Patents
Literature
46results about How to "Prevent setting errors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
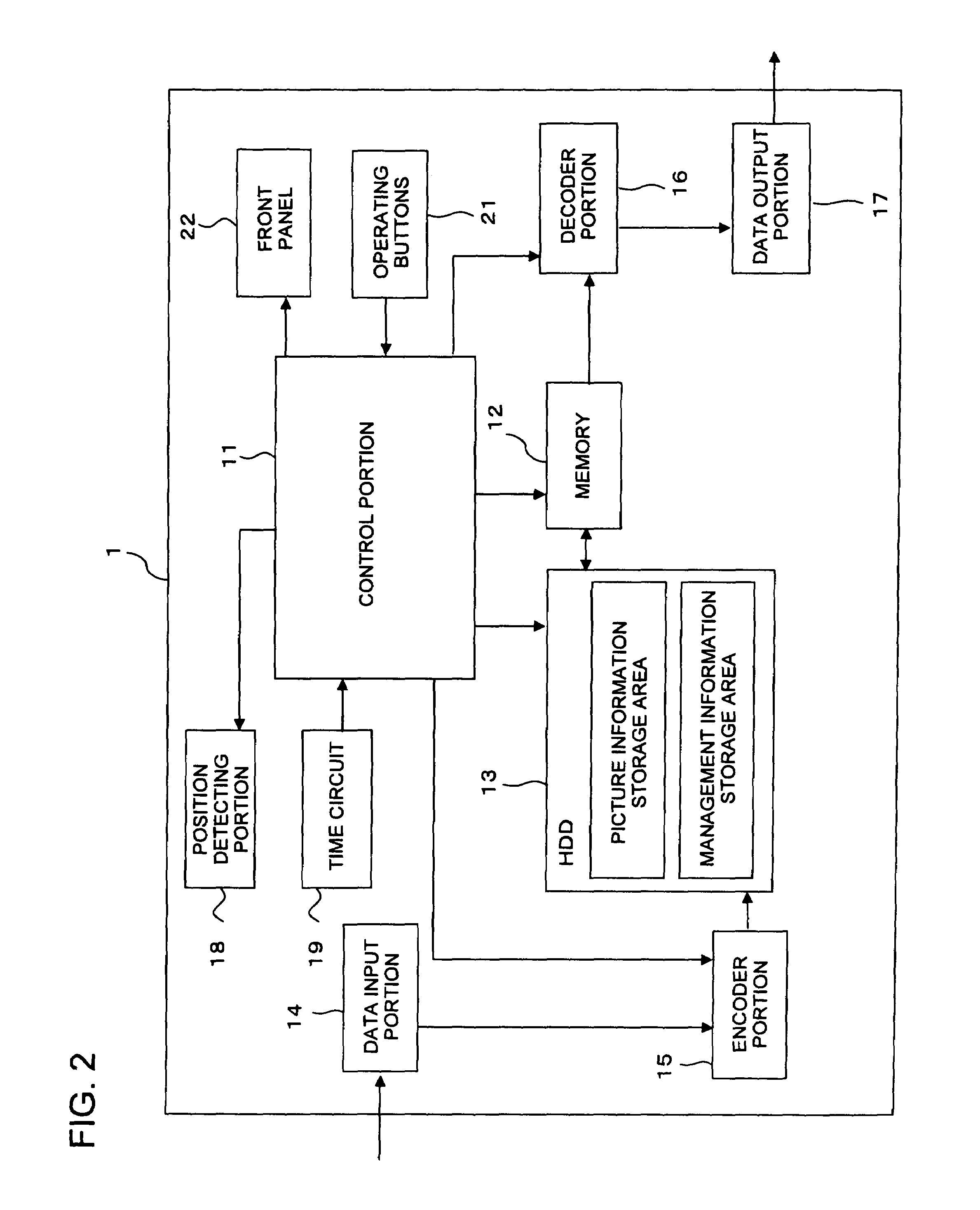
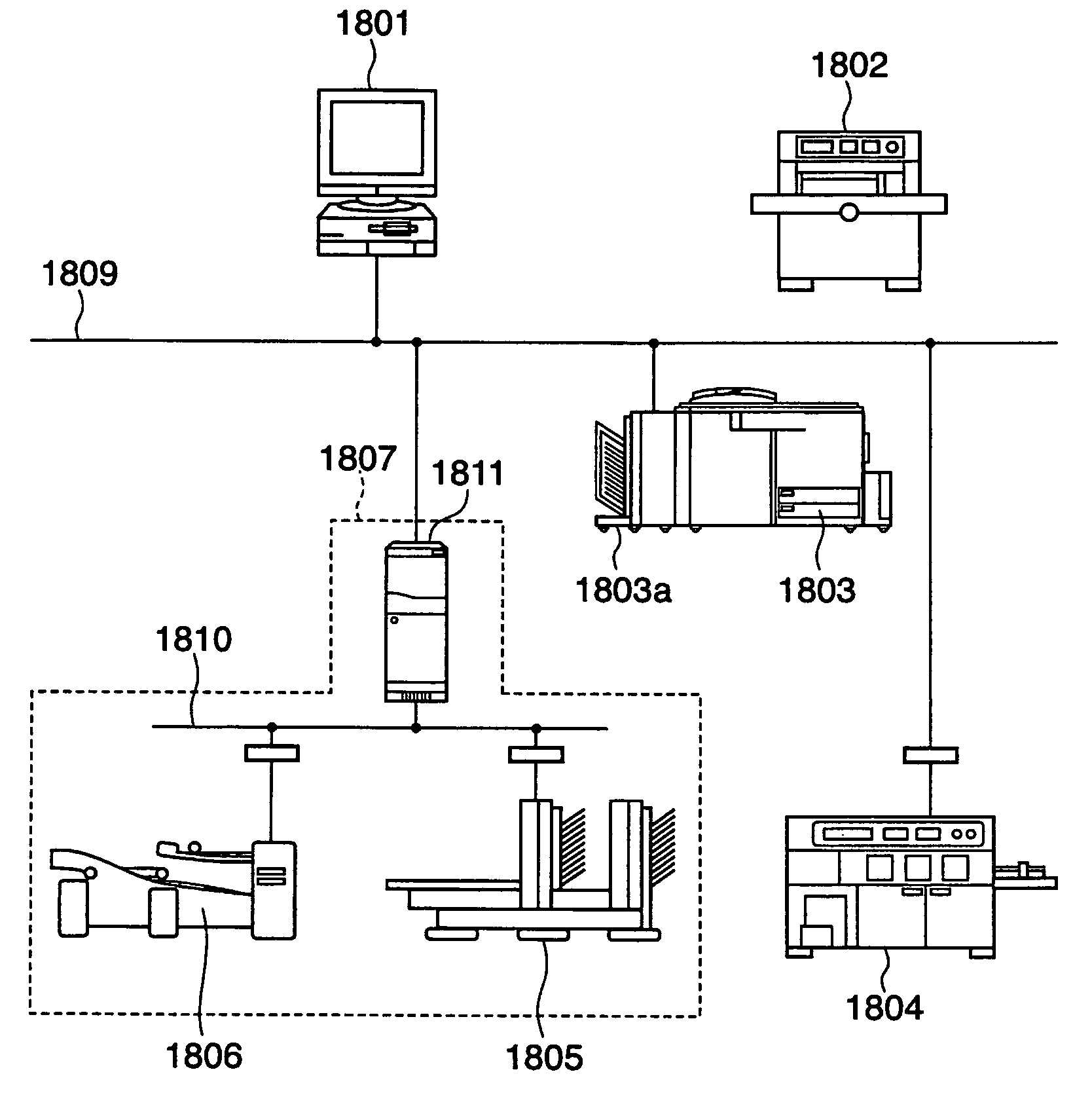
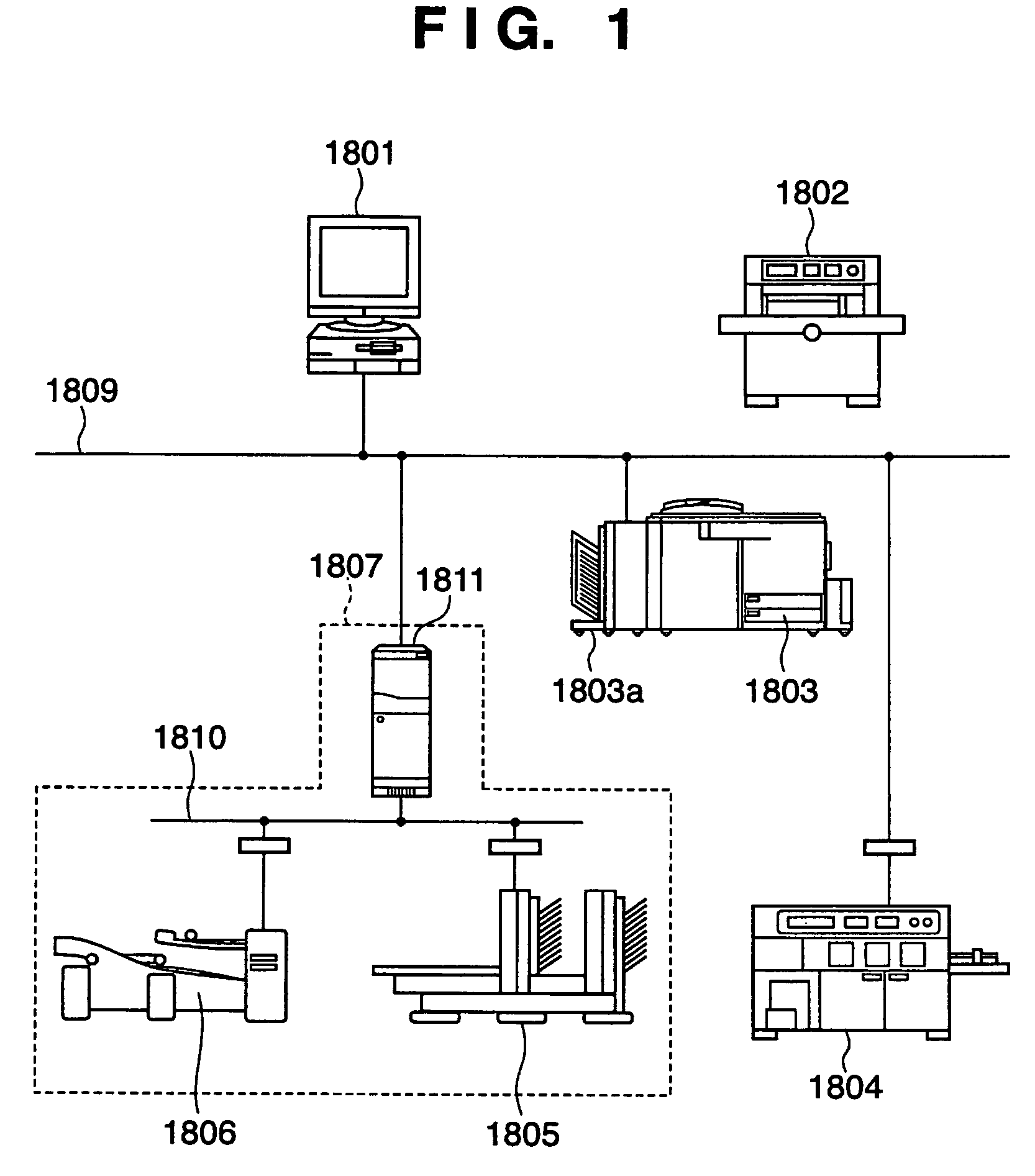
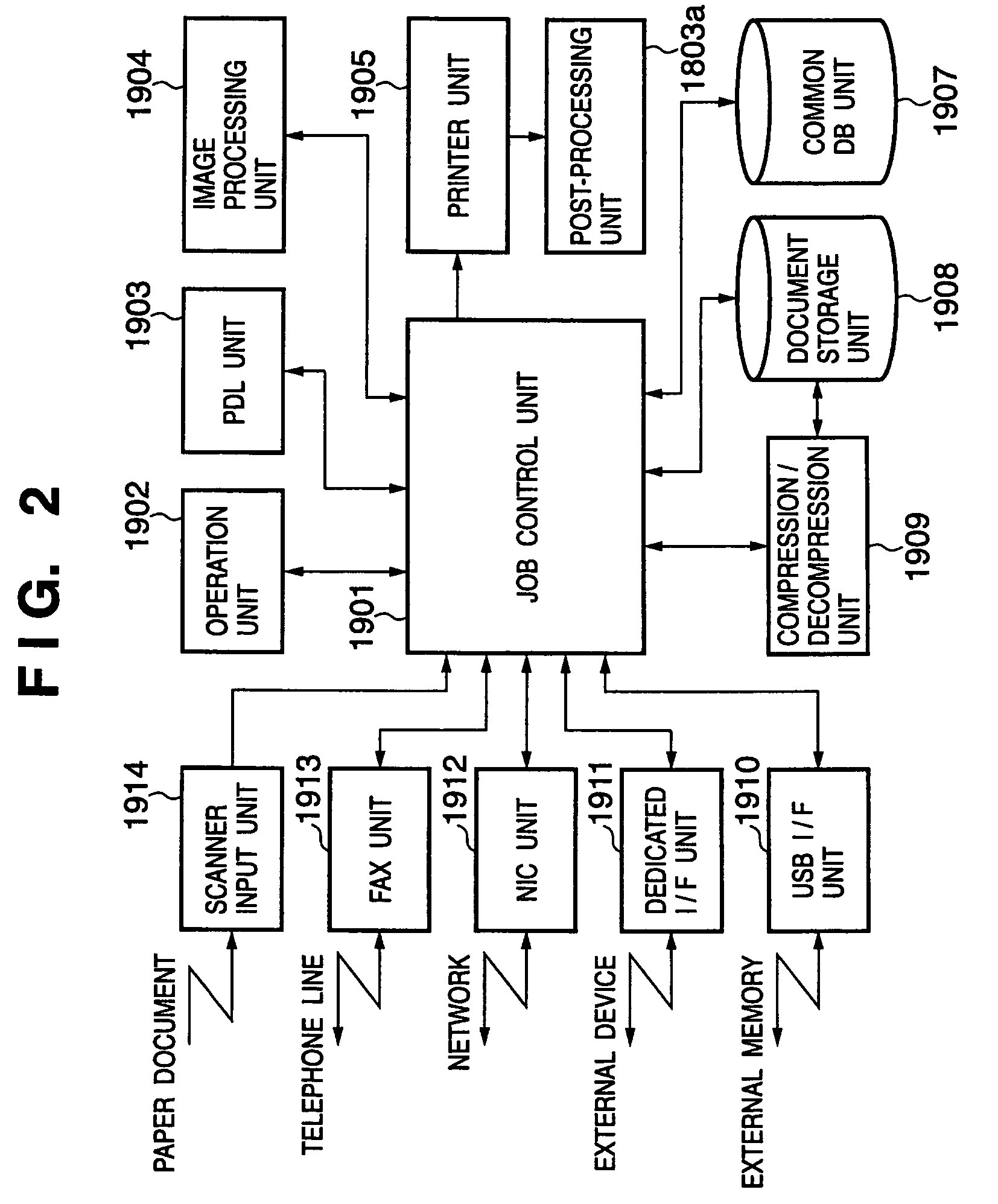
On-demand publishing system
ActiveUS20060238793A1Improve productivityAvoid it happening againVisual presentationPictoral communicationInformation processingComputer science
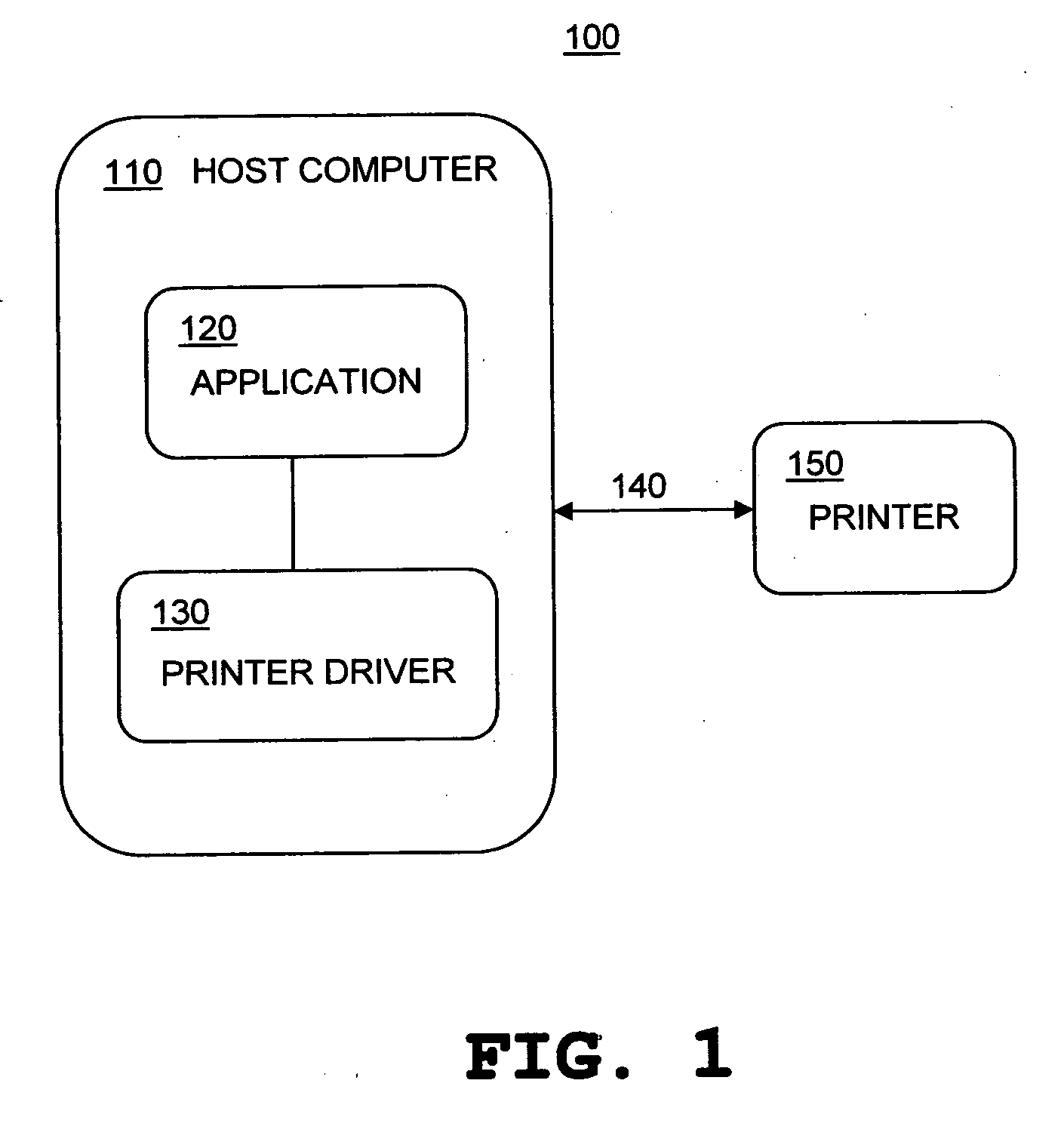
According to the present invention, an information processing apparatus comprises: a loading unit which loads function information representing a function of the post-printing processing device; an identification unit which identifies a printing function processible by the printing device and a post-processing function processible after printing by the post-printing processing device; a display control unit which displays a setting window