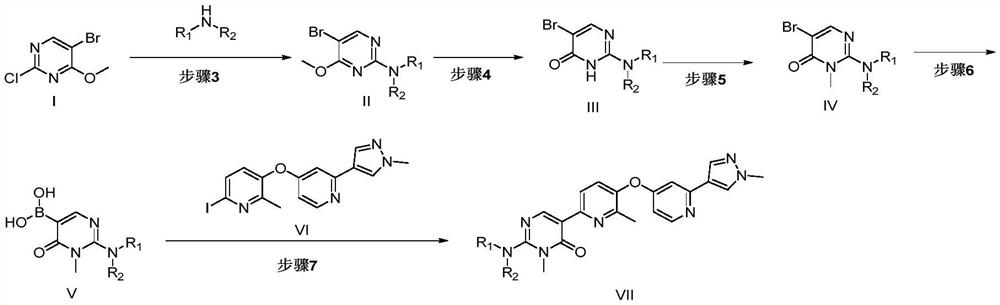
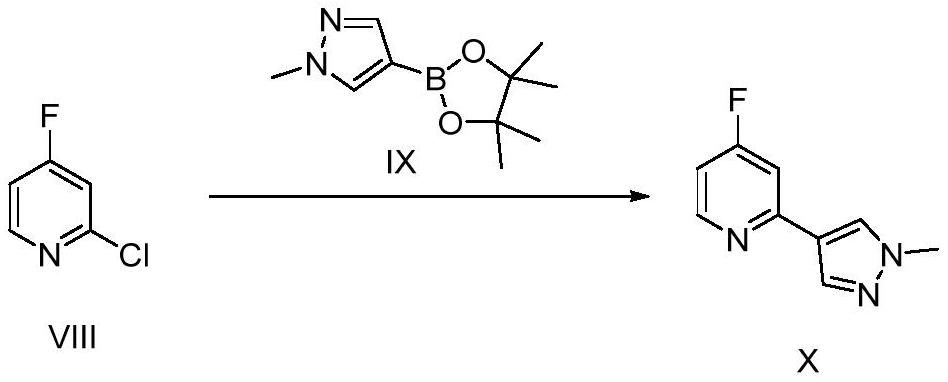
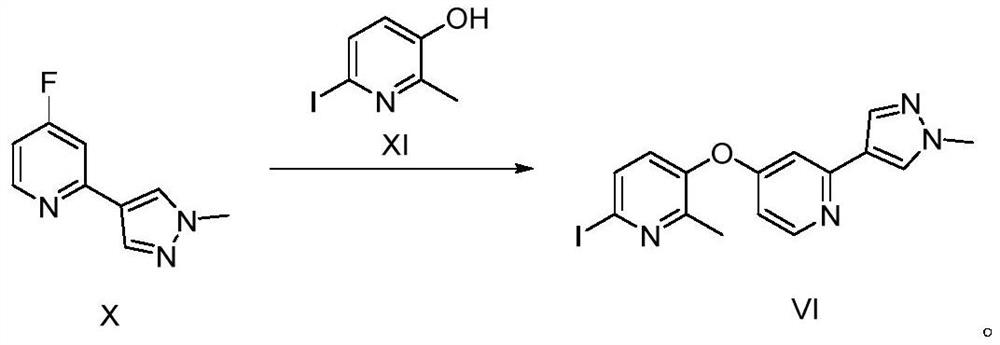
Patents
Literature
49results about How to "Reduce hazardous waste" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
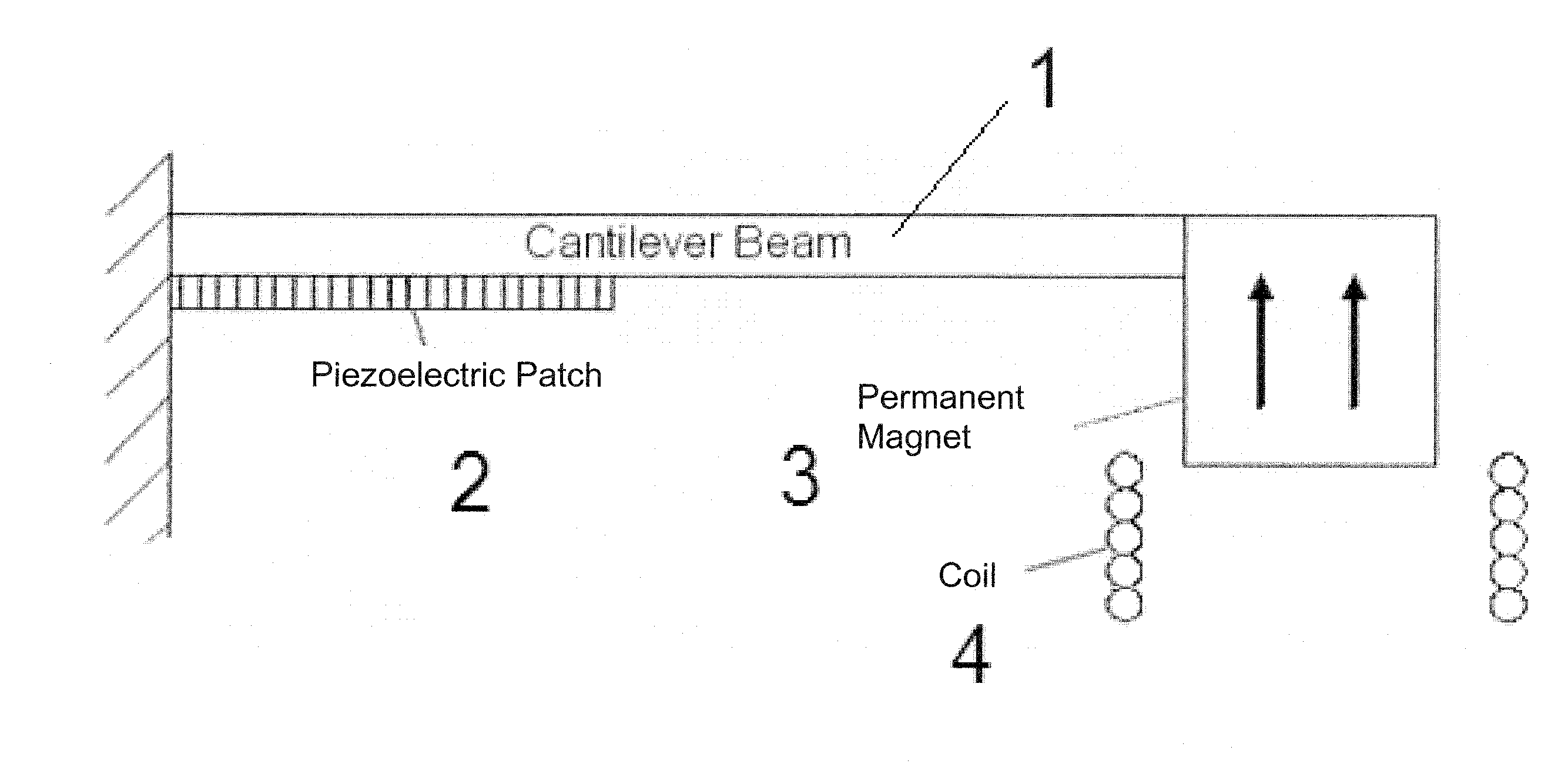
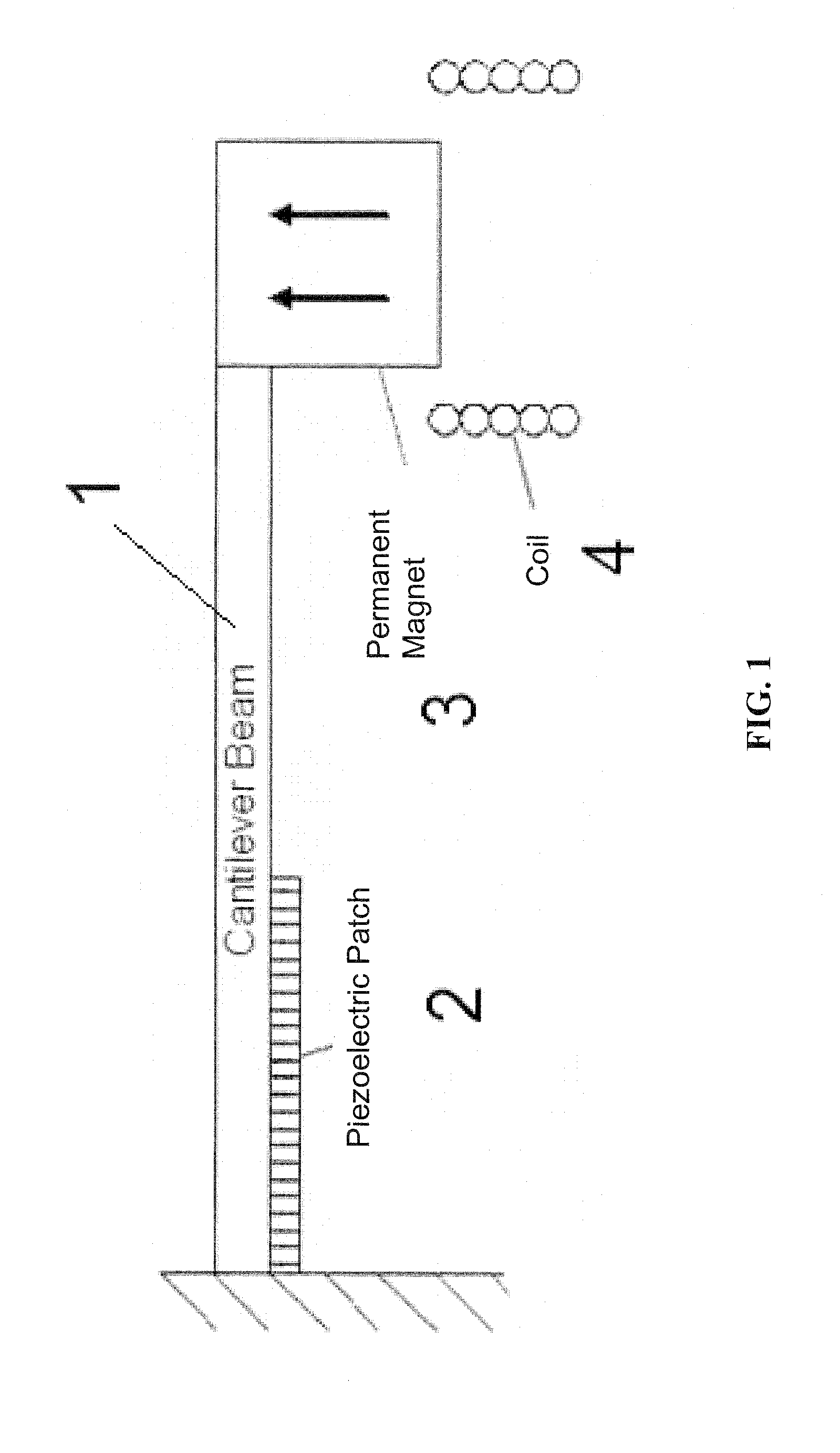
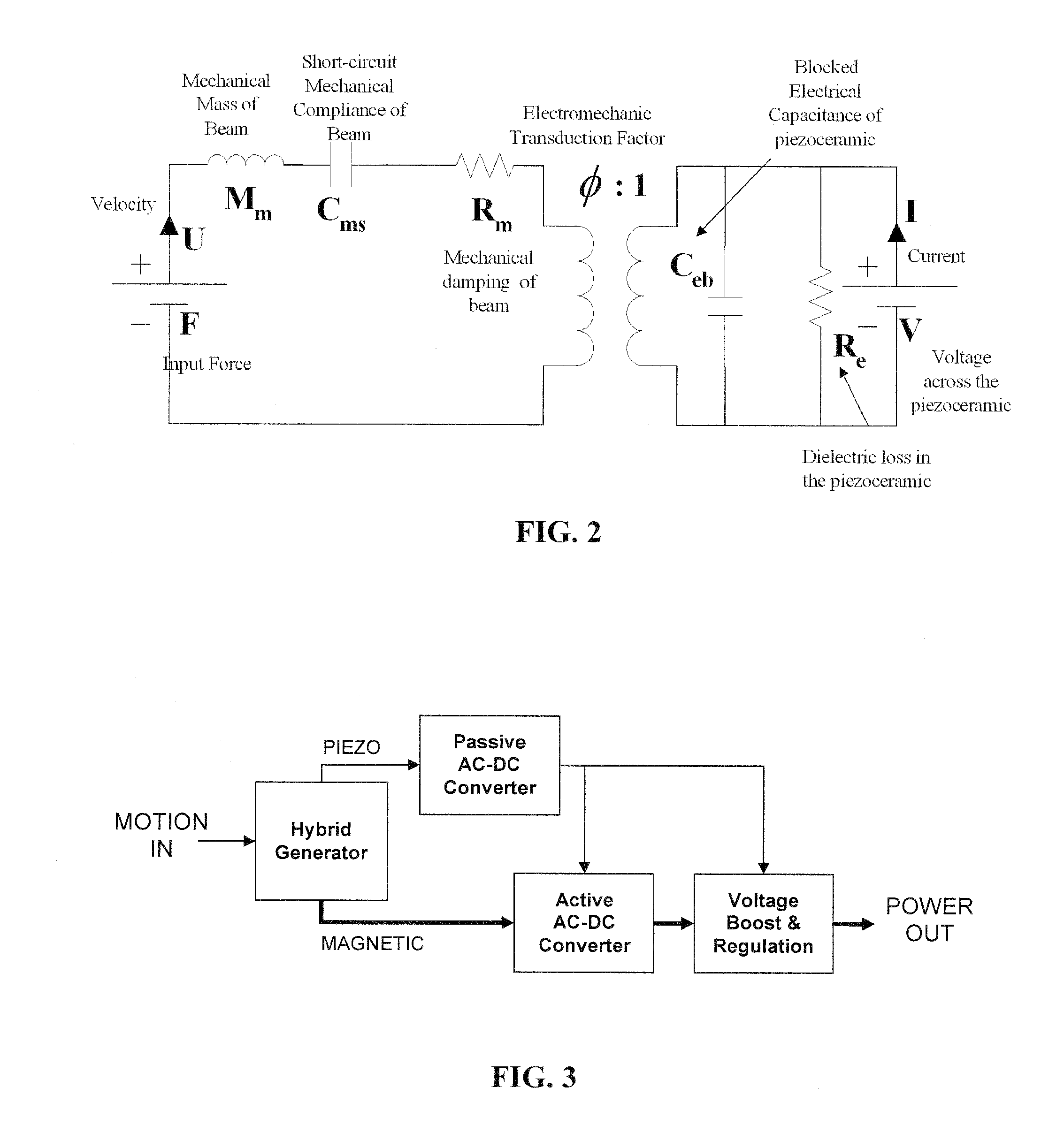
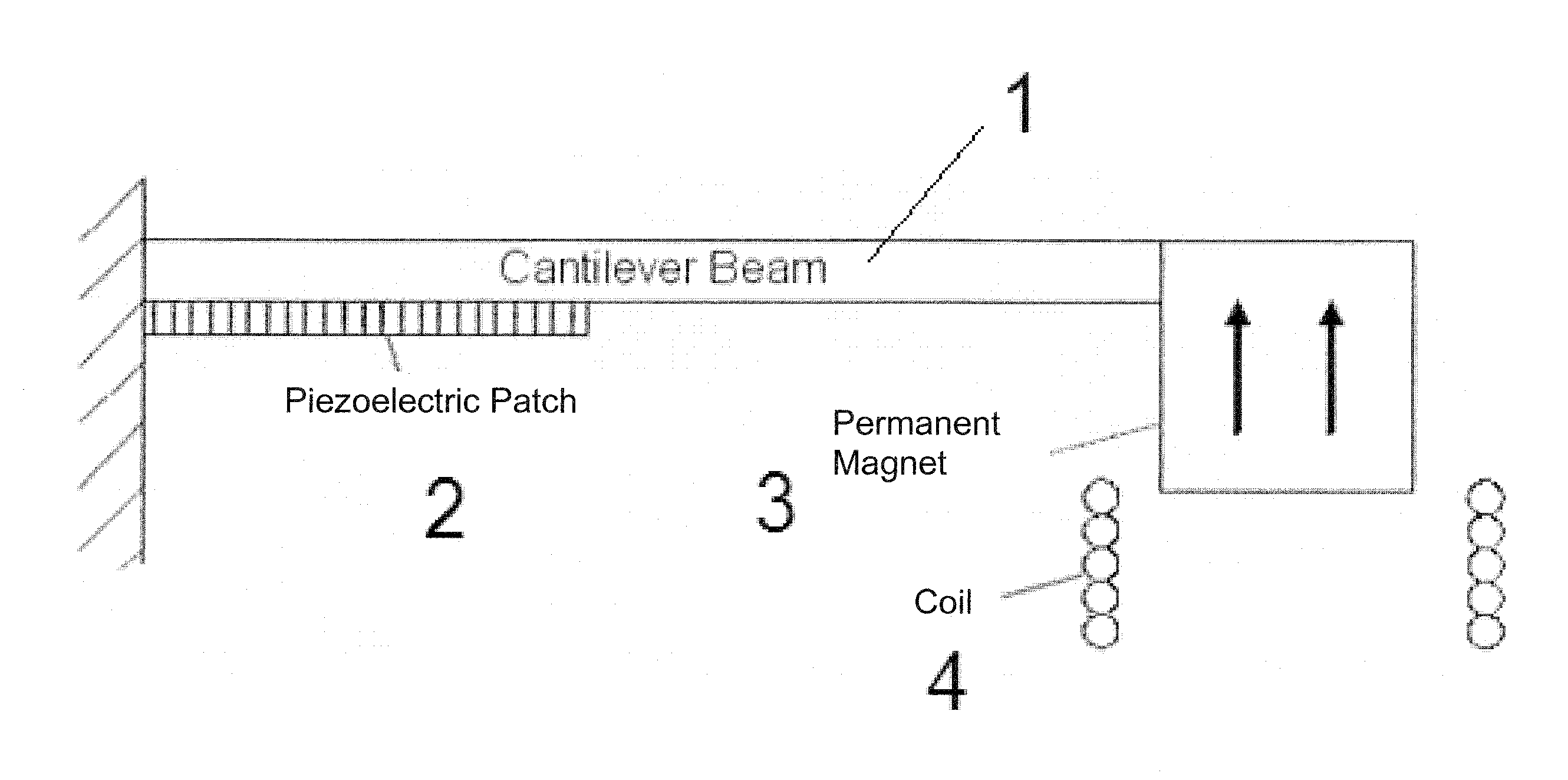
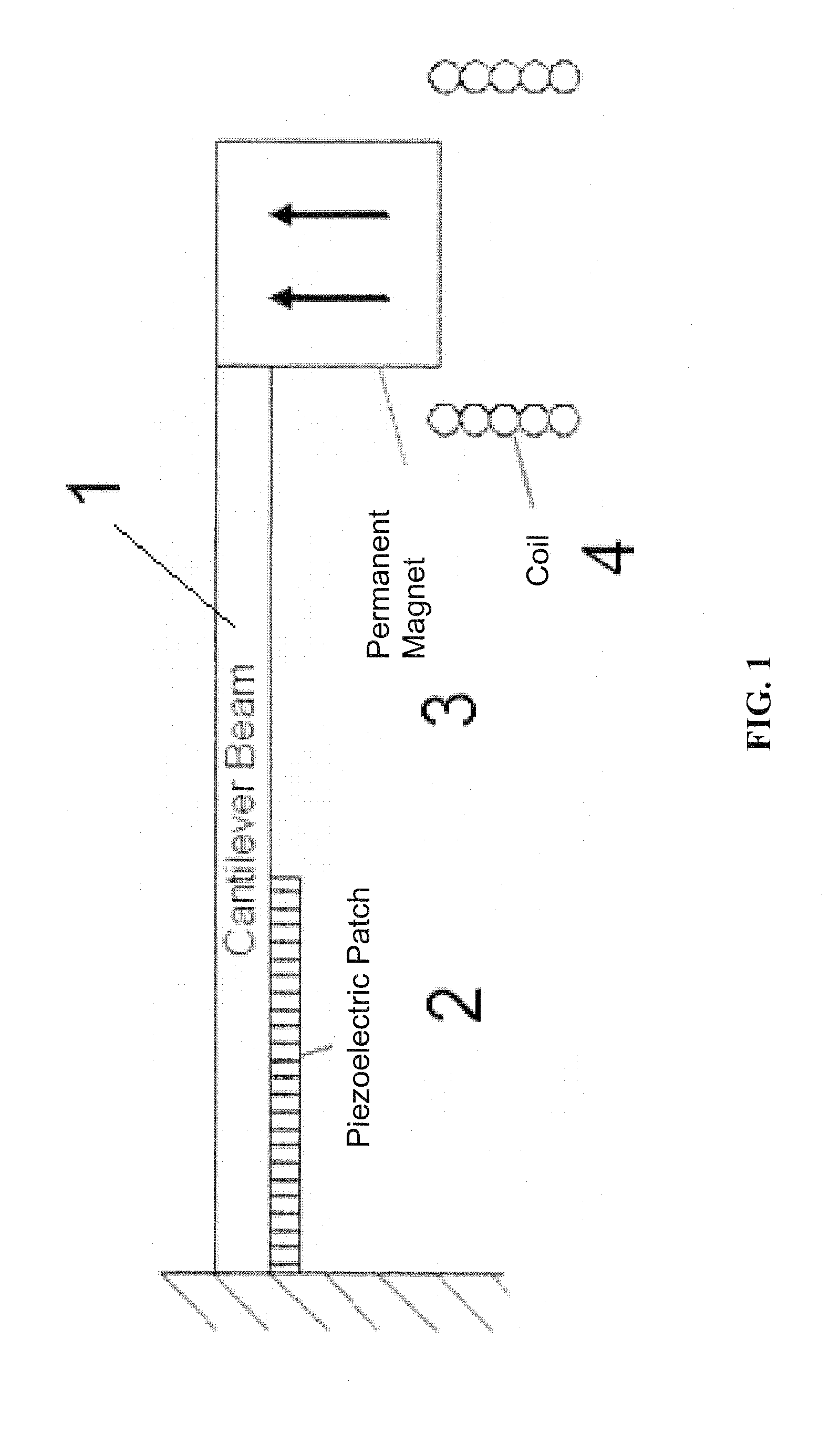
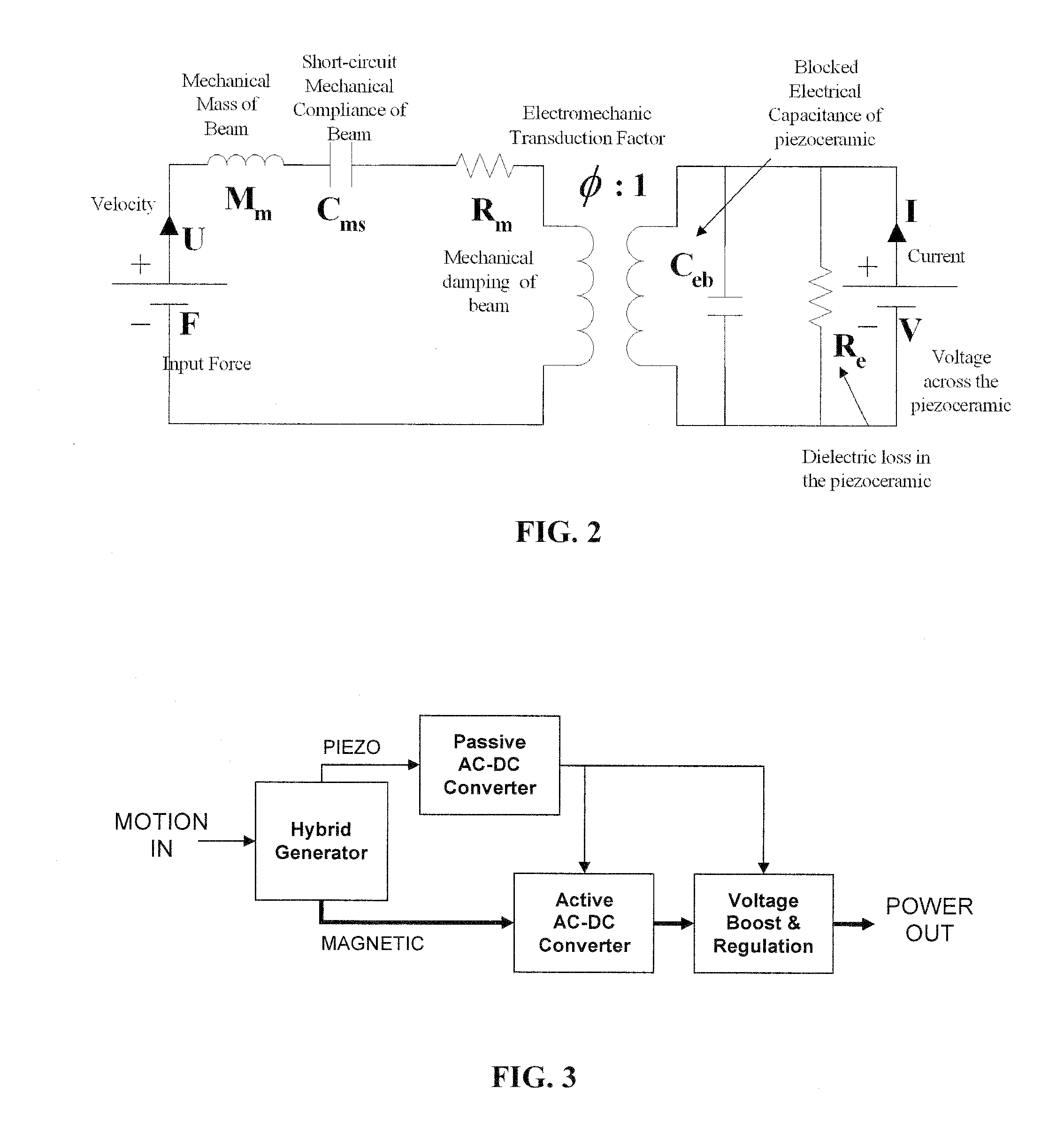
Dual-Mode Piezoelectric/Magnetic Vibrational Energy Harvester
ActiveUS20110215590A1Improve electricity efficiencyReduce hazardous wastePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesRelative displacementElectricity
Embodiments of a vibrational energy harvester are provided. A vibrational energy harvester can include a translator layer sandwiched between two stator layers. The translator layer can include a plate having an array of magnets and two or more piezoelectric patches coupled to a tether beam attached to the plate. The stator layers can have a printed circuit board with multilayer electrical windings situated in a housing. In operation, vibration of the housing can result in bending of the piezoelectric patches coupled to the tether beam. This bending simultaneously results in a relative displacement of the translator, which causes a voltage potential in the piezoelectric patches, and a relative velocity between the translator and the stators, which induces a voltage potential in the stator coils. These voltage potentials generate an AC power, which can be converted to DC power through a rectification circuit incorporating passive and active conversion.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Dual-mode piezoelectric/magnetic vibrational energy harvester
ActiveUS8354778B2Improve electricity efficiencyReduce and eliminate dependencePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical energy handlingRelative displacementElectricity
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
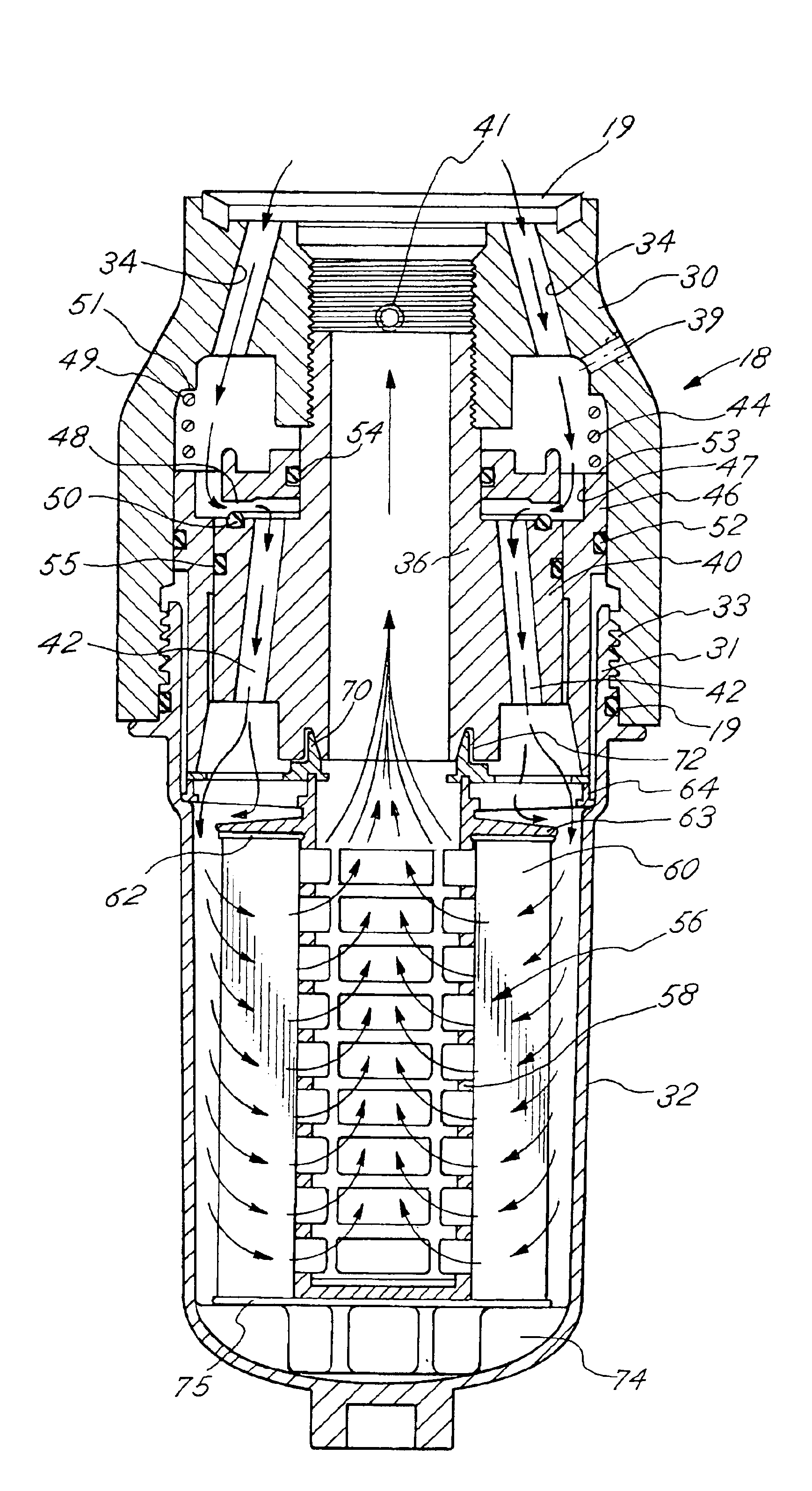
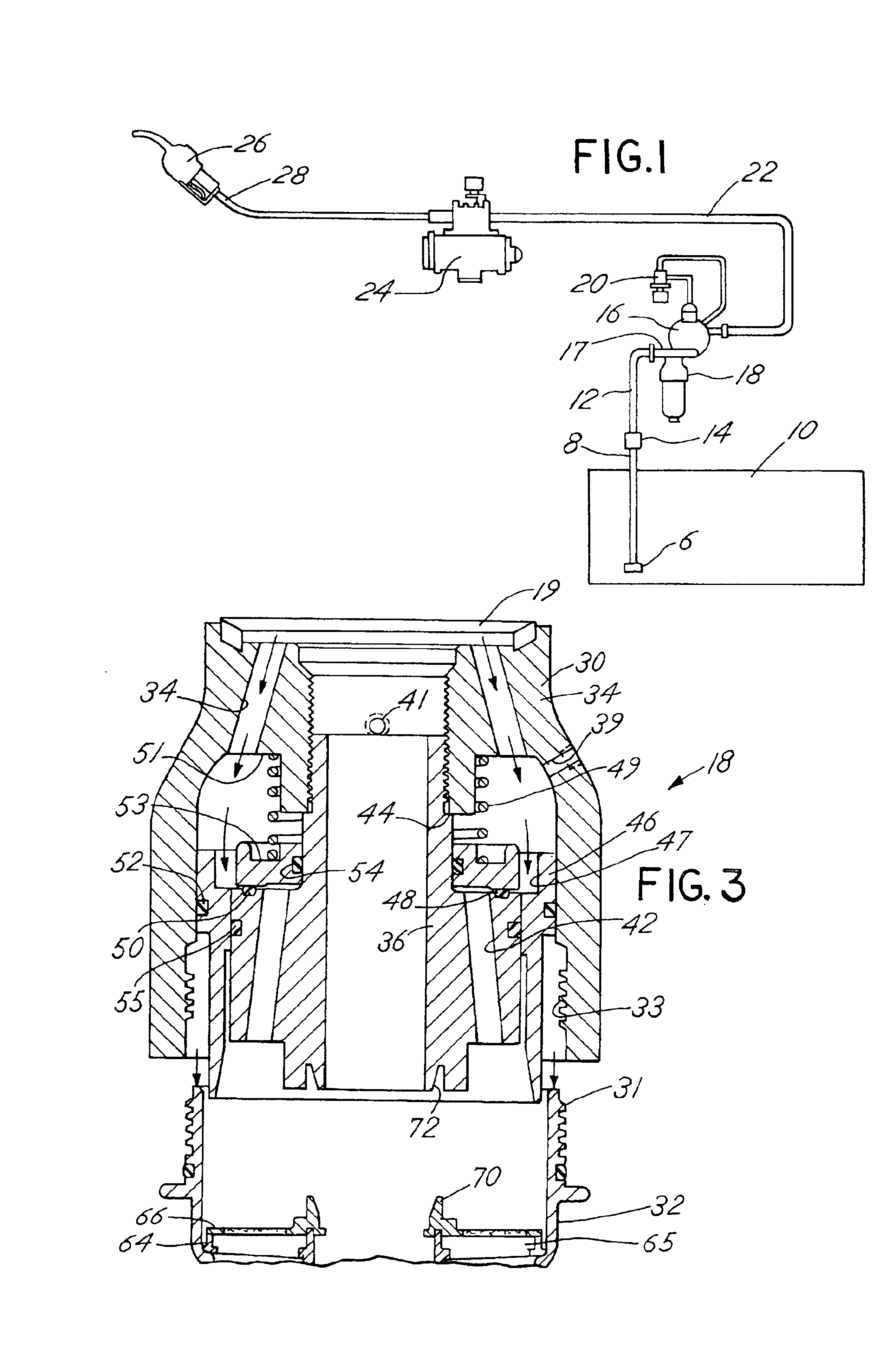
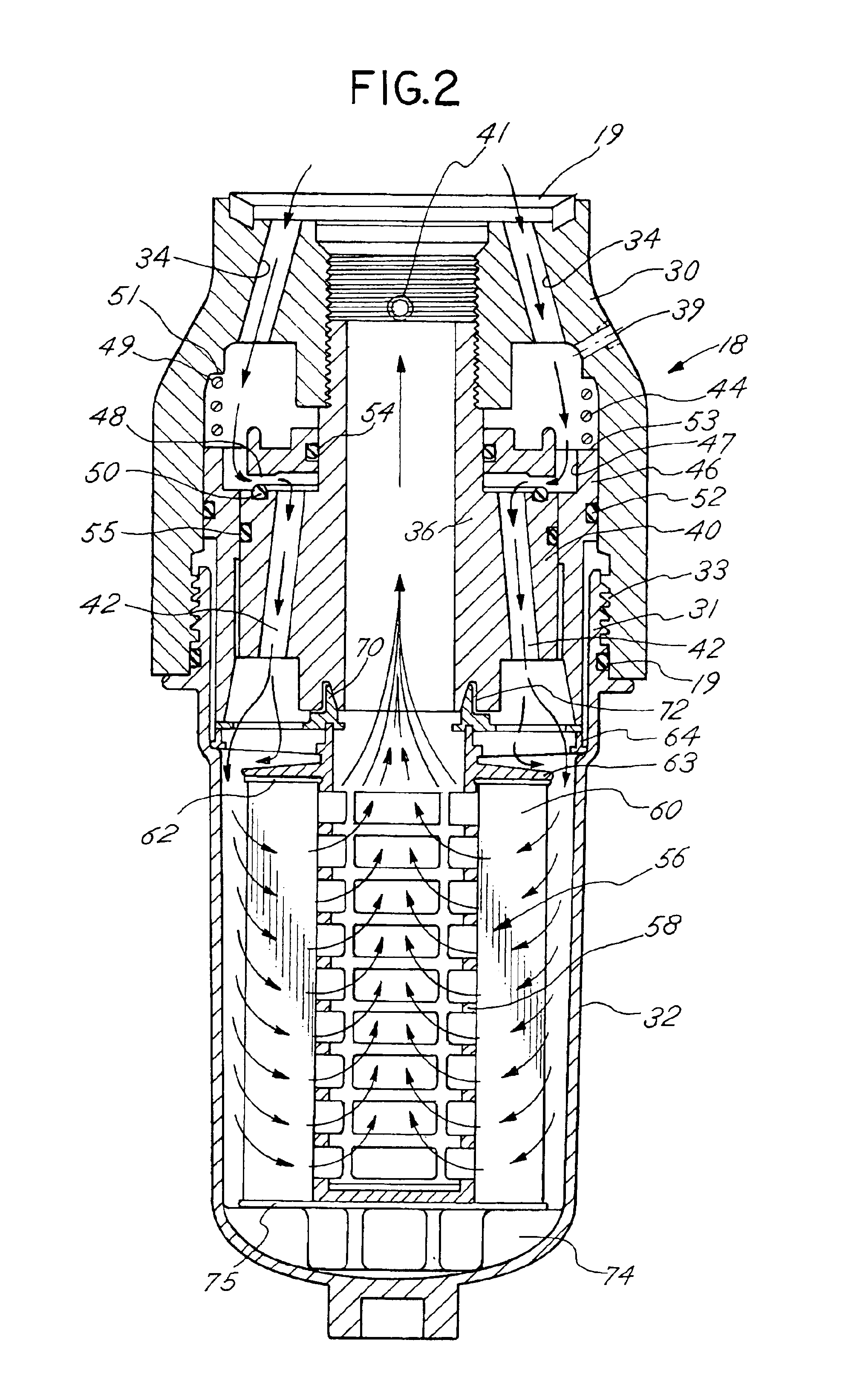
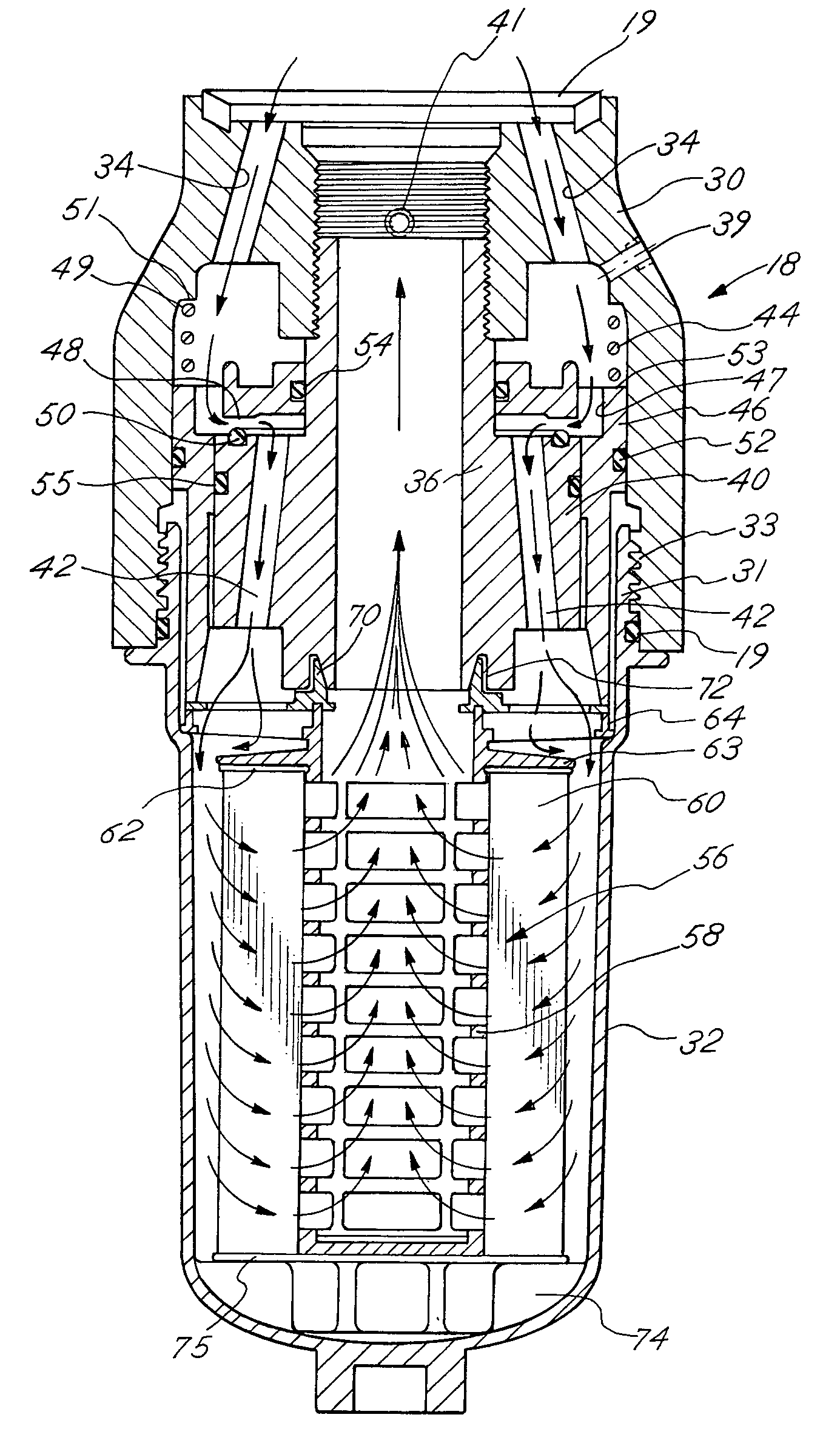
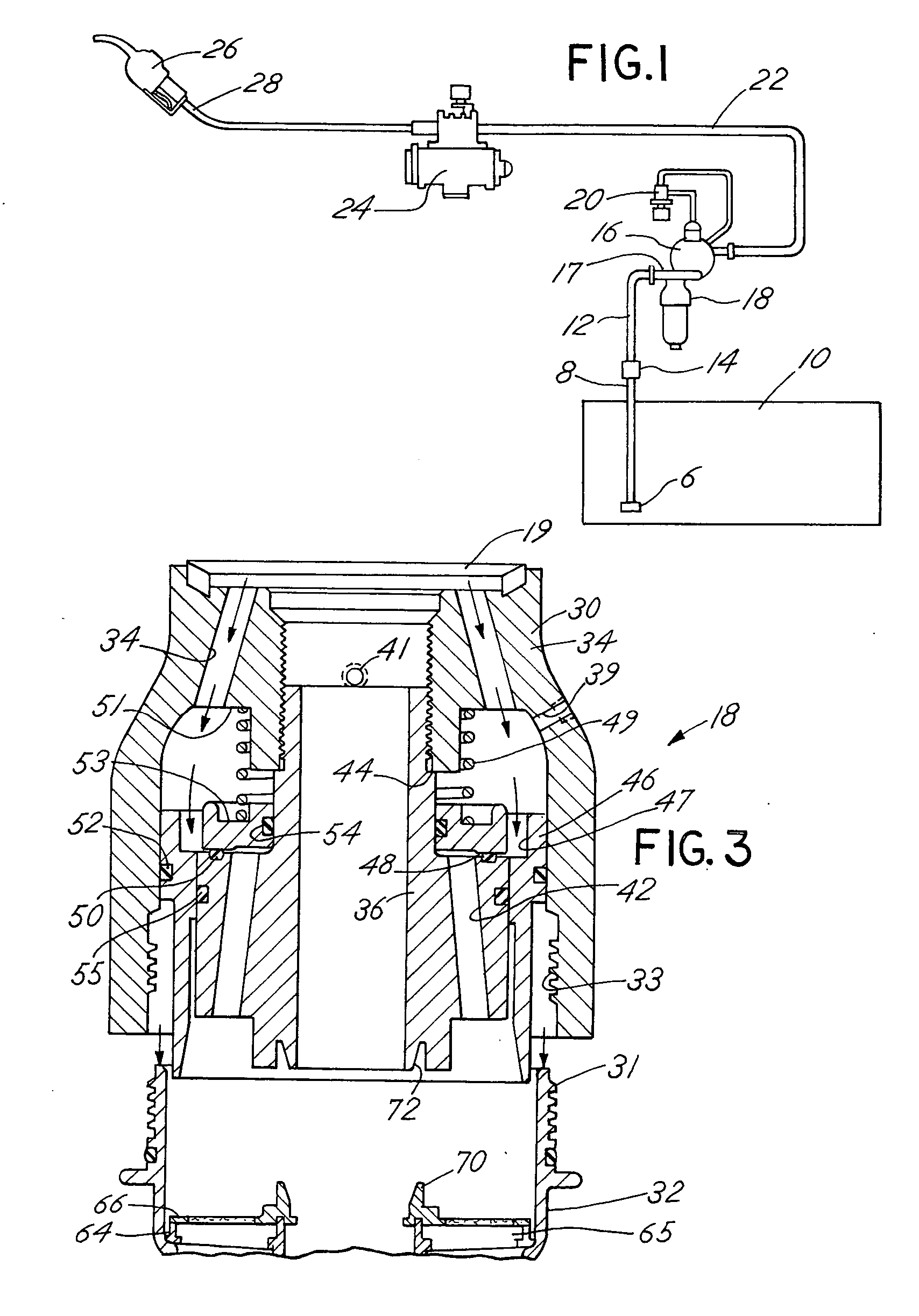
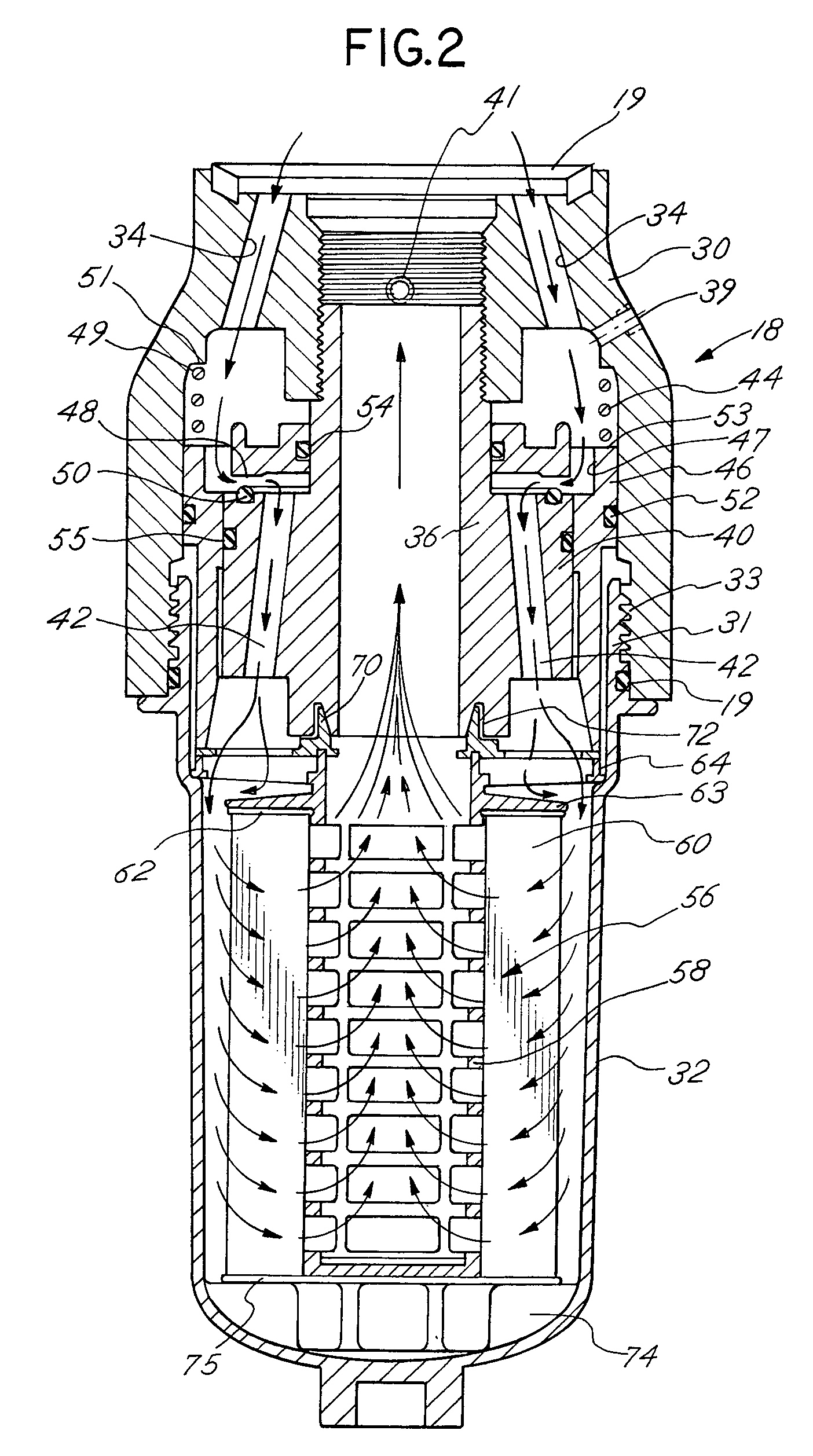
Fuel dispenser filter with removable filter media
InactiveUS6926827B2Reduce hazardous wasteReduce overflowIon-exchanger regenerationWater/sewage treatmentFuel distributionFilter media
A fuel dispenser filter for filtering fuel is adapted to be connected to a support in a fuel distribution system. The filter comprises a housing including an adaptor constructed and arranged to be secured to the support and a bowl operatively connected to the adaptor. A stud / spacer is secured in the adaptor. The stud / spacer defines a centrally disposed outlet flow passage and outwardly disposed inlet flow passages. A sleeve member is movably supported in the adaptor between the stud / spacer and the adaptor. The