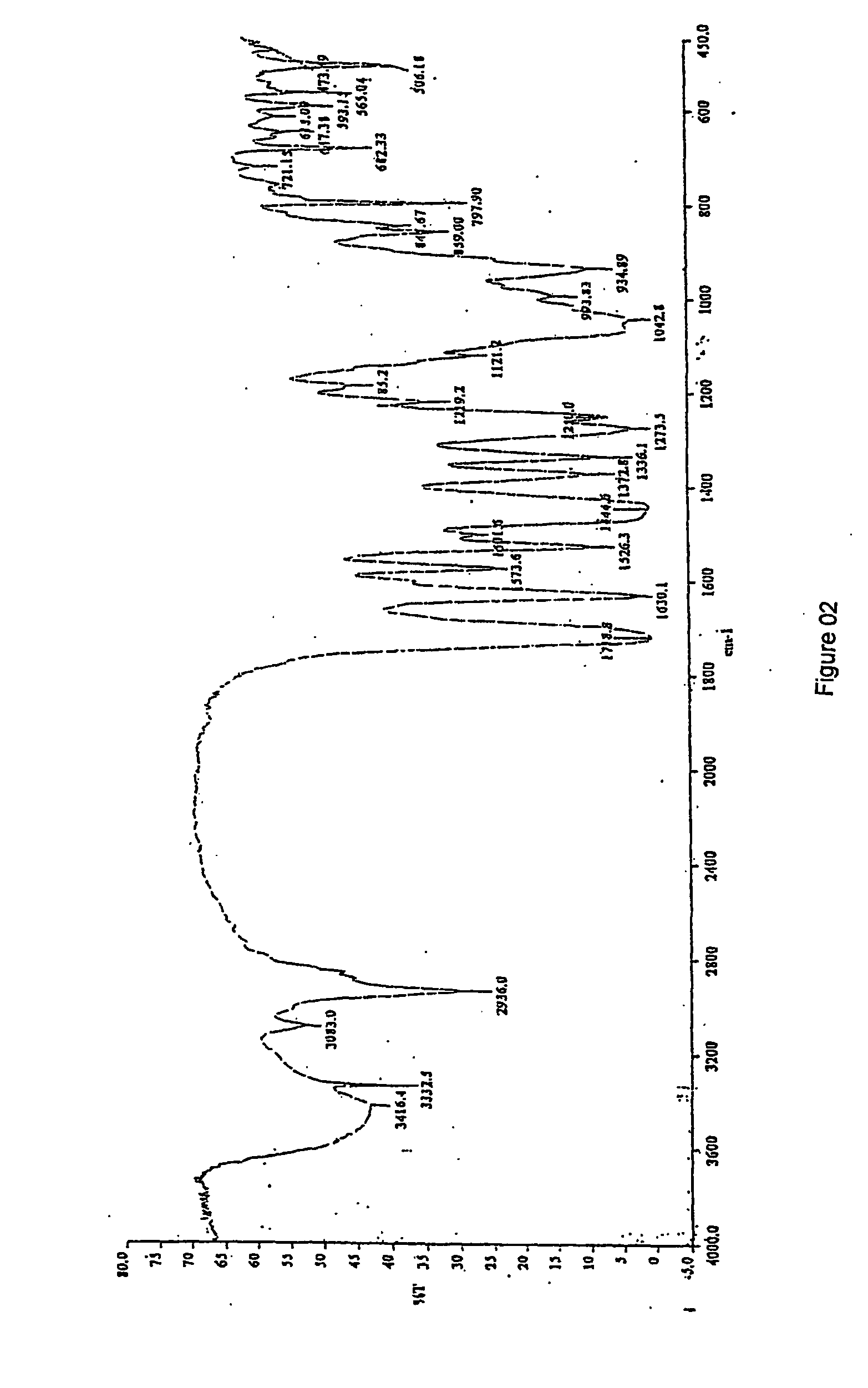
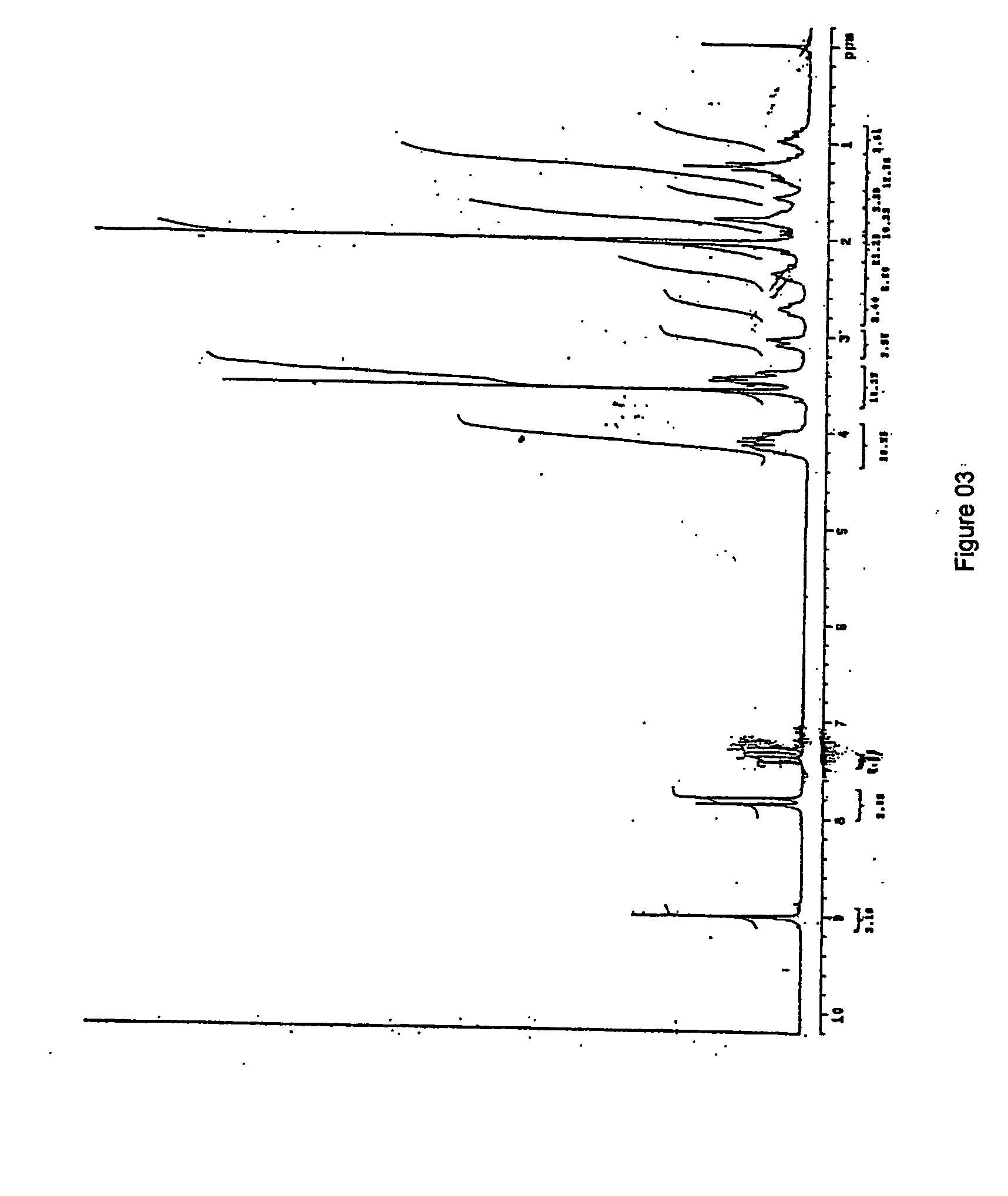
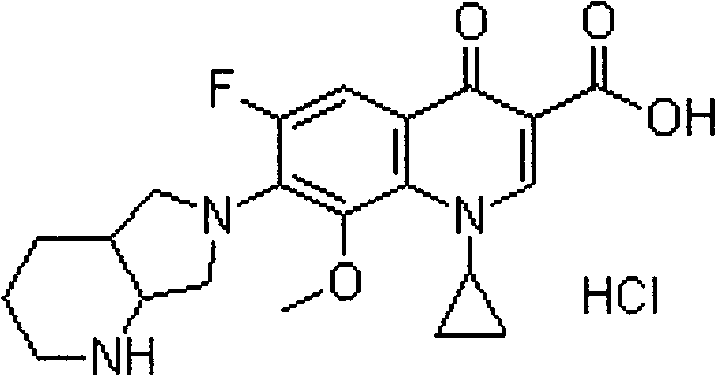
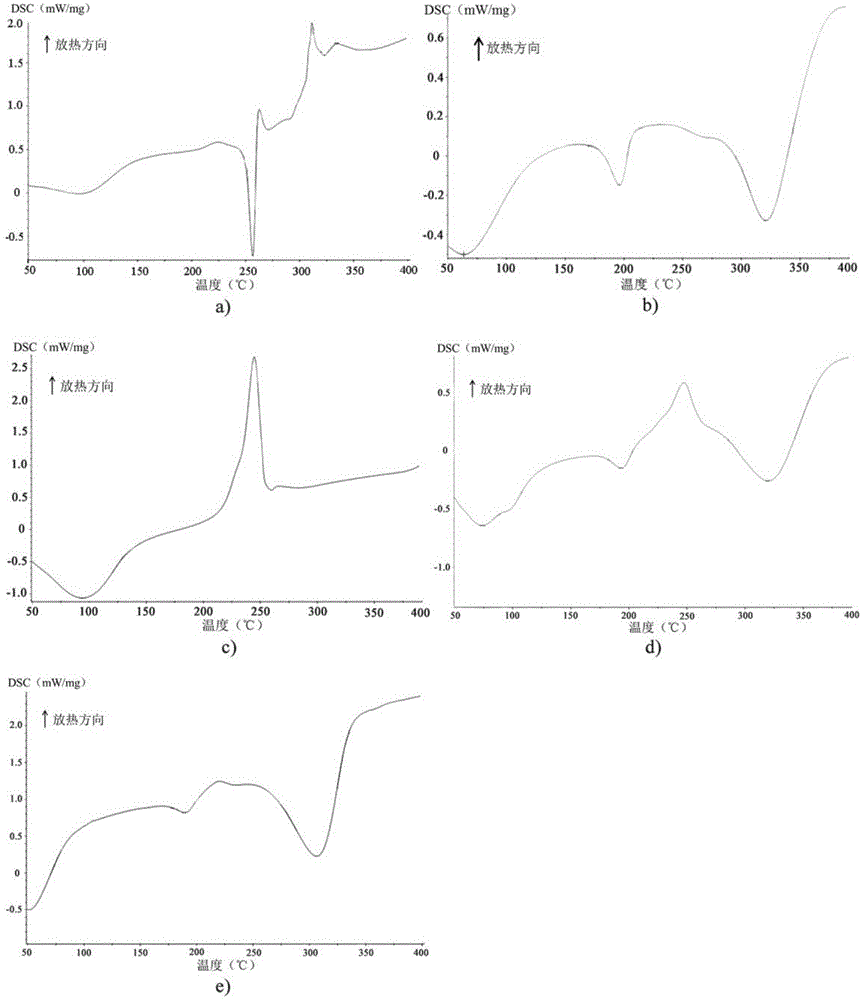
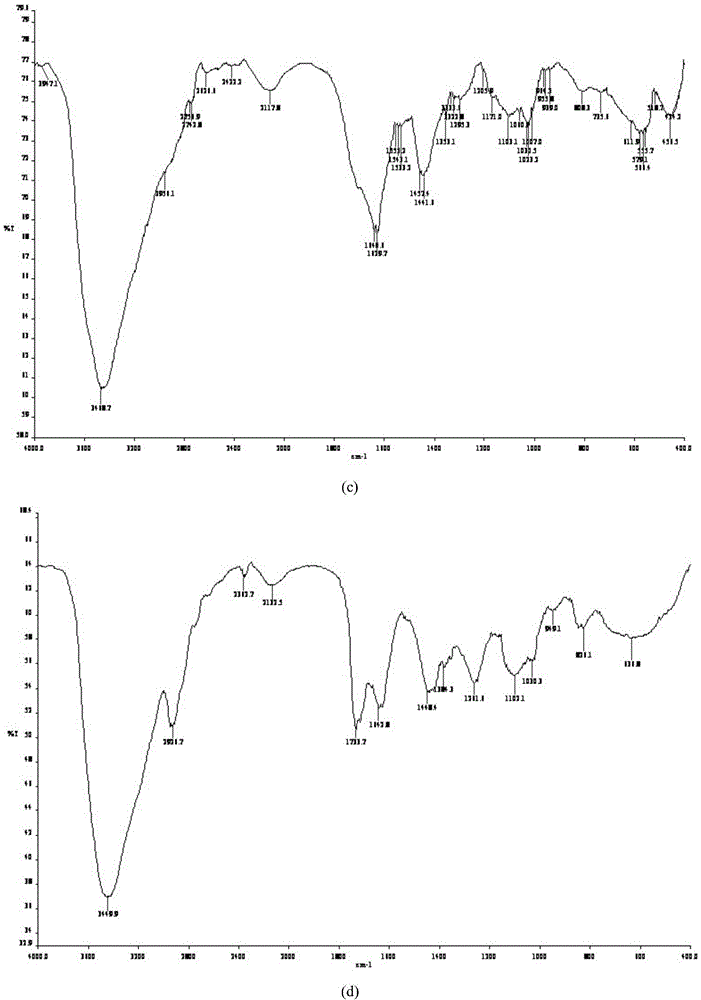
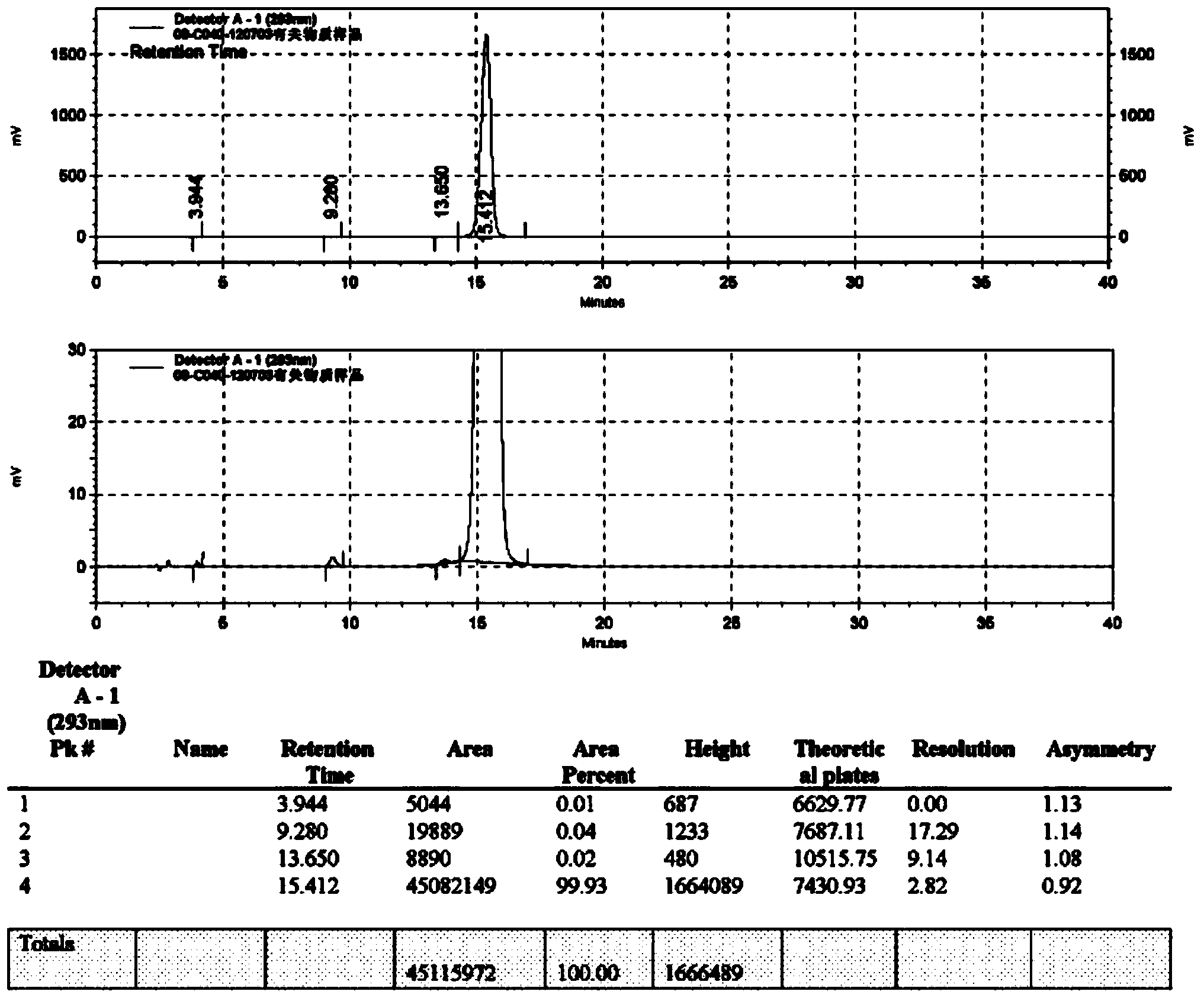
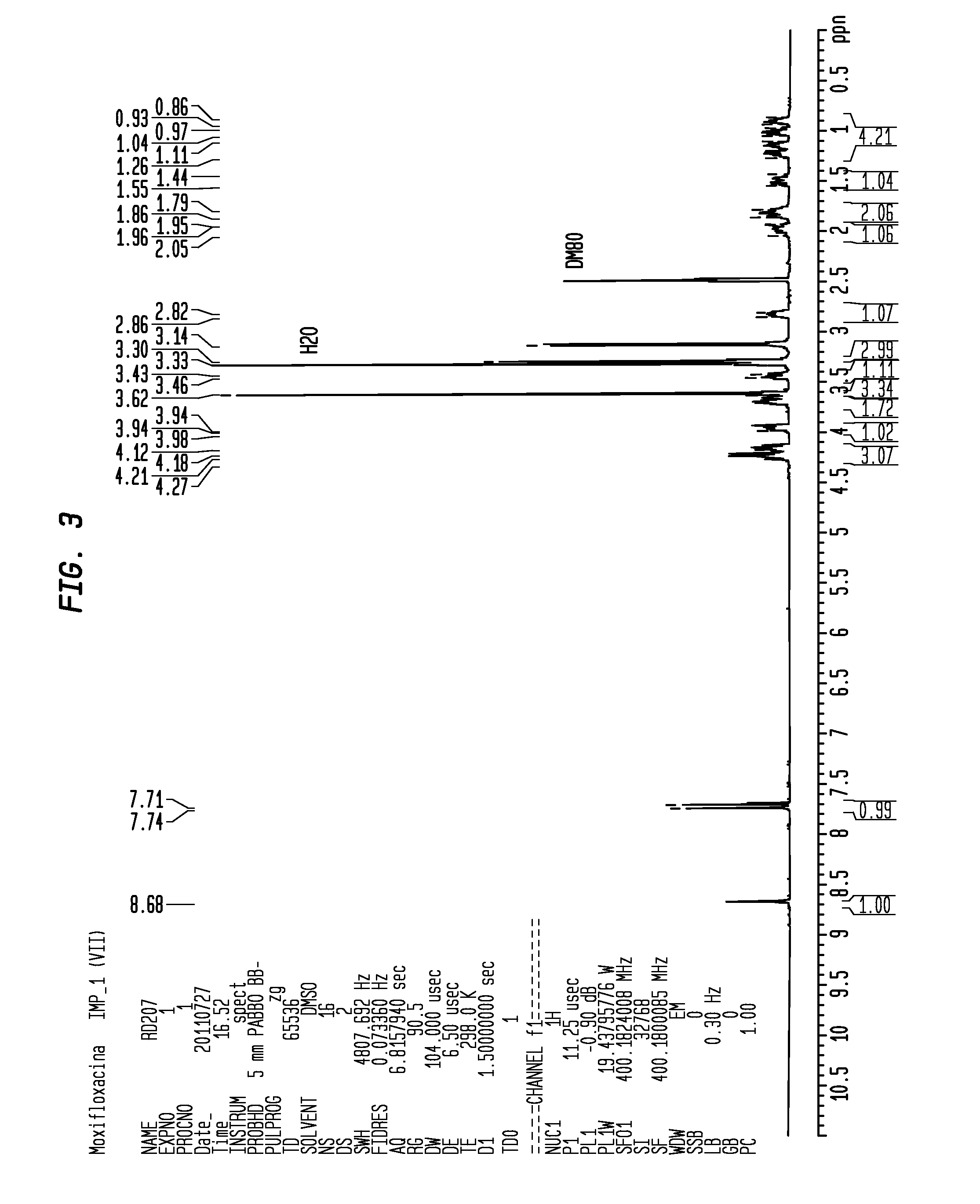
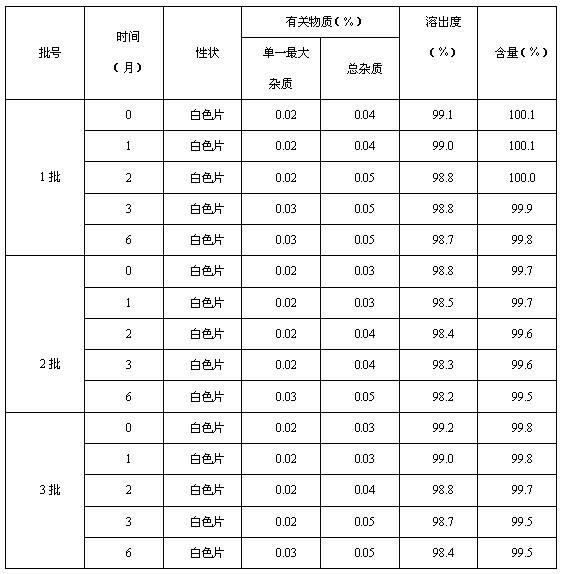
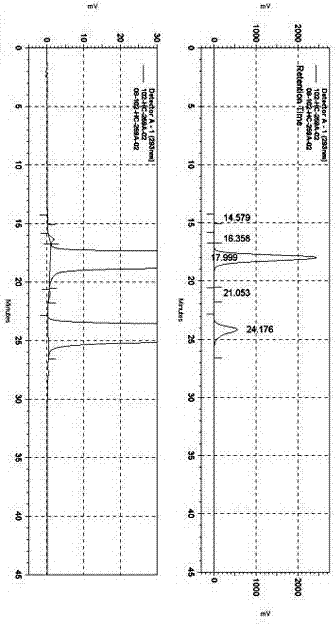
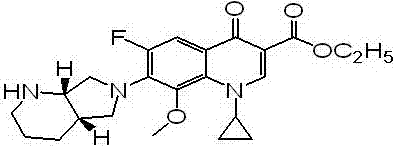
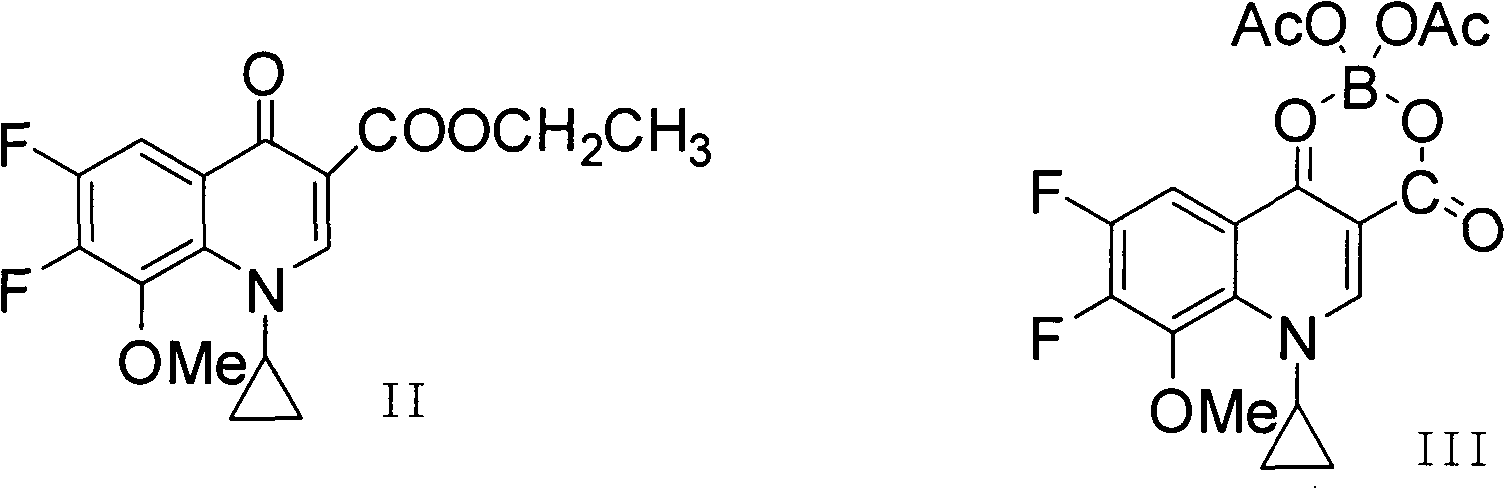Patents
Literature
188 results about "Moxifloxacin hydrochloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
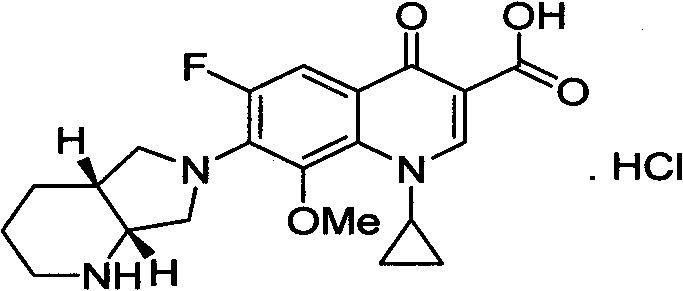
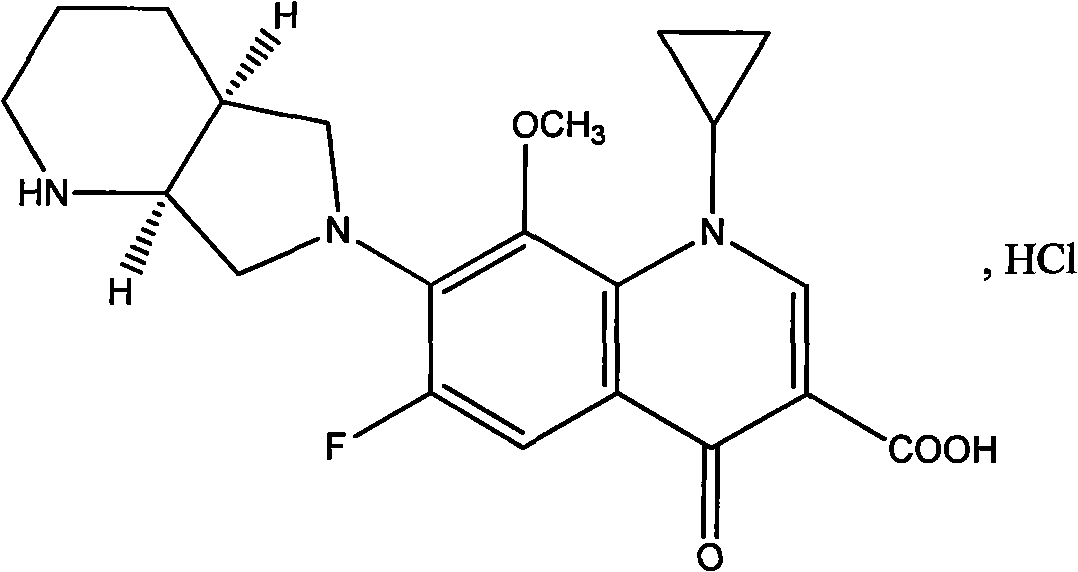
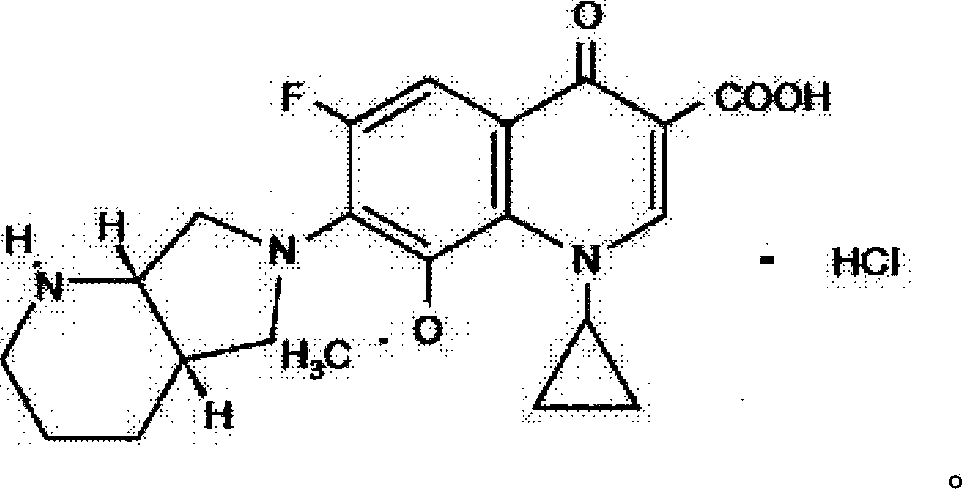
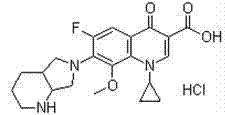
The hydrochloride salt of a fluoroquinolone antibacterial antibiotic. Moxifloxacin binds to and inhibits the bacterial enzymes DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II) and topoisomerase IV, resulting in inhibition of DNA replication and repair and cell death in sensitive bacterial species Check for http://www.cancer.gov/Search/ClinicalTrialsLink.aspx?id=306456&idtype=1 active clinical trials or http://www.cancer.gov/Search/ClinicalTrialsLink.aspx?id=306456&idtype=1&closed=1 closed clinical trials using this agent. (http://nciterms.nci.nih.gov:80/NCIBrowser/ConceptReport.jsp?dictionary=NCI_Thesaurus&code=C38696 NCI Thesaurus)
Method for synthesizing moxifloxacin hydrochloride
ActiveCN101817820AHigh yieldHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryAntiinfectivesMoxifloxacin hydrochlorideQUINOLONE ANTIBACTERIALS
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a broad-spectrum efficient moxifloxacin hydrochloride, which is a quinolone antimicrobial medicament and has a formula below.