for setting the printing function and post-processing function; a data generation unit which generates printing data to be printed by the printing device; and a setting information generation unit which generates post-processing setting information subjected to post-printing processing by the post-printing processing device, wherein the printing data is transmitted to the printing device, and the post-processing setting information is transmitted to the post-printing processing device.
Owner:CANON KK
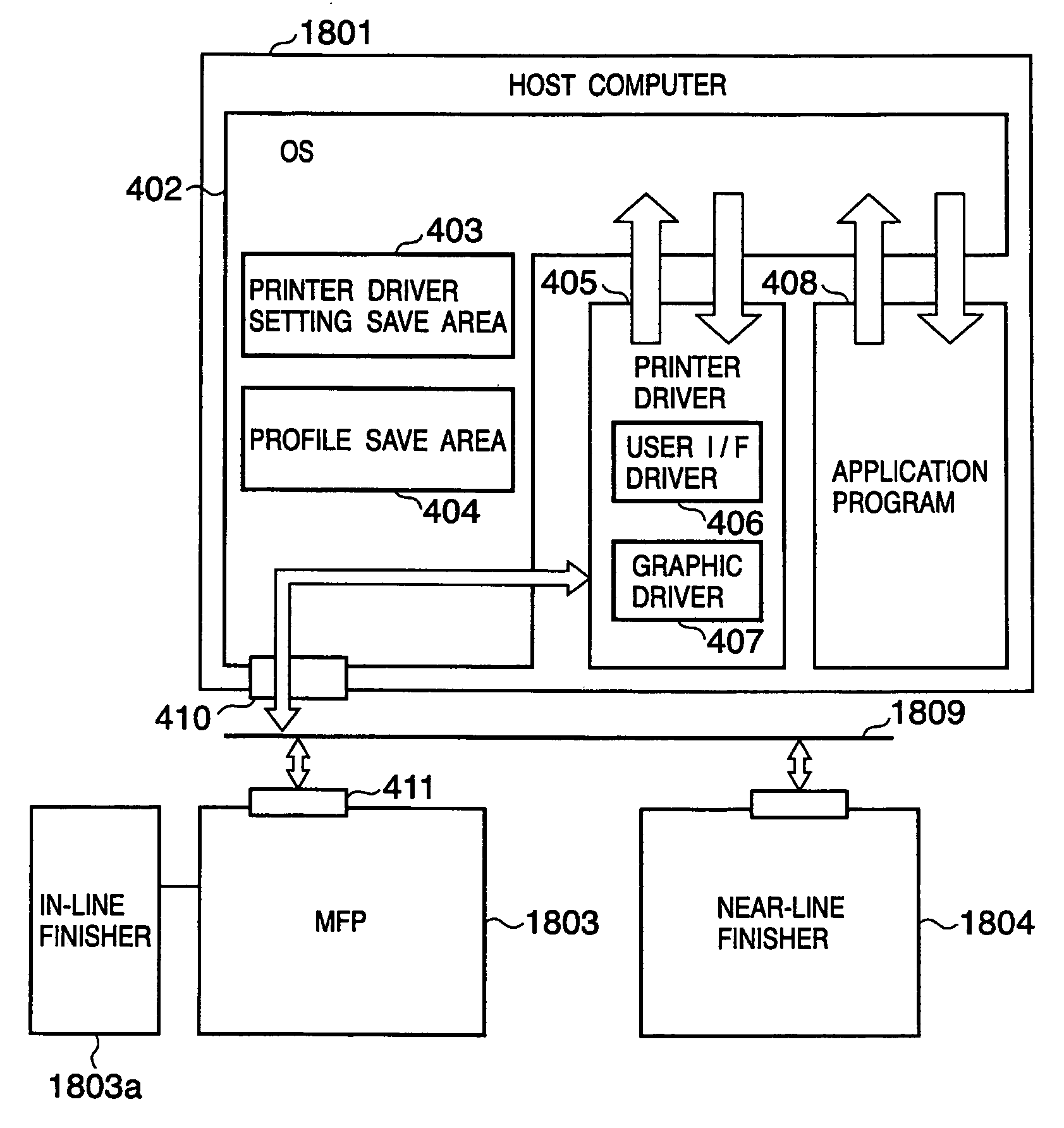
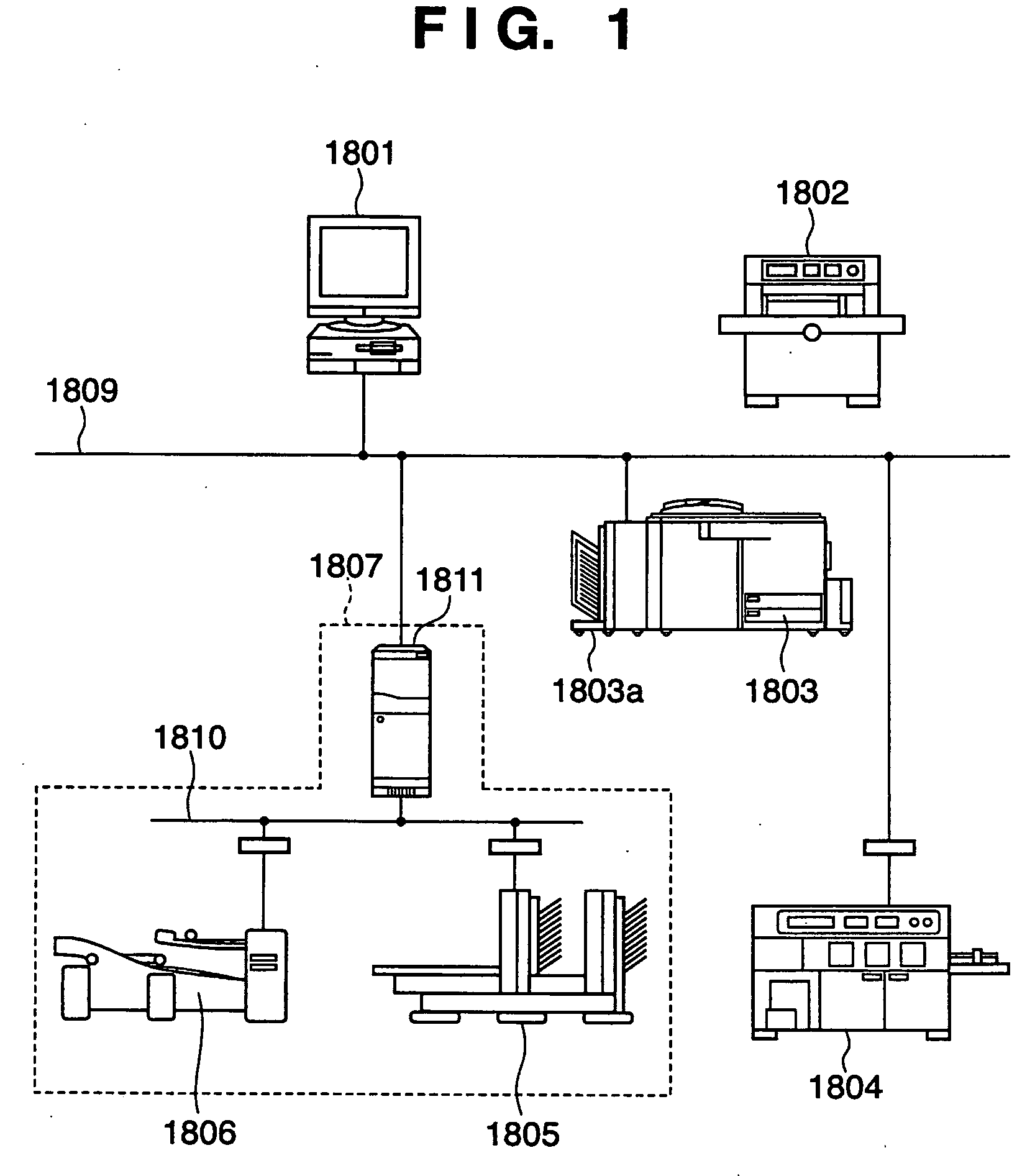
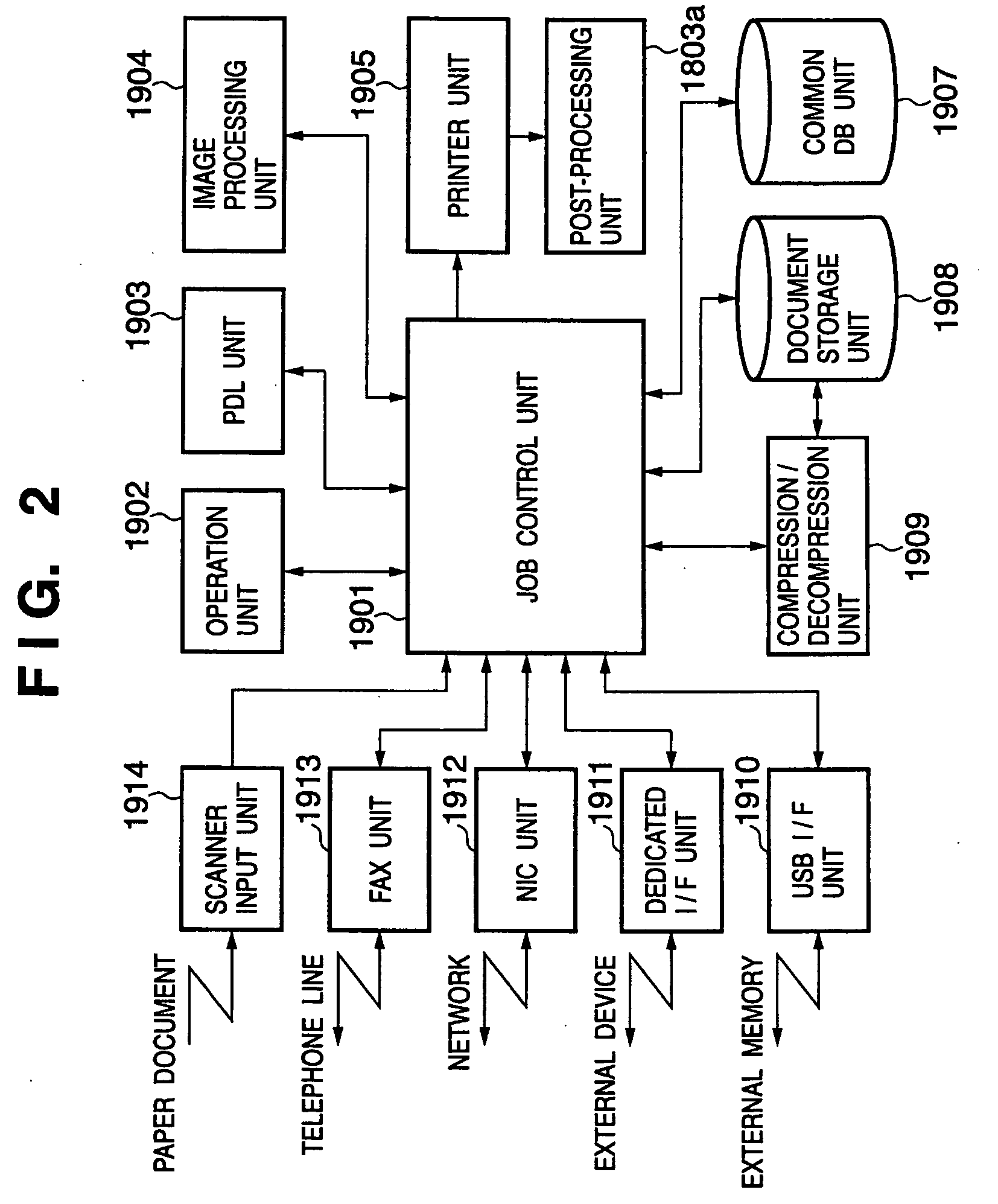
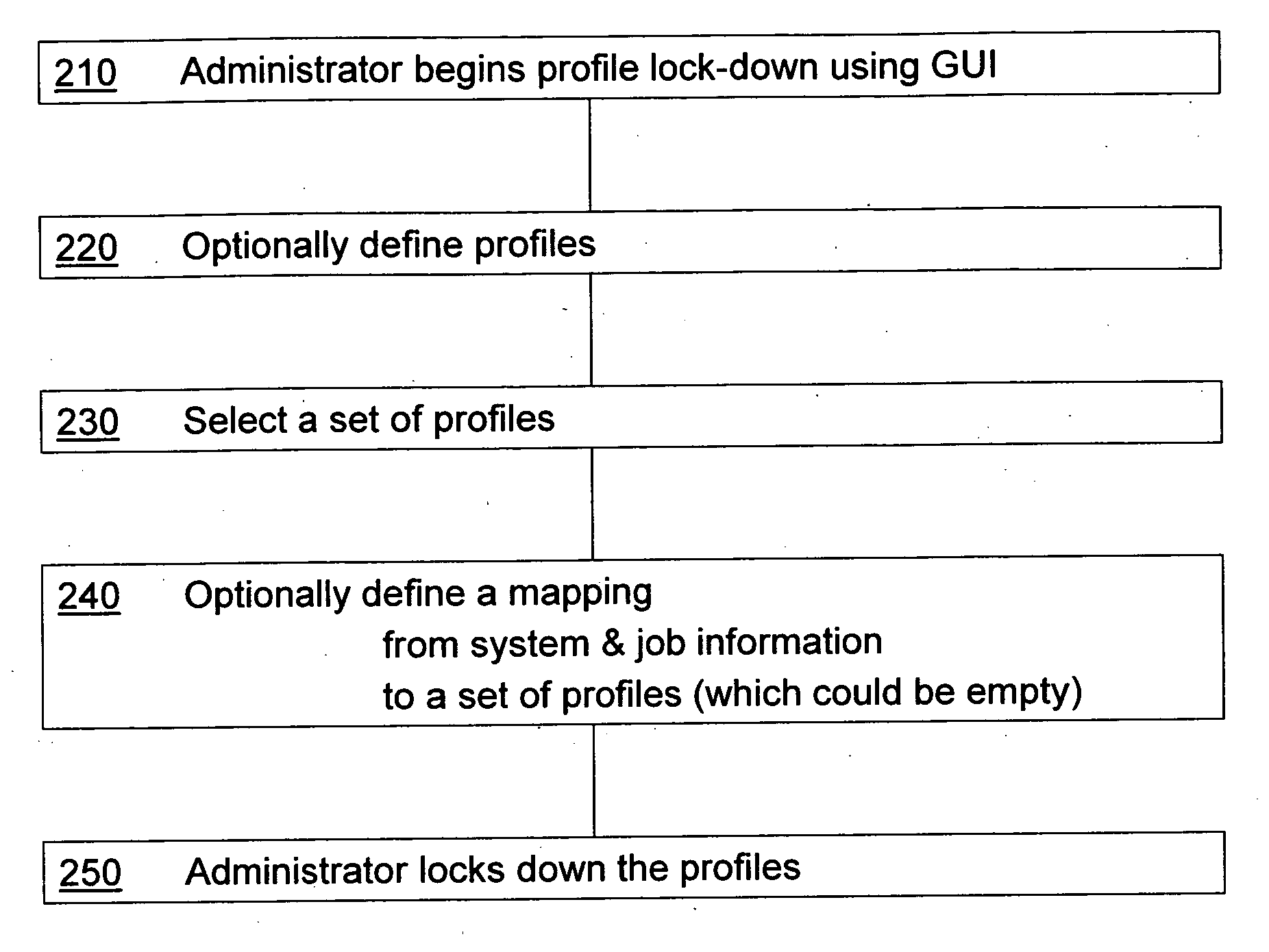
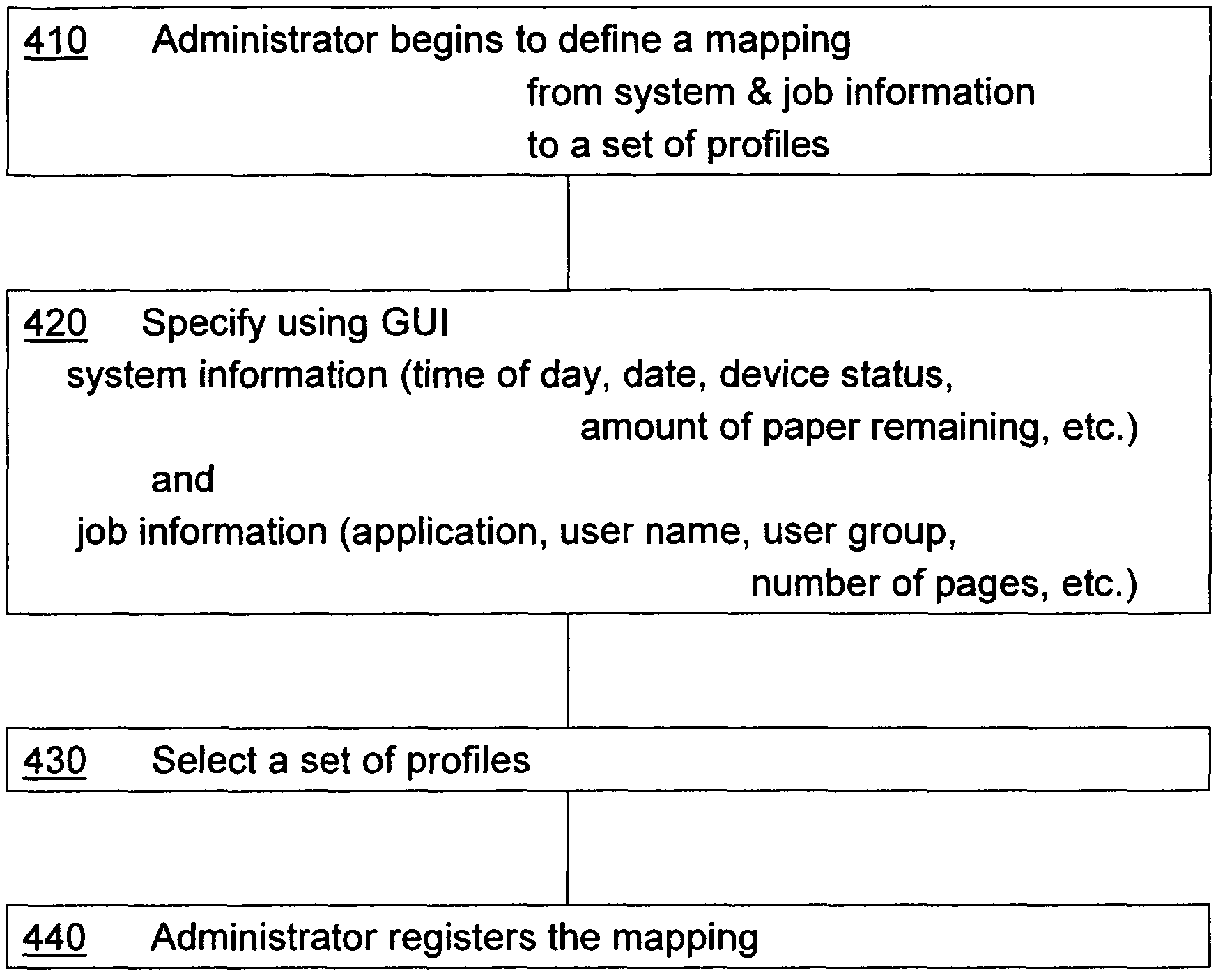
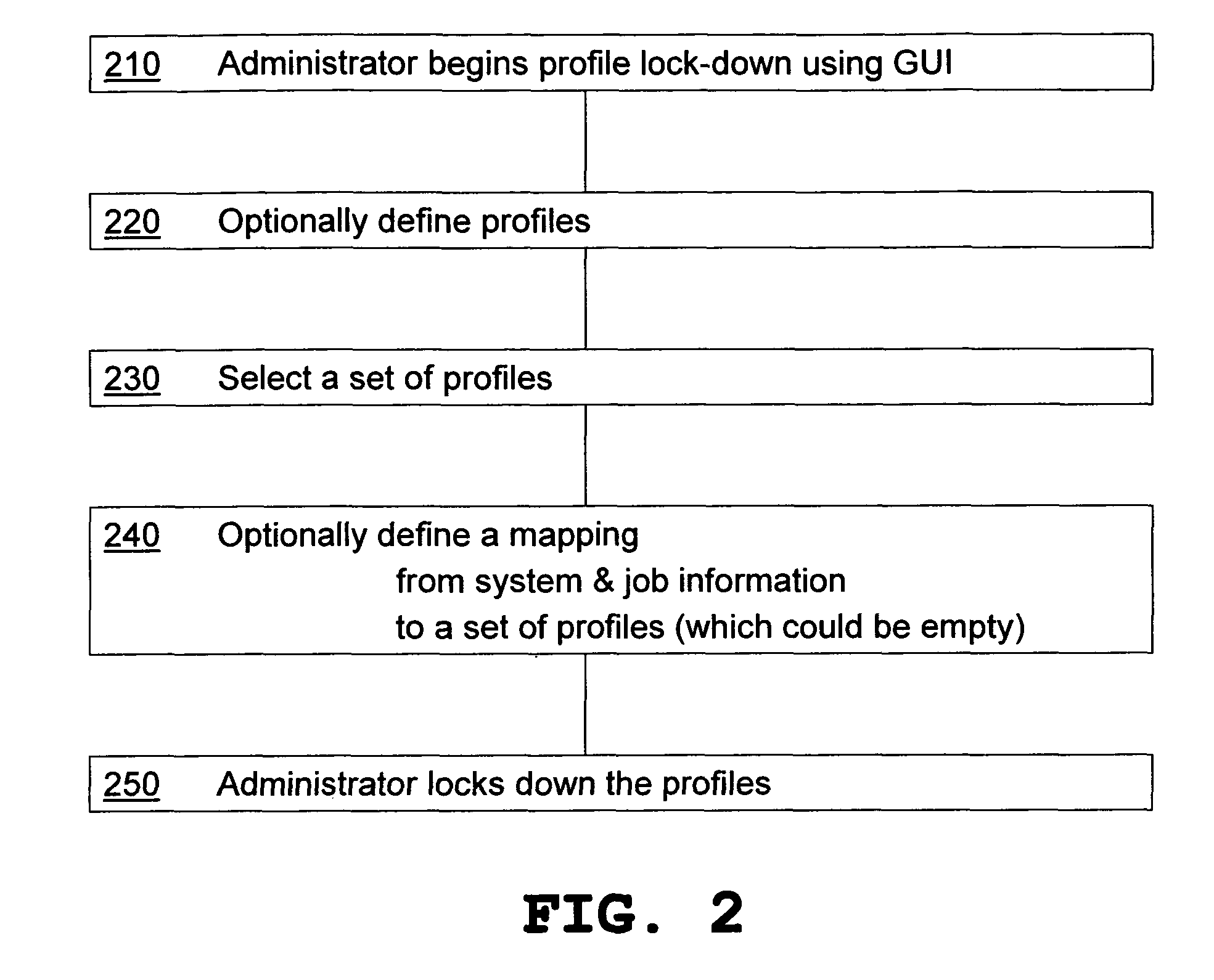
Device driver setting profile lock-down
InactiveUS20060282772A1Avoids waste from setting errorPrevent setting errorsDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionConfigfsComputer science
