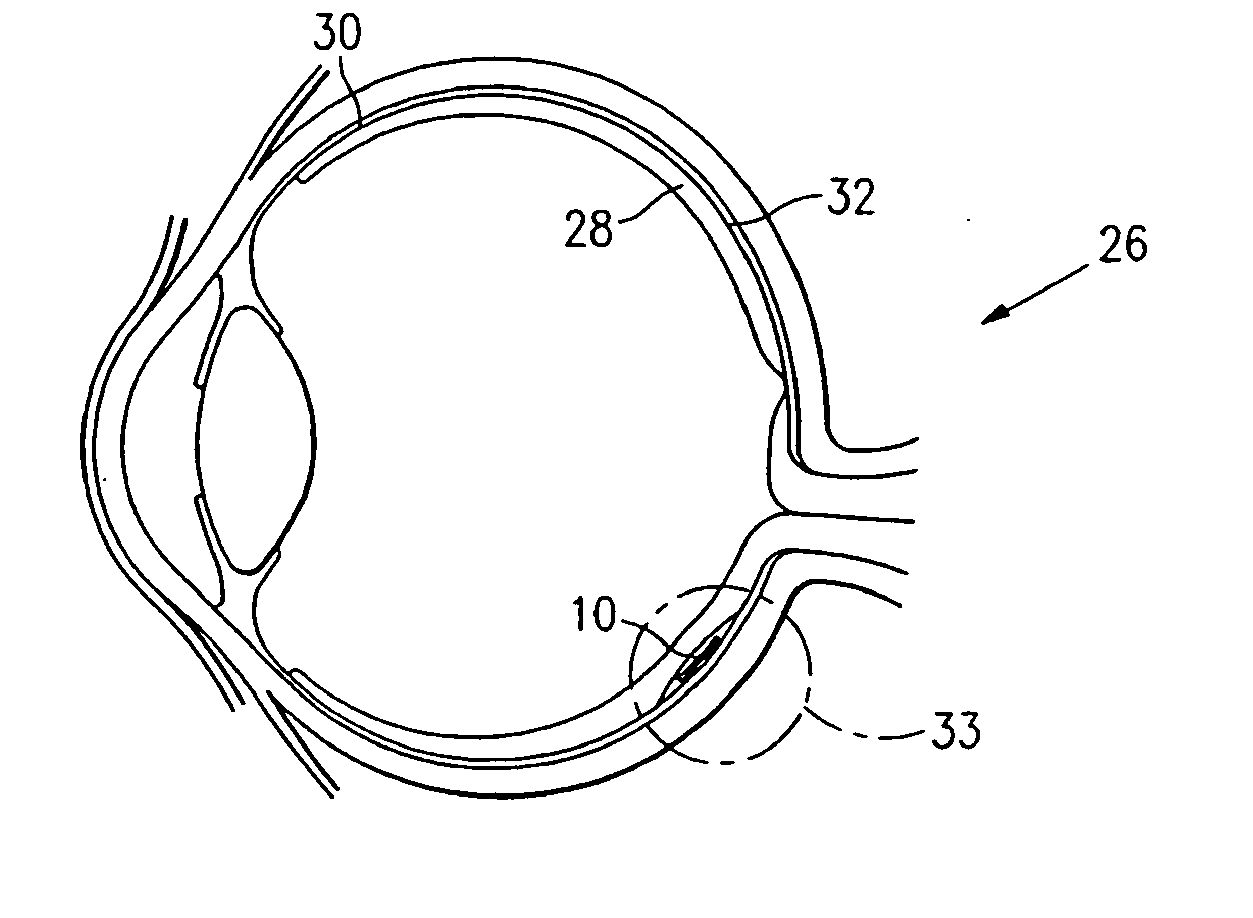
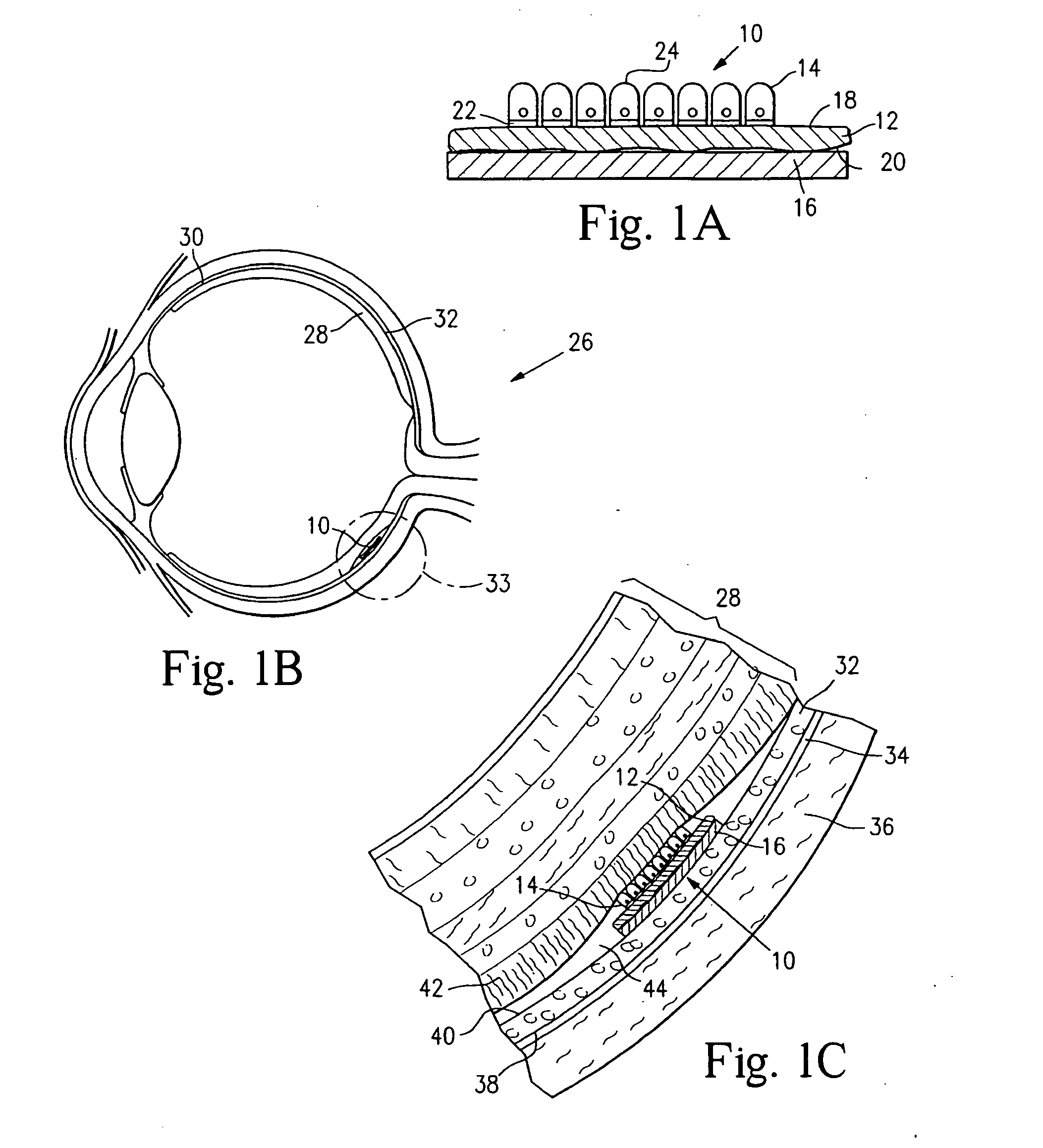
Microfabricated tissue as a substrate for pigment epithelium transplantation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
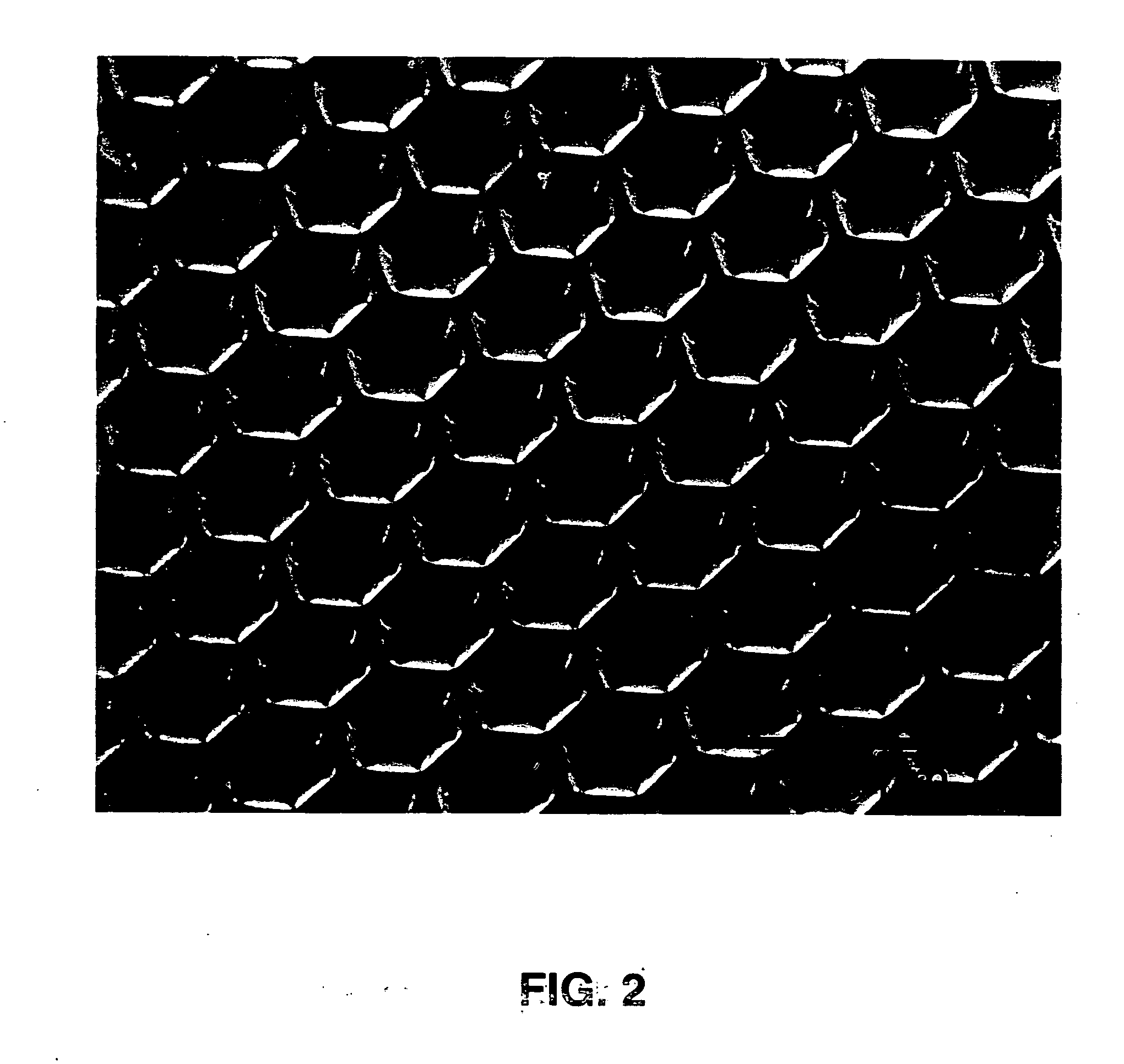
[0111] Microcontact printing was used to deposit micron-sized patterns of biomolecules onto lens capsule tissue. Poly(dimethyl siloxane) (PDMS) stamps were cast from masters containing a topological pattern of grid lines spaced 50 microns apart. The PDMS stamp was made from a master that was microfabricated from a silicon wafer. PDMS stamps were used to microfabricate patterns onto lens capsule tissue. Shown in FIG. 2 is a scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of a PDMS stamp used to deposit a micropattern onto a piece of human lens capsule tissue.
[0112] The PDMS stamp shown in FIG. 2 has a surface topology given by a hexagonal array of 5 μm-wide lines. Each line is separated by approximately 50 μm. FIG. 3 shows a human lens capsule stamped with the PDMS stamp shown in FIG. 2. The PDMS stamp was used to deposit hexagonal