Owner:PORTON FINE CHEM
Synthesizing method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride
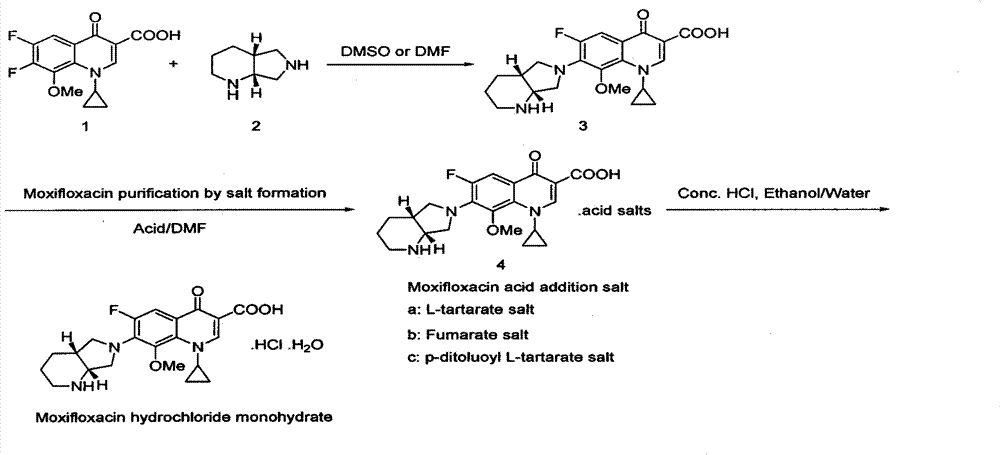
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmaceutical chemistry, relates to the novel preparation method of quinolone medicaments and disclosesa novel synthesizing method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing boric acid ester from boric acid, and reacting the boric acid ester and 8-methoxyquinoline carboxylic acid to form an intermediate I; and in a polar solvent, reacting the intermediate I and (s,s)-octahydro-6H-pyrrole[3,4-b] pyrrole at certain temperature, removing the reaction product from the solvent and curing the reaction product to obtain an intermediate II, hydrolyting the intermediate II in a mixed solvent at certain temperature with the aqueous solution of an inorganic alkali, treating the product with diluted hydrochloric acid to obtain the rough moxifloxacin hydrochloride, and recrystallizing the rough moxifloxacin hydrochloride to obtain the refined moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The method improves the reaction selectivity, avoids the generation of impurity at another selected position, effectively increases the yield of the main product, optimizes the technique and increases the yield to 87 percent. Therefore, the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:河南省健康伟业生物医药研究股份有限公司
Improvement of preparation method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride
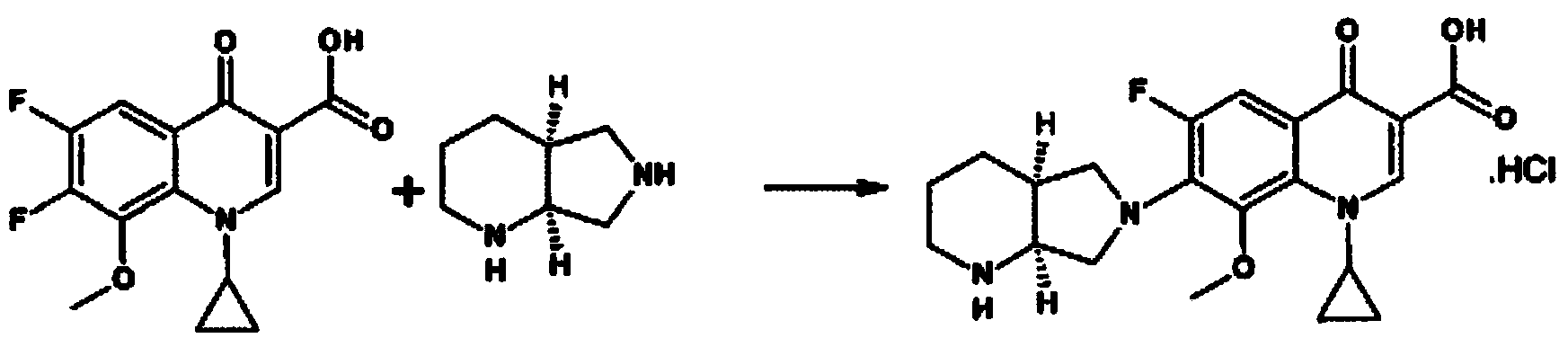
The invention belongs to the medicine synthesis field, which concretely relates to a method for preparing moxifloxacin hydrochloride by one-pot method. The method comprises is characterized in that 1-cyclopropyl-6,7- difluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxyl-4-oxo-3-quinoline carboxylic acid ethyl ester is taken as a raw material, then subjected to a chelating reaction by boron, is subjected to nucleophilic substitution reaction with (S,S)-2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]nonane and an acidifying step to prepare moxifloxacin hydrochloride, and the reaction products can be directly used for reaction in next step without post-treatment or separation. The improvement of the invention has the advantages that the reaction steps can be simplified, the operation is simple and the yield is high, and is adapted to more suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANDONG NEWTIME PHARMA
Preparation method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride
The invention discloses a preparation method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, comprising the steps of: reacting the 1-cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinoline carboxylic acid and the S,S-2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]nonane to prepare the moxifloxacin in the presence of organic base in organic solvent under the reaction temperature of 60 to 85 DEG C; separating the moxifloxacin, processing the moxifloxacin by concentrated hydrochloric acid in organic solvent under the reaction temperature of 60 to 85 DEG C to obtain the moxifloxacin hydrochloride.
Owner:JIANGSU CHIA TAI FENGHAI PHARMA
Method for performing industrialized production on moxifloxacin hydrochloride
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The method is characterized in that: moxifloxacin hydrochloride is precipitated from solution according to solubility difference of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride in sodium chloride solution with different concentrations so as to fulfill the aim of separation. The method particularly comprises the following steps of: adding sodium chloride into moxifloxacin hydrochloride-containing aqueous solution; stirring to crystallize; filtering; drying; recrystallizing with water; filtering; and drying to obtain the moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The method is simple and convenient in operation; the product has high purity; a single impurity is less than 0.1 percent; the total impurities are less than 0.2 percent; and the method is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:NANJING YOKO PHARMA
Method for preparing high-purity moxifloxacin hydrochloride
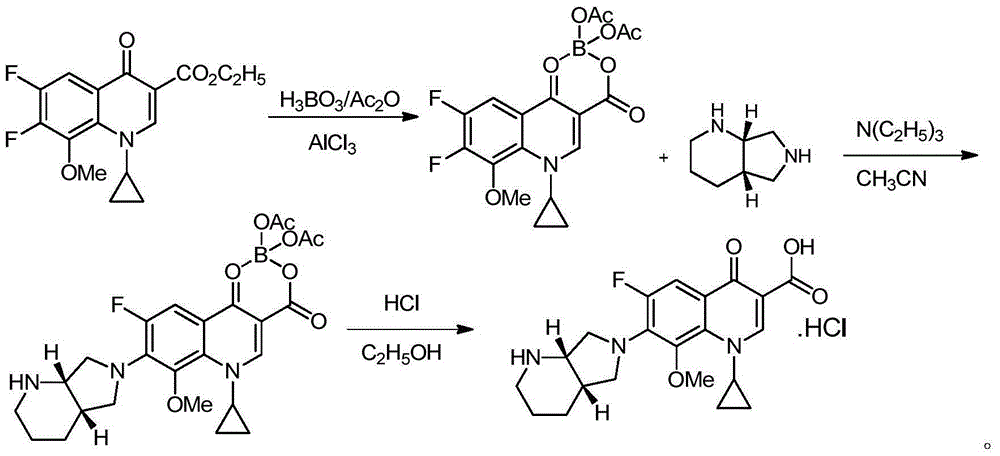
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The method includes the following steps: boric acid and acetic anhydride are adopted and subjected to a catalytic heating reaction at the presence of aluminium trichloride to generate B(OAc)3; B(OAc)3 and 1-cyclopropyl-6, 7-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid ethyl ester are subjected to a heating reaction to obtain chelate; chelate and S,S-2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0] nonane are subjected to a nucleophilic substitution reaction at the presence of Et3N; after the reaction, a mixed solvent of petroleum ether, ethyl acetate and N, N-dimethyl formamide is used to remove impurities, and ethyl alcohol and chlorhydric acid treatments are carried out; cooling crystallization is carried out to obtain the moxifloxacin hydrochloride crude product; ethyl alcohol and an aqueous solution are used for crystallization according to the fact that the volume ratio of ethyl alcohol to the aqueous solution is 1:3, so that the high-purity moxifloxacin hydrochloride is obtained. According to the invention, the route is simple and convenient, the operation and post-treatment are simple, the yield is relatively high, the purity is high, and the method is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:SHANDONG LUOXIN PARMACEUTICAL GROUP STOCK CO LTD
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride pharmaceutical composition and its preparation method
ActiveCN102204911AGood compressibilityHigh hardnessAntibacterial agentsHydroxy compound active ingredientsMANNITOL/SORBITOLPharmaceutical formulation
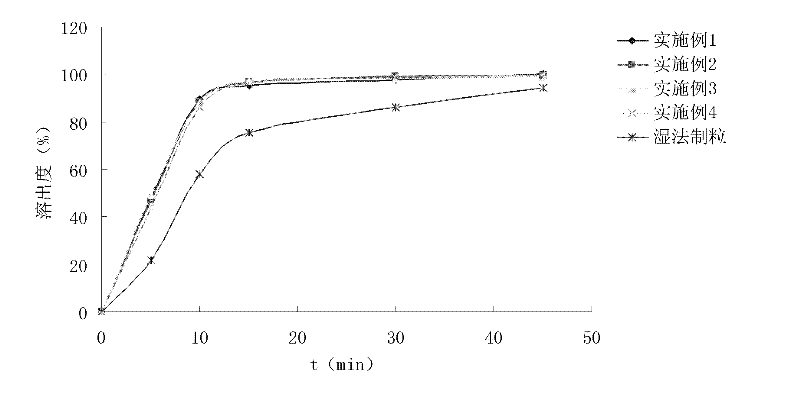
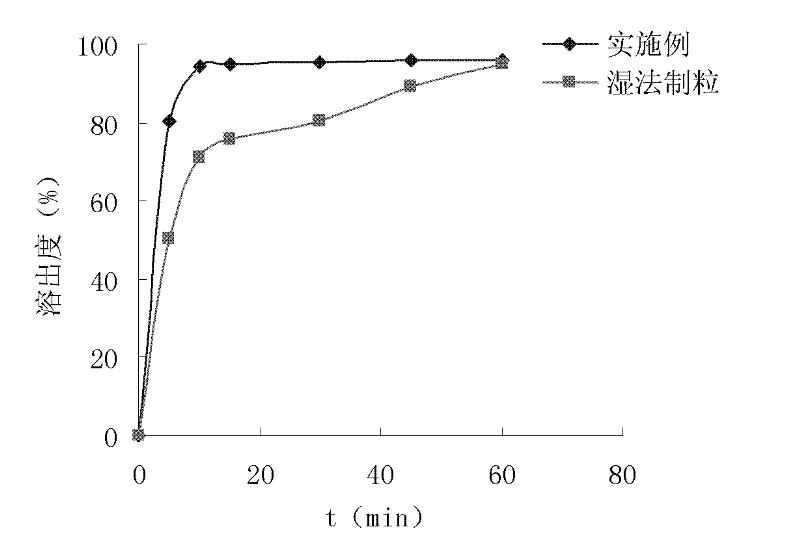
The invention provides a moxifloxacin hydrochloride pharmaceutical composition and its preparation method. The composition comprises moxifloxacin hydrochloride, mannitol and other excipients. The preparation method employs a dry-method granulating technology for preparing medicament particles, and then preparing a medicinal preparation.
Owner:CHINA RESOURCES SAIKE PHARMA
Preparation method, detecting method and application of moxifloxacin hydrochloride impurity
ActiveCN104292158AThe preparation method is safeEasy to prepareOrganic chemistryComponent separationCinoxacineBiochemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method and a detecting method of a moxifloxacin hydrochloride photodegraded impurity and an application of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride photodegraded impurity as an impurity reference substance during detection of a moxifloxacin hydrochloride related substance. Through the preparation of the compound, the reference substance is provided for analysis of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride related substance, so as to improve the quality standard of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, and provide important guidance significance for safe medication of moxifloxacin hydrochloride.
