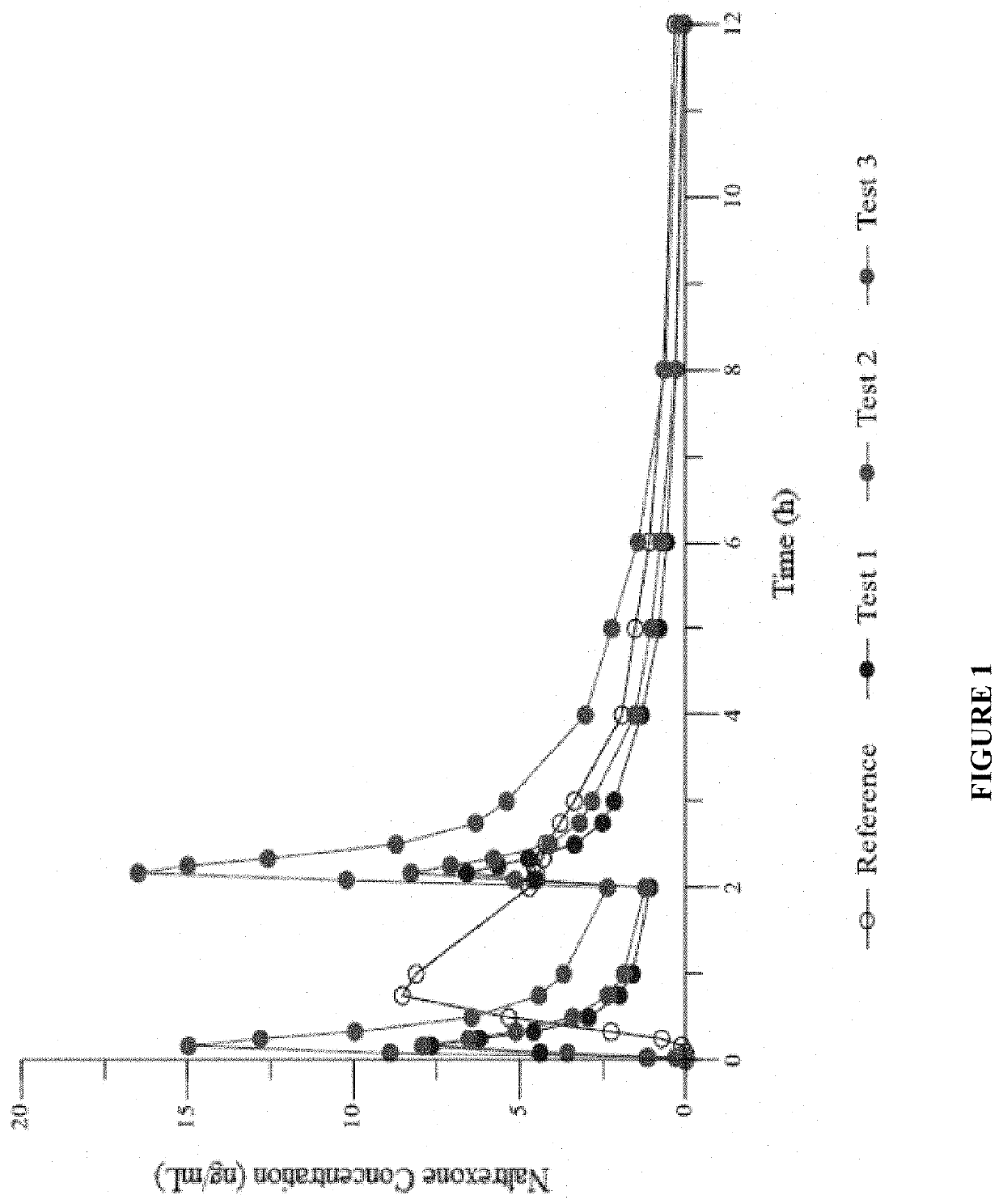
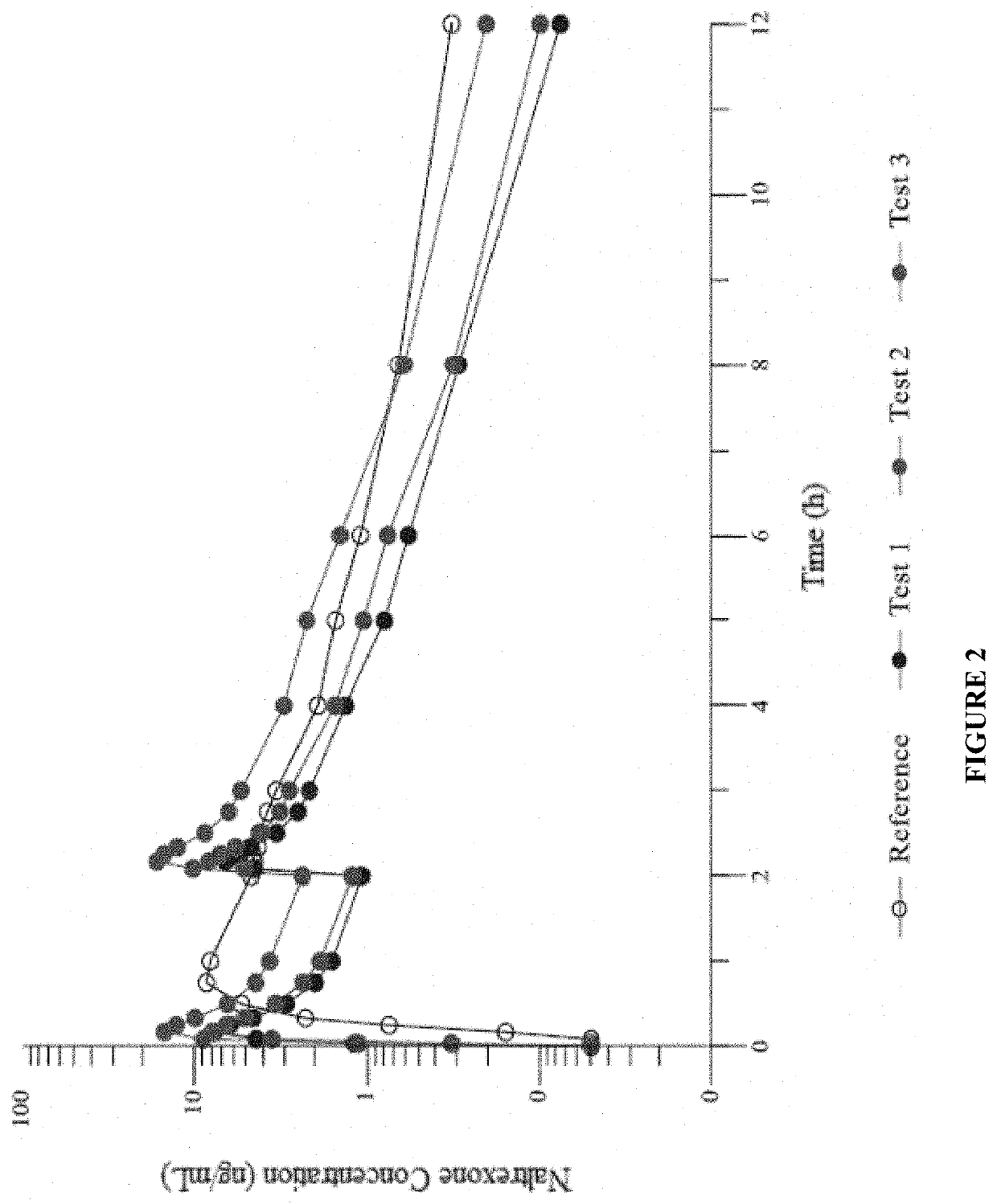
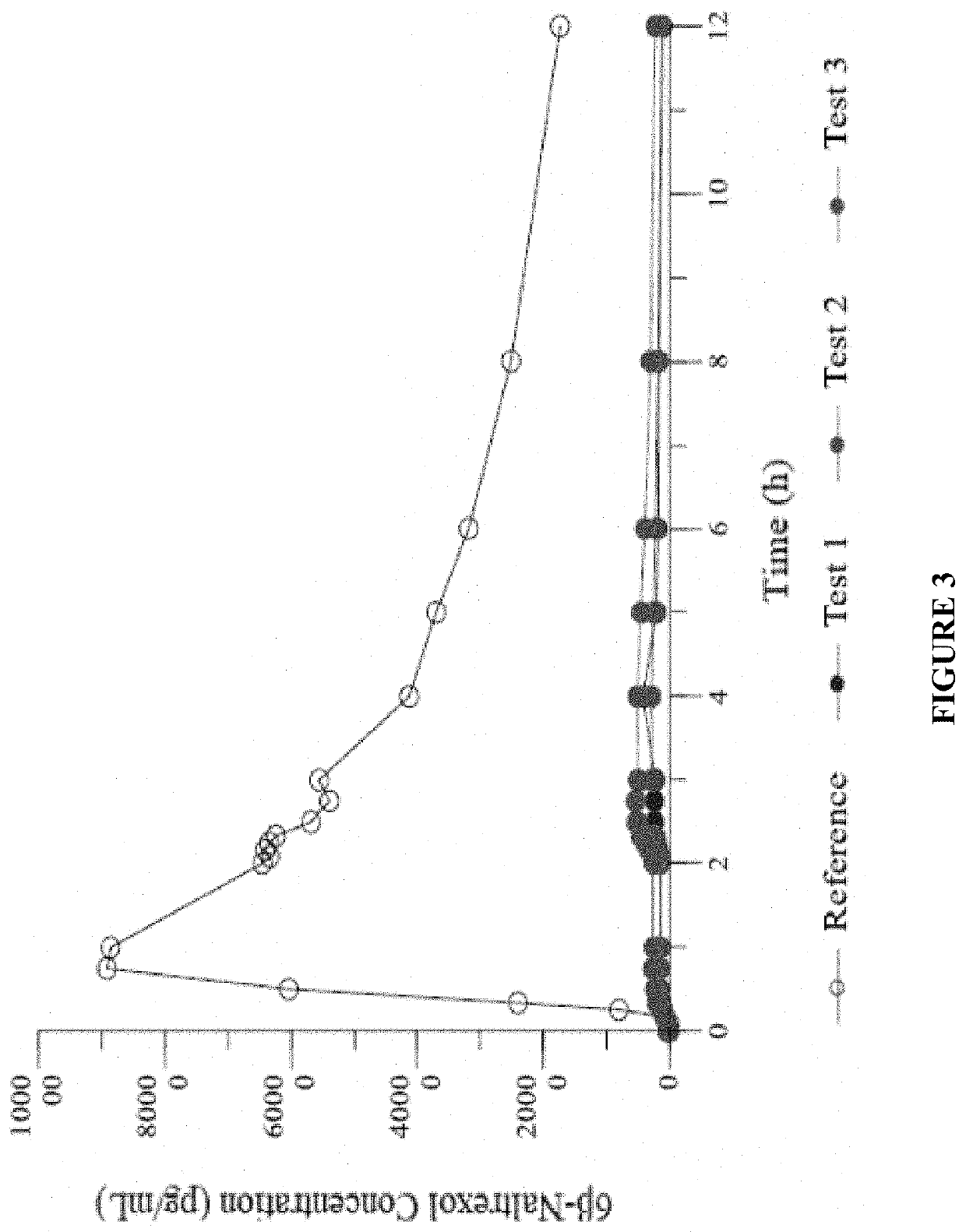
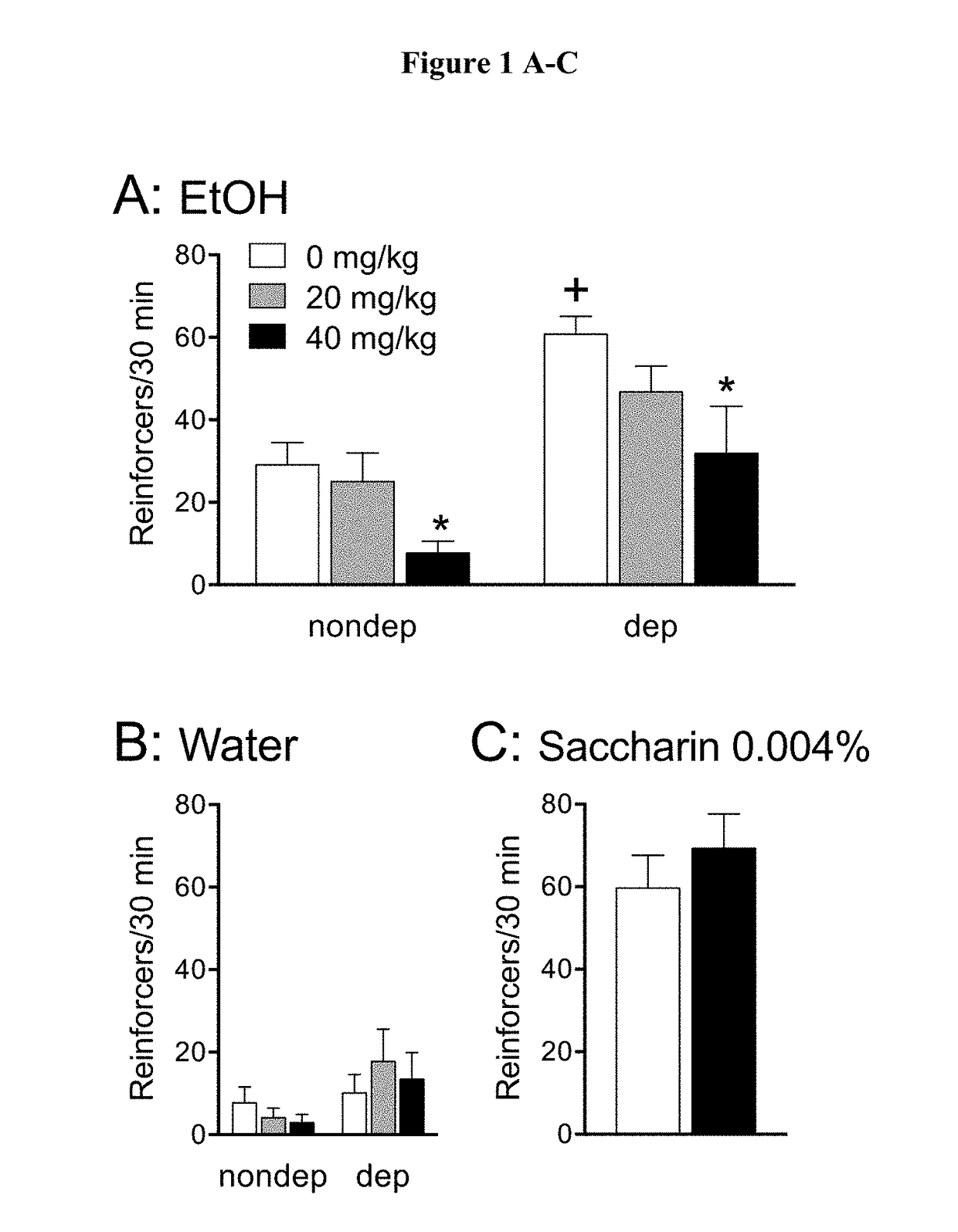
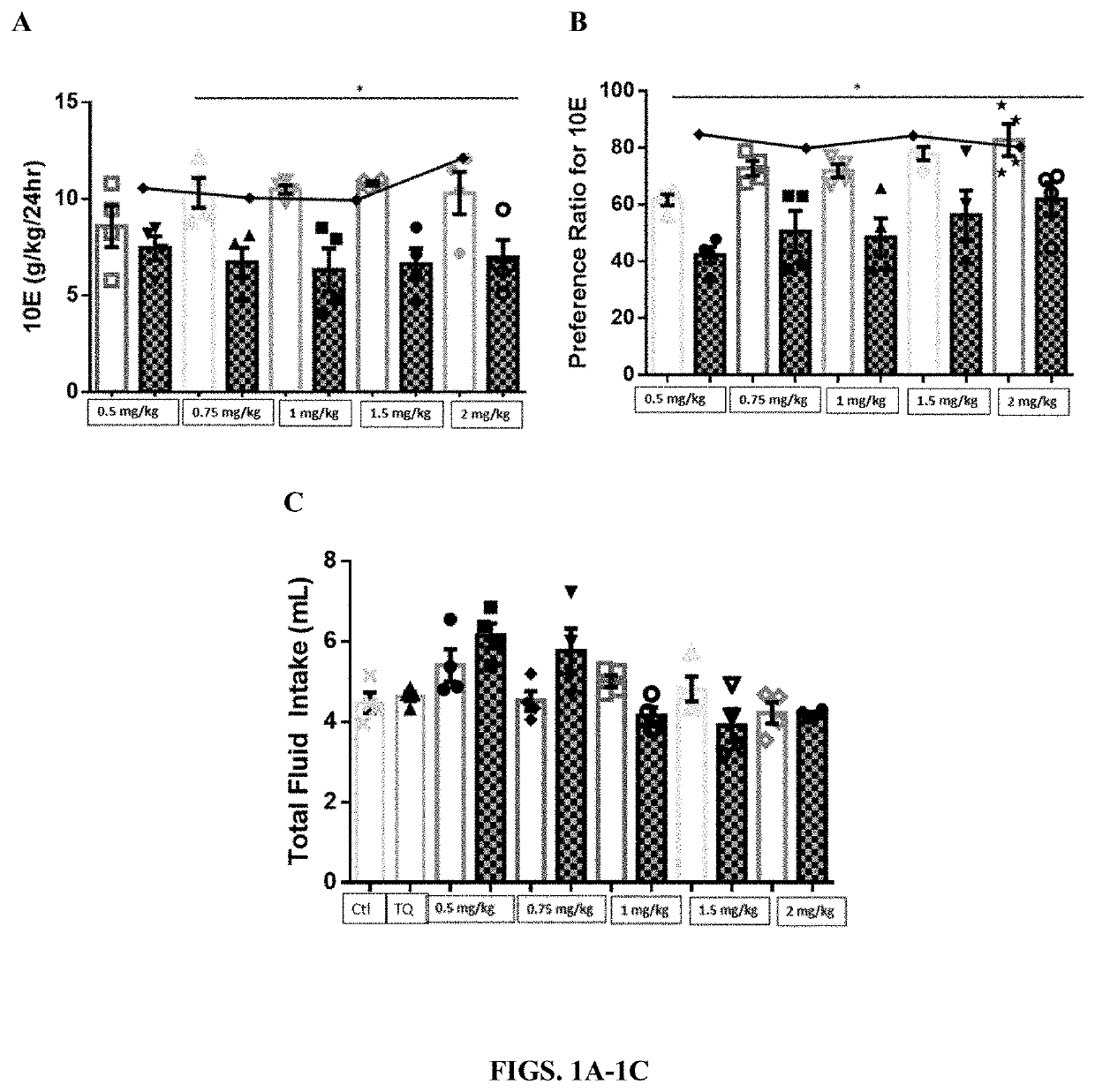
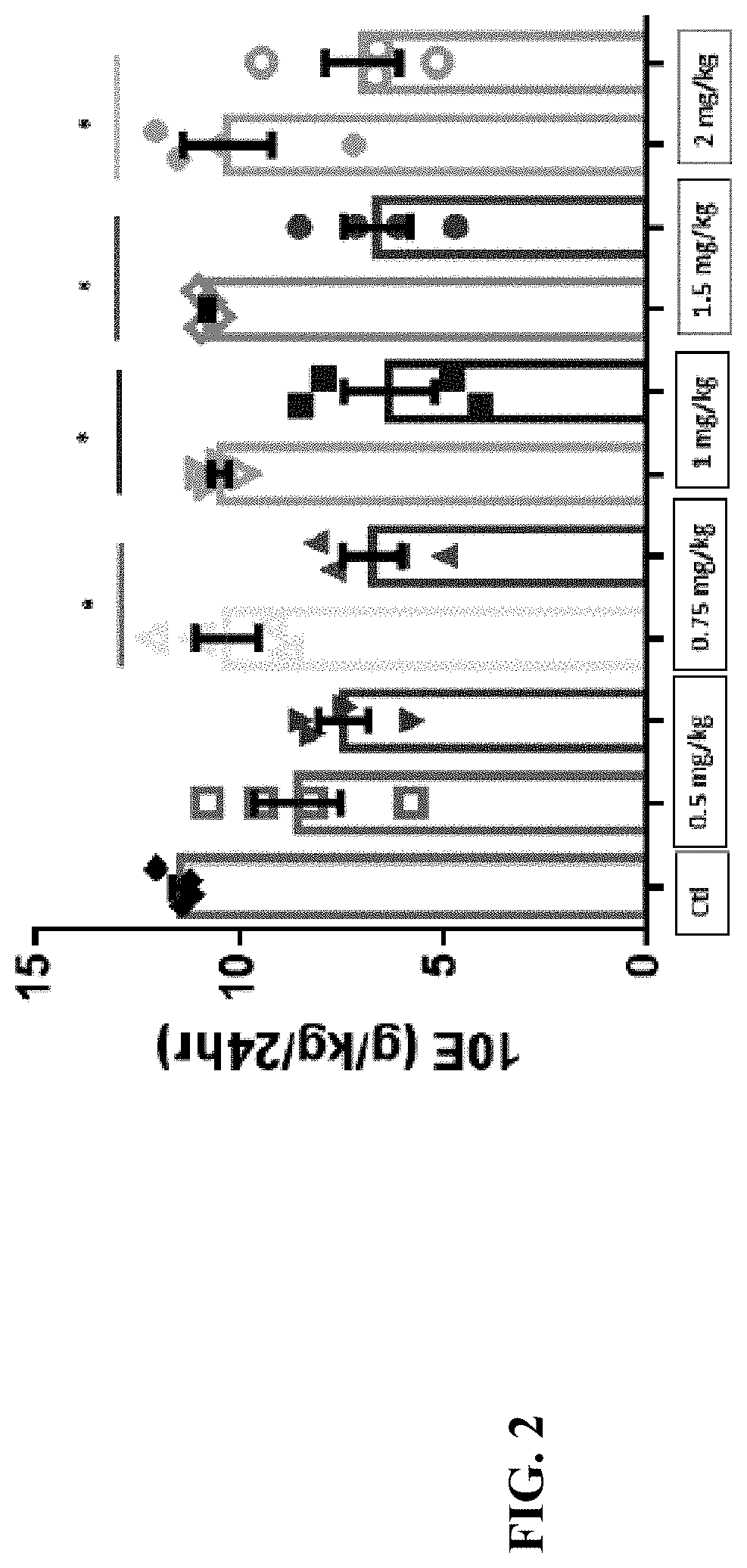
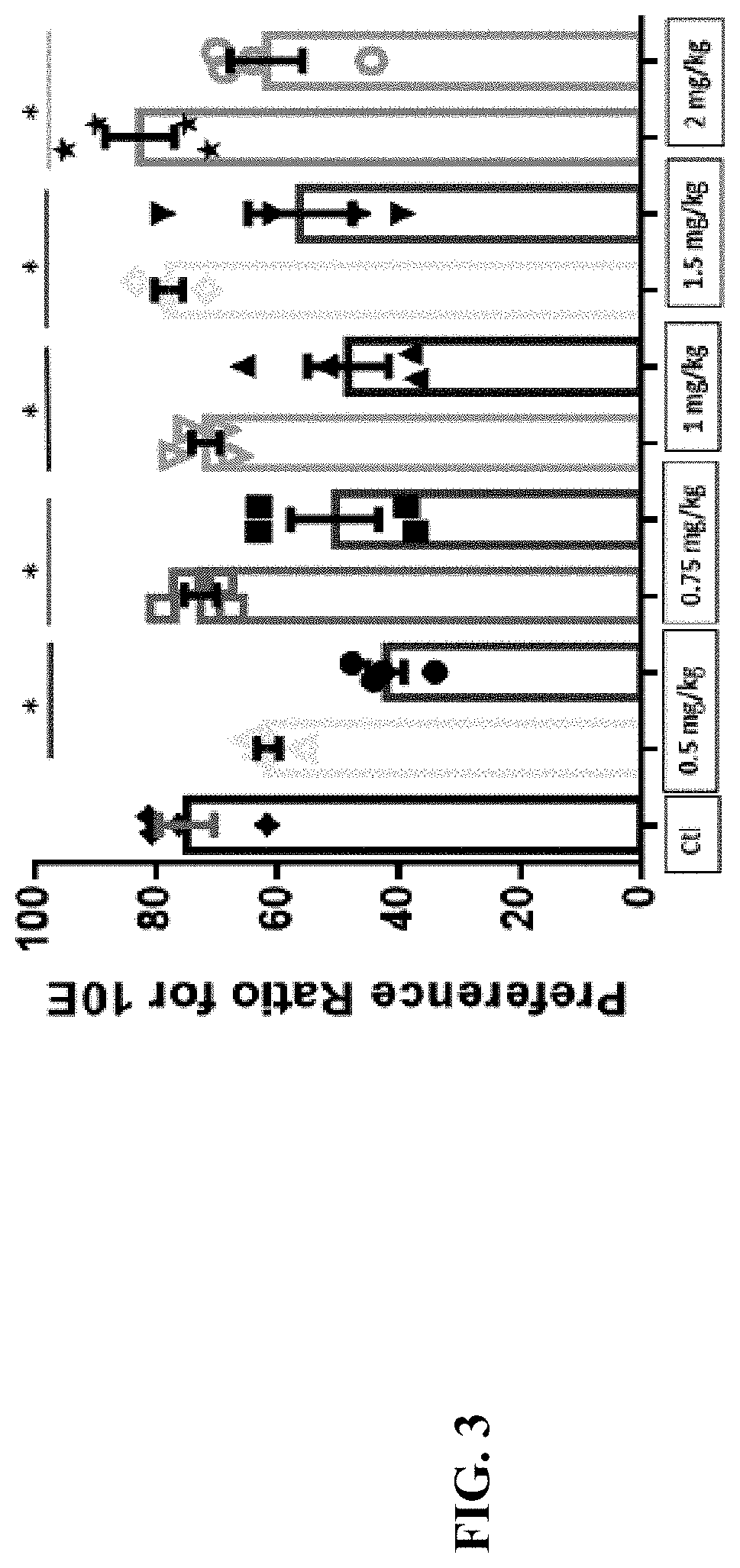
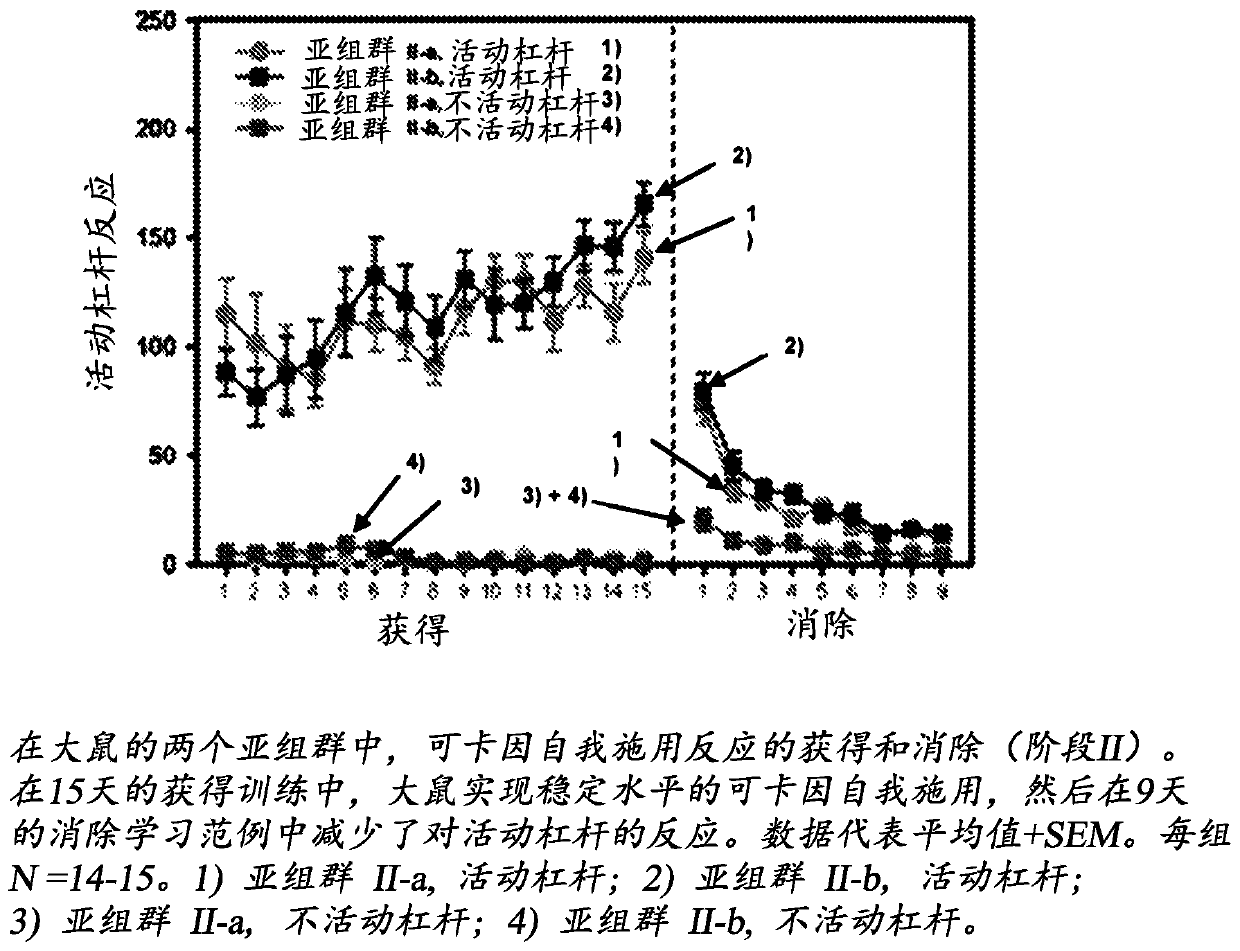
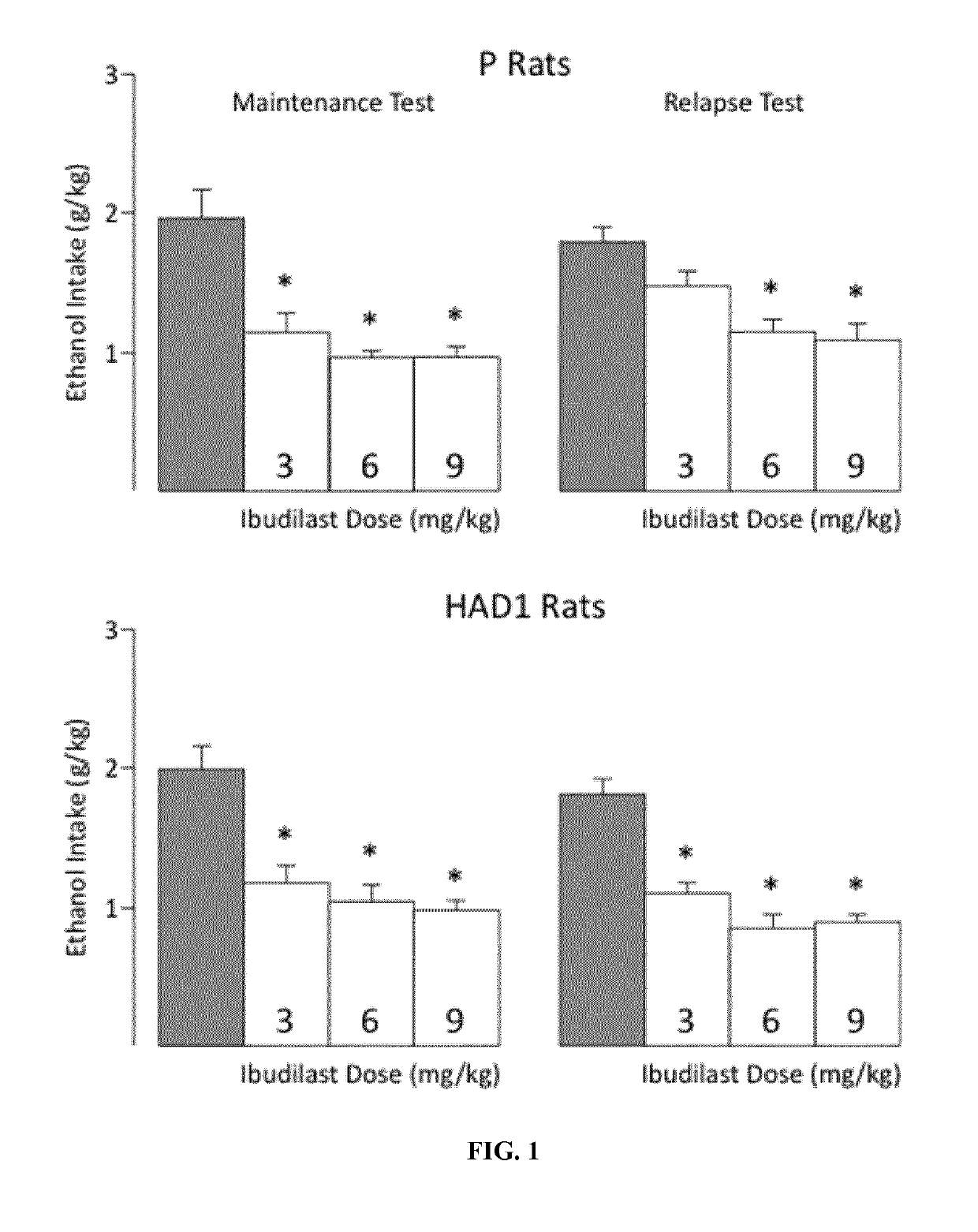
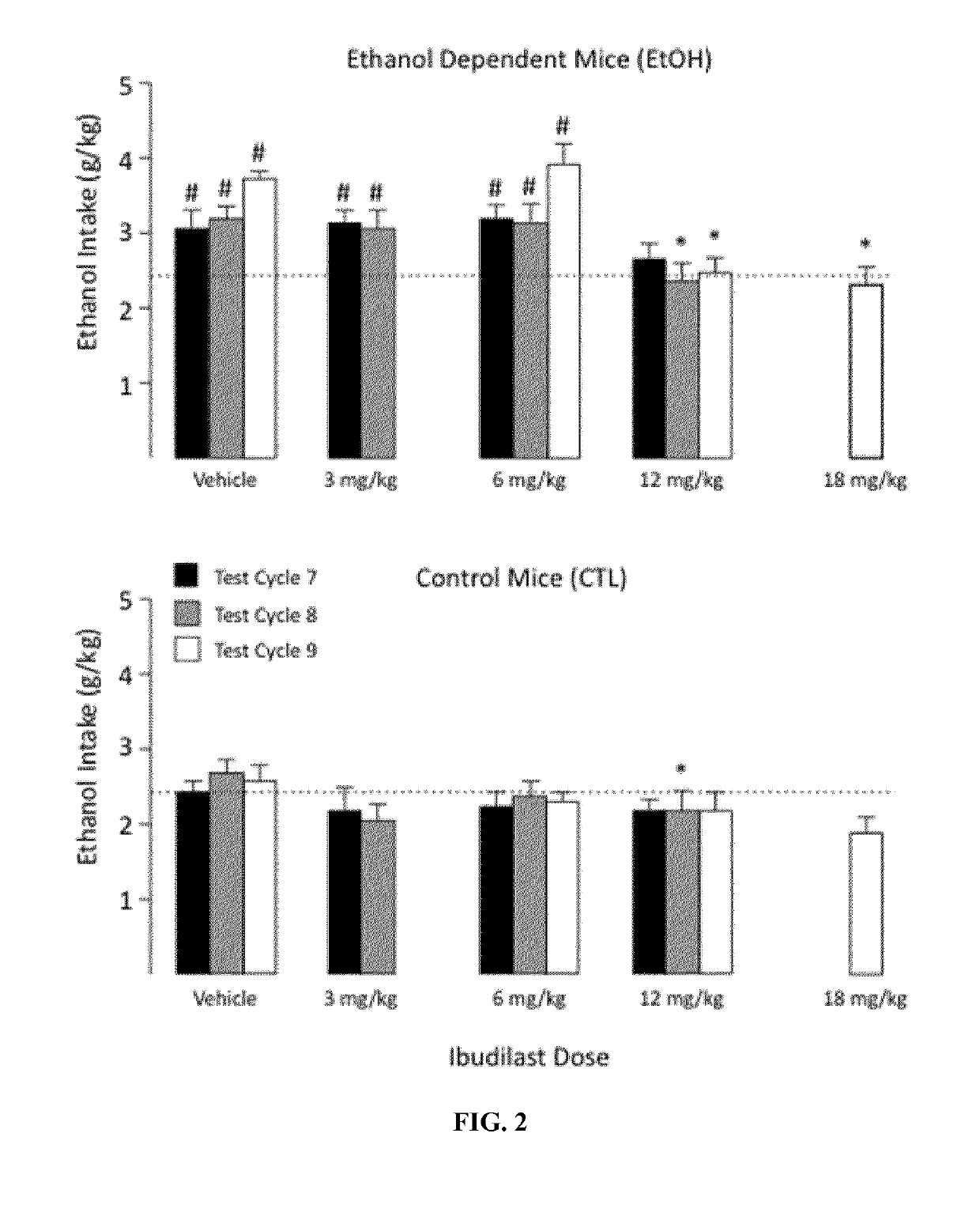