sleeve member is constructed and arranged to open and close the fuel flow through the inlet flow passages. A filter assembly including filter media is provided in the bowl for filtering the fuel passing through the filter. When the bowl is firmly engaged with the adaptor, the sleeve member is moved to open position to permit the flow of fuel through the filter and when the bowl is removed from the adaptor, the sleeve member is moved to a closed position to stop the flow of fuel. A spring is provided to bias the sleeve member to the closed position when the bowl is removed from the adaptor. Various seals are provided within the filter to confine fuel flow to the desired flow paths.
Owner:CHAMPION LAB
Fuel dispenser filter with removable filter media
InactiveUS20040217045A1Reduce hazardous wasteReduce overflowIon-exchanger regenerationWater/sewage treatmentFuel distributionFilter media
A fuel dispenser filter for filtering fuel is adapted to be connected to a support in a fuel distribution system. The filter comprises a housing including an adaptor constructed and arranged to be secured to the support and a bowl operatively connected to the adaptor. A stud / spacer is secured in the adaptor. The stud / spacer defines a centrally disposed outlet flow passage and outwardly disposed inlet flow passages. A sleeve member is movably supported in the adaptor between the stud / spacer and the adaptor. The sleeve member is constructed and arranged to open and close the fuel flow through the inlet flow passages. A filter assembly including filter media is provided in the bowl for filtering the fuel passing through the filter. When the bowl is firmly engaged with the adaptor, the sleeve member is moved to open position to permit the flow of fuel through the filter and when the bowl is removed from the adaptor, the sleeve member is moved to a closed position to stop the flow of fuel. A spring is provided to bias the sleeve member to the closed position when the bowl is removed from the adaptor. Various seals are provided within the filter to confine fuel flow to the desired flow paths.
Owner:CHAMPION LAB
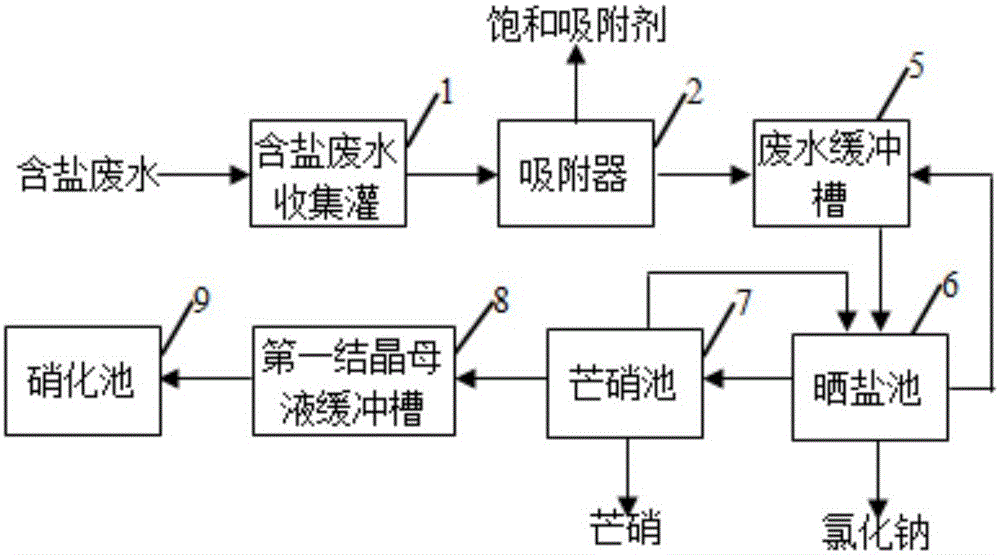
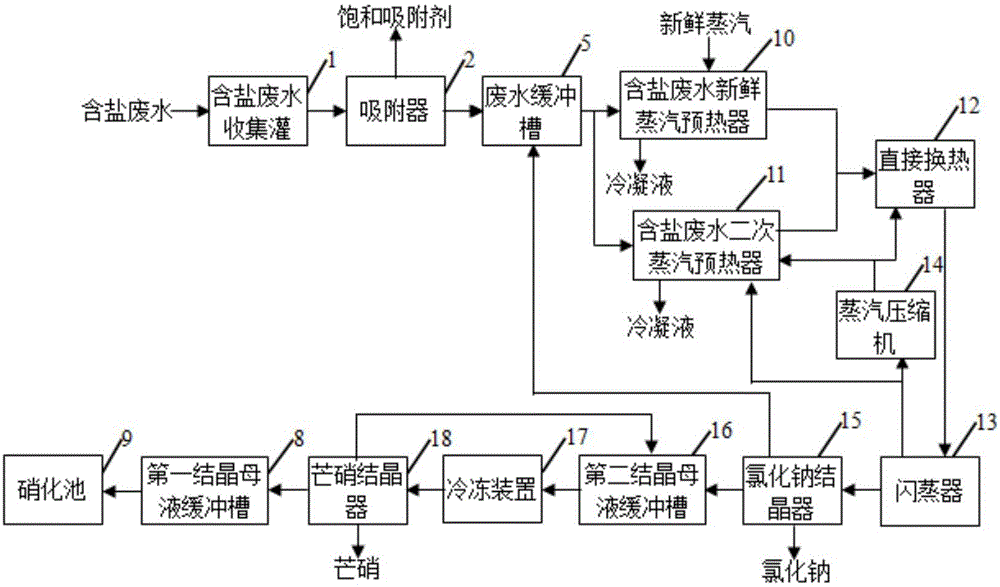
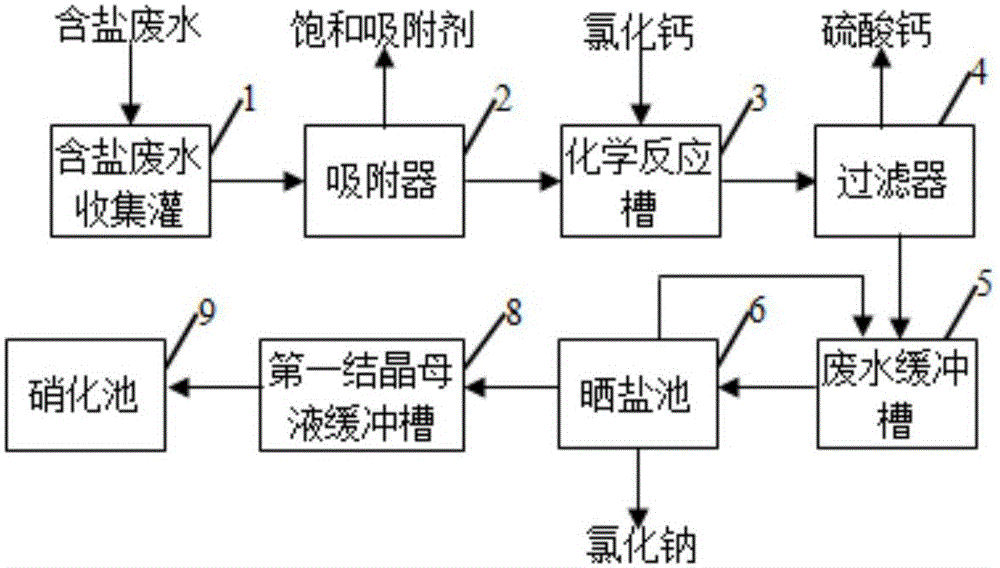
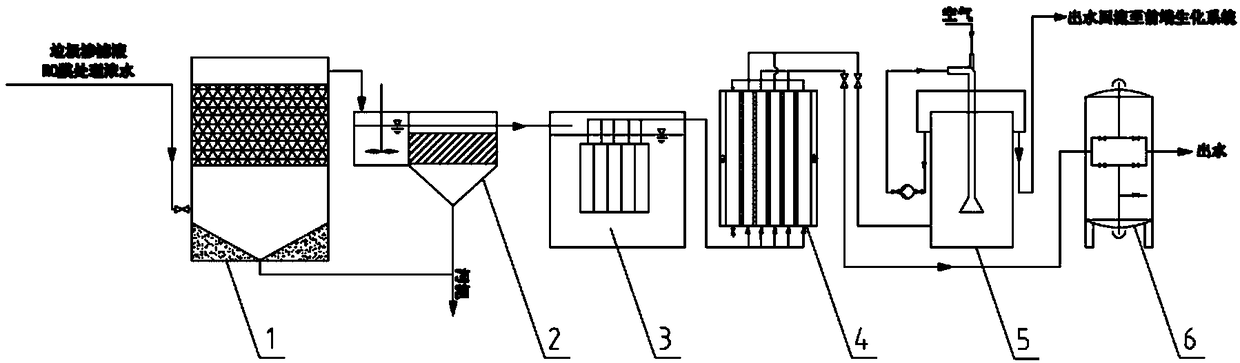
Purification treatment and pure-salt recovery process for strong-salt wastewater in coal chemical industry
ActiveCN105084651ARemove and reduce chromaRemove and reduce turbidityGeneral water supply conservationEnergy inputSulfate radicalsReverse osmosis
