Lignocellulose material efficient decomposition composite bacterial system and culture method thereof
A technology of lignocellulose and culturing method, which is applied in the field of efficient decomposition of lignocellulose materials and the field of culturing compound bacteria, can solve the problems of low decomposition efficiency of straw, and achieve the effects of improving flexibility and improving decomposition efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] A complex bacterial system for efficiently decomposing lignocellulosic materials, which includes Bacillus subtilis that secretes amylase and protease, Bacillus cereus that secretes protease, Pseudomonas aeruginosa that secretes ligninase, and fiber that secretes The clostridium papyrilyticum of suzyme, the Pichia pastoris that secretes hemicellulase, the colony forming unit number ratio of each strain of described composite bacteria is: Bacillus subtilis: Bacillus cereus: Pseudomonas aeruginosa: lysate Paper clostridium: Pichia pastoris=12-15:13-15:15-18:23-25:24-26, the concentration of enzyme in the composite strain is 5g / L;
[0056] The optimum growth temperature of the constituent microorganisms of the complex flora is between 30-37°C, while the optimum temperature for the secreted lignocellulose-decomposing enzymes to function is between 50-60°C, and each The strains are matched to secrete a corresponding amount of enzymes, so that various enzymes can synergistical...
Embodiment 2
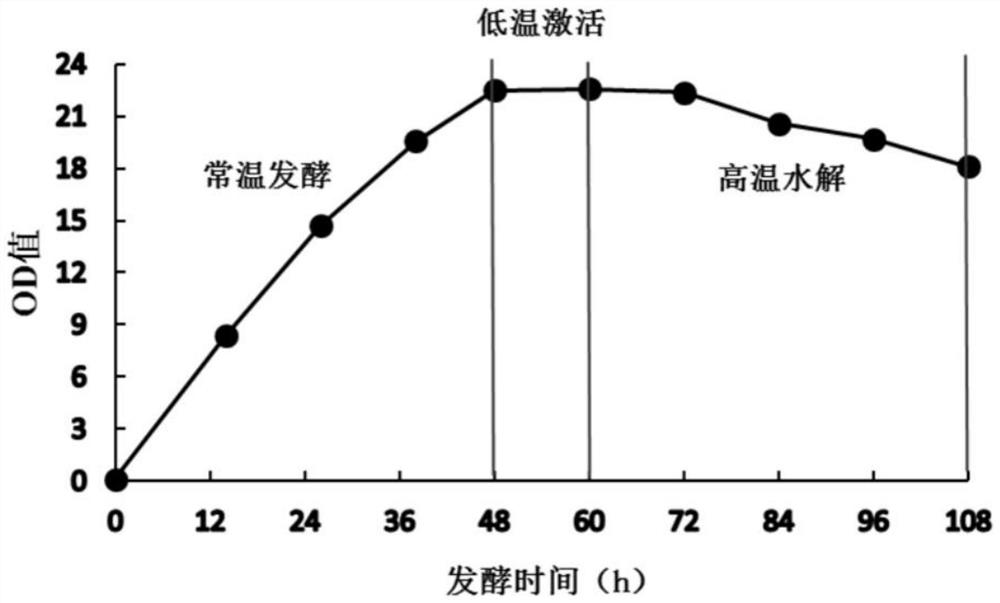
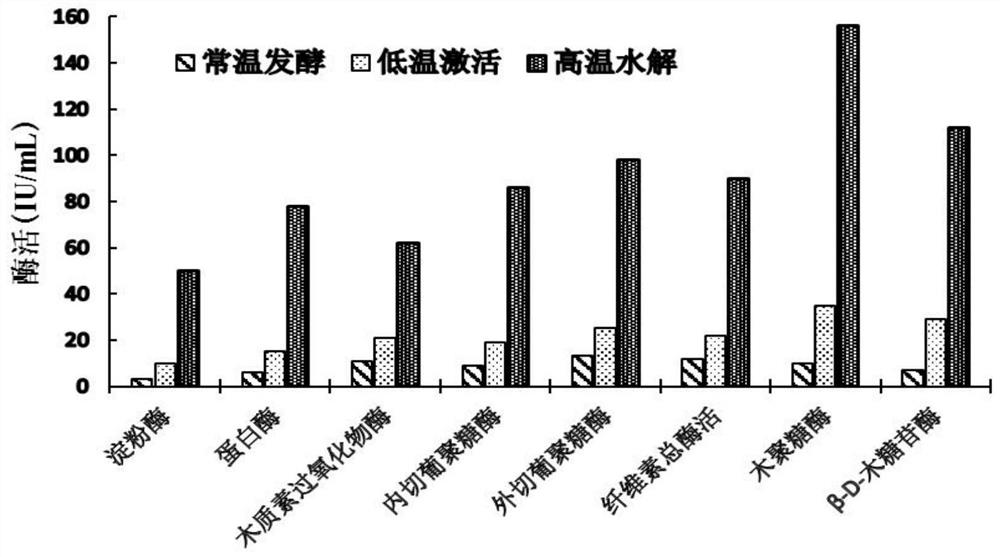
[0058] like Figure 1-2 As shown, the fermentation method of lignocellulosic materials efficiently decomposing complex bacterial strains:
[0059] Strain culture:
[0060] The seed liquid culture medium: peptone 12g, yeast extract powder 7g, NaCl 10g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.42g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.21g, agar 15g, distilled water to 1L, pH 7.0, sterilized at 121°C for 15min. After the sterilization is finished, pour it on a flat plate, cool and solidify for later use.