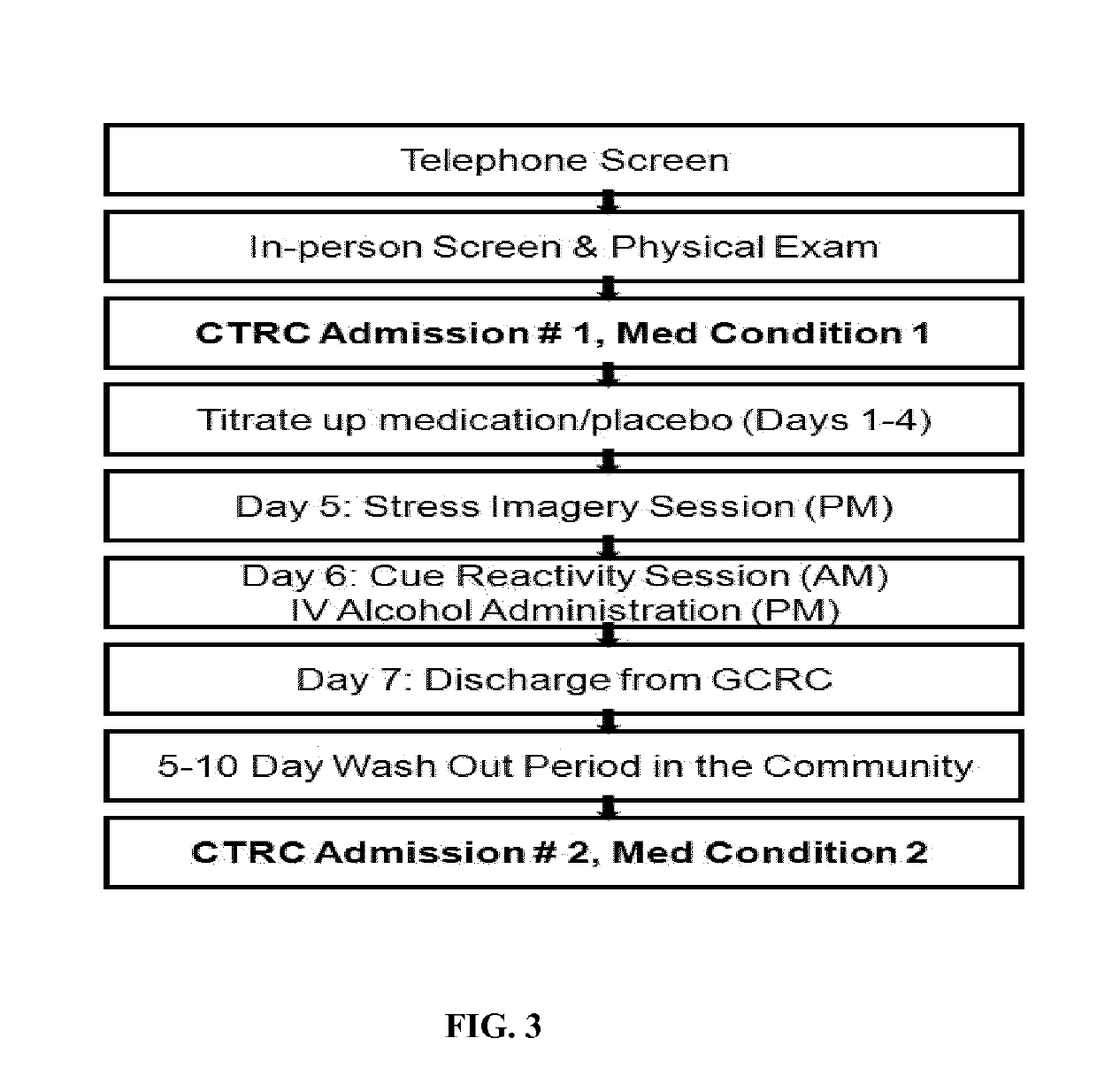
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Alcohol abuse disorder" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Alcoholism, also known as alcohol use disorder (AUD), is a broad term for any drinking of alcohol that results in mental or physical health problems. The disorder was previously divided into two types: alcohol abuse and alcohol dependence.