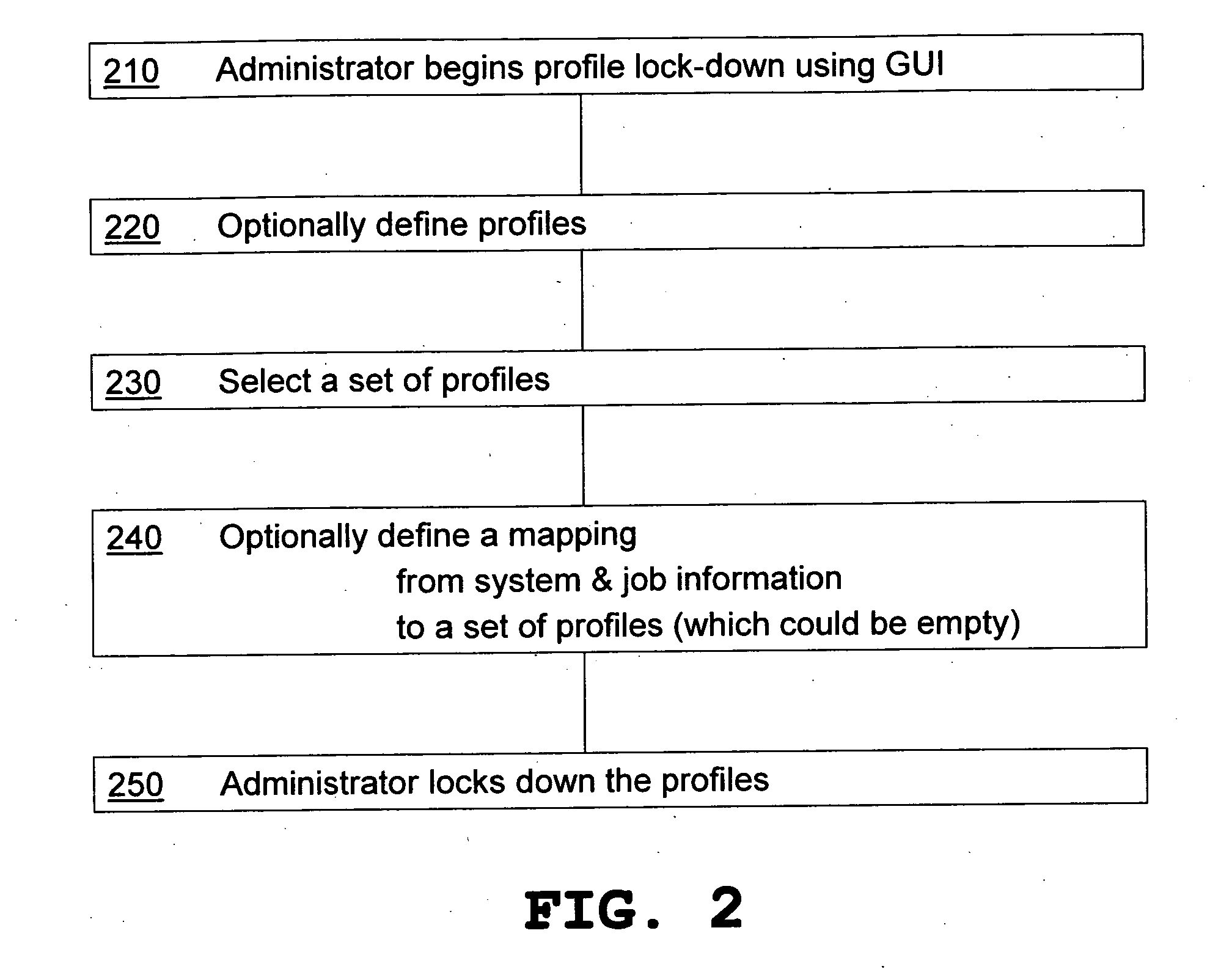
A method for providing a menu for a device, by providing a GUI for an administrator to select and lock-down device driver setting profiles, and providing a GUI for displaying to a user the locked-down profiles and permitting the user to select only from the listed profiles. Allowing a user to choose only from the pre-defined profiles makes for convenience and avoids waste from setting errors by novice users. The computer system detects the current system and job information (time, date, printer status, application, user information, etc.) using WMI and SNMP, applies mapping rules defined by an administrator, and displays only those profiles that are applicable to the current system and job status. Methods also include defining new profiles; alerting the user when no profiles are available, with mapping explanation and suggestion; profile detail display; and printer support.
