Zero discharge and chromium recovery method for iron and steel industry chromium-containing wastewater
A technology of chromium wastewater and zero discharge, applied in chemical instruments and methods, general water supply saving, metallurgical wastewater treatment, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the environmental and economic benefits of enterprises, and achieve the reduction of sludge hazardous waste and good environmental protection benefits And economic benefits, the effect of small footprint
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
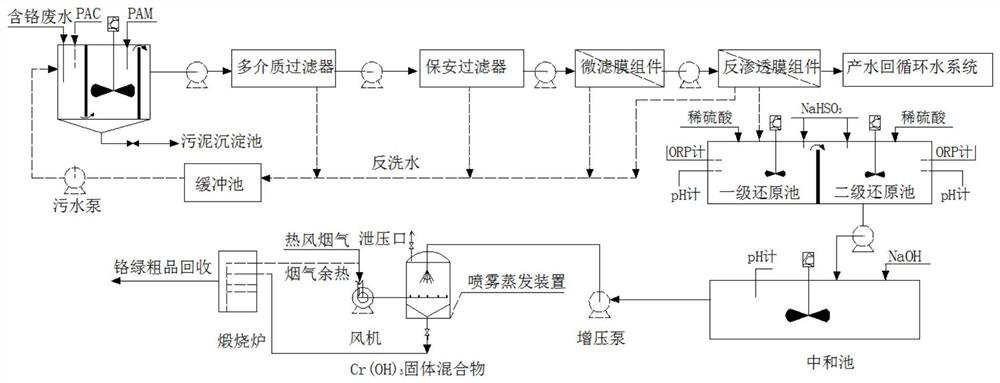
[0055] refer to figure 1 The flow chart of the zero discharge of chromium-containing wastewater in the iron and steel industry and the chromium recovery method shown in the following process:
[0056] Add PAC (polyaluminum chloride) and PAM (polyacrylamide) to the wastewater regulating tank for the chromium-containing wastewater from the iron and steel rolling process. The mass percentage of PAC is 3wt%, and the mass percentage of PAM is 2wt%. The coagulation condition is : The stirring speed is 50r / min, the dosage of PAC and PAM is 8mg / L and 1.5mg / L respectively, and the hydraulic retention time is 45min. Pumped to the sludge settling tank, after a certain amount is accumulated, the sludge is dehydrated and sent to sintering for disposal;
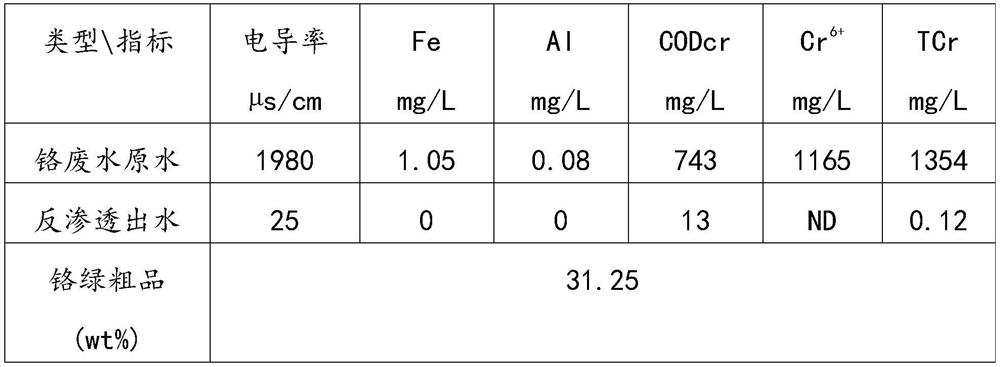
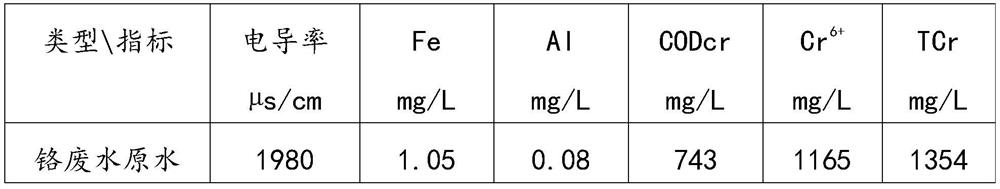
[0057] The chromium-containing wastewater is sent to the multi-media filter for pretreatment after passing through the wastewater conditioning tank, to remove suspended solids, colloids, turbidity, bacteria, microorganisms, viruses, etc. ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] refer to figure 1 The flow chart of the zero discharge of chromium-containing wastewater in the iron and steel industry and the chromium recovery method shown in the following process:
[0069] Add PAC (polyaluminum chloride) and PAM (polyacrylamide) to the wastewater regulating tank for the chromium-containing wastewater from the iron and steel rolling process. The mass percentage of PAC is 3wt%, and the mass percentage of PAM is 2wt%. The coagulation condition is : The stirring speed is 50r / min, the dosage of PAC and PAM is 12mg / L and 1mg / L respectively, and the hydraulic retention time is 60min. Sent to the sludge sedimentation tank, after accumulating a certain amount, send it to sintering disposal through sludge dehydration;
[0070] The chromium-containing wastewater is sent to the multi-media filter for pretreatment after passing through the wastewater conditioning tank, to remove suspended solids, colloids, turbidity, bacteria, microorganisms, viruses, etc. lar...
Embodiment 3
[0082] refer to figure 1 The flow chart of the zero discharge of chromium-containing wastewater in the iron and steel industry and the chromium recovery method shown in the following process:
[0083] Add PAC (polyaluminum chloride) and PAM (polyacrylamide) to the wastewater regulating tank for the chromium-containing wastewater from the iron and steel rolling process. The mass percentage of PAC is 3wt%, and the mass percentage of PAM is 2wt%. The coagulation condition is : The stirring speed is 50r / min, the dosage of PAC and PAM is 15mg / L and 0.5mg / L respectively, and the hydraulic retention time is 30min. Pumped to the sludge settling tank, after a certain amount is accumulated, the sludge is dehydrated and sent to sintering for disposal;
[0084] The chromium-containing wastewater is sent to the multi-media filter for pretreatment after passing through the wastewater conditioning tank, to remove suspended solids, colloids, turbidity, bacteria, microorganisms, viruses, etc....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com