Recombinant plasmid and engineering bacterium containing grass carp interferon gene and their application
A recombinant plasmid and interferon technology, applied in genetic engineering, medical preparations containing active ingredients, applications, etc., can solve the problems of high purity requirements, difficult and inappropriate natural extraction methods, etc., to enhance disease resistance, promote The effect of healthy and sustainable development and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1, grass carp interferon gene cloning
[0027] Subcutaneously inject 0.5ml of poly I:C (purchased from Tianjin Pharmaceutical Factory) from the dorsal fin of grass carp, induce another injection at 26°C for 12 hours, take about 10 grams of head kidney after 12 hours, and extract total RNA with TRizol (Gibco BRL, USA) , the extraction method was carried out according to the instructions. Then reverse transcription and PCR amplification were performed with the reverse transcription kit RNA PCR kit (AMV) Ver3.0 (TaKaRa, USA). Primer sequences are shown in Table 1.
[0028] After the amplified product was purified (using the PCR product purification kit DNA Gel Extraction Kit, V-gene), it was inserted into a T vector (TA cloning kit was purchased from Shanghai Sangong). The operation steps are all in accordance with the manual. The ligation product was transformed into Escherichia coli TOP10, and positive recombinants were screened for sequencing identificatio...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2, grass carp interferon gene sequence determination and analysis
[0031] Using NCBI ORF Finder to analyze the cDNA sequence obtained in Example 1, it can be seen that the open reading frame ORF is 543 bp long and encodes 180 amino acids. The rest of the 5'UTR is 34bp long, and the 3'UTR is 614bp long; the potential functional sites were analyzed with PROSITE database and the signal state analysis was carried out with the signal peptide analysis software SignalPprogram (version 3.0), and the conclusion was that the isoelectric point of the protein was 9.73 , and the gene has a signal peptide with a length of 22 amino acids, indicating that its mature peptide is 159 amino acids; using Prosite for site analysis, it is found that the gene has two N-terminal 14 acylation sites: GqcsAC and GTkvSF; 2 protein kinase II phosphorylation sites: SacE ShkE; one N-terminal glycosylation site: NESL; one protein kinase C phosphorylation site: ShK; two chromosomal nuclear l...
Embodiment 3
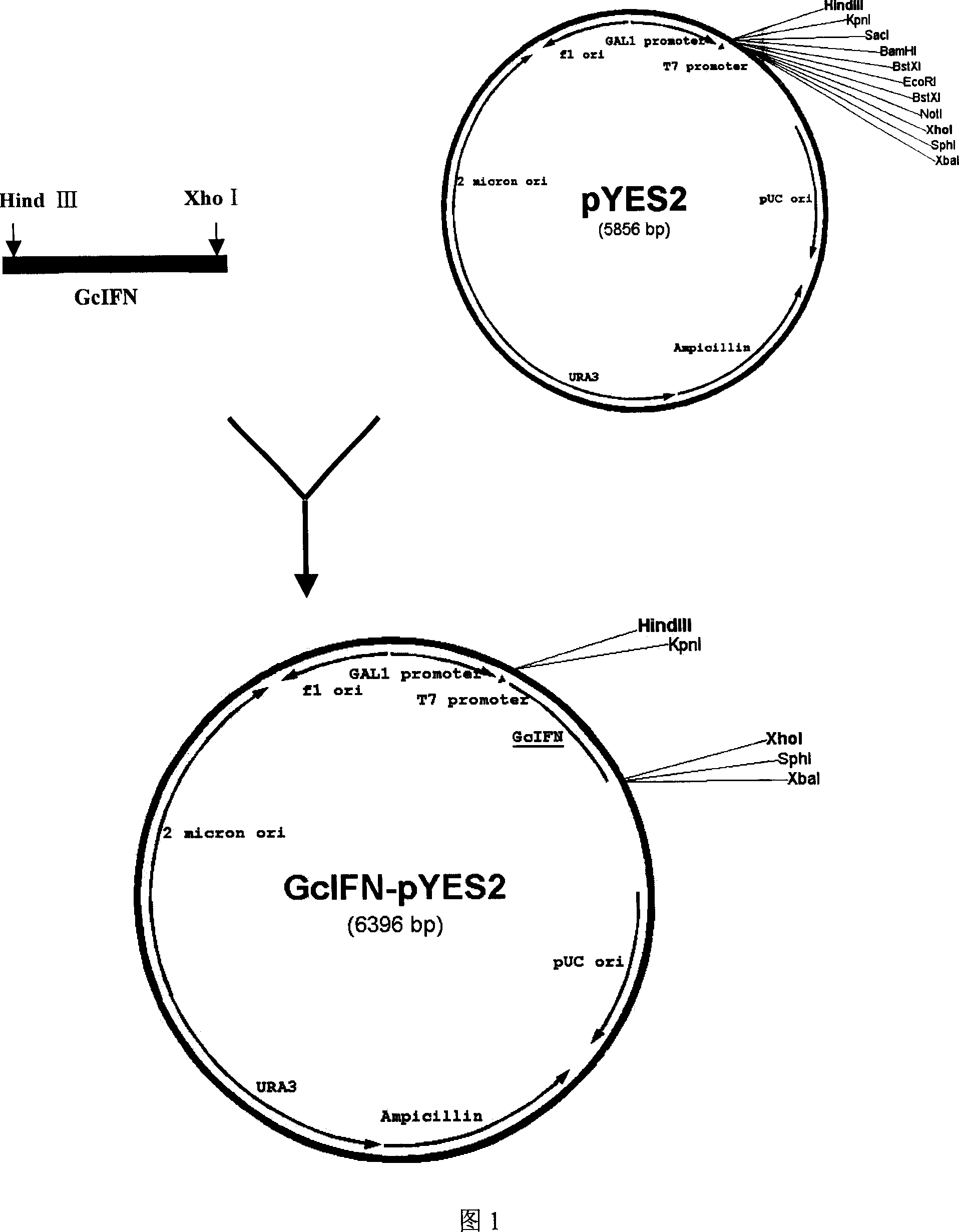
[0032] Embodiment 3, the construction of grass carp interferon expression plasmid
[0033] The interferon gene sequence design expression vector that obtains according to embodiment 1 constructs primer, and sequence is as follows:
[0034] The upstream primer starts from GcIFN ATG, and the 5' end contains Hind III restriction site and Kozak sequence ACC
[0035] gc-IFN-F3: 5'-CCC AAG CTT GGG ACC ATG GAA ACT CAA ATGTGG-3'
[0036] The downstream primer starts from the stop codon TAA, and an Xho I restriction site is added to the 5' end
[0037] gc-IFN-R3: 5'-GGCGAGCTCGCCTTATCGTCTGTTGGCAATGC-3'
[0038] Carry out PCR amplification according to the method in Example 1, carry out double digestion with Hind III and Xho I (TAKARA company) on the amplified product, insert into the expression vector pYES2, transform Escherichia coli TOP10, according to the "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide" The recombinant expression plasmid was extracted by the alkaline lysis method and sequence...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com