Owner:KYOCERA TECH DEV
Elevating device for window glass
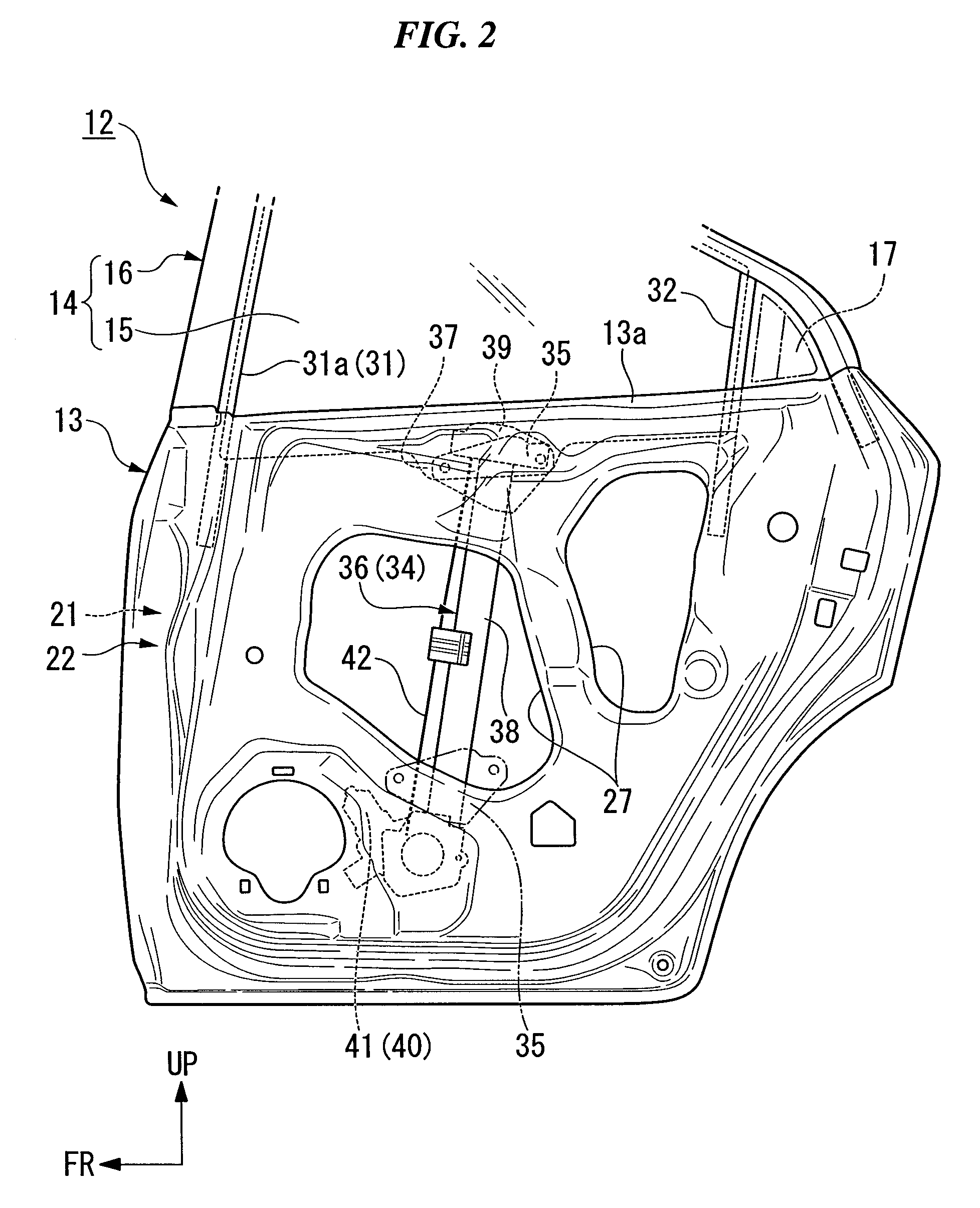
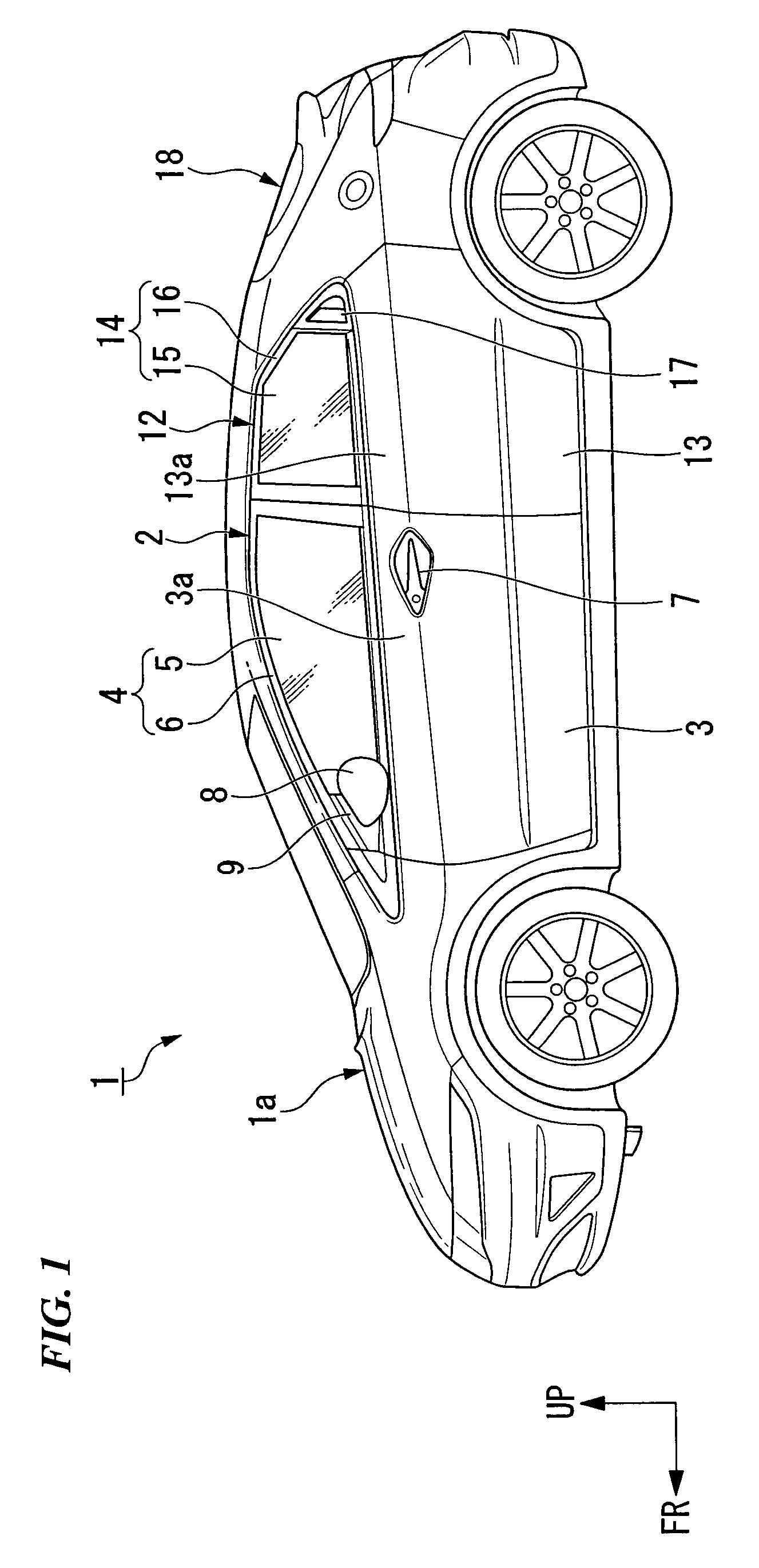
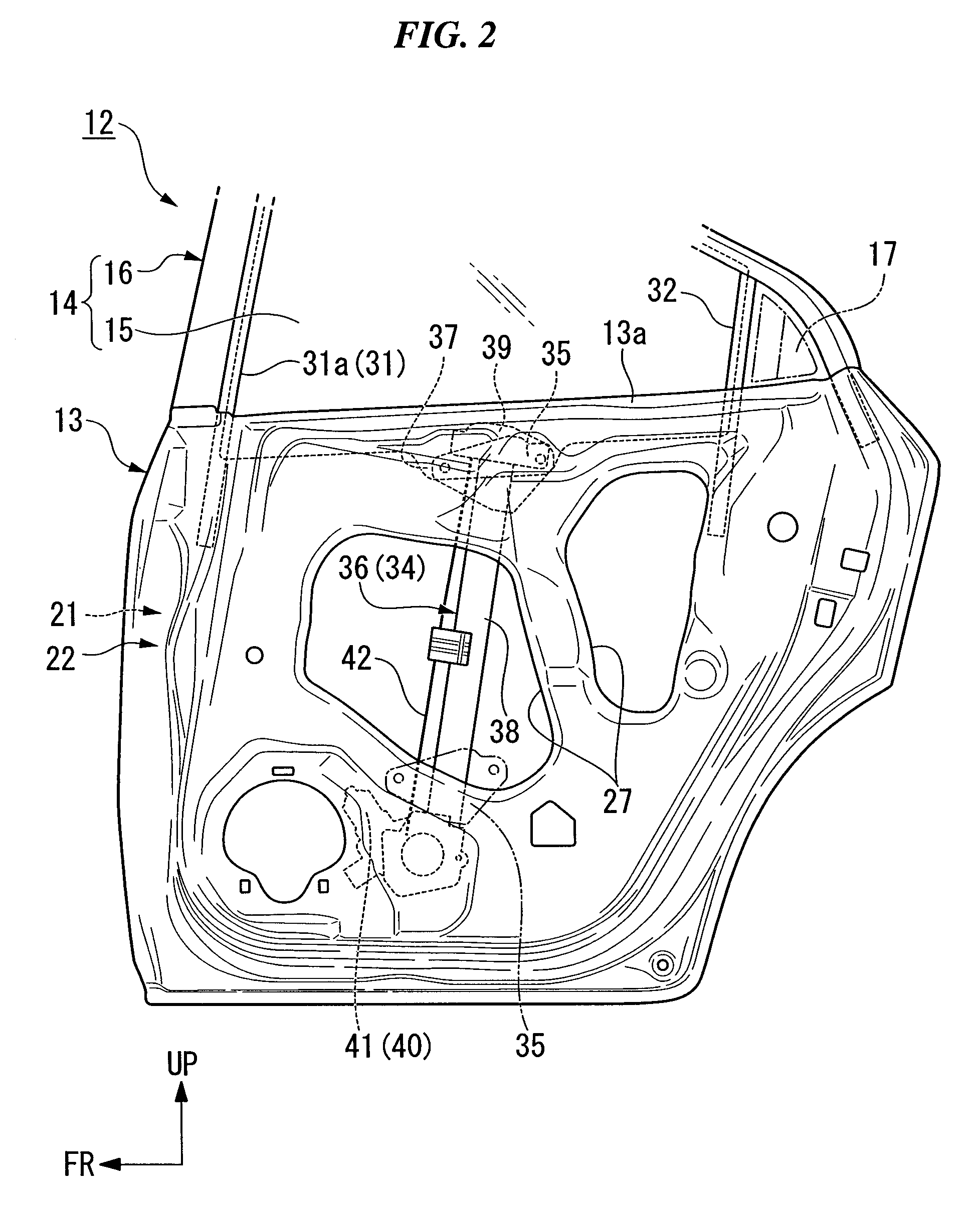
InactiveUS20070144073A1Prevent setting errorsAvoid knockingMan-operated mechanismPower-operated mechanismEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Image forming apparatus and display method thereof
InactiveUS20110242561A1Prevent setting errorsSetting error can be eliminatedDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsLiquid-crystal displayComputer graphics (images)
An image forming apparatus 100 includes: an image forming part 6, a liquid crystal display part 11, a storage device 92 storing a program for displaying a setting screen at the liquid crystal display part 11; an input part 1 receiving, for example, a setting made for a setting item; and a help key KH for displaying a help screen at the display part. When the help key KH has been pressed in the setting by the called program, the display part 11, before processing is performed for a referenced setting item as the setting item for which the help screen has been referenced, displays a confirmation screen for confirming whether or not the processing may be performed at the current setting for the referenced setting item.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