Owner:NANJING CHIA TAI TIANQING PHARMA
Synthetic method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride
ActiveCN104230924AReduce generationMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryMoxifloxacin hydrochlorideChelation
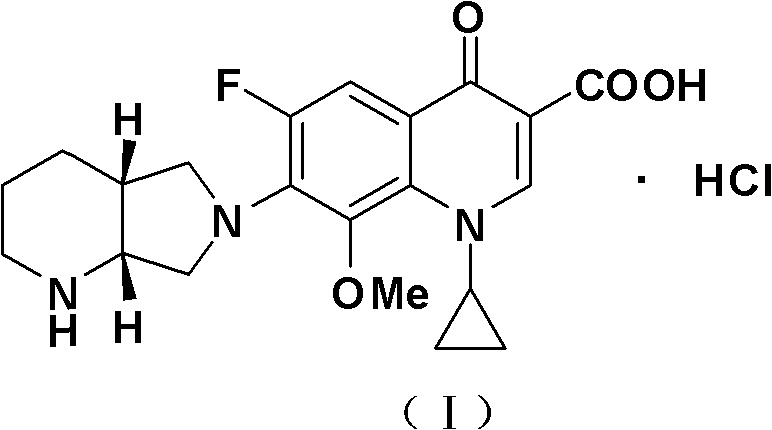
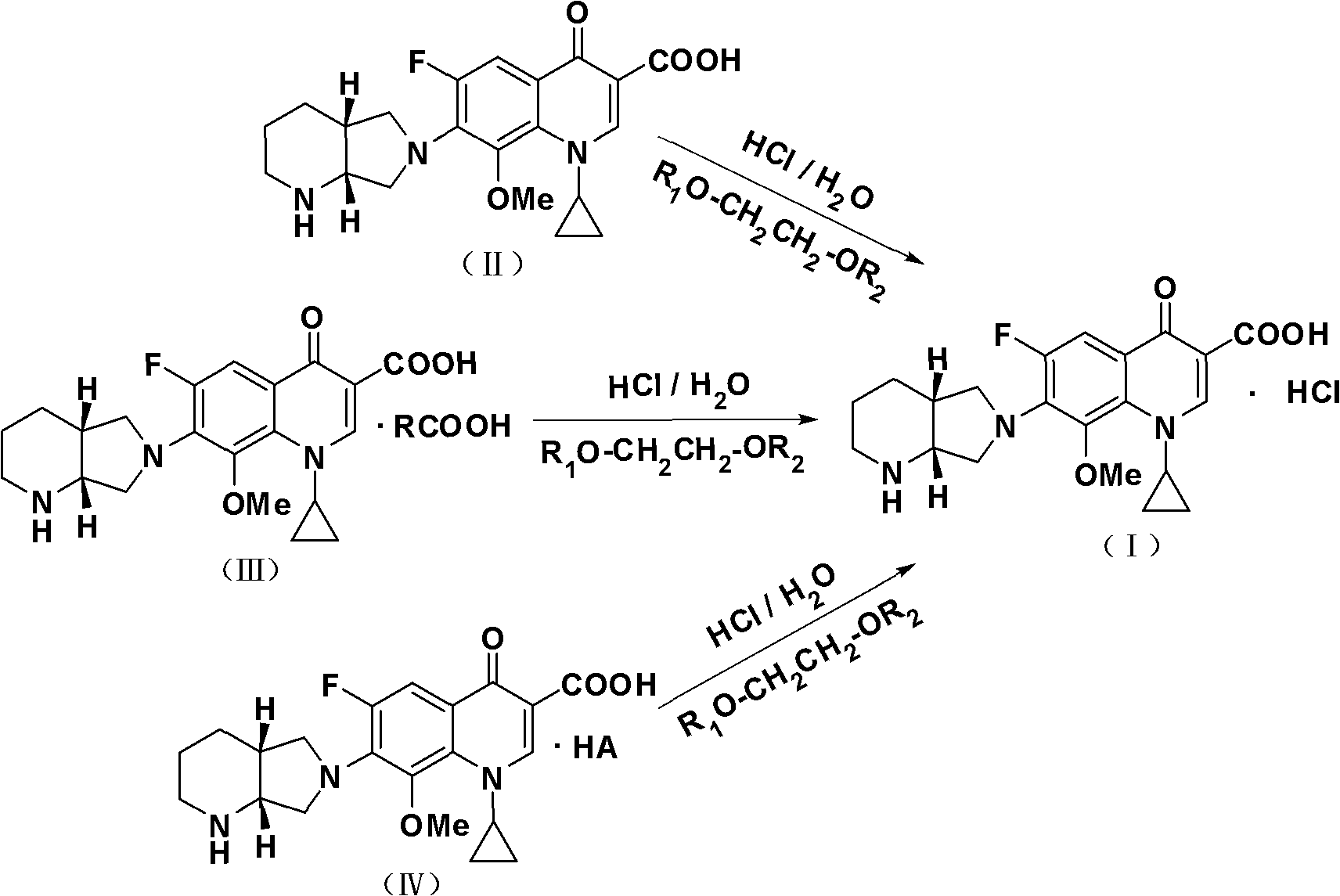
The invention provides a synthetic method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: by taking a primary ring chelate as shown in a formula (I) and (S, S)-2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0] nonane as raw materials and taking triethylamine as an acid absorber, carrying out condensation reaction in acetonitrile sufficiently; and concentrating, treating, then dissolving, carrying out acidolysis and salifying, crystallizing, filtering, washing and drying to obtain the moxifloxacin hydrochloride, wherein a weight ratio of the primary ring chelate to acetonitrile to triethylamine to (S, S)-2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0] nonane is 1 to (2-10) to (0.08-0.96) to (0.30-0.59). The synthetic method is characterized in that a condensation reaction temperature is larger than and equal to 30 DEG C and lower than 70 DEG C. The synthetic method has the following technical effects that nucleophilic substitution reaction is carried out in acetonitrile at a temperature not lower than 30 DEG C but lower than 70 DEG C, the reaction conditions are gentle, the production of impurities is greatly reduced and the energy resources are saved. After acetonitrile is evaporated, the treatment method is simple and rapid, acidification is carried out in alcohol to obtain moxifloxacin hydrochloride, and thus, the synthetic method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANYISHI PHARMA
Synthesis method of high-purity moxifloxacin hydrochloride
The invention provides a synthesis method of high-purity moxifloxacin hydrochloride, which comprises the following steps: protecting carbonyl of ethyl 1-cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-8-methoxy-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinolyl-3-carboxylate by using ethyl borate; performing condensation with (S,S)-2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]nonane; deprotecting with hydrochloric acid to obtain a moxifloxacin hydrochloride crude product; dissolving the obtained moxifloxacin hydrochloride crude product with an alkali water solution, extracting with organic solvent, removing the organic phase, and adding hydrochloric acid into the water phase to regulate the pH value to acidity; crystallizing, filtering to obtain a filter cake, and recrystallizing the obtained filter cake with water-containing organic solvent; and finally, filtering, and drying to obtain the high-purity moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The product prepared by the method has the advantages of high purity, high yield and favorable reproducibility, and has very high industrial operation feasibility.
Owner:天津康鸿医药科技发展有限公司
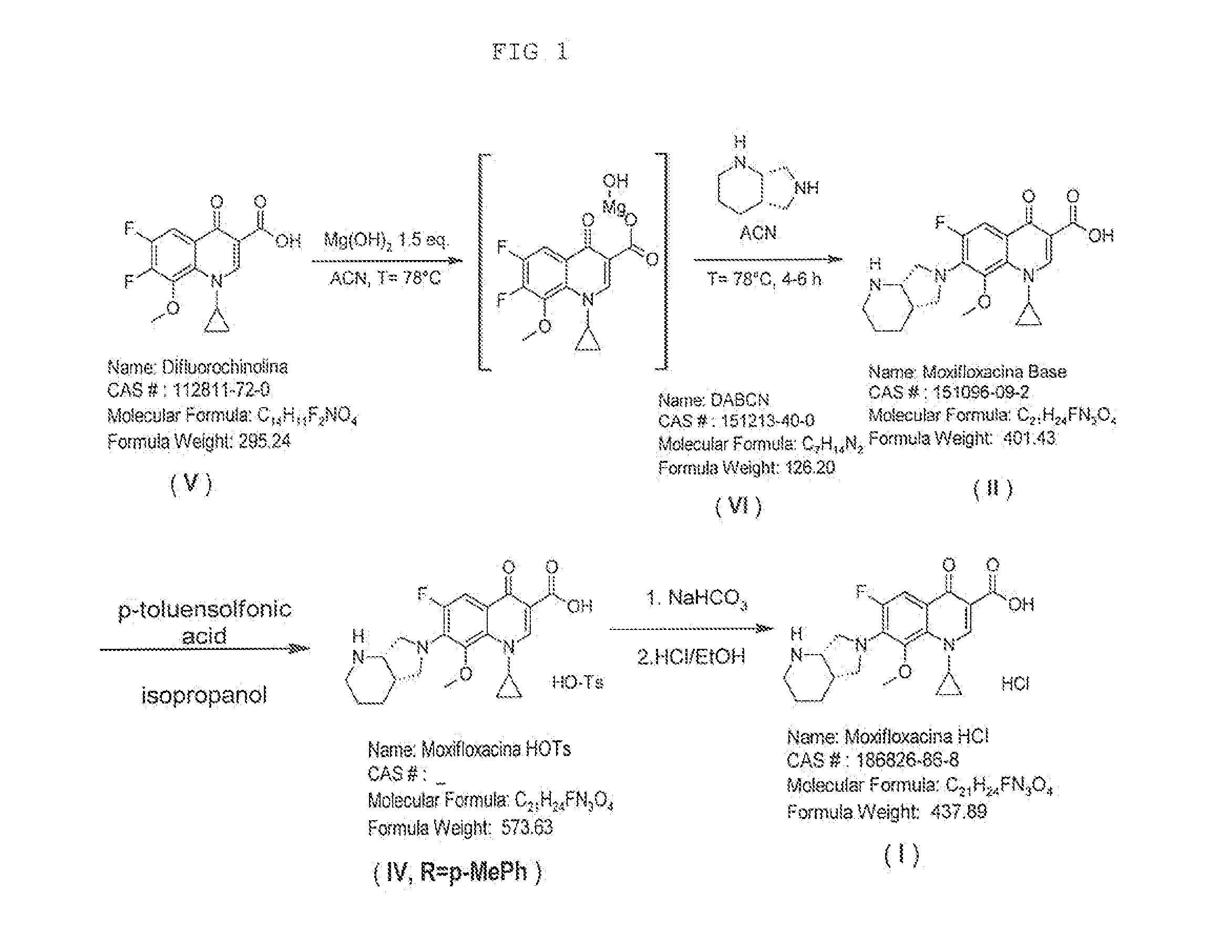
Process for the preparation of moxifloxacin hydrochloride
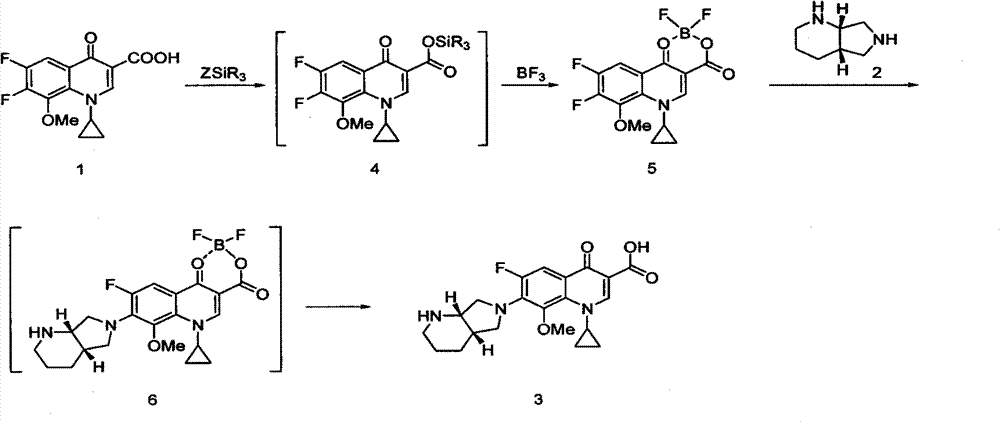
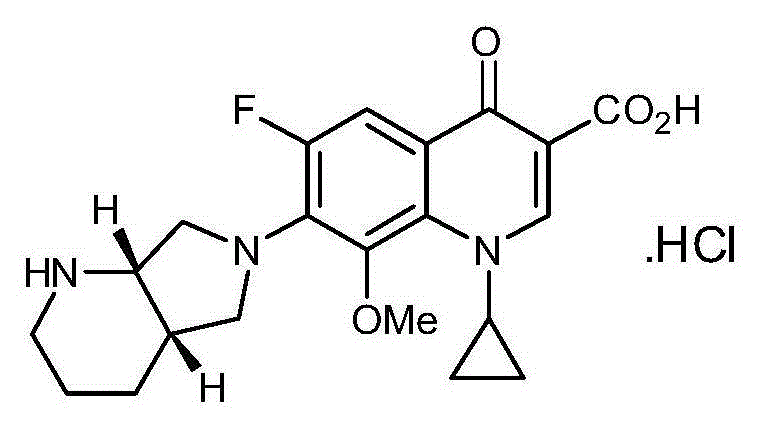
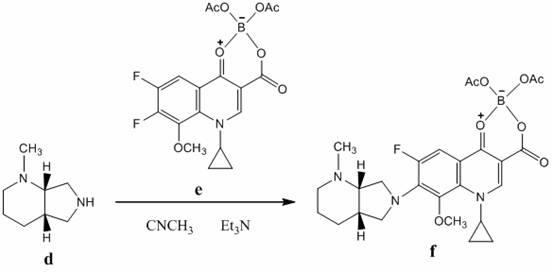
The present invention relates to an improved process for the preparation of Moxifloxacin hydrochloride from the ethyl 1-cyclopropyl 6,7-difluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylate through a novel intermediate (4aS-Cis)-1-cyclopropyl-7-(2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-8-yl)-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinoline carboxylic acid-03,04)bis(acyloxy-0) borate.
