Patents
Literature
135 results about "File locking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
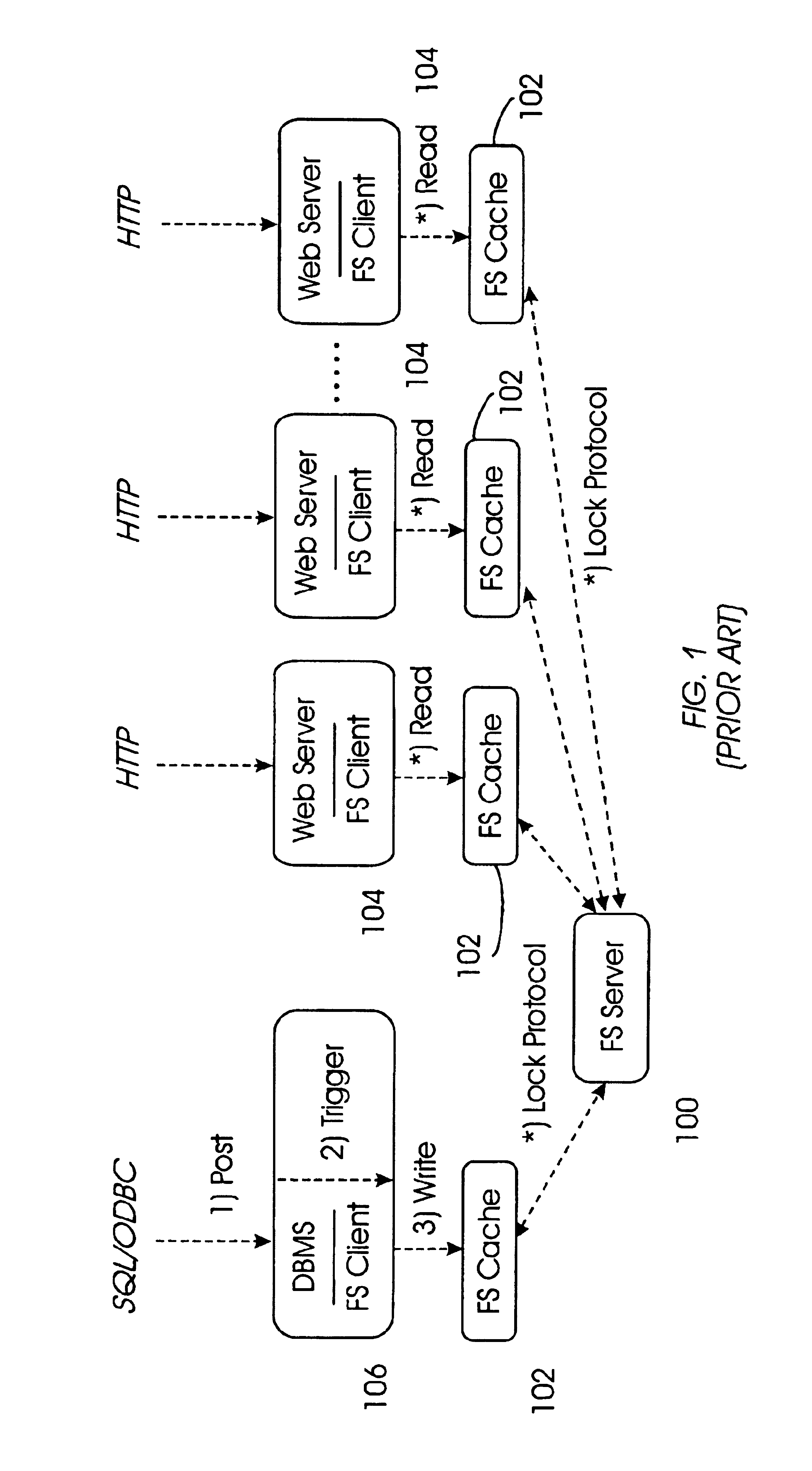
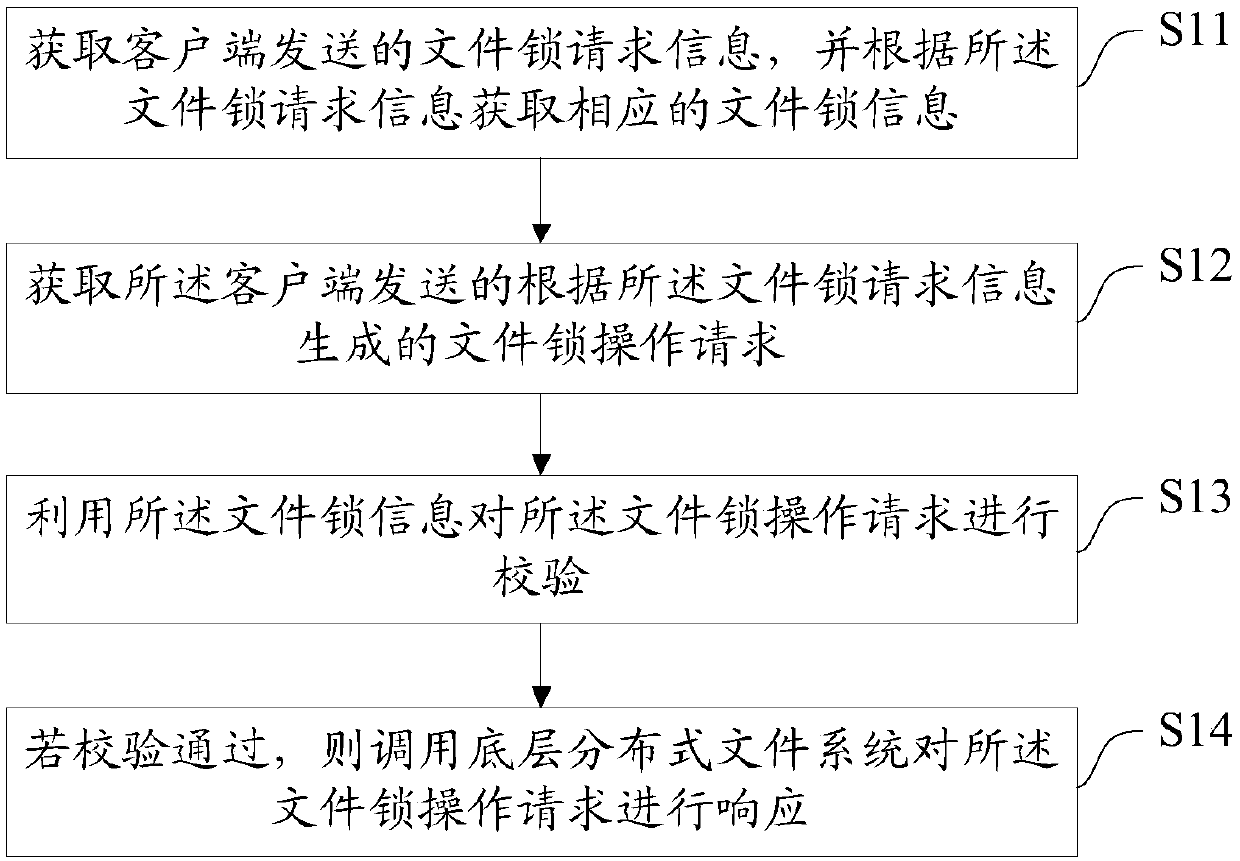
File locking is a mechanism that restricts access to a computer file by allowing only one user or process to access it in a specific time. Systems implement locking to prevent the classic interceding update scenario, which is a typical example of race condition, by enforcing the serialization of update processes to any given file.
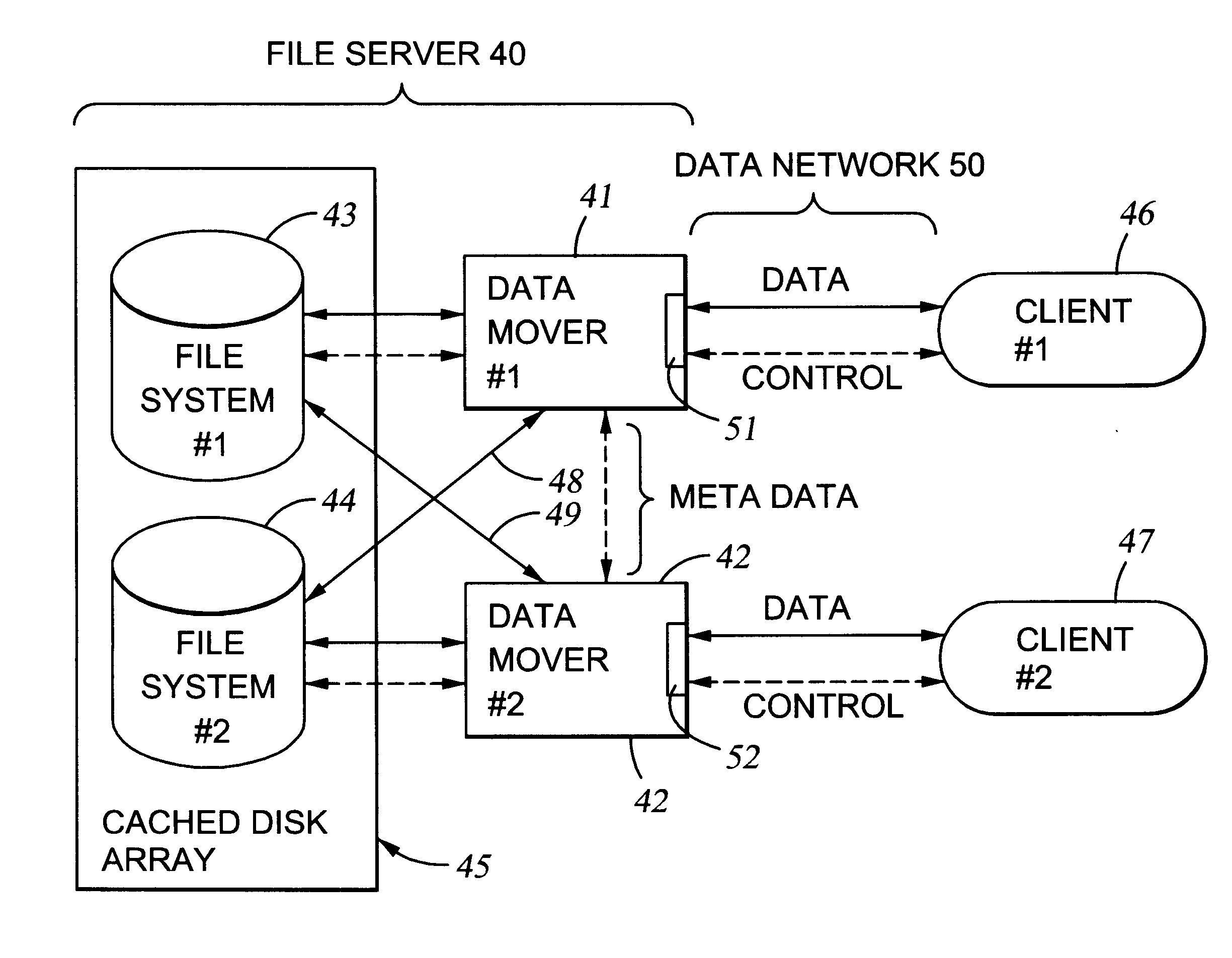
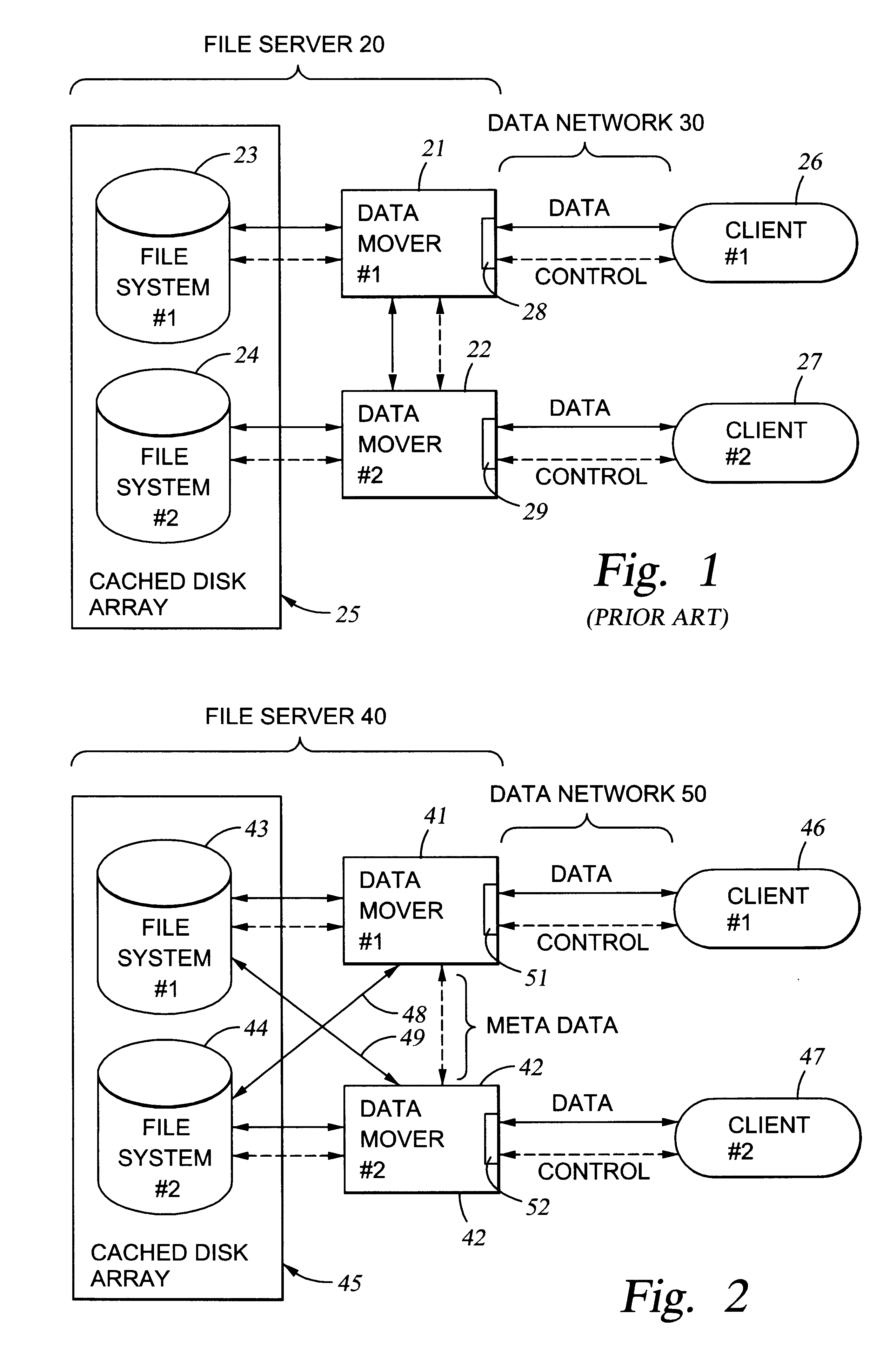
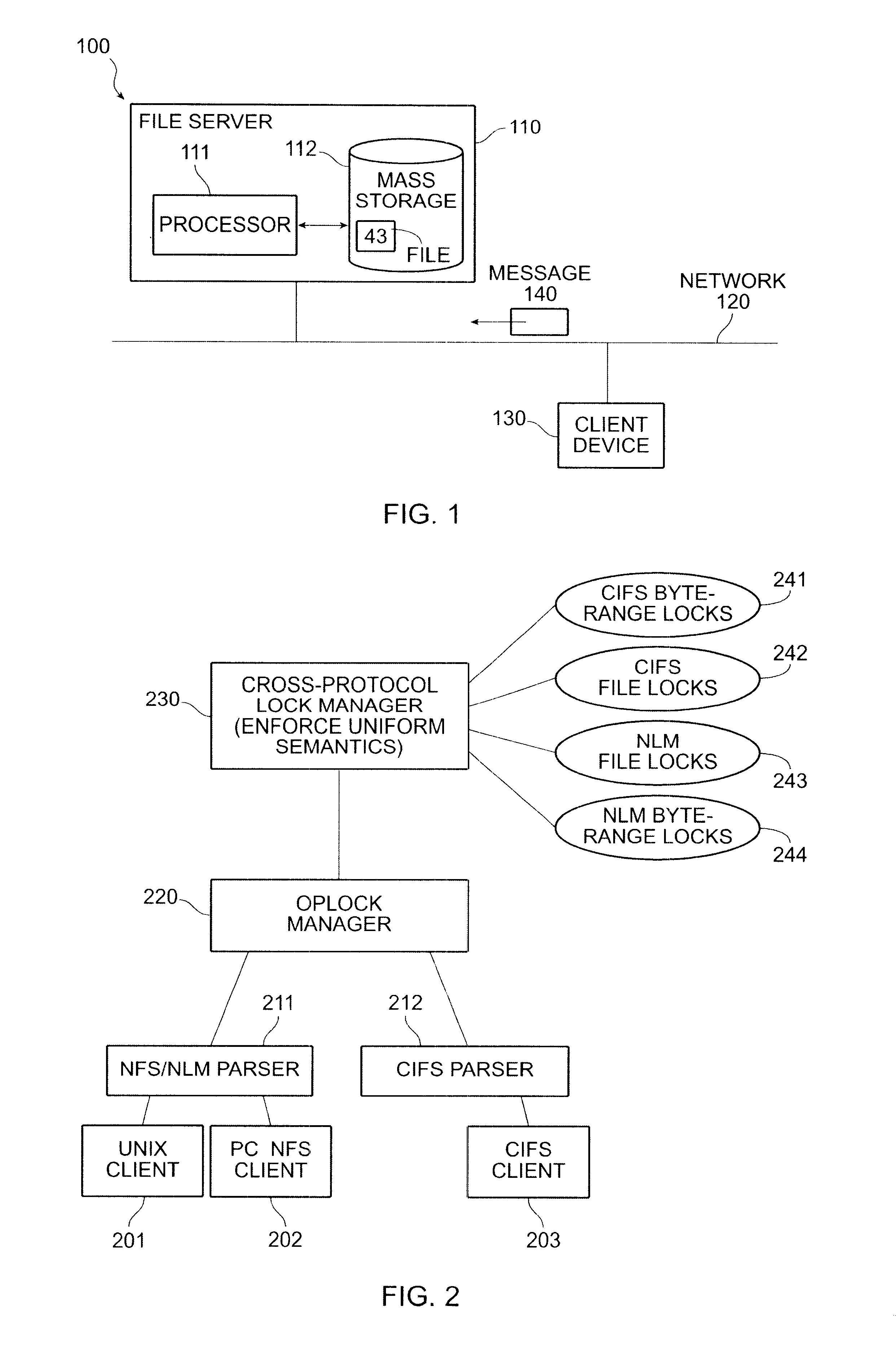
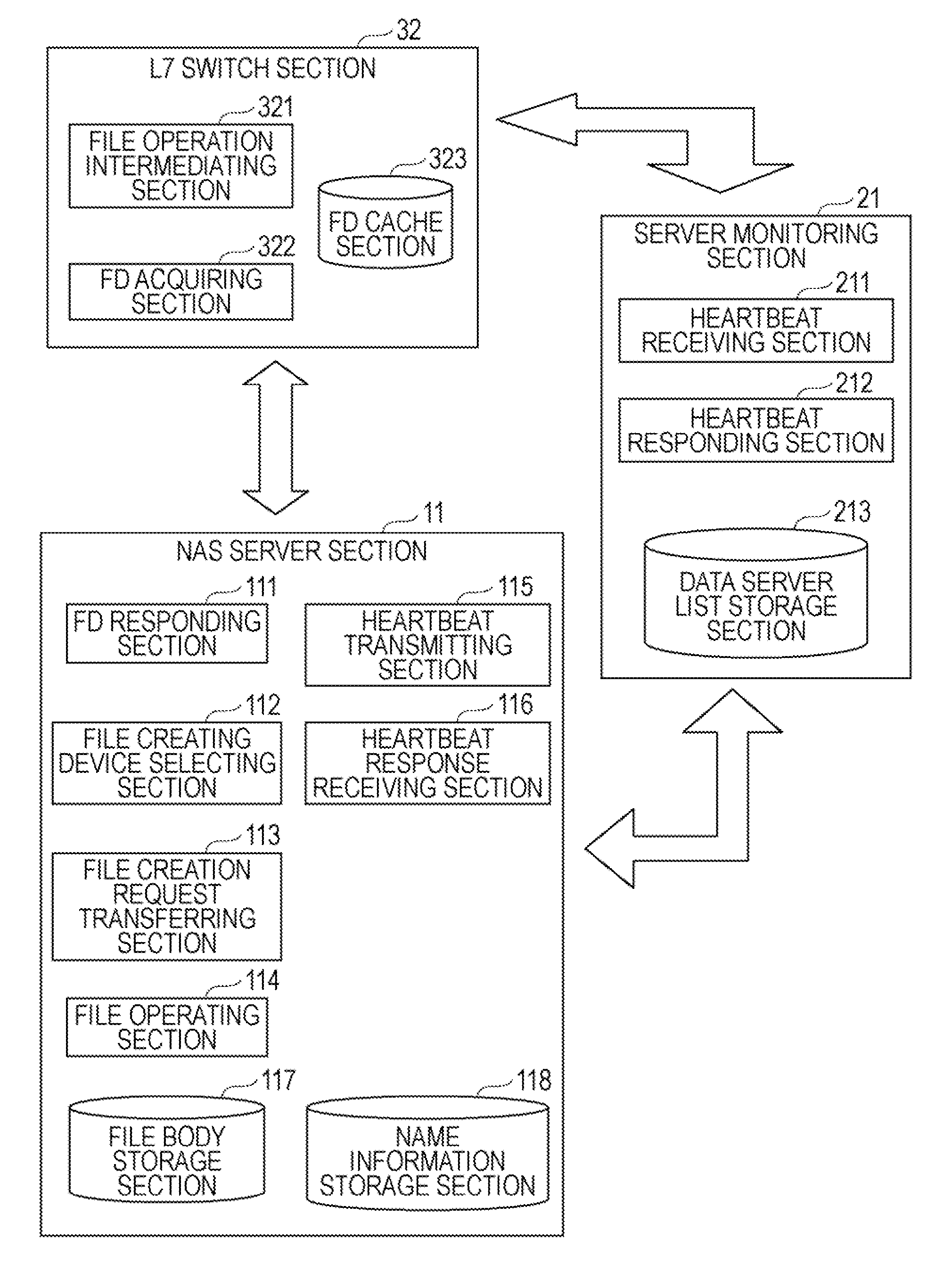
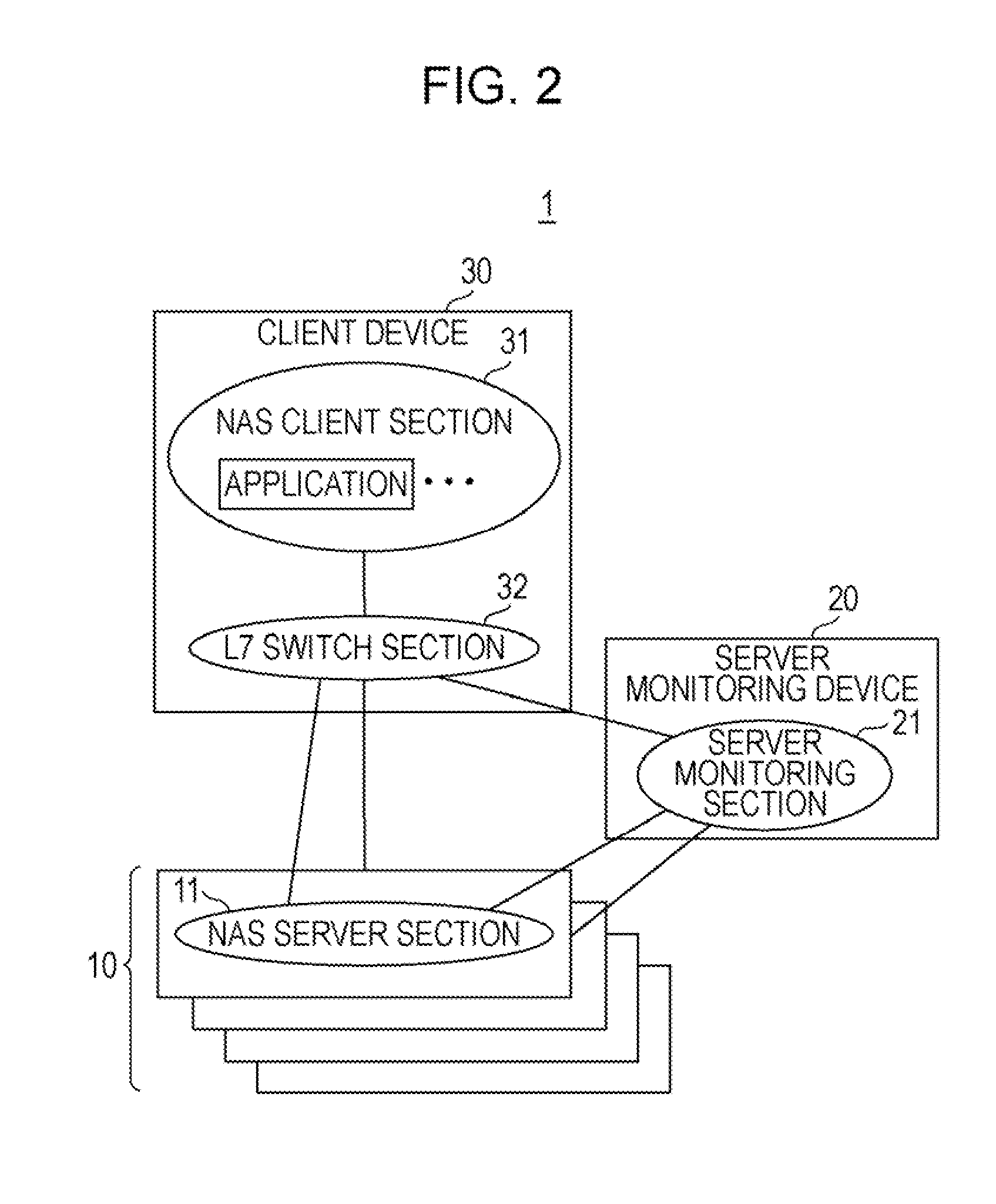
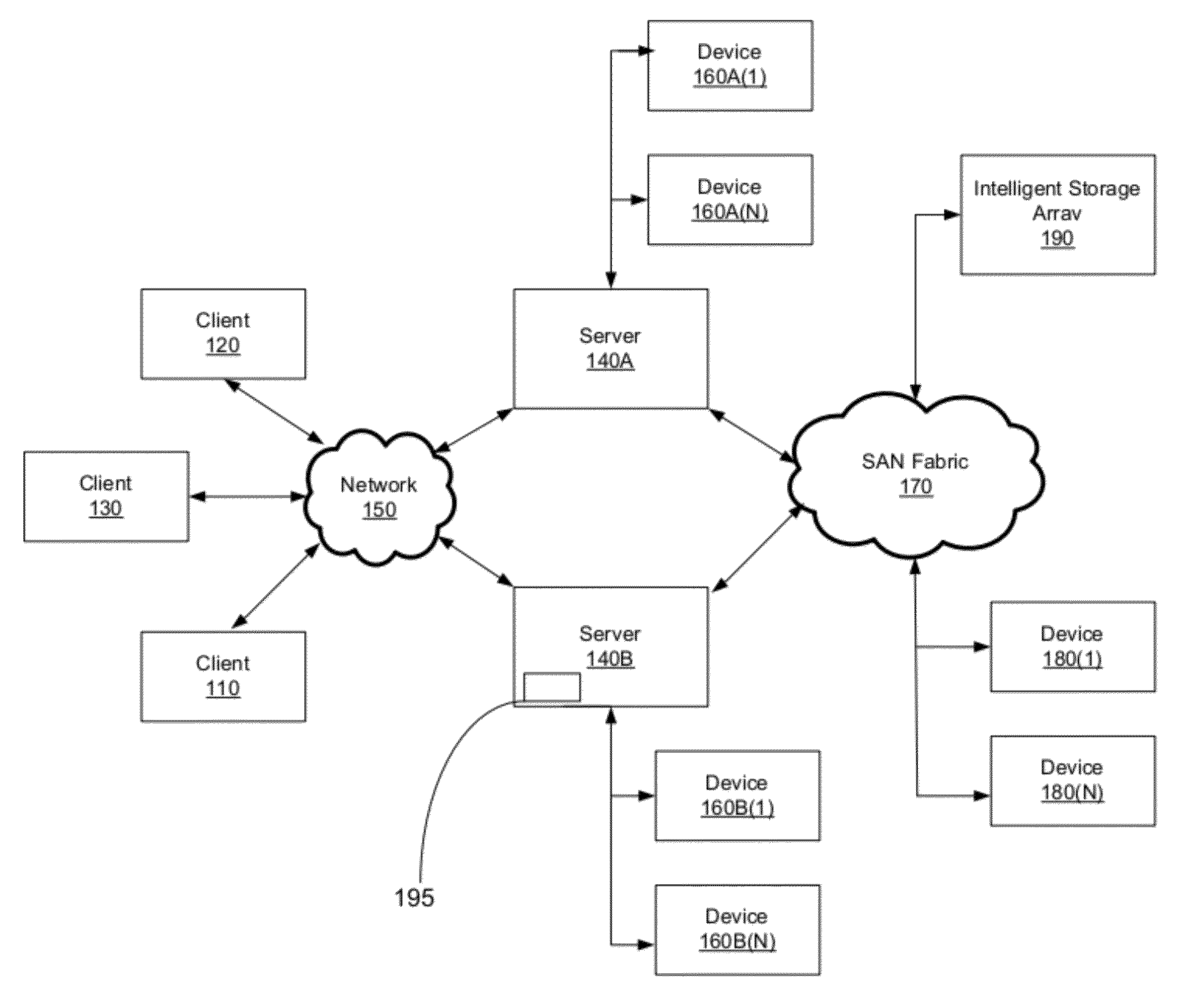
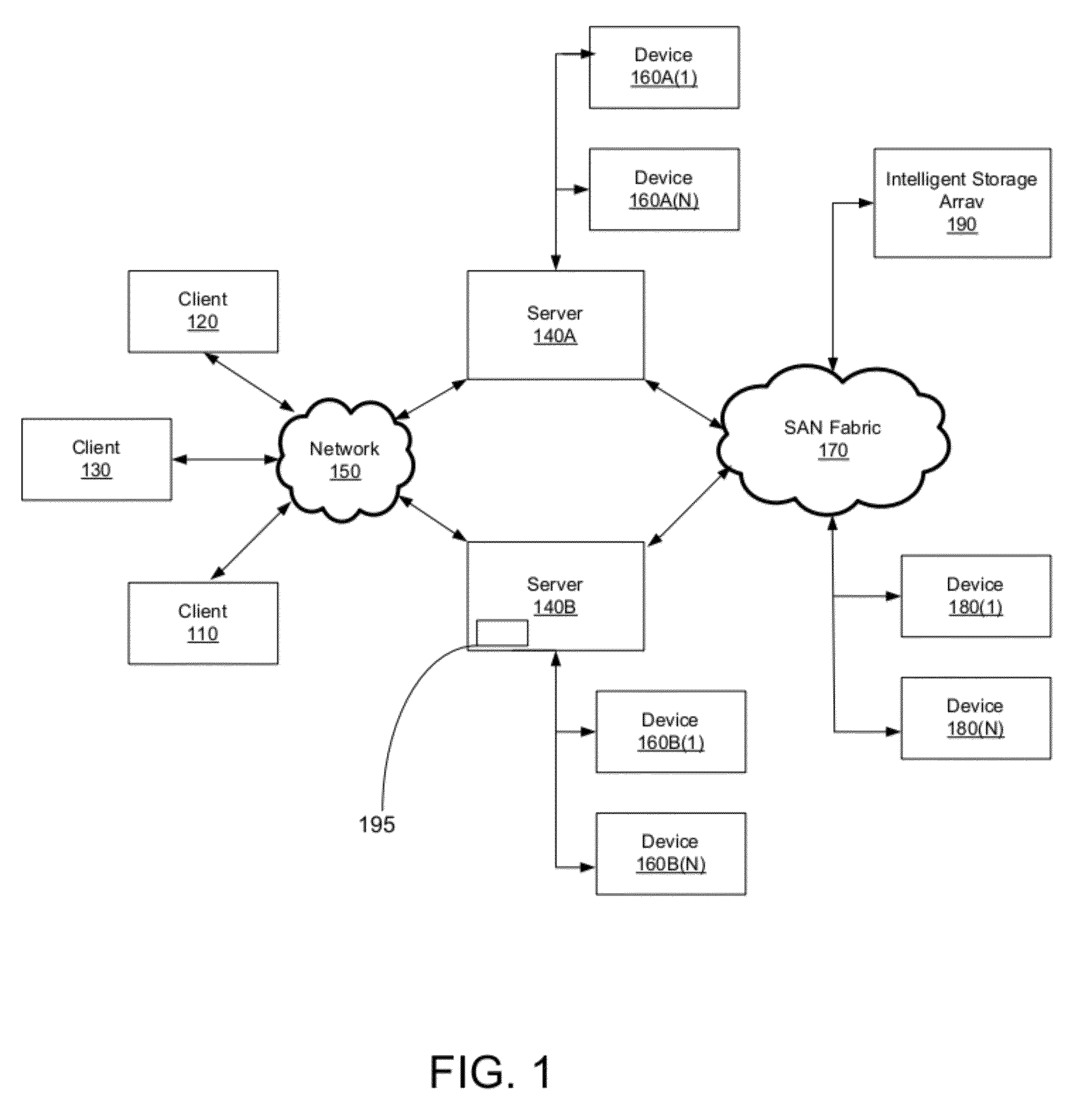
File server system using file system storage, data movers, and an exchange of meta data among data movers for file locking and direct access to shared file systems
InactiveUS6324581B1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsFile systemData access
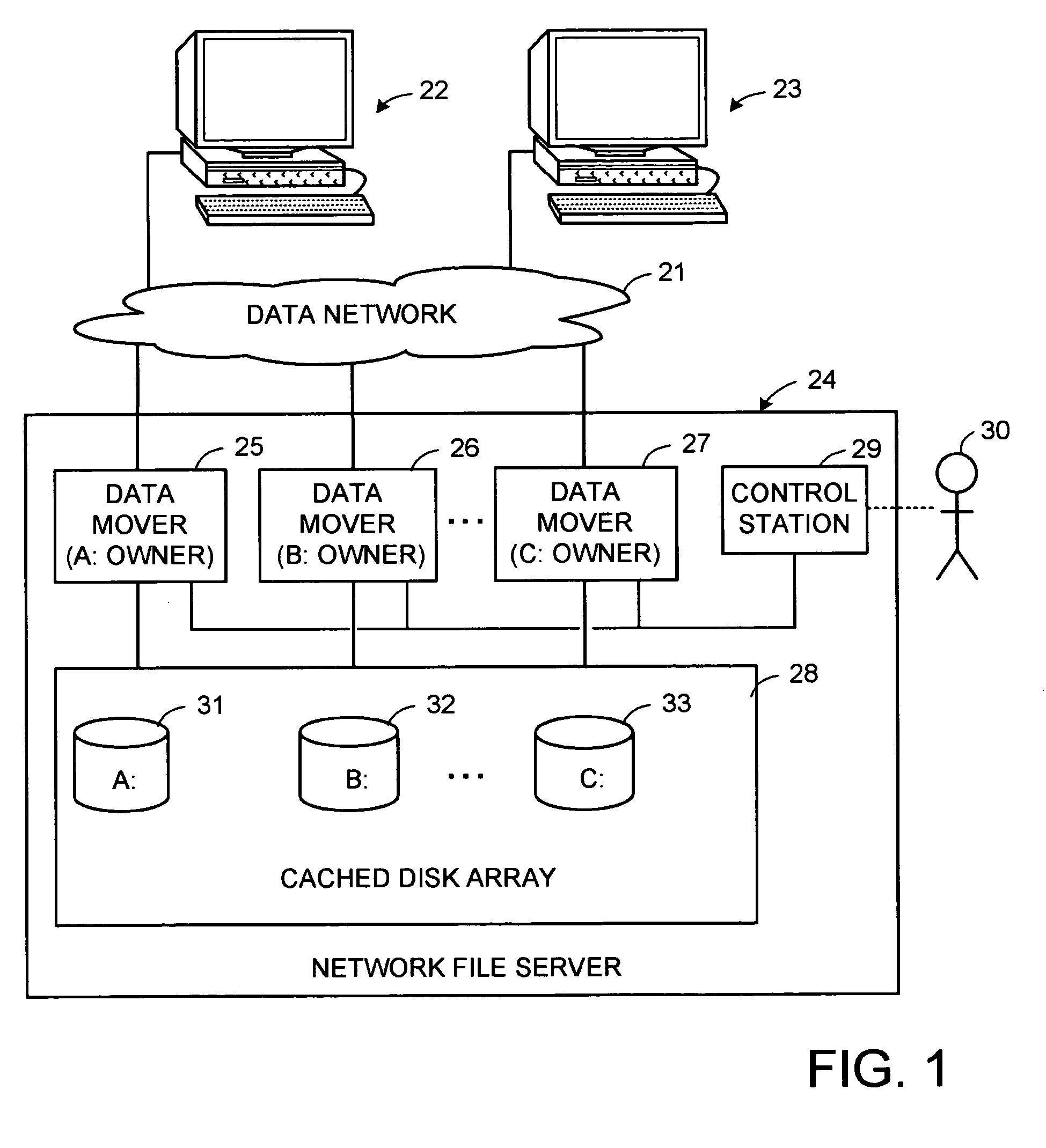
A plurality of data mover computers control access to respective file systems in data storage. A network client serviced by any of the data movers can access each of the file systems. If a data mover receives a client request for access to a file in a file system to which access is controlled by another data mover, then the data mover that received the client request sends a metadata request to the data mover that controls access to the file system. The data mover that controls access to the file system responds by placing a lock on the file and returning metadata of the file. The data mover that received the client request uses the metadata to formulate a data access command that is used to access the file data in the file system over a bypass data path that bypasses the data mover computer that controls access to the file system.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
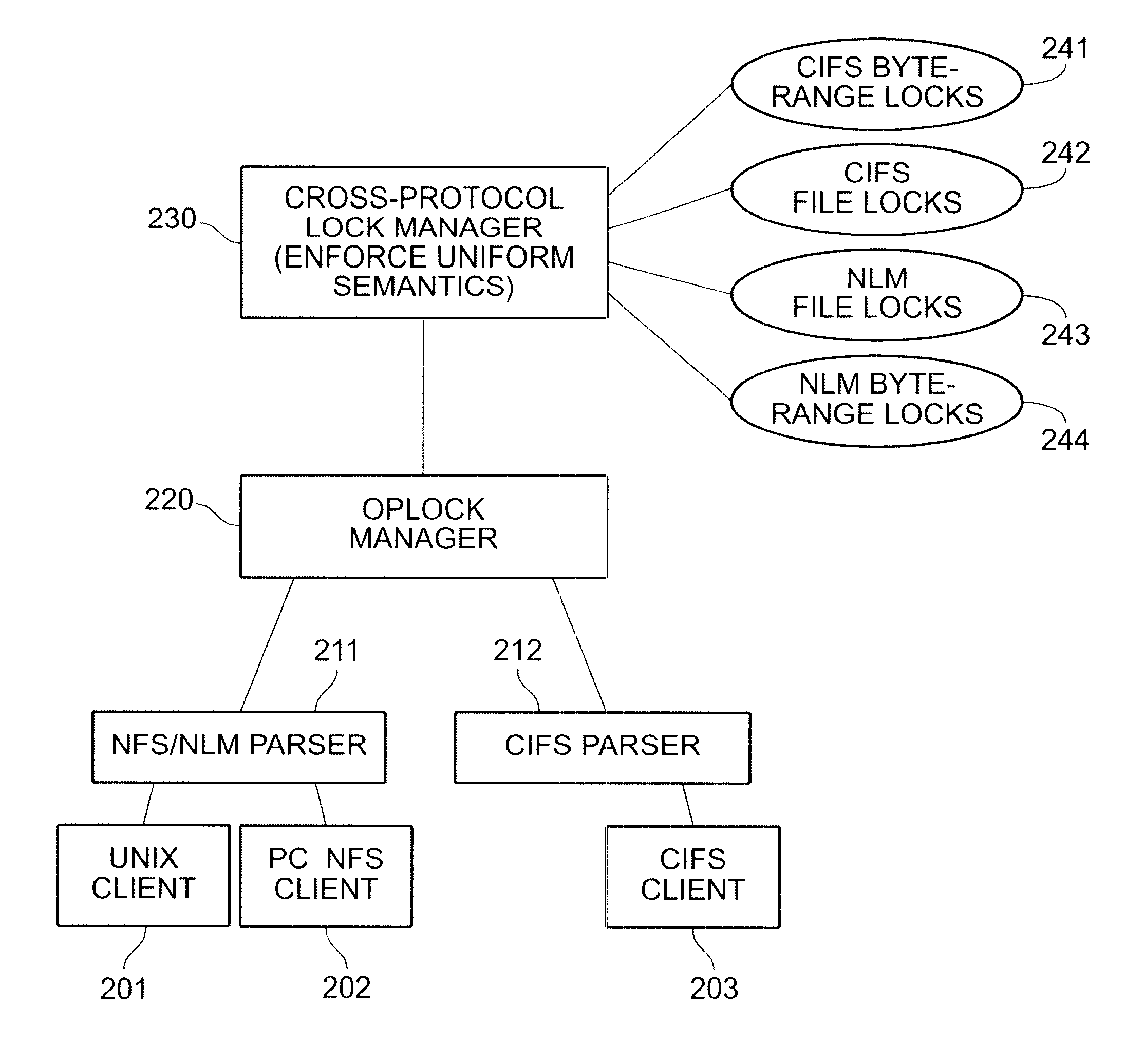
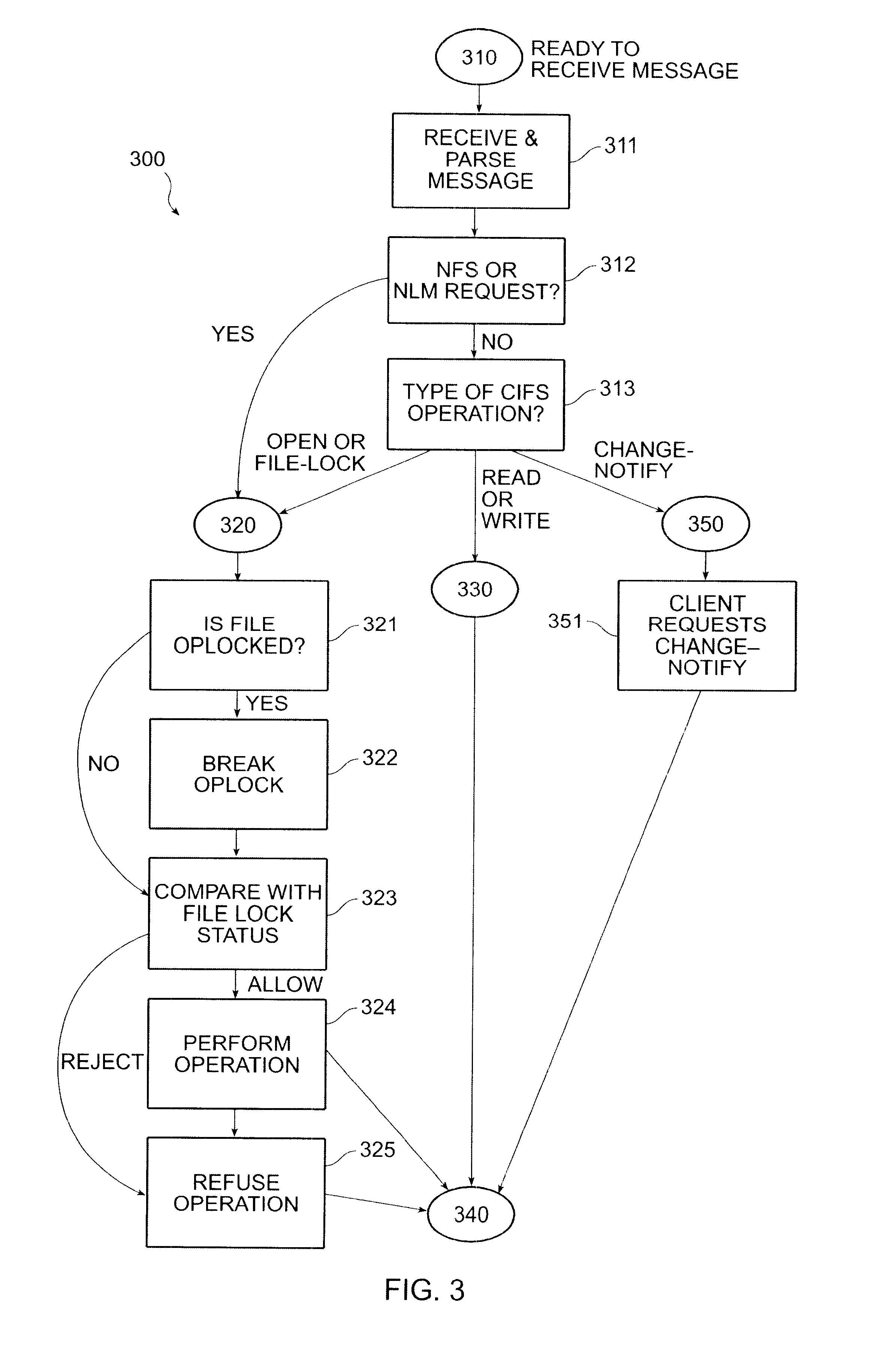
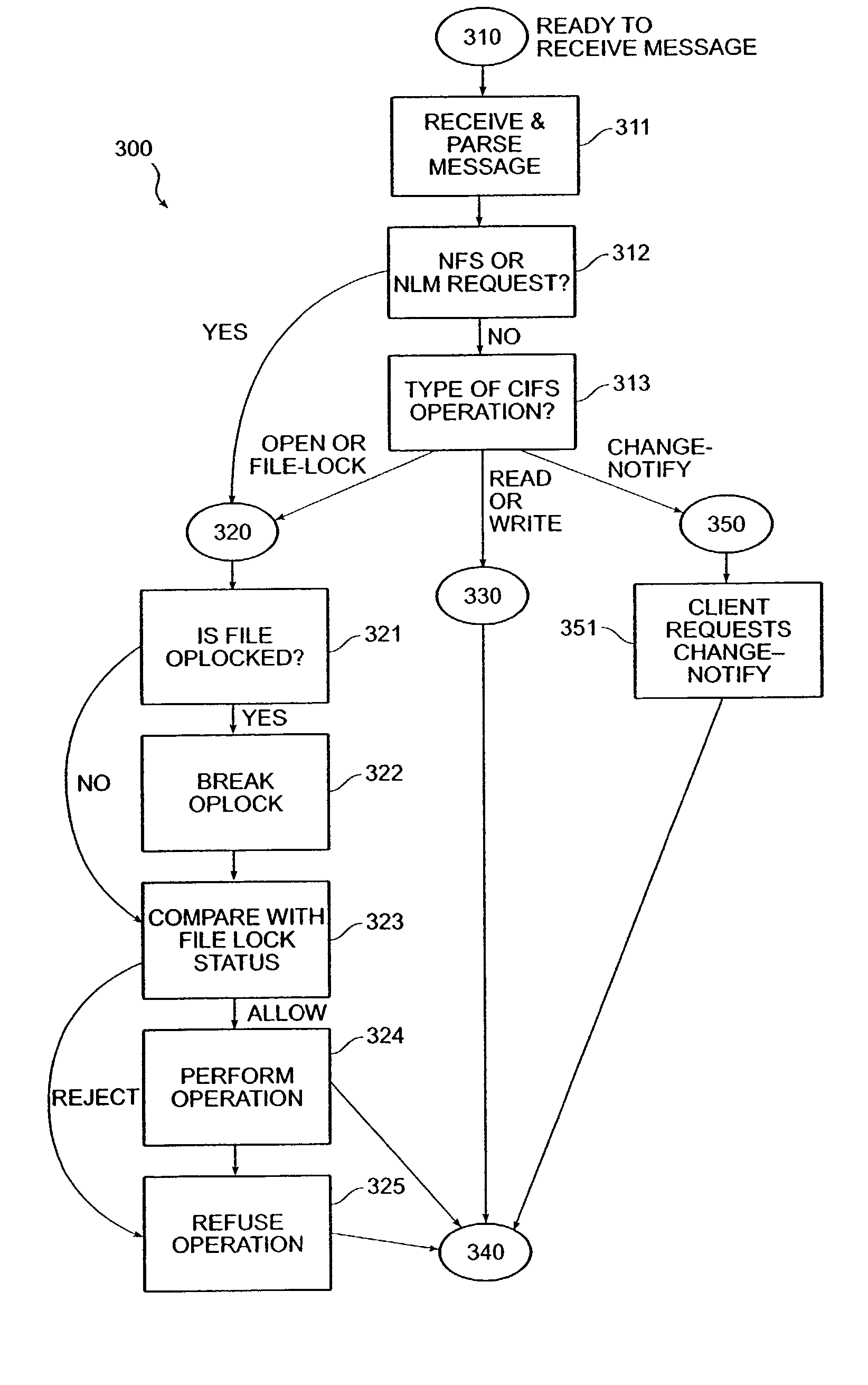
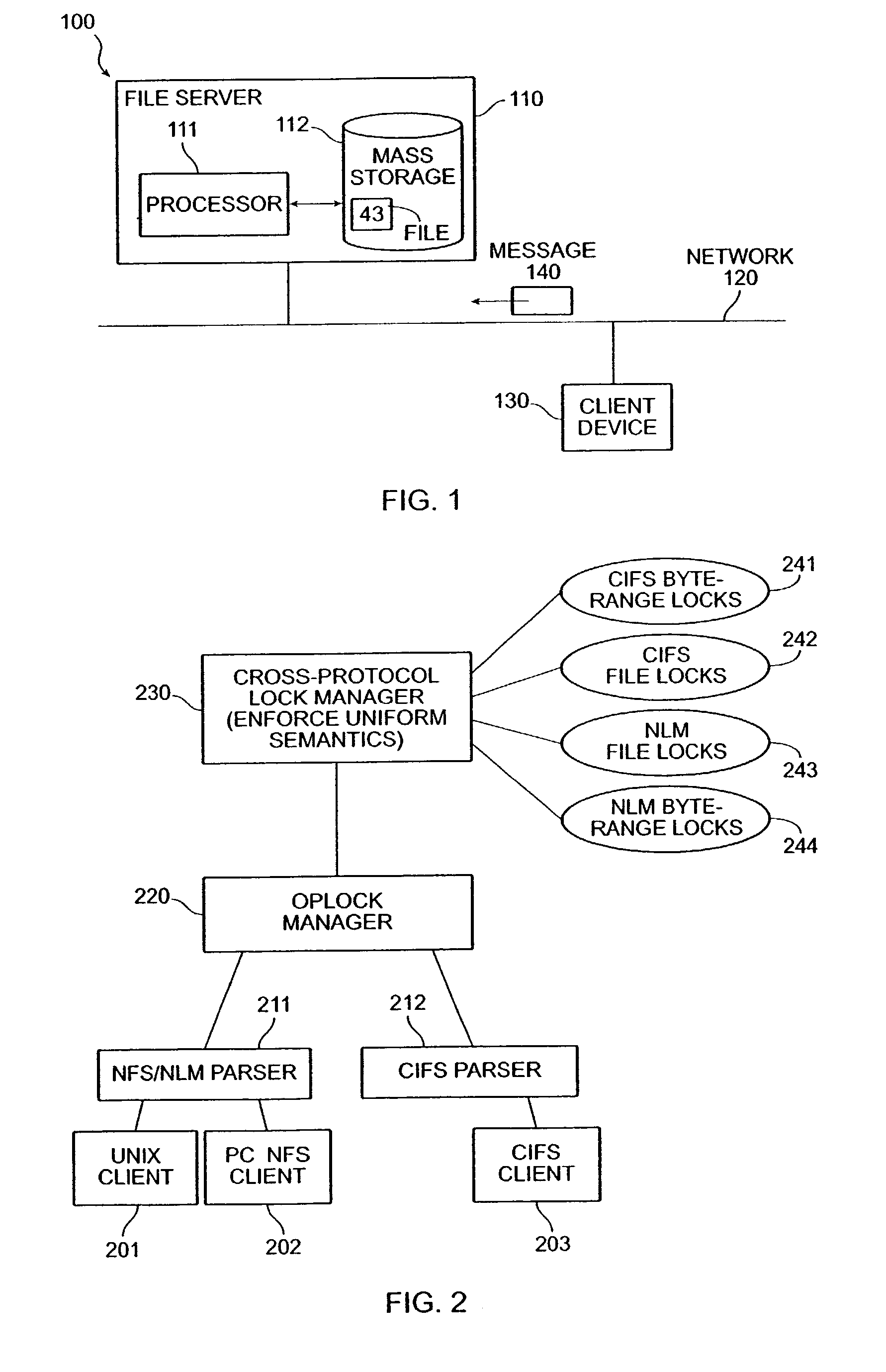
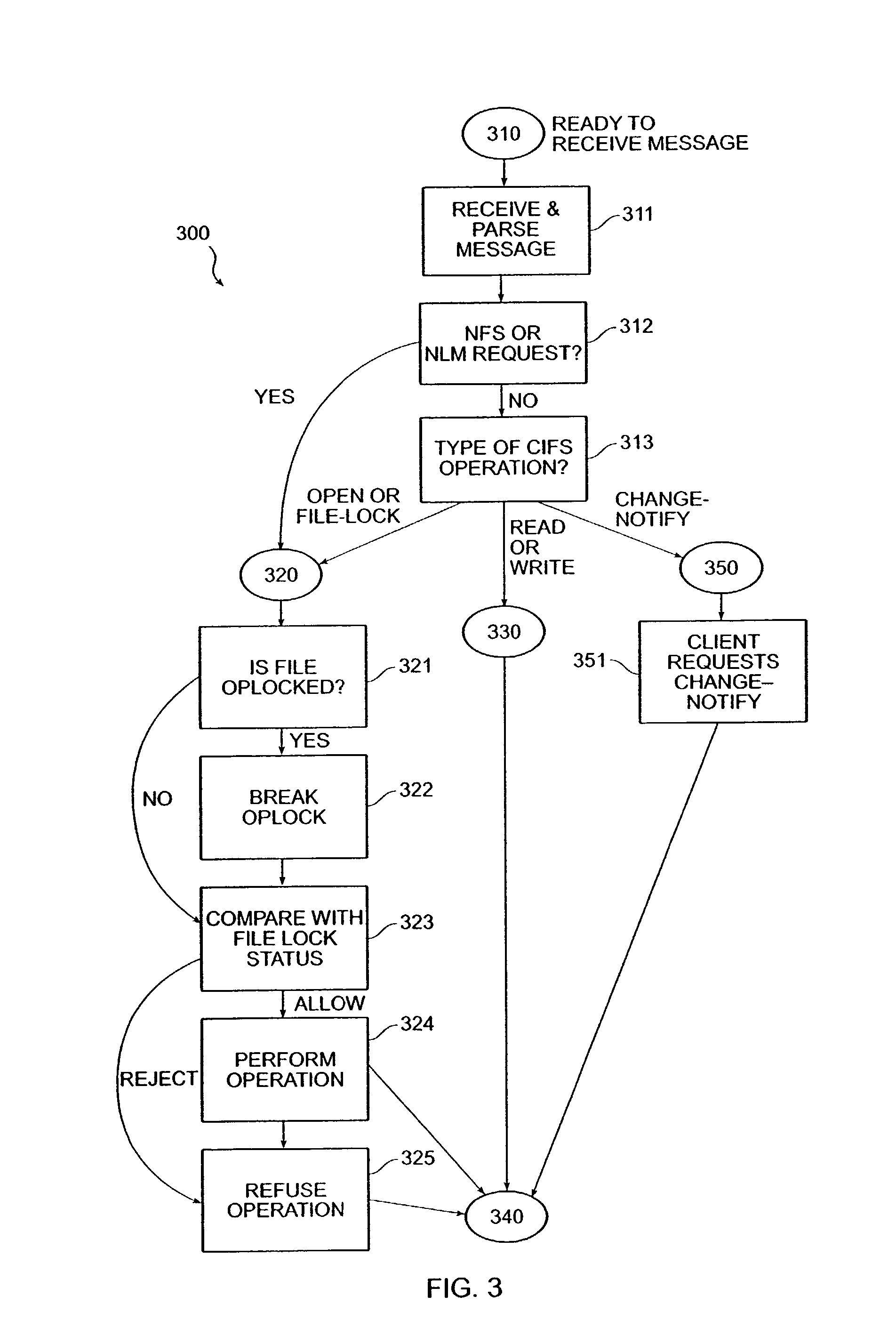
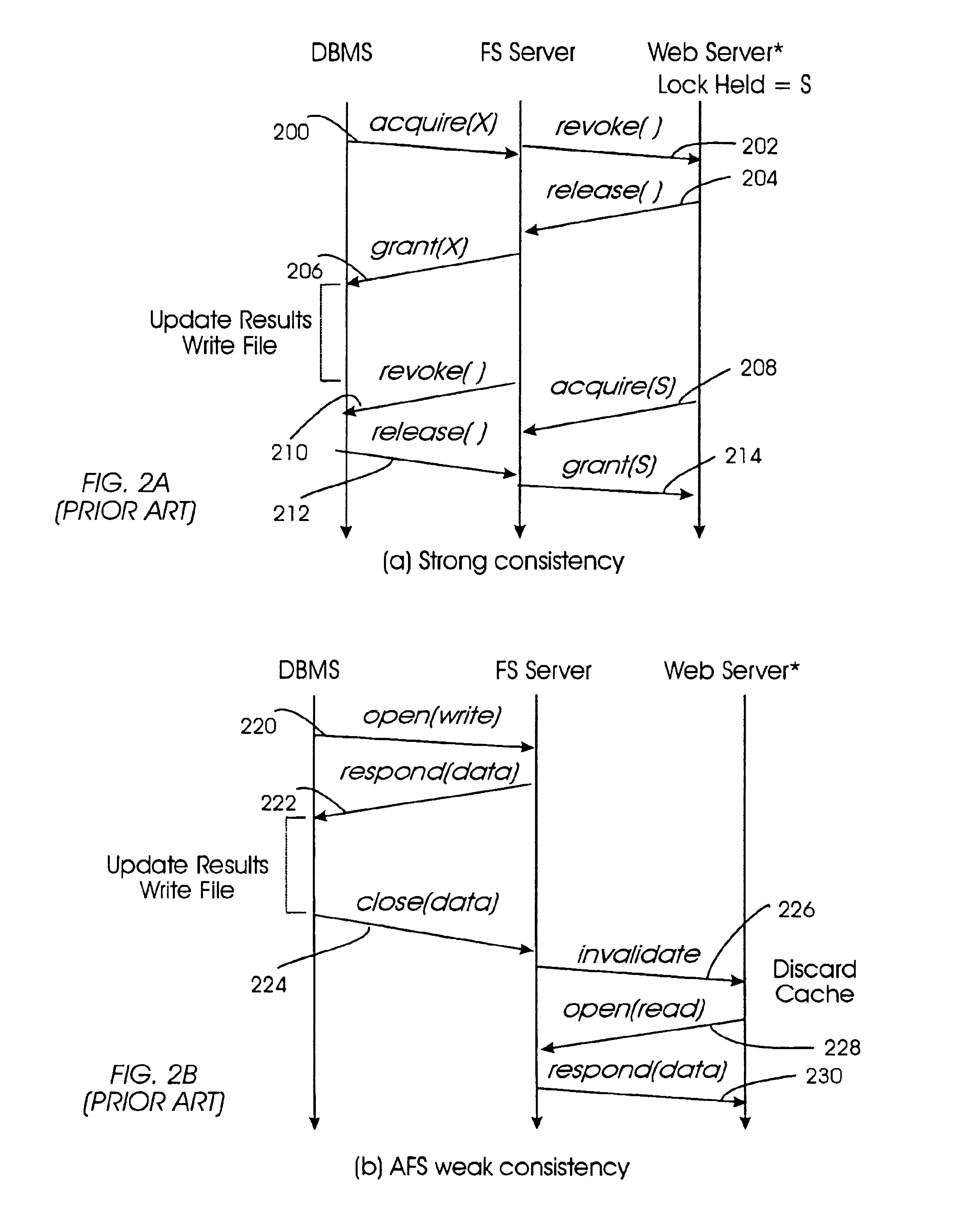
Enforcing uniform file-locking for diverse file-locking protocols
InactiveUS6516351B2Close fileData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalFile systemSemantics
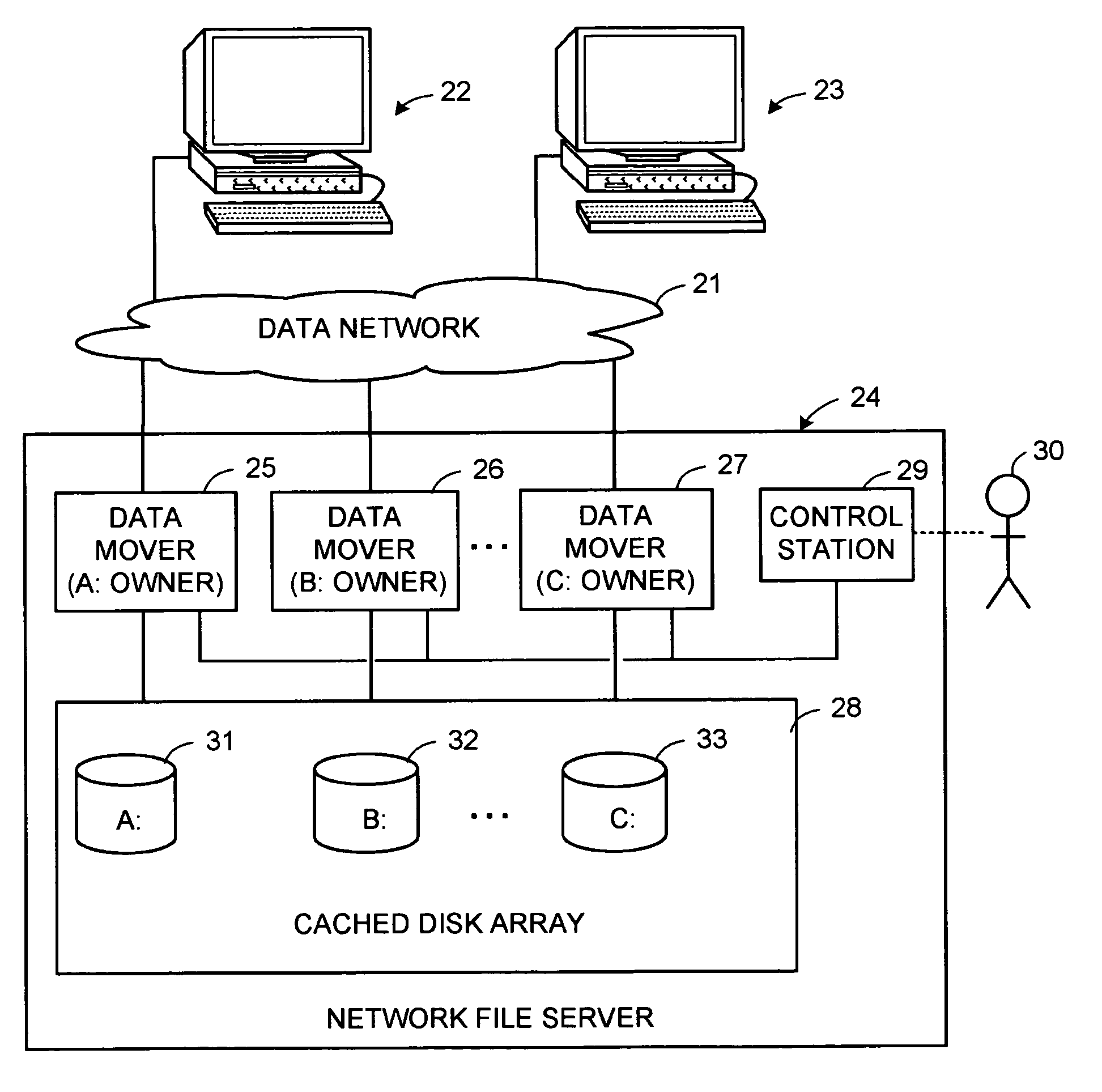
The invention provides a method and system for correct interoperation of multiple diverse file server or file locking protocols, using a uniform multi-protocol lock management system. A file server determines, before allowing any client device to access data or to obtain a lock, whether that would be inconsistent with existing locks, regardless of originating client device or originating protocol for those existing locks. A first protocol enforces mandatory file-open and file-locking together with an opportunistic file-locking technique, while a second