Work support apparatus
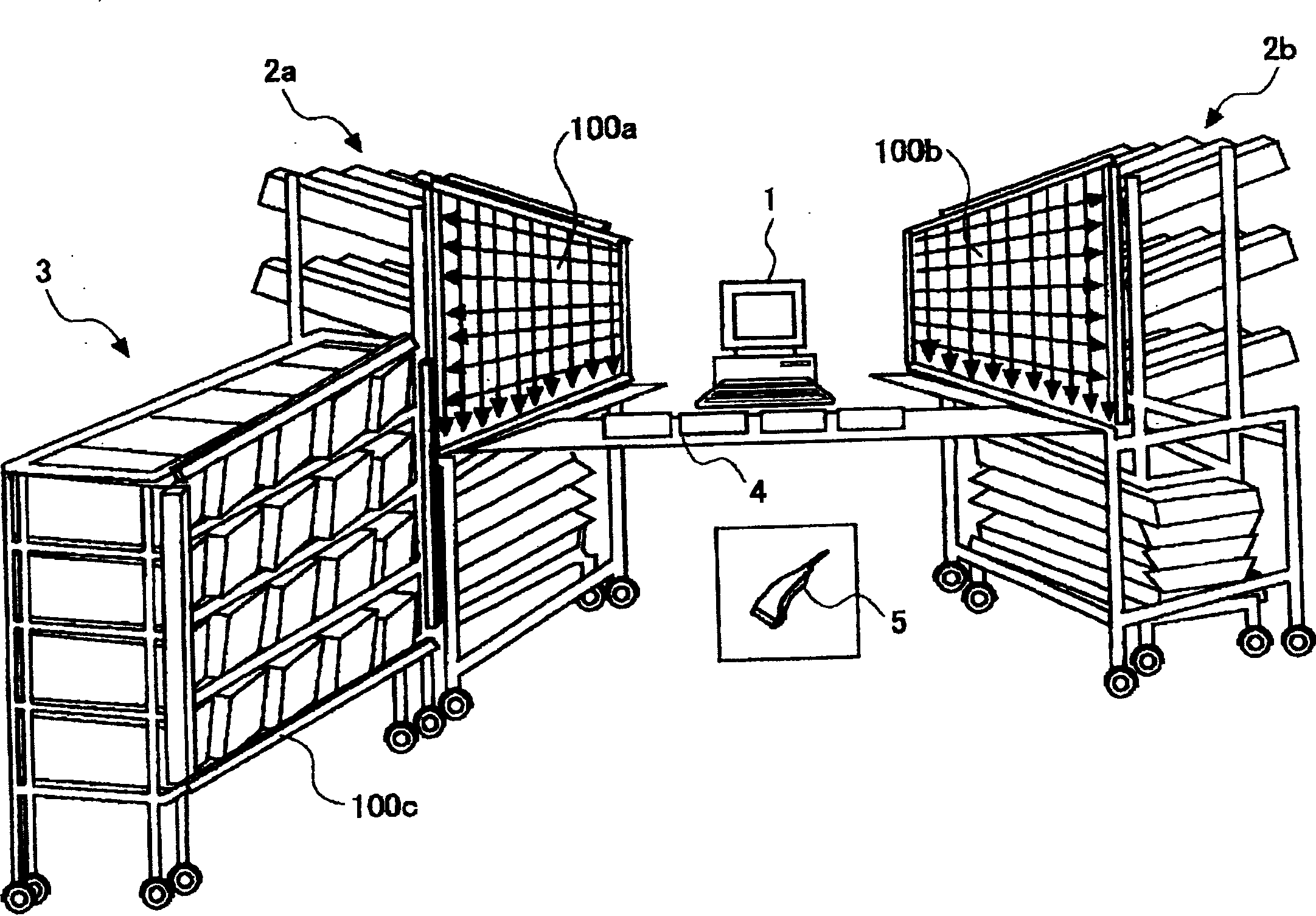
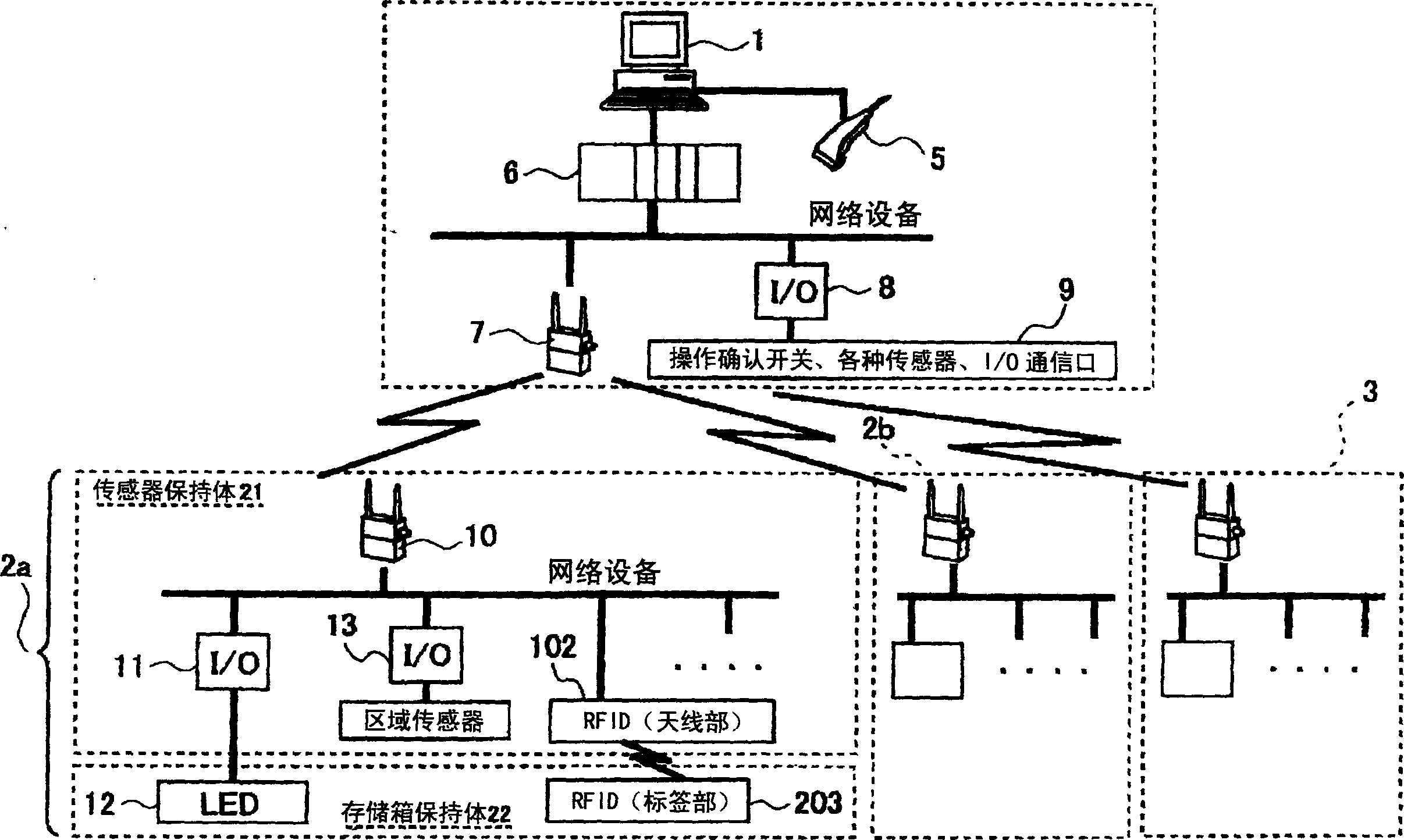
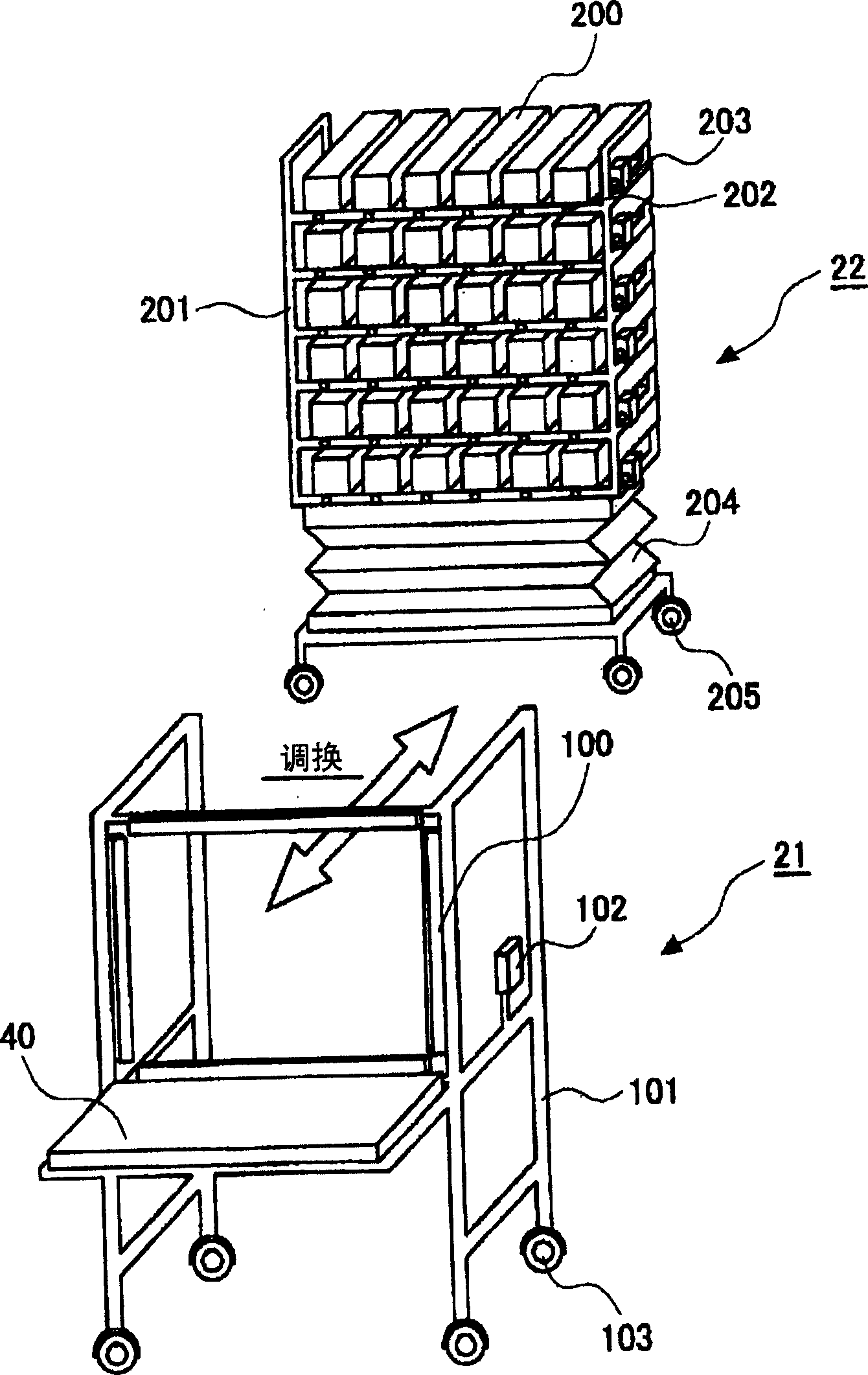
InactiveCN1572419ALow costCheap and easy to makeConveyorsAssembly machinesInformation processorPhotoelectric sensor
A parts shelf (2) has a configuration in which a storage box holding member for holding a plurality of parts storage boxes and a sensor holding member for holding photoelectric sensors are provided separately from each other. As the photoelectric sensor, an area sensor (100) capable of sensing coordinates of a position in which light is shielded in a predetermined two-dimensional area close to the front of the storage box holding member is employed. In an information processor (1), information of parts corresponding to a plurality of parts storage boxes of the storage box holding member and sizes and positions of the storage boxes is pre-stored. On the basis of the pre-stored information and the light-shielded position coordinates sensed by the area sensor, the storage box storing apart, the hand of the operator has reached is sensed.