Owner:MATRIX LABORATORIES LTD
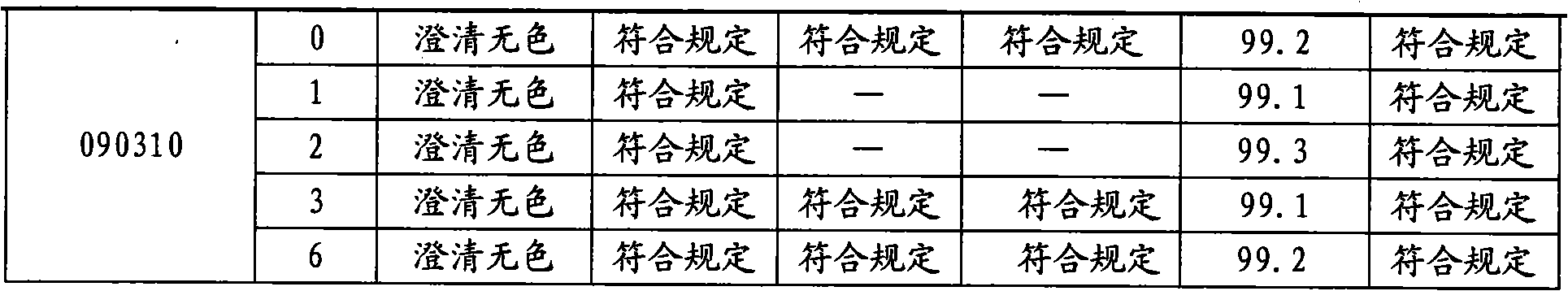
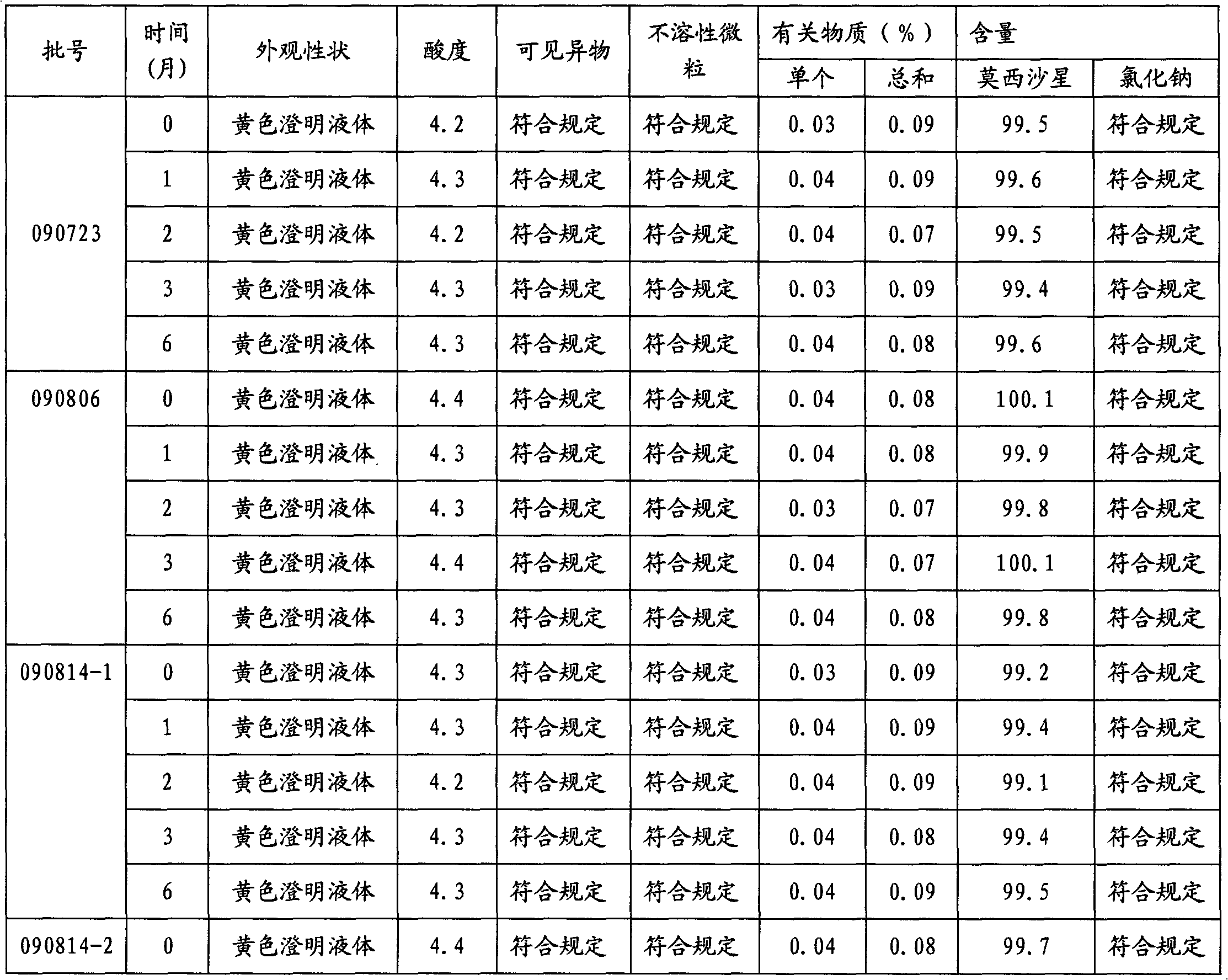
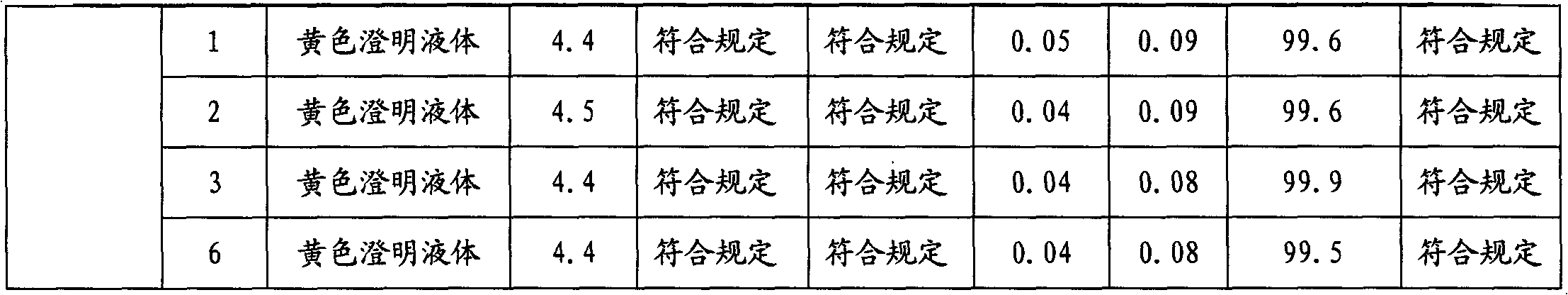
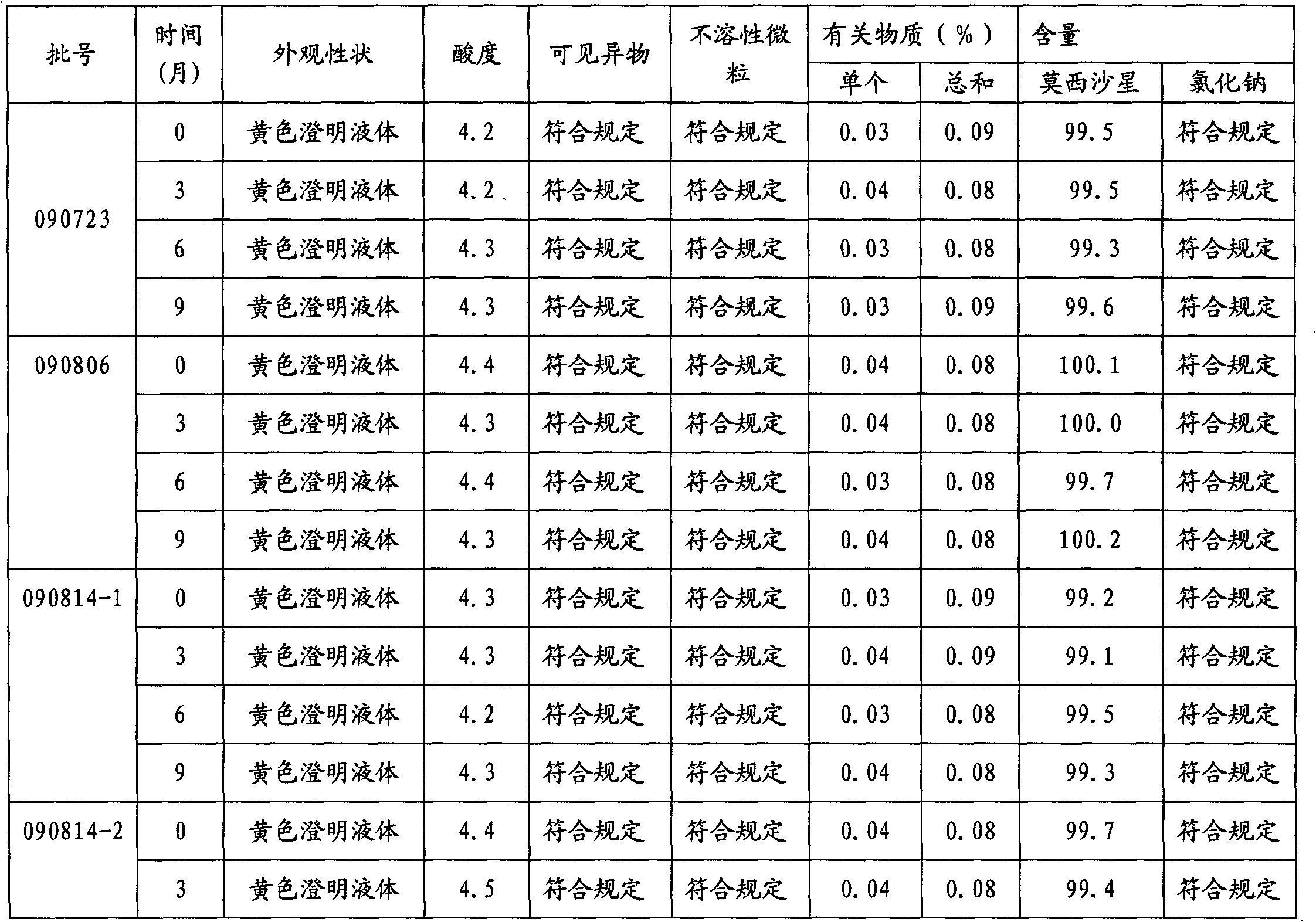
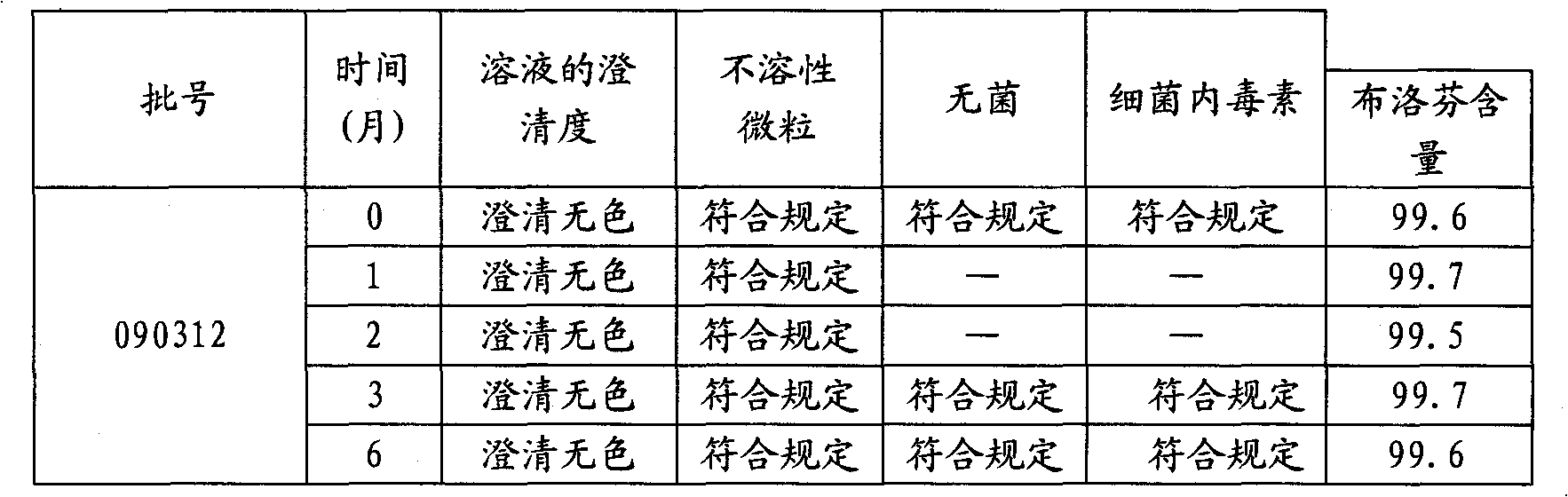
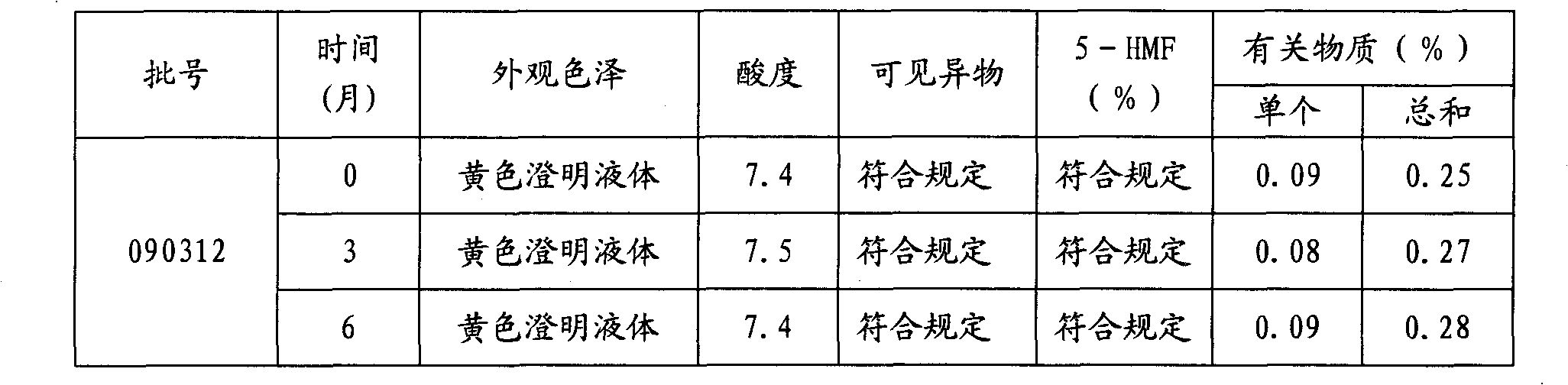
Stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride injection
InactiveCN102688183AImprove stabilityReduce formationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsFreeze-dryingSodium Chloride Injection
The invention relates to a stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride injection, which concretely contains moxifloxacin hydrochloride and xylitol. The injection can be in the forms of an injection, a transfusion and a freeze-drying powder injection. By the adoption of the stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride injection, stability of moxifloxacin hydrochloride-related substances, solution color, insoluble microparticles and the like during preparation, storage and usage processes of a moxifloxacin hydrochloride glucose or moxifloxacin hydrochloride sodium chloride injection in the present products or technologies is improved. The preparation process has no demanding requirements on equipment and is easy for industrial production.