protocol lacks file-open semantics and provides only for advisory byte-range and file locking. Enforcing file-locking protects file data against corruption by NFS client devices. A CIFS client device, upon opening a file, can obtain an "oplock" (an opportunistic lock). When a client device issues a non-CIFS protocol request for the oplocked file, the file server sends an oplock-break message to the CIFS client device, giving the CIFS client device the opportunity to flush any cached write operations and possibly close the file. Allowing NFS and NLM requests to break oplocks ensures that file data remains available to NFS client devices simultaneously with protecting integrity of that file data. A CIFS client device can obtain a "change-monitoring" lock for a directory in the file system, so as to be notified by the file server whenever there is a change to that directory. The file server notes changes to the directory by both CIFS and non-CIFS client devices, and notifies those CIFS client devices with "change-monitoring" locks of those changes.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
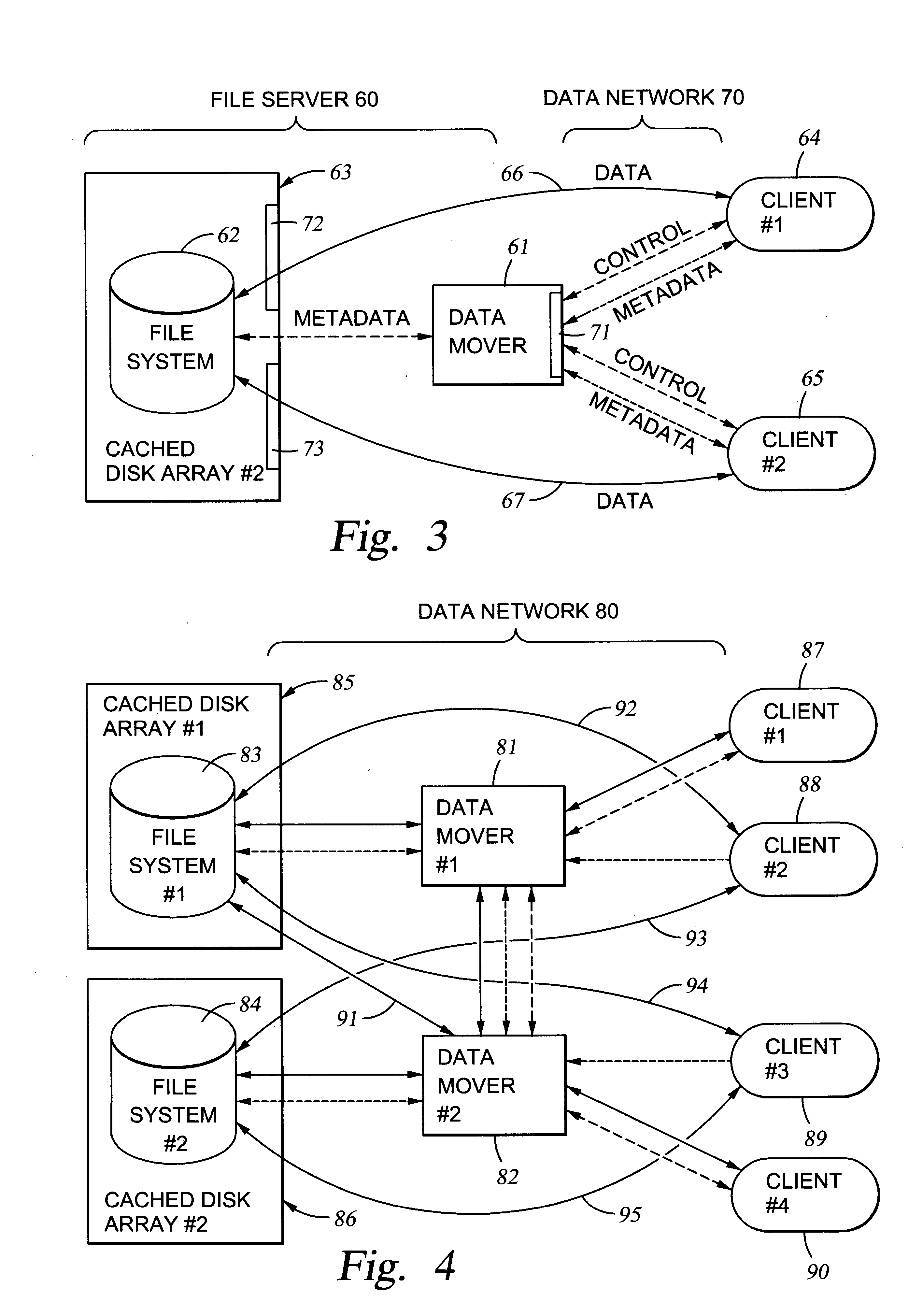
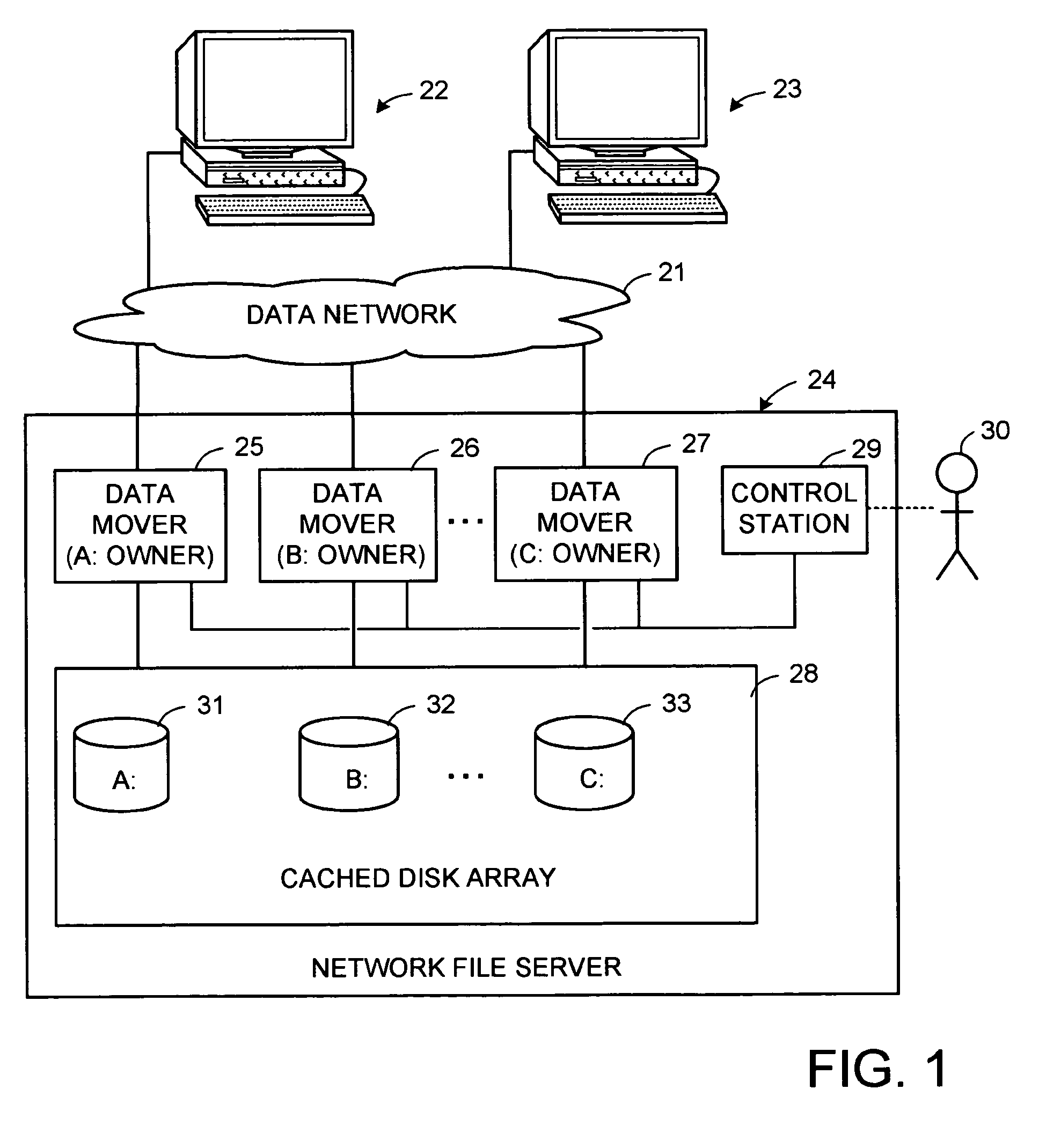
Lock management for concurrent access to a single file from multiple data mover computers
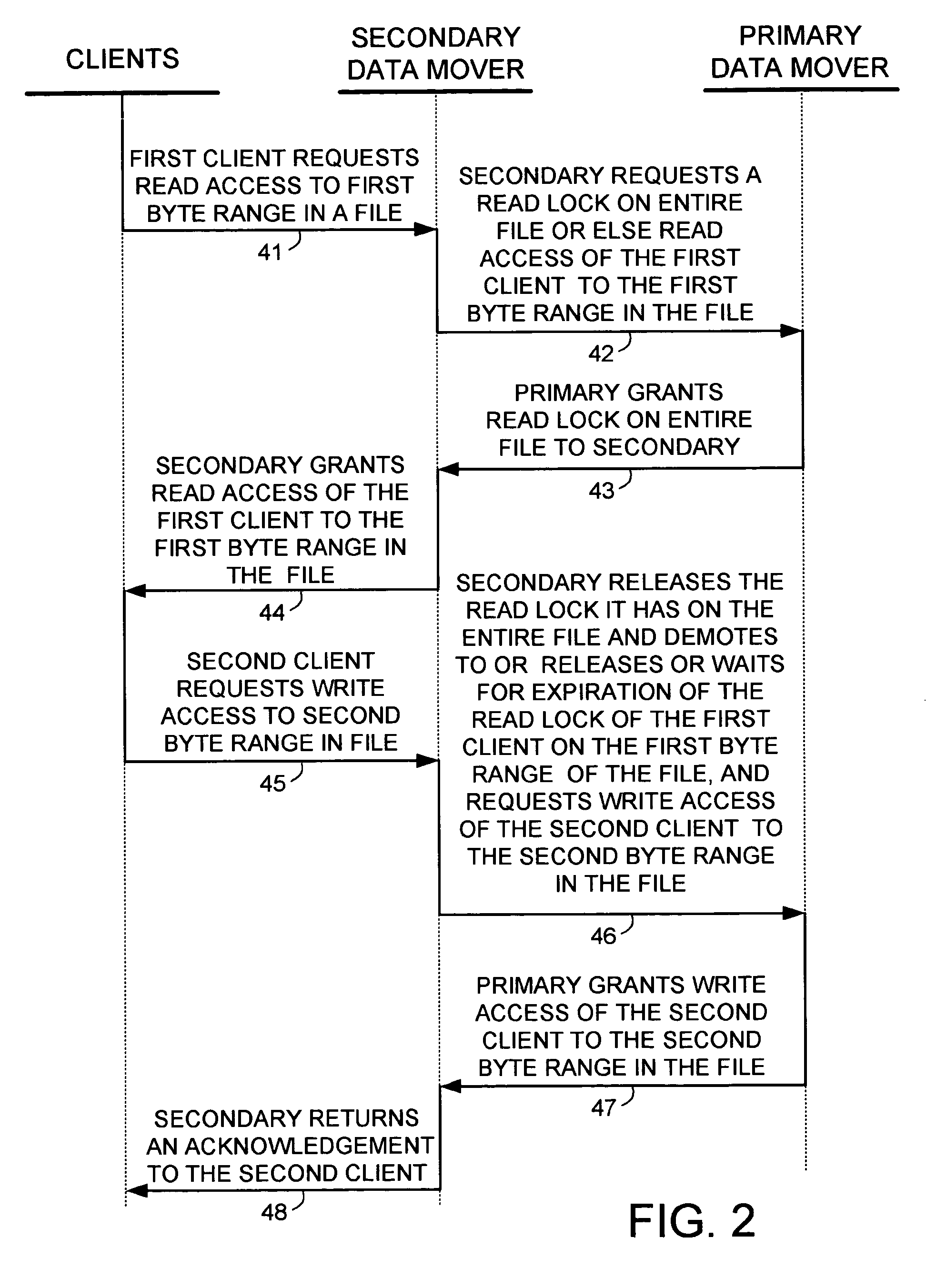
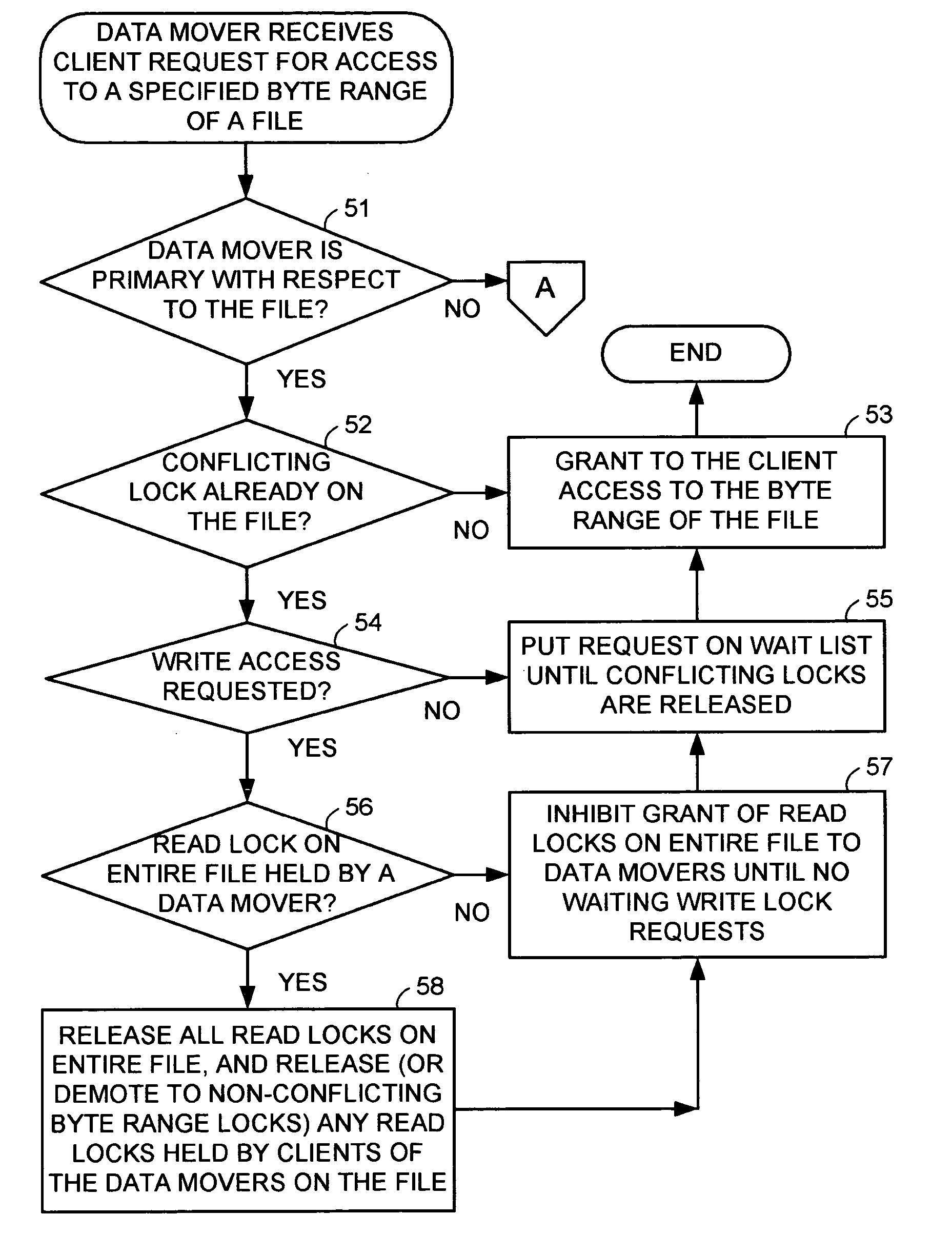
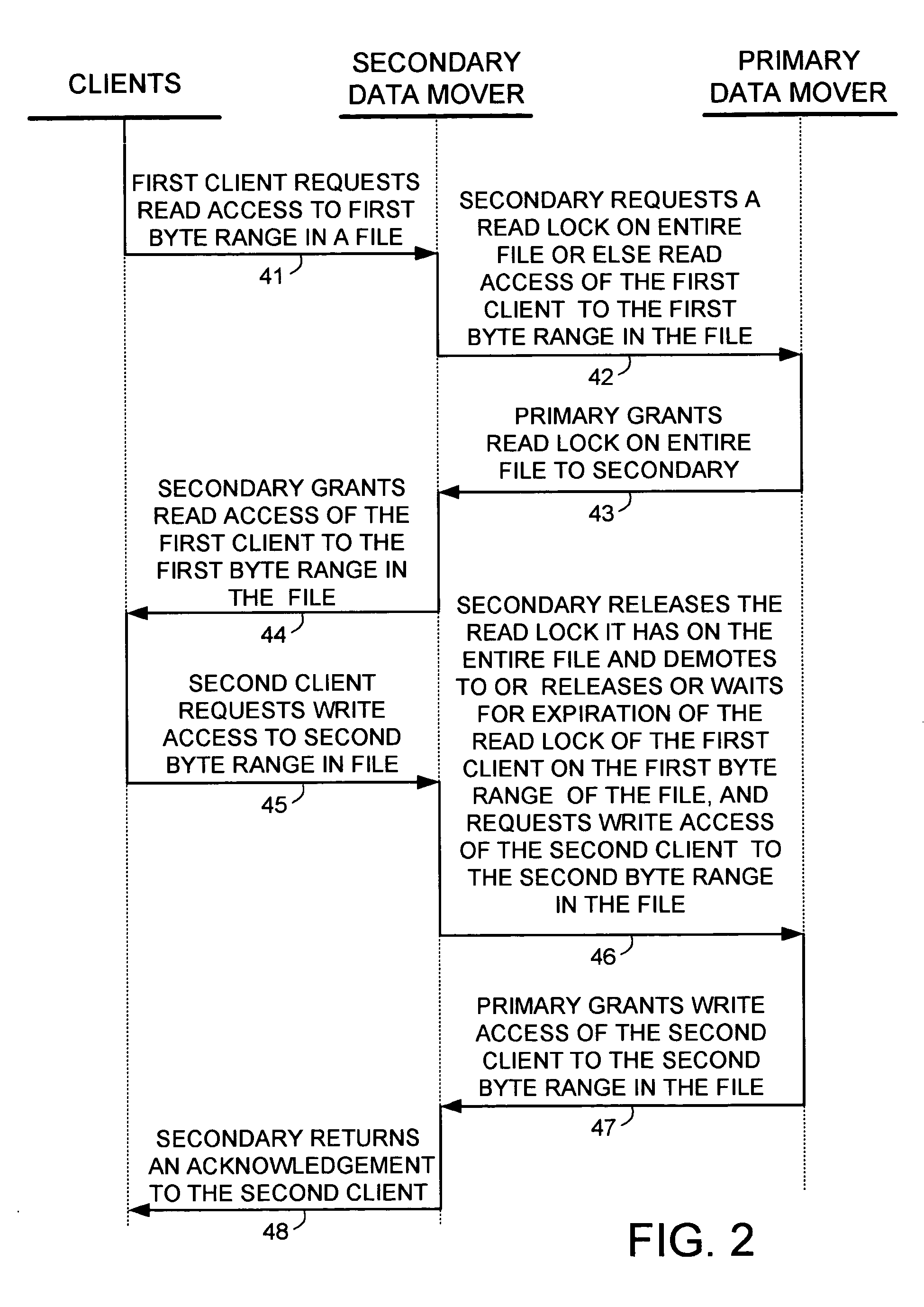
A protocol is provided for allocating file locking tasks between primary and secondary data mover computers in a network file server. When there is frequent read access and infrequent write access to a file, a primary data mover grants read locks to the entire file to secondary data movers, and the secondary data movers grant read locks to clients requesting read access. When write access to the file is needed, the read locks to the entire file are released and the read locks granted to the clients are released or expire or are demoted to non-conflicting byte range locks managed by the primary data mover. Concurrent read and write access to the same file is then managed by the primary data mover.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Lock management for concurrent access to a single file from multiple data mover computers
A protocol is provided for allocating file locking tasks between primary and secondary data mover computers in a network file server. When there is frequent read access and infrequent write access to a file, a primary data mover grants read locks to the entire file to secondary data movers, and the secondary data movers grant read locks to clients requesting read access. When write access to the file is needed, the read locks to the entire file are released and the read locks granted to the clients are released or expire or are demoted to non-conflicting byte range locks managed by the primary data mover. Concurrent read and write access to the same file is then managed by the primary data mover.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Enforcing uniform file-locking for diverse file-locking protocols