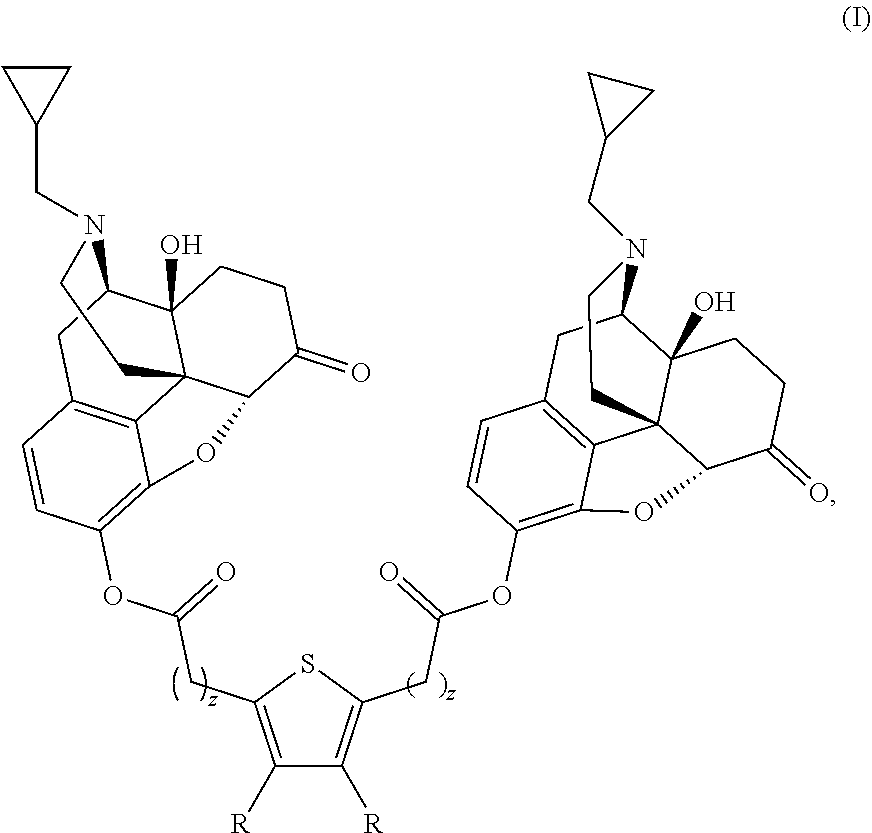
Compositions and methods for treating alcohol use disorders, pain and other diseases
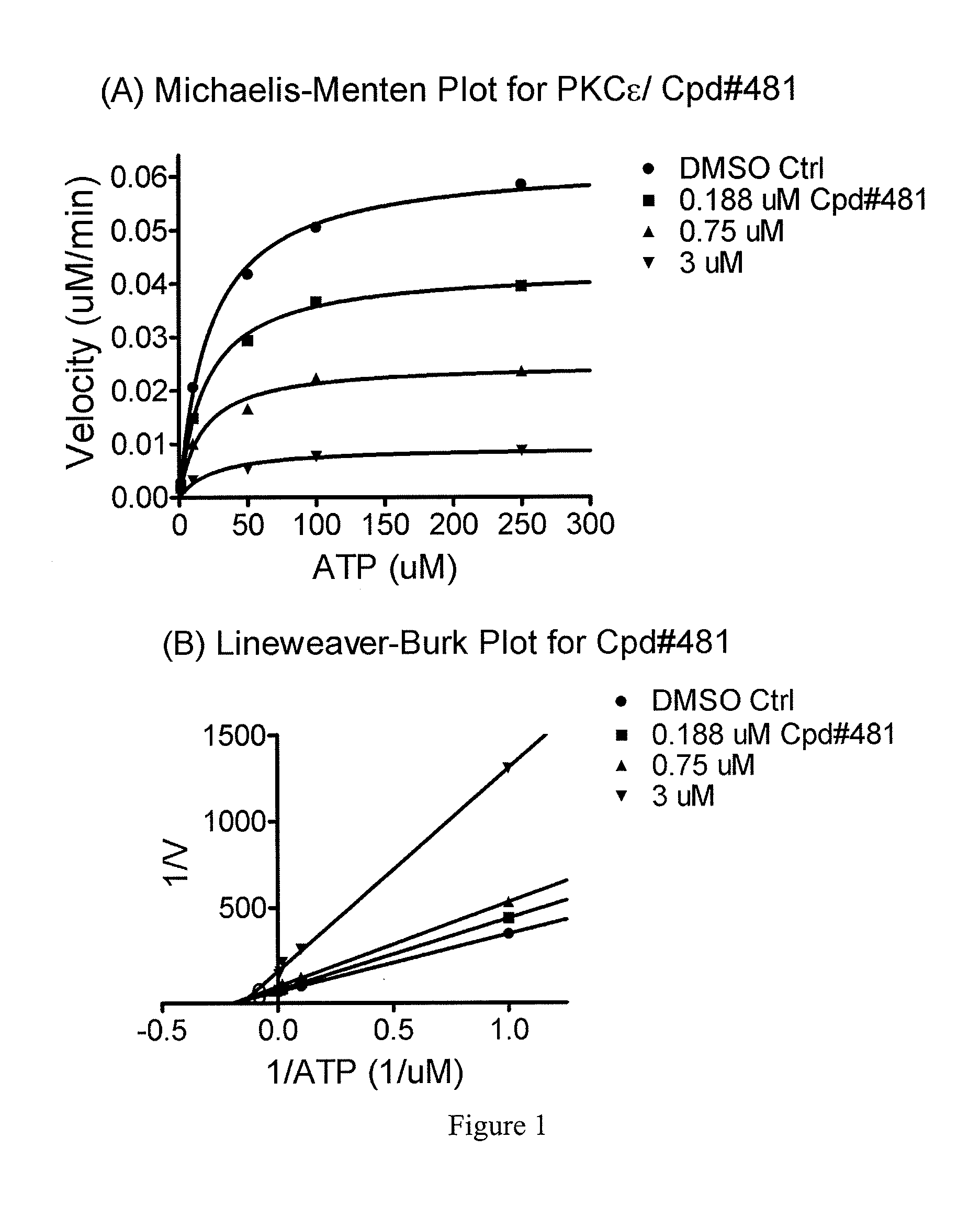
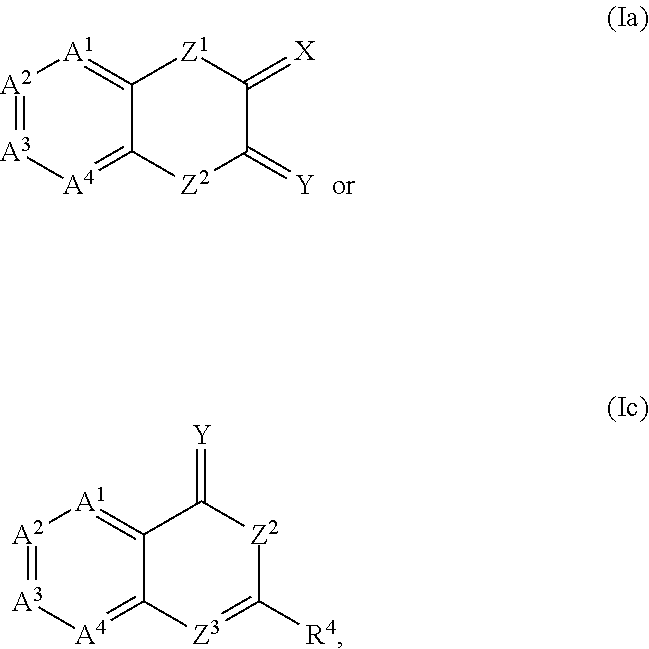
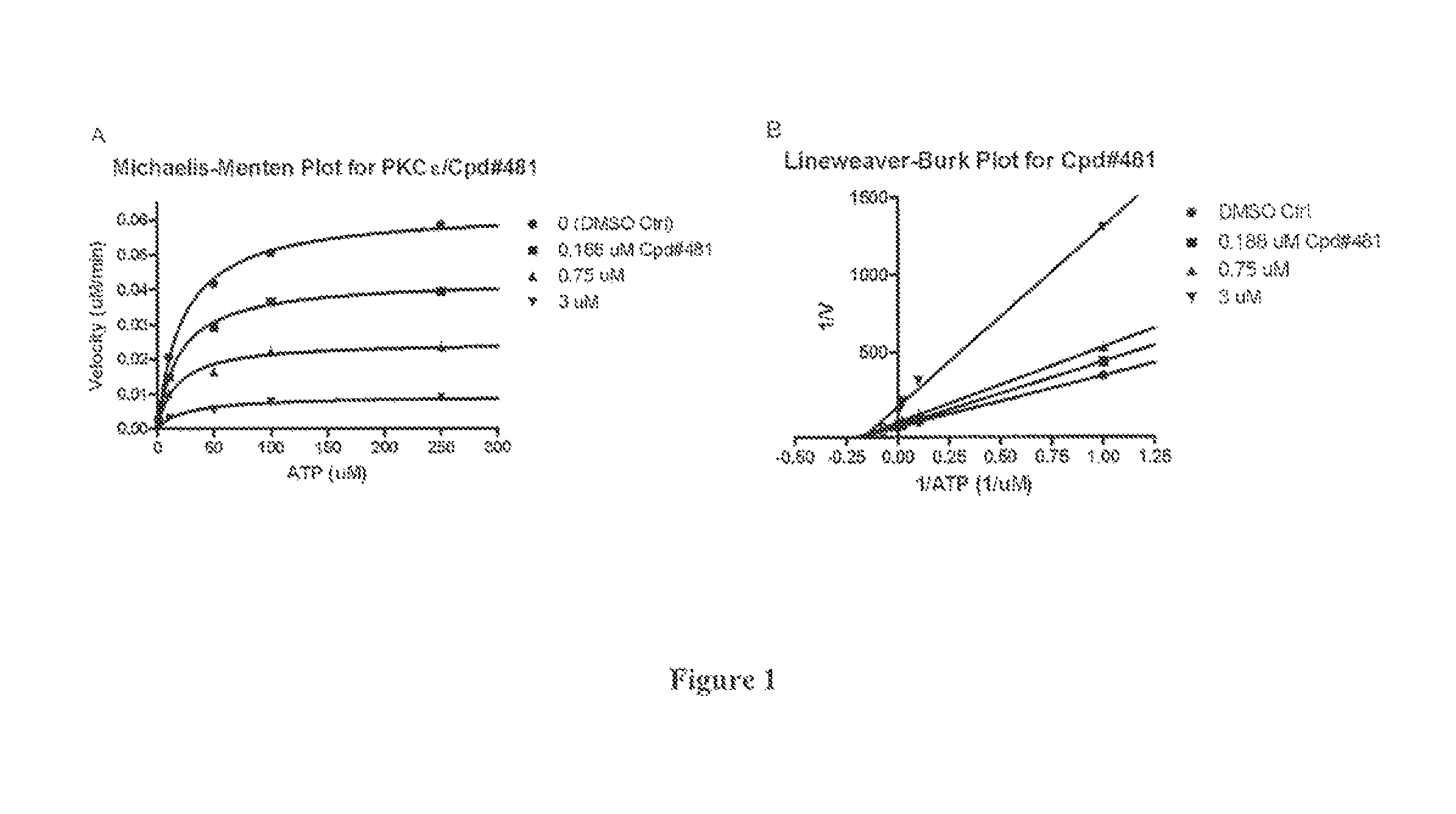
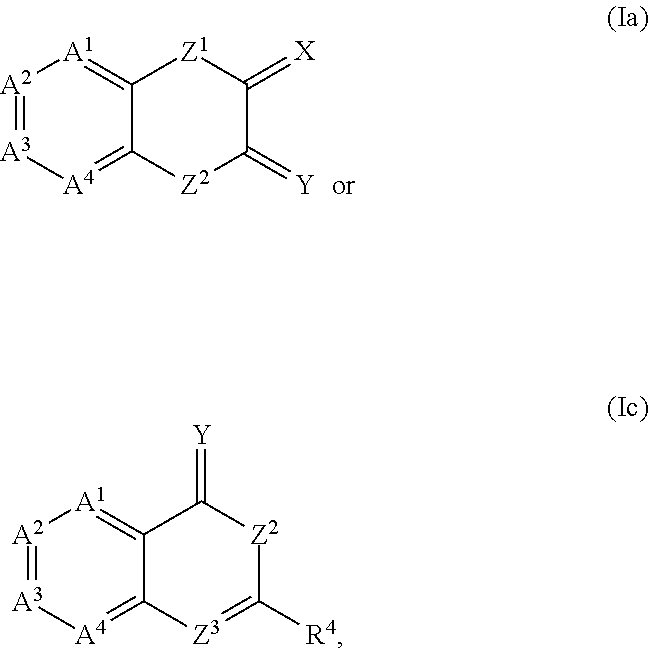
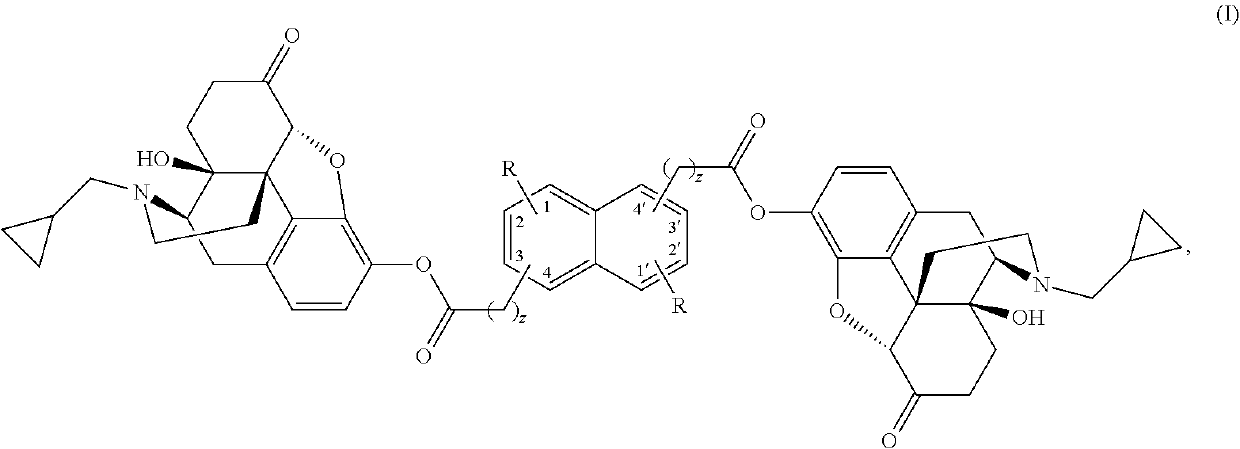
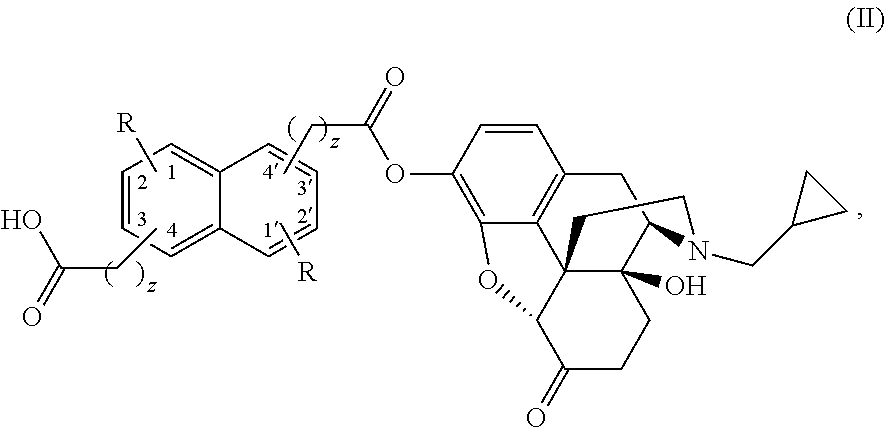
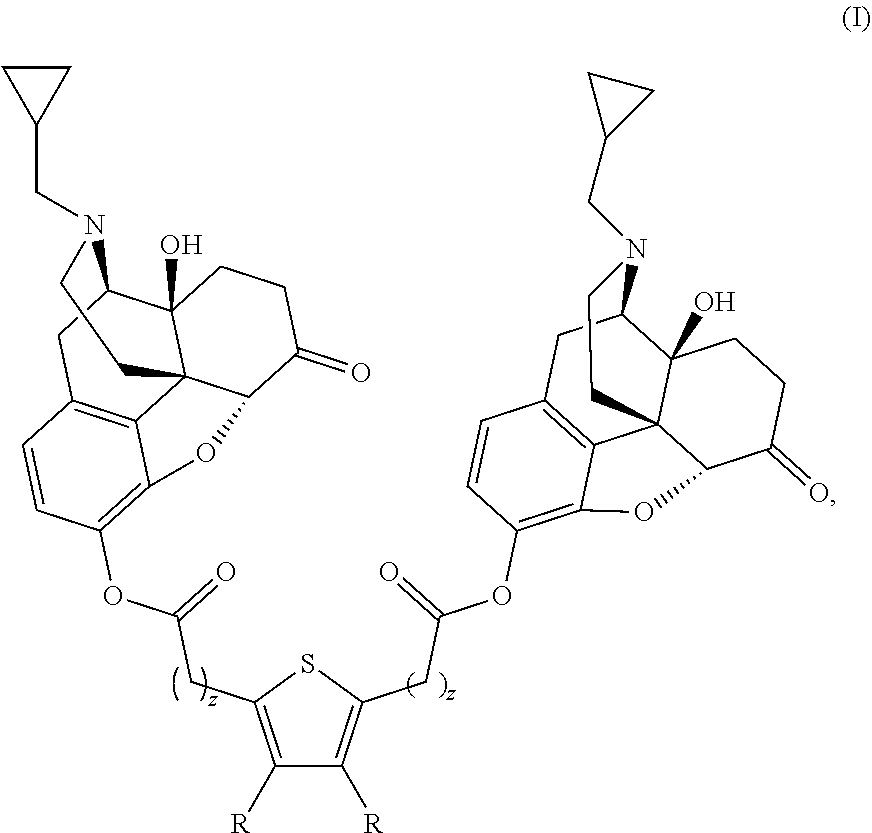
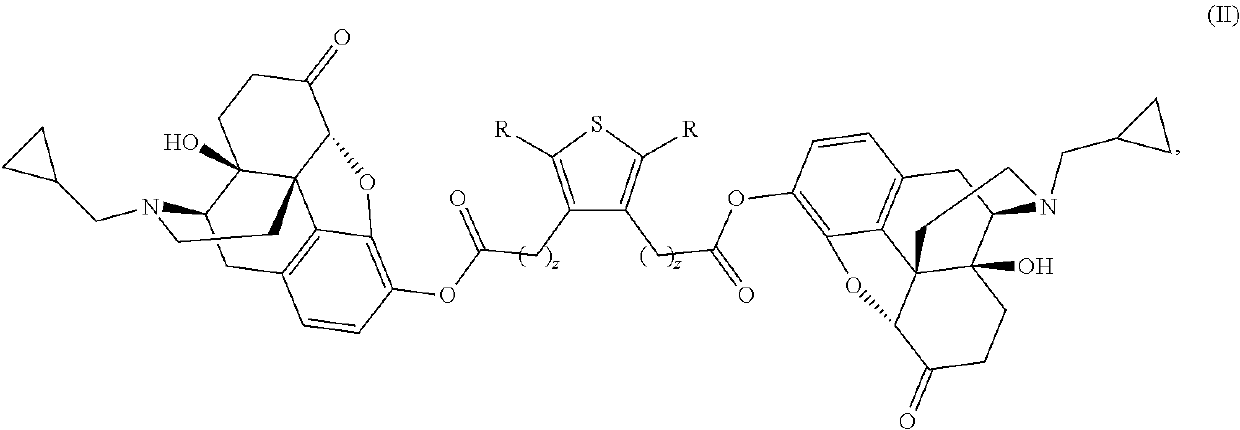
The present invention provides compounds which antagonize epsilon protein kinase C (PKCε). These compounds have a structural formula (Ia), (Ic) or (II). The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds and methods of treating various diseases, conditions, and / or symptoms by using these compounds.
Owner:VM DISCOVERY
Compositions for the prevention and/or treatment of alcohol use disorders
InactiveUS20190365675A1Easy to solveNervous disorderSulfonylurea active ingredientsPharmacy medicineAlcohol dependence syndrome
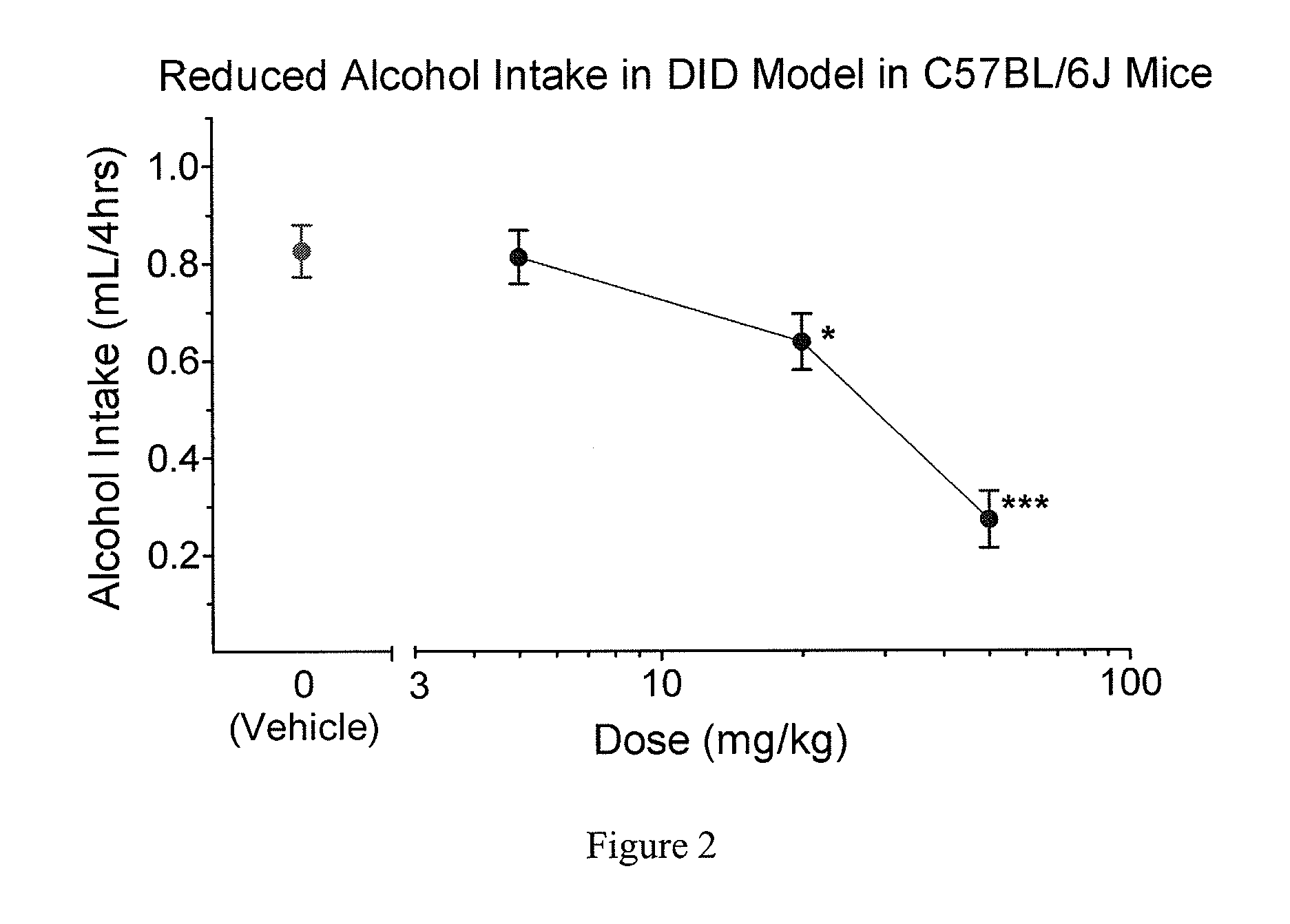
The invention relates to the use of acylethanolamides in the production of a medicinal product or nutraceutical for the prevention, relief, and / or treatment of alcohol use disorders in general, and of alcohol intoxication or pathological inebriation, and alcohol dependence syndrome in particular.