Owner:CHONGQING PHARMA RES INST
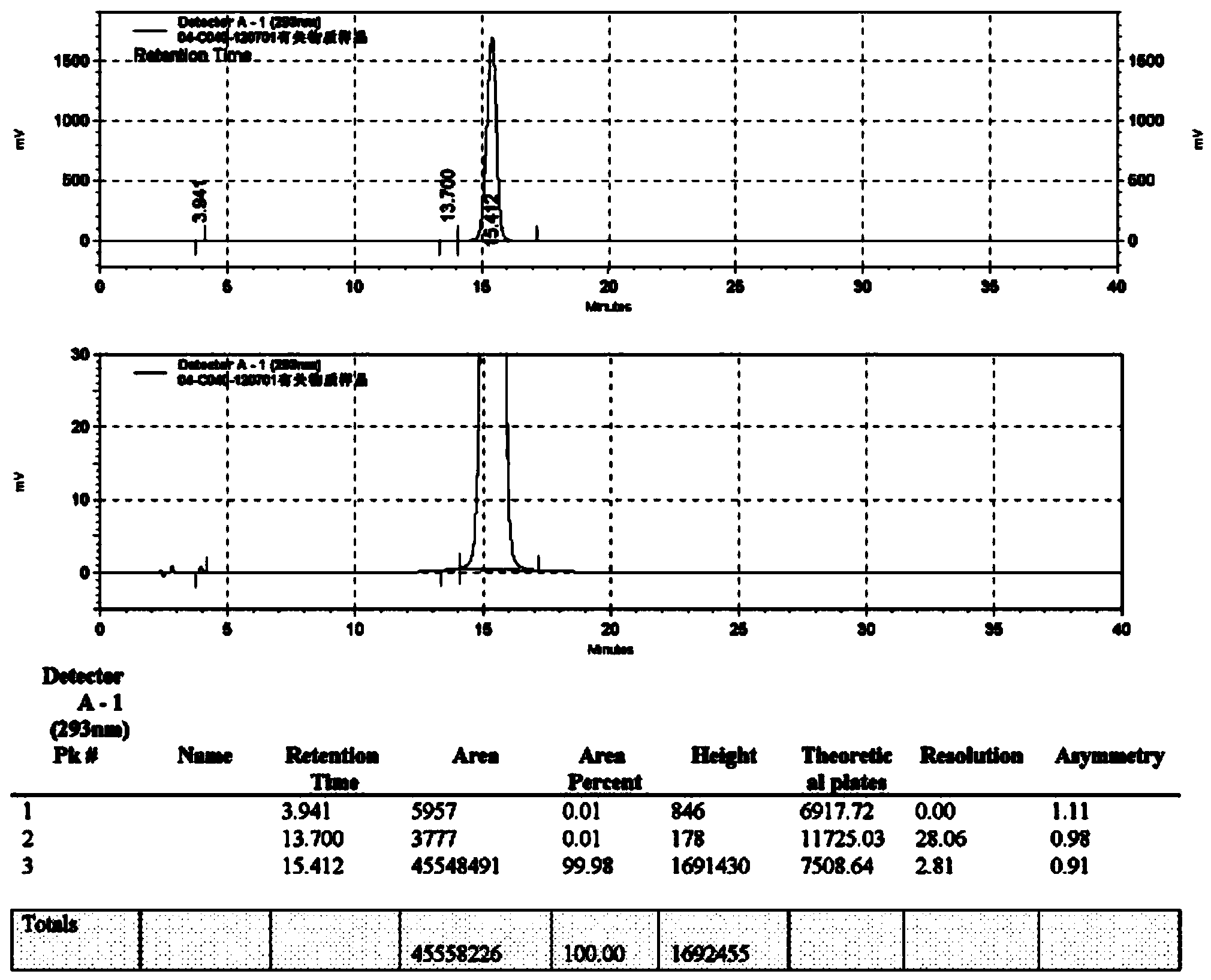
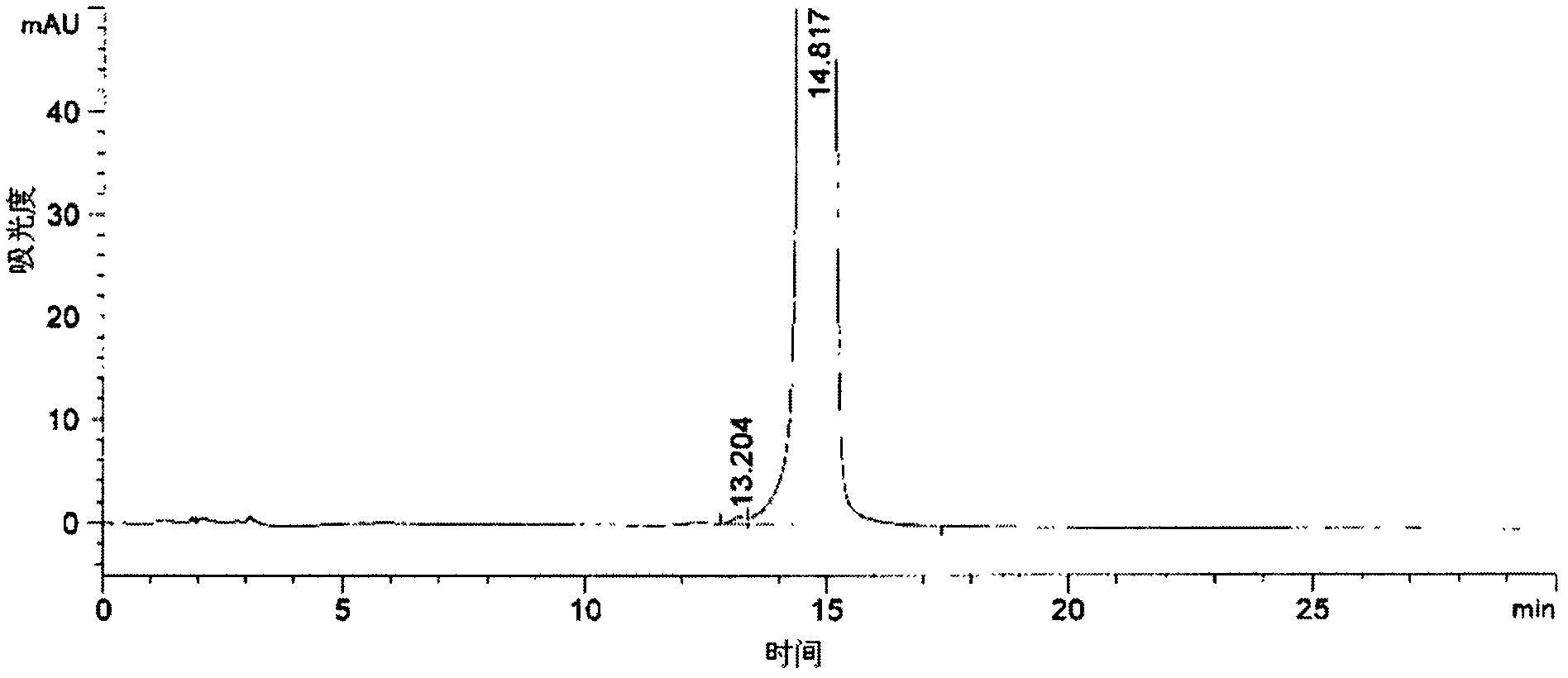
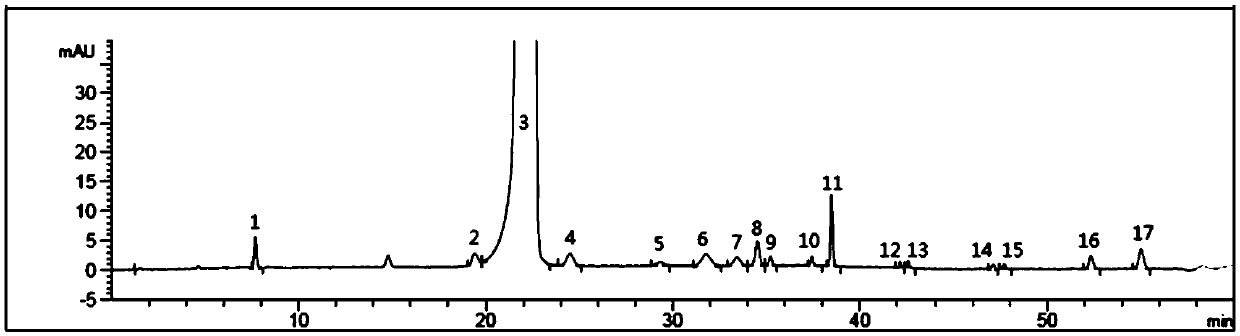
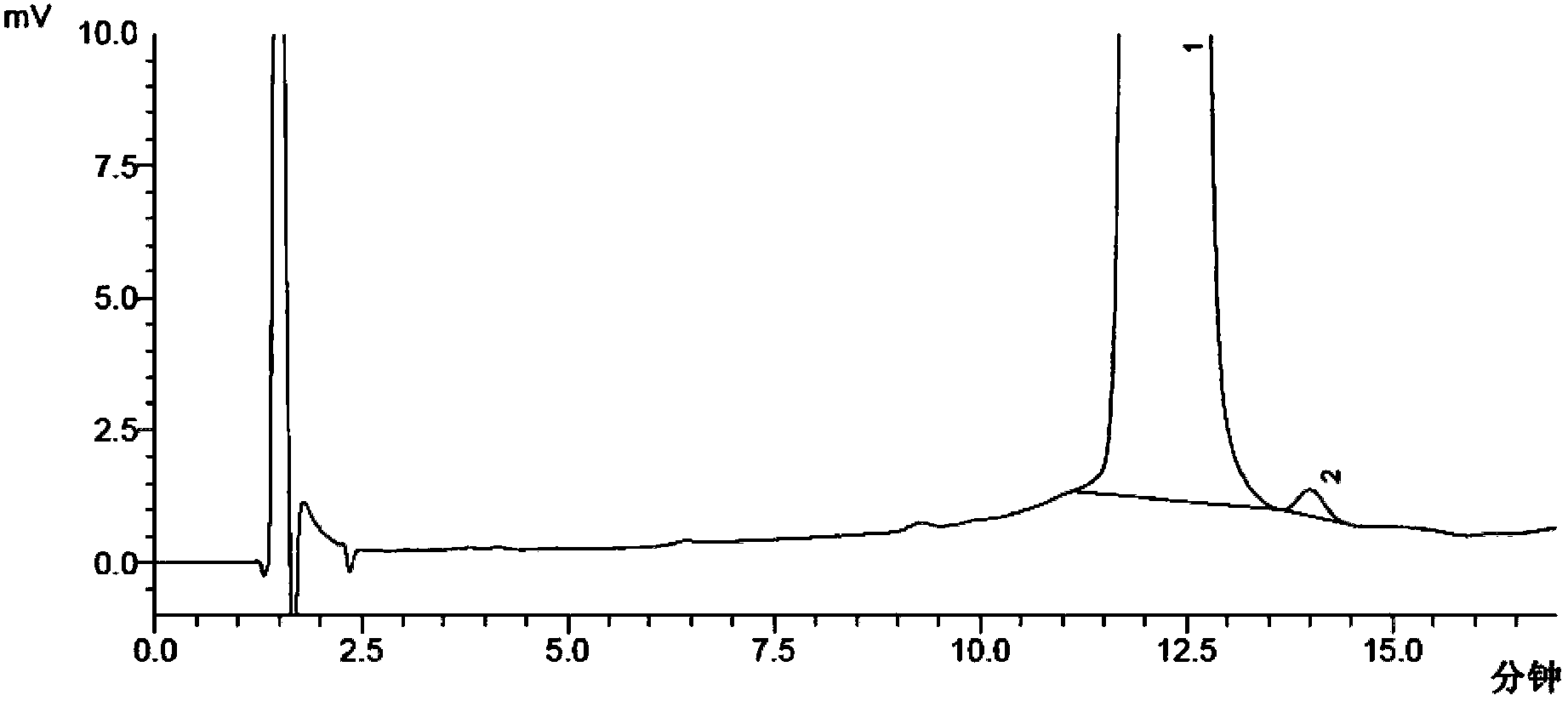
Method of detecting related substances of moxifloxacin hydrochloride by high performance liquid chromatography
PendingCN110470748AEffective separation detectionIncreased durabilityComponent separationElutionGradient elution
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry, and particularly relates to a detection method of related substances of moxifloxacin hydrochloride. Phenyl bonding silica gel is selected and used as a chromatographic column of a filler, and the mixed solvent gradient elution of a buffer and an organic phase is used as mobile phases for detection. The method realizes effective separationon 16 types of impurities of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride under the same chromatographic column condition through improvement on technology of the chromatographic column, elution gradients, columntemperature and the like. The method is good in stability, has good specificity, is high in sensitivity, and is high in resolution.
Owner:SICHUAN KELUN PHARMA RES INST CO LTD
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride glucose injection and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101836950APrecipitation does not occurReduce solubilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAdditive ingredientMoxifloxacin hydrochloride
The invention provides moxifloxacin hydrochloride glucose injection and a preparation method and use thereof. The method for preparing the injection comprises the following steps of: adding water for injection accounting for 20 to 98 percent of the batch volume into an ingredient tank, and adding glucose, a metal complexing agent and the moxifloxacin hydrochloride in a ratio; after stirring to fully dissolve the components, regulating the pH value to between 4.0 and 4.5 by using 1mol / L hydrochloric acid solution or 1mol / L sodium hydroxide, adding medicinal carbon accounting for 0.05 percent (W / V) of the total volume, uniformly stirring, maintaining the temperature of between 70 and 80 DEG C for 20 minutes, and performing circular filtering for over 20 minutes; replenishing the water for injection to the batch scale, stirring for 5 to 10 minutes, and detecting the pH value of the prepared solution (controlling to between 4.0 and 4.5); after determining that no residual water is present in an elevated tank and a pipeline, opening a valve of the elevated tank, and sampling liquid medicament at a self-circulation pipeline sampling port after the liquid medicament circulates for 20 minutes through a filter element and the elevated tank; detecting according to the intermediate quality standard, requiring that the content of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride is between 1.52 and 1.68 mg / ml, the glucose content is between 47.5 and 52.5 mg / ml, and the pH value is between 4.0 and 4.5; after the intermediate is detected to be qualified, beginning to fill; and conveying the filled semi-finished products into a sterilizing cabinet for sterilization, wherein the sterilization condition is to sterilize for 8 to 30 minutes at 121 DEG C through thermal pressure steam.