InactiveUS7293097B2Close fileData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalSoftware engineeringMulti protocol
The invention provides a method and system for connect interoperation of multiple diverse file server or file locking protocols, using a uniform multi-protocol lock management system. A file server determines, before allowing any client device to access data or to obtain a lock, whether that would be inconsistent with existing locks, regardless of originating client device or originating protocol for those existing locks. A first protocol enforces mandatory file-open and file-locking together with an opportunistic file-locking technique, while a second protocol lacks file-open semantics and provides only for advisory byte-range and file locking.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
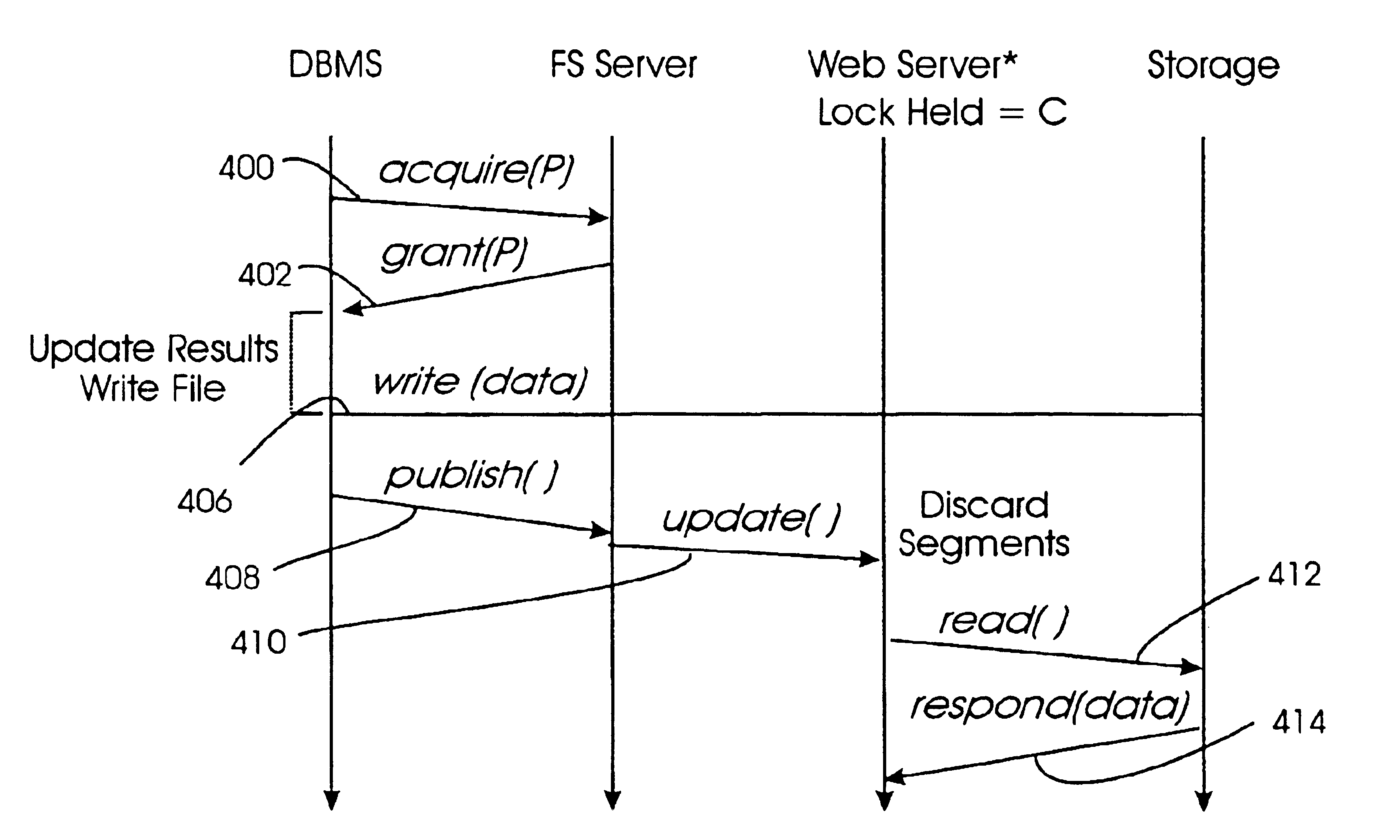
Producer/consumer locking system for efficient replication of file data
InactiveUS6925515B2Eliminates lock contentionEliminate the waiting processDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsQuality of serviceSystems design
In a distributed file system the distributed storage management is made useful to a variety of applications. Multiple quality of service options are provided through locking. Three locking systems are provided. The system offers a locking system designed for sequential consistency with write-back caching, typical of distributed file systems. A second locking system is provided for sequential consistency with no caching for applications that manage their own caches. Finally, a locking system that implements a weaker consistency model with write-back caching, designed for efficient replication and distribution of data is included. Locks for replication are suitable for serving dynamic data on the Internet and other highly-concurrent applications. The selection of the appropriate lock protocol for each file is set using the file metadata. Further, a novel locking system is provided for the lock system implementing a weak consistency model with write back caching. This system is implemented utilizing two whole file locks: a producer lock P and a consumer lock C. Any client can hold a consumer lock and when holding a consumer lock can read data and cache data for read. The producer lock is only held by a single writer and a writer holding a producer lock can write data, allocate and cache data for writing. When a writer performs a write, the write is performed as an out-of-place write. An out-of-place write writes the data to a different physical storage location than from which it was read. By performing an out-of-place write the old data still exists and is available to clients. Once the writer completes the write and releases the producer lock the previous data is invalidated and the clients are informed of the new location of the data. Clients can then read the new data from storage when needed and the server reclaims the old data blocks.