Owner:OMRON CORP
Elevating device for window glass
InactiveUS7765739B2Prevent setting errorsAvoid knockingMan-operated mechanismPower-operated mechanismEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
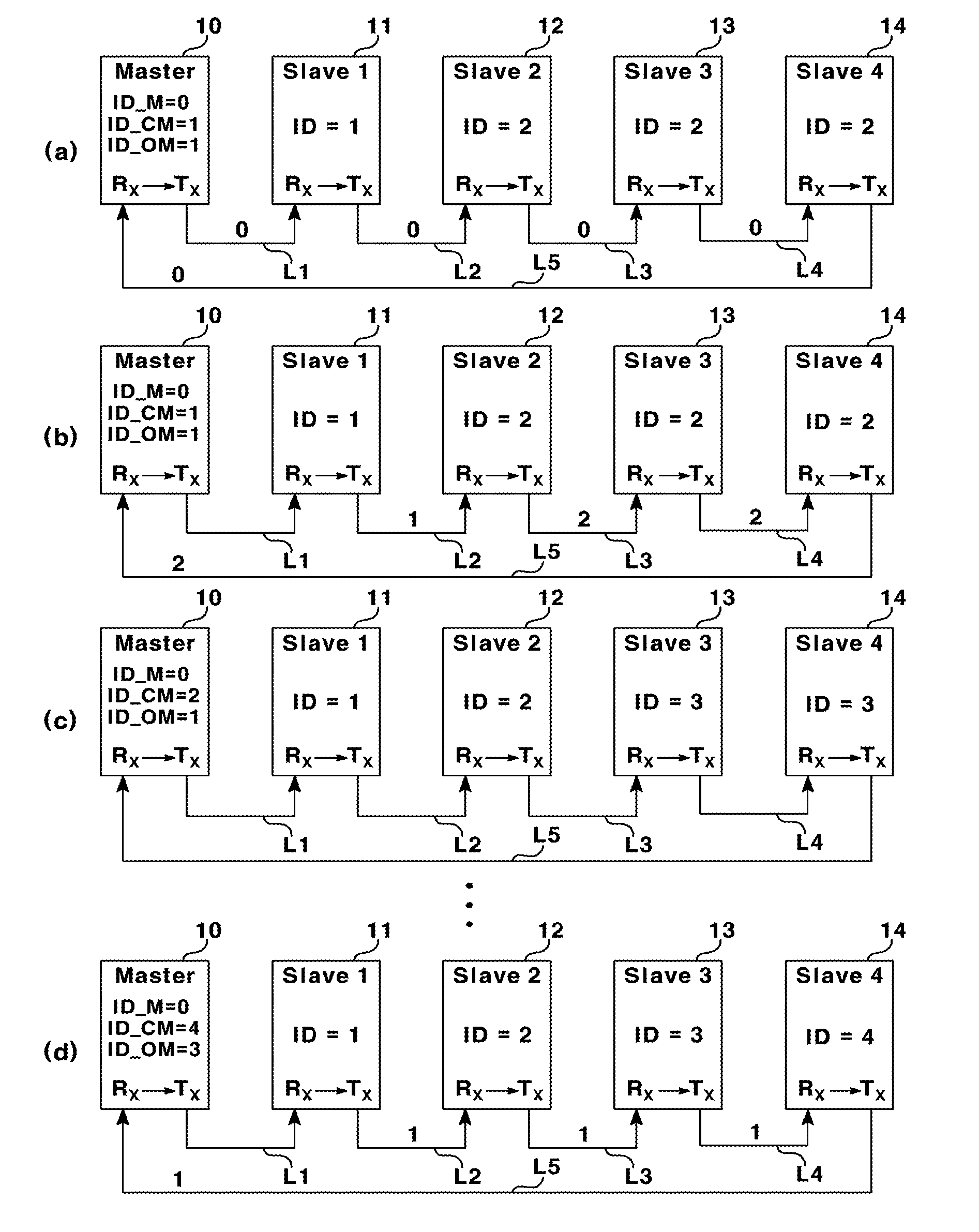
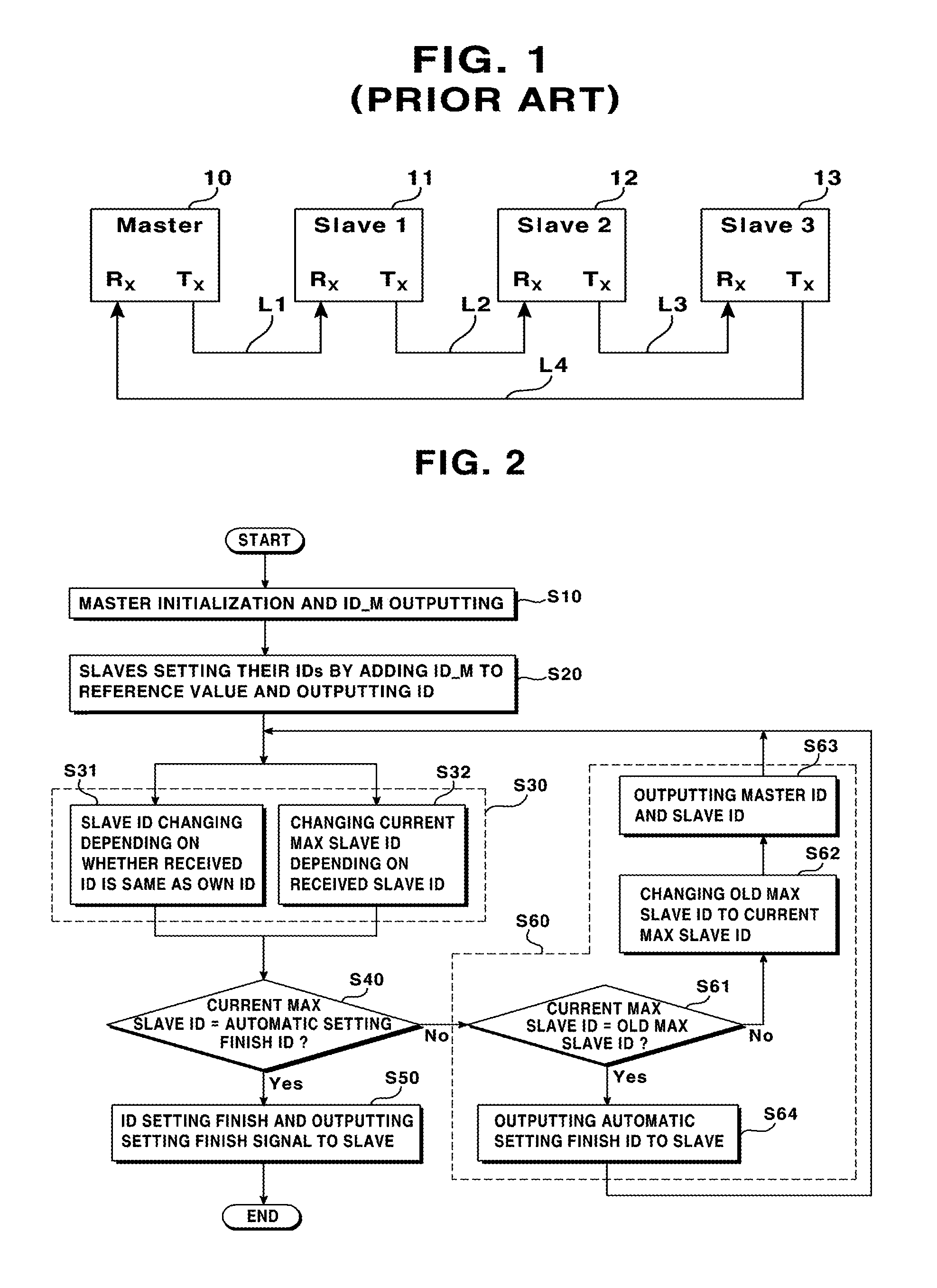
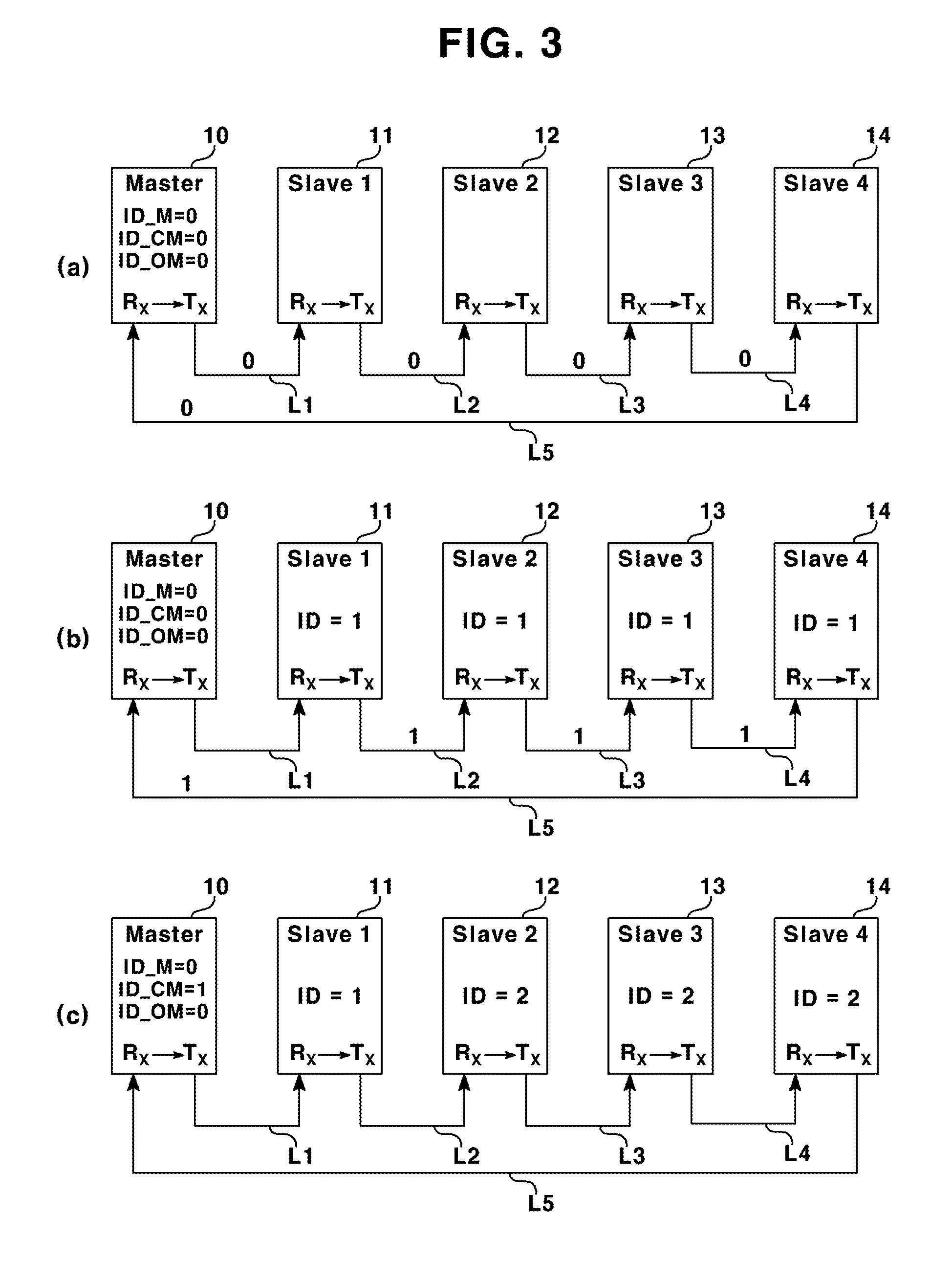
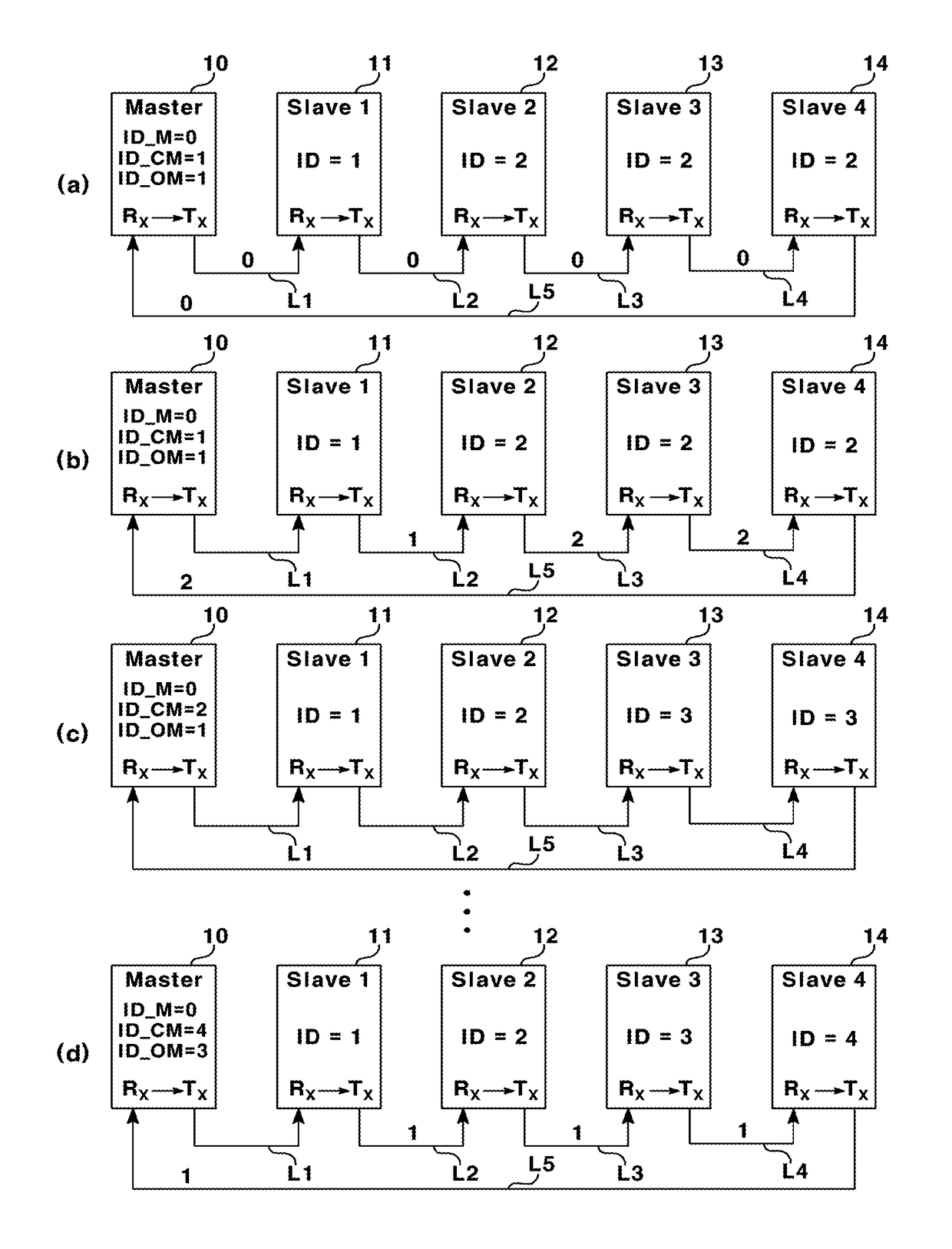
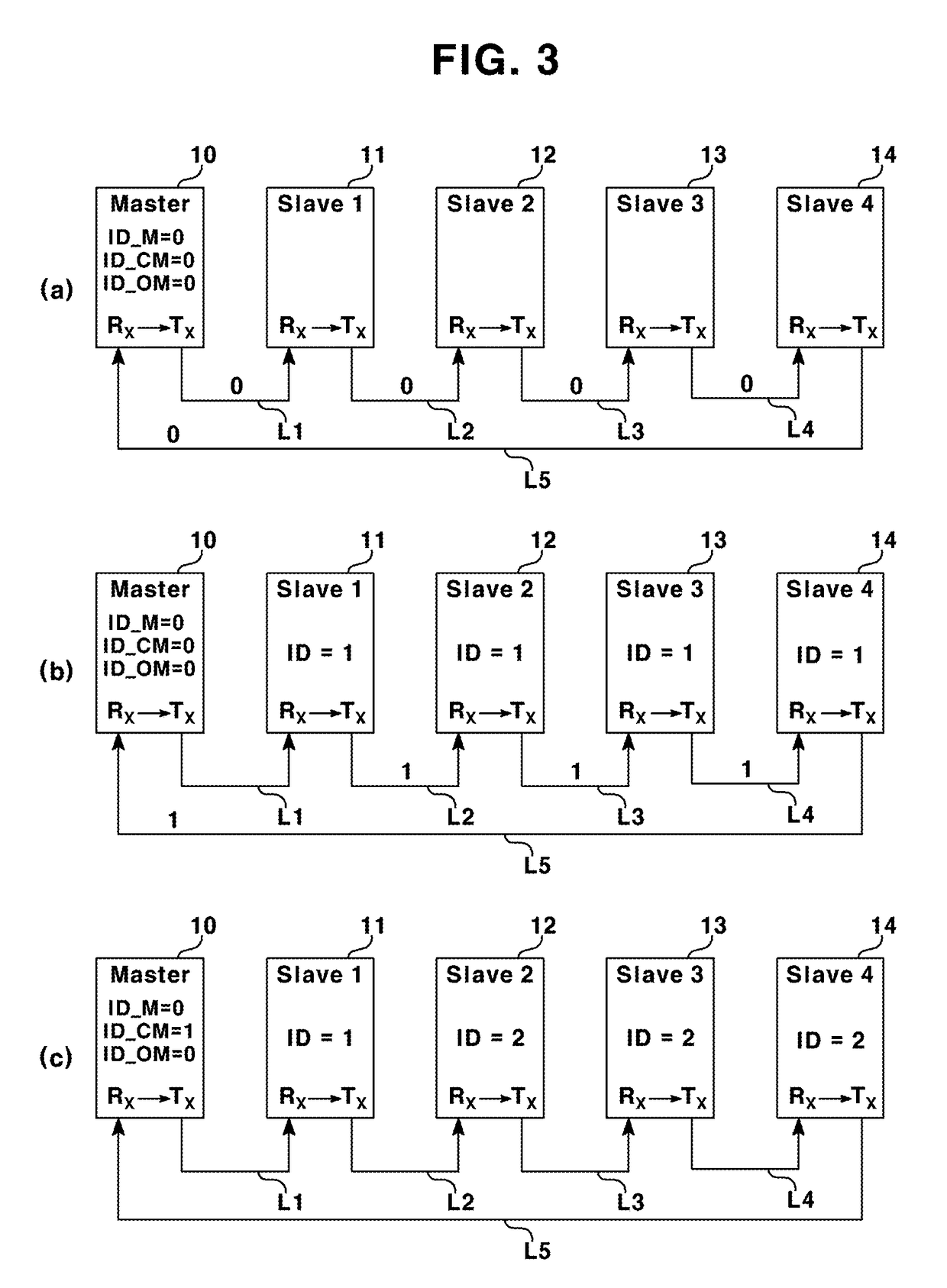
Method for automatically setting id in uart ring communication
ActiveUS20150095536A1Avoid Data ConflictsBlocking in networkSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlLoop networksComputer scienceRing type
Owner:LSIS CO LTD
Device driver setting profile lock-down
InactiveUS7797753B2Avoids waste from setting errorPrevent setting errorsDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionFile systemPersonal details
A method for providing a menu for a device, by providing a GUI for an administrator to select and lock-down device driver setting profiles, and providing a GUI for displaying to a user the locked-down profiles and permitting the user to select only from the listed profiles. Allowing a user to choose only from the pre-defined profiles makes for convenience and avoids waste from setting errors by novice users. The computer system detects the current system and job information (time, date, printer status, application, user information, etc.) using WMI and SNMP, applies mapping rules defined by an administrator, and displays only those profiles that are applicable to the current system and job status. Methods also include defining new profiles; alerting the user when no profiles are available, with mapping explanation and suggestion; profile detail display; and printer support.
