Hydrodynamic separation and wet stripping process for waste lithium ion battery broken materials
A technology for lithium-ion batteries and waste lithium batteries, which is applied in battery recycling, solid separation, waste treatment, etc., can solve problems such as difficult implementation, large influence of battery coating process, and difficulty in metal removal, so as to reduce equipment investment and operation cost, avoid a large amount of dust and powder explosion, and avoid the effect of powder entrainment loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
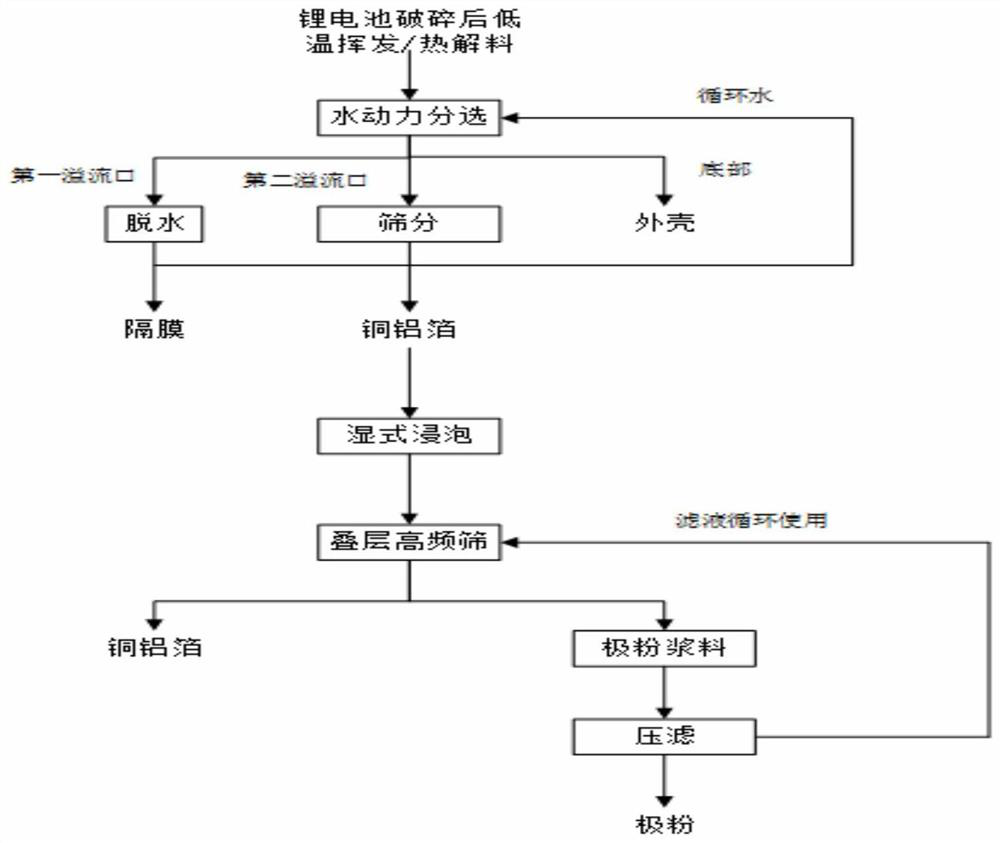
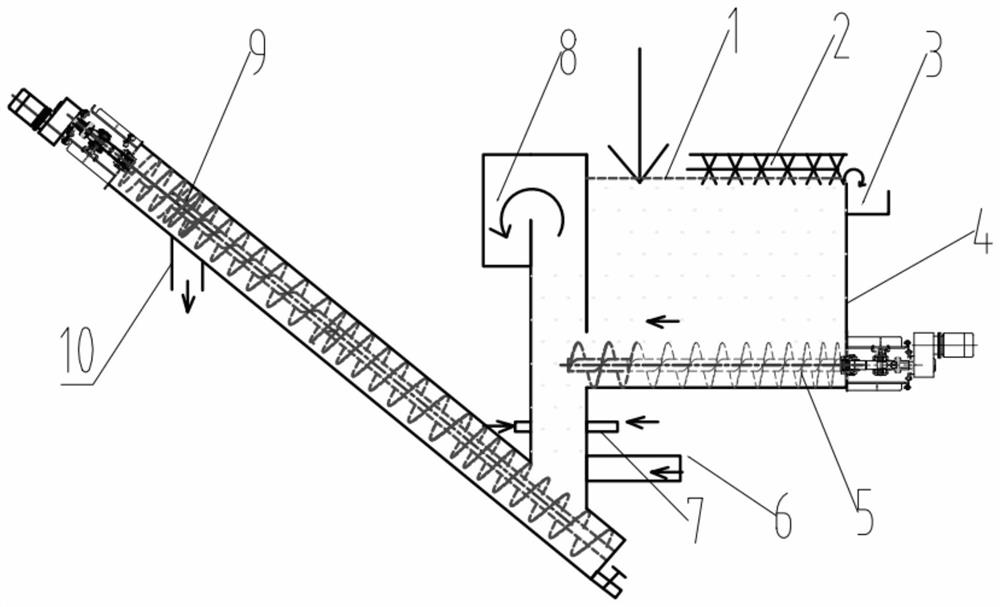
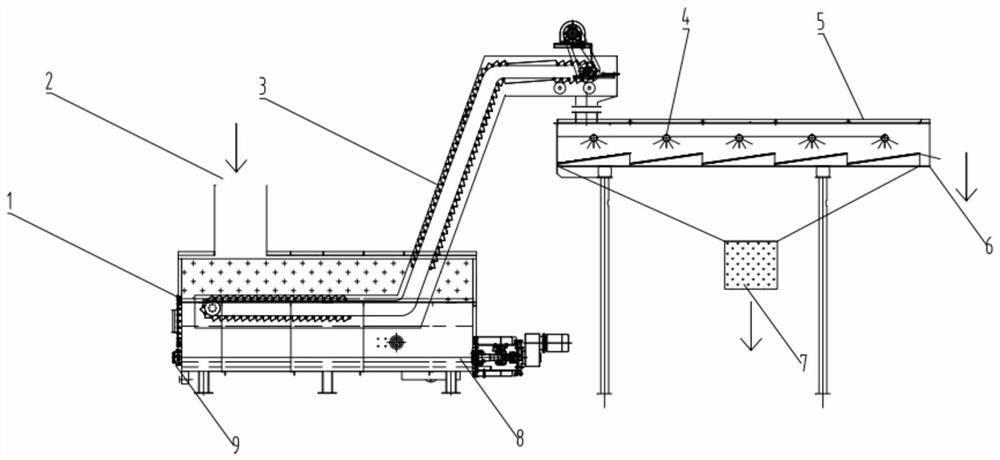
[0027] Send the waste lithium iron phosphate battery crushed material after charged crushing and electrolyte treatment to the hydrodynamic sorting device, separate the battery shell from the pole piece, put the obtained pole piece material into a wet soaking tank, add 25 % ammonia water, the liquid-solid ratio is 1:3, and the soaking time is 20min at 28°C. After soaking, the electrode pieces are screened and washed with high-pressure water, and the electrode pieces on the sieve are dried, granulated, and color selected Copper foil and aluminum foil with a purity of more than 99% are obtained, and the positive and negative electrode powder filter cake of the lithium iron phosphate battery obtained after the slurry under the sieve is press-filtered. The recovery rate of the electrode powder is 98.5%, and the grade of the electrode powder is 98% (the electrode powder contains 1.5% copper, 0.5% aluminum); according to the traditional friction dispersion + wind selection, the recove...