[0061] Firstly, the preserved composite bacteria system is activated on a slant to restore its best performance and prepare for making seeds. Then, the slant-activated seeds were cultured by streaking on the ultra-clean bench, and placed in a 32°C incubator for 3 days. The seeds cultivated to the logarithmic growth phase were transferred into a 1L Erlenmeyer flask under a sterile environment, and cultured at 32° C. and 200 rpm for 2 days.
[0062] Seed liquid expansion culture:
[006...
Embodiment 3
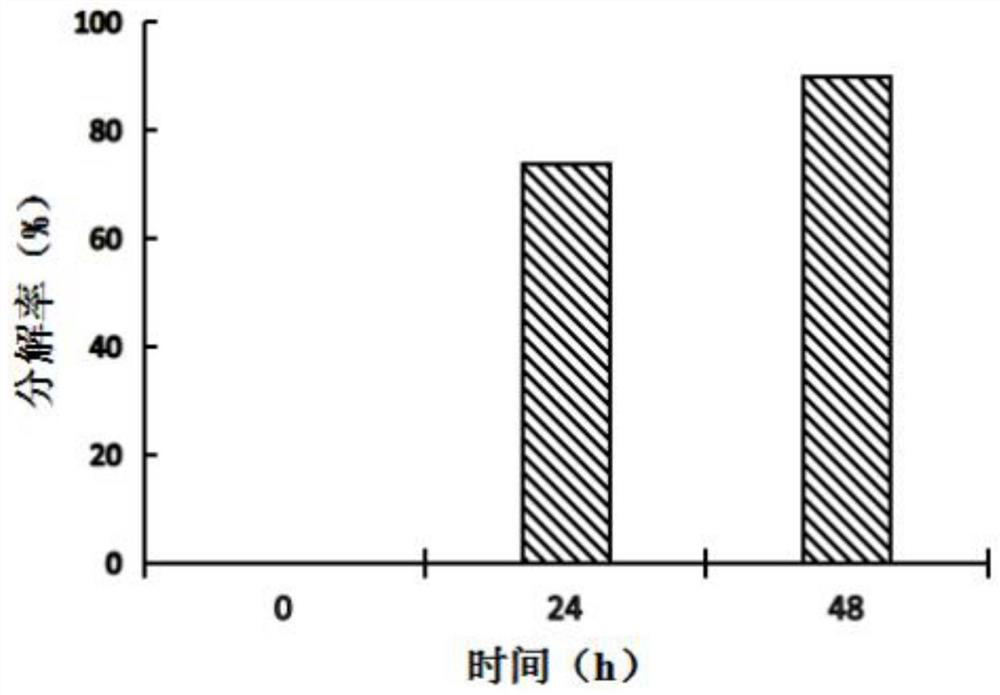
[0067] like Figure 3-4 As shown, the decomposition of bagasse by the composite bacterial system:
[0068] experimental method:
[0069] The method in Example 1 was used to cultivate complex strains to produce enzymes, and a 2t fermenter was used for three-stage fermentation to produce enzymes, and then 10% corn stalks were added to the produced enzyme solution for 48 hours of enzymatic hydrolysis. The total weight loss and the weight loss of each component of the bagasse decomposed by the composite bacteria were measured at 0, 24 and 48 hours during the decomposition process.
[0070] Experimental results:
[0071] Changes of Decomposition Rate in the Decomposition Process of Bagasse by Composite Bacteria
[0072] At the beginning of enzymatic hydrolysis (0h), the decomposition rate of bagasse was 0%, the decomposition rate at 24h was 74%, and at the end of enzymolysis (48h), the decomposition rate of bagasse reached 90% . It can be seen that the composite bacteria syste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com