Owner:IBM CORP
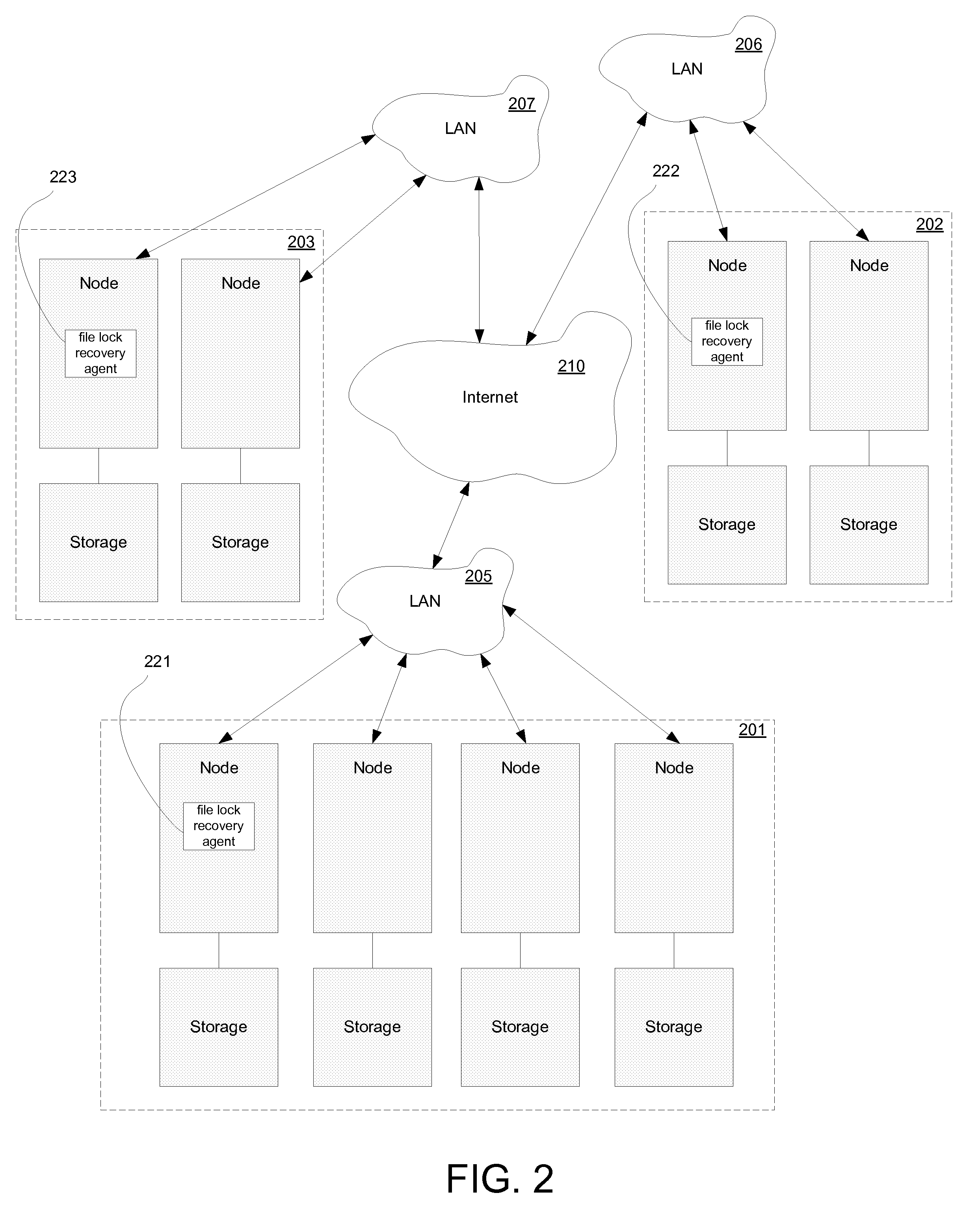
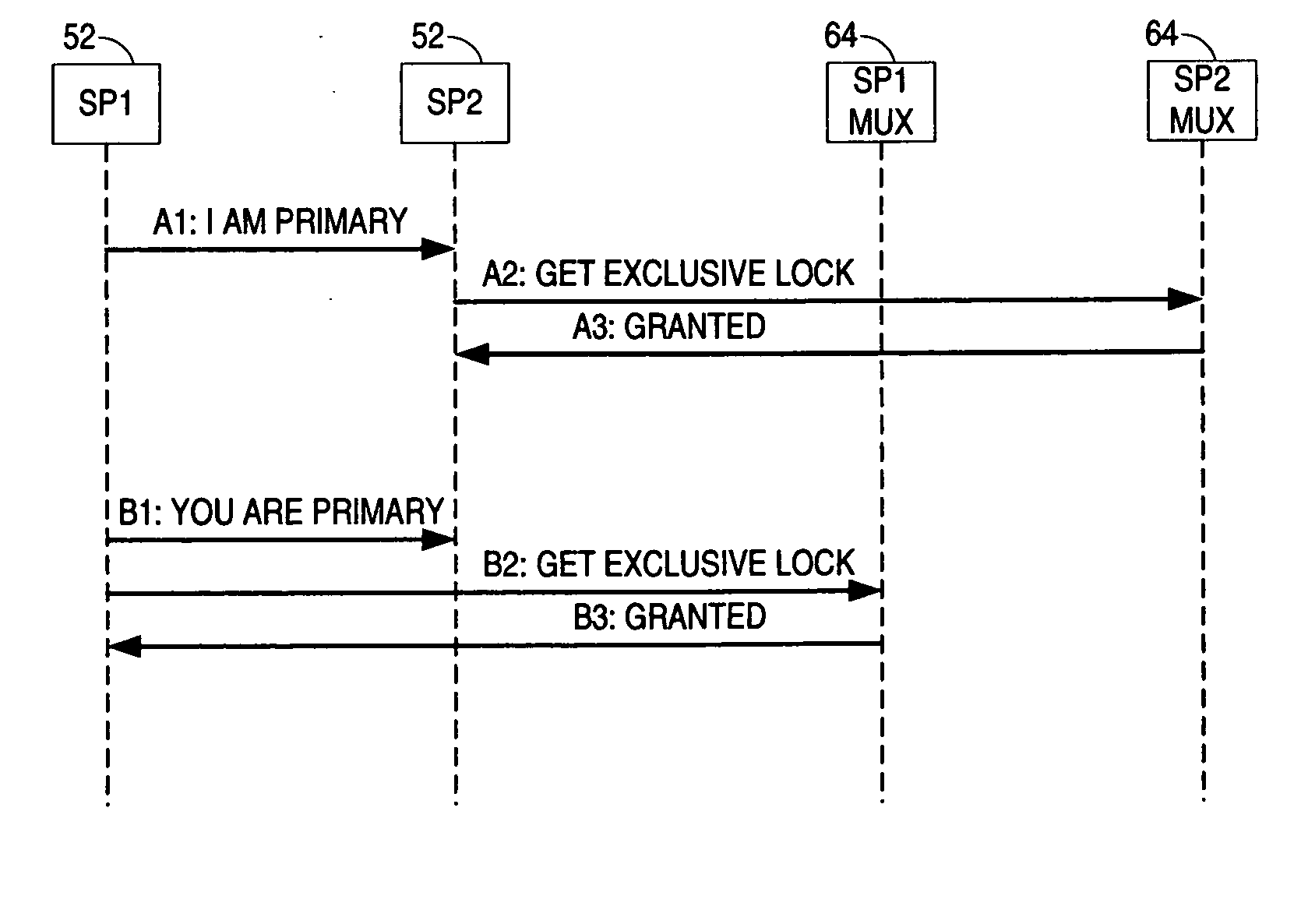
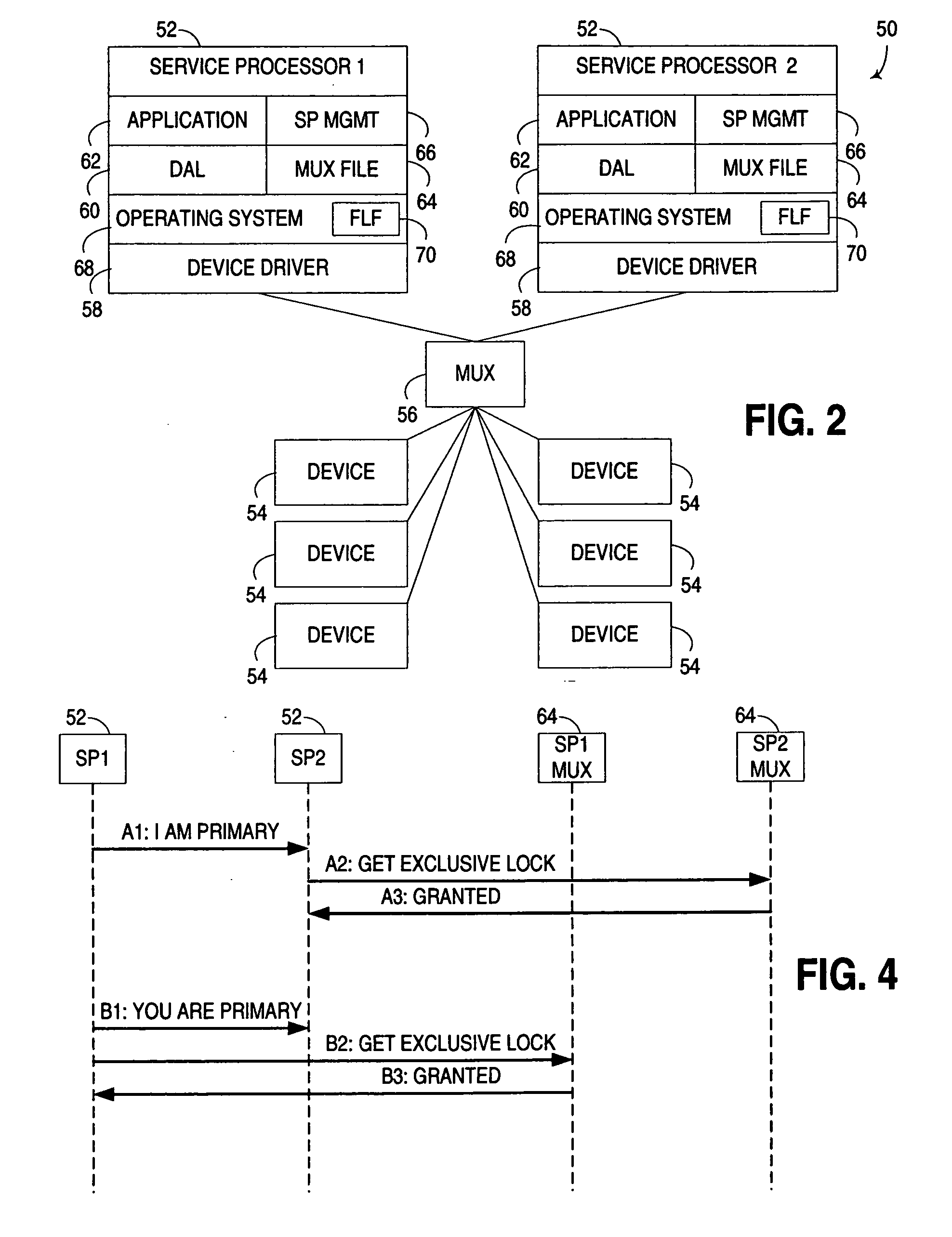
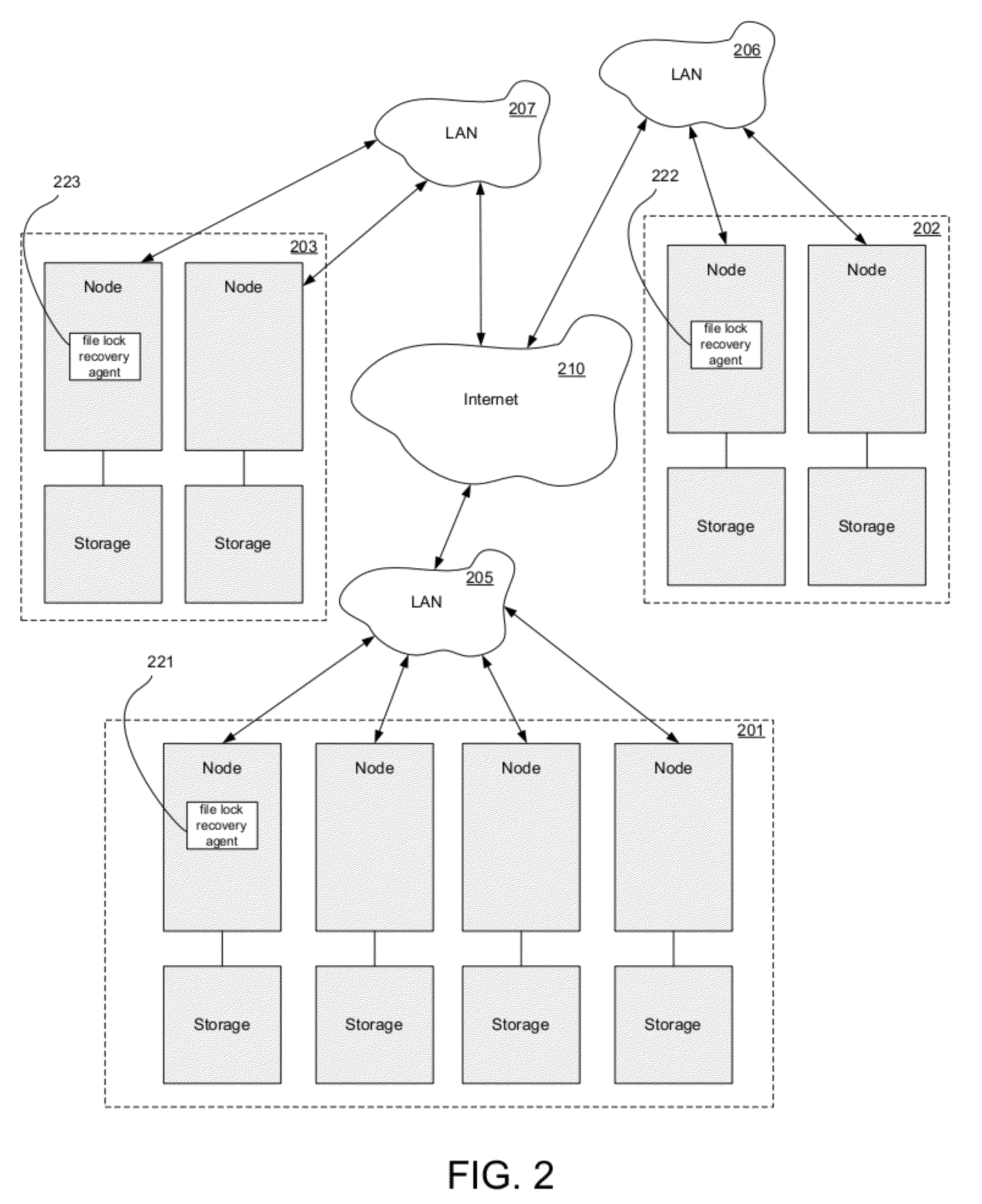
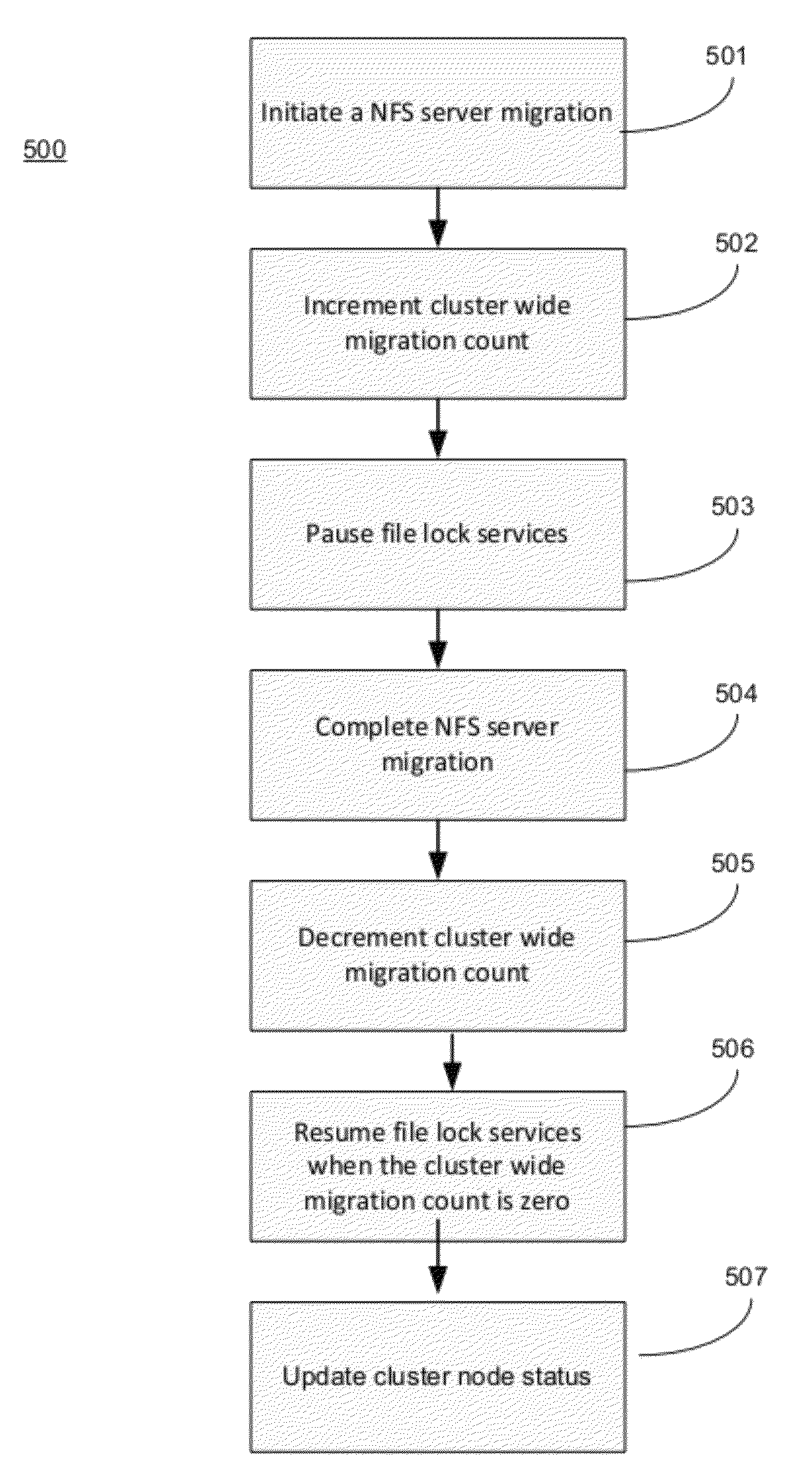
Method and system for performing a clean file lock recovery during a network filesystem server migration or failover
ActiveUS20120259819A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFailoverComputerized system
A method for file lock recovery in a distributed computer system. The method includes executing a distributed computer system having a plurality of nodes comprising a cluster, and initiating a network file system server migration from one node of the cluster to a different node of the cluster. A migration count is incremented, wherein the migration count is stored at each of the nodes comprising the cluster. File lock services are paused at each of the nodes comprising the cluster. The network file system server migration is completed at the different node of the cluster. The migration count is then decremented in response to the completion. File lock services are then resumed at each of the nodes comprising cluster.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
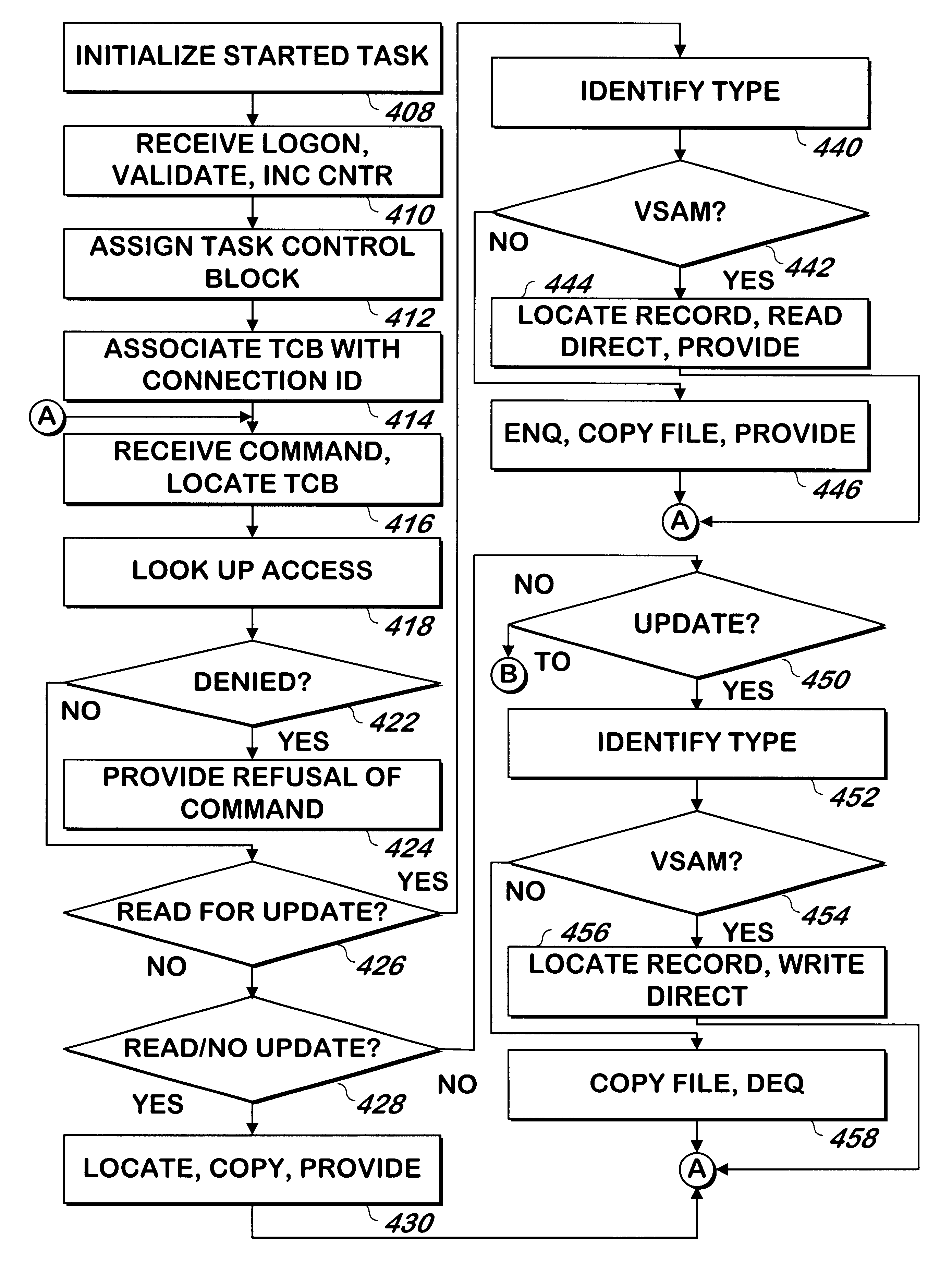
System and method for serving host computer files to one or more client computer systems
InactiveUS6253236B1Unauthorized memory use protectionComputer security arrangementsComputerized systemClient-side
A system and method allows a host computer to operate as a server in a client-server arrangement in response to requests from client computer systems. The system and computer program product performs reads, reads for update, update and deletes on some or all records in a file, depending on the type of file. Record or file locking is provided when applicable. Security is provided at the file level. Abnormal ends of communication with the client computer system are detected to allow resources and record or file locks to be freed in such event. A counter is incremented at the time a client computer system logs into the host computer system to enforce limits on the number of concurrent users, and ordinary log off as well as abnormal ends of communication decrement the counter to maintain its accuracy.