Provided is a purification treatment and pure-salt recovery process for strong-salt wastewater in the coal chemical industry. According to the purification treatment and pure-salt recovery process, a working procedure of absorption treatment is additionally conducted on organic matter macromolecules and heavy metals contained in high-concentration salt water after a wastewater reuse multistage reverse osmosis treatment process is carried out; working procedures of evaporation, freezing and desalination are additionally carried out to achieve the purposes of effective utilization of natural energy and industrial low-grade waste heat resources and effective removal of salt-containing wastewater after the working procedure of absorption treatment; a working procedure of chemical separation is added between the working procedure of absorption treatment and the working procedure of desalination to completely convert sulfate radical ions in the salt-containing wastewater into chloride ions and collect and reuse obtained solid, and a nitrate-rich mother solution subjected to crystallization and desalination is returned to a biochemical treatment stage for denitrification treatment. By means of the purification treatment and pure-salt recovery process, salt contained in the salt-containing wastewater is effectively separated out, meanwhile nitrate is returned for biochemical treatment, and secondary steam condensate is evaporated for recycle, so that the whole process achieves the purposes of zero discharge and effective resource utilization.
Owner:山西诺凯化工技术有限公司 +1
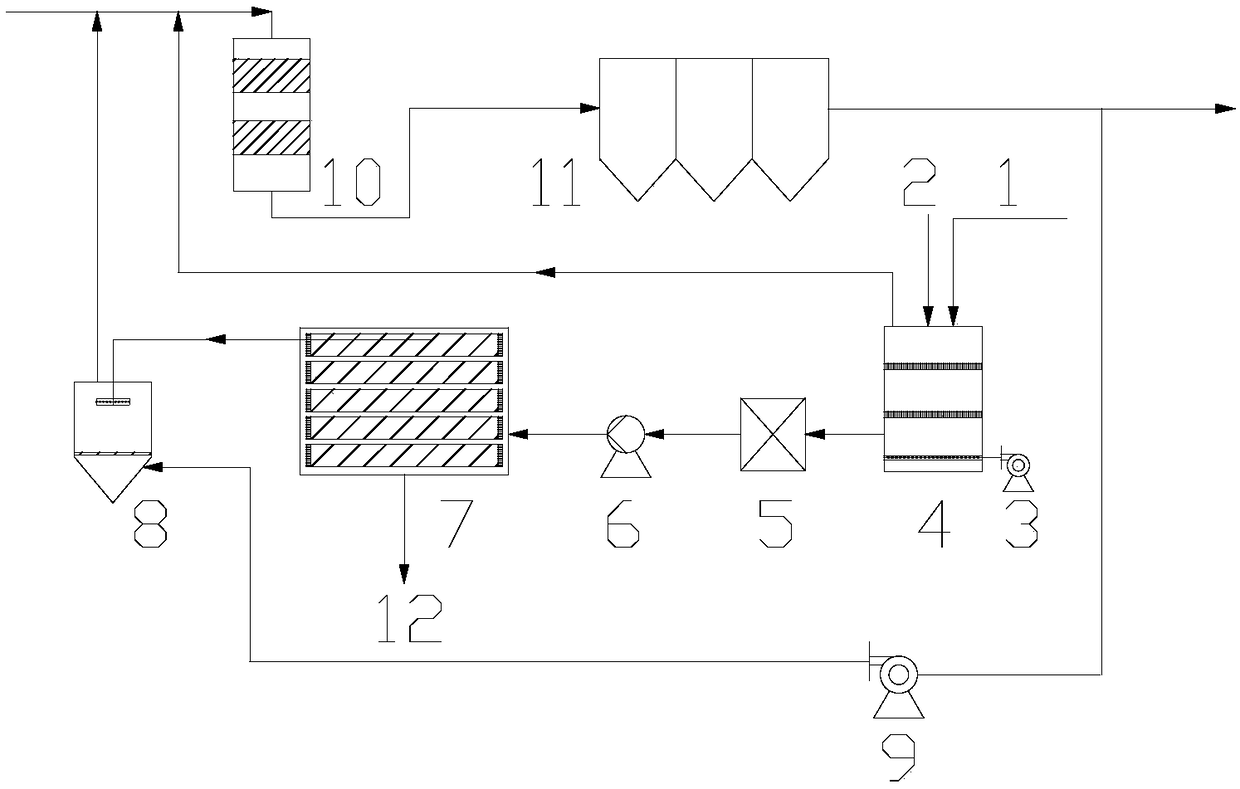
Technology and device for zero-drainage of desulfurization wastewater
InactiveCN109111009AHigh technical reliabilityImprove reliabilityWater treatment parameter controlGas treatmentUltrafiltrationReverse osmosis
The invention discloses a technology and a device for zero-drainage of desulfurization wastewater. The technology comprises the following steps of (1) sending the desulfurization wastewater and alkaline liquid to the top part of a deamination tower, sending an aeration fan into the deamination tower via the bottom part, and enabling the aeration fan to be in reverse contact with the desulfurization wastewater; (2) sending the ammonia-containing air after blowing into a deamination reactor, performing deamination, and sending into a deduster; sequentially sending the wastewater after deamination into an ultrafiltration device and a reverse osmosis device, recycling the fresh water of the reverse osmosis device, and sending the concentrated water into a spray-drying tower; leading the dedusted flue gas by the deduster into the spray-drying tower to exchange heat, enabling the dried crystal particles to fall into an ash hopper, and sending the flue gas after heat exchange into the deamination reactor. The technology has the advantages that the wet type desulfurization wastewater is performed with ammonia-nitrogen removal and recycling, wastewater concentration, spray-drying, evaporating and crystallizing, so as to complete the zero-drainage of the desulfurization wastewater; while the running reliability of the treatment device is improved, the recycling rate of the wastewater isimproved and the cycling utilization of the ammonia-nitrogen is realized, the investment running cost of the device for the zero-drainage of desulfurization wastewater is greatly reduced.
