Electrochemical deep degradation method of brominated phenolic compound under synergistic adsorption of surfactant
A technology of phenolic compounds and surfactants, applied in the field of brominated flame retardant treatment, can solve the problems of low electron transfer efficiency, incompatible with deep degradation, easy agglomeration of zero-valent iron, etc., and achieves low price, short reaction time, The effect of a wide range of concentrations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 0
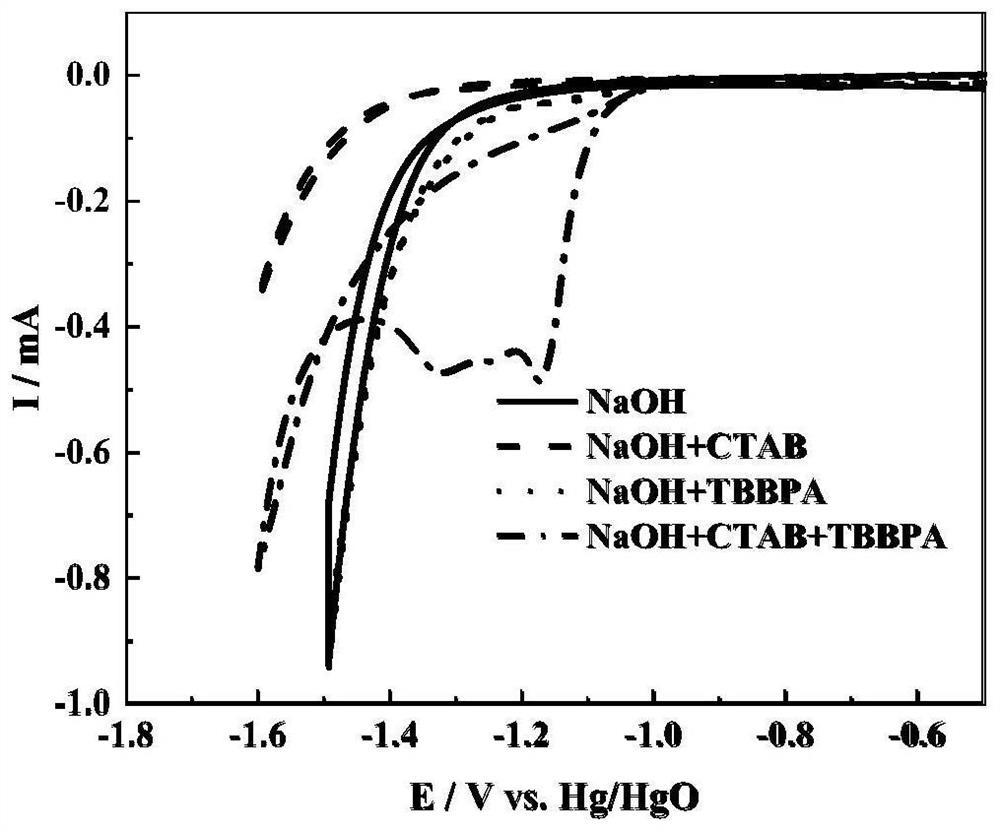
[0031] In order to study the effect of cationic surfactant CTAB on the TBBPA electrode process, a cyclic voltammetry test was carried out, and the test results are as follows figure 1 shown. The cyclic voltammetry test was carried out in a standard three-electrode system, with a silver disc electrode As the working electrode, the platinum sheet (20×20×0.2mm) is used as the counter electrode, and the standard mercury oxide electrode (Hg / HgO) is used as the reference electrode. The scan rate is 50mV / s, and the test temperature is 25°C. There is no redox peak in 0.4mol / L NaOH solution. When 1mmol / L CTAB was added to the blank NaOH solution, the hydrogen evolution potential of the system shifted negatively, indicating that CTAB was adsorbed on the electrode surface to form a hydrophobic film, which blocked the accumulation of solvent molecules on the electrode surface, thereby broadening the electrochemical window. When 10mmol / L TBBPA is added to 0.4mol / L NaOH solution, the hyd...
Embodiment 1-5
[0032] Embodiment 1-5: a kind of electrochemical deep degradation method of TBBPA in water, comprises the steps:
[0033] Step 1: Select a jacketed single-chamber electrolyzer that can accommodate 30mL of liquid, weigh CTAB (0.0054g, 1mmol / L,) and TBBPA (0.0815g, 10mmol / L) and dissolve in 15mL of NaOH (0.12g , 0.2mol / L) aqueous solution, the resulting electrolyte is added to the electrolytic cell, a suitable cathode material and anode material are selected, and a DC stabilized voltage power supply is connected to the electrodes.
[0034] Step 2: Connect the constant temperature circulating water instrument and set it to 25°C, add a 6mm×10mm size stirrer, set the magnetic stirring to 600rpm, start the DC stabilized power supply and control the current density to 4mA / cm 2 , Measure a certain amount of reaction solution at the reaction time of 0h, 1h, 2h, 3h, 4h, and 5h and pass it through a 0.22μm microporous membrane, and the obtained supernatant is subjected to the following t...