Owner:SERENA SOFTWARE
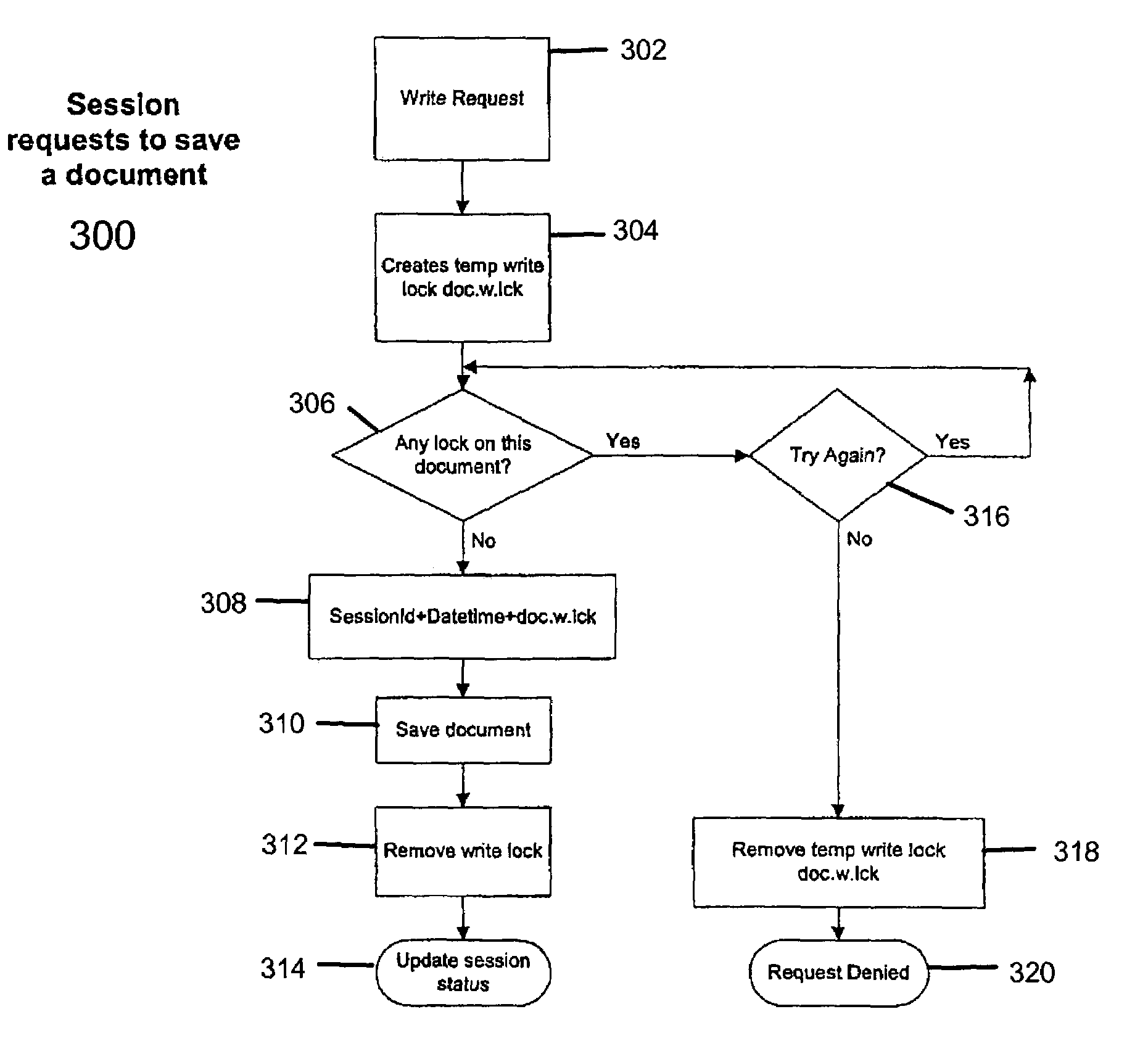
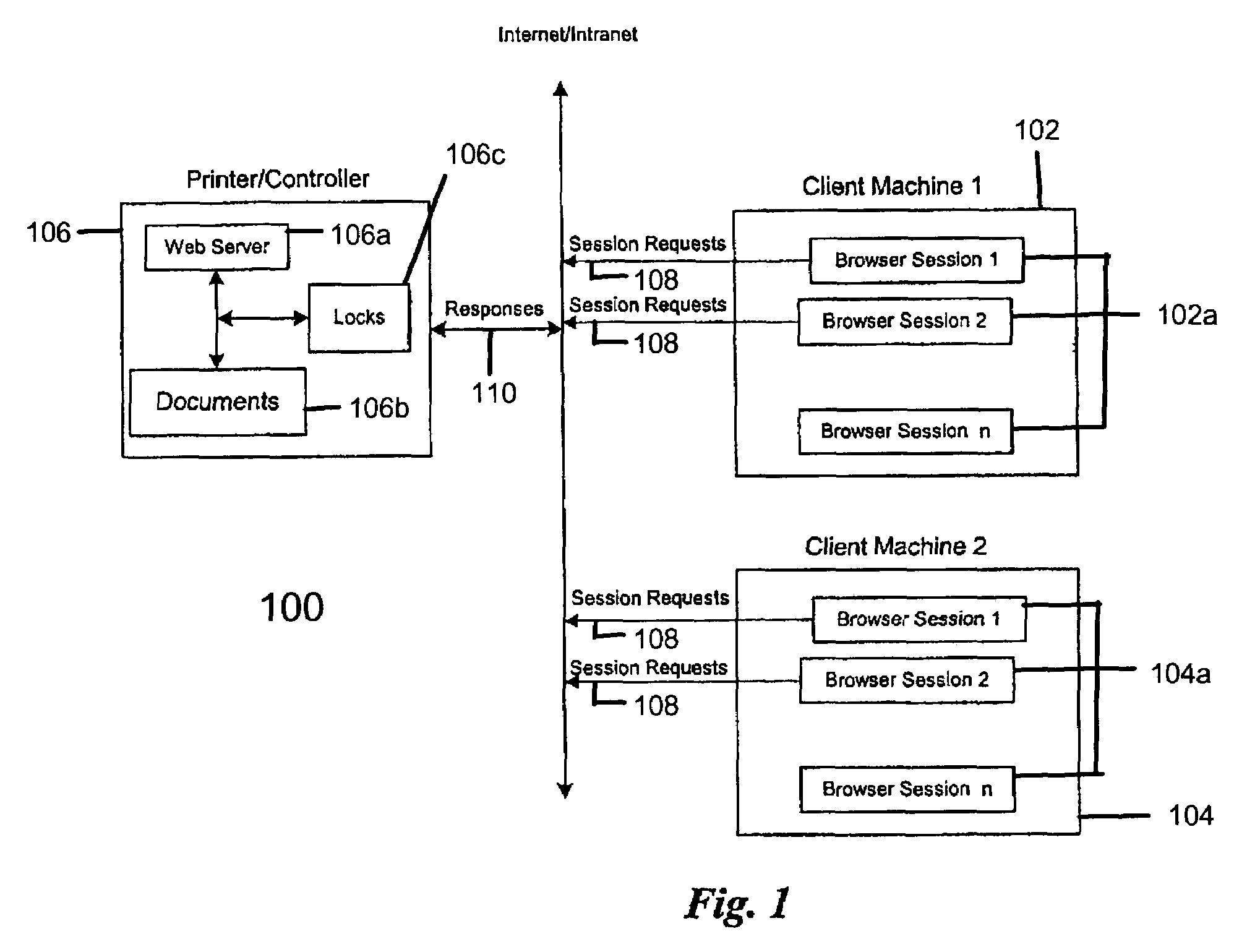
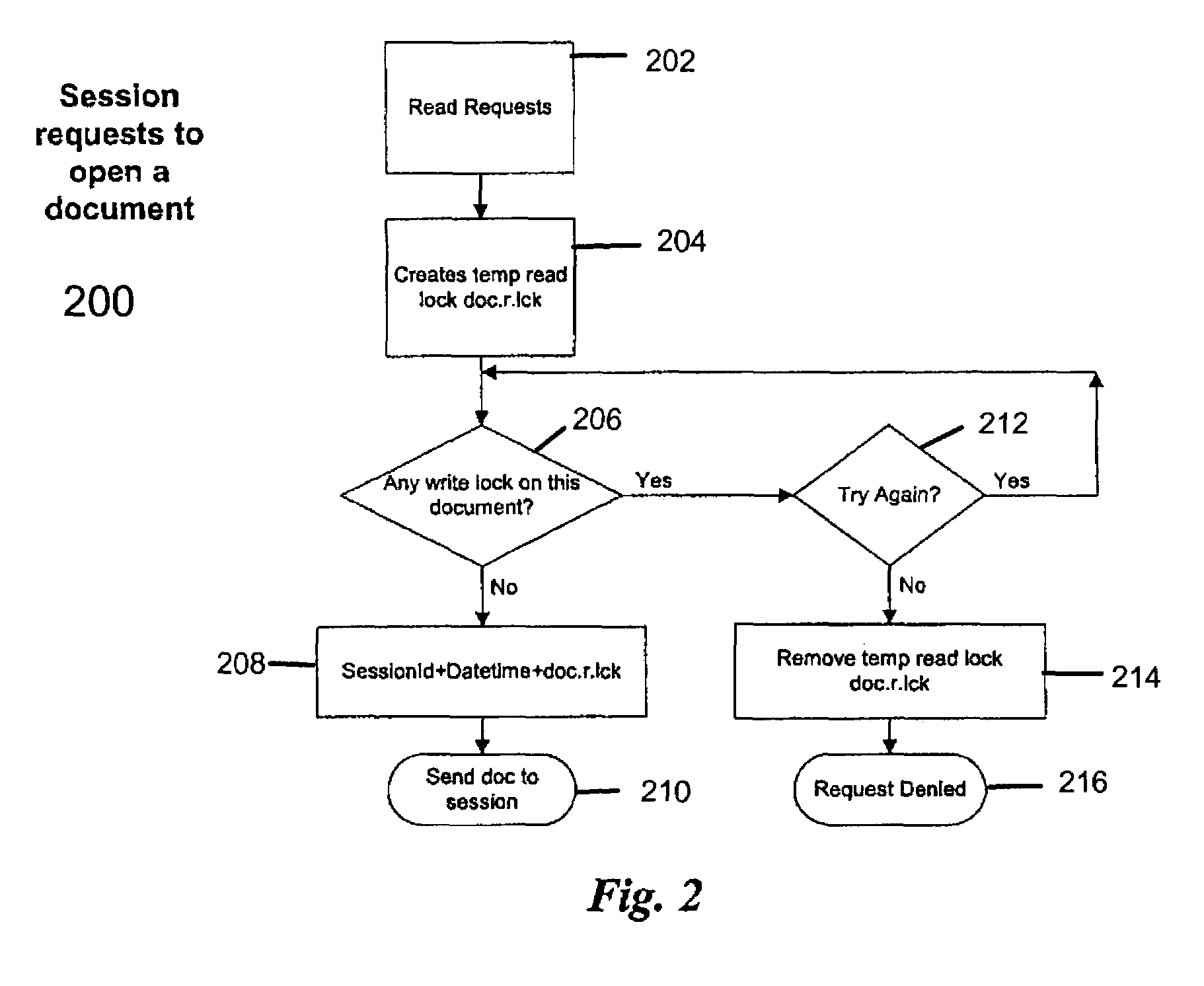
Method and implementation of session-based file locking for network applications
InactiveUS7246119B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData displayApplication software
A file locking method and implementation are disclosed which allows a plurality of user sessions to open and read a file, but at any one time, only one session will be allowed to change the data displayed in the browser window and to update the file. This file locking method sets up a file access priority by using file locks that are date-time stamped and session stamped. The types of lock associated with the present invention include read lock, authority lock, write lock, and folder lock. When a session / user requests access to a file, the application will check a lock table associated with the requested file. For each lock on the file, there is an entry in the lock table for each of the attributes of the lock: lock type, session owner, date-time stamp. Depending on the lock and the existing locks on the file, the requesting session may be granted a lock. After the access request is fulfilled, the file lock may be removed. When a session expires, all the locks owned by this session will be invalidated and removed.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
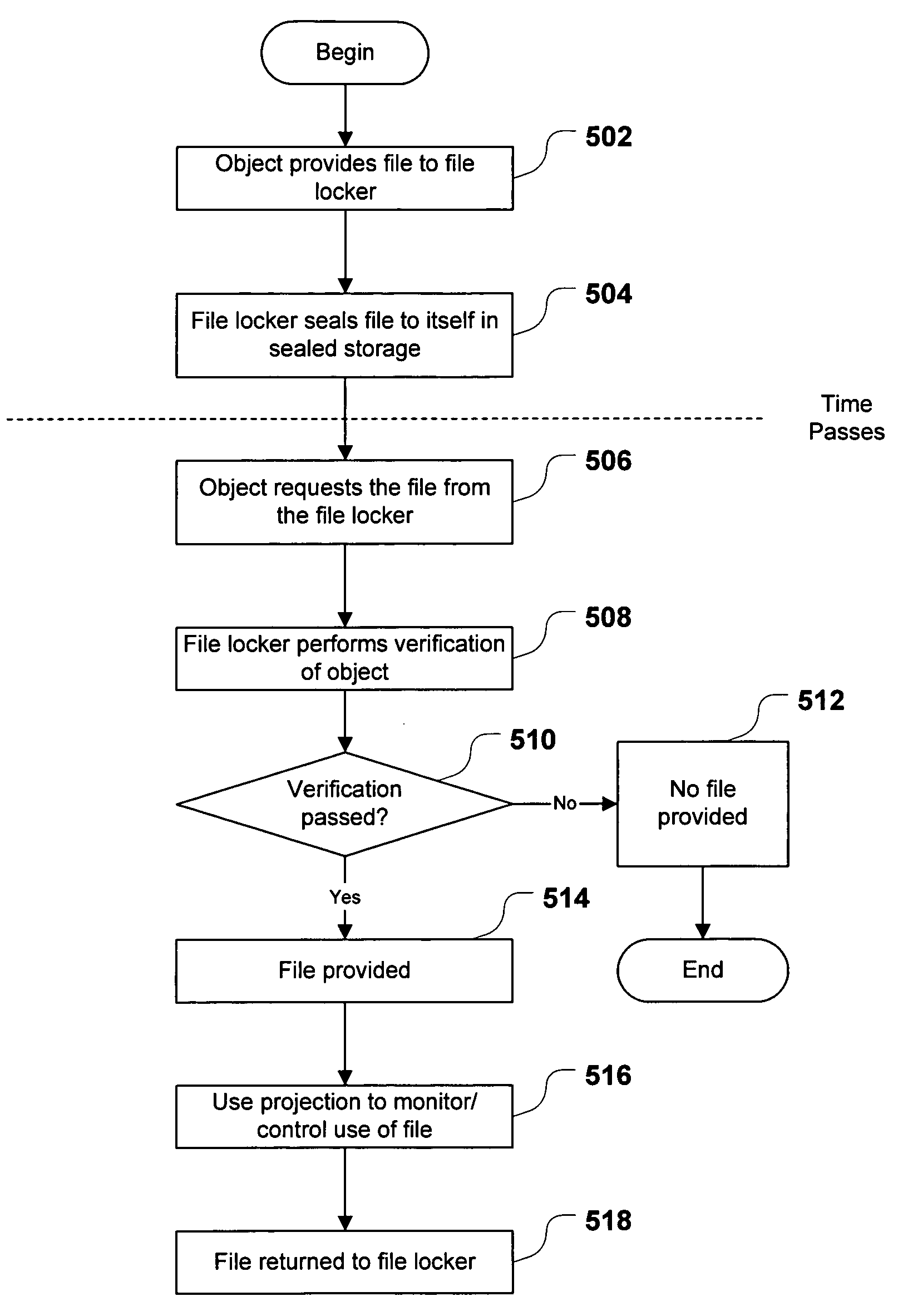
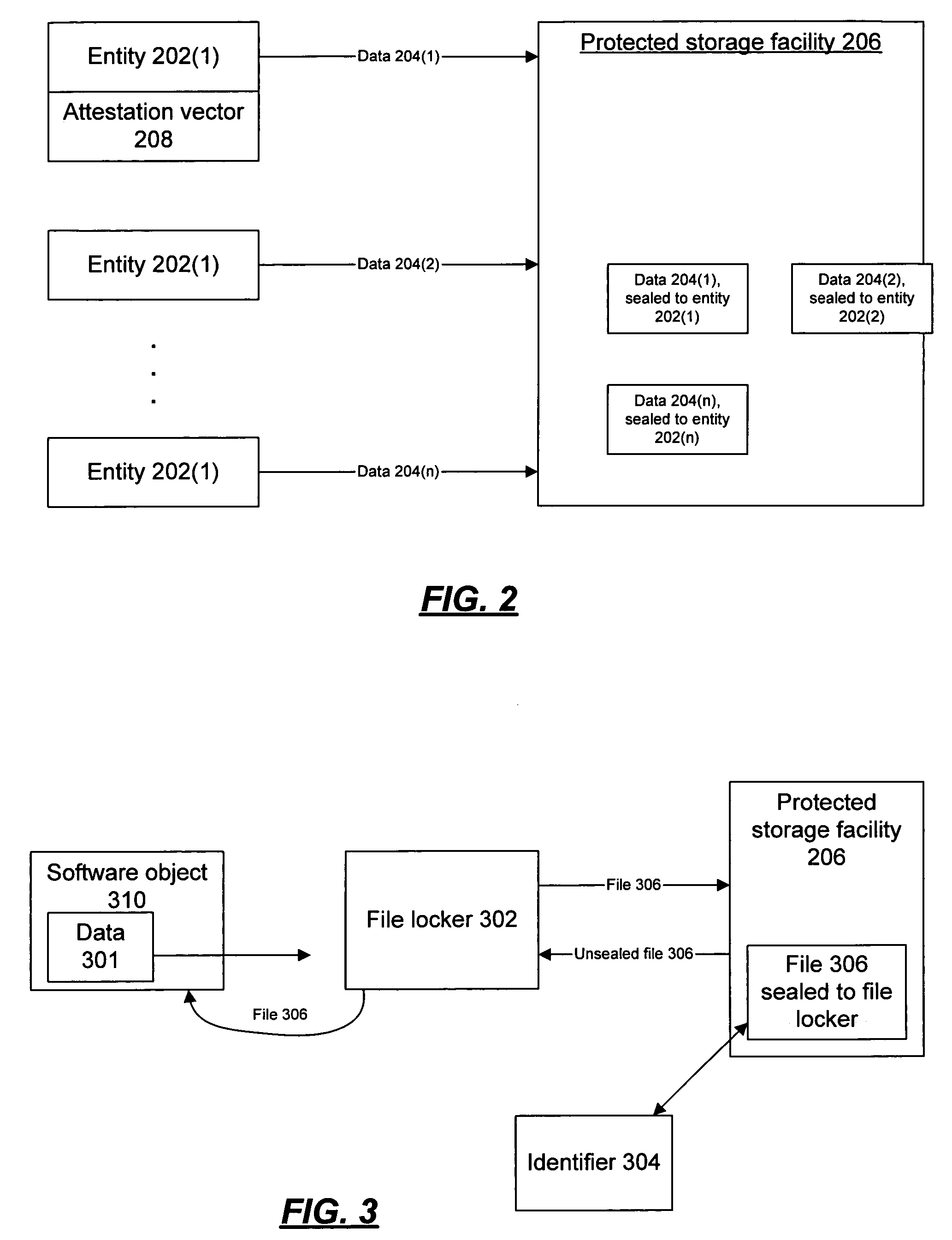
File locker and mechanisms for providing and using same
A file locker manages the storage and use of protected data for software objects. A protected environment maintains the cryptographic and isolative infrastructure to support sealing of data items for use by a trusted agent. The file locker uses the protected environment's sealing functionality to seal data items for the file locker's exclusive access. The file locker seals, to itself, files received from software objects, and provides those files upon request, and upon sufficient proof of the requestor's trustworthiness, authenticity, and / or identity. The file locker may be used to extend the protected environment's sealing functionality to legacy applications, without the legacy applications having to implement agents that can run in the protected environment and access the sealing functionality directly.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
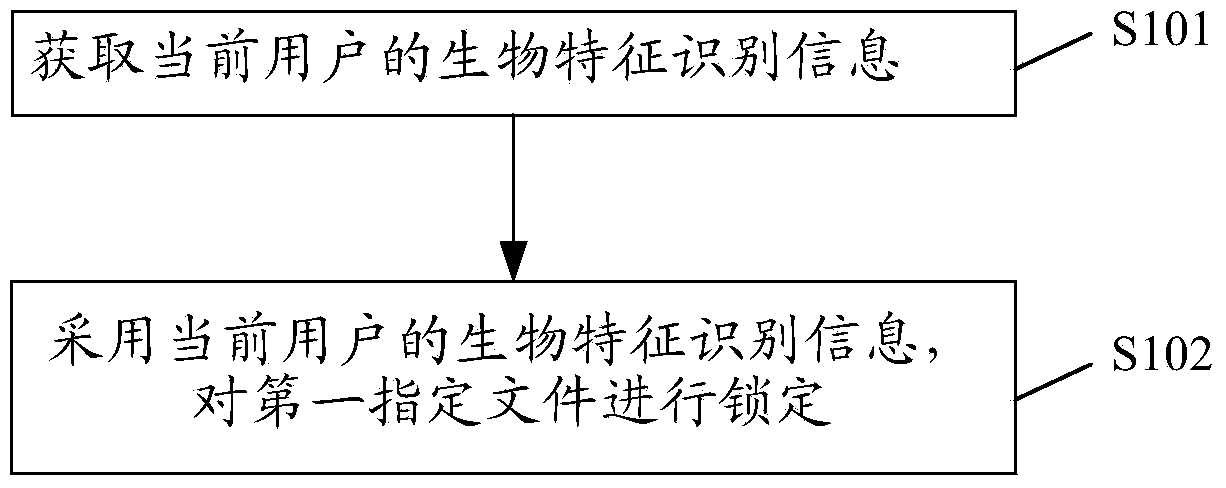
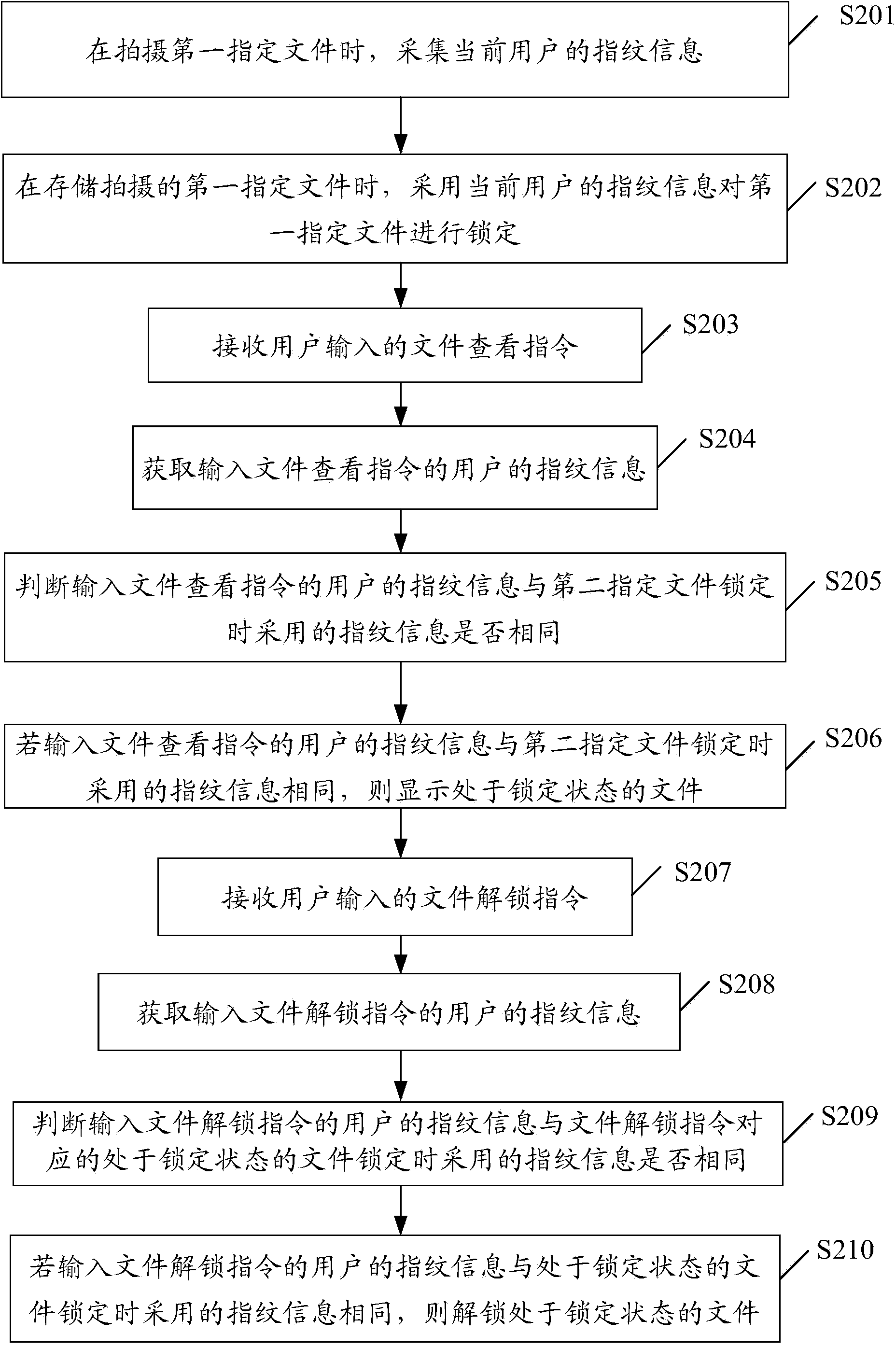
File locking method and device
InactiveCN104112091AProtect personal privacyImprove experienceDigital data authenticationSpeech recognitionFile lockingComputer science
The invention provides a file locking method and belongs to the technical field of electronic equipment. The file locking method comprises the steps of obtaining biological feature recognition information of a current user, wherein the biological feature recognition information comprises fingerprint information or voice print information or iris information or facial information; locking a first specified file according to the biological feature recognition information of the current user. Because the specified file is locked according to the biological feature recognition information, pictures or videos can be hidden, personal privacy of the current user is effectively protected, and user experience is enhanced. In addition, users can select files for locking according to needs, so that use is very flexible. The invention further provides a file locking device.
Owner:XIAOMI INC
Lateral File Locking System
A locking system for a file cabinet which prevents opening of more than one drawer of the cabinet. The locking system includes a camming system which blocks opening of any secondary drawers after a first drawer has been opened. A rotatable cam having a hook mounts to an individual lock lever. The hook engages an opening in the file drawer or door to prevent retraction while also blocking the interlocking mechanism for the file drawers.
Owner:LASALLE BANK NAT ASSOC
Method for achieving file lock and metadata server
InactiveCN103514298AAchieve releaseTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsFile lockingComputer science
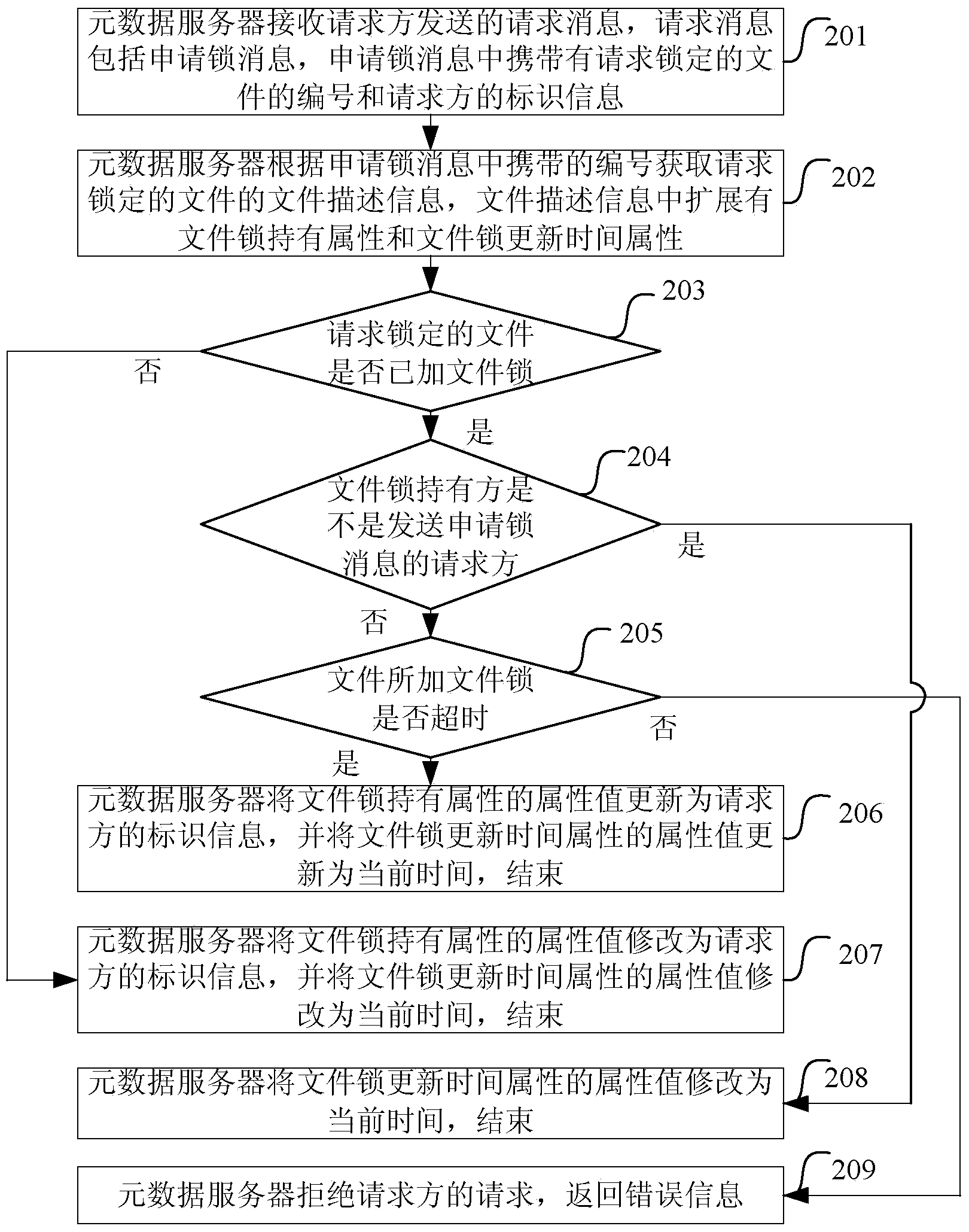
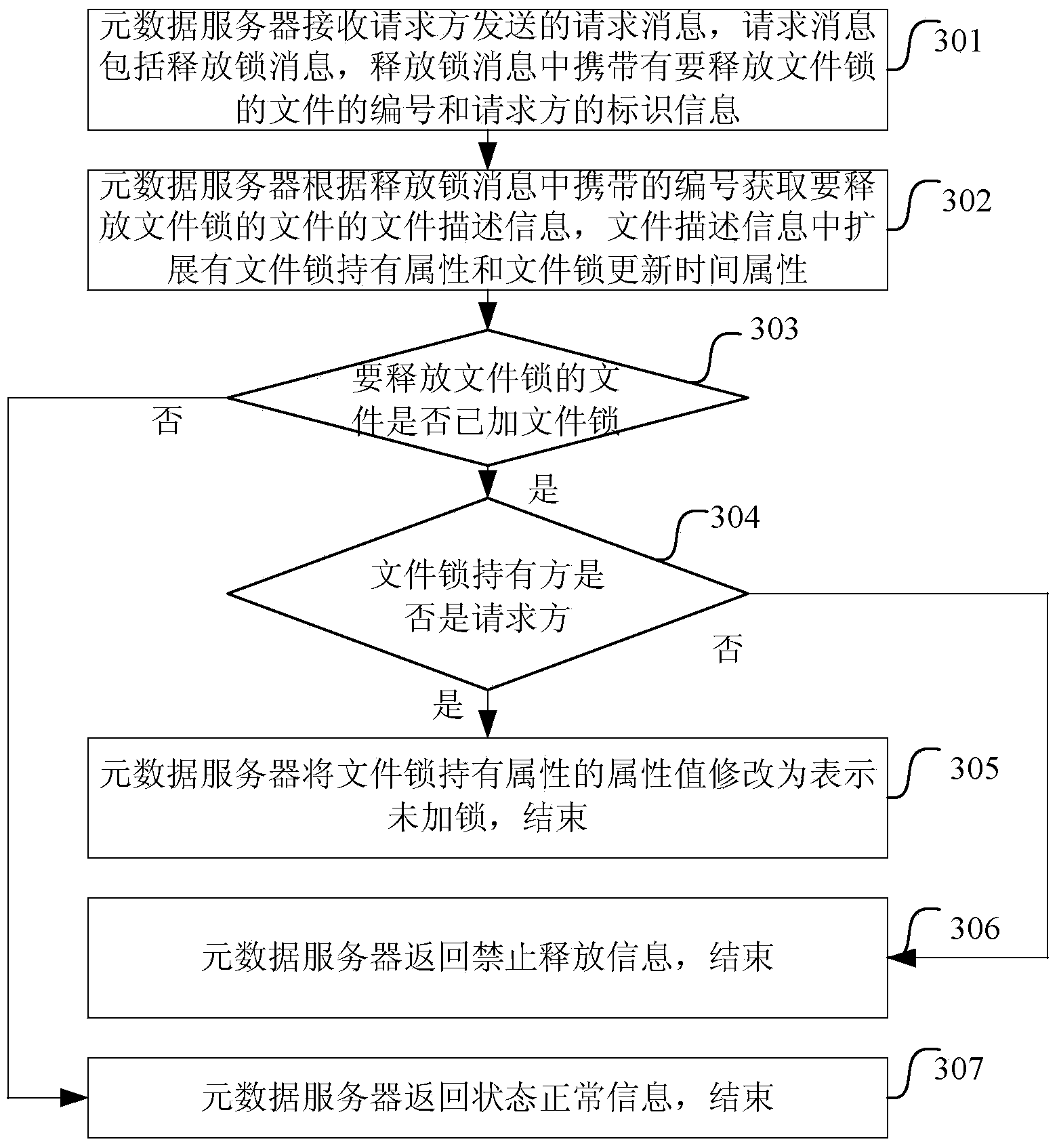
The invention discloses a method for achieving a file lock and a metadata server. The method comprises the steps of enabling the metadata server to receive a request message sent by a request party, wherein the request message comprises a lock applying message, and a serial number of a file requested to be locked and identification information of the request party are carried in the lock applying message; enabling the metadata server to obtain file description information of the file according to the serial number, wherein file lock holding attributes and file lock update time attributes are contained in the file description information in an extended mode; enabling the metadata server to judge whether the file lock is added in the file or not according to the file lock holding attributes, if the file lock is already added and a holding party of the file lock is not the request party, judging whether the file lock added on the file is overtime or not according to the file lock update time attributes, and updating an attribute value of the file lock holding attributes to be the identification information of the request party and updating an attribute value of the file lock update time attributes to be the current time if the file lock added on the file is overtime.