Owner:杭州天蓝净环保科技有限公司
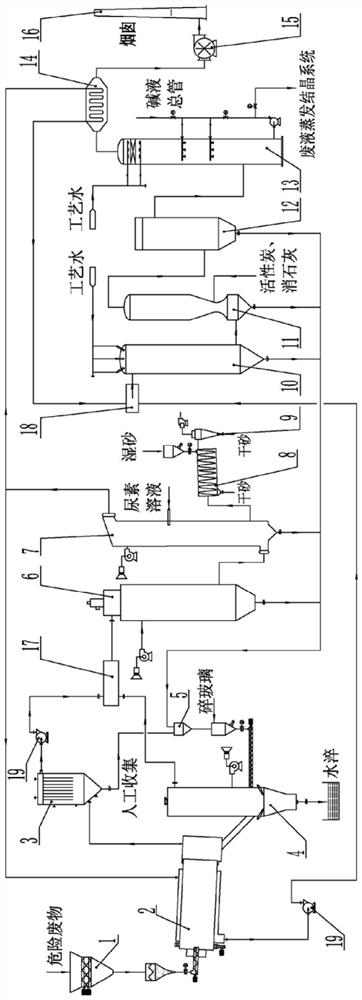
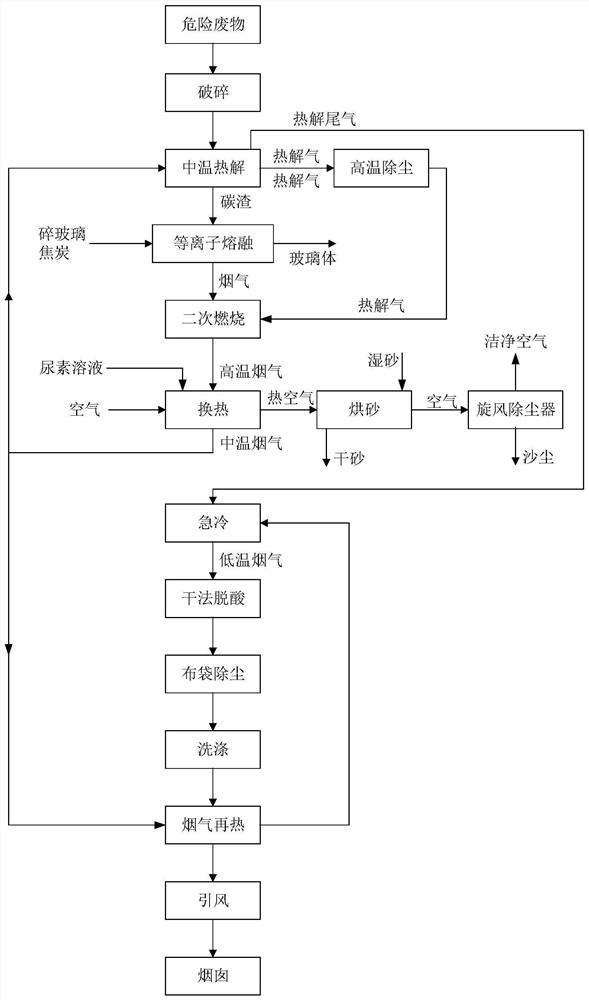
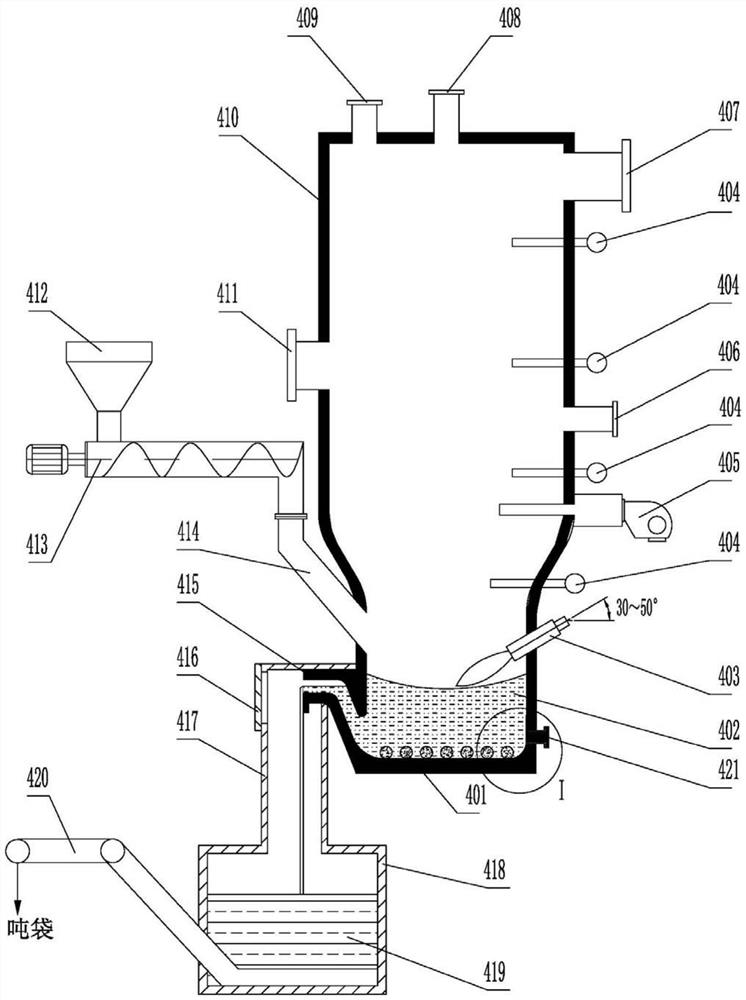
Hazardous waste treatment system and method based on medium-temperature pyrolysis and plasma high-temperature melting
ActiveCN113182311AHigh degree of harmlessnessHarmlessSolid waste disposalTransportation and packagingCombustion chamberDust control
The invention provides a hazardous waste treatment system and method based on medium-temperature pyrolysis and plasma high-temperature melting. The problems that existing hazardous waste incineration treatment is low in harmless degree, pyrolysis treatment is not thorough, and plasma melting treatment cost is high are solved. According to the system and method, hazardous waste is broken and then subjected to medium-temperature pyrolysis in an oxygen-deficient environment, pyrolytic carbon residues form harmless glass bodies through a plasma melting furnace, pyrolysis gas and smoke generated by plasma melting enter a combustion chamber to be subjected to secondary combustion, high-temperature smoke obtained after secondary combustion exchanges heat with air and then is cooled into medium-temperature smoke, the medium-temperature smoke is divided into two parts, one path enters a pyrolyzing furnace to heat materials, the other path enters a flue gas reheater to exchange heat, pyrolysis tail gas obtained after the materials in the pyrolyzing furnace are heated is mixed with flue gas obtained after heat exchange of the flue gas reheater, and after mixing, quenching cooling, dry-process deacidification, cloth bag dust removal, washing and reheating are conducted in sequence, and then a mixture is sent to a chimney to be discharged through an induced draft fan; and air is heated after heat exchange, is used as a heat source of a sand dryer, and is discharged after sand drying and cyclone dust removal.
Owner:ACADEMY OF AEROSPACE PROPULSION TECH +1
TCCA (trichloroisocyanuric acid) mother liquor wastewater treatment method
ActiveCN104803531AReduce processing energy consumptionThorough purification and recoveryMultistage water/sewage treatmentNature of treatment waterHypochloriteSulfite salt
The invention belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment and discloses a TCCA (trichloroisocyanuric acid) mother liquor wastewater treatment method. The TCCA mother liquor wastewater treatment method is mainly technically characterized by comprising the following steps: wastewater is regulated by a regulation tank and then enters a chlorinolysis tank, hydrochloric acid is added to the chlorinolysis tank, hypochlorite is removed, treated water enters a dechlorination tank, produced chlorine enters a nitrogen removal tank in the step 3, and small amount of sodium bisulfite is added to the dechlorination tank to remove redundant hypochlorite; alkali is added to precipitate melamine cyanurate, the precipitated melamine cyanurate is recovered, chlorine is introduced into the nitrogen removal tank, ammonia and excessive chlorine react to produce nitrogen which is exhausted, then sodium sulfite is added to remove excessive hypochlorite, finally, evaporative crystallization is performed, coarse salt which is separated out is collected, and evaporated condensate is discharged up to standard. According to the TCCA mother liquor wastewater treatment method, cyanuric acid is recovered, the energy consumption for wastewater treatment is low, salt is purified and recovered completely, investment for recovery equipment is small, and the hazardous waste amount is reduced.
Owner:济宁璟华环保科技有限公司
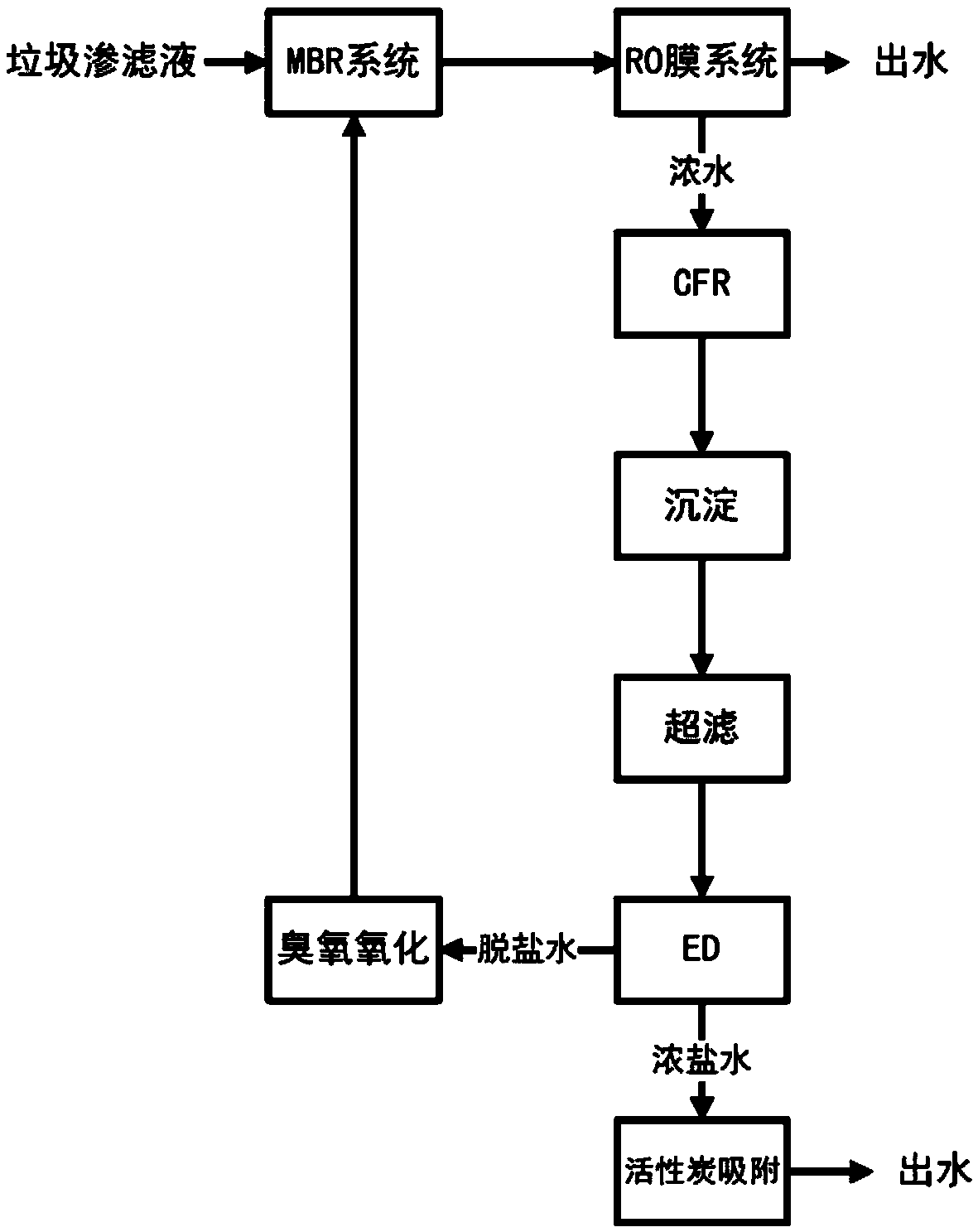
Treatment method for reverse osmosis concentrated-water of landfill leachate
PendingCN108929002AImprove processing efficiencyLow investment costWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeUltrafiltrationCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a treatment method for reverse osmosis (RO) concentrated-water of landfill leachate. The method comprises the following steps: after the RO concentrated water enters a CFR forflocculation catalytic treatment, CFR effluent water is subjected to mud-water separation through a sedimentation tank, the supernatant is subjected to built-in ultrafiltration, the effluent water enters an ED system for desalting, the obtained desalted water enters an ozone catalytic oxidation device, the effluent water flows back to an original landfill leachate biochemical system, and the obtained concentrated brine enters an activated carbon adsorption tank to be discharged out or evaporated to dryness without discharge. The method disclosed by the invention can effectively separate organic matter and salts in the RO concentrated water, greatly improve biodegradability of the organic matter, and effectively reduce a concentration of RO concentrated-water pollutants; the desalted RO concentrated water flows back to the original landfill leachate biochemical system without recharge or return spraying, and treatment efficiency of wastewater is improved while secondary pollution is reduced; and in addition, compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention has small activated carbon consumption, a less yield of hazardous waste, a membrane not easy to pollute and block, and significantly-reduced investment and operating costs of treatment of the RO concentrated water.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHIYUAN ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION TECH
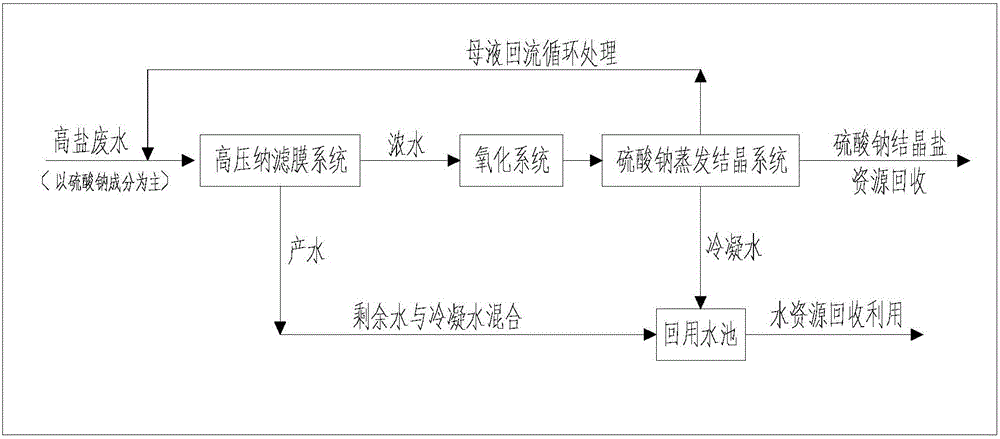
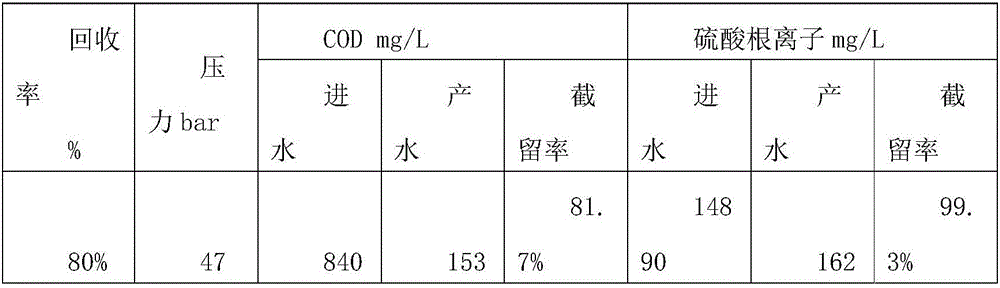
Separation and reuse method of sodium sulfate from high salinity wastewater
InactiveCN106517622AEfficient removalReasonable processWater contaminantsAlkali metal sulfite/sulfate purificationSolubilityTotal dissolved solids
The invention relates to a separation and reuse method of sodium sulfate from high salinity wastewater. Divalent salts and organic matters are separated from monovalent salts by means of nanofiltration membrane characteristics to remove a great amount of organic matters in wastewater, then evaporation concentration and crystallization steps are carried out to obtain a sodium sulfate solid with few impurity. The method has the characteristics of reasonable process, resource recovery, economical efficiency and high efficiency, and stable operation, can be used as an advanced treatment technology to effectively remove organic matter and inorganic salt based total dissolved solids (TDS) from high salinity wastewater, at the same time acquires the sodium sulfate solid with few impurity, can well make up for the shortcomings of existing high salinity wastewater treatment technology, and makes the high salinity concentrated solution treatment reach the purpose of "zero emission of solid and liquid".