Owner:KYOCERA TECH DEV
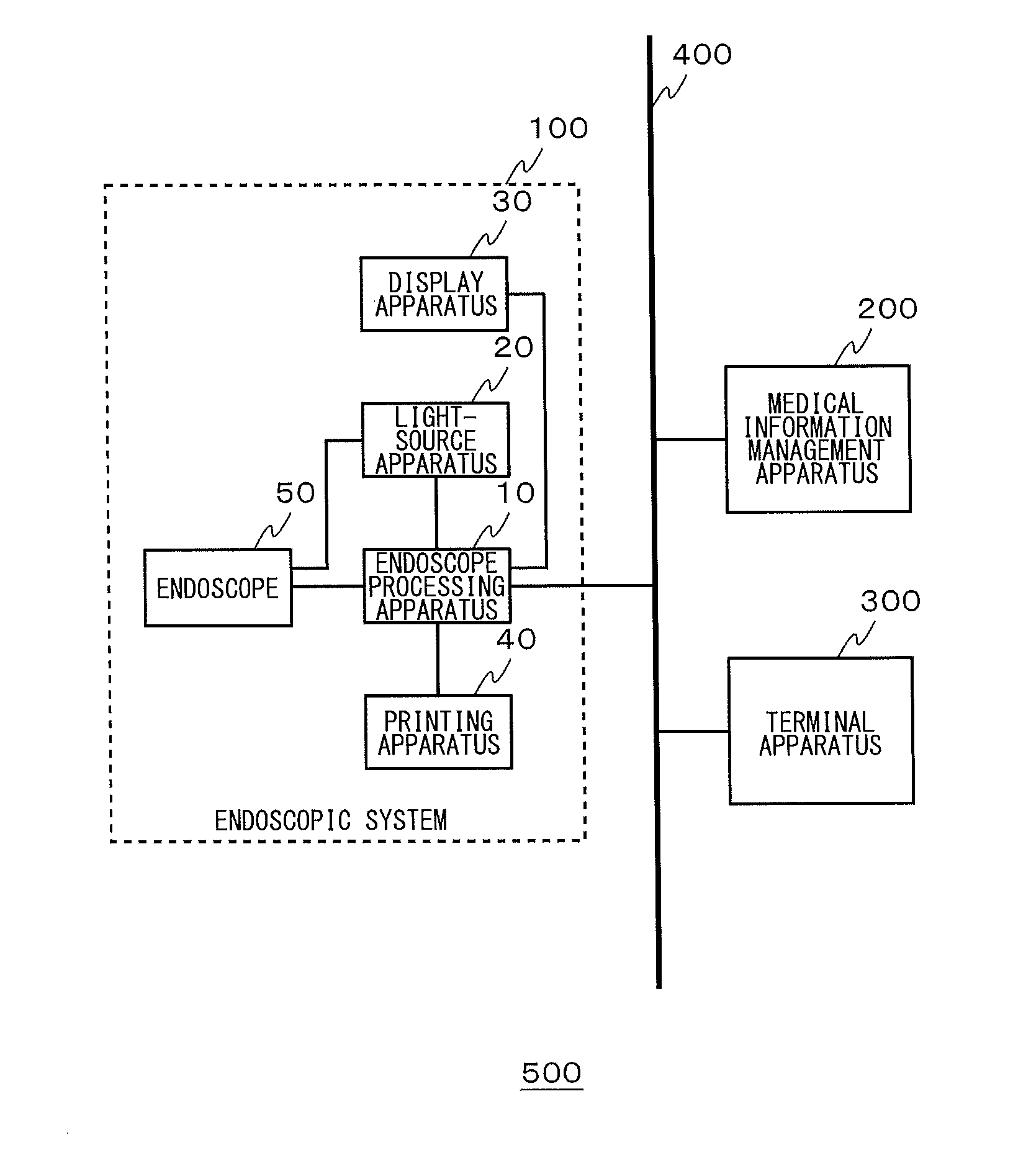
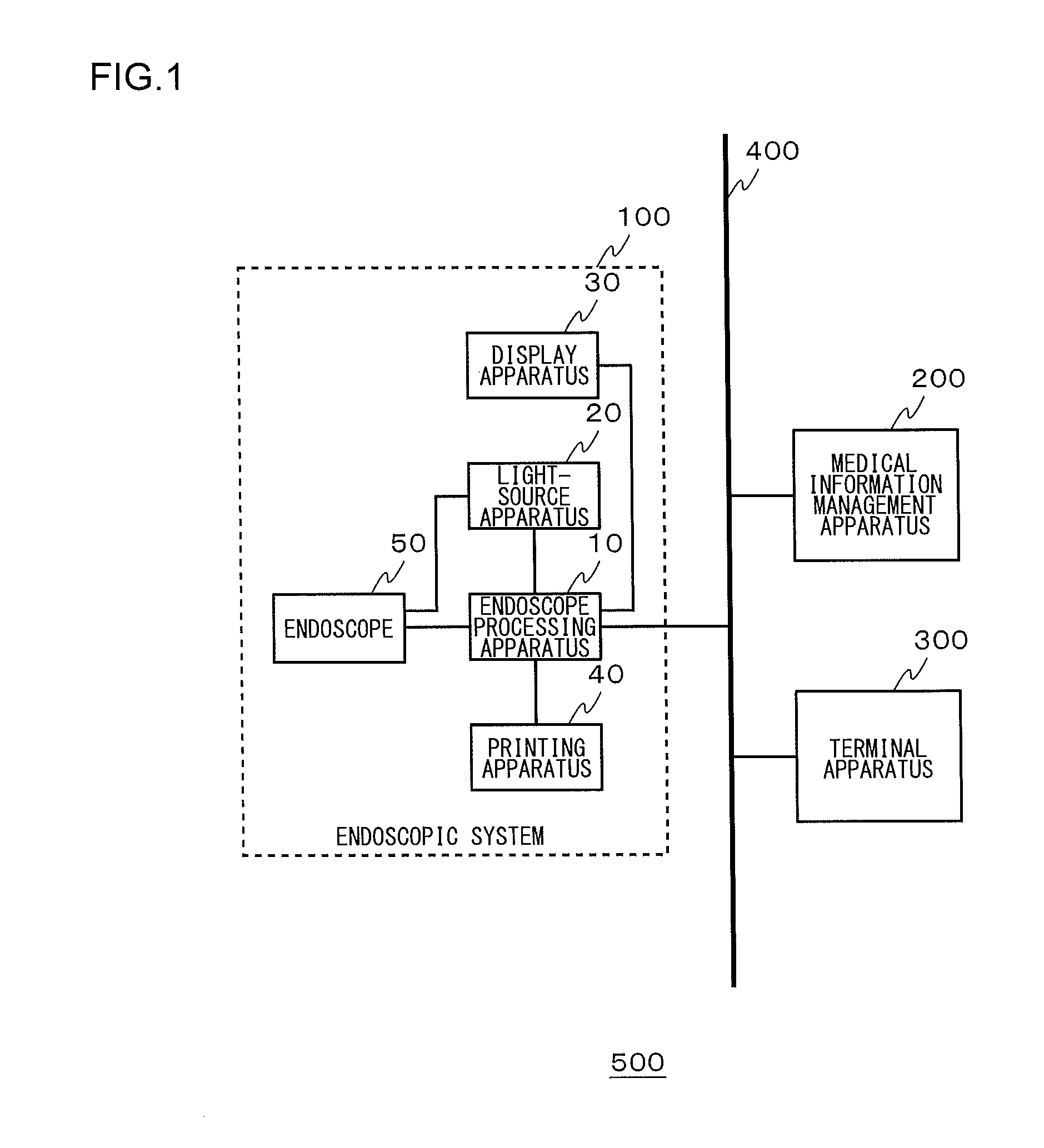
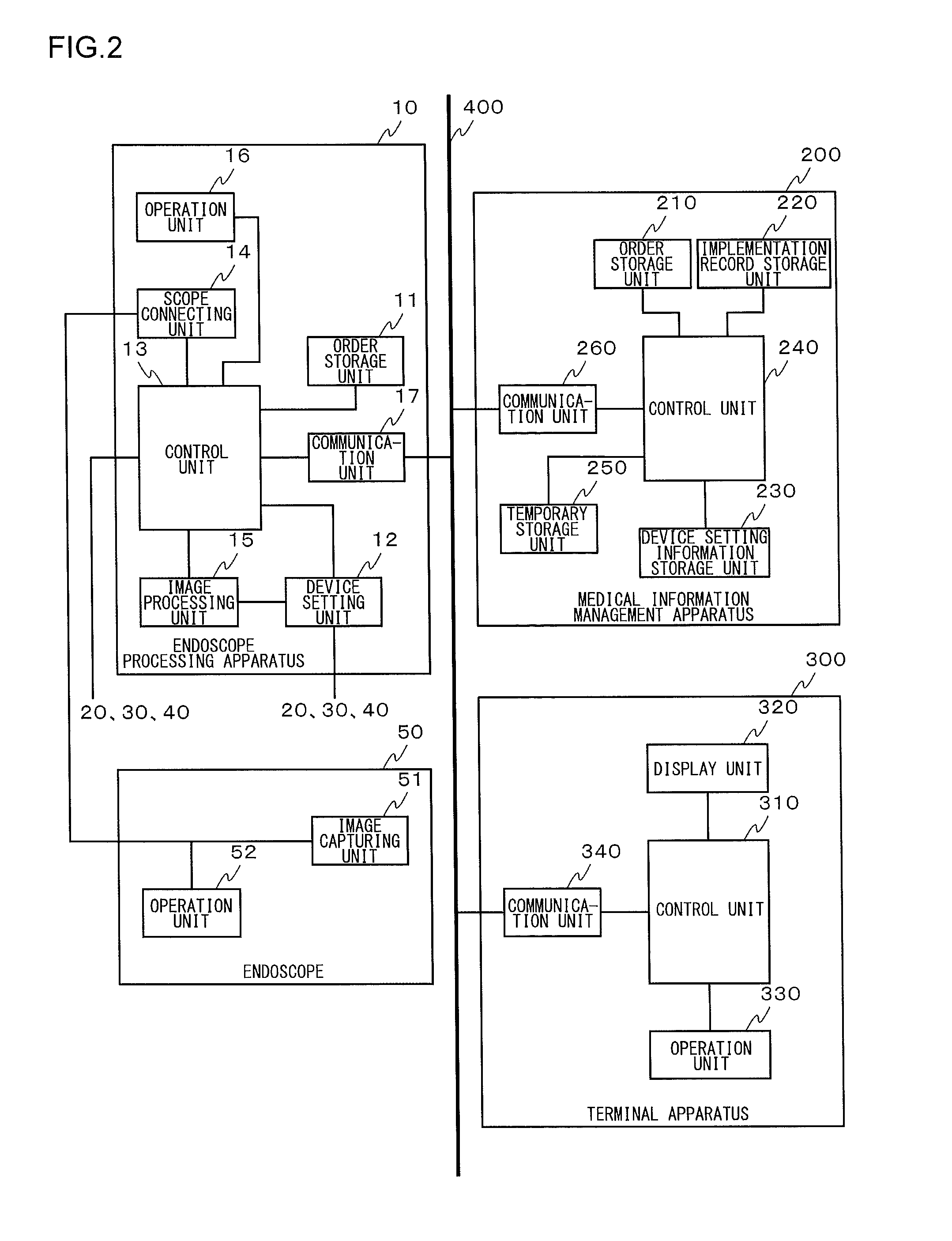
Medical information management apparatus and medical information management system
ActiveUS20140118517A1Reduce the burden onDelay progressEndoscopesColor television detailsMedical practiceComputer science
An order storage unit stores an order for a medical practice to be performed using an endoscopic system. A control unit transmits an order to the endoscopic system via a communication line and also transmits device setting information linked to at least one of a doctor and a medical practice type specified by the order. When the control unit receives a notification of a change from the endoscopic system while the medical practice specified by the order is being performed, the control unit transmits new device setting information corresponding to the change to the endoscopic system.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
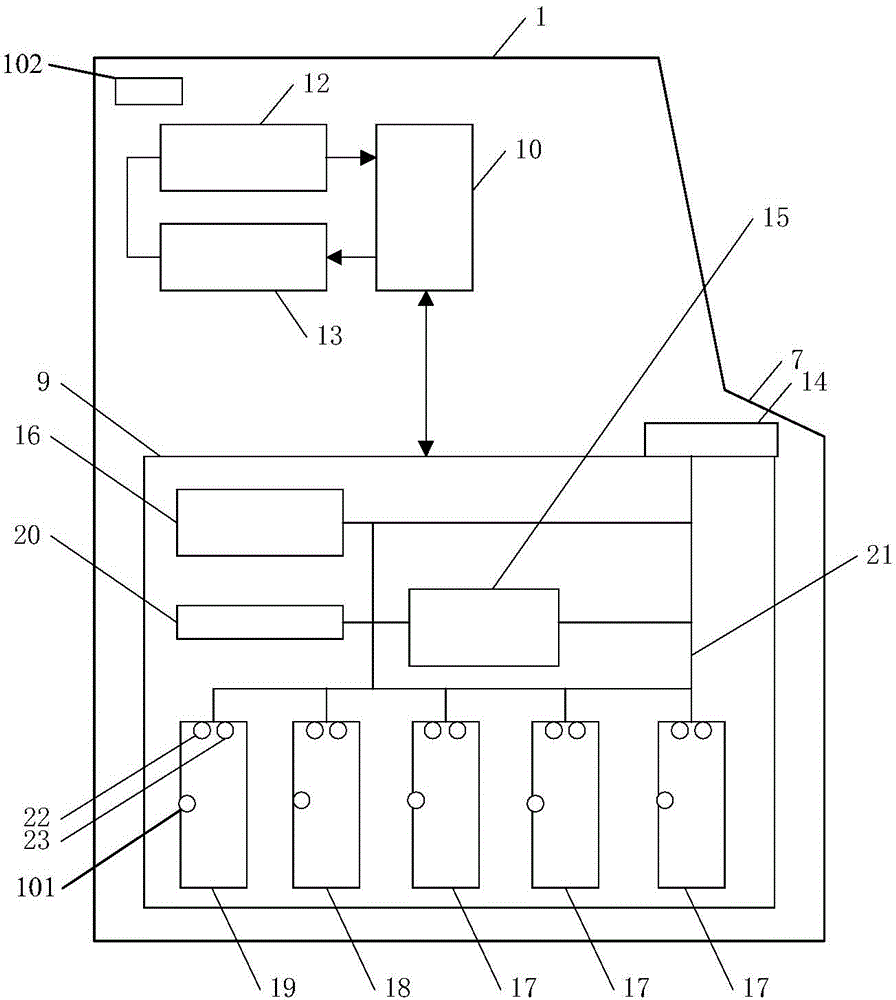
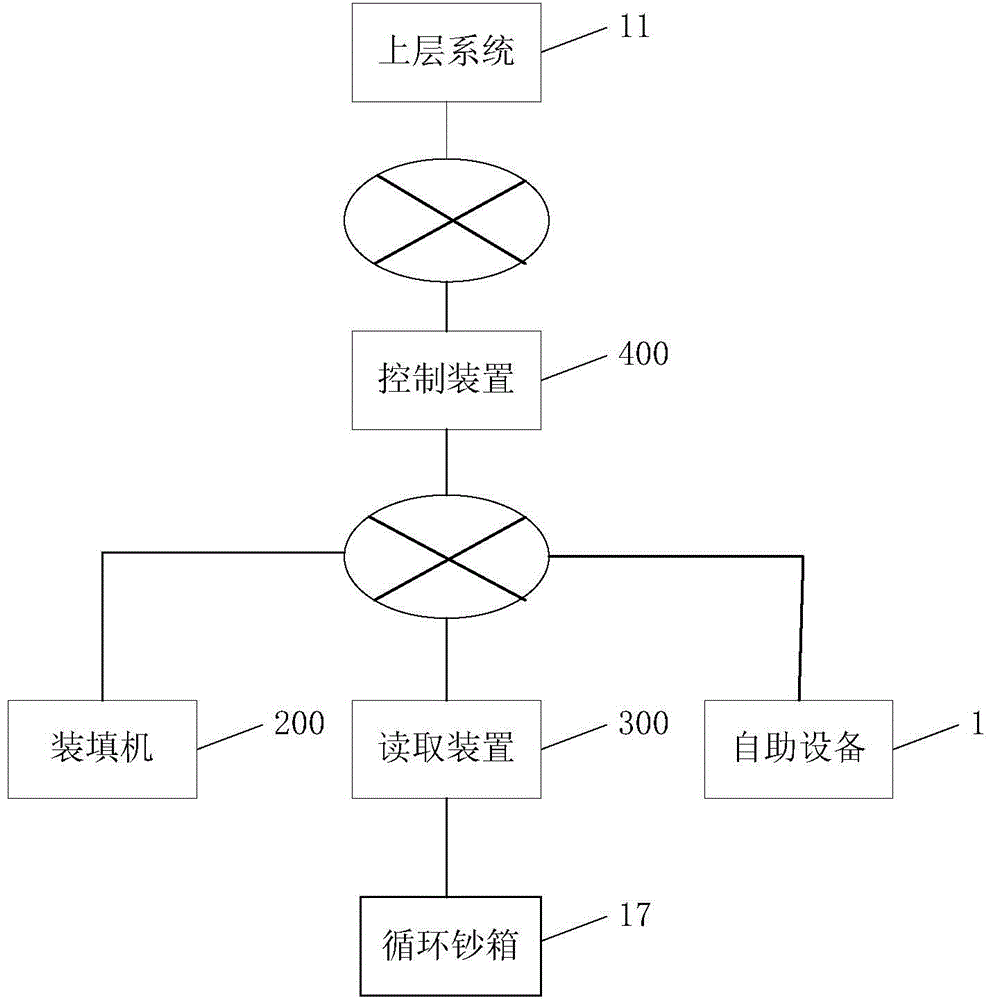
Cash bill case management system and cash bill case management method
InactiveCN105447994AImprove latencyPrevent setting errorsComplete banking machinesProgram planningSoftware engineering
