Denitration catalyst with low SO2/SO3 conversion rate and preparation method thereof
A denitrification catalyst, SO3 technology, applied in the direction of metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalyst, catalyst activation/preparation, physical/chemical process catalyst, etc., can solve the problems of catalyst denitrification activity reduction, air preheater influence, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
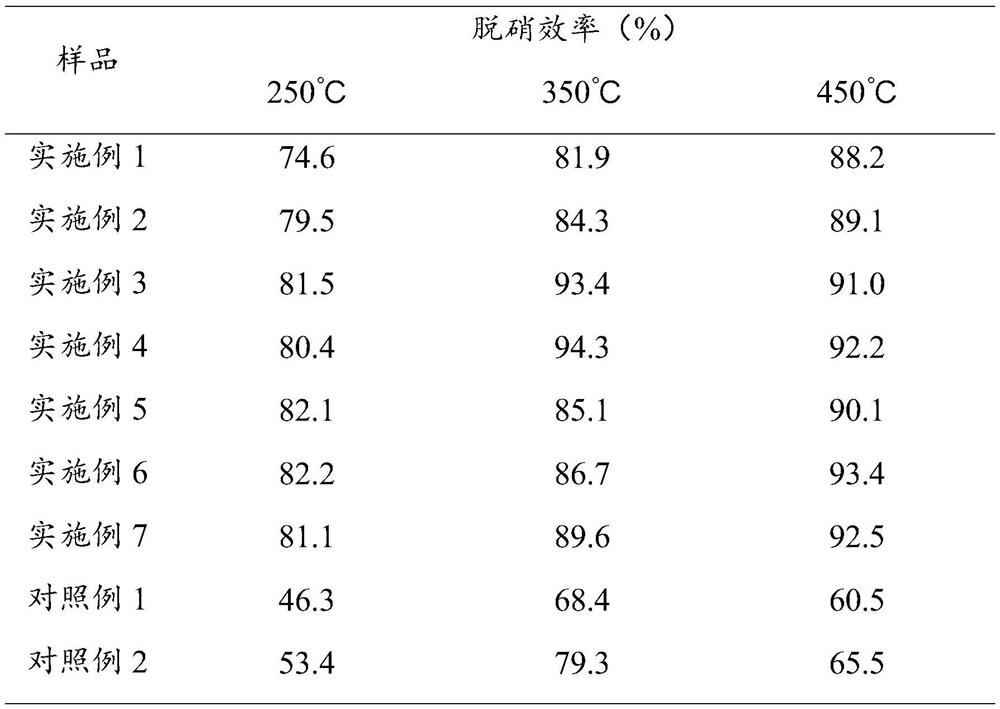
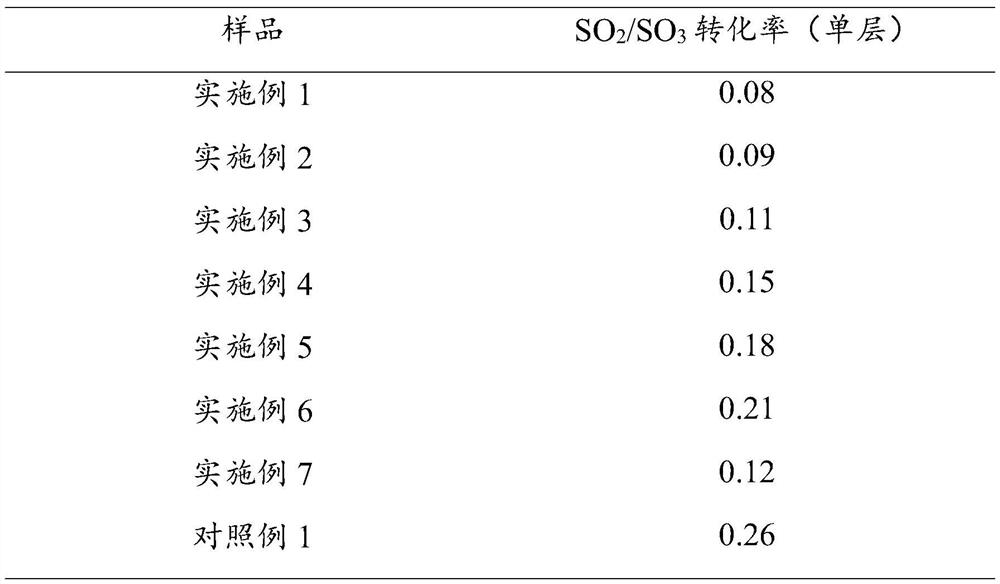
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] S11. Weigh ferric nitrate and place it in a crucible, add glycine, sodium chloride and deionized water to stir and dissolve, put the mixture in a muffle furnace and calcinate at 750°C for 4 hours, and cool to obtain powder A, wherein glycine and nitric acid The ratio of the amount of iron is 1:1, and the quality of sodium chloride is 5% of the quality of ferric nitrate;
[0036] S12. Weighing the titanium dioxide, and immersing the titanium dioxide in an aqueous solution of ammonium metavanadate and ammonium heptamolybdate, stirring and drying the water, calcining at 400° C. for 4 hours, and cooling to obtain powder B;
[0037] S13. Put powder A and powder B in a high-shear disperser, and shear and disperse at 16,000 rpm for 1 hour to prepare a denitration catalyst.
[0038] V of the prepared denitration catalyst 2 o 5 Content is 0.5%, MoO 3 The content is 8%, iron oxide content is 8%, and the rest is TiO 2 .
Embodiment 2
[0040] S21. Weigh aluminum nitrate and place it in a crucible, add glycine, sodium chloride and deionized water to stir and dissolve, put the mixture in a muffle furnace and calcinate at 800°C for 3 hours, and cool to obtain powder A, wherein glycine and nitric acid The ratio of the amount of aluminum is 1.5:1, and the quality of sodium chloride is 6% of the quality of aluminum nitrate;
[0041] S22. Weighing the titanium dioxide, and immersing the titanium dioxide in an aqueous solution of ammonium metavanadate and ammonium heptamolybdate, stirring and drying the water, calcining at 450° C. for 3.5 hours, and cooling to obtain powder B;
[0042] S23. Put powder A and powder B in a high-shear disperser, and shear and disperse at 15,000 rpm for 1.5 hours to prepare a denitration catalyst.
[0043] V of the prepared denitration catalyst 2 o 5 Content is 1%, MoO 3 The content is 5%, the alumina content is 6%, and the rest is TiO 2 .
Embodiment 3
[0045] S31. Weigh cerium nitrate and place it in a crucible, add glycine, potassium chloride and deionized water to stir and dissolve, put the mixture in a muffle furnace and calcinate at 800°C for 3 hours, and cool to obtain powder A, wherein glycine and nitric acid The ratio of the amount of cerium is 2:1, and the quality of potassium chloride is 8% of the quality of cerium nitrate;
[0046] S32. Weighing the titanium dioxide, and immersing the titanium dioxide in an aqueous solution of ammonium metavanadate and ammonium heptamolybdate, stirring and drying the water, calcining at 600° C. for 1 hour, and cooling to obtain powder B;
[0047] S33. Put powder A and powder B in a high-shear disperser, and shear and disperse at 14,000 rpm for 2 hours to prepare a denitration catalyst.
[0048] V of the prepared denitration catalyst 2 o 5 Content is 2%, MoO 3 The content is 4%, the cerium oxide content is 4%, and the rest is TiO 2 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com