Owner:JIANGSU XINYU TIANCHENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENG
Telescopic filter element, and filter with replaceable filter element
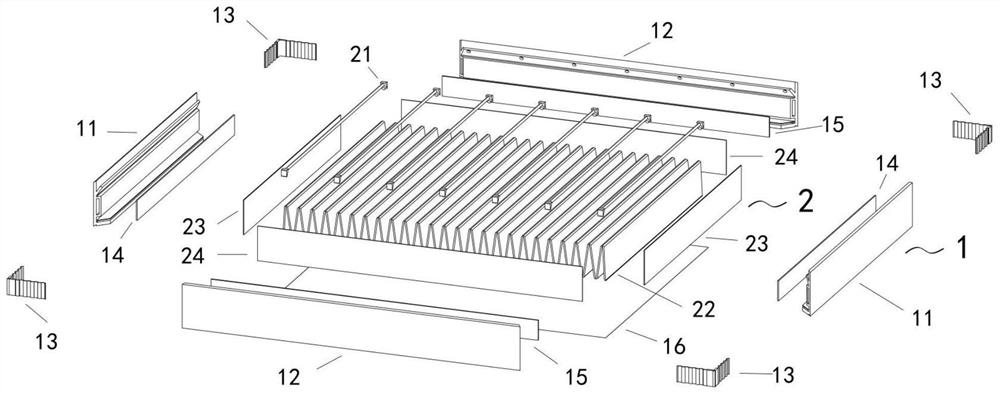
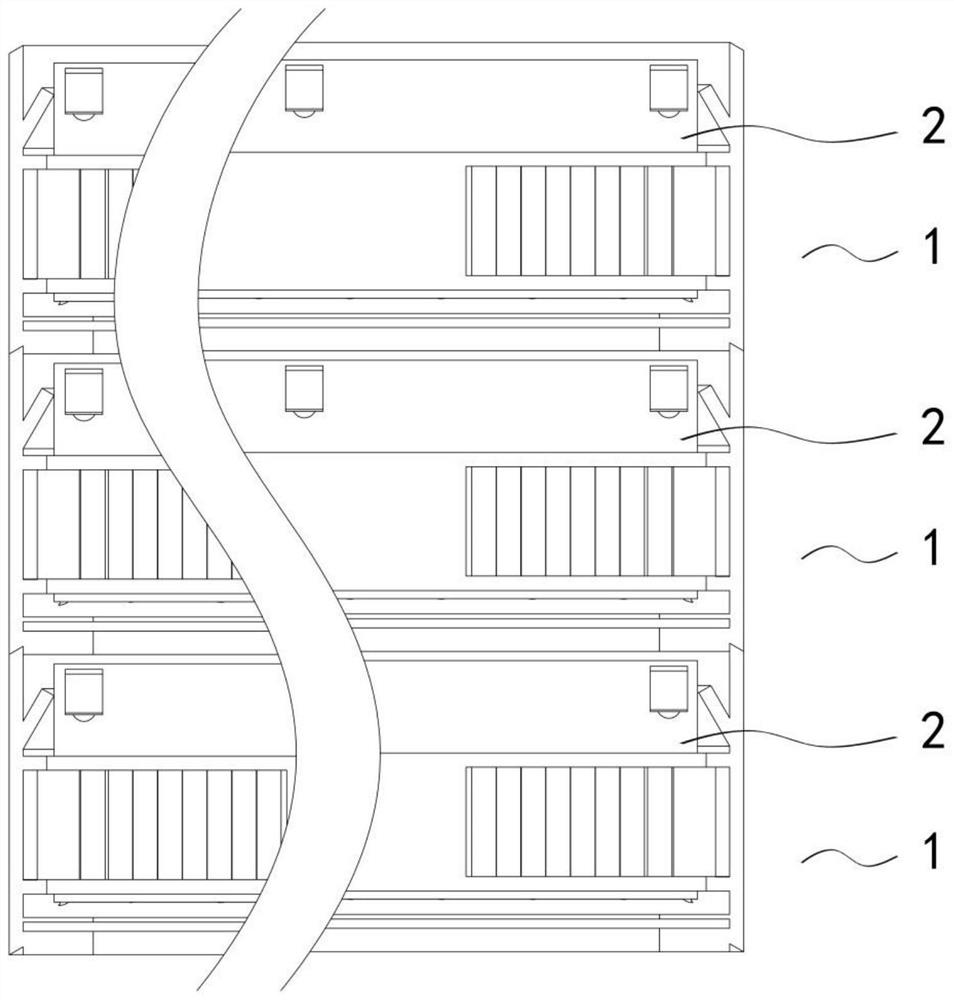
ActiveCN113856367ASave manpower and material resourcesReduce hazardous wasteDispersed particle filtrationStructural engineeringControl theory
The invention discloses a telescopic filter element, and a filter with a replaceable filter element. The telescopic filter element comprises a wave-shaped filter part, first edge sealing strips and second edge sealing strips are arranged on the periphery of the wave-shaped filter part, the first edge sealing strips are arranged on the two sides of the folded edge of the filter part, the second edge sealing strips are arranged on the two sides of the multi-folded edge of the filter part, and fixing pieces are further arranged on the two sides of the multi-folded edge; and the filter with the replaceable filter element comprises the filter element and a frame, the frame is formed by splicing a first frame piece and a second frame piece, the whole frame piece is of an L-shaped structure, the upper edge of the top end of the long side of the frame piece is arranged to be an inclined face, an inclined protruding strip, a hollow reinforcing rib and a protective net baffle are sequentially arranged on the inner side of the long side from top to bottom, a surface protecting net is installed between the protective net baffle and the L-shaped short edge, and the filter element is installed in the upper space of the surface protecting net. The frame body and the filter element can be separated, the frame can be reused, the filter element can be replaced regularly, and energy conservation and consumption reduction are achieved; and the filter element is telescopic and is convenient to transport and store after being compressed.
Owner:MAYAIR TECH (CHINA) CO LTD
System and method for removing heavy metal chromium, dyes and short wool fibers in leather wastewater
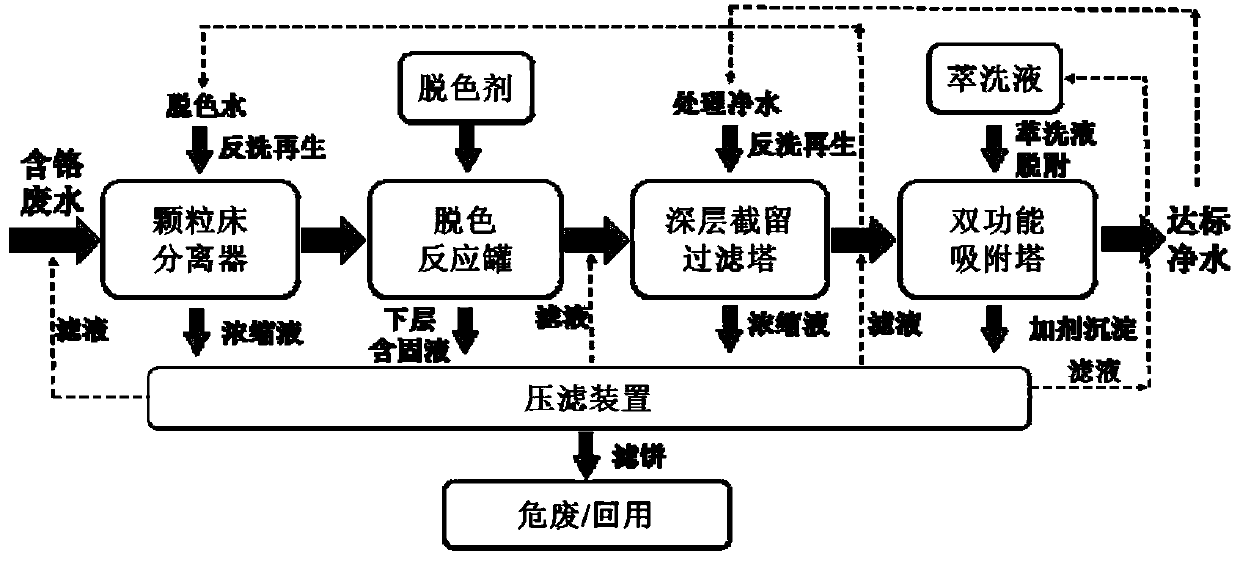
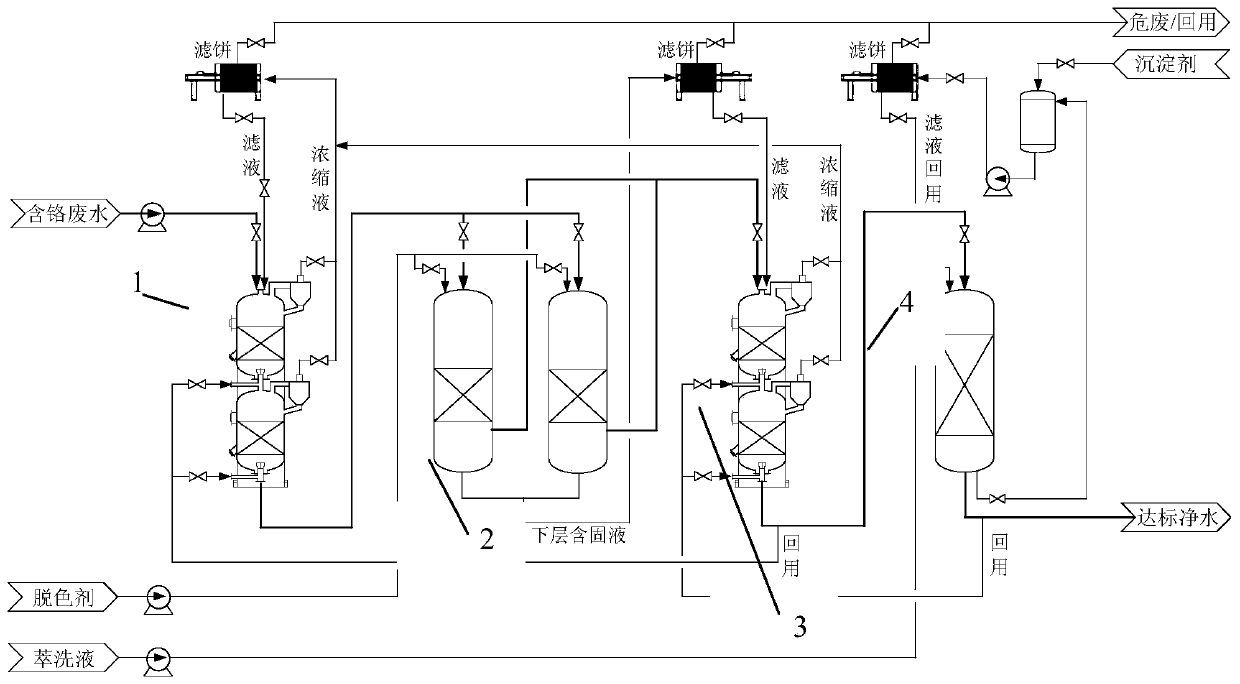
ActiveCN111423013ASolve the problem of purificationEmission reductionSludge treatmentWater treatment compoundsPapermakingWastewater
The invention relates to an advanced treatment system and method for leather wastewater containing heavy metals, dyes and short wool fibers. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, deeply removing the short wool fibers and other impurity solid particles in the leather wastewater by using a particle bed separator; then adding a decolorizing agent to decompose dye molecules in the wastewater; then, removing solid particles generated by a decoloration reaction by using a deep interception filtering tower; and finally, carrying out in-depth removal of heavy metal chromium ions, dye molecules and fragments thereof in the wastewater by using a dual-functional adsorption tower so as to allow effluent to meet reuse requirements or related discharge standards and greatly reduce the discharge amount of chromium-containing hazardous wastes. The treatment method and system can realize synchronous deep removal of heavy metals, dyes and fibers in wastewater produced in the industries of leather, textile, printing and dyeing, papermaking and the like, effluent quality meets reuse requirements, and the effluent reaches relevant national and local discharge standards in China.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of phthalate plasticizer
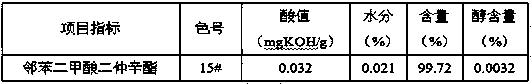
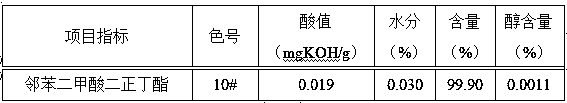
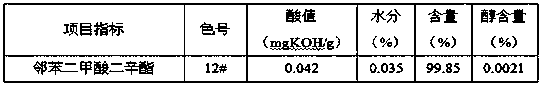
ActiveCN111517950AReduced neutralization washing stepsShorten production timeOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPlatinumPhthalic anhydride
The invention provides a preparation method of a phthalate plasticizer. The method specifically comprises the steps of esterification, crude dealcoholization, cooling, addition of a deacidifying agent, dealcoholization and filtration. The preparation method is adopted; treatment is carried out without a decolorizing agent, the chromaticity of the prepared phthalate plasticizer product can reach 10-15 # through platinum-cobalt standard colorimetry; phthalic anhydride and sec-octyl alcohol are used as raw materials; the acid value of the dioctyl phthalate prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention is less than or equal to 0.05 mgKOH / g; wherein the water content is less than or equal to 0.05%, the alcohol content is more than or equal to 99.5% and the alcohol content is less than or equal to 0.005%, and meanwhile, neutralizing and washing steps can be reduced, the wastewater amount is reduced, the alkali washing, washing and settling time is saved, the production cost is greatly reduced and the production benefit is increased.
Owner:山东元利科技有限公司
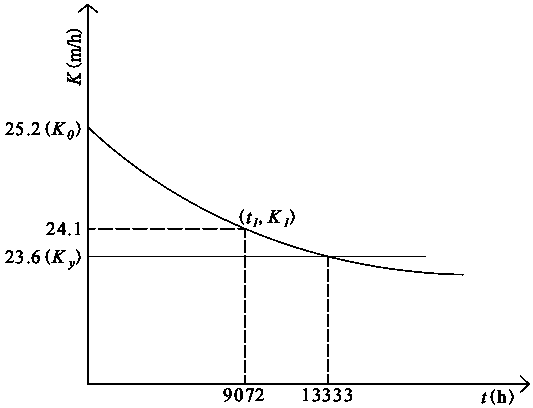
Method for predicting residual life of in-service denitration catalyst based on actual operating conditions
ActiveCN109411031AReduce environmental risksAvoid wastingChemical property predictionGas treatmentProcess engineeringHazardous waste
The invention provides a method for predicting the residual life of an in-service denitration catalyst based on actual operating conditions. The method includes sampling and detecting the in-service denitration catalyst to measure the current activity K1 of the in-service denitration catalyst; collecting data such as average flue gas flow rate V, average coal consumption mass M, initial activity K0 of the denitration catalyst, the current in-service time T1 of the denitration catalyst and the like of the unit in a coal-fired power plant, substituting the collected and detected data into a formula to calculate a correction coefficient lambda to obtain an in-service denitration catalyst deactivation graph; and predicting the residual life ts of the in-service denitration catalyst according to the catalyst activity threshold Ky provided by a manufacturer when the denitration catalyst is initially mounted, and calculating the residual life ts of the in-service catalyst. The method realizesthe prediction of the residual life of the in-service denitration catalyst, provides a guarantee for the power plant to replace the deactivated catalyst in time at a catalyst failure point, so that the waste of catalyst potential is avoided, and the generation of solid hazardous waste is reduced.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU NORMAL UNIV
Oil-water separation filter
PendingCN111135606AExtended service lifeEasy to useLiquid separationElectric machineProcess engineering
The invention discloses an oil-water separation filter. The oil-water separation filter comprises a liquid inlet, a filter end cover and a filter main shell, wherein the filter end cover is connectedwith the filter main shell; a spiral extrusion structure is arranged in the filter main shell and comprises a fixed plate, a filling material net bag and a movable plate; the filling material net bagis respectively connected with the fixed plate and the movable plate; the other end of the movable plate is connected with a rotating rod which is connected with a motor through an oil seal; and the motor rotates the rotating rod to drive the filling material net bag to rotate and extrude. According to the invention, through arrangement of the spiral extrusion structure in the oil-water separationfilter, automatic extrusion oil discharge of a filling material in the spiral extrusion structure is realized; the service life of the filling material is prolonged; meanwhile, the replacement frequency is reduced; and the cost is reduced.
Owner:江苏瑞尔丽新材料科技有限公司
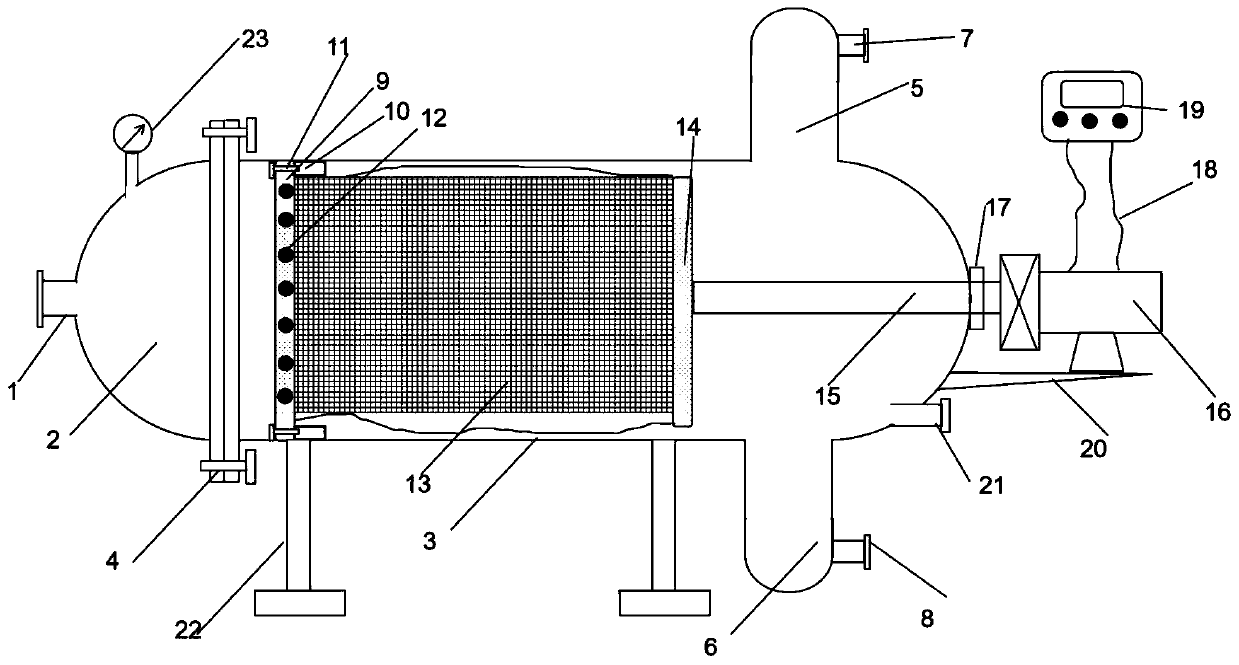
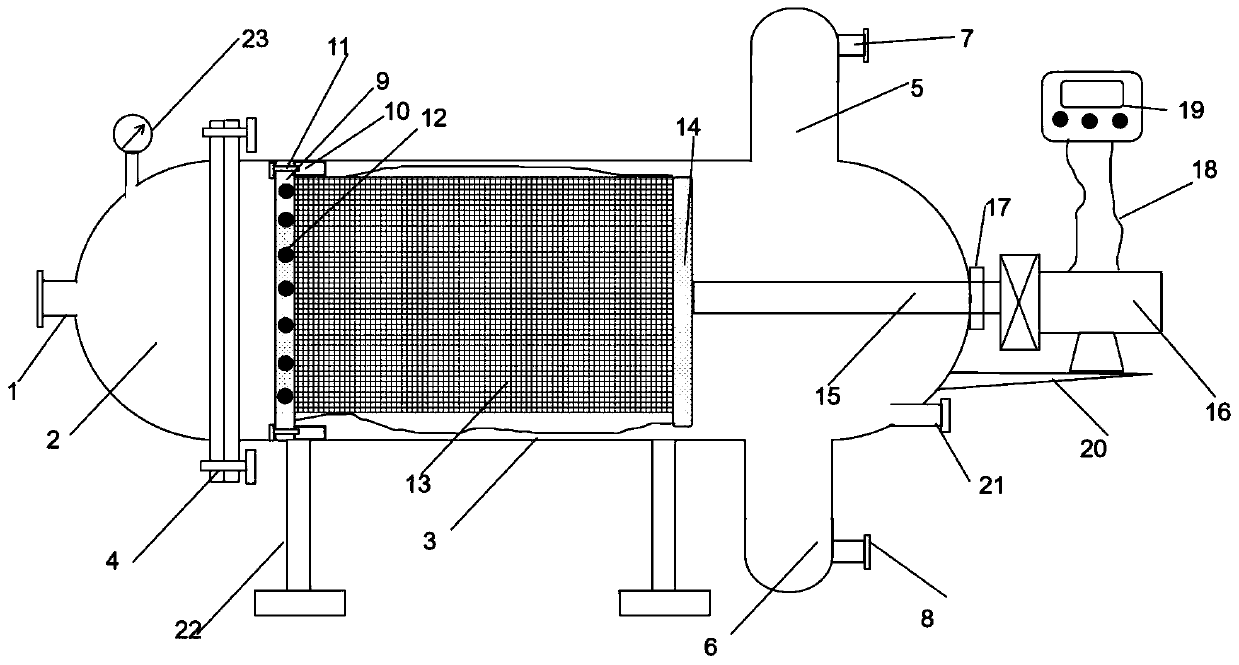
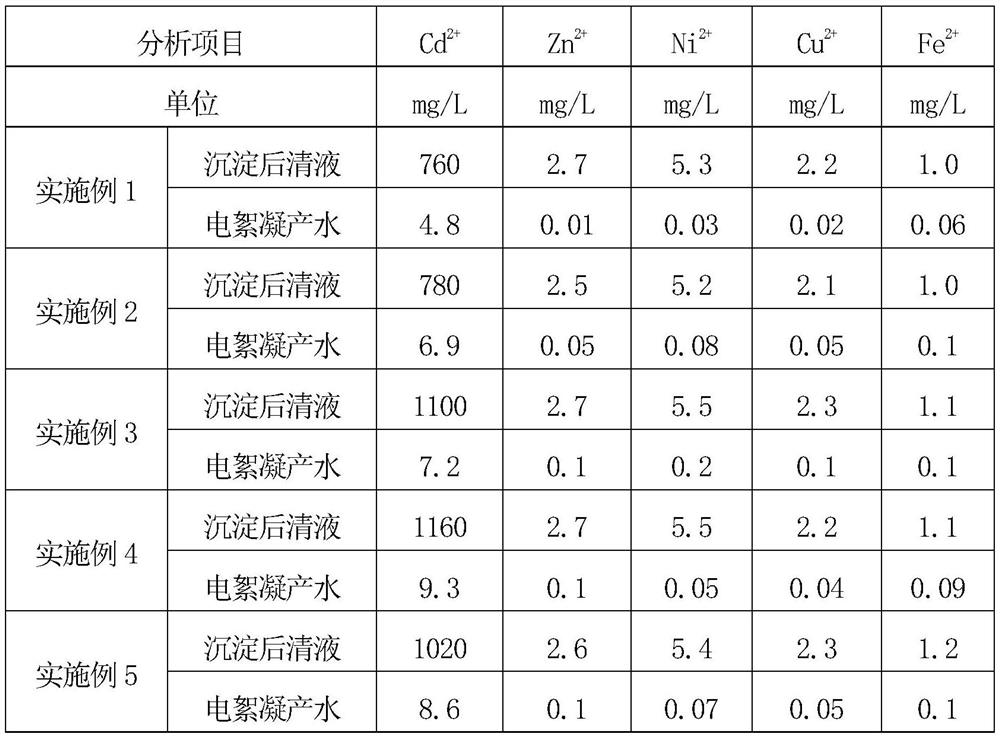
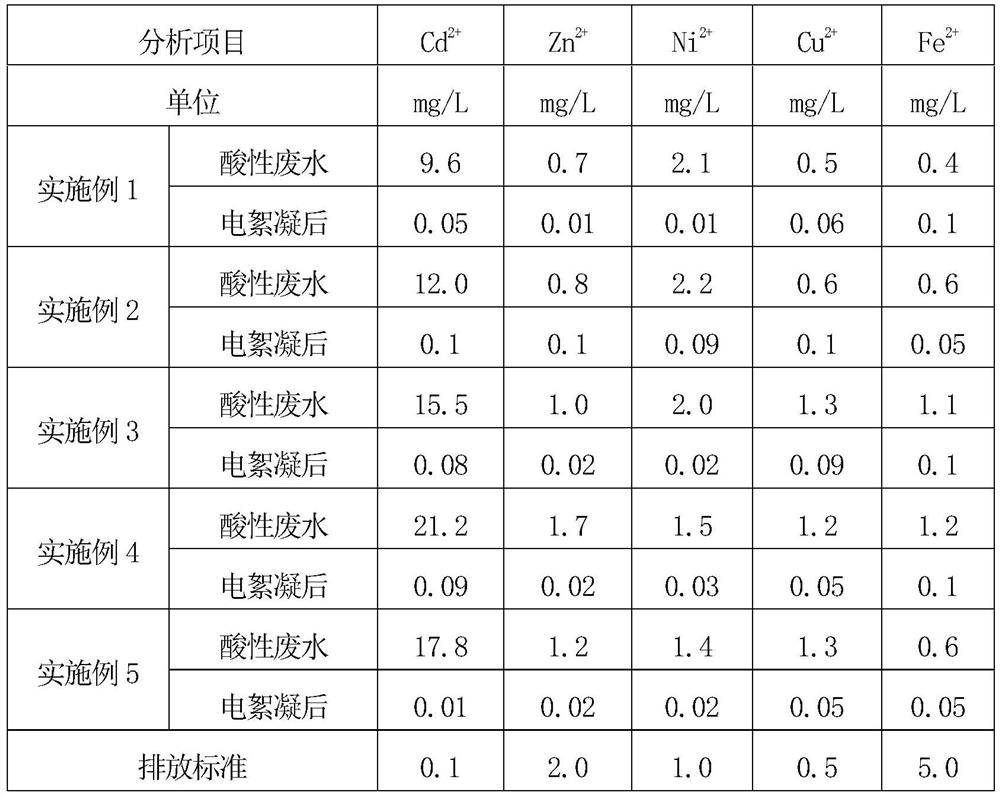
Method for resourceful treatment of cadmium-containing heavy metal wastewater
InactiveCN112429888ASolve processing problemsTo achieve the purpose of resource utilizationWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsSludgeElectro flocculation
The invention discloses a method for resourceful treatment of cadmium-containing heavy metal wastewater, which comprises the following steps: adding a precipitant into cadmium-containing wastewater togenerate cadmium carbonate precipitate aiming at cadmium plating layer stripping solution wastewater, washing the cadmium salt precipitate, filtering, and carrying out heat treatment to thermally decompose cadmium carbonate to generate cadmium oxide which is used for preparing cyaniding cadmium plating solution for continuous resourceful utilization; after precipitation, removing heavy metal ionsin a supernatant through electric flocculation, and recycling electric flocculation produced water or partially discharging as cadmium-containing plating piece stripping mother liquor; performing electric flocculation treatment on acidic wastewater generated by nitric acid washing and filtering to remove heavy metal ions and then discharging after reaching the standard. According to the method, the cadmium element and the wastewater in the cadmium-containing wastewater are recycled, the purpose of recycling is achieved, the amount of hazardous waste sludge is reduced, the operation cost is low, the problem of heavy metal treatment is solved, and the method has obvious economic benefits and environmental protection benefits.