Owner:UNIV COMPLUTENSE DE MADRID +1
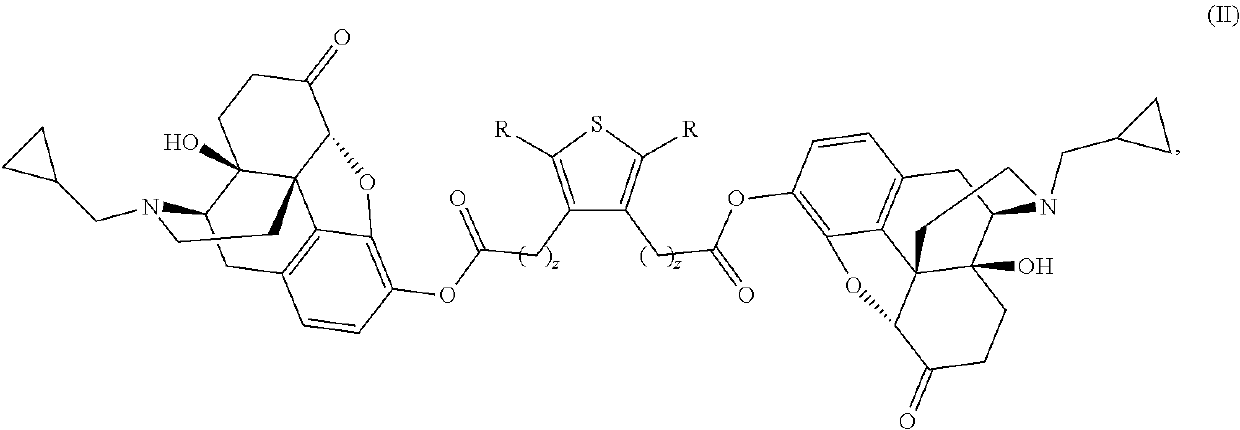
Compositions and methods for treating alcohol use disorders, pain and other diseases
The present invention provides compounds which antagonize epsilon protein kinase C (PKCε). These compounds have a structural formula (Ia), (Ic) or (II). The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds and methods of treating various diseases, conditions, and / or symptoms by using these compounds.
Owner:VM DISCOVERY
Scaffold of adenylyl cyclase inhibitors for chronic pain and opioid dependence
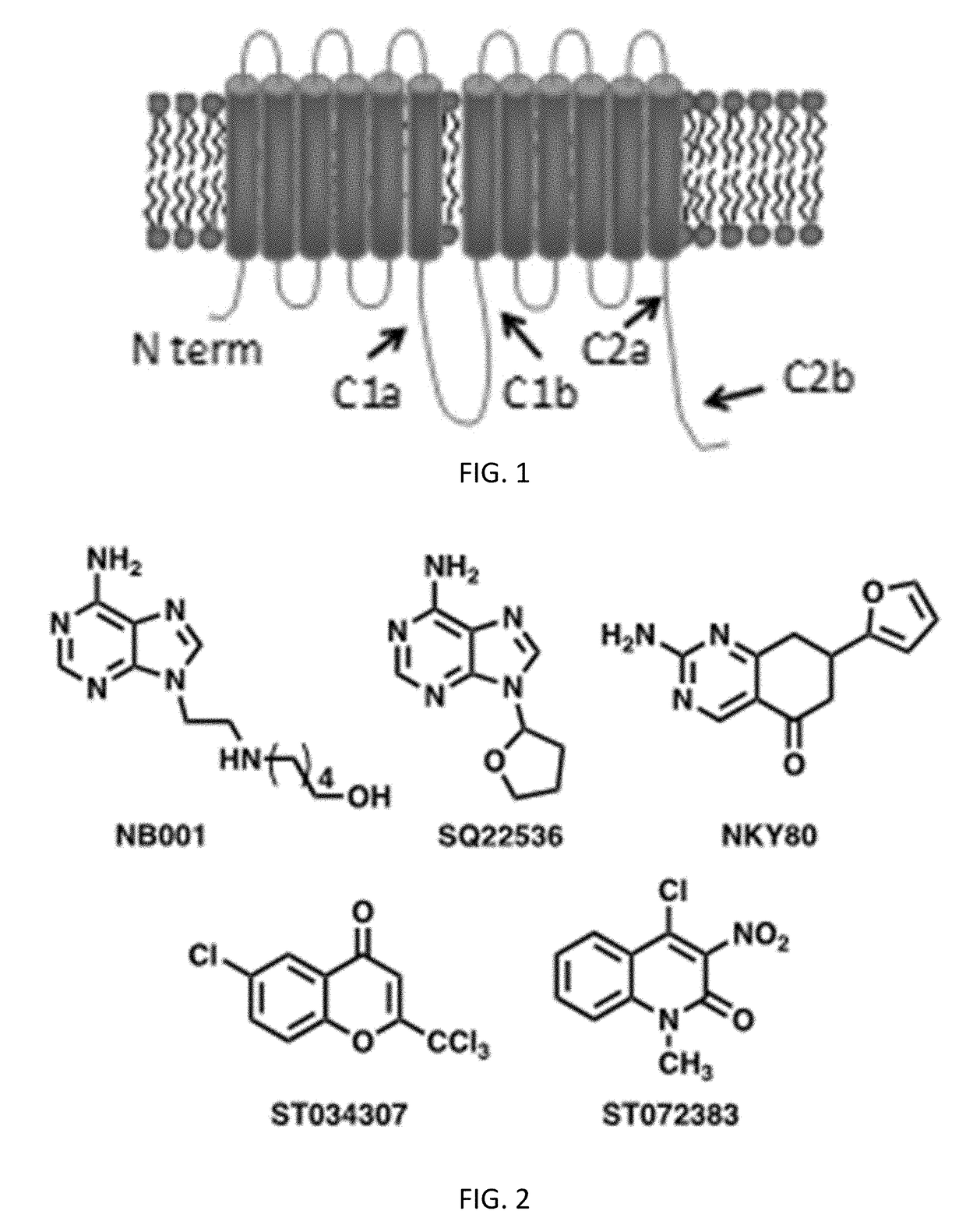
The present invention relates to a method of treatment for chronic pain, opioid dependence, alcohol use disorder or autism using a class of pyrimidinone compounds, an adenylyl cyclase 1 (AC1) inhibitor. The invention described herein also pertains to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating diseases in mammals using those compounds disclosed herein.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Compositions, devices, and methods for the treatment of overdose and reward-based disorders
Drug products adapted for nasal delivery, comprising a device filled with a pharmaceutical composition comprising naltrexone are provided. Formulations and methods of treating alcohol use disorder and related conditions with the drug products are also provided.
Owner:INDIVIOR UK +1
Methods and compositions for treating alcohol use disorders
ActiveUS20170232007A1Reducing alcohol use disorderReduce abuseNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsEnantiomerAlcohol abuse disorder
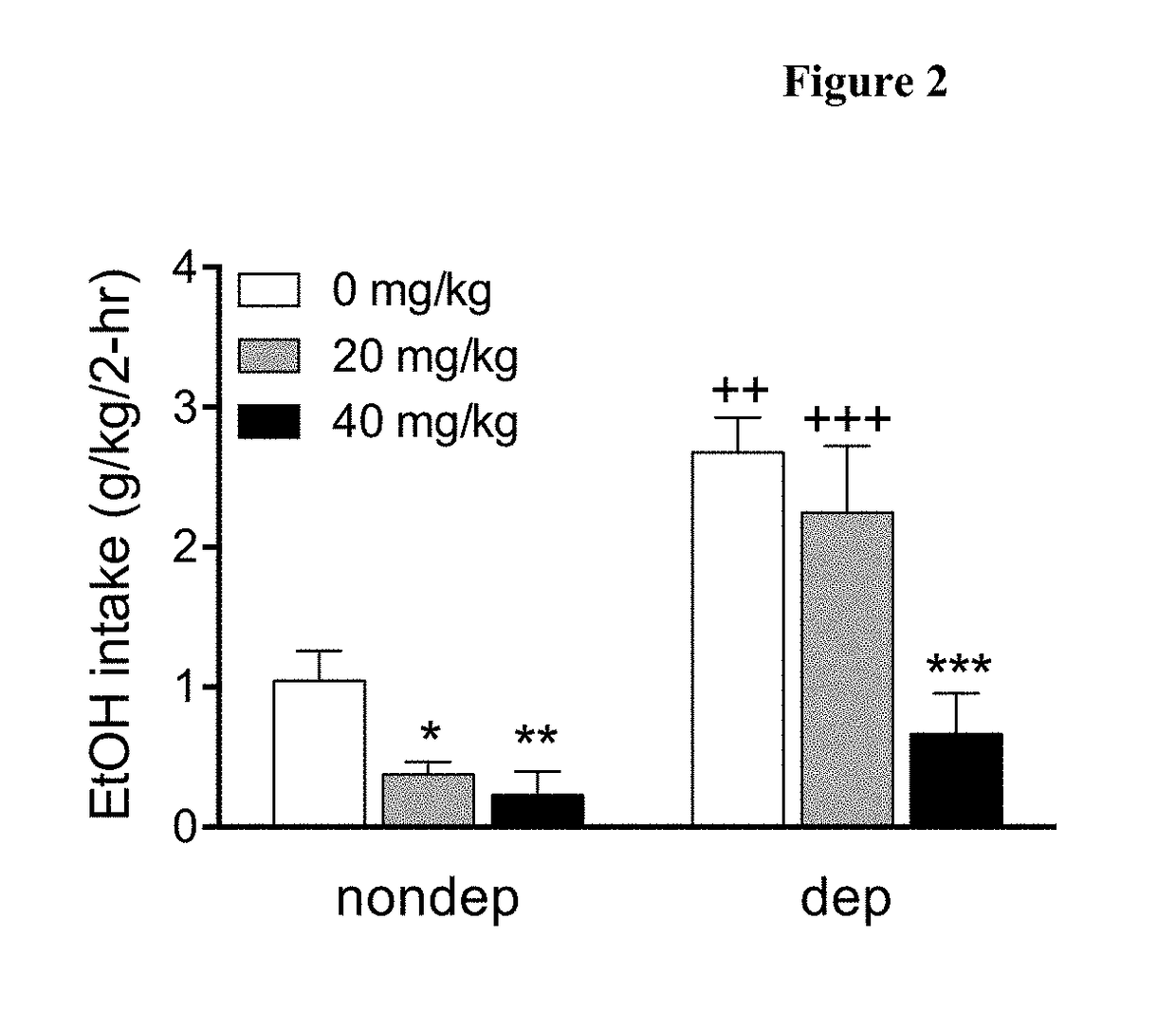
Disclosed are methods and compositions for treating alcohol dependence by administration to a patient of an inhibitor of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (11β-HSD) to modulate glucocorticoid effects. One such compound is the 11β-HSD inhibitor carbenoxolone (18β-glycyrrhetinic acid 3β-O-hemisuccinate), which has been extensively employed in the clinic for the treatment of gastritis and peptic ulcer. Carbenoxolone is active on both 11β-HSD1 and 2 isoforms. Here, carbenoxolone is surprisingly shown to reduce both baseline and excessive drinking in rats and mice. The carbenoxolone diastereomer 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid 3β-O-hemisuccinate (αCBX), which the applicants discovered to be selective for 11β-HSD2, was also effective in reducing alcohol drinking in mice. Thus, 11β-HSD inhibitors are a new class of candidate alcohol abuse medications and existing 11β-HSD inhibitor drugs may be re-purposed for alcohol abuse treatment.
Owner:SANNA PIETRO PAOLO
Compositions and methods for the modulation of the corticotropin releasing factor binding protein and the treatment of alcohol use disorder