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Send the waste 523 ternary lithium battery broken material after charged crushing and electrolyte treatment into the hydrodynamic sorting device, separate the battery shell from the pole piece, and put the waste ternary lithium ion battery pole piece into the wet soaking tank , add 10% dimethylamine to the soaking tank, the liquid-solid ratio is 1:2, and when the soaking time is 10min at 25°C, the pole pieces are screened and washed with high-pressure water after soaking, and the pole pieces on the sieve are baked Copper foil and aluminum foil with a purity of more than 99% are obtained after drying, granulation, and color separation. The positive and negative electrode powder filter cake of the ternary lithium battery is obtained after the slurry under the sieve is press-filtered. The recovery rate of the electrode powder is 98.8%, and the grade of the electrode powder is 98.5% (including 1% copper and 0.5% aluminum in the electrode powder); the recovery rate of the ele...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Send the waste lithium iron phosphate battery crushed material after charged crushing and electrolyte treatment to the hydrodynamic sorting device, separate the battery shell from the pole piece, and put the waste lithium iron phosphate battery pole piece into a wet soaking tank, Add 30% methoxybenzaldehyde in the stirring tank, the liquid-solid ratio is 1:2, and when the soaking time is 20min at 30°C, the pole pieces are screened and washed with high-pressure water after soaking, and the pole pieces on the sieve are washed Copper foil and aluminum foil with a purity of more than 99% are obtained after drying, granulation, and color sorting. The positive and negative electrode powder filter cakes of lithium iron phosphate batteries obtained after the slurry under the sieve are press-filtered. The recovery rate of the electrode powder is 98%. The grade is 98% (including 1.5% copper and 0.5% aluminum in the electrode powder); the recovery rate of the electrode powder obtai...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com