Owner:SHAANXI RES DESIGN INST OF PETROLEUM CHEM IND
Preparation method of CSF-IR inhibitor
PendingCN113880812AOvercome yieldOvercoming economyOrganic chemistryBiochemical engineeringChemical compound
The invention relates to a preparation method of a CSF-IR inhibitor. According to the invention, a compound I is used as a raw material, reaction conditions are further optimized according to the characteristics of reactants and intermediate products, side reactions are reduced, post-treatment difficulty can be reduced, post-treatment experimental operation steps are reduced, the defects of long route (eight steps), low yield and poor atom economy in the prior art are overcome, and the target product can be prepared by using easily available and cheap starting raw materials. The synthesis method is mild in reaction condition, simple and convenient to operate, suitable for small-amount preparation in a laboratory and suitable for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAOYUAN MEDCHEMEXPRESS CO LTD
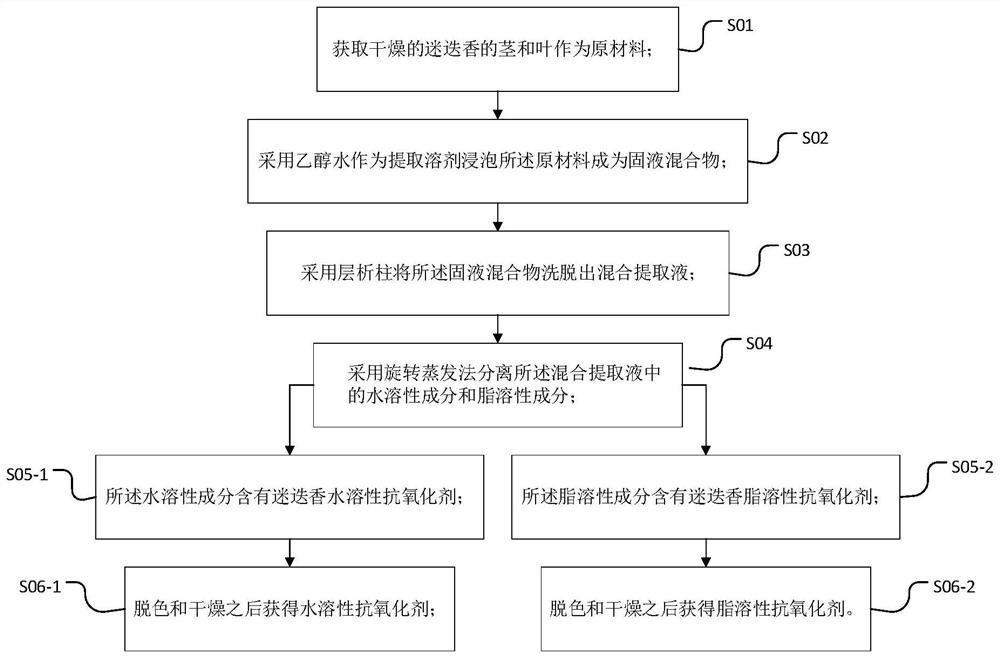
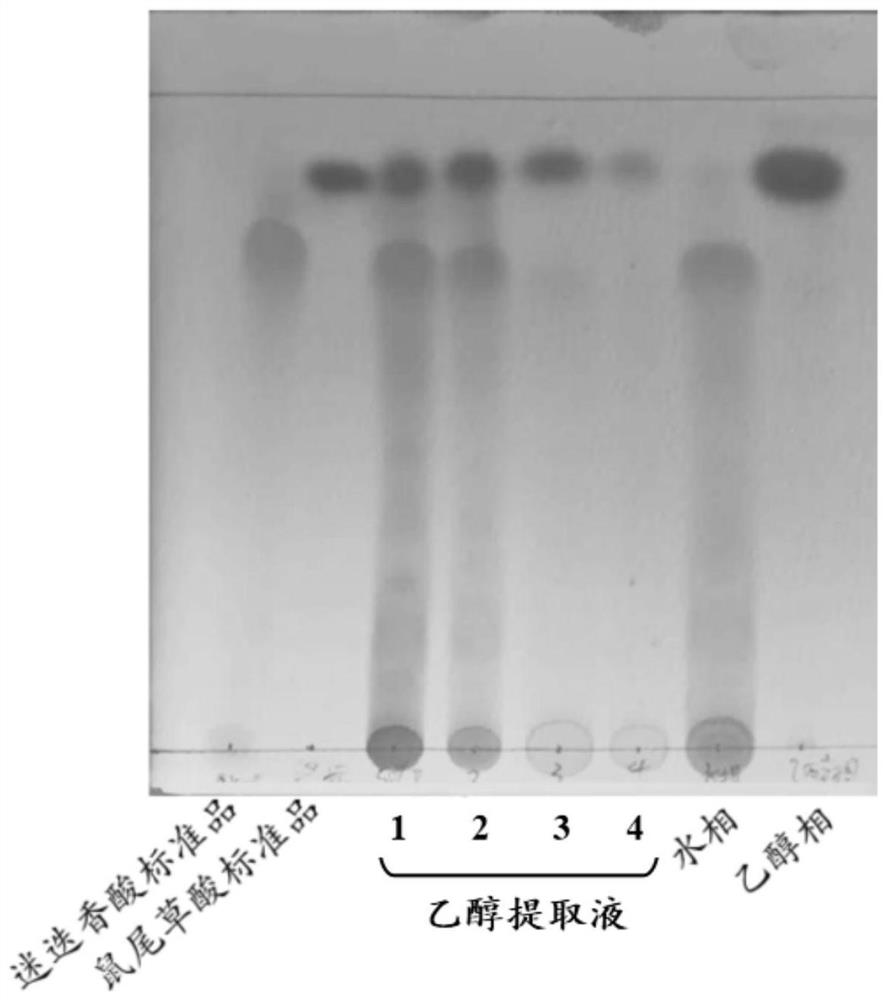
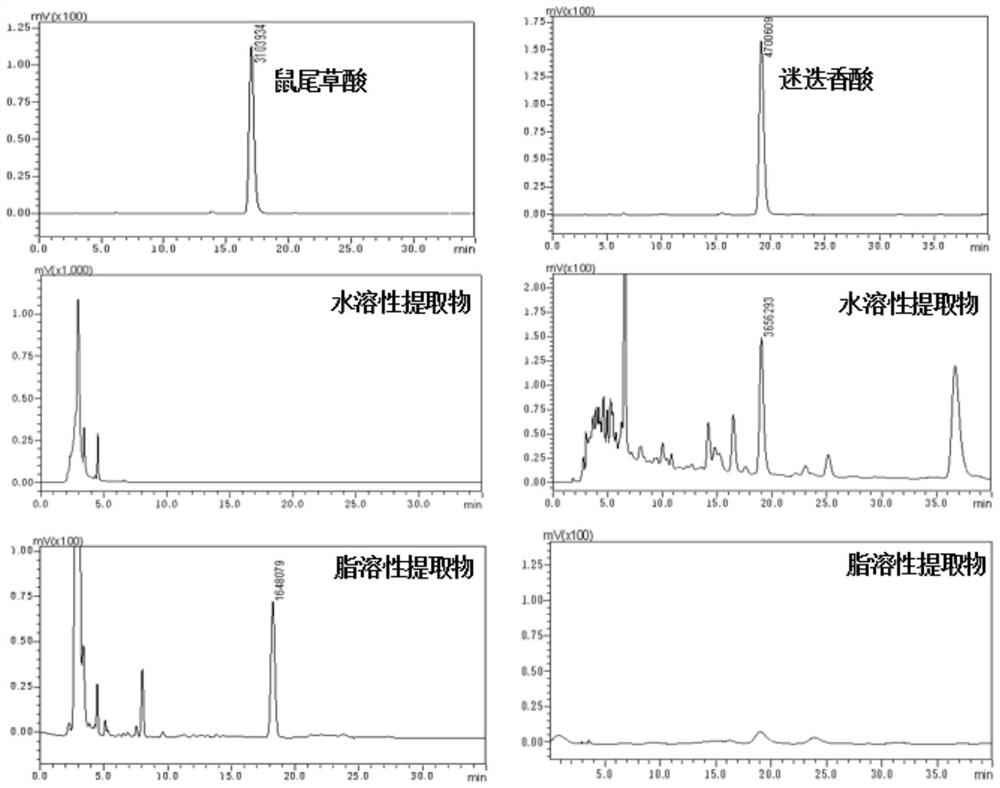
Method for simultaneously preparing rosemary water-soluble and fat-soluble antioxidants
PendingCN114315566AReduce pollutionSimple processOrganic compound preparationAntinoxious agentsProcess engineeringWater soluble
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously preparing rosemary water-soluble and fat-soluble antioxidants. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining dry rosemary stems and leaves as raw materials; soaking the raw materials into a solid-liquid mixture by using ethanol water as an extraction solvent; eluting the solid-liquid mixture by adopting a chromatographic column to obtain a mixed extracting solution; separating water-soluble components and fat-soluble components in the mixed extracting solution by adopting a rotary evaporation method; the water-soluble component contains a rosemary water-soluble antioxidant; the fat-soluble component contains a rosemary fat-soluble antioxidant. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple process, high efficiency, high extraction rate, large yield, easy realization of industrial and batch production, good product safety, recyclable solvent used in the preparation process, low production cost, less generation of hazardous wastes, and small environmental pollution.
Owner:绿谷植源(清远)生物科技有限公司 +1
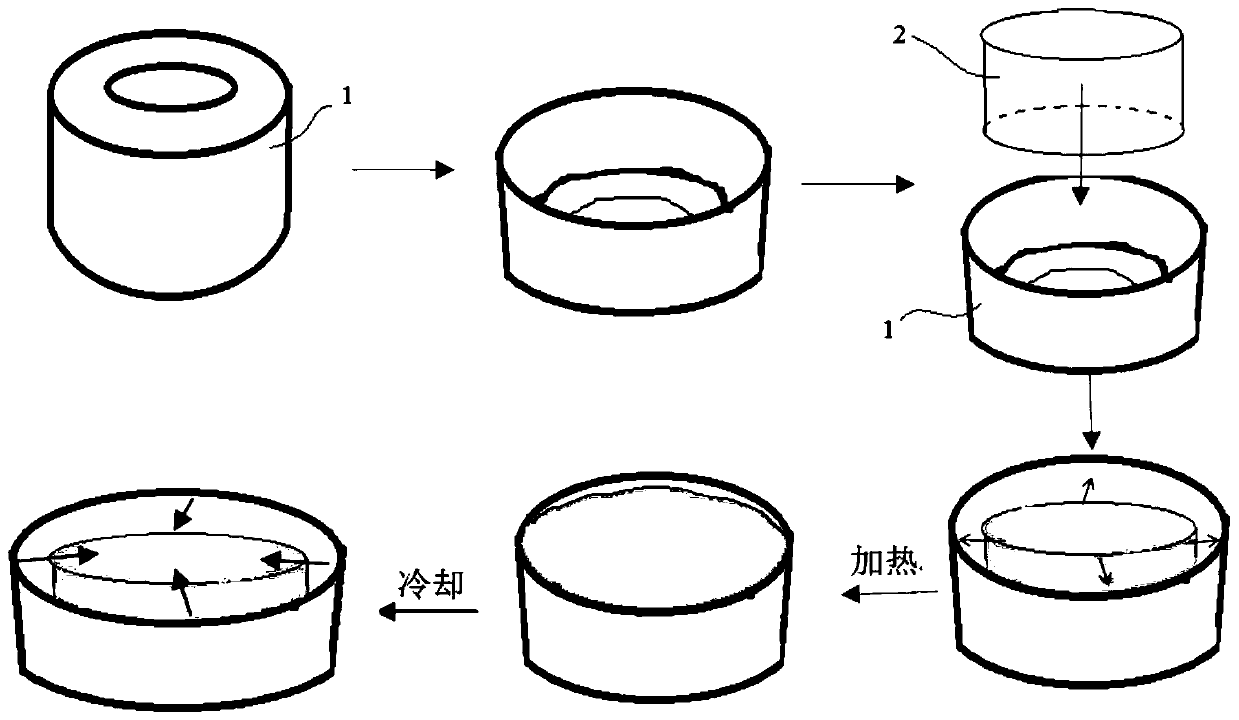
Motor outer rotor magnetic pole protection layer forming method
PendingCN110676986AFast heat transferImprove protectionManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesThermal dilatationElectric machine
The invention discloses a motor outer rotor magnetic pole protection layer forming method. In the method, a glue injection requirement and automatic separation of a thermal expansion non-metal block and a magnetic pole protection layer after glue injection are achieved through thermal expansion and cold contraction of the thermal expansion non-metal block, auxiliary glue injection components suchas a vacuum bag film, demolding cloth and a flow guide net do not need to be used, a preparation procedure before glue injection is simplified, a workload is greatly reduced, and a glue injection period can be shortened. And by using the forming method, through controlling pressure between the thermal expansion non-metal block and an internal portion of an annular component, the magnetic pole protection layer is tighter, a solid heat transfer speed is high, the high-quality magnetic pole protection layer can be formed only through one-time glue injection, and a production period is further shortened. Furthermore, the thermal expansion non-metal block is naturally separated from the magnetic pole protection layer after the glue injection is completed, there is almost no residual resin on the surface of the thermal expansion non-metal block, dangerous wastes are greatly reduced, and an environment is protected while cost is reduced.