ActiveUS11278527B2Organic chemistryHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsAspartic acid receptorsSubstance abuser
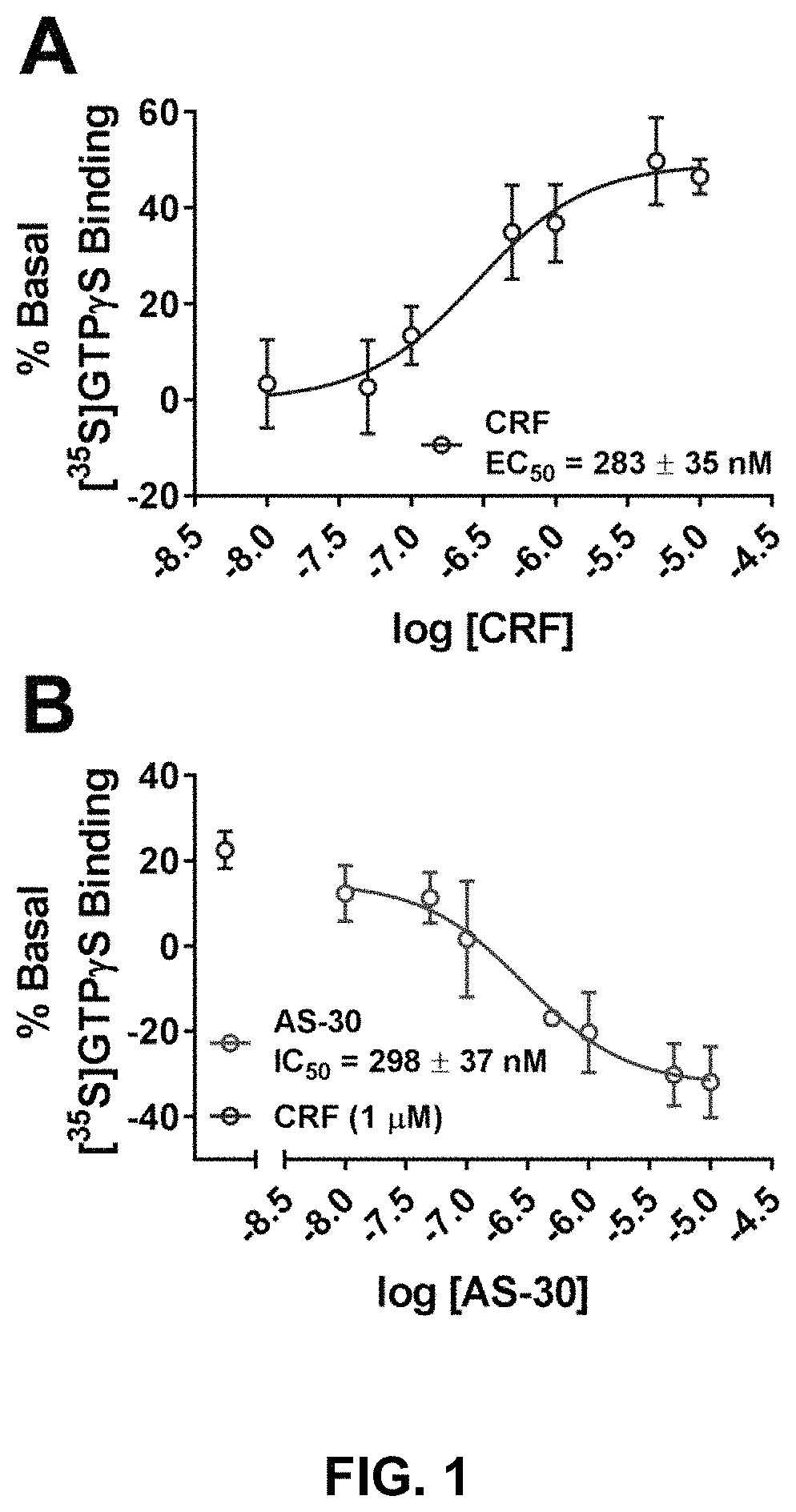
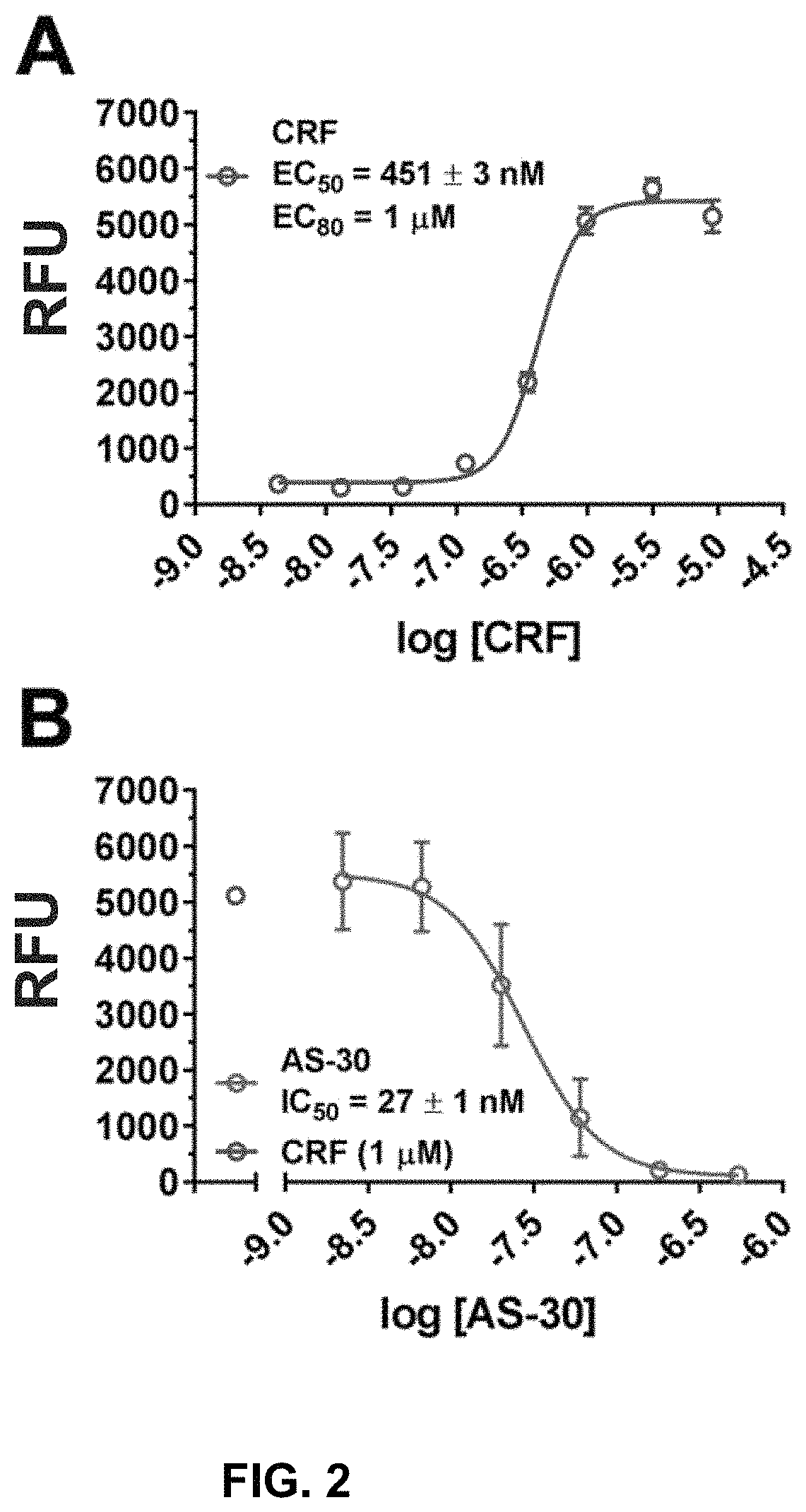
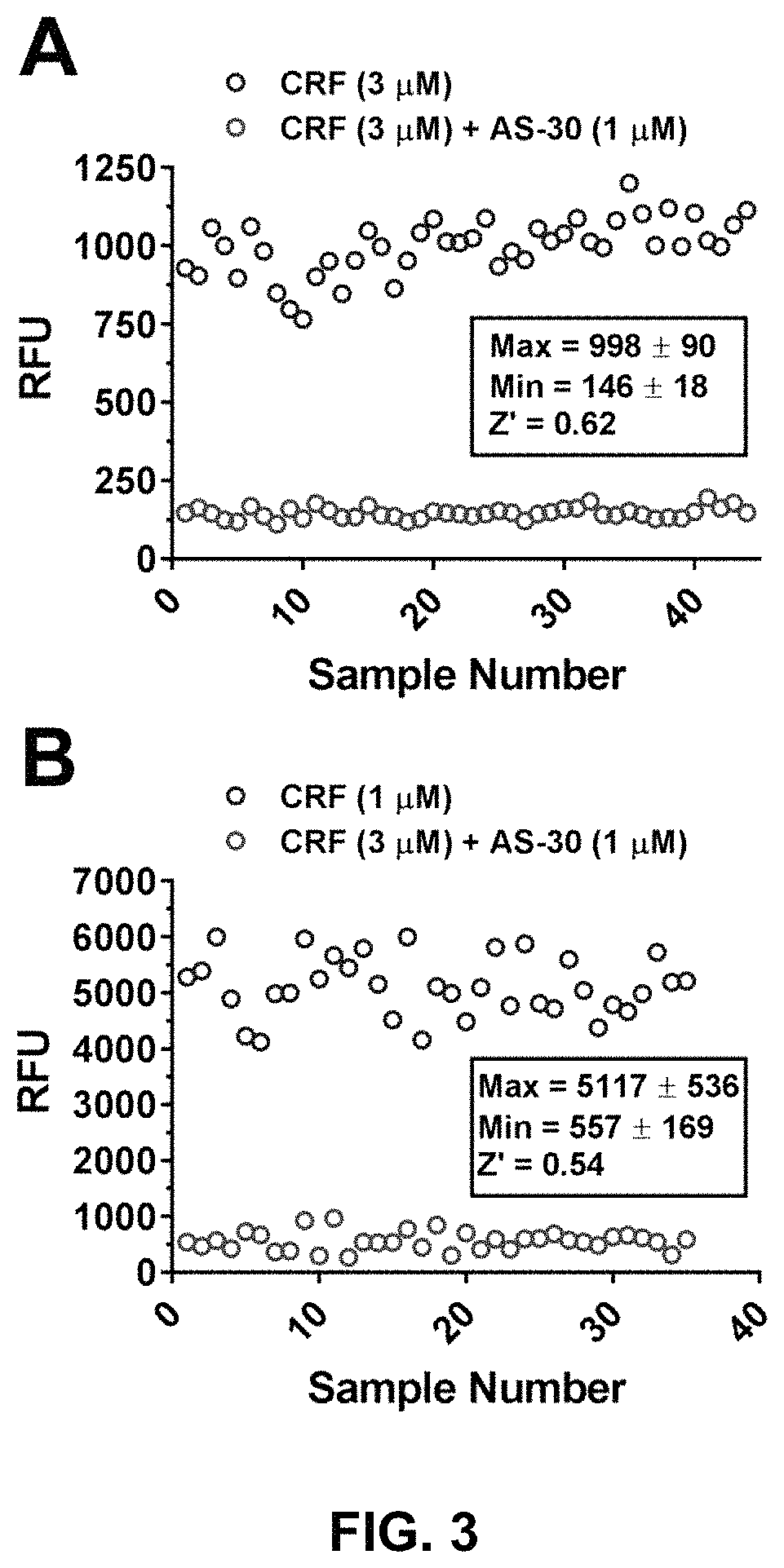
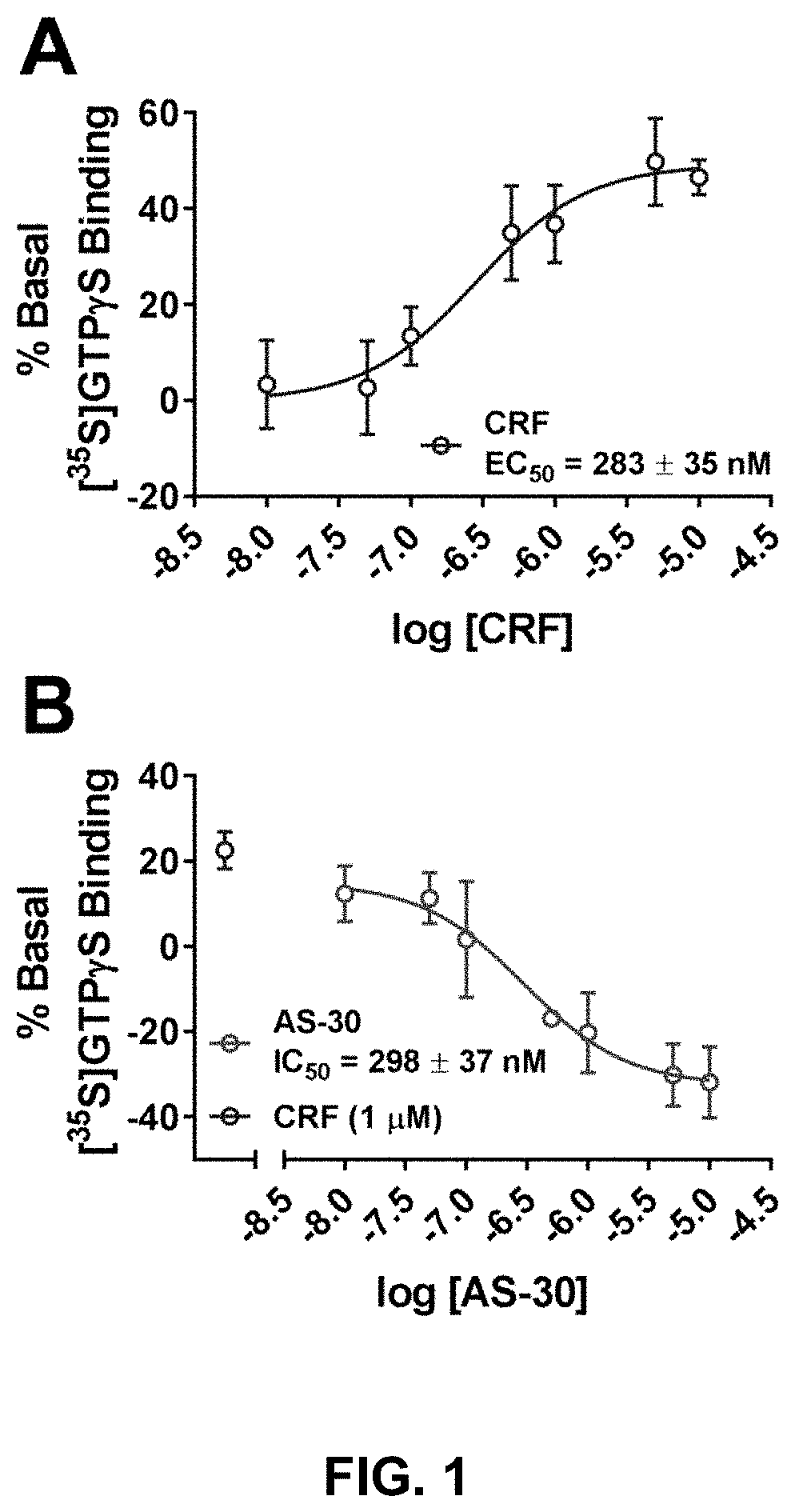
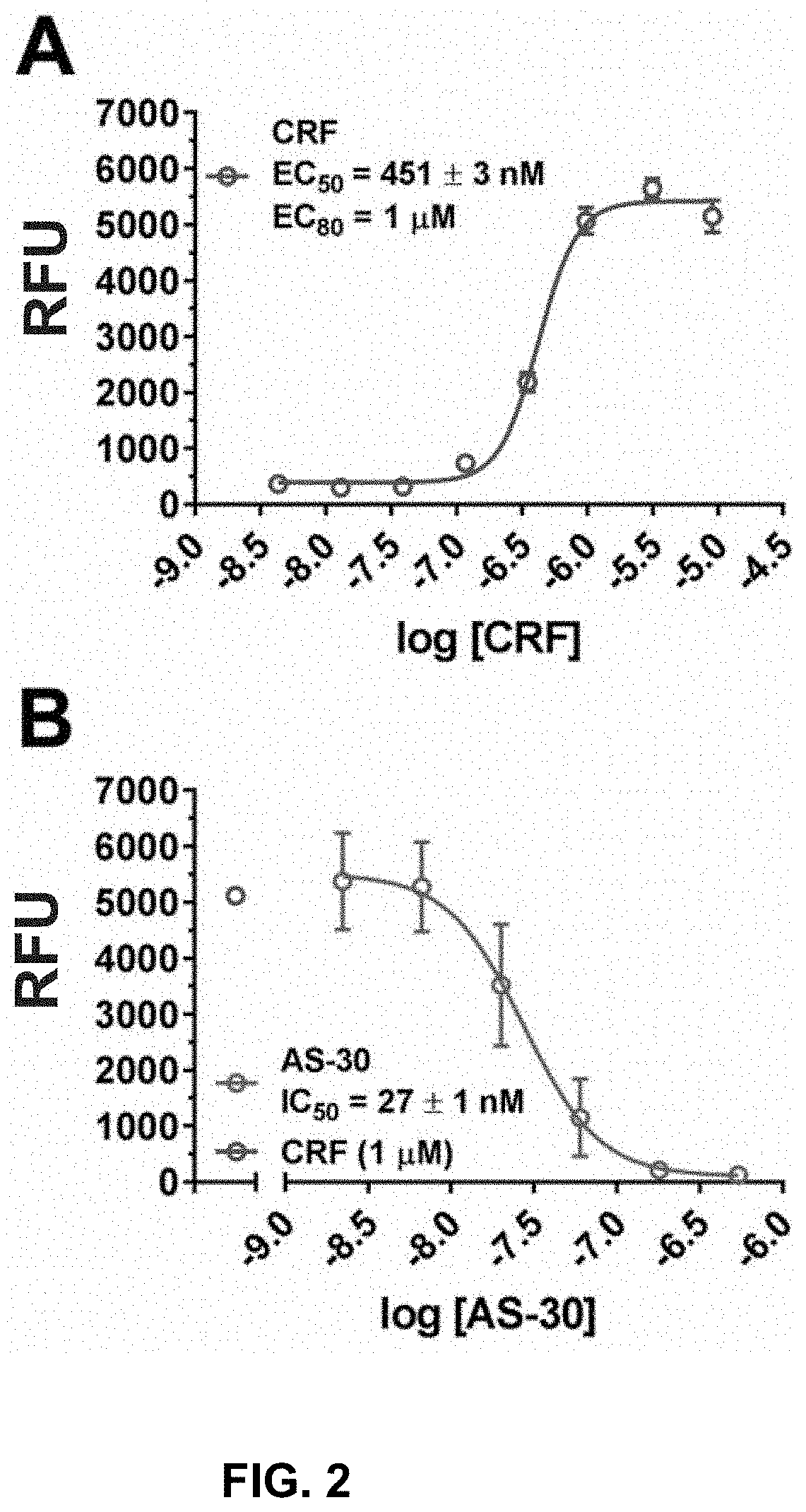
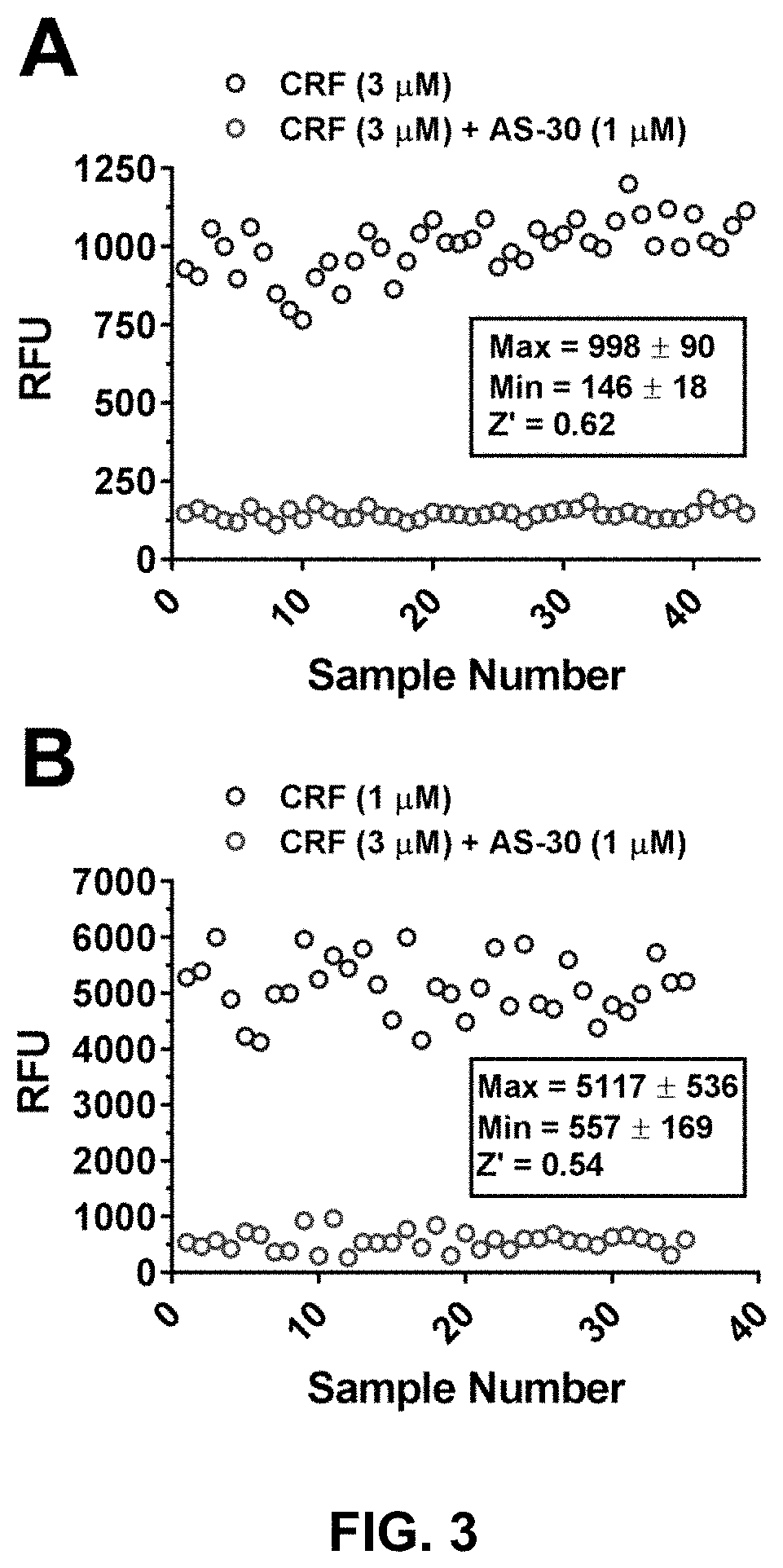
Stress responses involve corticotropin releasing factor (CRF), the two cognate receptors (CRF1 and CRF2) and the CRF-binding protein (CRFBP). Utilizing a novel cell-based assay, a C-terminal CRFBP fragment [CRFBP(10 kD)] was found to potentiates CRF-intracellular Ca2+ release, demonstrating that CRFBP possesses excitatory roles in addition to the inhibitory role established by the N-terminal fragment of CRFBP [CRFBP(27 kD)]. This interaction was CRF2-specific, as CRF1 responses were not potentiated by CRFBP(10 kD). As there were currently no small molecule ligands available that selectively interact with either CRFBP or CRF2, a cell-based assay was miniaturized, wherein CRFBP(10 kD) was fused as a chimera with CRF2α, that allowed us to a perform a high-throughput screen (HTS) of approximately 350,000 small molecules. This resulted in the identification of negative allosteric modulators (NAMs) of the CRFBP(10 kD)-CRF2 complex that blunt CRF-induced potentiation of N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor (NMDAR)-mediated synaptic transmission in dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA). These results provide the first evidence of specific roles for CRF2 and CRFBP in the modulation of neuronal activity and suggest that NMDARs in the VTA may be a target for the treatment of stress and substance abuse disorders such as alcohol use disorder.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Treatment of alcoholism and depression and/or dysphoric mood using ibudilast
InactiveCN109475538ANervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAlcoholismsAlcohol abuse disorder
Alcoholism, and symptoms and negative effects thereof may be treated using ibudilast or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. Patients diagnosed with alcohol use disorder and who exhibit symptoms of depression and / or dysphoric mood can be treated using ibudilast or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:MEDICINOVA INC
Methods and compounds for treating alcohol use disorders and associated diseases
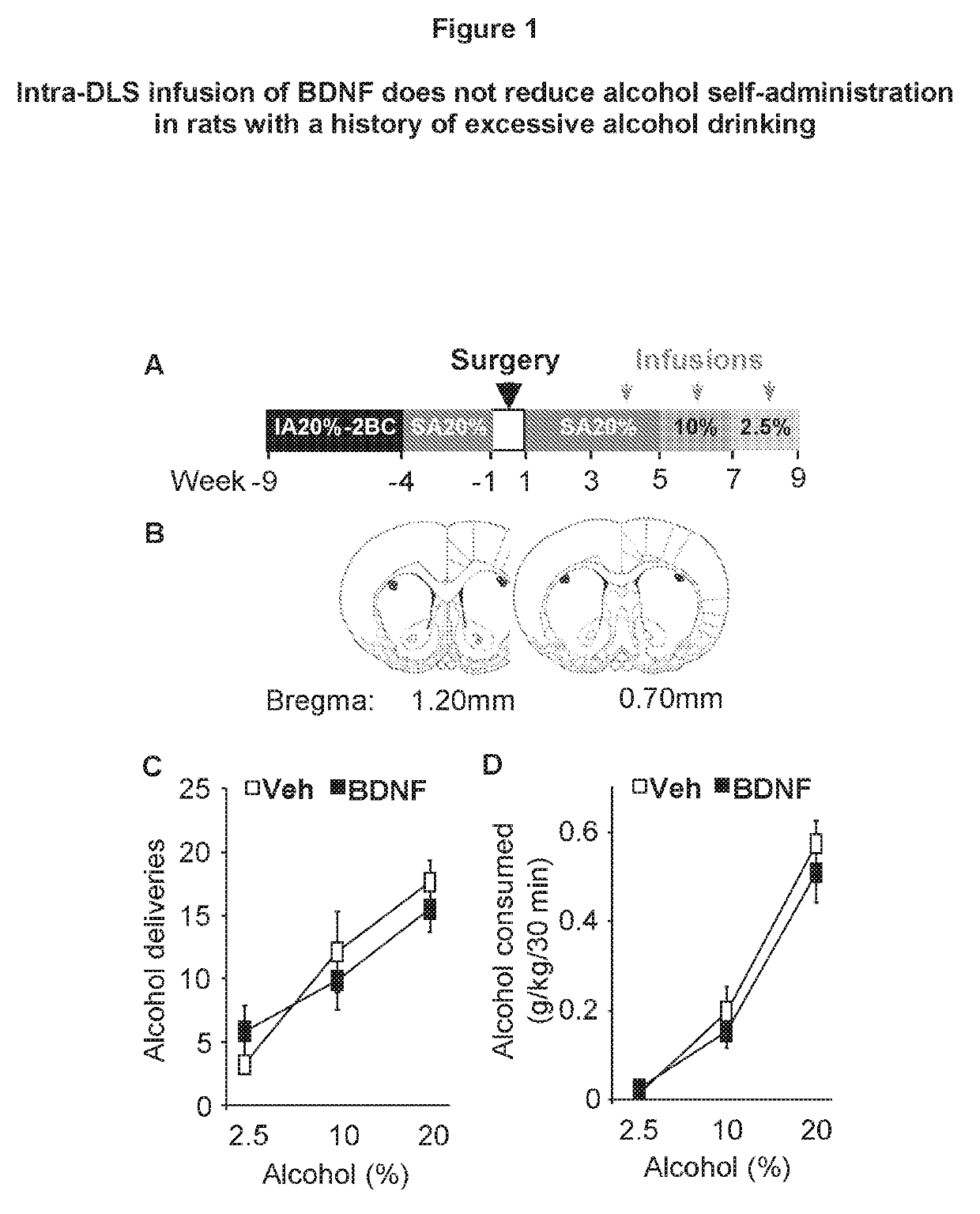
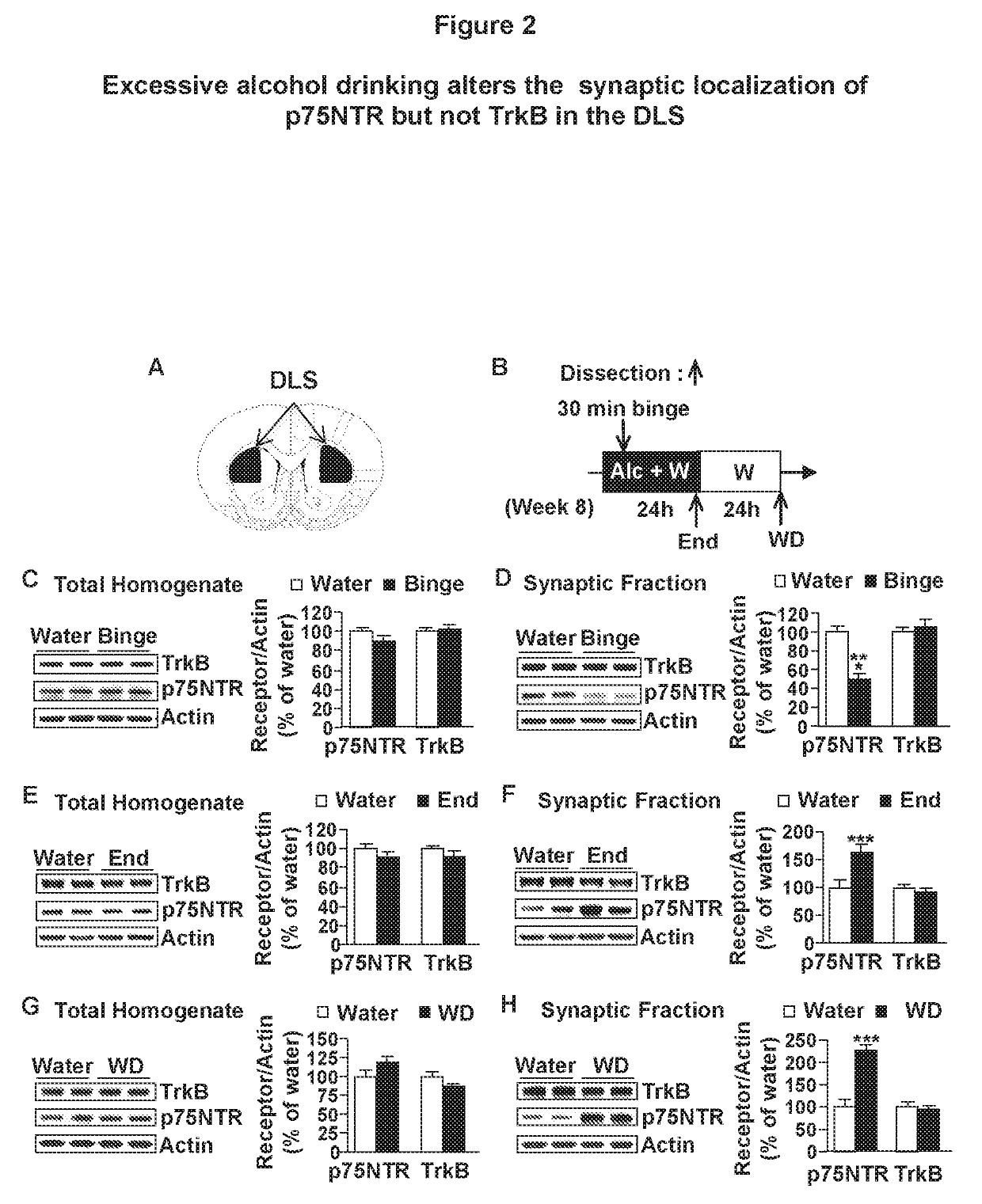
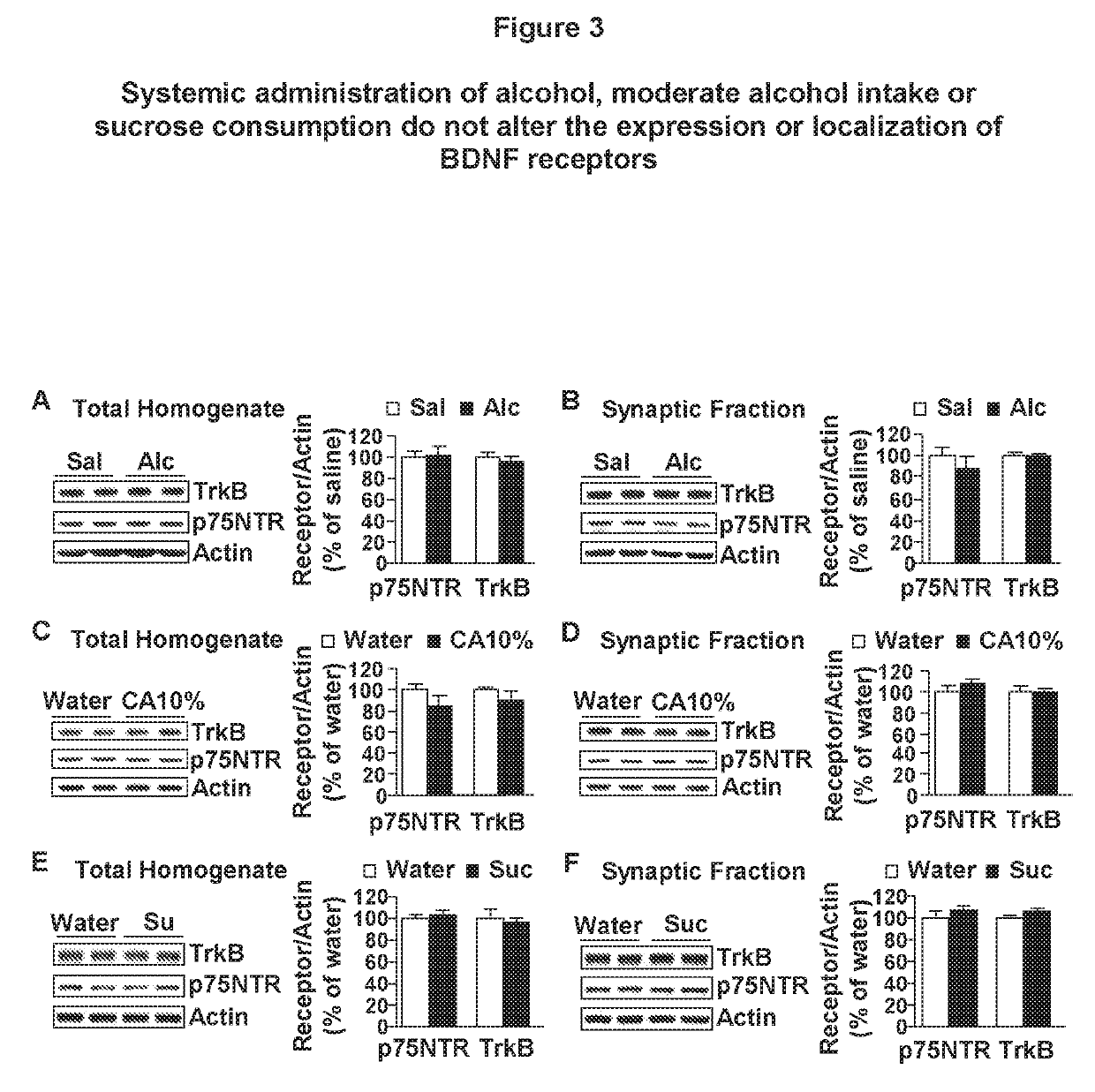
Methods and compounds for treating alcohol use disorder and associated diseases. Included is the administering to a subject in need there of an effective amount of a compound having a modulating effect on p75NTR.