Owner:HC SYNTHETIC PHARMA CO LTD
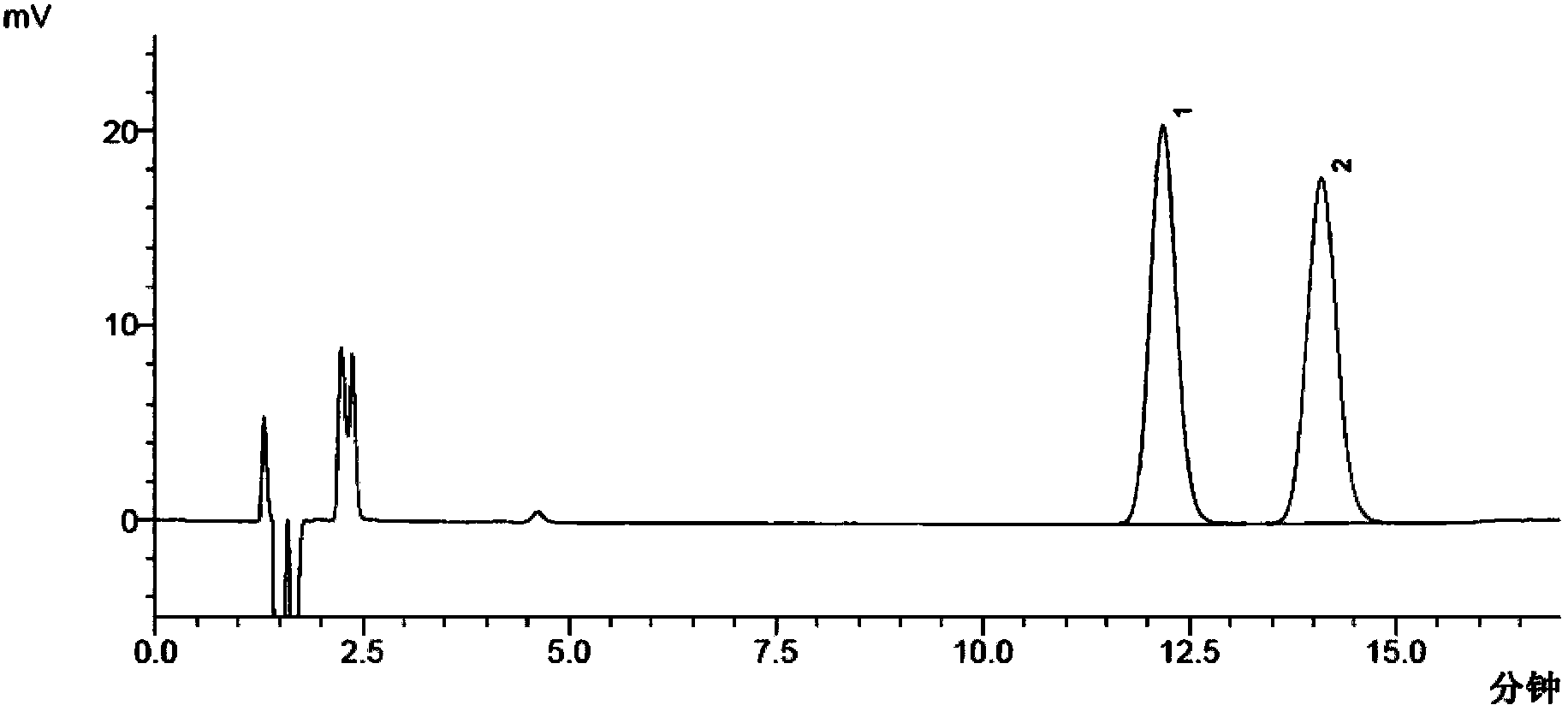
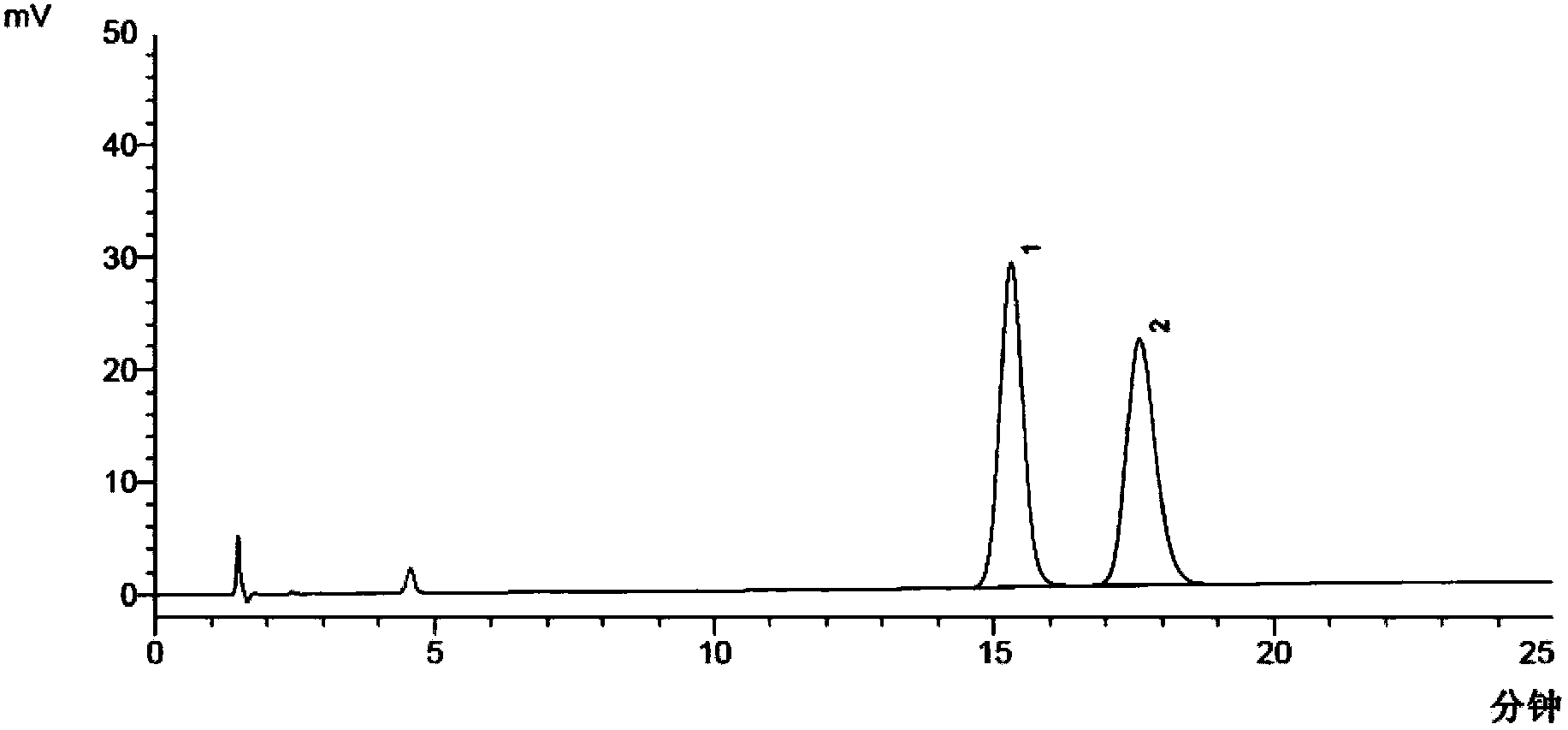
Method for separating and measuring moxifloxacin hydrochloride and enantiomer thereof
InactiveCN103543230AChiral resolution achievedAccurate detectionComponent separationControl releaseEnantiomer
The invention discloses a method for separating and measuring moxifloxacin hydrochloride and an enantiomer thereof. According to the method, high performance liquid chromatography is adopted, a reversed phase column is used, a chiral reagent serves as a mobile phase, the enantiomer in the moxifloxacin hydrochloride is positioned according to a moxifloxacin hydrochloride racemate, the enantiomer of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride existing in various dosage forms including sustained release type, controlled release type or common tablets, capsules, granules, oral liquid, injection, eye drops, nasal drops, auristilla, suppository or injection can be checked, the quality standard of the conventional moxifloxacin hydrochloride is improved, and a basis is provided for setting an enantiomer measurement standard of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride in the future.
Owner:NEW FOUNDER HLDG DEV LLC +2
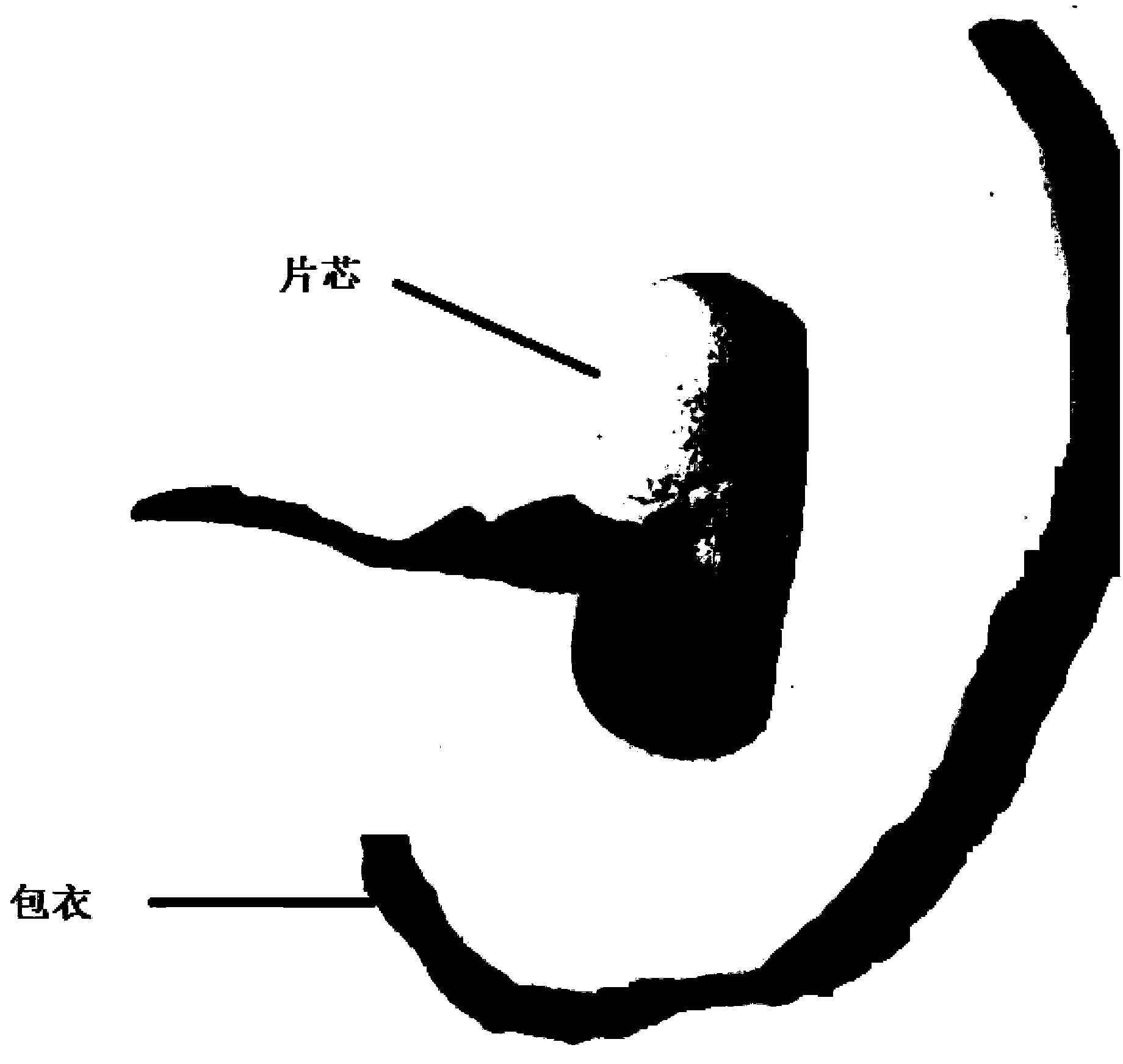
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride pharmaceutical composition and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103768063ASave energySave costsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHypromelloseMoxifloxacin hydrochloride
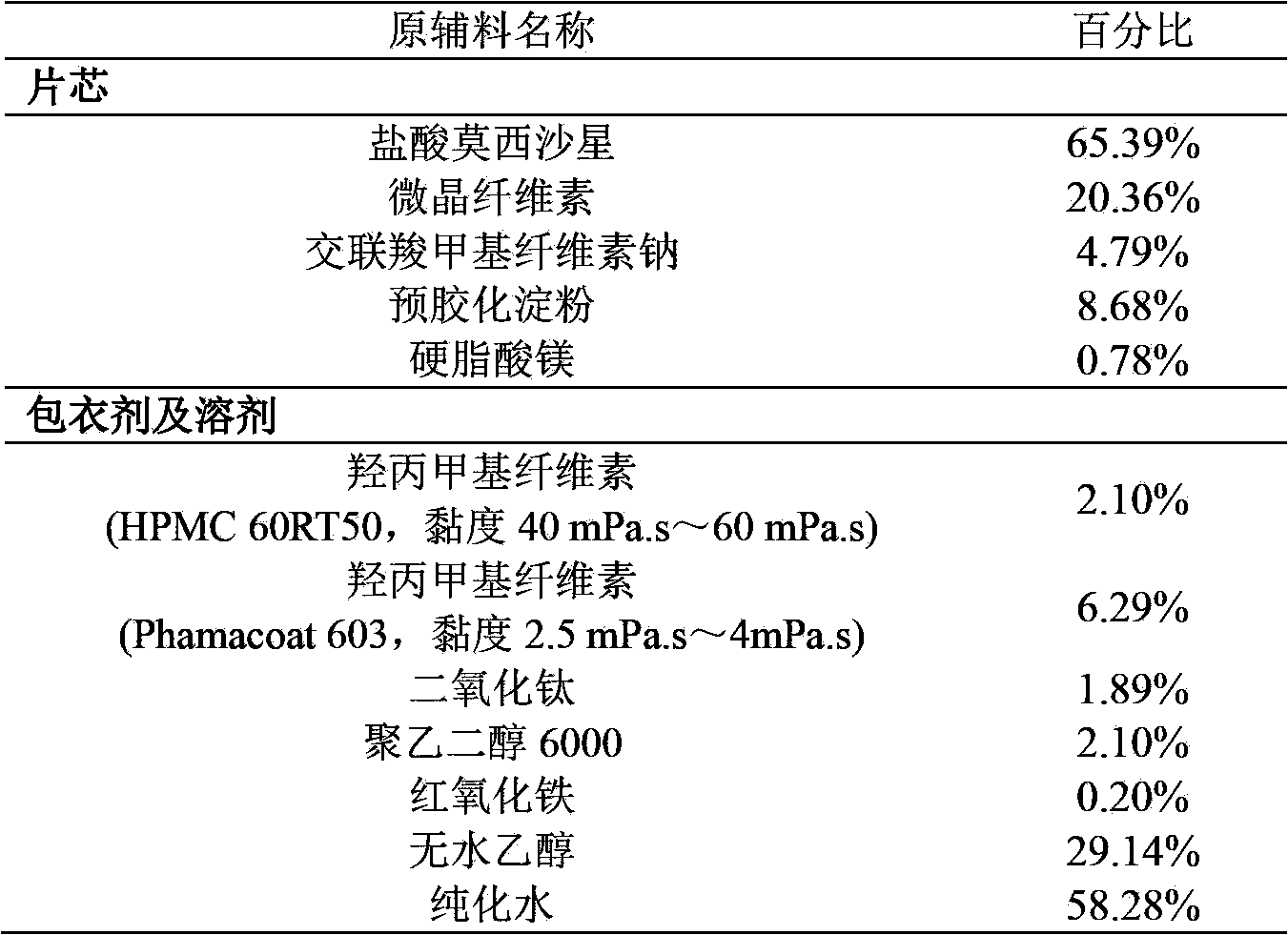
The invention provides a moxifloxacin hydrochloride pharmaceutical composition and preparation method thereof. The invention is characterized in that: tablet core is prepared by moxifloxacin hydrochloride, more than one excipient and a coating material, wherein, the weight of moxifloxacin hydrochloride is 60-70% of that of the tablet core, and the weight of excipients is 30-40% of that of the tablet core, and the weight of the coating material which is used for coating the tablet core and is composed of hypromellose with two or more than two viscosities is 1.0-4.0% of that of the pharmaceutical composition tablet core, and the weight ratio between hypromellose with viscosity of 40-120mPa.s and hypromellose with viscosity of 2.5-1.8mPa.s is 1:5-1:2. The pharmaceutical composition has the advantages of good stability, simple preparation technology and easy reproduction; the preparation method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHENZHEN SALUBRIS PHARMA CO LTD
Preparation method of moxifloxacin impurity F
ActiveCN103396416AHigh purityShort synthetic routeOrganic chemistrySodium bicarbonateAlkaline hydrolysis
The invention discloses a preparation method of moxifloxacin impurity F. The method comprises the following steps of: alkalifying moxifloxacin hydrochloride with sodium bicarbonate solution to get moxifloxacin free alkali, treating the moxifloxacin free alkali with methylation and alkaline hydrolysis reaction, and finally, obtaining high-purity moxifloxacin impurity F by recrystallization. The preparation method has the characteristics that the synthetic routes are simple and short, operations are simple and convenient, the obtained impurity product has higher purity, and the preparation method can be used for moxifloxacin impurity reference substance research, and so on.