Owner:INSPUR BEIJING ELECTRONICS INFORMATION IND
File interval lock generation interface system and method
ActiveUS7233946B1Improve efficiencyAllow accessDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsPublic interfaceLocking mechanism
A computer system having a kernel interface that provides a file lock generation system for generating file interval locks and granting simultaneous access to these locks to application programs requesting access to file objects or portions thereof and provides a common interface to operations upon those objects. An interval is a starting location and length and the locking mechanism grants access to non-overlapping intervals independently.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
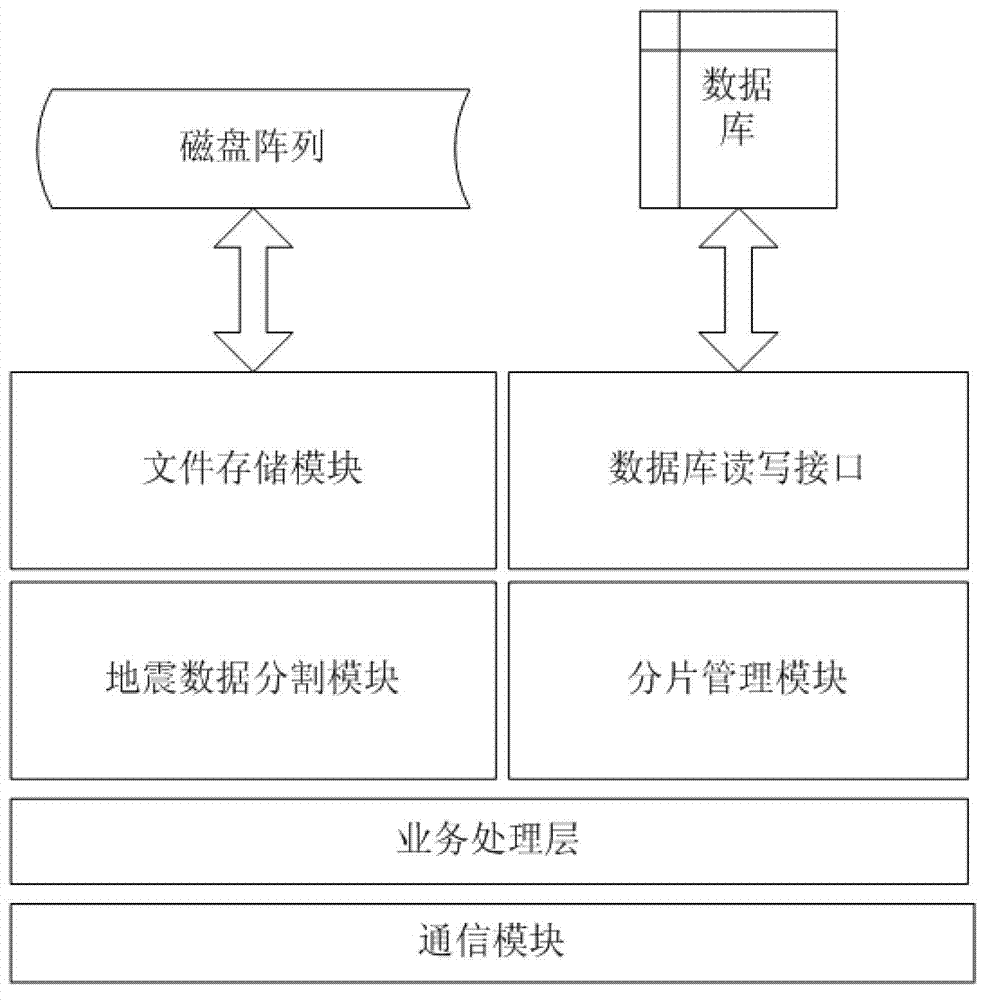
Distributed file management system based on seismic data processing
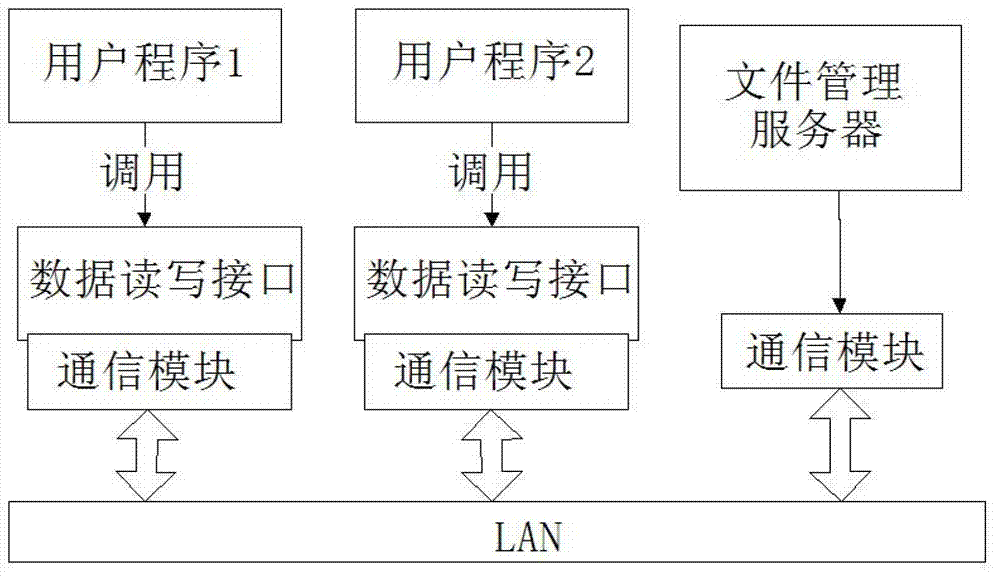
InactiveCN102880658AResolving Competitive ConflictsAvoid the problem of large I/O performance degradationSpecial data processing applicationsDistributed File SystemFile system
The invention discloses a distributed file management system based on seismic data processing, which includes data read-write interfaces, a file management server and communication modules, wherein the communication modules are provided with interfaces for information receiving and transmission, which are utilized by the data read-write interfaces and the file management server. The invention has the benefits as follows: the distributed file system principle is adopted to automatically slice and manage files, so as to realize the high-speed paralleling I / O and provide simple and efficient file management; users only simply call the corresponding interface to realize operation for data, and files can be sliced and managed completely and automatically through programs without manual intervention; the problem of competition conflict that a plurality of computation nodes access the same file on a unified magnetic disc array under the cluster environment can be solved; and the method for slicing the files fundamentally solves the problem of sharp performance reduction of I / O caused by the file locking protection of a file system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
File-based access control for shared hardware devices
InactiveUS20070150630A1Digital data information retrievalUnauthorized memory use protectionVirtualizationOperational system
An apparatus, program product and method effectively virtualize a hardware device shared between multiple processors by a file accessible by a processor such that access to the hardware device may be controlled via a lock associated with the file. By doing so, file-based locking, e.g., as provided by a file locking facility in an operating system running on a processor, may be used to control access to the hardware device on behalf of the processor.
Owner:IBM CORP
Blended operational transformation for multi-user collaborative applications
ActiveUS20160173594A1Well formedDigital data information retrievalNatural language data processingOperational transformationApplication software
Multi-user collaborative software applications may synchronize data between multiple users or multiple devices. There are multiple existing ways to synchronize data. Some of these synchronization methods, such as file locking, are easy to implement but have performance or functionality drawbacks. Operational transformation (OT) is a high performance synchronization method, but difficult and time-consuming to implement in many cases, and cannot be partially implemented throughout a system. Methods and systems provide for blending operational transformation with other synchronization methods in the same collaborative software application, allowing operational transformation to be used in situations where it cannot be implemented throughout a system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
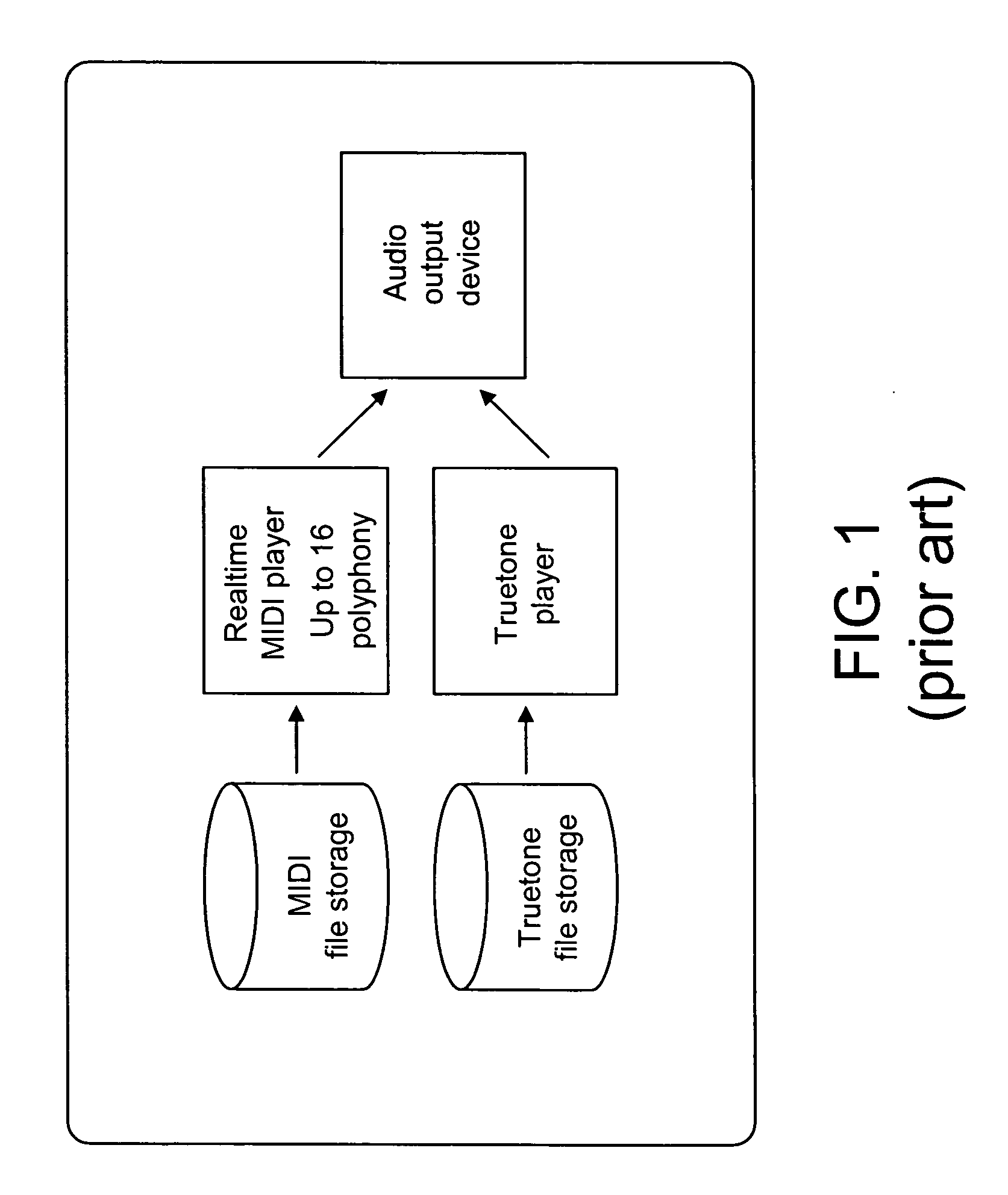
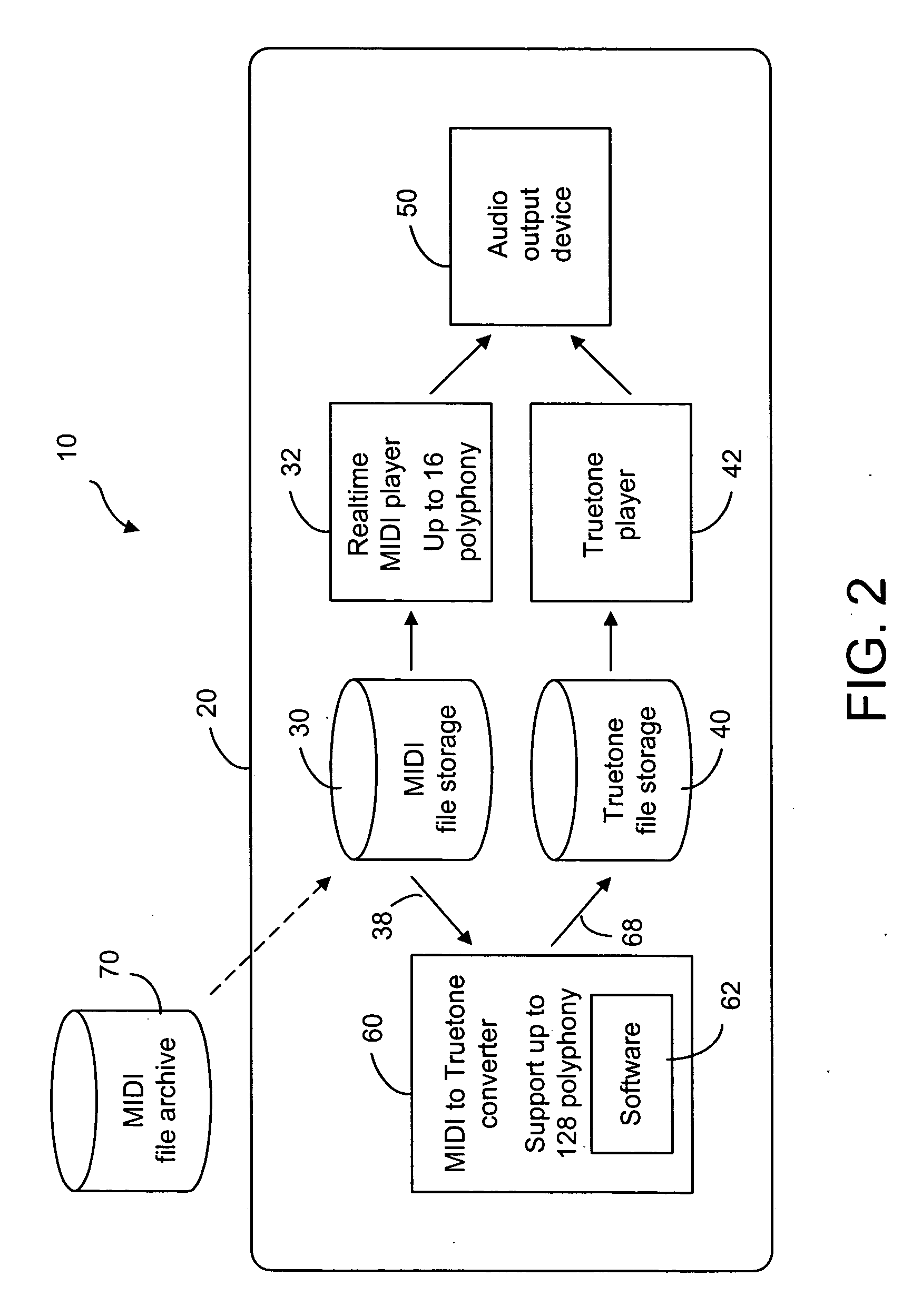
Method and device for enhancing ring tones in mobile terminals
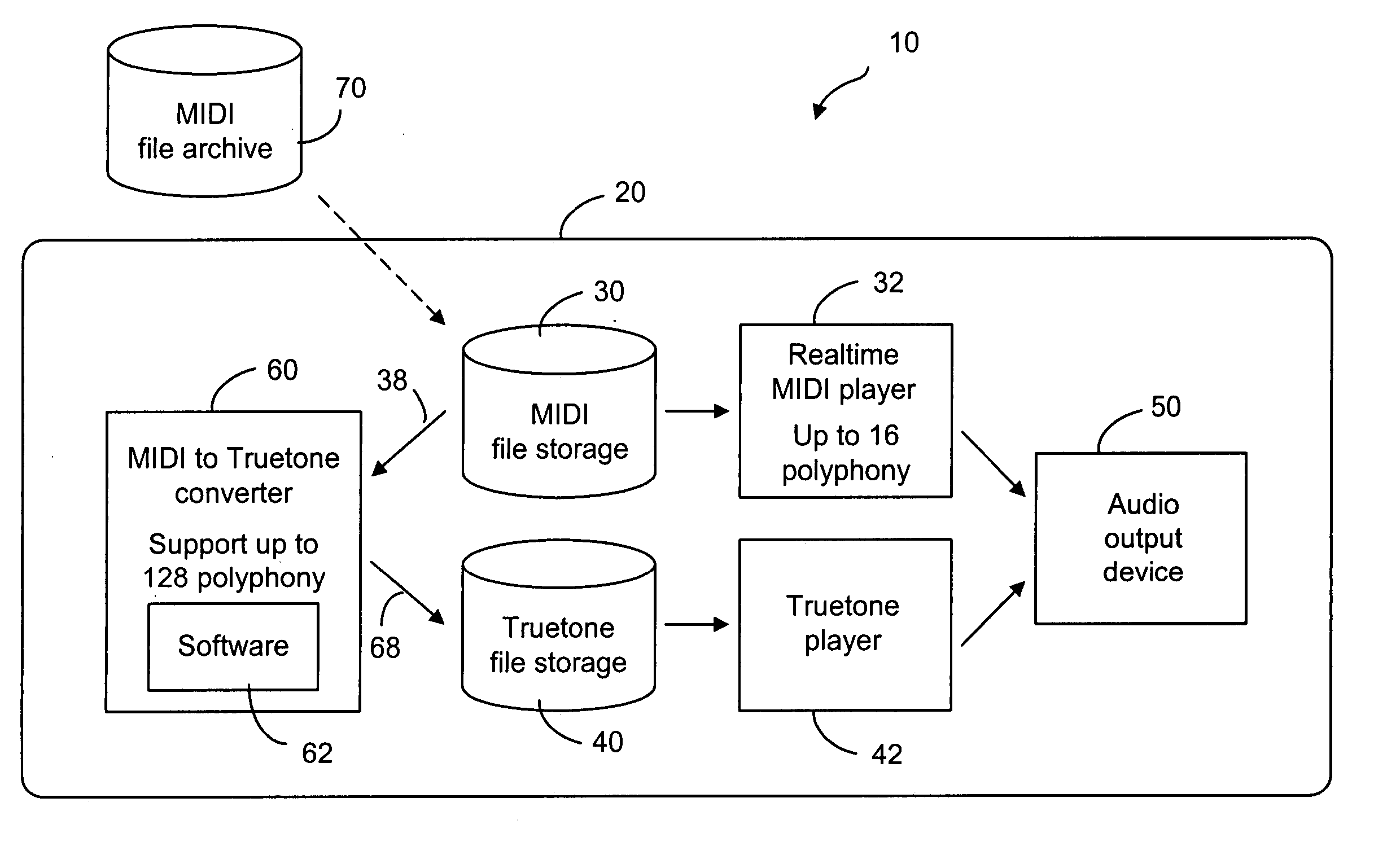
ActiveUS20060060069A1Improve sound qualityElectrophonic musical instrumentsCurrent supply arrangementsNon real timeService provision
A method and device for producing ring tones in high polyphony in real-time in a network component such as a mobile terminal or a server of a service provider. The network component has one or more ring tones in MIDI files of high polyphony, and a MIDI player of lower polyphony for producing sounds from the scaled down version of the MIDI files in real-time. In order to produce sounds indicative of the high-polyphony ring tones in real-time, the high-polyphony MIDI files are converted to compressed files in a non real-time manner. The converted files are stored in a storage so as to allow a compressed file player (such as Truetone, MP3, wav, AAC, RealAudio, Vorbis) to produce sounds from the converted files. A file lock is provided to the converted files so that they cannot be forwarded, thereby protecting the copyrights of the ring tone composer.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
Redo log management method and device and storage medium
ActiveCN111125040AAvoid file locksImprove the efficiency of writing redo logsDatabase updatingSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringFile locking
The invention discloses a redo log management method and device and a storage medium, and belongs to the technical field of databases. The method comprises the following steps of receiving a submission instruction of the first transaction, selecting the first redo log file for the first transaction from the multiple redo log files, and then using the determined first non-persistent redo log directly as the first redo log file, so that the situation that the file locks for the multiple redo logs need to be queued and competed is avoided, and the redo log writing efficiency can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