Owner:PHARMATROPHIX +2
Novel scaffold of adenylyl cyclase inhibitors for chronic pain and opioid dependence
The present invention relates to a method of treatment for chronic pain, opioid dependence, alcohol use disorder or autism using a class of pyrimidinone compounds, an adenylyl cyclase 1 (AC1) inhibitor. The invention described herein also pertains to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treating diseases in mammals using those compounds disclosed herein.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Methods of treating alcohol abuse disorder
ActiveUS11154591B2Reduce consumptionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAlcohol abuse disorderPsychiatry
Owner:ATONOMICS +1
Thiophene compounds for long-acting injectable compositions and related methods
ActiveUS10975099B2Effective treatmentLong duration of releaseOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcohol abuse disorderPharmaceutical drug
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Cannabinoid derivatives
The present disclosure relates to a cannabinoid derivative, a pharmaceutical composition comprising it, as well as its use in the treatment and prevention of diseases associated with a cannabinoid receptor in a subject in need thereof, such as acute pain, ADHD / ADD, alcohol use disorder, allergic asthma, ALS, Alzheimer's, anorexia, etc. The cannabinoid derivative has the following formula:
Owner:CANOPY GROWTH CORP
Compositions and methods for the treatment of aud
PendingUS20220125816A1Increase in liabilityIncreased toxicityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcohol abuse disorderEfflux transporters
Provided herein are methods to improve transport or uptake of an avermectin compound in a cell or tissue expressing an efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (Pgp) by co-administering an effective amount of the avermectin compound and a Ppg inhibitor to the cell or tissue. The method also provides improved efficiency transport or uptake of an avermectin compound in the cell or tissue. The methods can be used therapeutically to treat Alcohol Use Disorder.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Novel naphthylenyl compounds for long-acting injectable compositions and related methods
ActiveUS20200016151A1Effective treatmentLong duration of releaseOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcohol abuse disorderPsychiatry
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Compositions, devices, and methods for treatment of overdose and reward-based disorders
PendingCN113573696AOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcohol abuse disorderPharmaceutical drug
Drug products adapted for nasal delivery, comprising a device filled with a pharmaceutical composition comprising naltrexone are provided. Formulations and methods of treating alcohol use disorder and related conditions with the drug products are also provided.
Owner:AEGIS THERAPEUTICS LLC +1
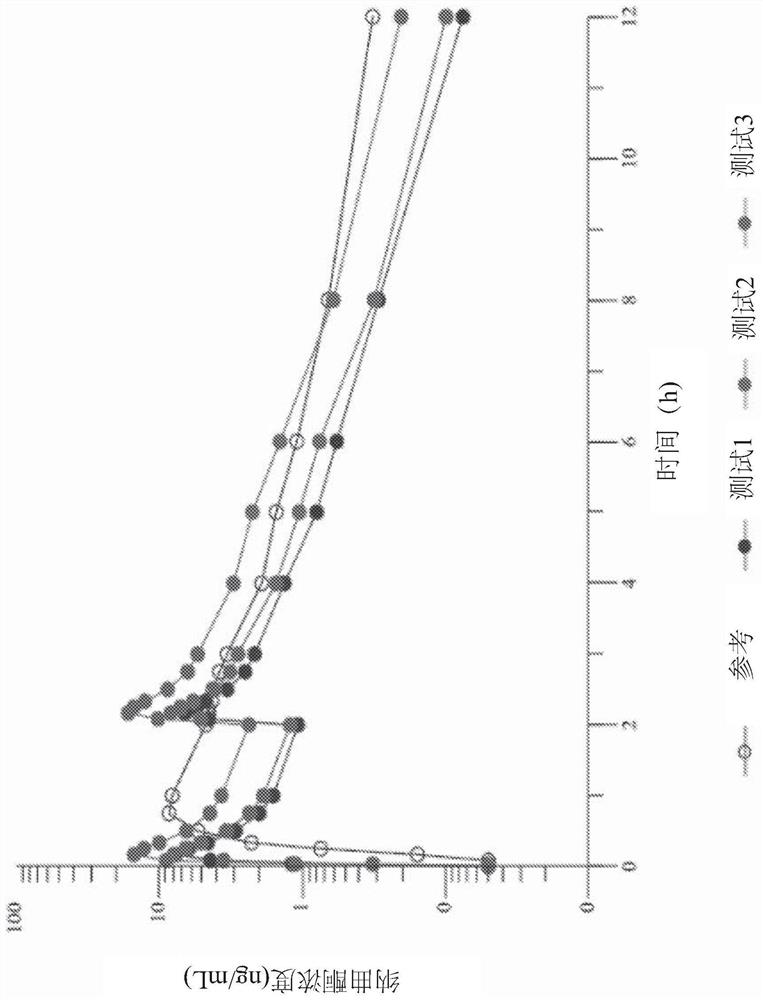
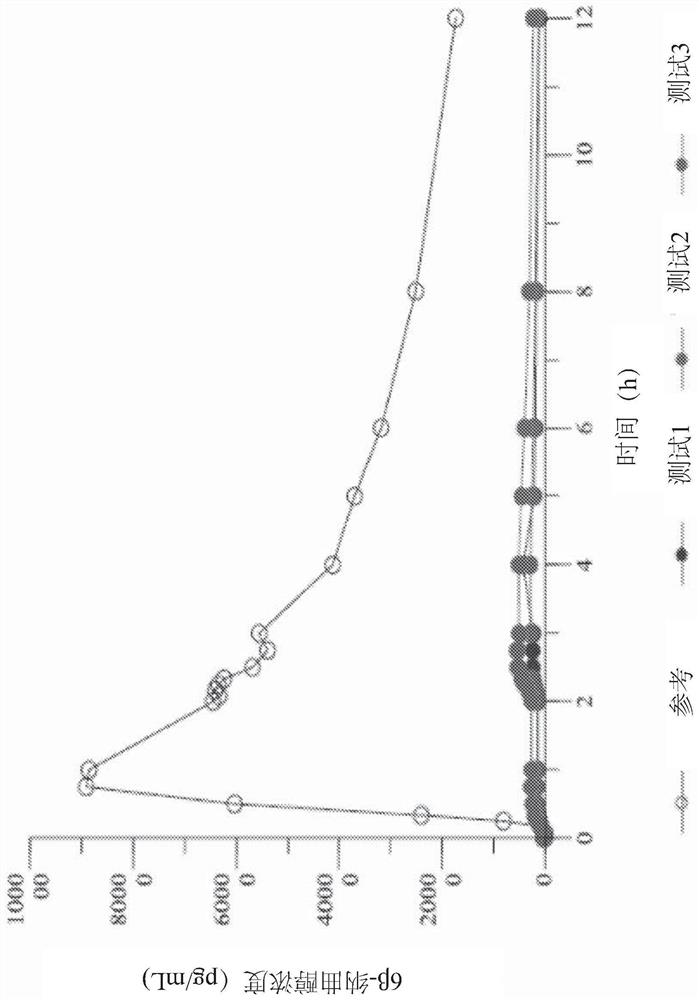
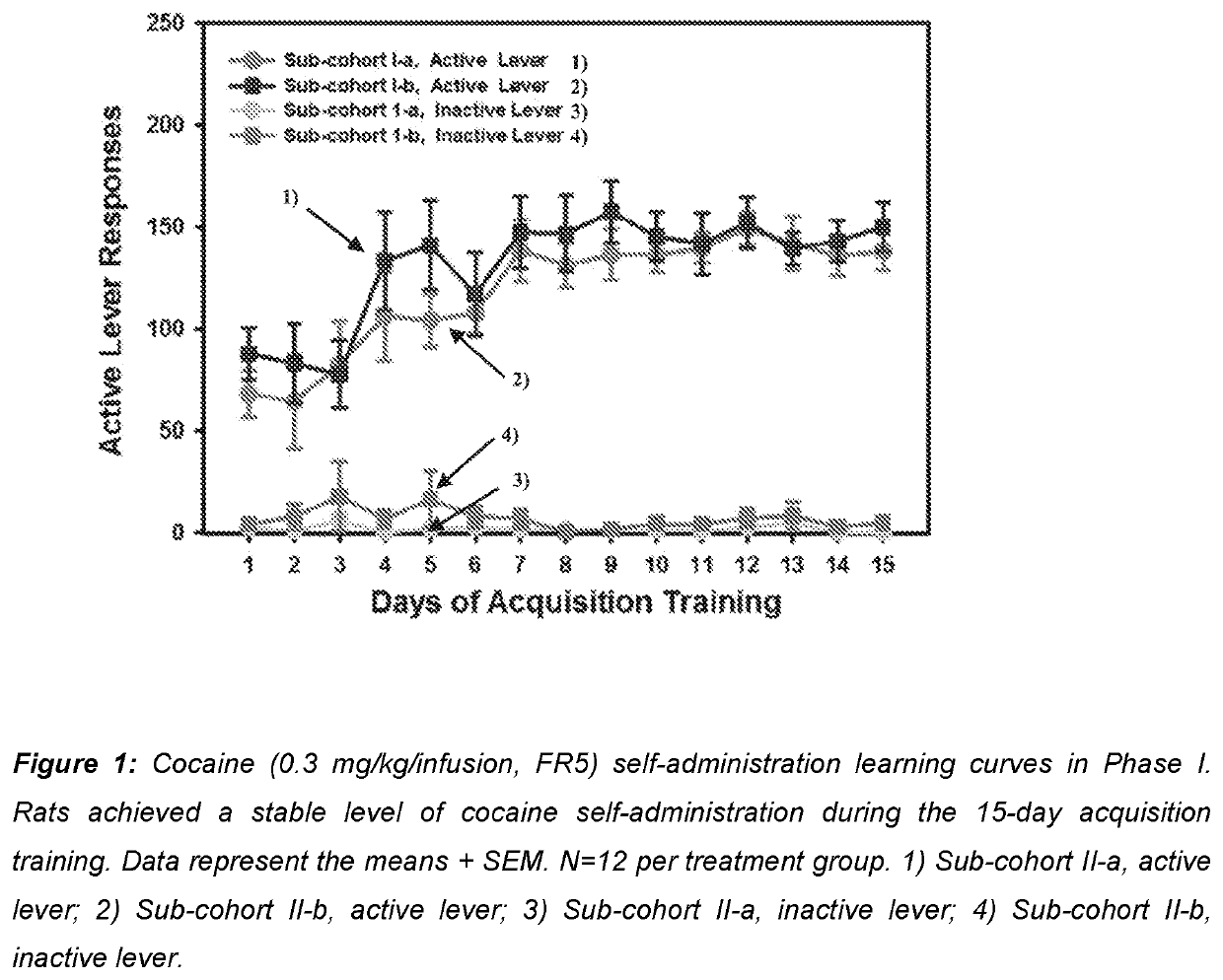
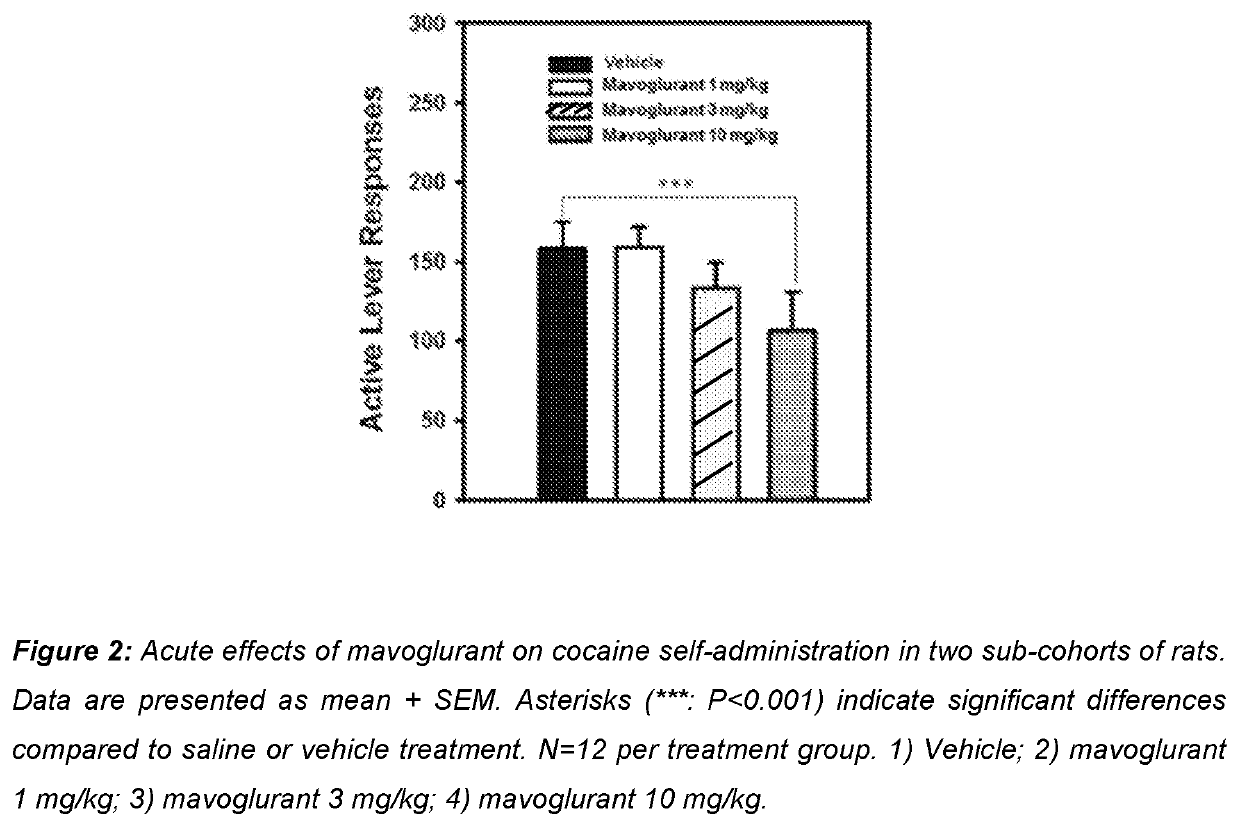
Use of mavoglurant in the reduction of alcohol use or in preventing relapse into alcohol use
PendingUS20200237721A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcohol abuse disorderPharmaceutical medicine
The invention relates to the use of mavoglurant, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof: in the reduction of alcohol use by an alcohol use disorder patient; in preventing relapse into alcohol use by an alcohol use disorder patient; in the promotion of alcohol abstinence by an alcohol use disorder patient; in the treatment of the symptoms of depression or anxiety associated with alcohol use disorder.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Naphthylenyl compounds for long-acting injectable compositions and related methods
ActiveUS10799496B2Effective treatmentLong duration of releaseOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcohol abuse disorderPsychiatry
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
A medicinal and edible homologous composition for alcohol use disorder and its application
ActiveCN113521195BEasy to shapeInhibition decreasedNervous disorderDigestive systemAlcohol abuse disorderAdrenocortical hormone
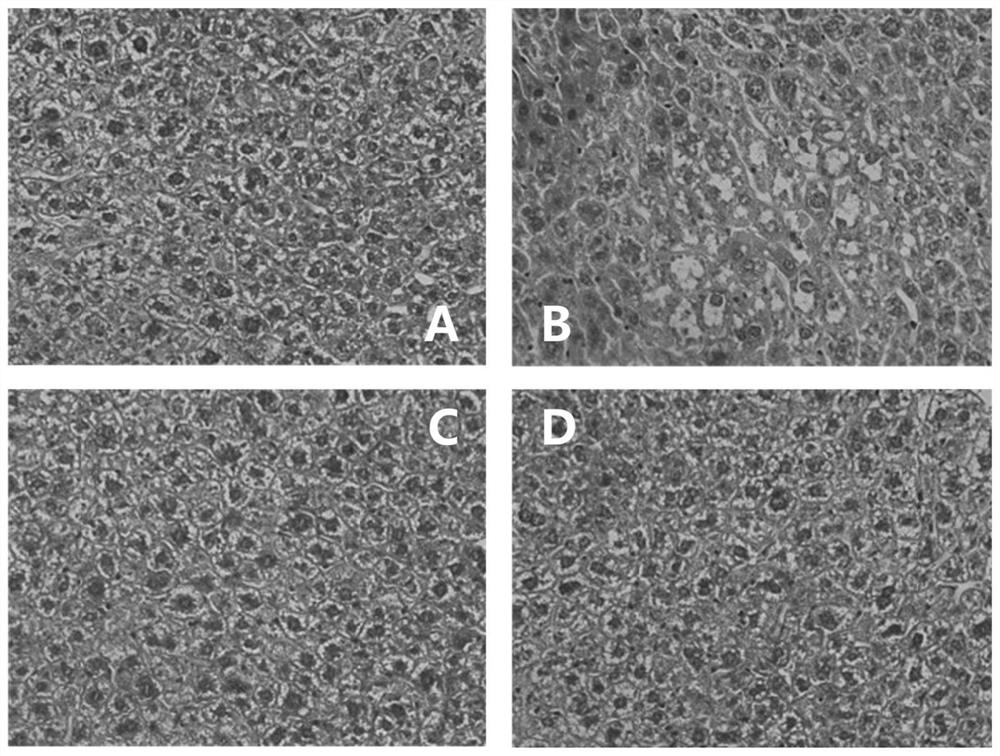
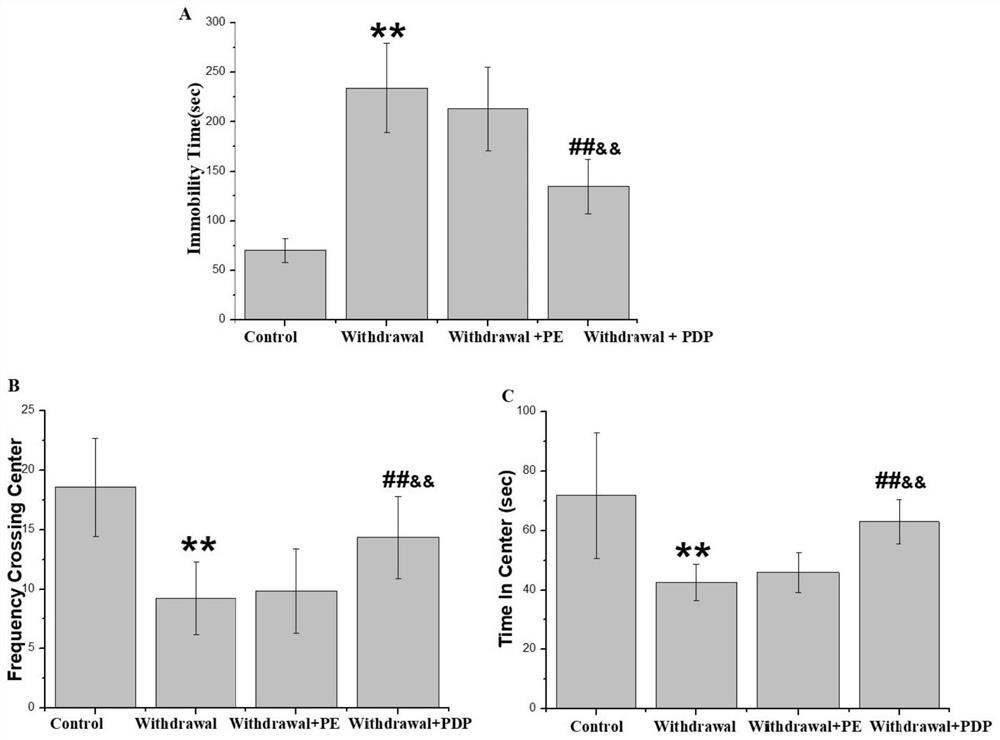
The invention discloses a medicine and food homologous composition for alcohol use disorder and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of health food. The composition of the invention is composed of dendrobium, polygonatum and kudzu root. The composition of the invention has significant protective effect on alcoholic liver injury in mice, including improving the morphology and structure of liver cells, improving liver function and liver lipid metabolism. On the other hand, the composition of the present invention can improve depression and anxiety-like reactions after alcohol withdrawal, reduce the elevation of corticotropin-releasing hormone, corticotropin and corticosterone caused by alcohol withdrawal; inhibit alcohol withdrawal Causes a decrease in the monoamine transmitters dopamine and norepinephrine.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Compositions and methods for the modulation of the corticotropin releasing factor binding protein and the treatment of alcohol use disorder