Owner:XINJIANG GOLDWIND SCI & TECH
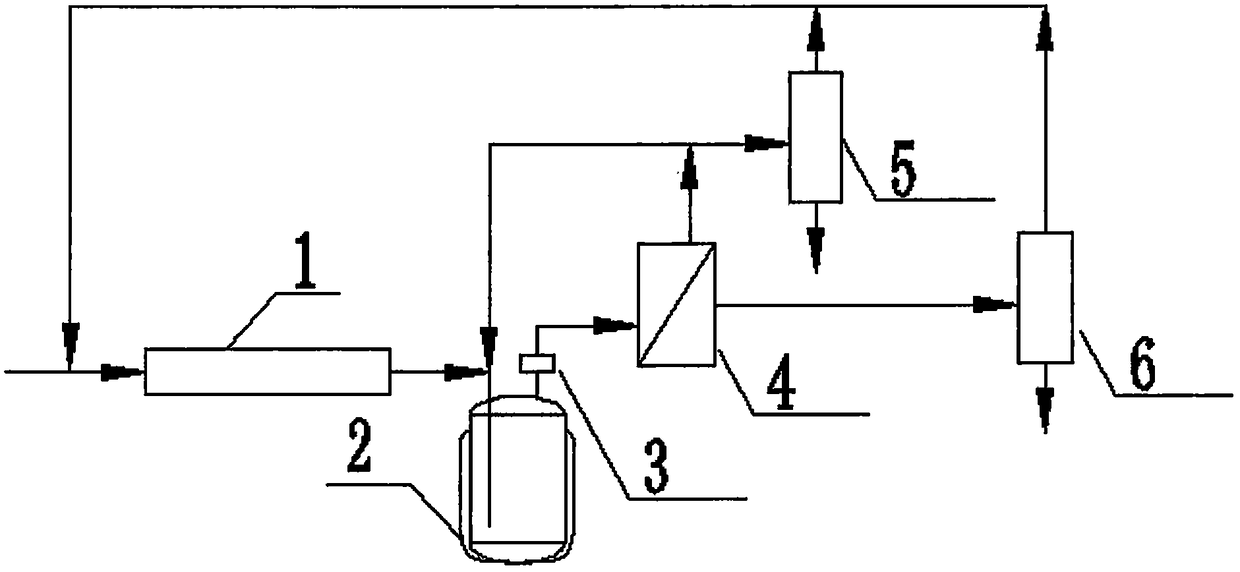
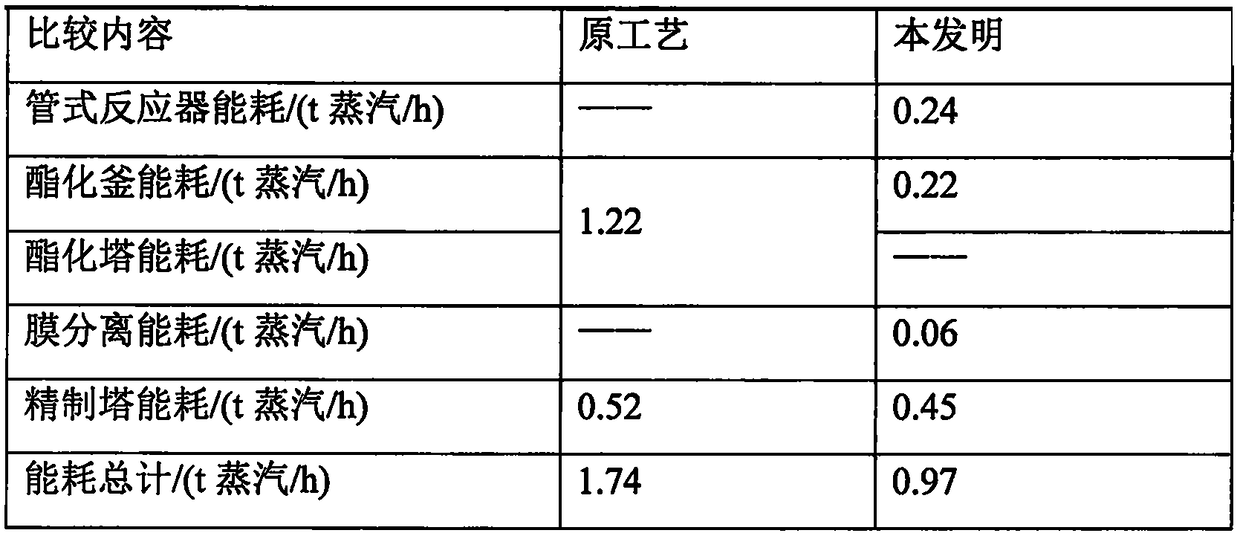
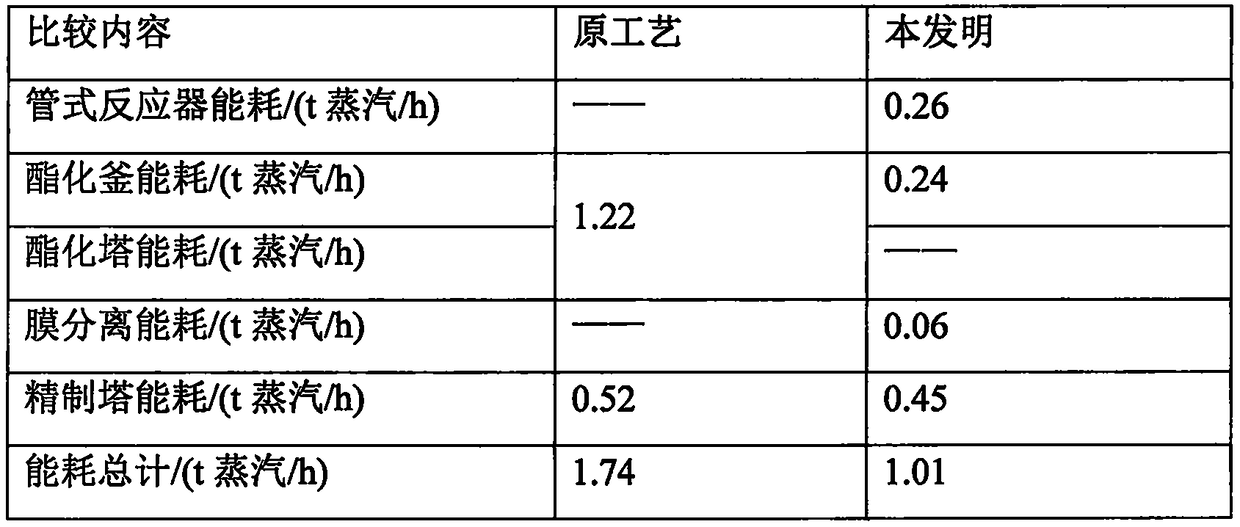
A kind of ethyl acetate energy-saving production process
ActiveCN106478415BReduce dosageMultiple side effectsOrganic compound preparationChemical industryAcetic acidEthyl ester
Owner:JINJIANG TAIXING CHEM IND CO LTD
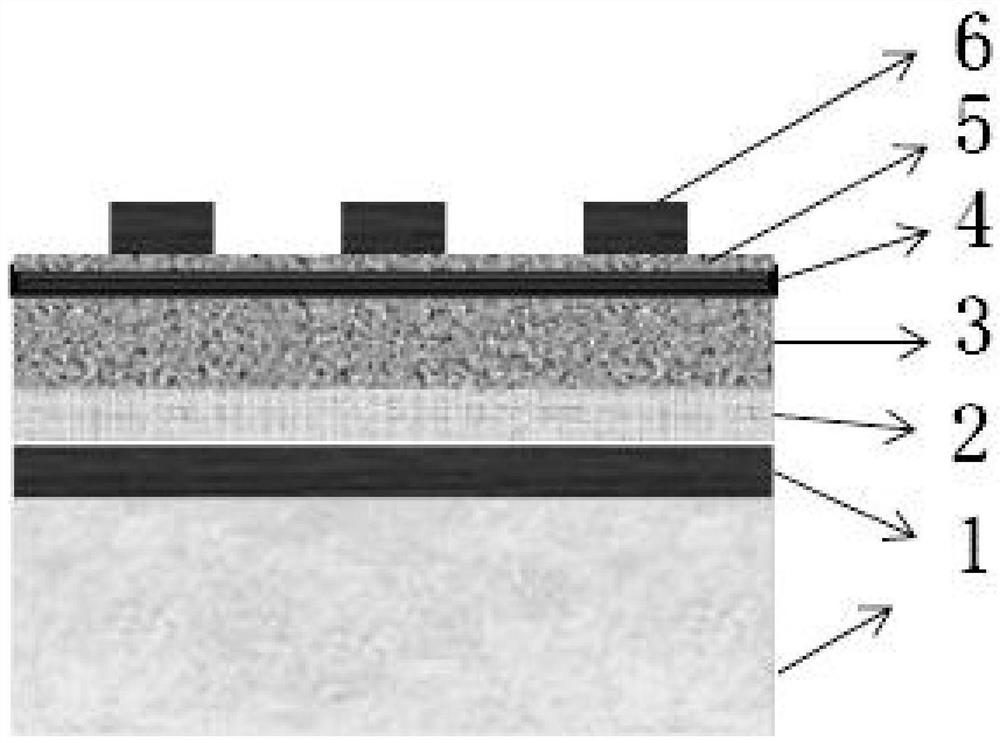
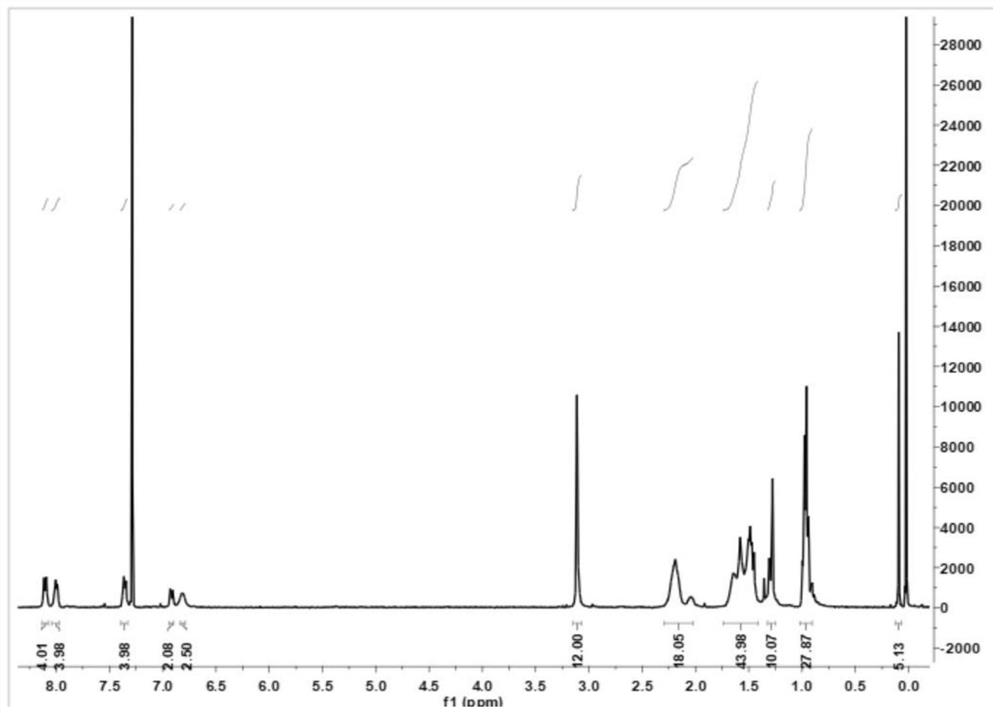
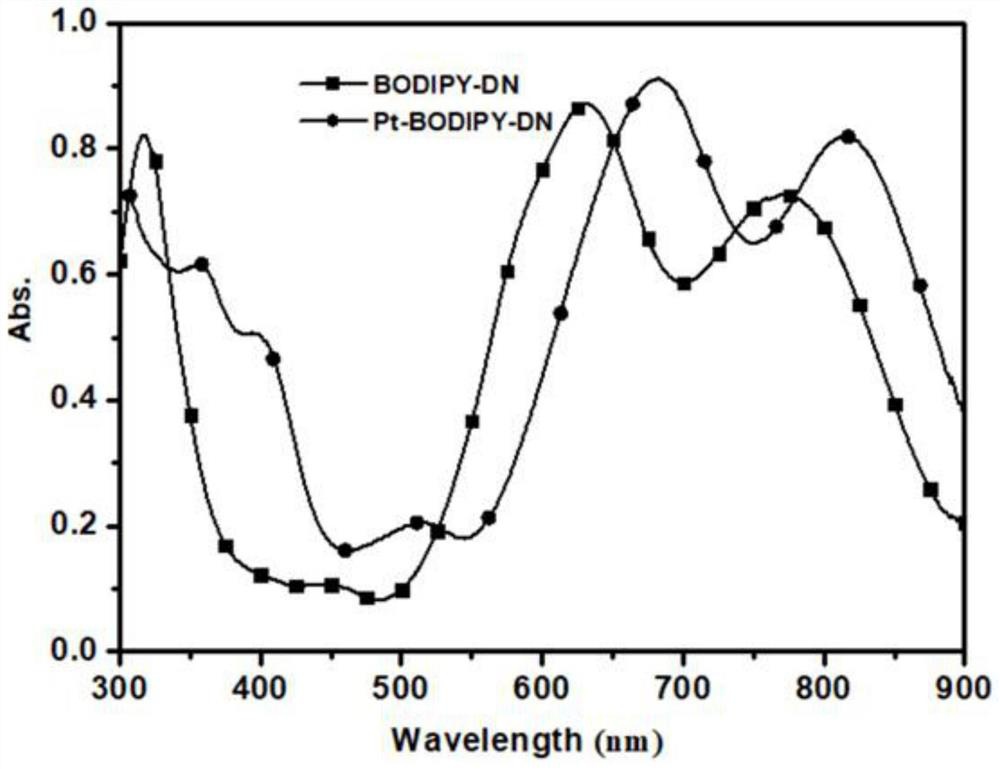
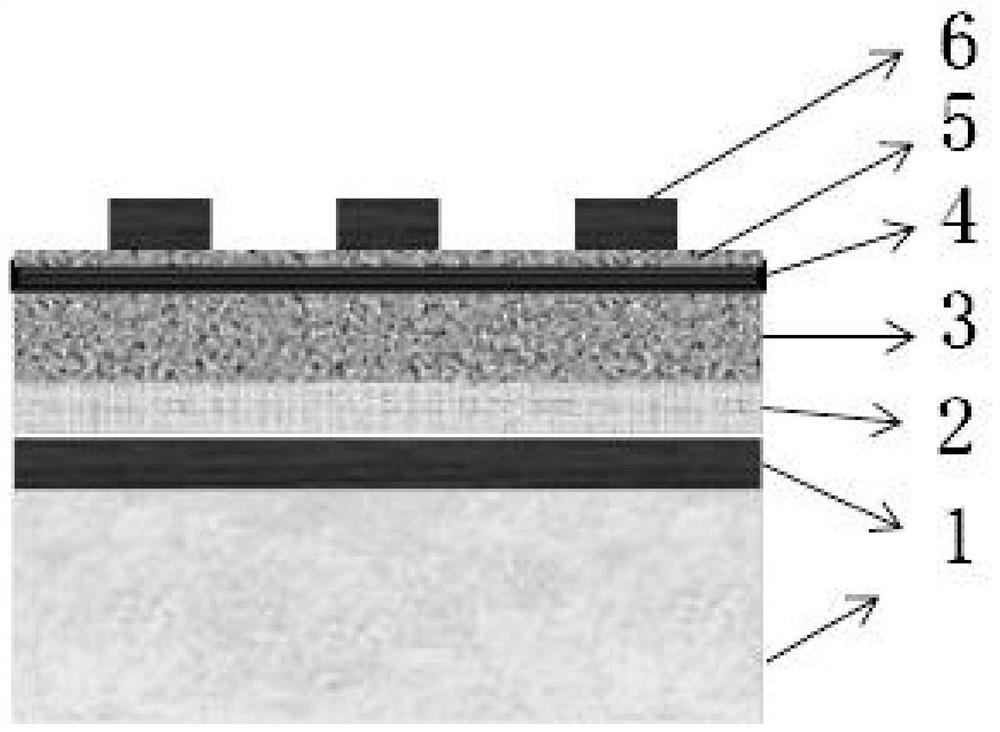
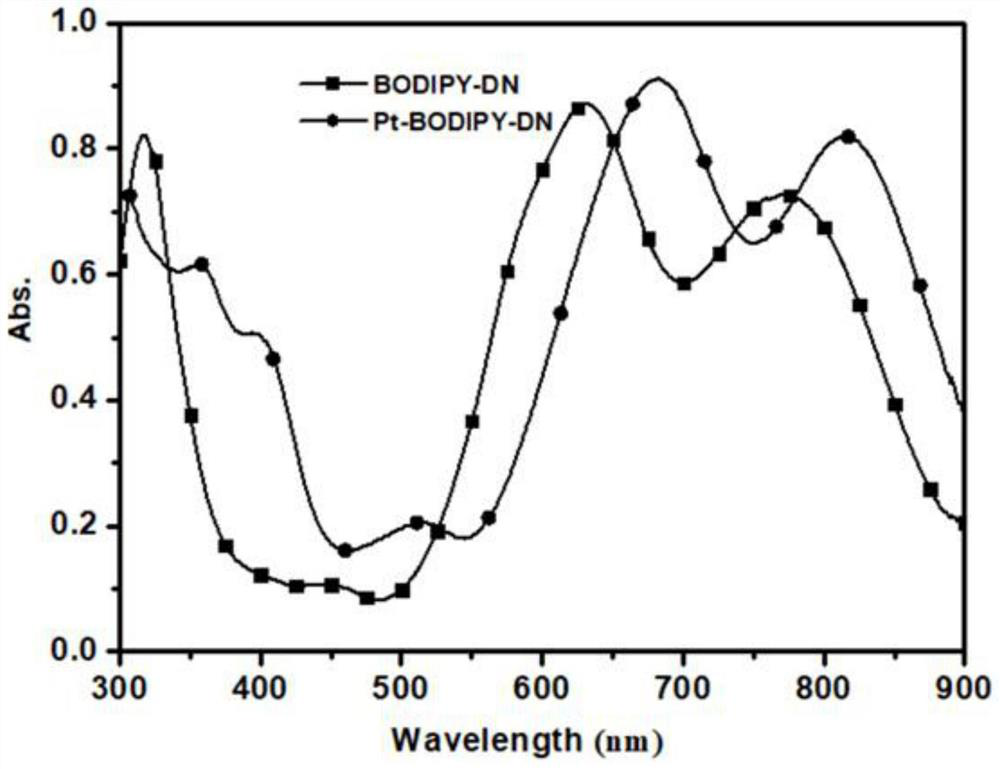
Boron-dipyrromethene derivative, preparation method thereof and photoelectric detector doped with boron-dipyrromethene derivative as donor
ActiveCN113072589AFacilitate dissociationIncrease photocurrentFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a boron-dipyrromethene derivative, a preparation method thereof and a photoelectric detector doped with the boron-dipyrromethene derivative as a donor. Alkynyl is introduced into the boron-dipyrromethene derivative to serve as a P-type semiconductor material, and the derivative is sensitive to ultraviolet-visible-near infrared light. A bulk heterojunction in the broad-spectrum photoelectric detector comprises a P-type boron-dipyrromethene derivative and a traditional N-type fullerene material, and a hole transport layer PEDOT: PSS and transparent conductive substrate ITO glass are sequentially arranged on one side of an anode of a heterojunction film in a detector device. An electron transport layer C60, an electron buffer layer LiF and a metal back electrode Al are sequentially arranged on one side of the cathode of the heterojunction film. The broad-spectrum photoelectric detector is simple in device structure and manufacturing process, insensitive to temperature, high in responsivity and high in response speed, and has good application value in the fields of photoelectric communication and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Compressor oil and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN112159690AImprove oxidation capacityEasy to useLiquid carbonaceous fuelsOil and greasePolyolester
The invention provides compressor oil as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of hydraulic grease; the compressor oil comprises a base oil and an antioxidant additive. The base oil is mainly composed of long-chain synthetic hydrocarbon, polyol ester, benzoate compounds and benzene ring-containing synthetic hydrocarbon; the antioxidant additive ismainly composed of a phenol antioxidant, an amine antioxidant, a metal deactivator, an antirust agent and a defoaming agent. According to the compressor oil, the preparation method and the application thereof, all the components are deeply studied, and the physicochemical properties and the synergistic effect of all the components are fully utilized, and therefore the performance indexes such asthe oxidation performance and the using effect of the compressor oil are greatly improved. The use test proves that the oil change period of the compressor oil is greatly prolonged, the use efficiencyof the air compressor is further improved, the hazardous waste amount is reduced, and good practicability and comprehensive economic benefits are achieved.
Owner:吴鸿江
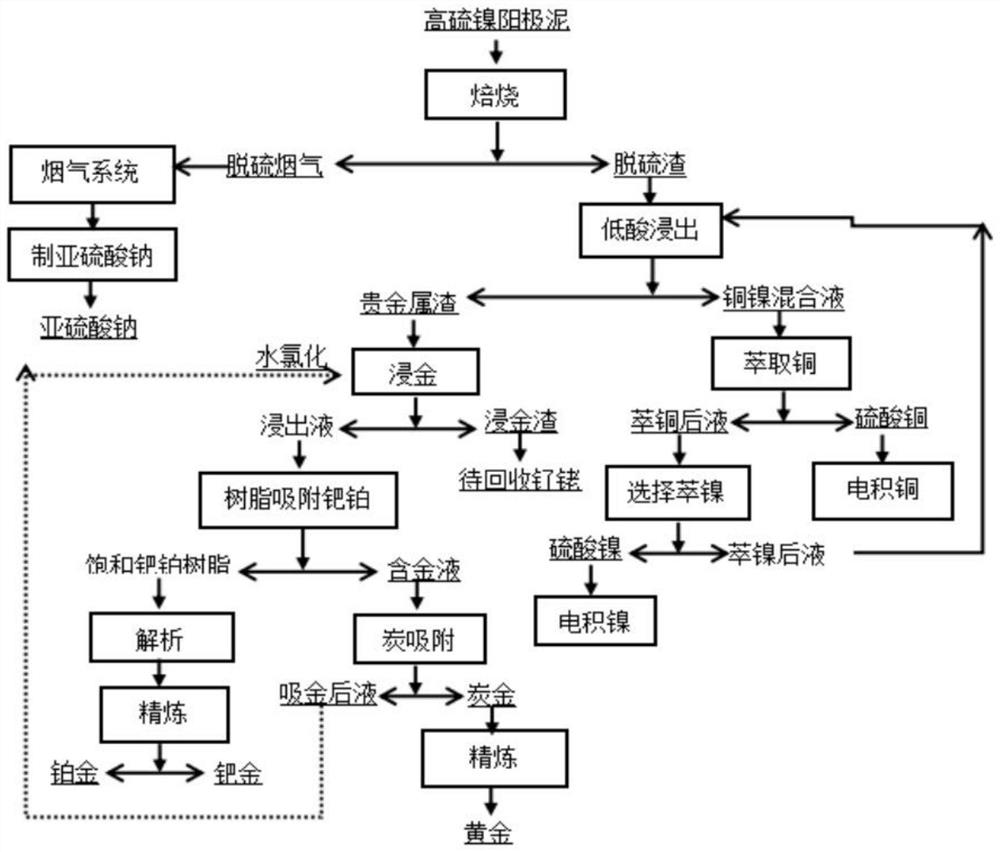
System and method for comprehensively recovering precious metal from high-sulfur nickel anode slime
InactiveCN114182096AHigh recovery rateReduce consumptionPhotography auxillary processesEnergy inputPlatinumSulfite salt
Compared with the prior art, the system for comprehensively recovering the precious metal from the high-sulfur nickel anode slime comprises rotary roasting equipment used for roasting the high-sulfur nickel anode slime; the flue gas treatment system is connected with the rotary roasting equipment and is used for treating desulfurized flue gas; the sodium sulfite preparation device is connected with the flue gas treatment system; the desulfurization residue acid leaching system is connected with the roasted product; the noble metal slag storage chamber is connected with the sodium sulfite preparation device and the desulfurization slag acid leaching system; the gold leaching system is connected with the precious metal slag storage chamber; the palladium-platinum adsorption system is connected with the gold leaching system; the analysis system is connected with the palladium-platinum adsorption system; and the first refining system is connected with the analysis system. According to the technical scheme, compared with the prior art, the production process is short, operability is high, and the recovery rate of precious metal can be increased. The invention further relates to a method for comprehensively recovering the precious metal from the high-sulfur nickel anode slime, and the method also has the above beneficial effects.