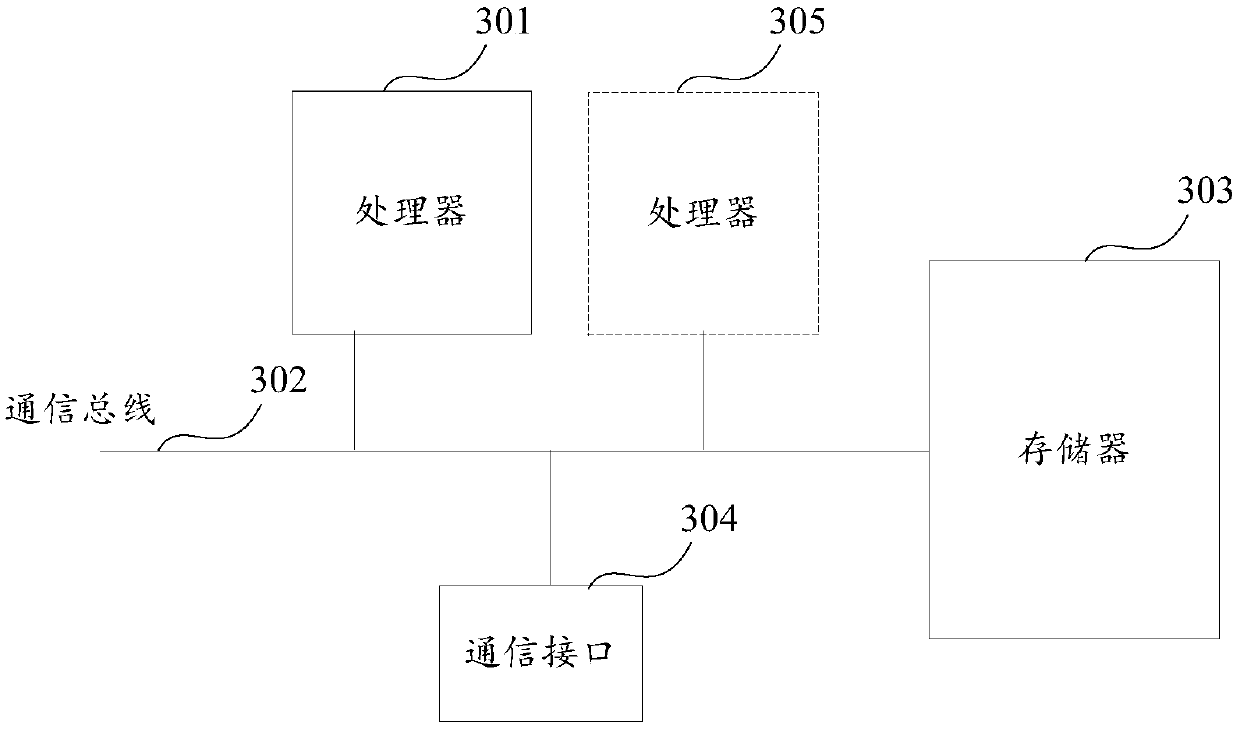
Information processing device, file management method, and recording medium for file management program
InactiveUS20120117131A1Multiple digital computer combinationsFile access structuresInformation processingFile descriptor
A computer-readable, non-transitory medium storing a program causing a computer to execute a process, the computer being connected through a network to a plurality of file management devices which store a plurality of files distributed in the plurality of file management devices, the process including: extracting an identification information of a file management device by a file descriptor specified in a request for locking a file, the request being generated by an application that is activated on the computer; and transmitting the request for locking the file through an interface section to the file management device corresponding to the identification information.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
User mode network file system file lock method, device and equipment
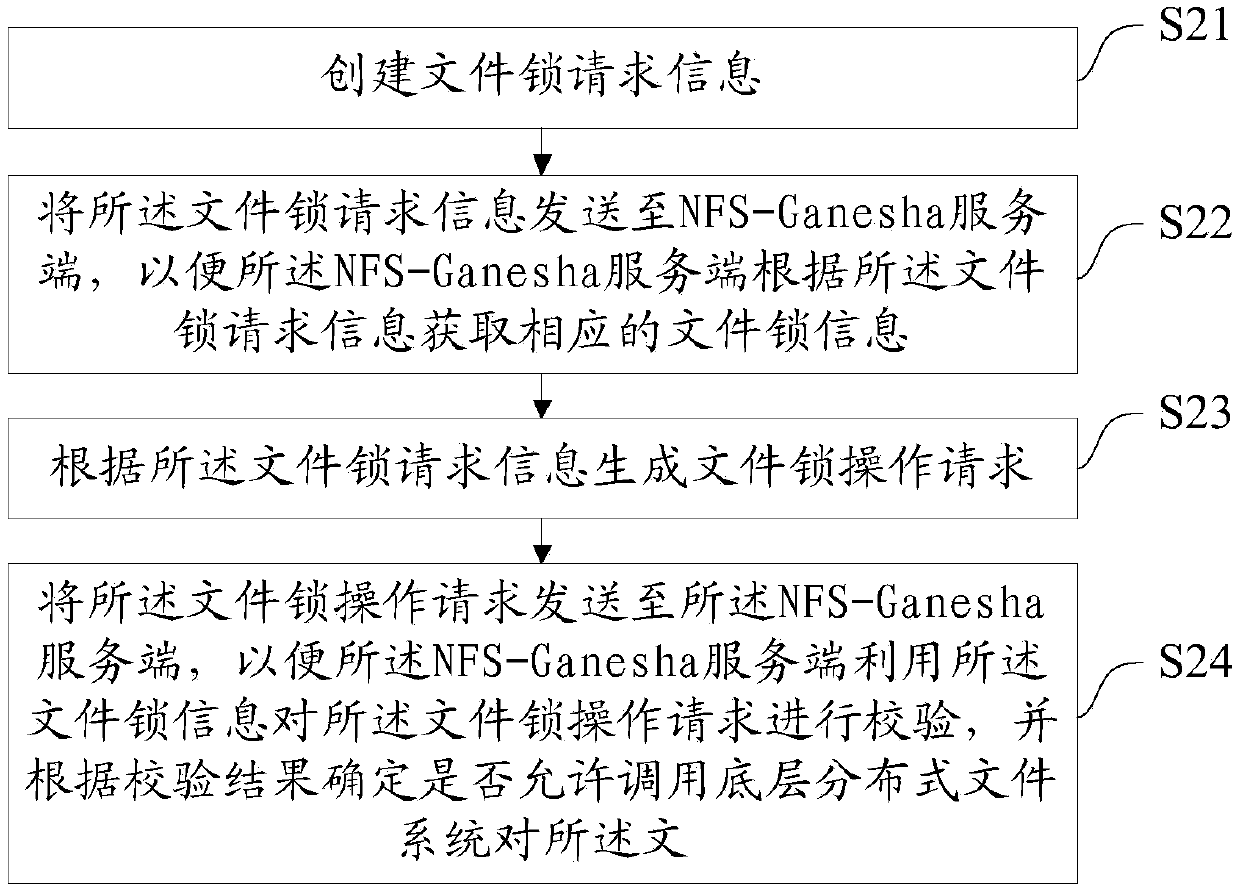
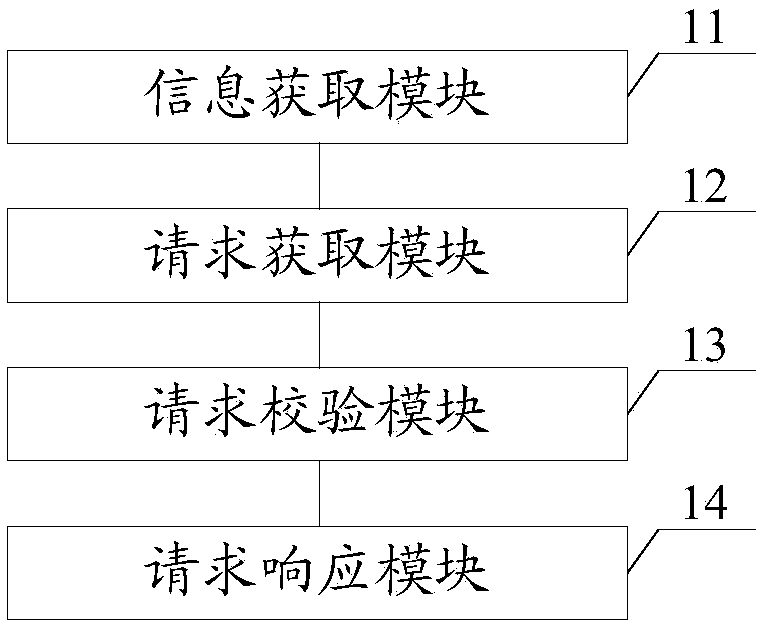
ActiveCN109684285AAvoid file conflict eventsImprove stabilityDigital data information retrievalTransmissionDistributed File SystemDistributed object
The invention discloses a user mode network file system file lock method, device and equipment, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining file lock request information sent by a client, and obtaining the corresponding file lock information according to the file lock request information; Obtaining a file lock operation request which is sent by the client and generated according to the file lockrequest information; Verifying the file lock operation request by using the file lock information; And if the verification is passed, calling a bottom distributed file system to respond to the file lock operation request. Therefore, according to the invention, the file lock technology and the distributed object storage NFS-Ganesha are combined; the data consistency of the distributed file systemin the concurrent access process is ensured through the file lock technology, so that the occurrence of a file conflict event is effectively avoided, and the stability of the system is improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
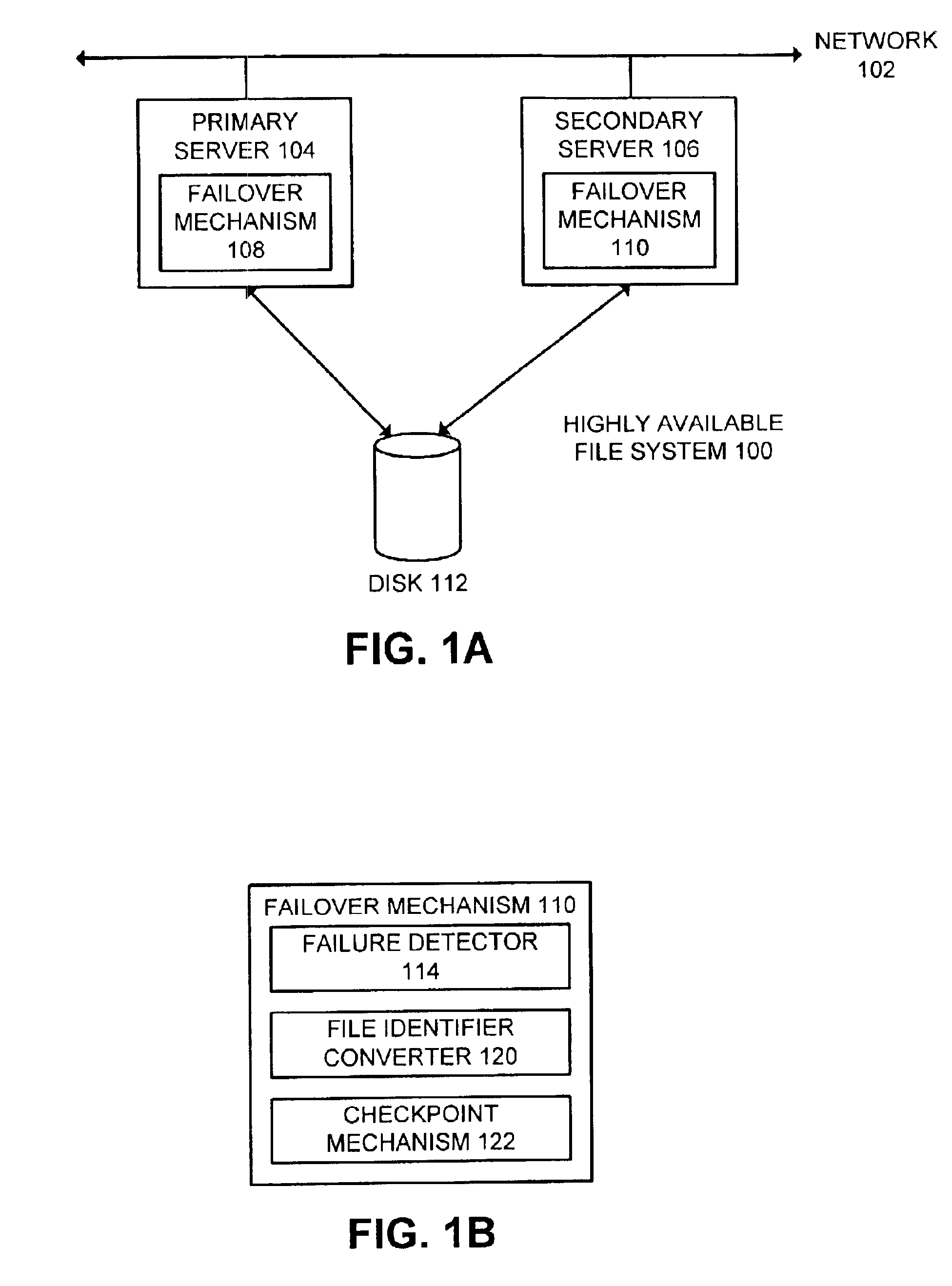
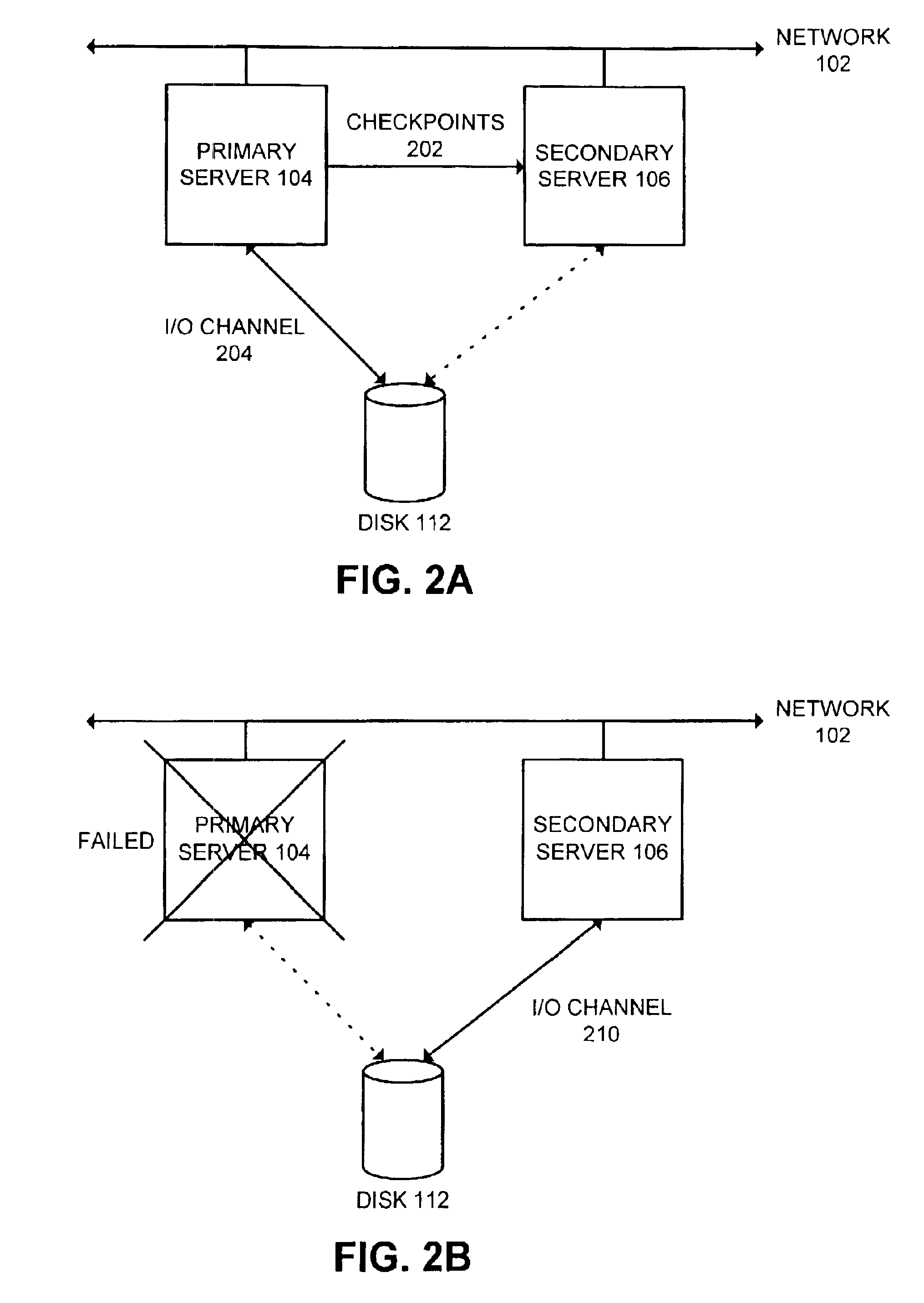
Facilitating failover to a secondary file server in a highly available file system
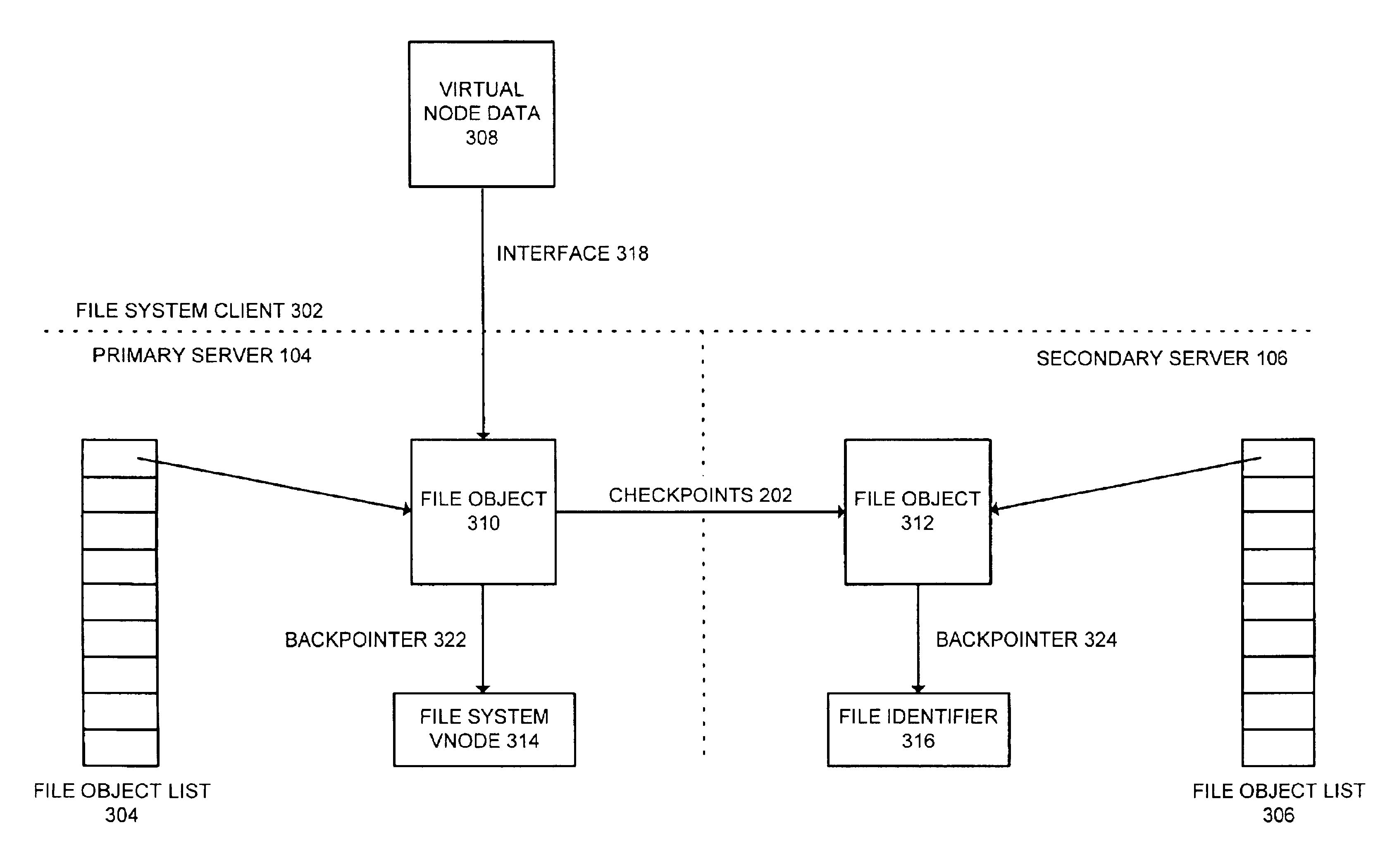
InactiveUS6883010B2Improve availabilityProcessing speedData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalFailoverFile system
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for elevating a secondary file server to act as a new primary file server in a highly available file system. Upon determining that a primary file server in the highly available file system has failed, the system promotes the secondary file server to become the new primary file server. During this process, the new primary file server scans file objects to look for a file lock indication. Upon finding a file lock indication, the new primary file server converts an associated file identifier into a virtual node. Otherwise, conversion of file identifiers into virtual nodes is delayed until the first time a file is subsequently accessed by the new primary server, thereby speeding up the failover process.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
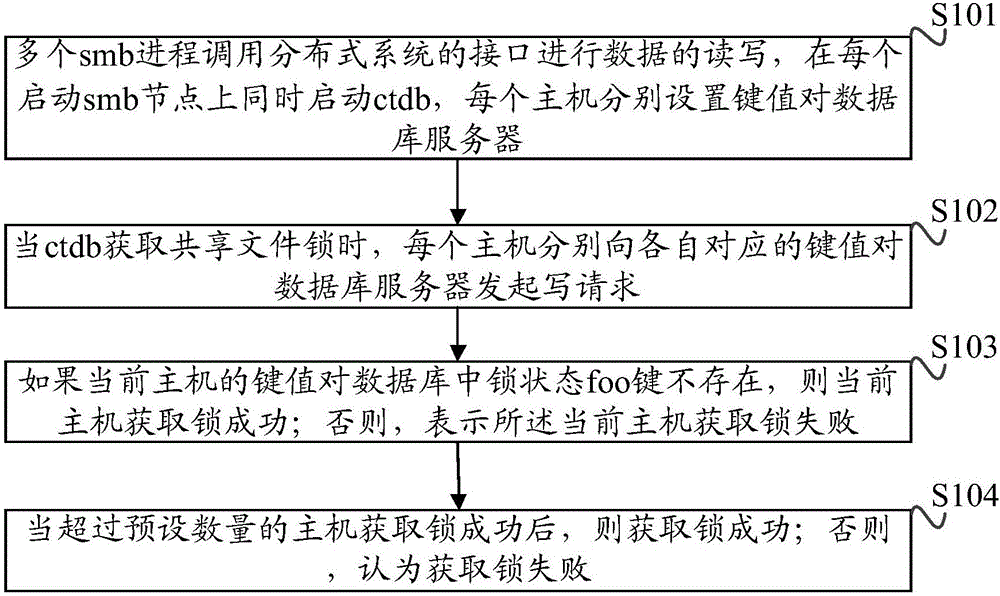
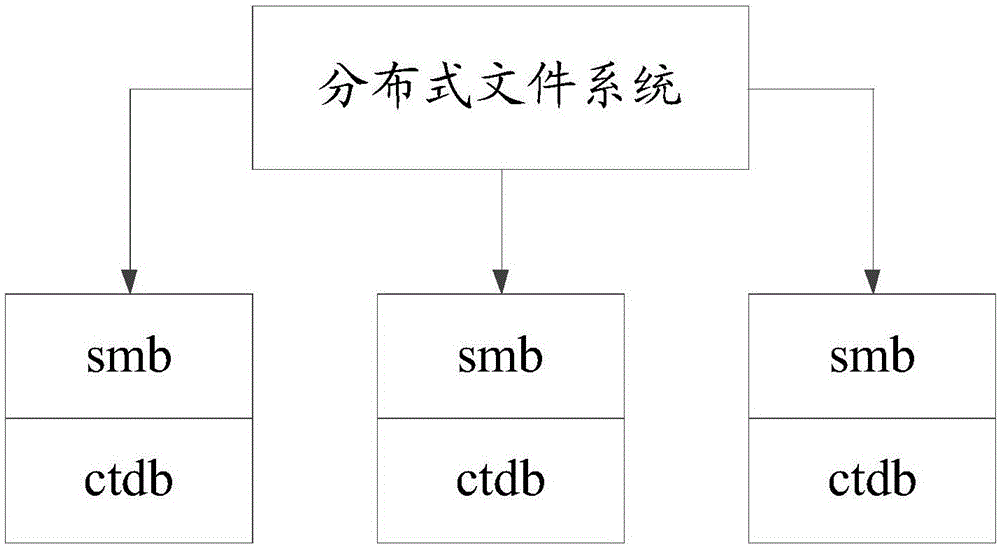
High-availability service management method based on distributed locks
InactiveCN106293954AWill not affect normal useAchieve decouplingProgram synchronisationTransmissionDistributed File SystemDatabase server
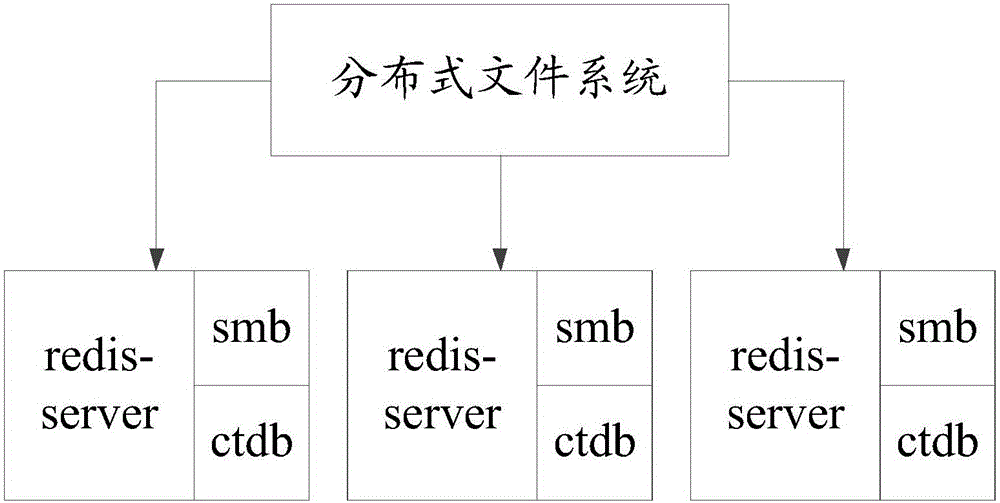
The invention discloses a high-availability service management method based on distributed locks. Multiple smb processes call interfaces of a distributed system for data reading and writing, a ctdb is started simultaneously at each starting smb node, and a key-value pair database server is set for each host; when each ctdb acquires a shared file lock, each host launches a writing request for the corresponding key-value pair database server; if a lock state foo key in the key-value pair database server of the current host doesn't exist, the current host successfully acquires the locks, and otherwise, the current host fails to acquire the locks; when more than a preset number of hosts successfully acquire the locks, the locks are successfully acquired, and otherwise, acquisition of the locks fails. In the scheme, each ctdb doesn't use a rear-end distributed file system of an smb to store the shared file locks, so that normal use of the ctdb cannot be affected by faults of the distributed system; high availability of the smb and decoupling of the read-write distributed file system are realized.
Owner:INSPUR BEIJING ELECTRONICS INFORMATION IND
File locking and unlocking method and system
ActiveCN103795813AAvoid modificationPrevent or allow modificationDigital data protectionTransmissionComputer hardwareFile locking
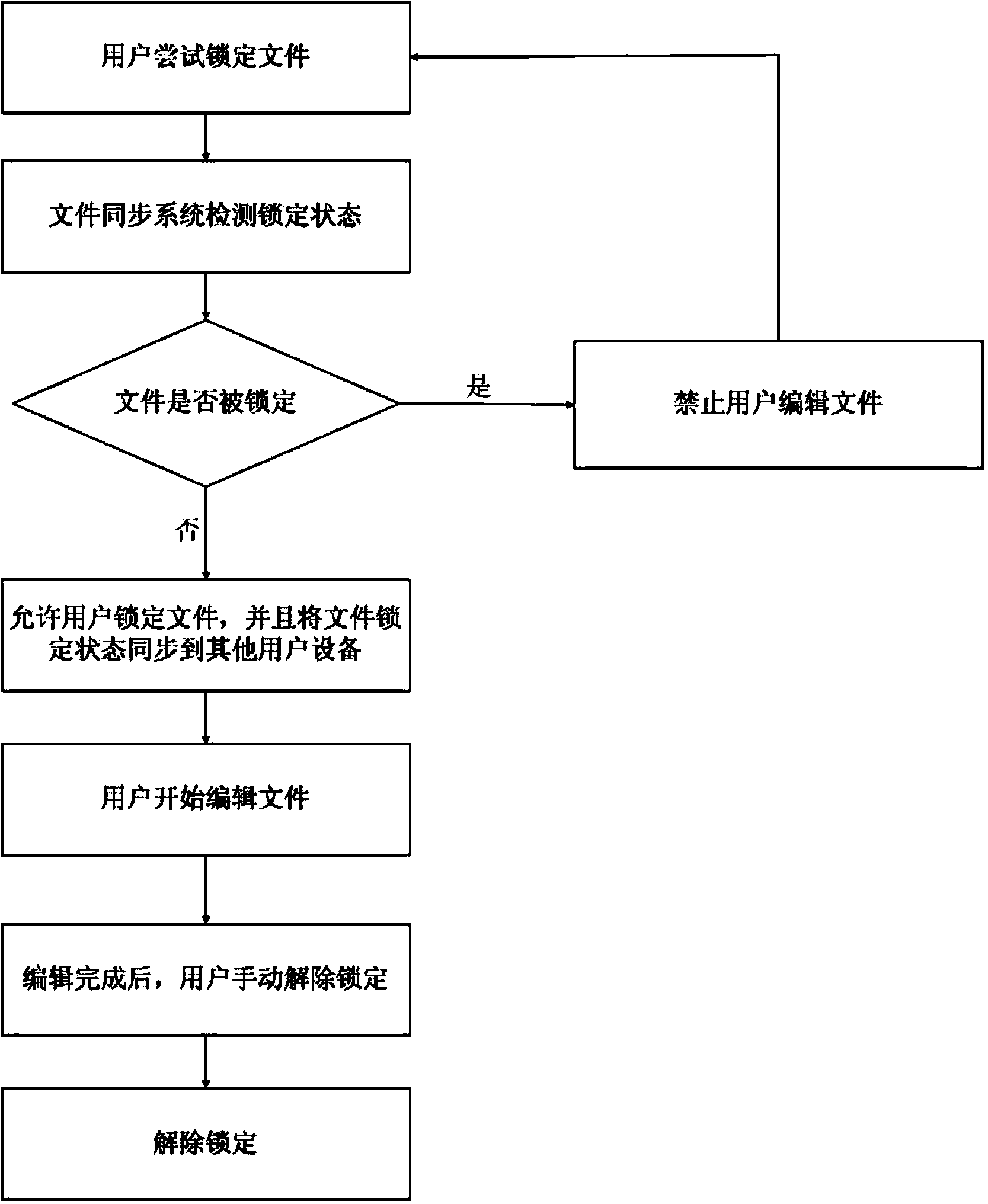
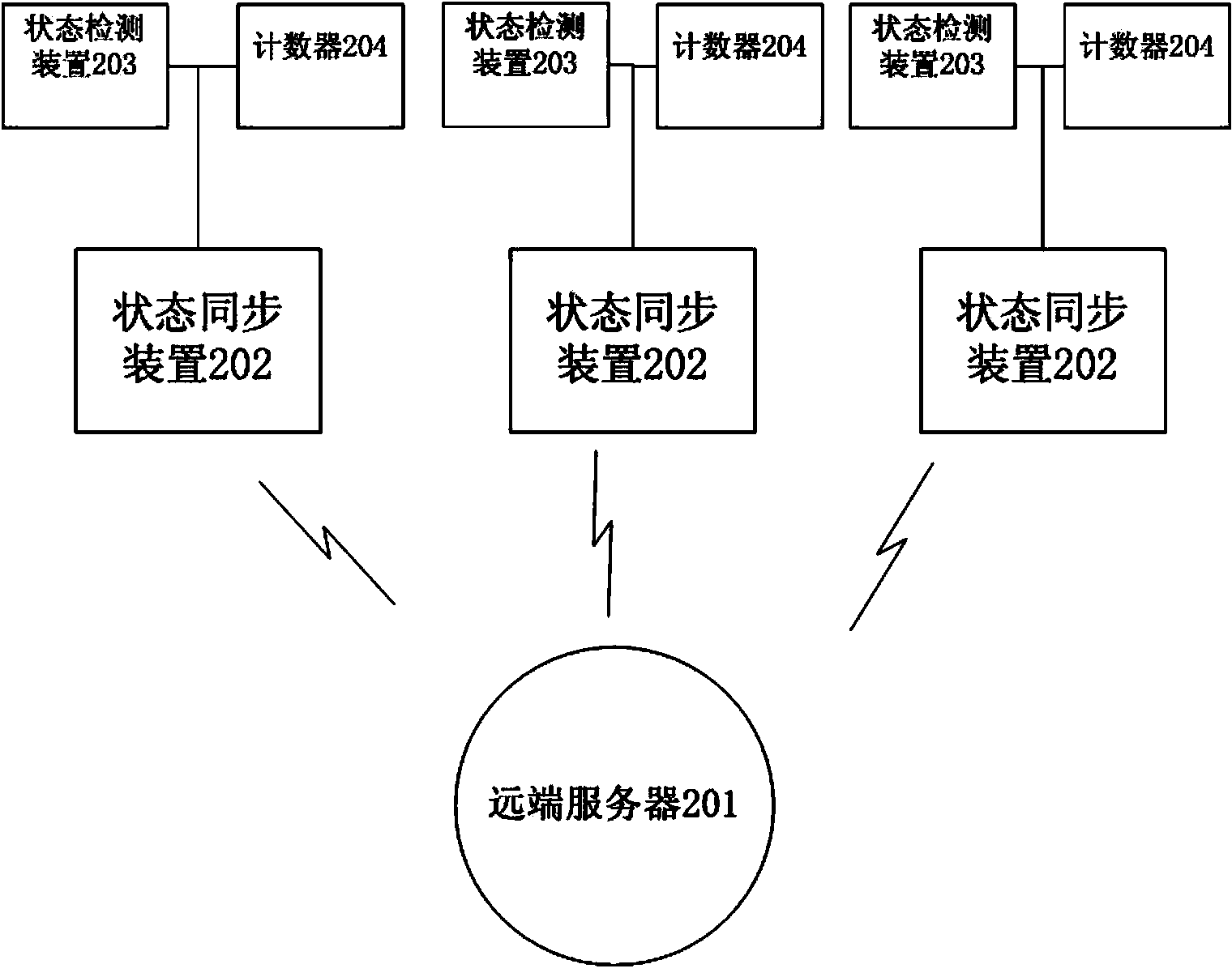
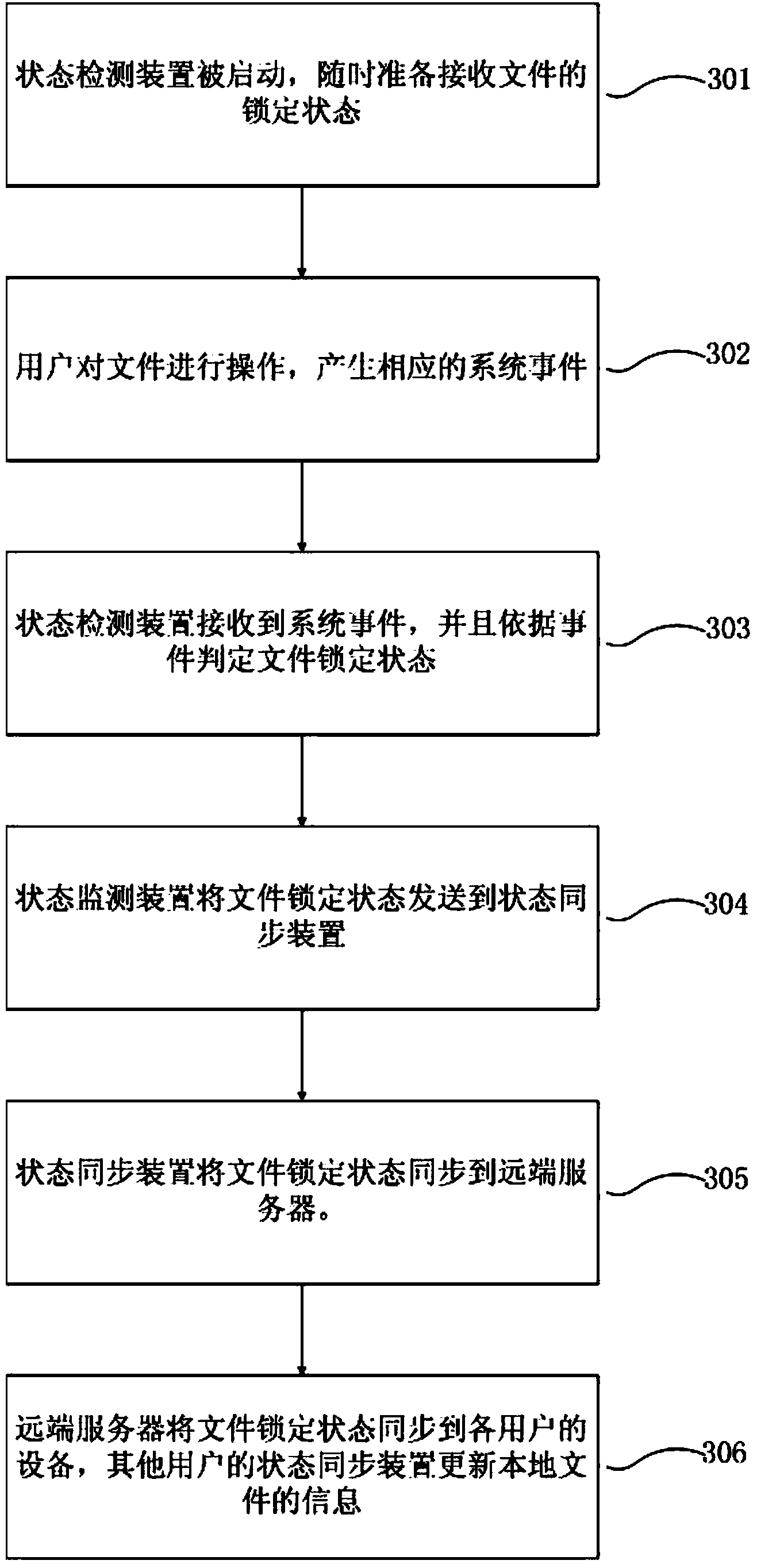
The invention provides a file locking method and system which achieve the purpose that a file is automatically locked when the file is edited by multiple users in a cooperation mode. The system comprises a state detection device, a state synchronizing device and a far end server. The file locking method is based on events, when the file is opened and edited, a certain system event is generated, the state detection device judges the locking state of the file after the corresponding event is received, the state synchronizing device synchronizes the locking state to the far end server, the far end server synchronizes the state to devices of other users, and the state synchronizing devices on the devices of other users update the local file information.