ActiveUS20210308107A1Organic chemistryHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsAspartic acid receptorsSubstance abuser
Stress responses involve corticotropin releasing factor (CRF), the two cognate receptors (CRF1 and CRF2) and the CRF-binding protein (CRFBP). Utilizing a novel cell-based assay, a C-terminal CRFBP fragment [CRFBP(10 kD)] was found to potentiates CRF-intracellular Ca2+ release, demonstrating that CRFBP possesses excitatory roles in addition to the inhibitory role established by the N-terminal fragment of CRFBP [CRFBP(27 kD)]. This interaction was CRF2-specific, as CRF1 responses were not potentiated by CRFBP(10 kD). As there were currently no small molecule ligands available that selectively interact with either CRFBP or CRF2, a cell-based assay was miniaturized, wherein CRFBP(10 kD) was fused as a chimera with CRF2α, that allowed us to a perform a high-throughput screen (HTS) of approximately 350,000 small molecules. This resulted in the identification of negative allosteric modulators (NAMs) of the CRFBP(10 kD)-CRF2 complex that blunt CRF-induced potentiation of N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor (NMDAR)-mediated synaptic transmission in dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA). These results provide the first evidence of specific roles for CRF2 and CRFBP in the modulation of neuronal activity and suggest that NMDARs in the VTA may be a target for the treatment of stress and substance abuse disorders such as alcohol use disorder.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
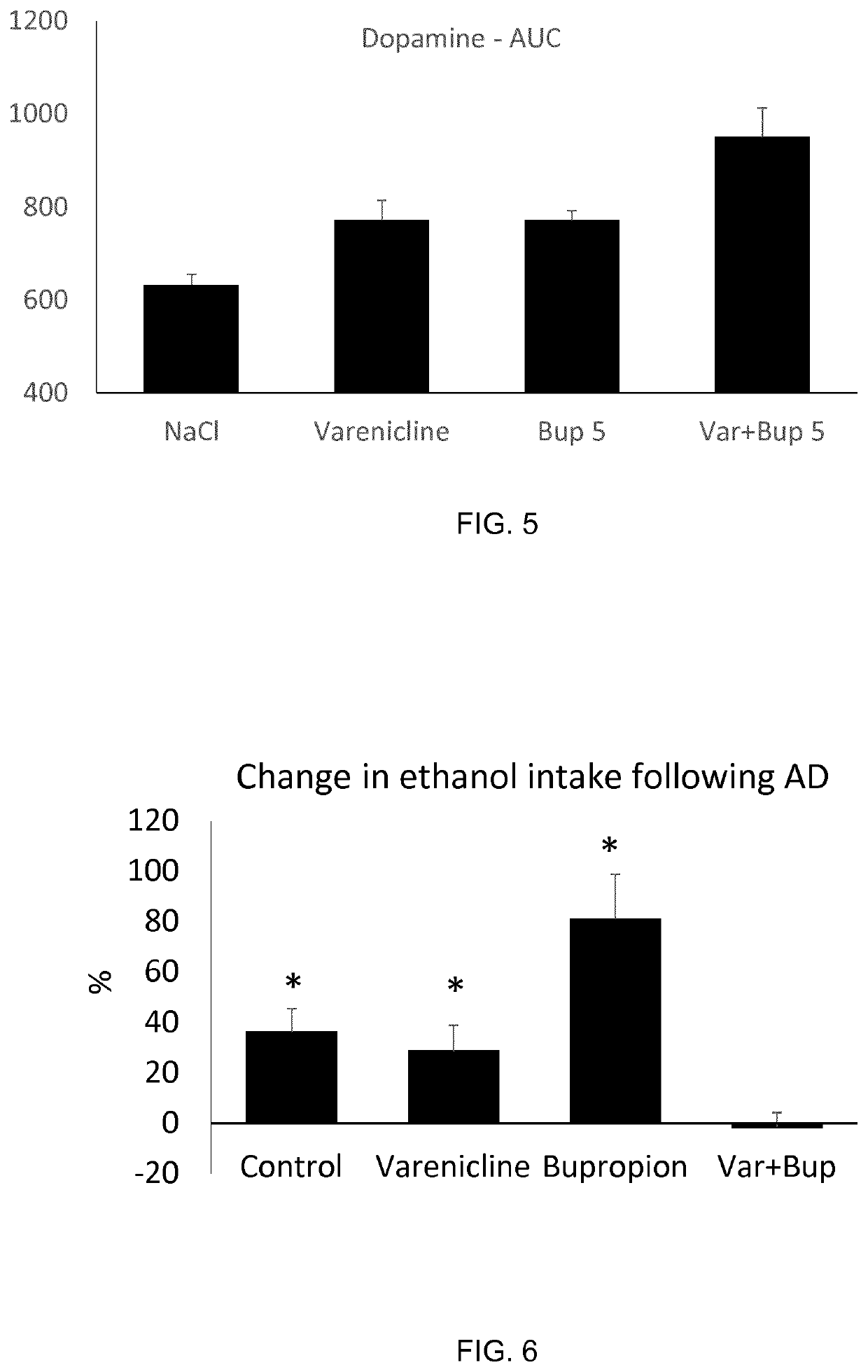
Treatment of alcohol use disorder
ActiveUS11318143B2Block nAChR activationFacilitated releaseNervous disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsAlcohol abuse disorderPharmacology
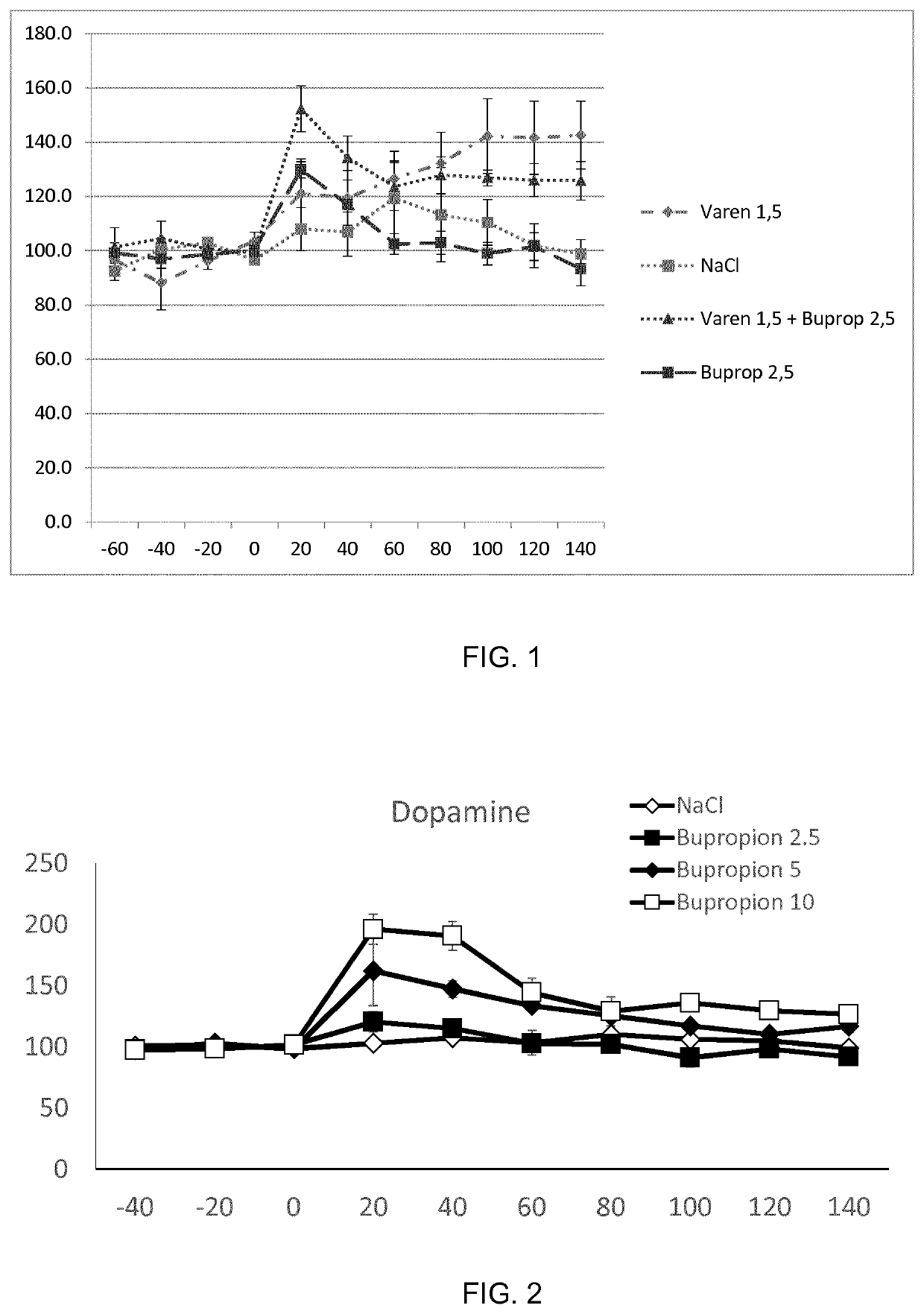
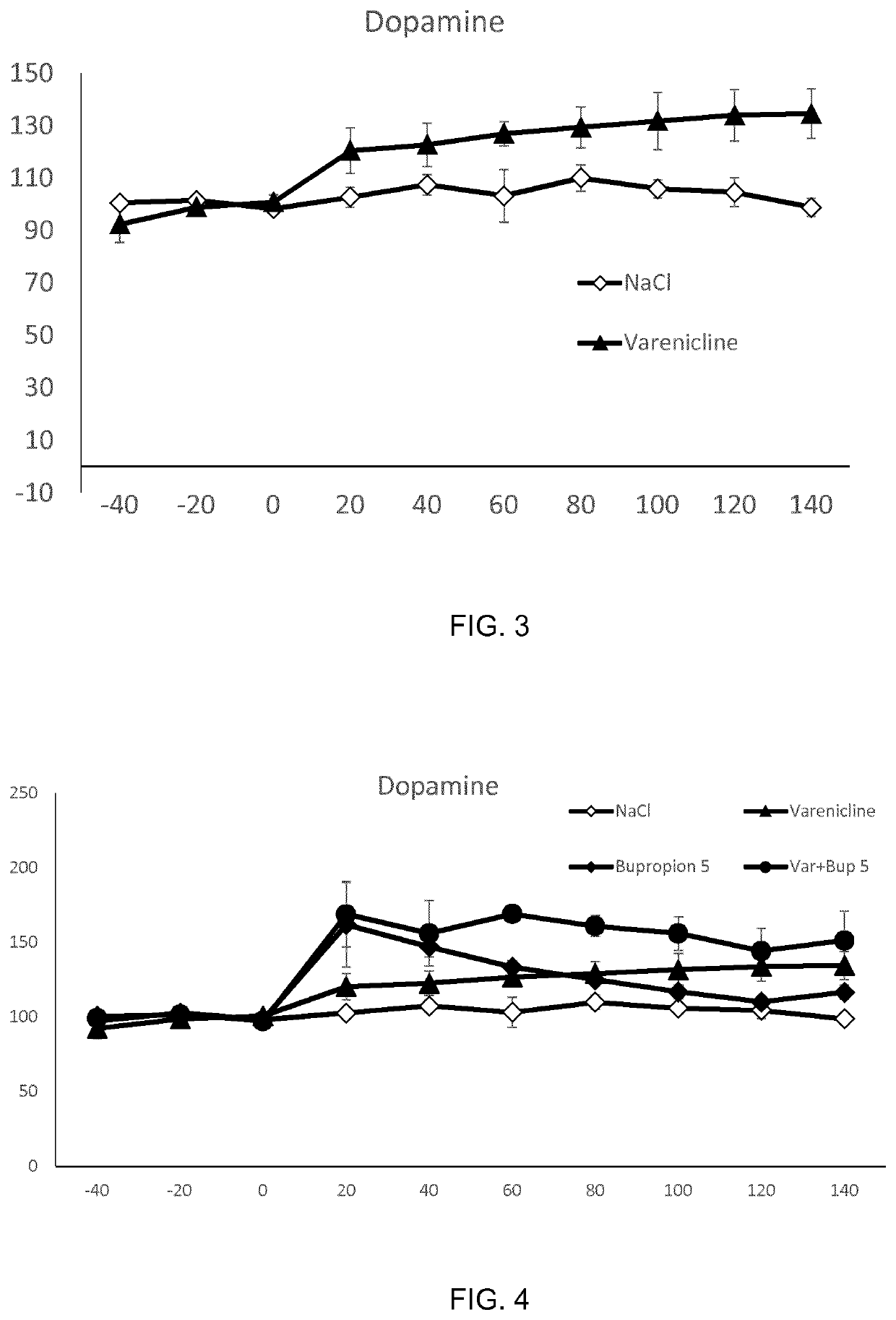
The present invention is directed to a combination of varenicline and bupropion for use in treating alcohol use disorder (AUD) and / or treating alcohol risk consumption in a subject in need thereof. Corresponding compositions, uses and methods of treatment are also provided.
Owner:SODERPALM BO +1
Methods of treating alcohol abuse disorder
ActiveUS20190314457A1Reduce consumptionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAlcohol abuse disorderPsychiatry
Owner:ATONOMICS +1
Methods and compositions for treating alcohol use disorders
ActiveUS10039772B2Reduce dependenceAvoid prolonged useNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsEnantiomerAlcohol abuse disorder
Disclosed are methods and compositions for treating alcohol dependence by administration to a patient of an inhibitor of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (11β-HSD) to modulate glucocorticoid effects. One such compound is the 11β-HSD inhibitor carbenoxolone (18β-glycyrrhetinic acid 3β-O-hemisuccinate), which has been extensively employed in the clinic for the treatment of gastritis and peptic ulcer. Carbenoxolone is active on both 11β-HSD1 and 2 isoforms. Here, carbenoxolone is surprisingly shown to reduce both baseline and excessive drinking in rats and mice. The carbenoxolone diastereomer 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid 3β-O-hemisuccinate (αCBX), which the applicants discovered to be selective for 11β-HSD2, was also effective in reducing alcohol drinking in mice. Thus, 11β-HSD inhibitors are a new class of candidate alcohol abuse medications and existing 11β-HSD inhibitor drugs may be re-purposed for alcohol abuse treatment.
Owner:SANNA PIETRO PAOLO
Thienothiophene compounds for long-acting injectable compositions and related methods
ActiveUS10807995B2Effective treatmentLong duration of releaseNervous disorderOrganic chemistryAlcohol abuse disorderPsychiatry
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Novel Thiophene Compounds for Long-Acting Injectable Compositions and Related Methods
ActiveUS20200325157A1Effective treatmentLong duration of releaseOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcohol abuse disorderPharmaceutical Substances
Owner:ALKERMES PHARMA IRELAND LTD
Analytic method and kit for diagnosing alcohol use disorders
PendingUS20210324475A1Effectively overcome limitationHigh expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAlcohol abuse disorderGene
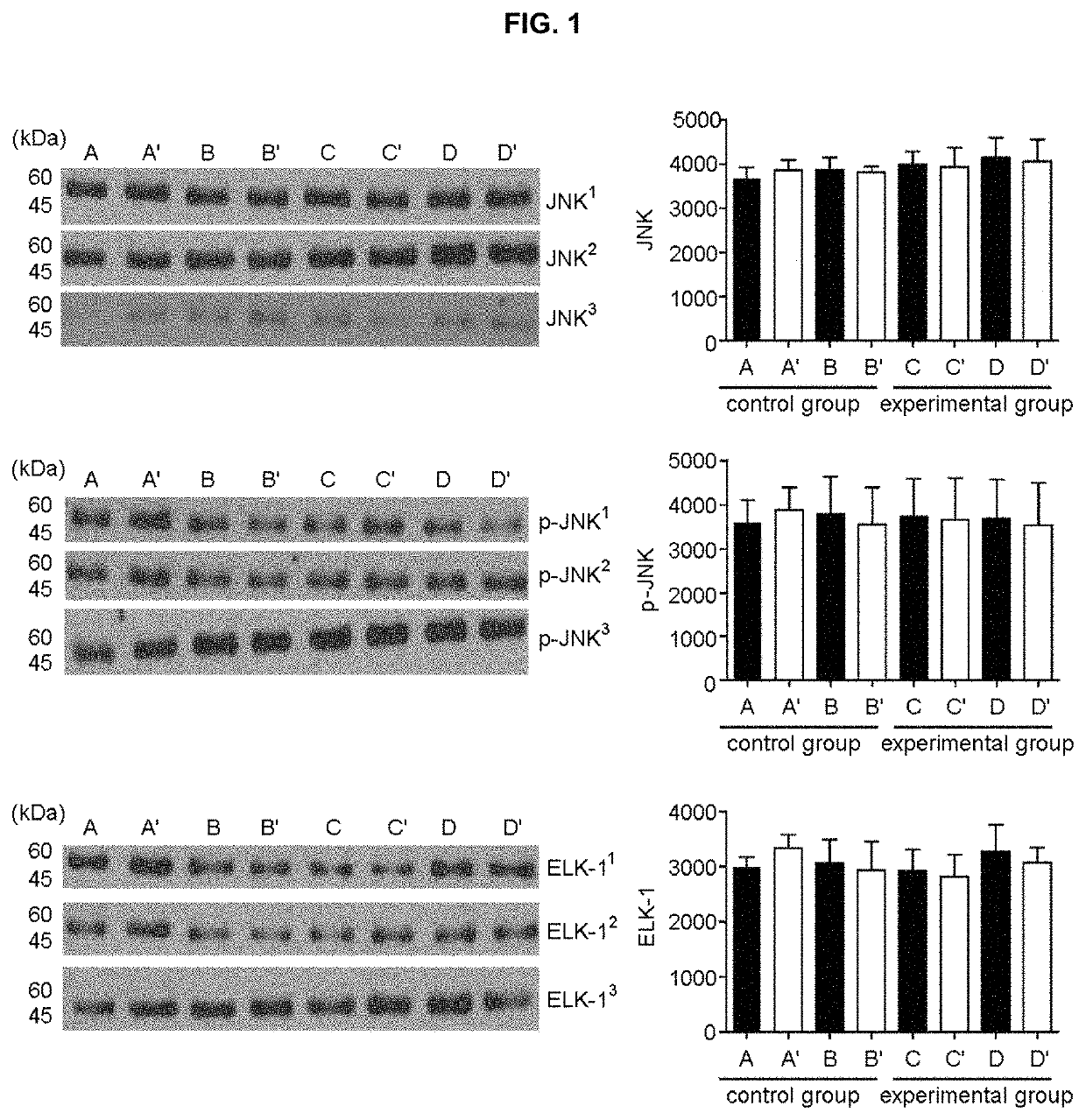
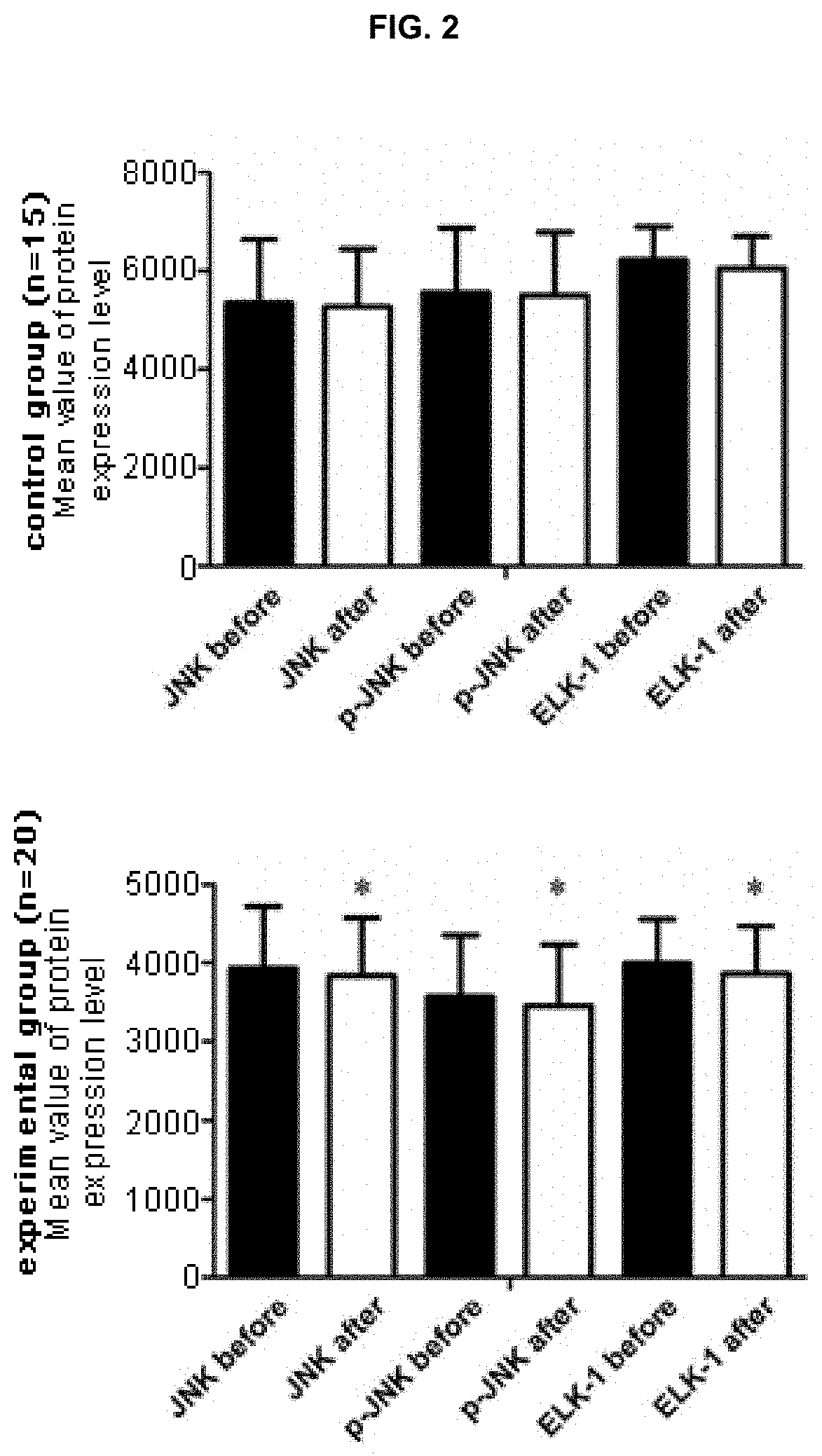
Provided is an analytical method for providing information necessary for a diagnosis of alcohol use disorder, including measuring (i) an expression level of a gene encoding a JNK or p-JNK protein in a subject's sample, (ii) an expression level of a gene encoding a JNK or p-JNK protein and an expression level of a gene encoding the Elk-1 protein in a subject's sample, or (iii) expression levels of genes encoding JNK, p-JNK, and Elk-1 proteins in a subject's sample, respectively; and a kit for a diagnosis of alcohol use disorder which is used in the analytical method.