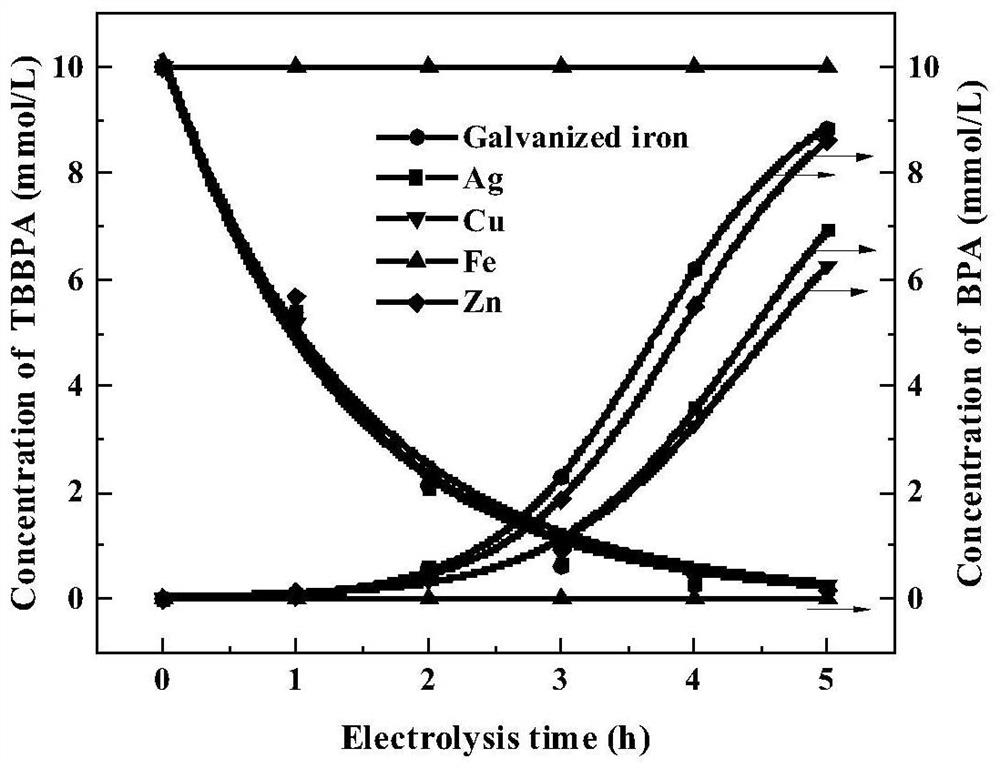
Embodiment 6-10
[0037] Embodiment 6-10: a kind of electrochemical deep degradation method of TBBPA in water, comprises the steps:
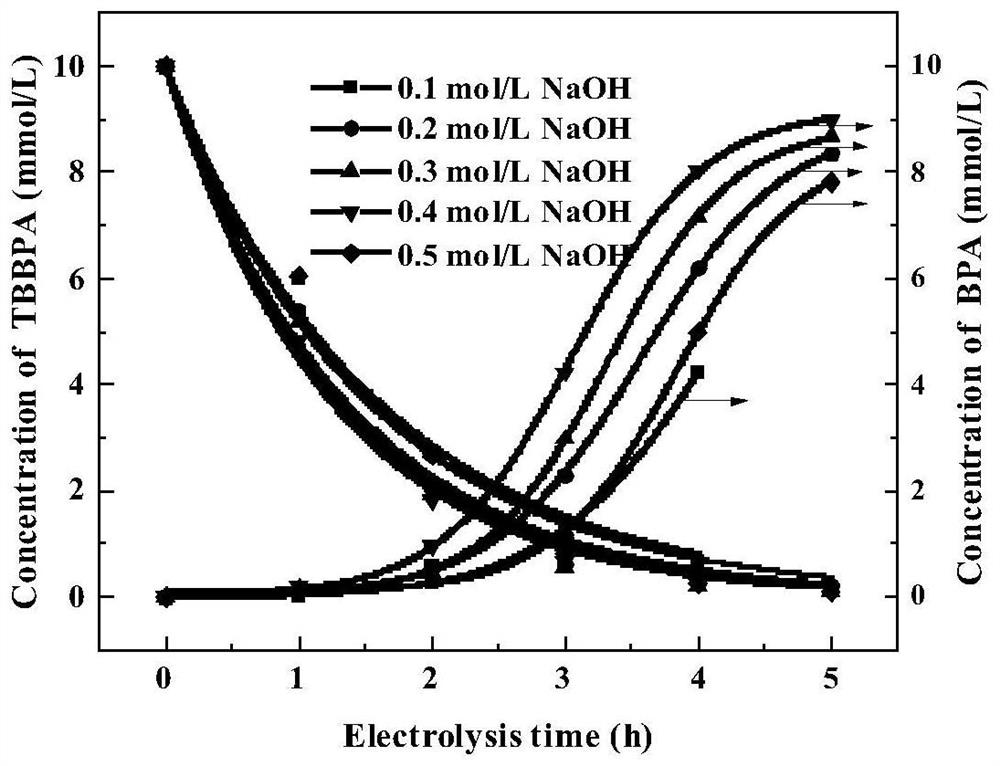
[0038] What is different from Examples 1-5 is: the cathode material is 20 × 20 × 0.2mm galvanized iron sheet in step one, and the NaOH concentration is respectively 0.1mol / L (embodiment 6) and 0.2mol / L (embodiment 7) in step one ), 0.3mol / L (embodiment 8), 0.4mol / L (embodiment 9), 0.5mol / L (embodiment 10), all the other electrolysis conditions are constant, and the obtained results are as follows image 3 shown. image 3 It shows that the concentration of NaOH between 0.2mol / L and 0.4mol / L has almost no effect on the degradation rate of TBBPA, and the degradation rate of TBBPA at 10mmol / L can reach 99% after 5 hours. The concentration of NaOH has a certain influence on the deep degradation of TBBPA to the product BPA. In the case of 0.4mol / L NaOH, 92% of 10mmol / L TBBPA is degraded to BPA. When the NaOH concentration increased to 0.5mol / L, the degradation rate o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com