Saccharomyces cerevisiae culture rich in active probiotics, preparation method and special equipment thereof
A technology of active probiotics and cultures, applied in the field of feed, can solve the problems of low drying output, large steam consumption, large power consumption, etc., and achieve the effect of shortening the fermentation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Preparation of mixed bacterial liquid
[0036] The selected strains of yeast culture produced by this patent are Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain number Saccharomyces cerevisiae CICC 1355), Candida utilis CICC 31188, Bacillus coagulans (strain number Bacillus subtilis CICC 10071), plant milk Bacillus (strain number Lactobacillus plantarum CICC 21790), the two yeast strains use PDA medium, Bacillus coagulans and Lactobacillus plantarum use LB and MRS medium respectively, and the equipment used is controllable temperature, rotation speed, pH, solution. Oxygen fermenter, four strains culture conditions are shown in Table 1. After the cultivation was completed, the viable bacterial contents of the four bacterial strains were all >10. 10 CFU / mL. Mix 1-2 parts of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, 0.8-1.5 parts of Candida utilis, 0.2-0.4 parts of Lactobacillus plantarum and 0.2-0.4 parts of Bacillus coagulans to prepare a mixed bacterial liquid.
[0037] Table 1 Four str...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Preparation of solid state fermentation premix
[0040] The raw materials, components and functions used in this patent are as follows:
[0041] Mixed bacterial liquid of Example 1: 2.2-4.3 parts.
[0042] Main fermentation raw materials (providing slow-acting carbon sources, slow-acting nitrogen sources, phosphorus elements, trace elements, etc.): 40-60 parts of sprayed corn husks; 10-20 parts of feed-grade jujube powder; 10-20 parts of bran; 1-5 servings.
[0043] Fast-acting carbon source: 2-6 parts of glucose; 1-5 parts of flour.
[0044] Fast-acting nitrogen source: 1-3 parts of feed-grade urea.
[0045] Phosphorus source: 1-3 parts of calcium hydrogen phosphate.
[0046] Source of trace elements: 0.1-0.3 part of ferrous sulfate; 0.1-0.3 part of manganese sulfate; 0.1-0.3 part of magnesium sulfate.
[0047] Source of chloride ion: 0.5-2 parts of feed-grade sodium chloride.
[0048] Raw materials for pH adjustment: 0-3 parts of stone powder, 0-1 par...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3: Preparation of yeast cultures
[0051] 1) Solid state fermentation:
[0052] The solid-state fermentation premix prepared from the above mixed bacterial liquid and fermentation raw materials is mixed with water in a ratio of 7:3, and a square fermentation pile with a length of more than 2 meters, a width of more than 2 meters, and a height of 0.5-0.8 meters is stacked on the fermentation bed.
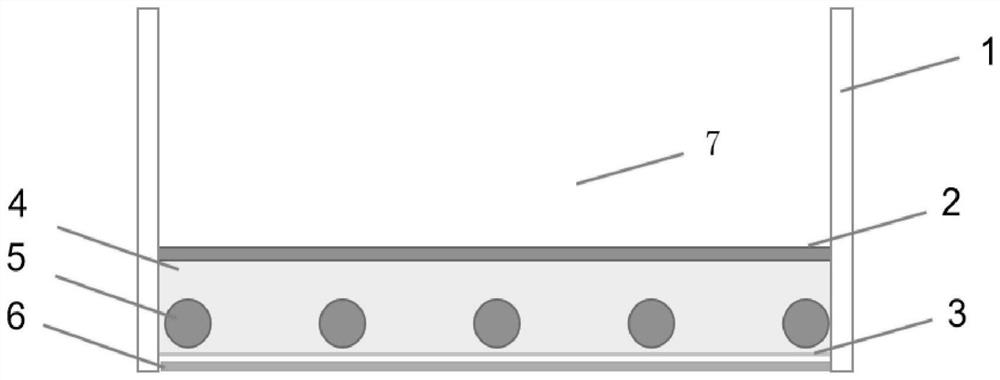
[0053] like figure 1 As shown, the fermentation bed includes a fermentation bed area 7 and an outer wall 1 of the fermentation bed, and a temperature-adjusting water pipe 5 is laid on the lower layer; a radiant film 3 is laid under the water pipe, and a thermal insulation board 6 is laid under the radiation film 3; above the temperature-adjusting water pipe 5 A 4cm cement layer 4 is laid, floor tiles 2 are laid above the cement layer 4, and above the floor tiles 2 is the fermentation bed area 7, and the fermentation bed outer wall 1 is provided around the fermentation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com