Owner:陈崇文
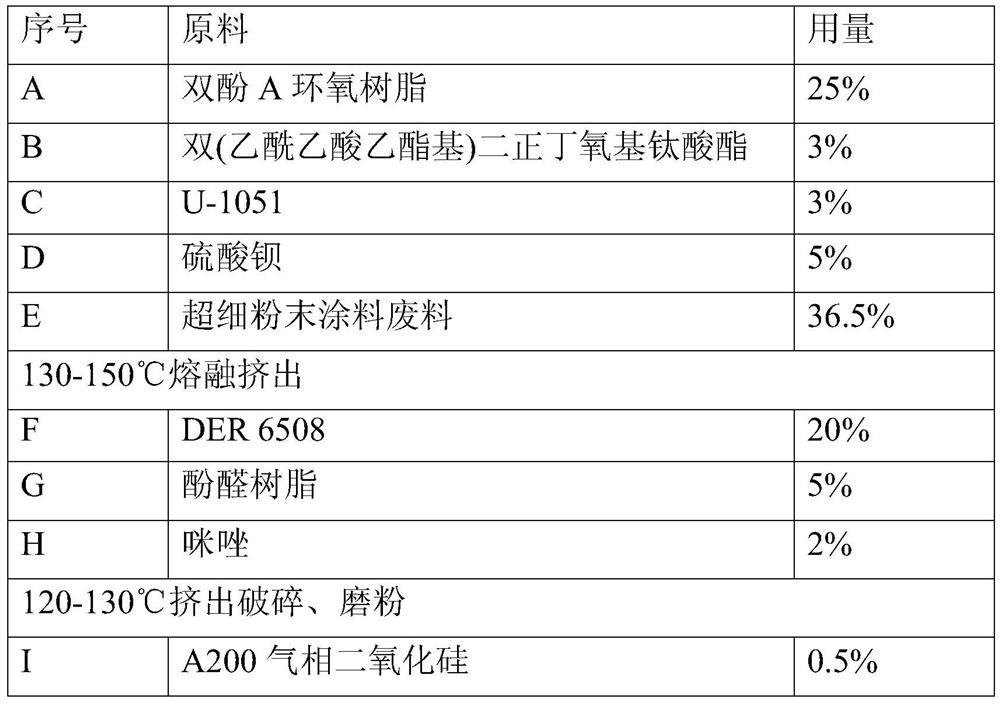
A kind of powder coating composition prepared by utilizing ultra-fine drill pipe and oil pipe inner coating epoxy powder waste
ActiveCN112852256BEasy to wrapQualified performancePowdery paintsEpoxy resin coatingsBis epoxideBisphenol
Owner:海隆石油产品技术服务(上海)有限公司
A class of fluoroboron dipyrrole derivatives and its preparation method and photodetector using it as donor doping
ActiveCN113072589BFacilitate dissociationIncrease photocurrentFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHeterojunctionSemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a class of fluoroboron dipyrrole derivatives, a preparation method thereof and a photodetector using it as a donor doping; said fluoroboron dipyrrole derivatives introduce alkynyl groups as a P-type semiconductor material, And it is sensitive to ultraviolet-visible-near-infrared light; the bulk heterojunction in the broad-spectrum photodetector includes P-type fluoroboron dipyrrole derivatives and traditional N-type fullerene materials, and the detector device is located in the The anode side of the heterojunction film is sequentially provided with a hole transport layer PEDOT:PSS and a transparent conductive substrate ITO glass, and the cathode side of the heterojunction film is sequentially provided with an electron transport layer C 60 , electron buffer layer LiF and metal back electrode Al. The broad-spectrum photodetector of the present invention has a simple device structure and manufacturing process, is insensitive to temperature, has high responsivity, fast detector response speed, and has good application value in fields such as photoelectric communication.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
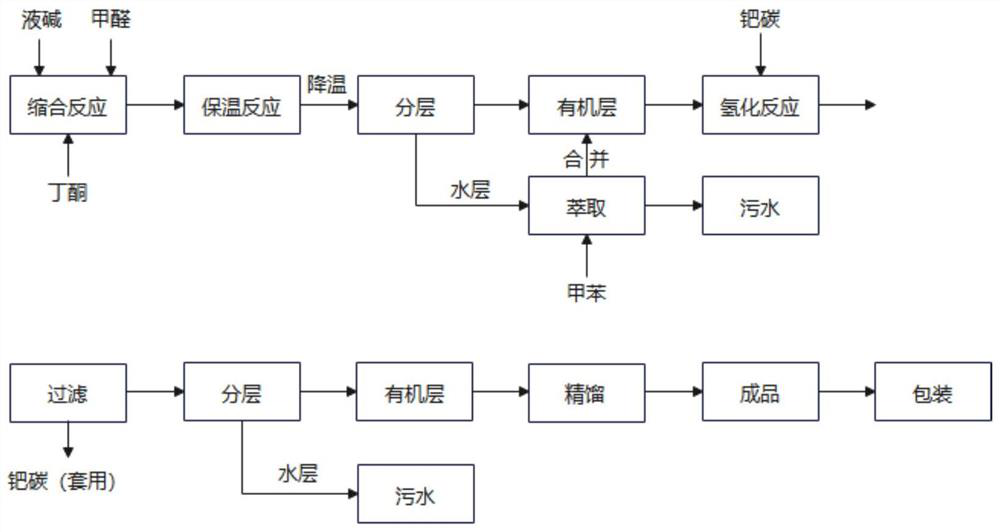
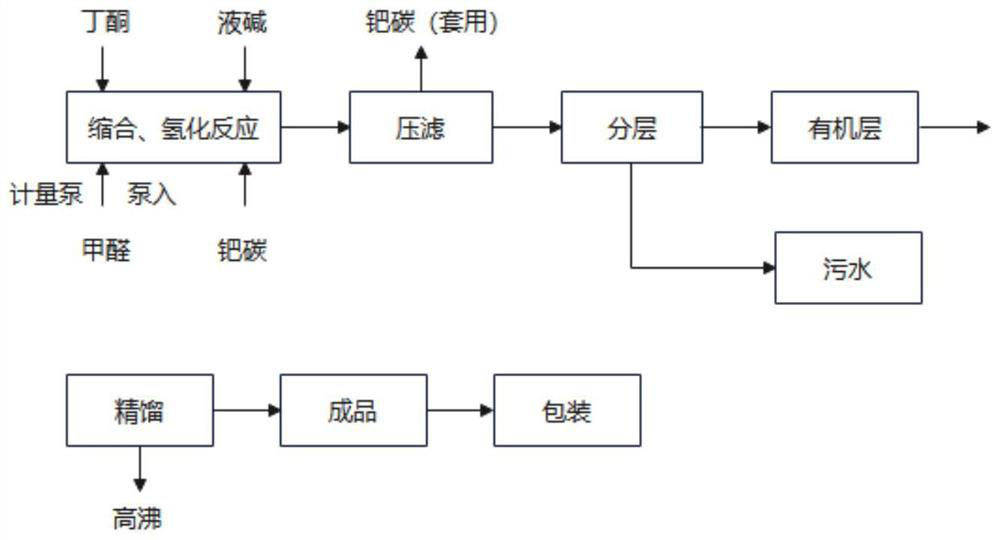
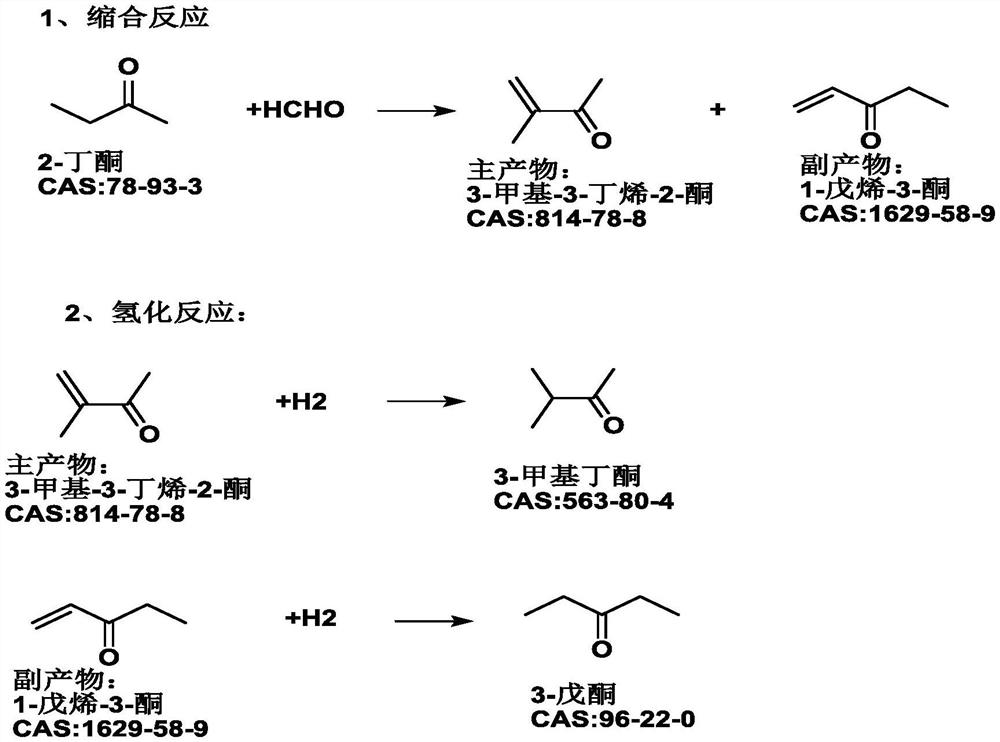
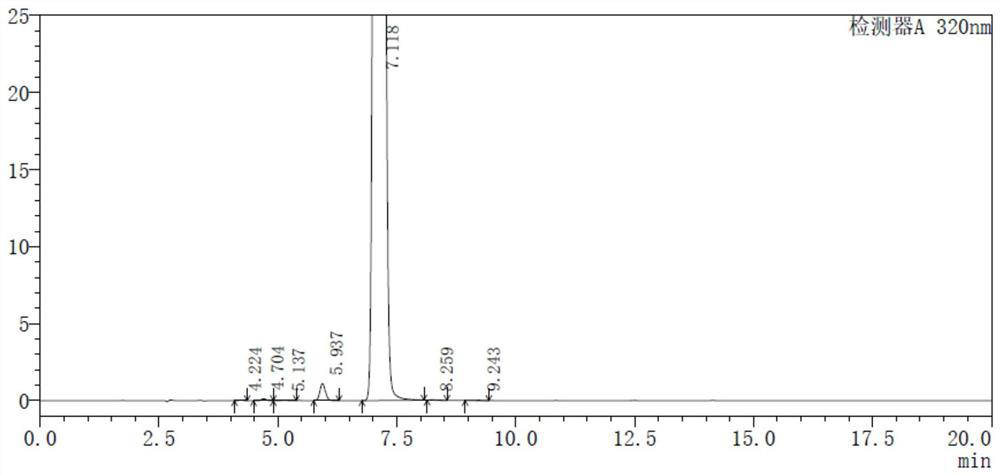
One-pot production process of methyl isopropyl ketone
PendingCN114591161AReduce consumptionHigh reaction yieldOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationPalladium on carbonChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a one-pot production process of methyl isopropyl ketone, and relates to the field of chemical synthesis. The process comprises the following steps: adding a certain amount of butanone, palladium on carbon and a basic catalyst into a hydrogenation reaction kettle, after nitrogen and hydrogen are replaced until no air is left in the reaction kettle, increasing the pressure in the reaction kettle to a certain pressure by using hydrogen, and heating the materials in the reaction kettle to a temperature required by reaction; starting the reaction kettle for stirring, adding the formaldehyde aqueous solution into the hydrogenation reaction kettle, and controlling the reaction temperature and the reaction pressure at the same time; the addition time of the formaldehyde is controlled within 1-10 hours; and after the reaction is finished, pressing out the materials in the reaction kettle, layering, rectifying an organic layer, obtaining a finished product, and packaging. The method has the beneficial effects that the process flow can be shortened, the energy consumption and the equipment investment are reduced, and the wastewater amount is reduced; the reaction yield is improved, and safety and controllability are realized.
Owner:李昌龙
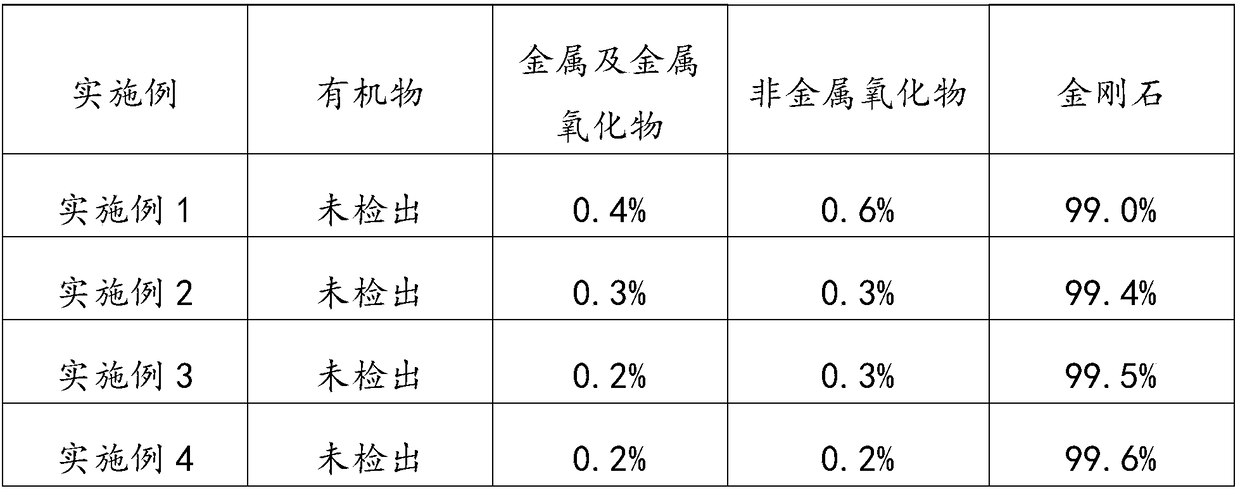
Method and product for recovering and reusing diamond
ActiveCN106829953BWithout compromising performanceLow costDiamondPolishing compositions with abrasivesCombustionSlurry
The invention provides a diamond recovery and reutilization method and a product of the method. The method is simple in procedures, can recover diamonds from sapphire grinding waste slurry, and does not damage the properties of the diamonds, thereby reutilizing the diamond, greatly enhancing the efficiency and reducing the hazardous waste generated in the saponifying step and petroleum ether cleaning. The method does not increase additional hazardous waste products, and thus, is more environment-friendly and prevents the hidden danger of material combustion in the drying step. The diamond powder particles have high purity, can be reutilized, and can effectively lower the cost of the sapphire grinding processing technique.
Owner:BEIJING GRISH HITECH
Anti-sticking paint as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111793391AEasy to cleanIncrease productivityLiquid surface applicatorsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyurethane dispersionCoated surface
The invention belongs to the technical field of spraying, and specifically discloses an anti-sticking paint as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The anti-sticking paint is preparedfrom the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 40-60% of polyethylene wax emulsion; 25-35% of polyurethane dispersion; 1-3% of color paste; 2-10% of a coalescing agent, 0-1% of an antifoaming agent, 0-1% of a leveling agent, 0-1% of a dispersant and 0-2% of a thickener. Ethylene wax particles can float on the surface of a coating after the anti-sticking paint is sprayed on a hanger to form a film, and due to low surface tension of wax, the surface of the coating is difficult to adhere, the adhesion force of paints on the surface is weak, and thus the paints can be easily removed.
Owner:上海缔朴水性涂料有限公司
A kind of tinidazole process impurity and synthetic method thereof
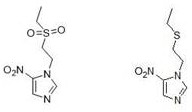
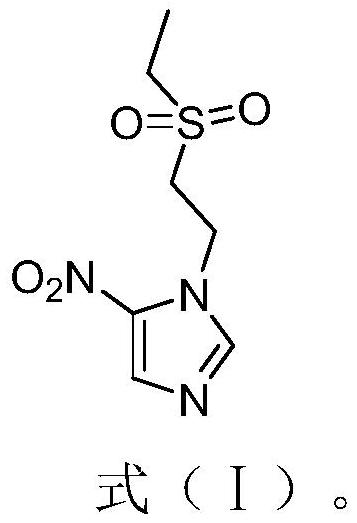
ActiveCN113683569BSolve the problem of the sourceAdd control type detectionOrganic chemistryComponent separationNitroimidazoleChemical synthesis
The invention relates to the technical field of chemical synthesis, and specifically discloses a technical impurity of tinidazole and a synthesis method thereof. The structure of the tinidazole process impurity is shown in formula (I), and the synthetic method comprises the steps of: taking 4-nitroimidazole and hydroxyethyl sulfide as raw materials, taking benzene compounds as solvent, under the action of concentrated sulfuric acid Condensation reaction is carried out to obtain the compound shown in formula (II); under the catalysis of soluble molybdate, the compound shown in formula (II) is oxidized by hydrogen peroxide to obtain the tinidazole process impurity shown in formula (I). The present invention prepares tinidazole process impurities with a purity of more than 99.7% through a specific synthesis process, solves the problem of the source of tinidazole process impurities reference substances, and is conducive to further improving the production of tinidazole raw materials or preparations thereof Quality Standard.
Owner:河北广祥制药有限公司
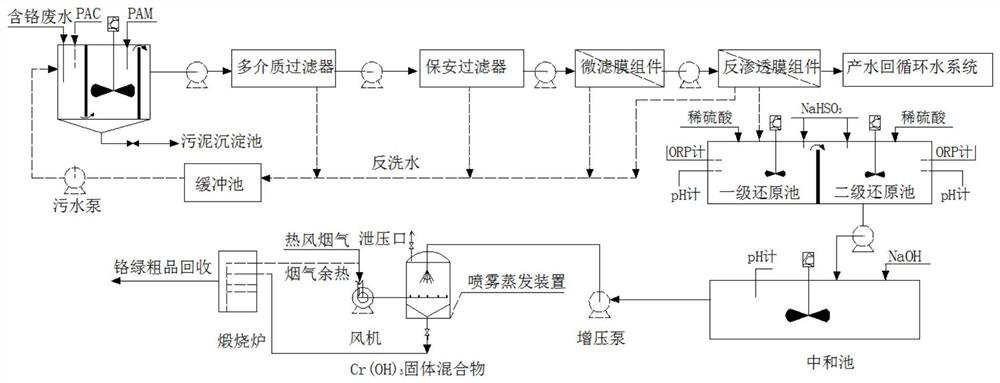
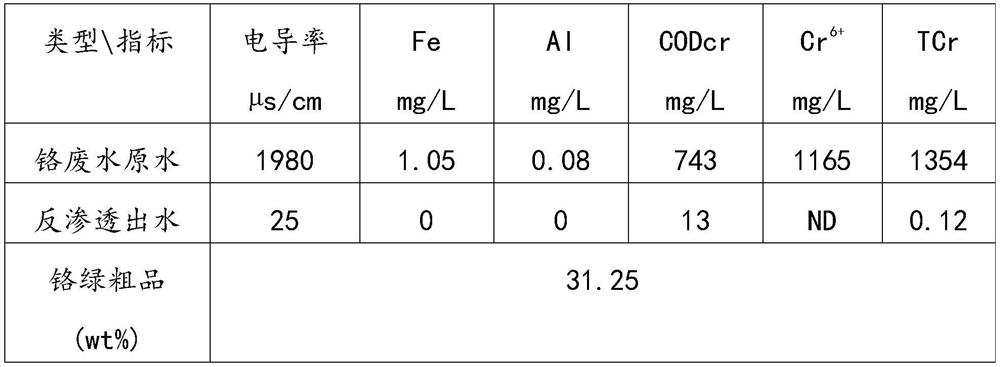
Zero discharge and chromium recovery method for iron and steel industry chromium-containing wastewater
InactiveCN111747565AAchieving zero emissionsAchieve recyclingGeneral water supply conservationTreatment involving filtrationSludgeFiltration
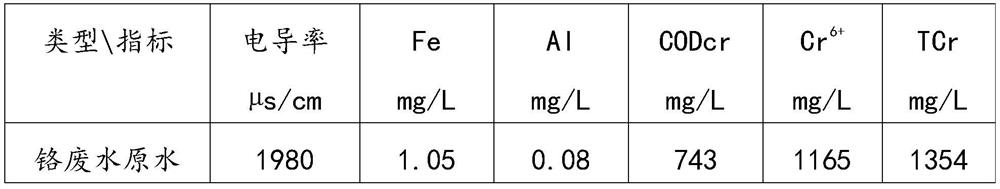
The invention relates to a zero discharge and chromium recovery method for iron and steel industry chromium-containing wastewater. The method includes: sending chromium-containing wastewater generatedin a steel rolling process into a wastewater regulating tank for pretreatment, adding a flocculant into the wastewater regulating tank for precipitation, and discharging sludge for sintering treatment; sending supernatant wastewater in the wastewater regulating tank sequentially into a multi-medium filter and a security filter for filtration treatment, and then sequentially enabling the treated wastewater to enter a micro-filtration membrane assembly for filtration and a reverse osmosis membrane assembly for desalination, recycling the produced water desalinated by the reverse osmosis membrane assembly to a circulating water system to replace new water or soft water, and sending reverse osmosis concentrated water into a reduction tank for reduction and detoxification; feeding a Cr(OH)3-containing suspension into a spray evaporation system after detoxification, and carrying out spray drying to generate a Cr(OH)3 crude product; putting the Cr(OH)3 crude product into a calcining furnace,and performing calcining at 1050DEG C-1150DEG C to obtain a chrome green crude product. The method has the beneficial effects that: the occupied area is small, the operation is stable, and zero discharge of wastewater and recycling of chromium resources are realized.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com