Owner:SHANGHAI YICUN NETWORK TECH
Method and system for performing a clean file lock recovery during a network filesystem server migration or failover
ActiveUS8655851B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFailoverFile system
A method for file lock recovery in a distributed computer system. The method includes executing a distributed computer system having a plurality of nodes comprising a cluster, and initiating a network file system server migration from one node of the cluster to a different node of the cluster. A migration count is incremented, wherein the migration count is stored at each of the nodes comprising the cluster. File lock services are paused at each of the nodes comprising the cluster. The network file system server migration is completed at the different node of the cluster. The migration count is then decremented in response to the completion. File lock services are then resumed at each of the nodes comprising cluster.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
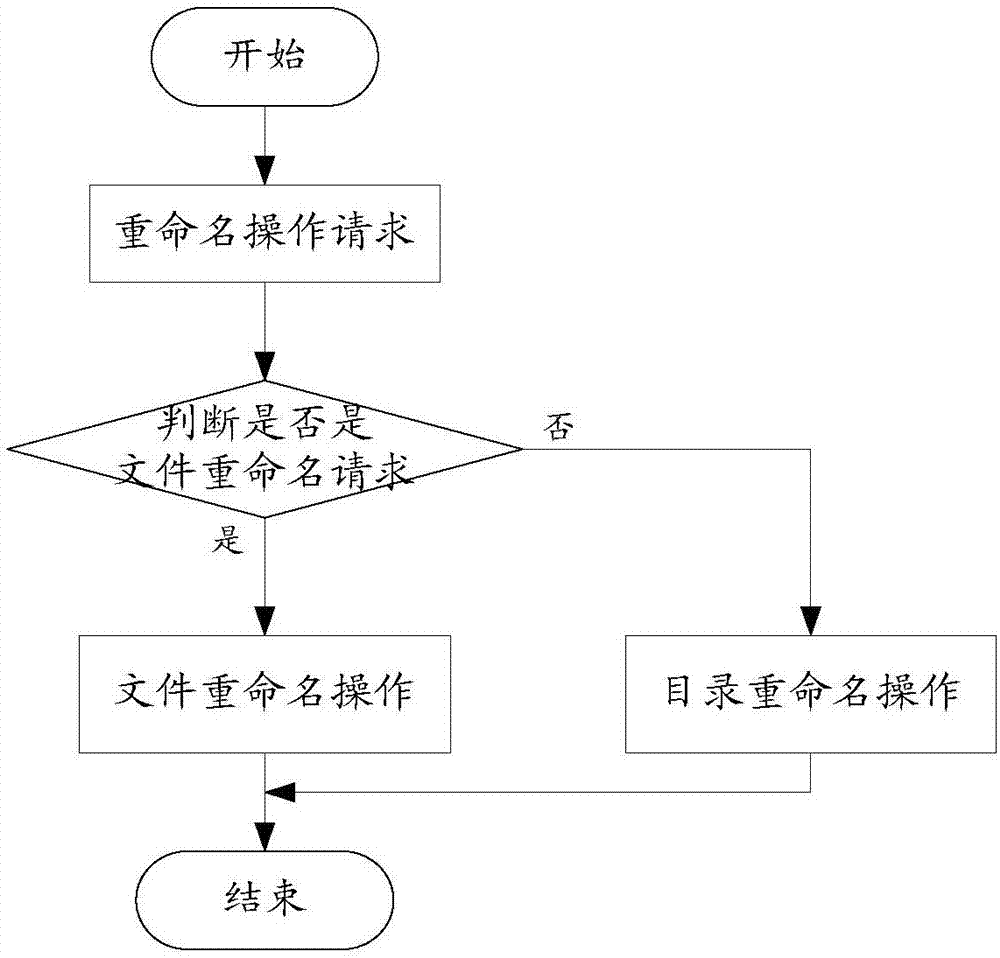
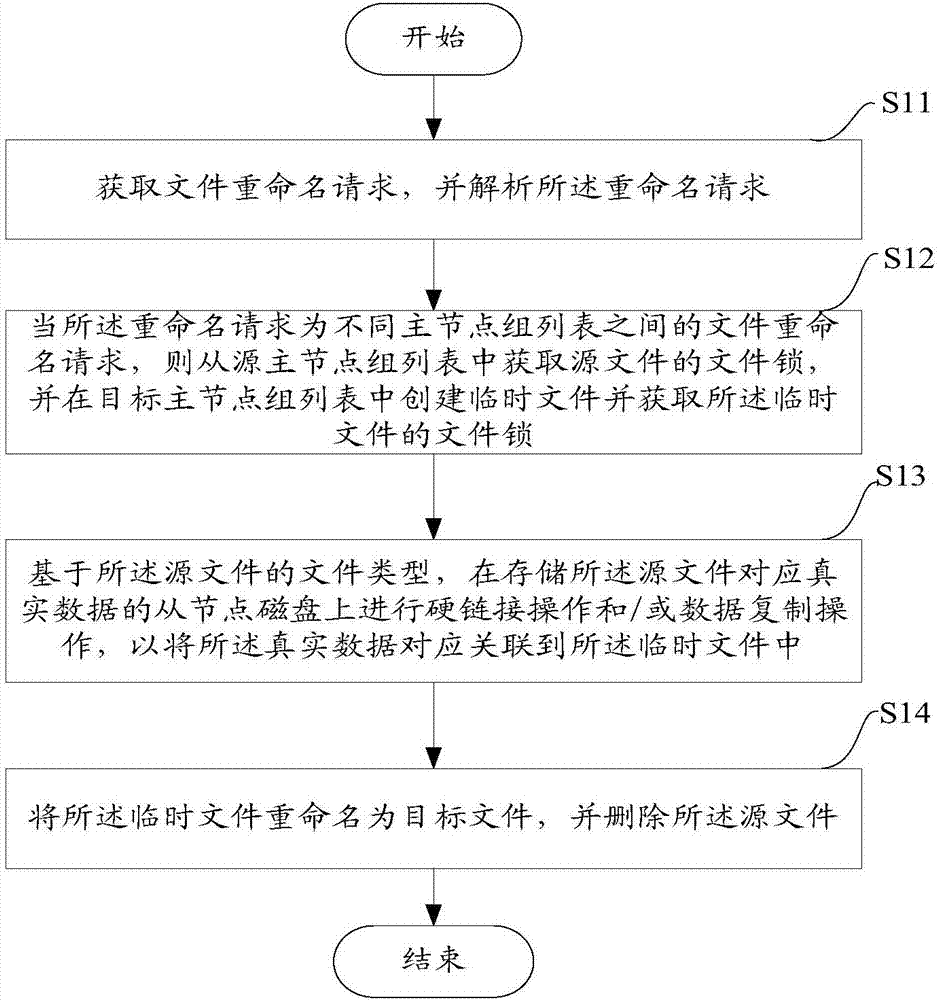
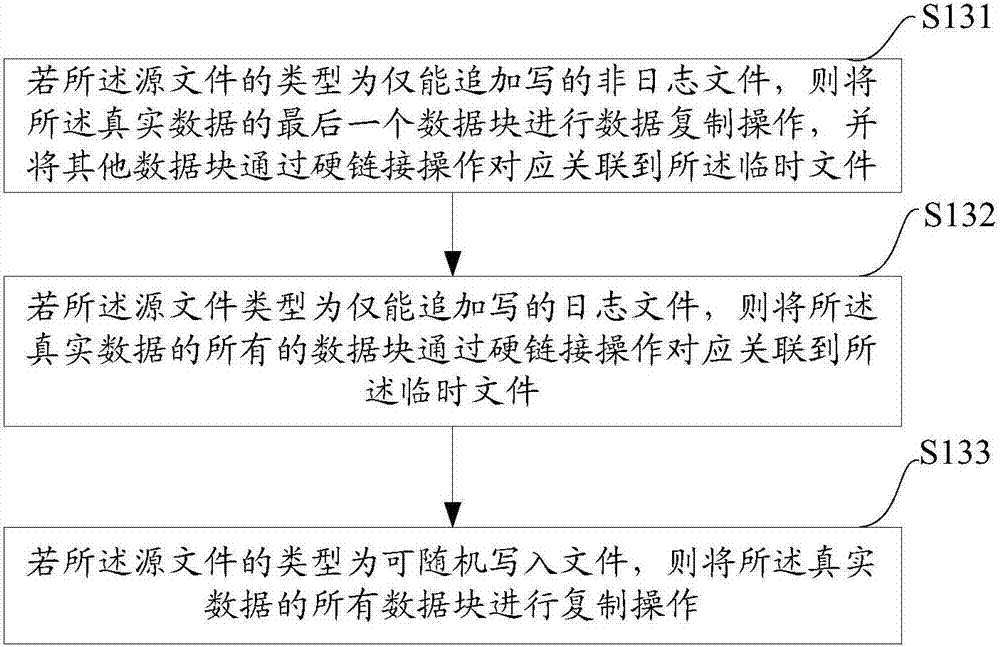
Method and equipment for executing renaming operation by distributed file system
ActiveCN107239480AReduce copy operationsAvoid lossSpecial data processing applicationsDistributed File SystemFile system
The application aims at providing a method and equipment for executing a renaming operation by a distributed file system. The method comprises the following steps: resolving a renaming request of a file, determining whether the renaming request is in the same host node group list, if the renaming request is not in the same main host node group list, acquiring a file lock of a source file from a source host node group list, and creating a temporary file in a target host node group list and acquiring the file lock of the temporary file; performing a hard link operation and / or data copy operation on a slave node disk for storing the corresponding real data of the source file, thereby correspondingly associating the real data to the temporary file; finally, renaming the temporary file as the target file, and deleting the source file to accomplish the file renaming operation among different host node group lists, wherein the semantic of the original file system is maintained to the greatest extent, and the upper layer user can continuously use the file system without perception.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
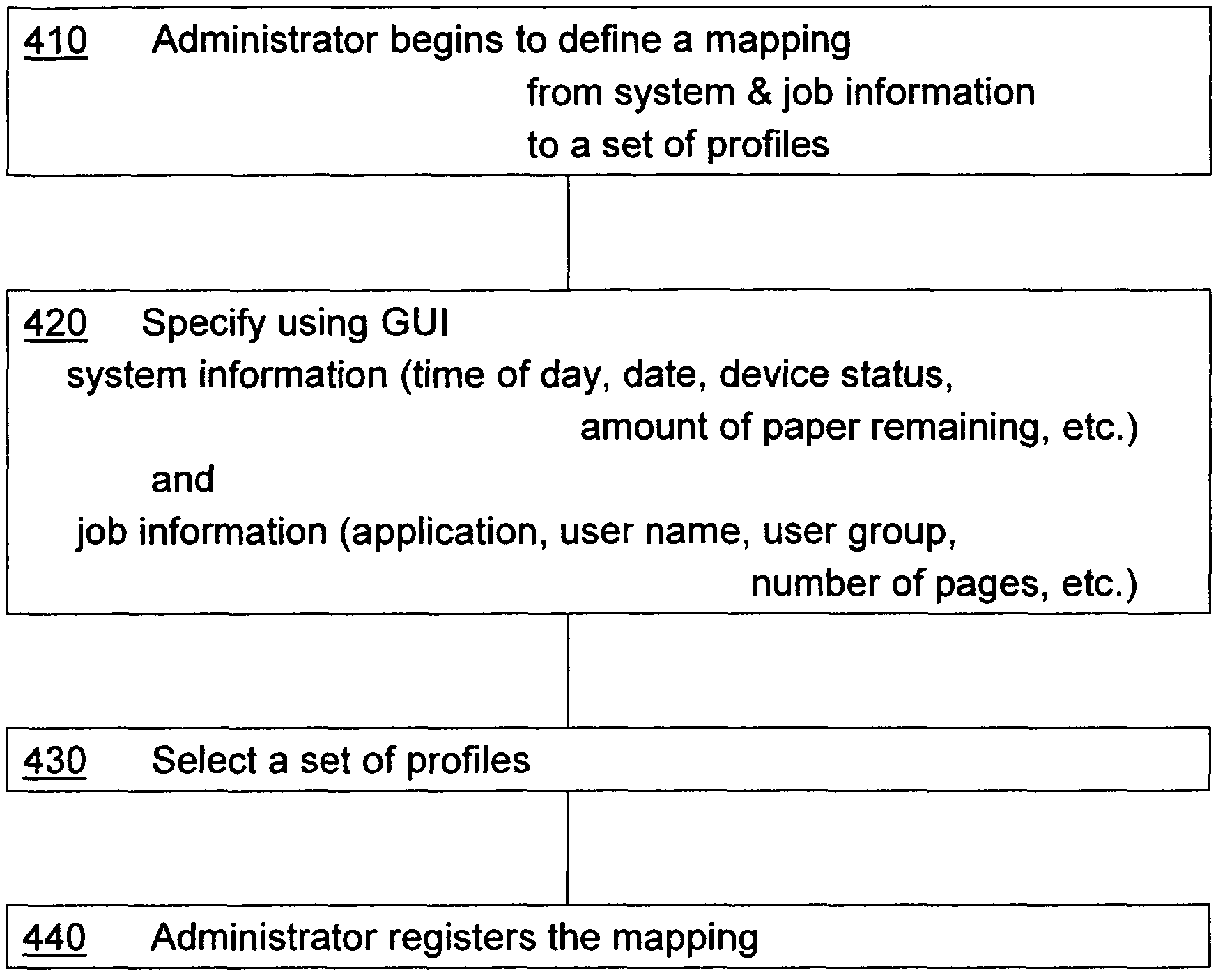
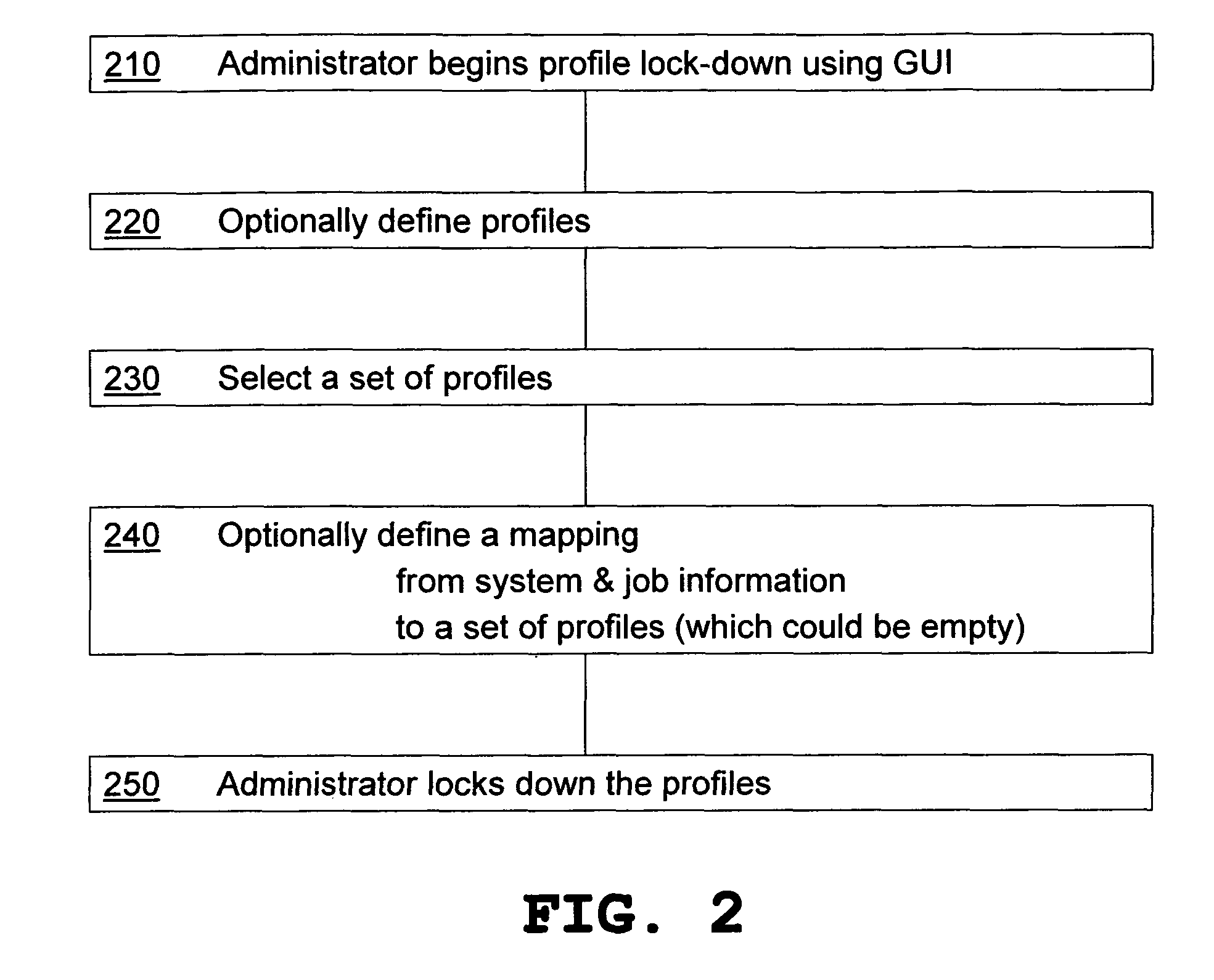
Device driver setting profile lock-down
InactiveUS7797753B2Avoids waste from setting errorPrevent setting errorsDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionFile systemPersonal details
A method for providing a menu for a device, by providing a GUI for an administrator to select and lock-down device driver setting profiles, and providing a GUI for displaying to a user the locked-down profiles and permitting the user to select only from the listed profiles. Allowing a user to choose only from the pre-defined profiles makes for convenience and avoids waste from setting errors by novice users. The computer system detects the current system and job information (time, date, printer status, application, user information, etc.) using WMI and SNMP, applies mapping rules defined by an administrator, and displays only those profiles that are applicable to the current system and job status. Methods also include defining new profiles; alerting the user when no profiles are available, with mapping explanation and suggestion; profile detail display; and printer support.
Owner:KYOCERA TECH DEV
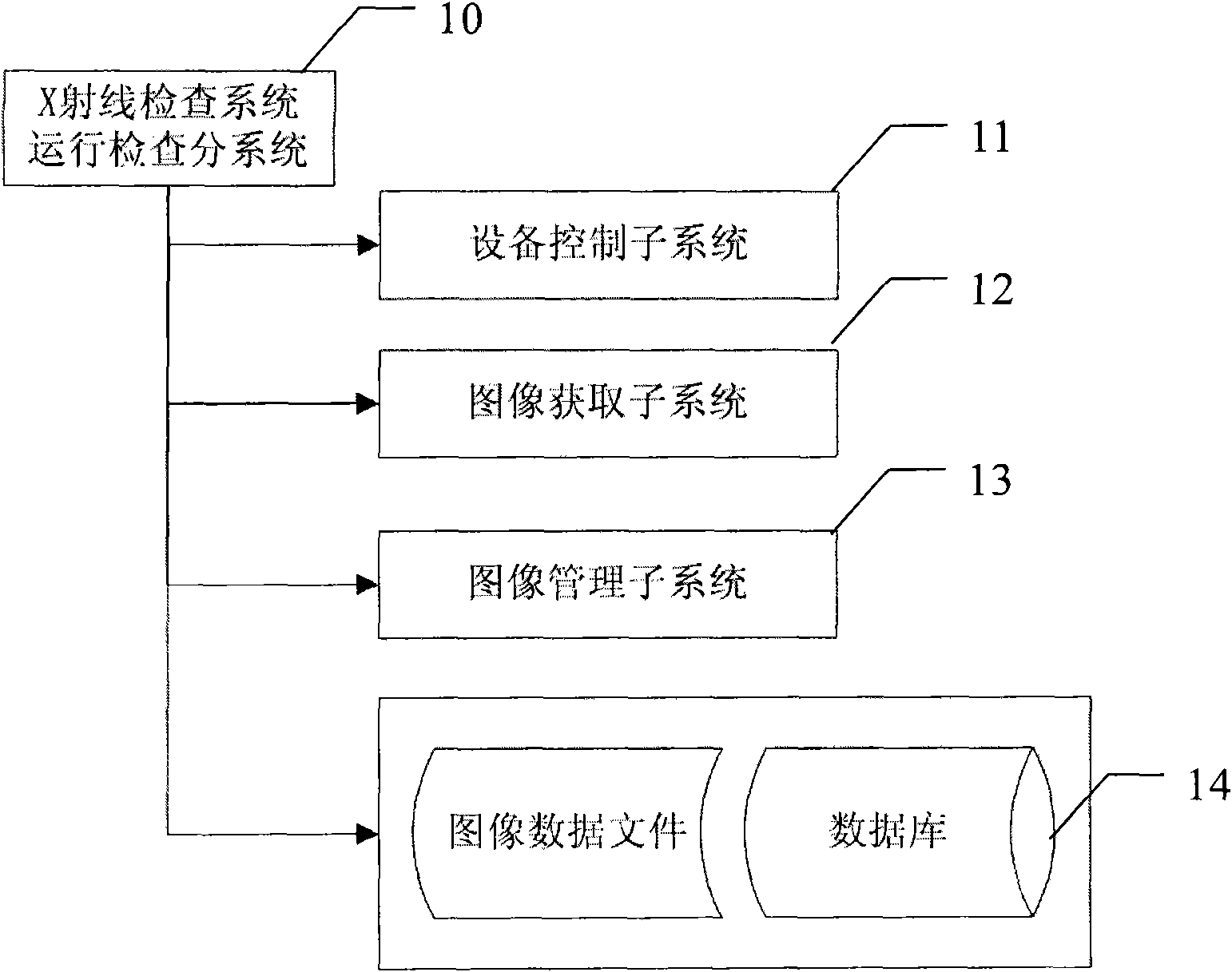
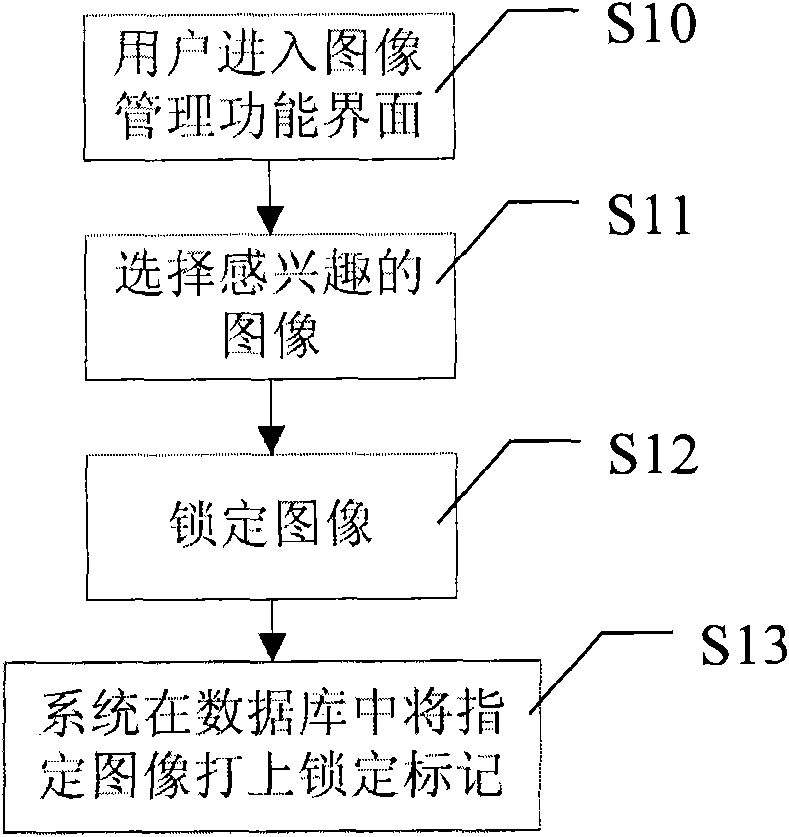
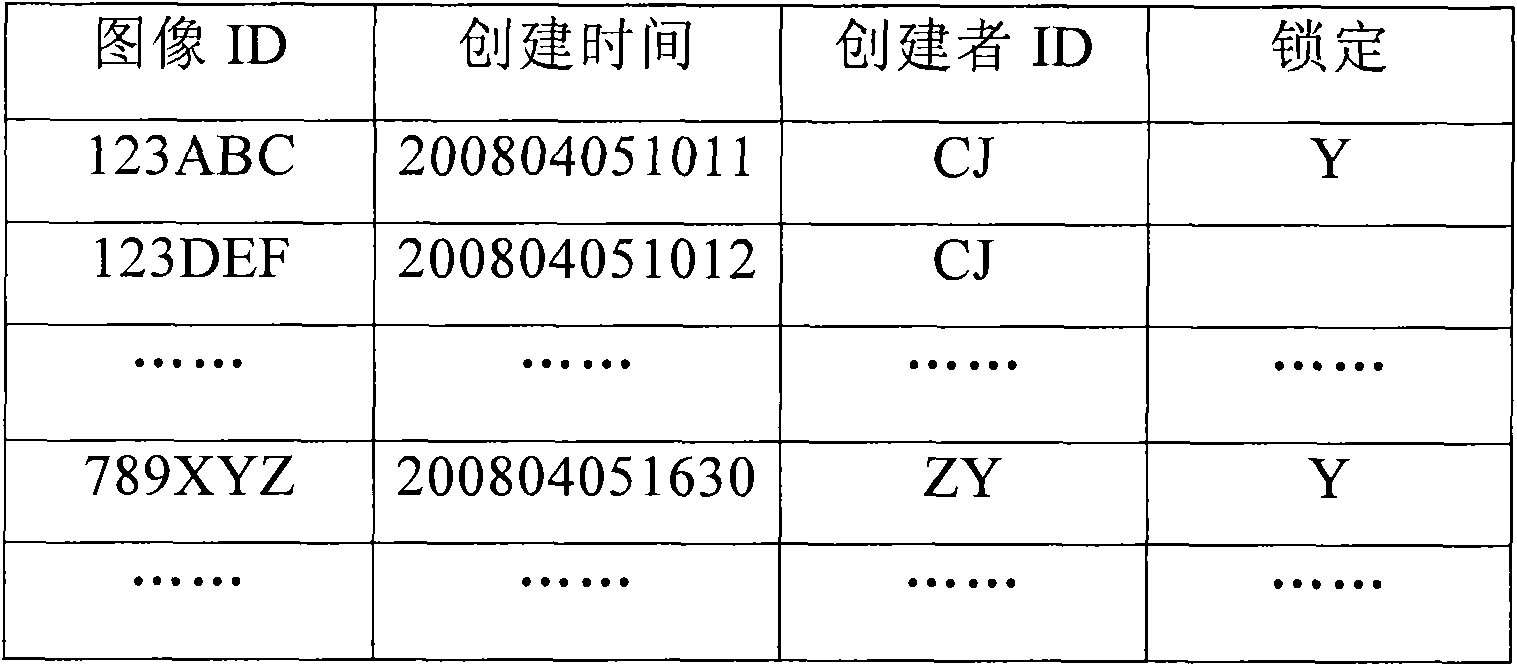
Image file locking method and image file maintenance method
InactiveCN101673269AIndividual entry/exit registersSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)File locking
The invention discloses an image file locking method and an image file maintenance method. A user sets a locking flag for an image file when managing the image file, and then determines whether to delete an image according to whether the image file has the locking flag or not in the process that a system automatically maintains the image.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD
Method and system for restarting file lock services at an adoptive node during a network filesystem server migration or failover
ActiveUS8533171B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFailoverFile system
A method for file lock recovery in a distributed computer system. The method includes executing a distributed computer system having a plurality of nodes comprising a cluster, and initiating a network file system server fail over from one node of the cluster to an adoptive node of the cluster. File lock services are then stopped at the adoptive node. File lock services are subsequently restarted at the adoptive node, wherein the restart causes the adoptive node to commence a grace period for other network file system clients to connect to the adoptive node and reclaim file locks. After restarting file lock services, a cluster file system is updated on the adoptive node with process identifiers, and file lock services are resumed at the adoptive node. The cluster file system can be simultaneously exposing the file lock services to other clients as well, like CIFS, etc.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
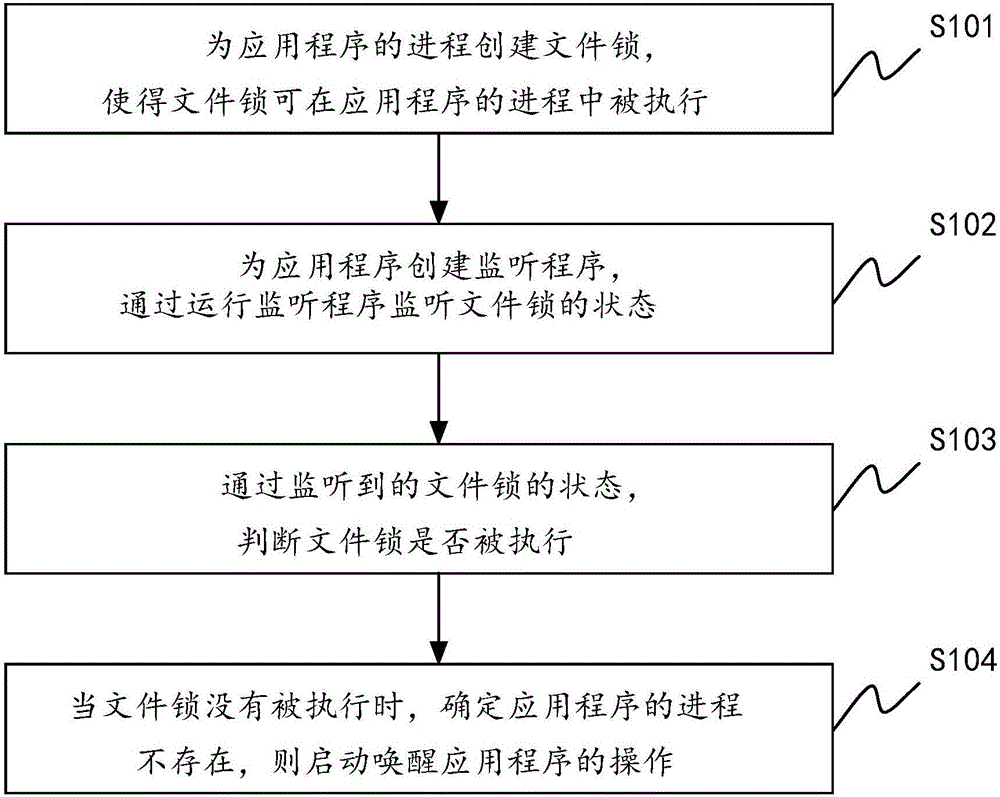
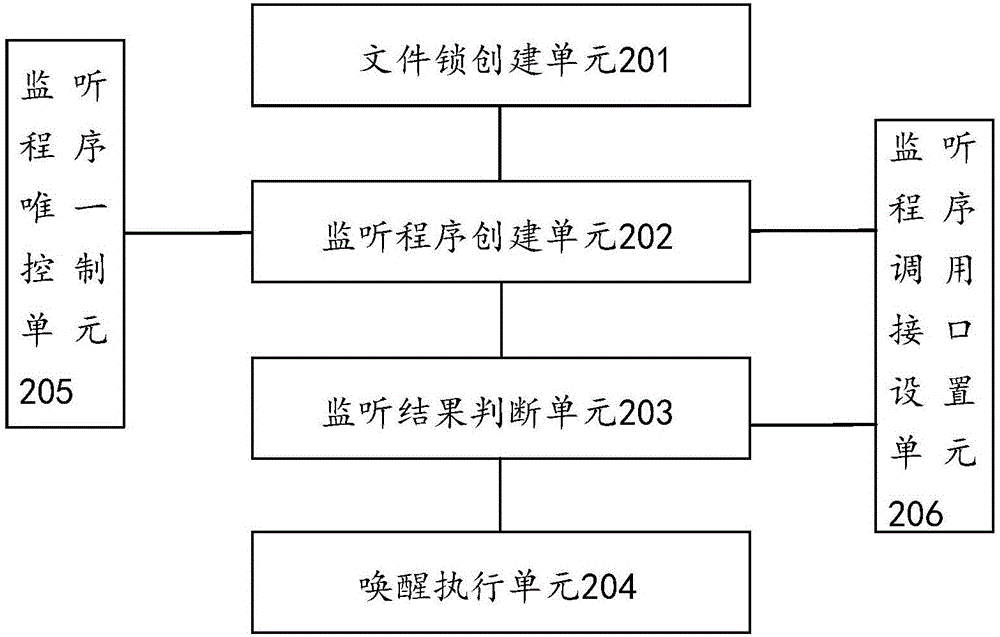
Method and device for wakening application program of terminal
The invention discloses a method and device for wakening an application program of a terminal. The method comprises the steps that a file lock is created for a process of the application program, and therefore the file lock can be executed in the process of the application program; a monitoring program is created for the application program, and the state of the file lock is monitored by operating the monitoring program; whether the file lock is executed or not is judged according to the monitored state of the file lock; when the file lock is not executed, it is determined that the process of the application program does not exist, and an operation of wakening the application program is enabled. According to the method and device, the killed application program can be wakened in time.
Owner:WUHAN DOUYU NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com