Owner:NANJING YOUKE BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL RES +2
Preparation method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride
The invention relates to a preparation method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, which comprises the steps of: making 1-cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-8-methoxyl-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylate-03,04-broron ester acetate and (S,S)-2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0] nonane as raw materials completely react in a solvent, then cooling, adding hydrochloric acid, regulating the pH value to 4-6, stirring and crystallizing for more than 10 minutes, then adding the hydrochloric acid, regulating pH value to 0.5-2, cooling to 0-40 DEG C, crystallizing, leaching, washing, and drying to prepare the moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process, low cost, high yield and high purity, and is more suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:SICHUAN GOWELL PHARMA
Salt of carbostyril formic acid compound as well as preparation method and application of salt
ActiveCN102584819ARealize determinationEasy to separateOrganic chemistryComponent separationQuinoloneCinoxacine
The invention relates to an N-methylated 8-methoxyl carbostyril formic acid compound, acid addition salt or alkali metal salt shown in the formula I, as well as a preparation method and an application in quality detection and analysis of moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The compound or salt thereof is taken as an impurity reference substance, and moxifloxacin hydrochloride is detected and analyzed through an external standard method, so that moxifloxacin hydrochloride raw materials produced industrially and the impurity possibly contained in a preparation can be controlled quantificationally, further the quality of moxifloxacin hydrochloride can be increased, and the security in clinical medication can be improved. The formula I is shown in the description.
Owner:NANJING YOUKE BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL RES +2
Topical ophthalmic or otic solution formulations containing moxifloxacin hydrochloride and dexamethasone phosphate
Topical ophthalmic and otic solution compositions of moxifloxacin and dexamethasone phosphate are disclosed.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride injection, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102000024AWill not crystallizePrecipitation does not occurAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsOrganic acidOrganic base
The invention relates to a moxifloxacin hydrochloride injection comprising the following components in percentage by weight / volume: 0.03-1 percent of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, 0.0001-3 percent of pH regulating agent (organic acid, organic base, inorganic acid and inorganic base), 0.0001-0.1 percent of metal ion complexing agent and 0.65-0.95 percent of sodium chloride.
Owner:HC SYNTHETIC PHARMA CO LTD
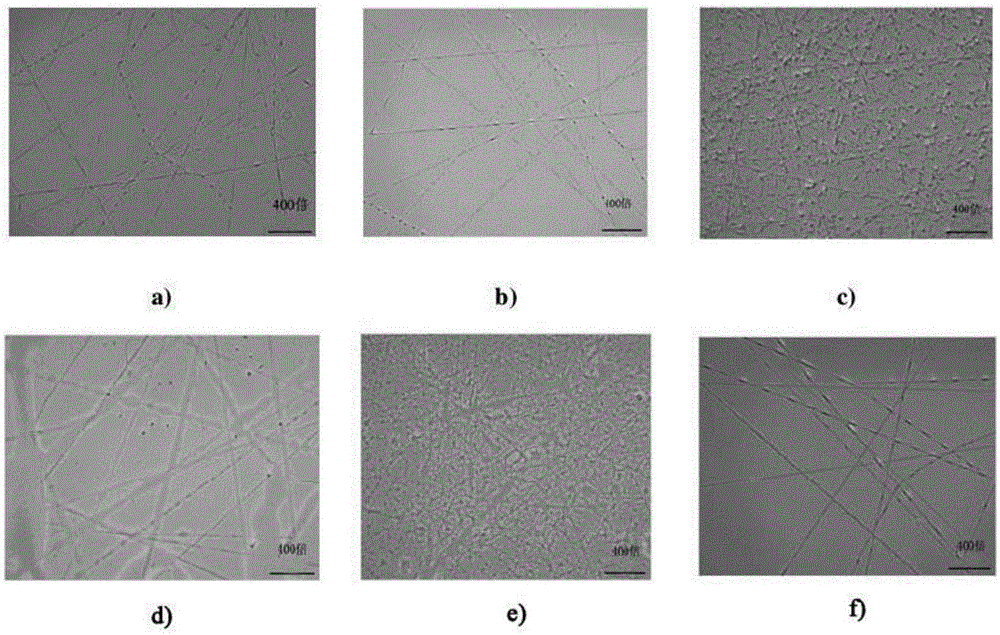
Preparation method of moxifloxacin-loaded electro-spinning film antibacterial dressing
The invention discloses a preparation method of moxifloxacin-loaded electro-spinning film antibacterial dressing. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) solution with the mass concentration being 8%-14%; preparing a sodium alginate (SA) solution with the mass concentration being 2%-3%; transferring and mixing the PVA solution and the SA solution at the volume ratio of (1:4) to (4:1), and adding a certain amount of moxifloxacin hydrochloride (MH) to prepare a spinning solution; and carrying out electrostatic spinning on the spinning solution, thus obtaining a spinning film. The spinning film dressing prepared by adopting the method has the good absorption property and good breathability, is free of irritation, can not cause the foreign body reaction, and can well release drugs on a wound surface, so that the wound healing is promoted, and the nursing is simple.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
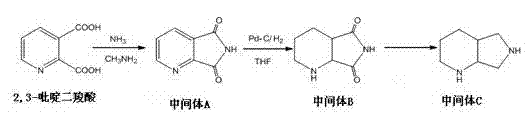
Method for preparing moxifloxacin hydrochloride intermediate
The invention discloses a method for preparing a moxifloxacin hydrochloride intermediate, which comprises the following steps of: adding methylamine and 2,3-dipicolinic acid into a reaction vessel to perform a reflux reaction until the 2,3-dipicolinic acid is reacted completely, and carrying out post treatment to obtain an intermediate A; dissolving the intermediate A into alcohol, adding Pd-C with stirring, carrying out catalytic hydrogenation in a high pressure kettle with a pressure of 3Mpa and a temperature of 65 DEG C until the intermediate A is reacted completely, and carrying out post treatment to obtain an intermediate B; and adding tetrahydrofuran into the reaction vessel, carrying out ice-bath cooling to a temperature of below 5 DEG C, adding sodium borohydride and boron fluoride etherate, controlling a temperature in a range of below 15 DEG C, adding the intermediate B, performing a reflux reaction until the intermediate B is reacted to be disappeared, and carrying out post treatment to obtain an intermediate C. The method for preparing the moxifloxacin hydrochloride intermediate, which is provided by the invention, is simple to operate and has few steps and high yield, and the industrial production is easy to realize.
Owner:太仓市运通化工厂
Novel preparation method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride
ActiveCN104230925AReduce generationReduce complicated stepsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsNonaneEvaporation
The invention provides a method for preparing a moxifloxacin intermediate and moxifloxacin hydrochloride, which comprises the following steps: carrying out condensation reaction on main ring chelate disclosed as Formula (I) and (S,S)-2,8-diazabicyclo-[4.3.0]nonane in the presence of an acid acceptor in a solvent, acidifying for salification, crystallizing, filtering, washing and drying to obtain the moxifloxacin hydrochloride. The method is characterized in that the solvent in the condensation reaction is alcohol. The condensation reaction is carried out in the alcohol solvent at the controlled temperature of 30-80 DEG C (preferably lower temperature), so the method has the advantage of mild reaction conditions, greatly reduces the generation of impurities, saves the energy; the alcohol solvent can be directly acidified after sufficient reaction, thereby saving the complex step of removing acetonitrile by evaporation and greatly simplifying the steps; and the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANYISHI PHARMA
Process for crystallizing moxifloxacin hydrochloride
ActiveCN102030751AGood volatilization effectEasy to recycleOrganic chemistryOrganic acidOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a process for crystallizing moxifloxacin hydrochloride. In the conventional crystallization methods, the yield of the moxifloxacin hydrochloride is lower, the amount of organic solvents residual in the moxifloxacin hydrochloride is larger, a crystallization solvent plays a role in inhibiting the growth of microbes and even poisoning the microbes, and normal function of a wastewater treatment station is influenced. The technical scheme comprises the following steps of: adding water and glycol alkyl ether successively into moxifloxacin, organic acid salt of the moxifloxacin or inorganic weak-acid salt of the moxifloxacin, stirring for dissolving at the temperature of between 40 and 100 DEG C, decoloring, filtering and collecting filtrate; heating the filtrate to the temperature of between 40 and 100 DEG C, dripping concentrated hydrochloric acid, and stirring to separate out a crystal; and dripping the glycol alkyl ether, stirring, cooling, keeping the temperature, crystallizing, performing suction filtration, rinsing, and drying to prepare the moxifloxacin hydrochloride crystal. Due to the crystallization solvent, the moxifloxacin hydrochloride is more completely separated out in a crystallization system, and the product yield is higher.
Owner:SHANGYU JINGXIN PHARMA
Synthesis method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride impurity
The invention discloses a synthesis method of moxifloxacin hydrochloride impurity shown in a formula (I). The synthesis method comprises the following steps of: (a) weighting moxifloxacin or moxifloxacin hydrochloride, methanoic acid and formaldehyde in a molar ratio of 1: (45-145): (20-77), putting in a reflux device, carrying out heating reflux till completely reacting, concentrating reaction liquid to be dry, washing with water, drying, dissolving obtained residues with water, then carrying out decoloring treatment, adjusting the pH value of obtained filtrate to neutral, cooling, crystalizing, separating out crystals, and drying, thus obtaining a midbody; and (b) dissolving the midbody by using an organic solvent, adjusting the pH value of an obtained solution to 1-4 by using hydrochloric acid, then carrying out decoloring treatment, adding water to obtained filtrate, cooling, crystalizing, separating out crystals, and drying, thus obtaining the compound shown in the formula (I). The synthesis method is simple and easy to operate; and the obtained product has high purity (above 99.5%) and can be directly used as an impurity comparison substance.
Owner:GUILIN PHARMA
Intravenous drug delivery system for ibuprofen and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101785754AThe preparation process is feasibleImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticActivated carbonMedicine
The invention relates to moxifloxacin hydrochloride glucose injection and the preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: A. adding injection water into the ingredient tank and a proper amount of auxiliary material and ibuprofen, B. stirring and adjusting the PH value with base regulator to 6.5 - 9.0. Adding injection water to the needed amount and stirring by activated carbon pole for needle injection, decarbonising the titanium stick and refine the solution by millipore filter. C. conducting the encapsulation after the pass of the test. D. delivering the encapsulated semi-product into the sterilization case for autoclave sterilization.
Owner:HC SYNTHETIC PHARMA CO LTD
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride compounds and intermediates and methods for making same
Owner:F I S FAB ILTALIANA SINTETICI SPA
Stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride medicinal composition
InactiveCN102525982ASolve the problems of poor stability and slow dissolutionHigh yieldAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCinoxacineCyclodextrin
The invention discloses a stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride medicinal composition and a preparation method thereof. The stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride medicinal composition consists of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, hydroxypropyl betacyclodextrin, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose 12 and magnesium stearate. The stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride medicinal composition is high in stability, has the obvious advantages of improving the yield of products, reducing cost and implementing industrialization and is better applied clinically, and preparations of the stable moxifloxacin hydrochloride medicinal composition have high stability.
Owner:TIANJIN HANKANG PHARMA BIOTECH
Moxifloxacin analogue as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a moxifloxacin analogue Y shown in a figure. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking moxifloxacin as a raw material, firstly protecting a protection group on a secondary amino group on a 7-position side chain, then performing acyl chlorination and ethyl ester esterification on a 3-bit carboxyl group and removing an amino-group protective agent to obtain the moxifloxacin analogue Y. The preparation of the analogue Y provides a reference substance for moxifloxacin hydrochloride-related substances.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANYISHI PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com