Owner:COLLEGE OF MEDICINE POCHON CHA UNIV IND
Use of mavoglurant in the reduction of alcohol use or in preventing relapse into alcohol use
PendingCN110891564AOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcohol abuse disorderPharmaceutical medicine
The invention relates to the use of mavoglurant, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof: in the reduction of alcohol use by an alcohol use disorder patient; in preventing relapse into alcohol use by an alcohol use disorder patient; in the promotion of alcohol abstinence by an alcohol use disorder patient; in the treatment of the symptoms of depression or anxiety associated with alcohol usedisorder.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Treatment of alcoholism and depression and/or dysphoric mood using ibudilast
InactiveUS20190151294A1Nervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAlcoholismsAlcohol abuse disorder
Alcoholism, and symptoms and negative effects thereof may be treated using ibudilast or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. Patients diagnosed with alcohol use disorder and who exhibit symptoms of depression and / or dysphoric mood can be treated using ibudilast or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:MEDICINOVA INC
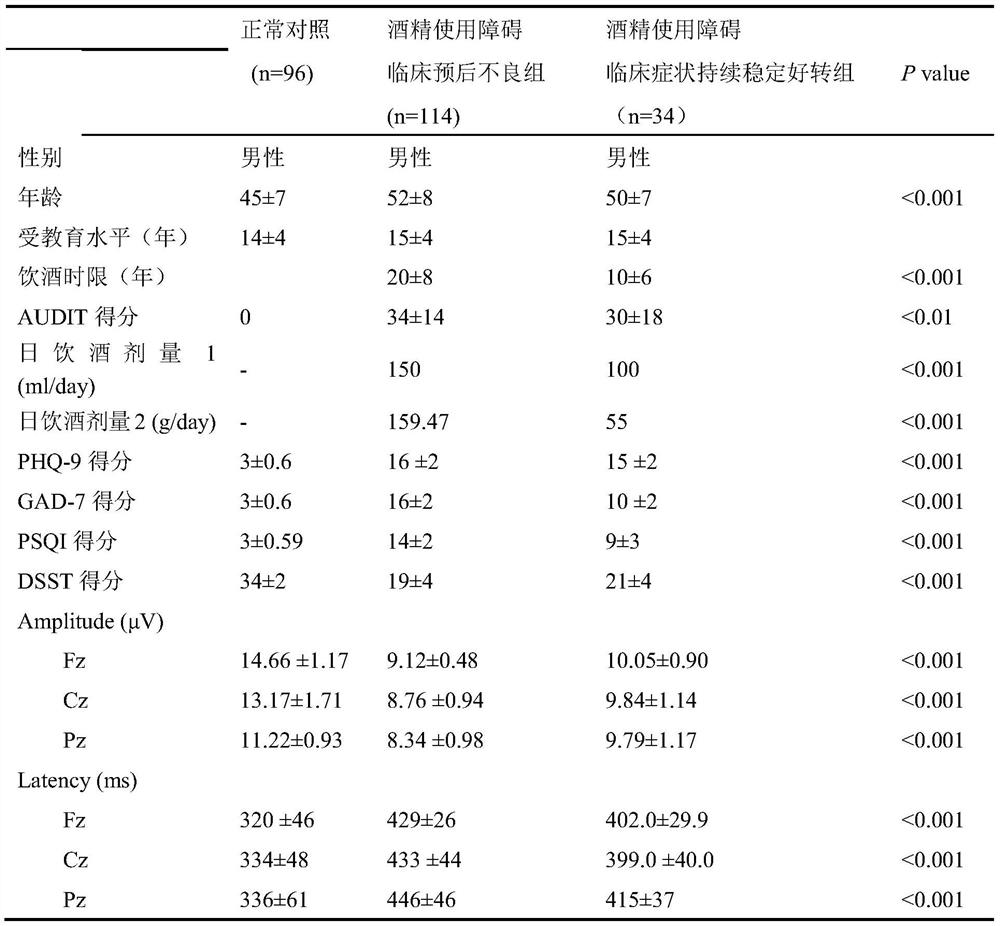
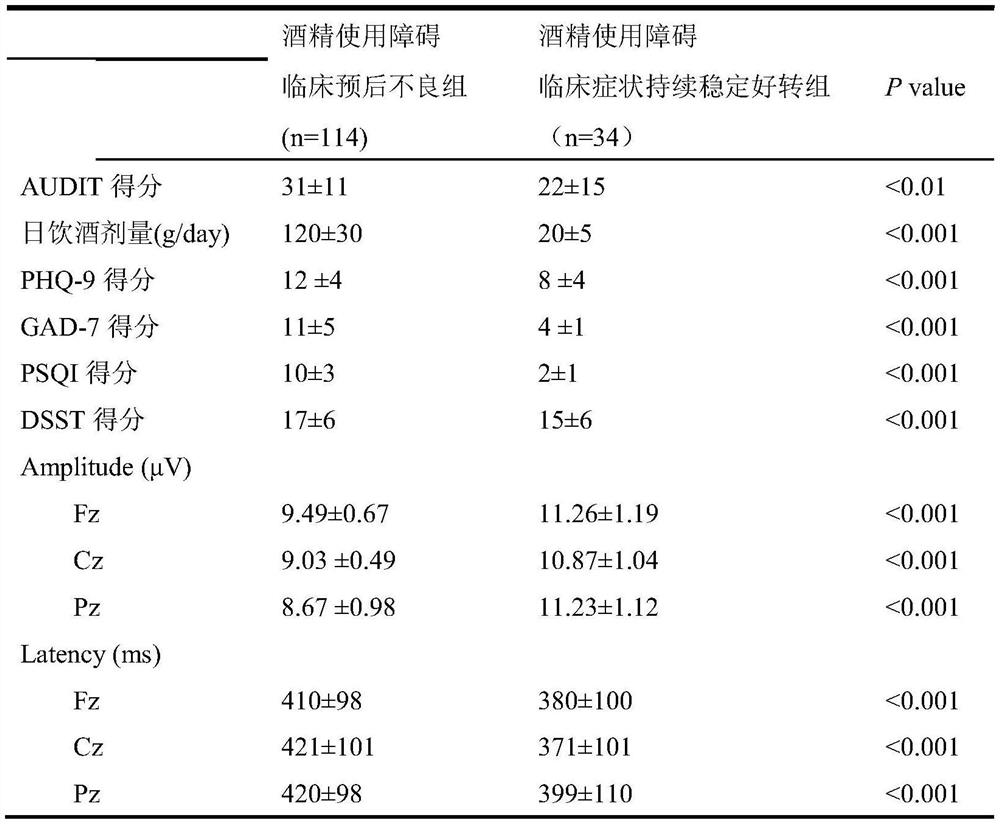
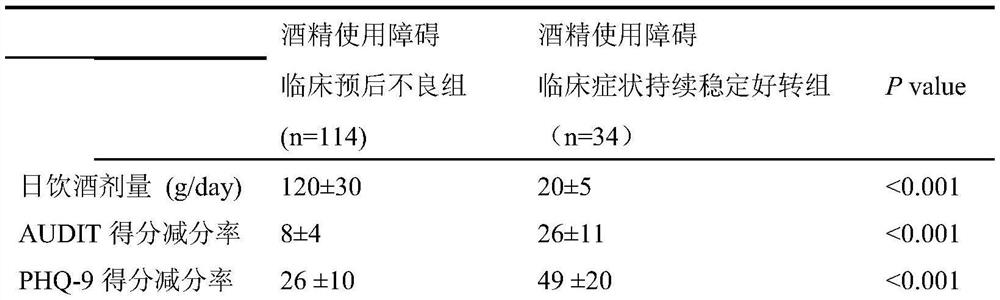
Alcohol use disorder clinical poor prognosis prediction model and construction method thereof
PendingCN113380415AImproved prognosisMedical data miningMental therapiesClinical prognosisEarly prediction
The invention discloses an alcohol use disorder clinical poor prognosis prediction model and a construction method thereof According to the method, an alcohol use disorder clinical poor prognosis prediction model is established mainly according to psychological evaluation indexes and prediction values of electrophysiological markers. The alcohol use disorder clinical poor prognosis prediction model constructed by the invention can achieve the clinical target of early screening of patients with poor prognosis, is used for judging the clinical prognosis of alcohol use disorder, makes early prognosis prediction, early timely intervention and prognosis improvement possible, and has important clinical significance.
Owner:昆明医科大学第二附属医院
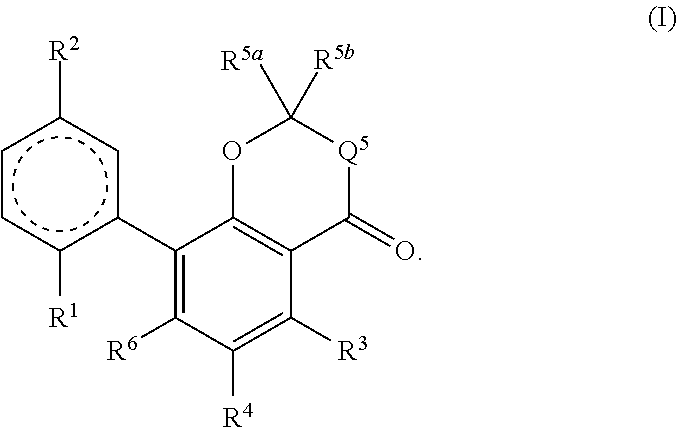
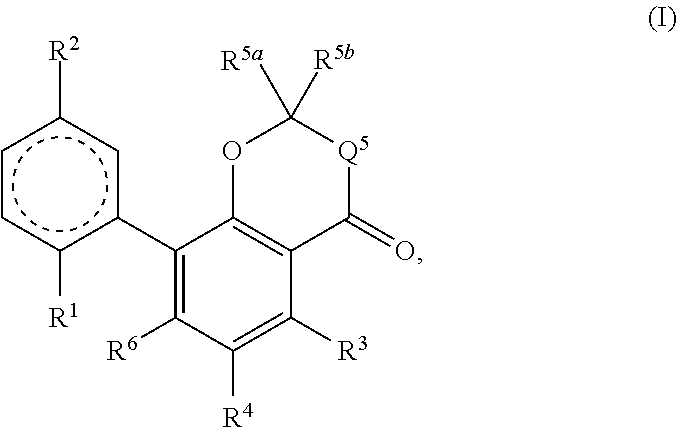
Therapeutic agent for alcohol use disorders
InactiveUS20200237720A1Suppression problemOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcohol abuse disorderPharmacometrics
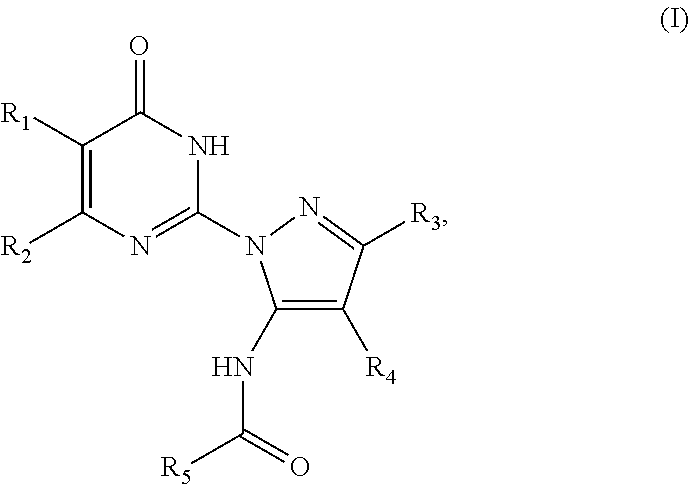
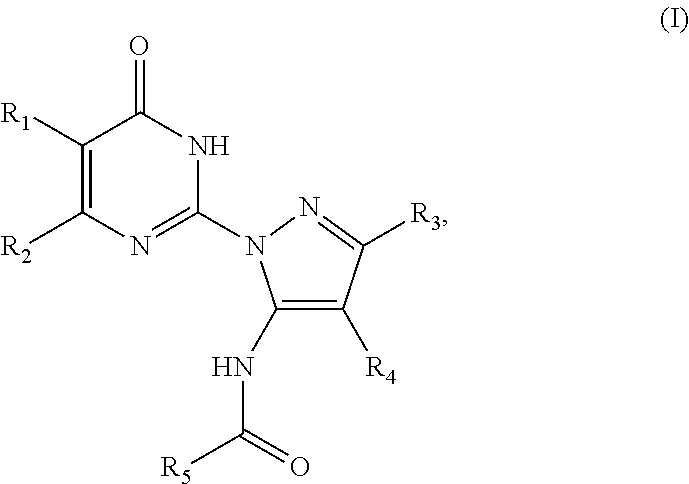
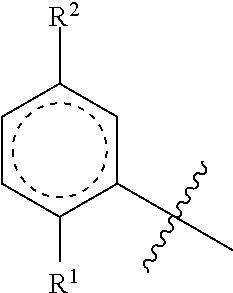
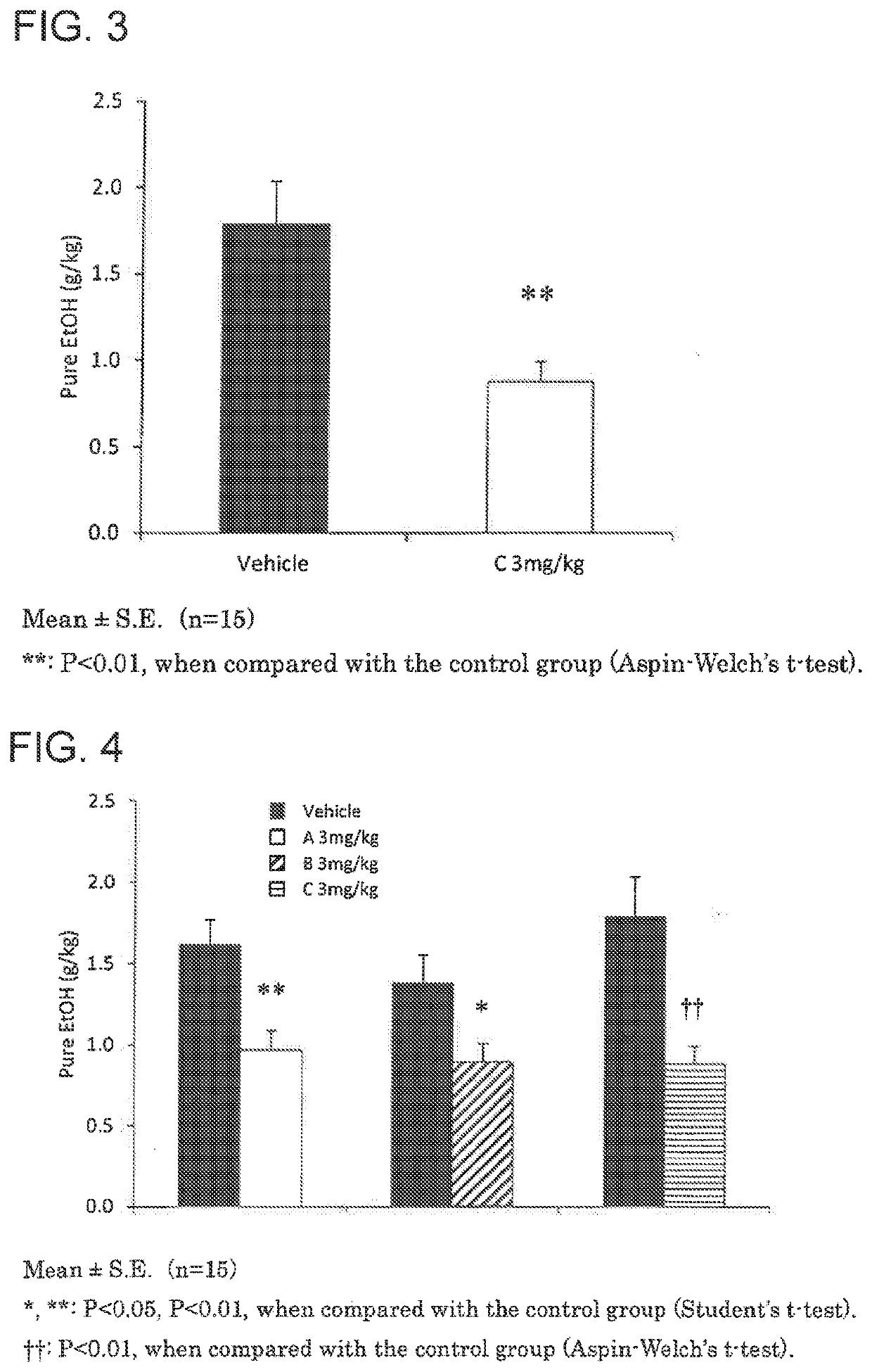
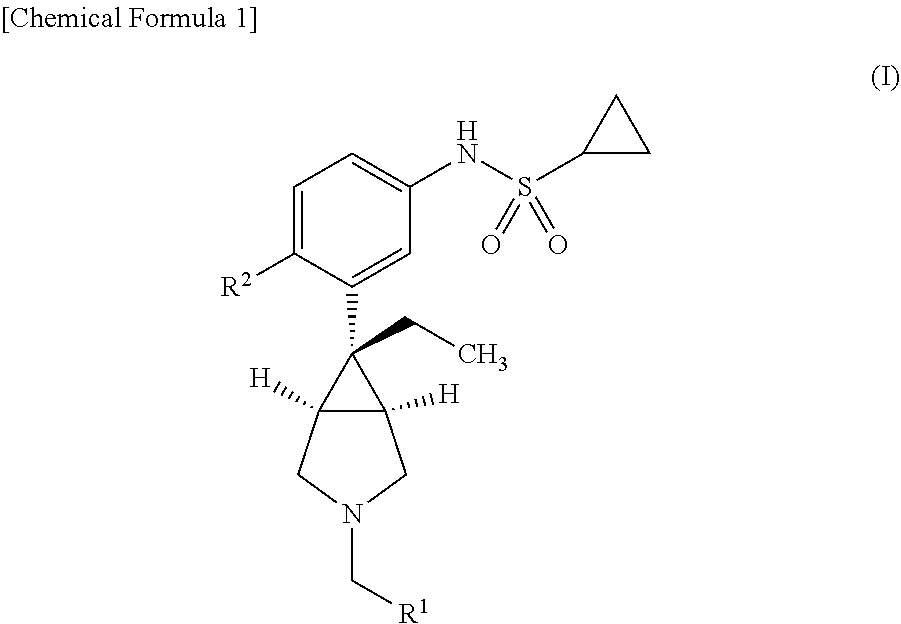
An object he present invention is to provide a medicament for therapy of alcohol use disorder. The present invention relates to a medicament for therapy of alcohol use disorder, containing a compound represented by the following general formula (I) or a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof as an active ingredient:wherein R2 represents a hydrogen atom or a halogen atom and R1 represents a group selected from the grown consisting of
Owner:UBE IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com