patterns of a PVA and fluorescein solution (2% PVA and 0.1 mg / mL fluorescein) onto the lens capsule. This example shows that the stamp is effective to produce a patte...
example 2
[0113] A SEM of a PDMS stamp with circular patterns used for micropatterning tissue is shown in FIG. 4. As shown, the stamp has a surface topology given by an array of circular wells of approximately 50 μm in diameter. When the relief pattern is coated with an inhibitory molecule, such as PVA or mucilage, and the stamp applied to a lens capsule, the inhibitory molecules are transferred to the lens capsule in the pattern shown. FIG. 5 shows the surface of a lens capsule that has been patterned with a PDMS stamp having a pattern as shown in FIG. 2 and RPE cells grown on it. This example shows that the stamp is effective to place a pattern on the lens capsule surface that corresponds to the pattern of the stamp, and for cell growth to be patterned according to the pattern of the stamp.
[0114] Thus, application of the stamps of the invention are able to deposit inhibitory molecules in patterns that can direct the growth of cells growing on a patterned substrate. Because the lens capsule...
example 3
[0115] Masking of the surface of lens capsule tissue and then irradiating the exposed surface, but not the masked surface, with UV radiation is accomplished by placement of a SEM grid onto the surface of lens capsule tissue. A SEM grid with spacing of 50 microns is placed onto the exposed surface of an excised lens capsule tissue resting on a glass coverslip immersed in phosphate-buffered saline. The surface of the lens capsule tissue and the SEM grid are not immersed in the phosphate-buffered saline, but rise above the level of the phosphate-buffered saline. UV light is directed onto the exposed surface of the lens capsule tissue effective to irradiate the lens capsule tissue not resting immediately below the SEM grid material. After irradiation, the SEM grid is removed. The lens capsule surface has a micropattern of lines including tissue not irradiated (regions under SEM grid material) enclosing regions comprising irradiated tissue.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com