The invention provides a cash bill case management system and a cash bill case management method. The cash bill case management system comprises: a cash bill case, a self-service device, a loading device, a reading device, a control device, and an upper-level system. The cash bill case is provided with an identifying information storage part which can store inherent identifying information of the cash bill case, and a receive-send part which performs signal communication to the identifying information. The self-service device, the loading device and the reading device are all provided with identifying information reading parts which can identify the inherent identifying information of the cash bill case, and receive-send parts which can communicate with the control device. The control device is provided with a receive-send part which is used for communicating with the self-service device, the loading device, the reading device and the upper-level system; a recording part which is used for recording loading planning information from the upper-level system and information from the self-service device, the loading device and the reading device; and a control part which manages the recorded information. The upper-level system is provided with a receive-send part which sends the cash loading planning information to the control device.
Owner:HITACHI FINANCIAL EQUIP SYST SHEN ZHEN +1
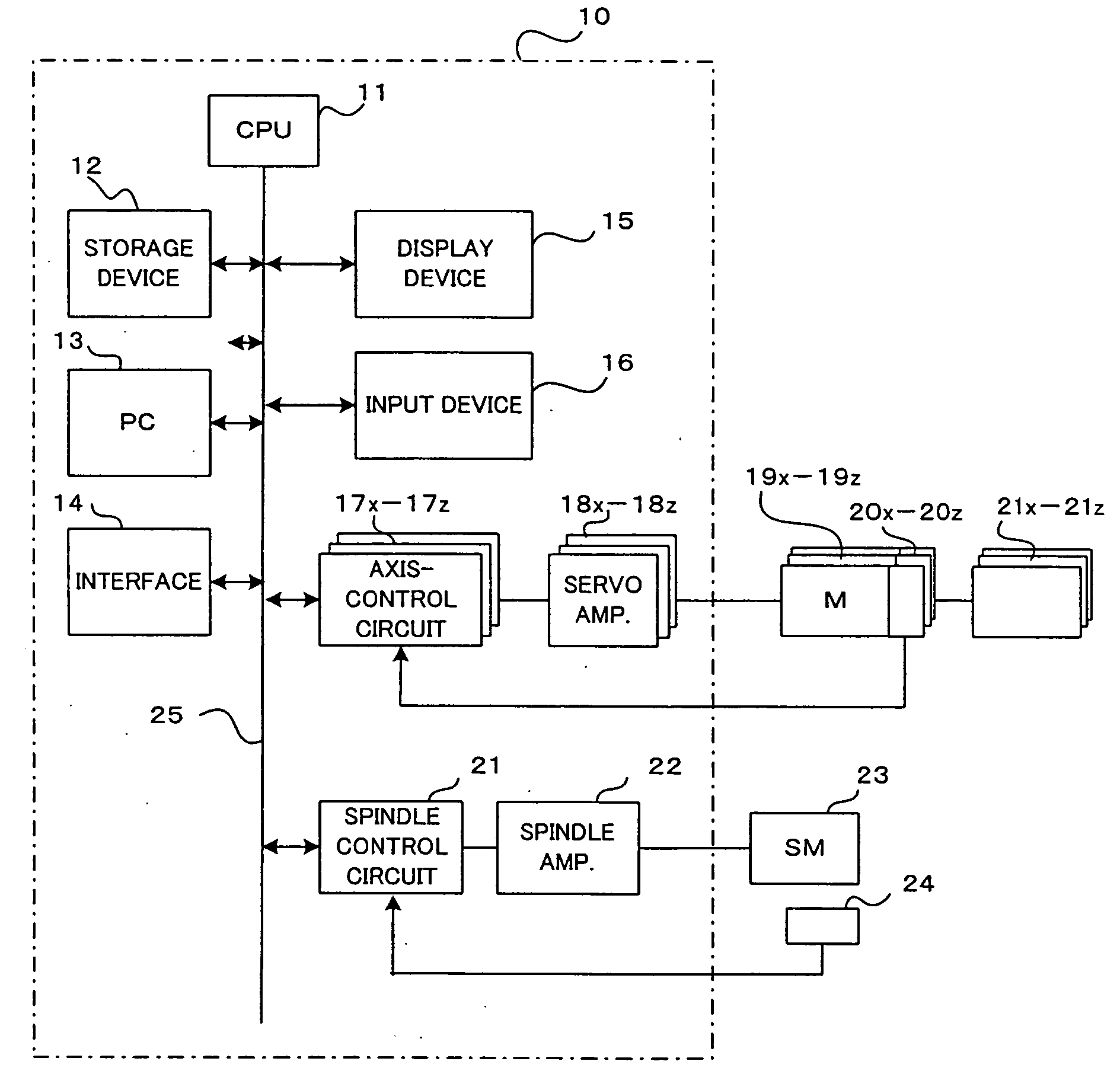
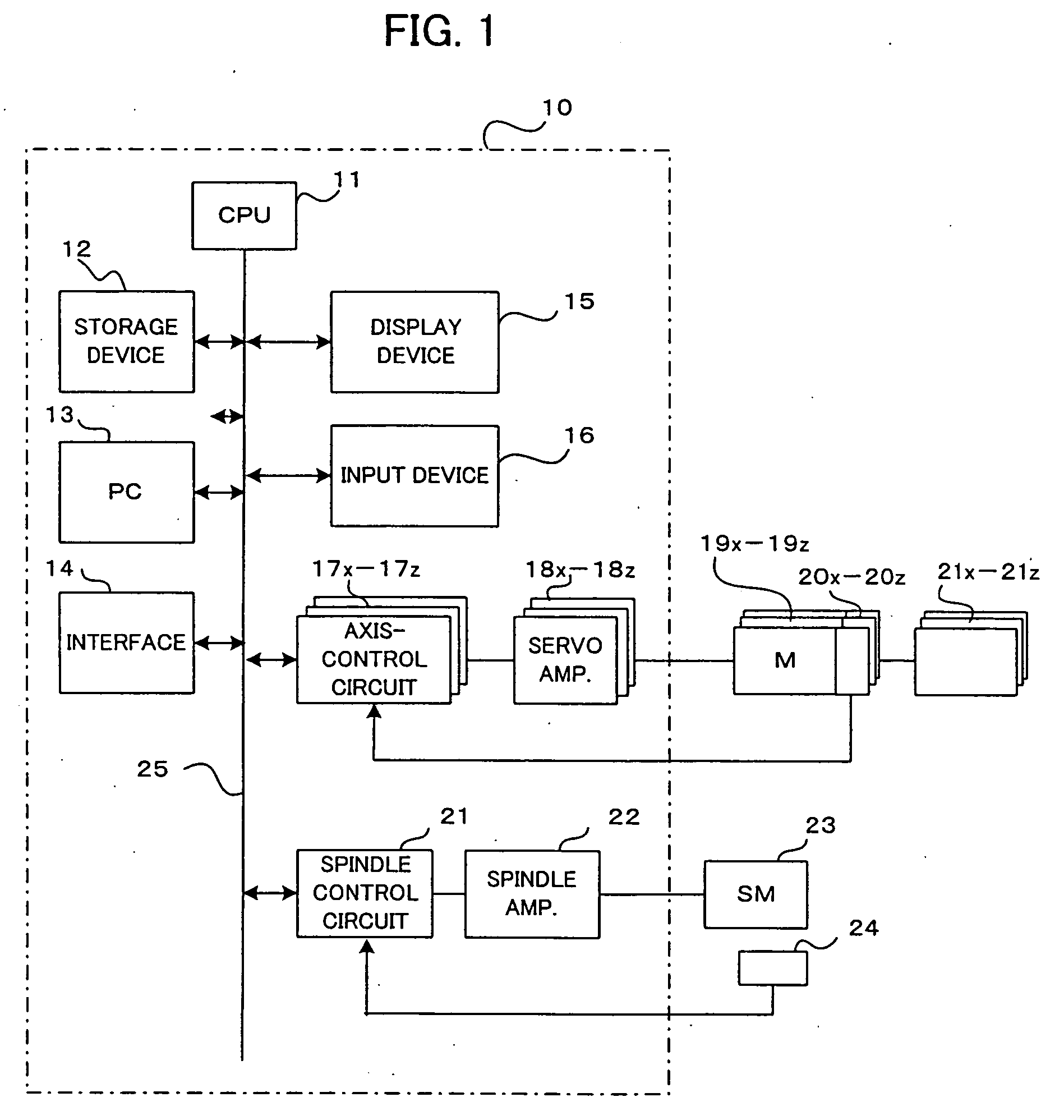
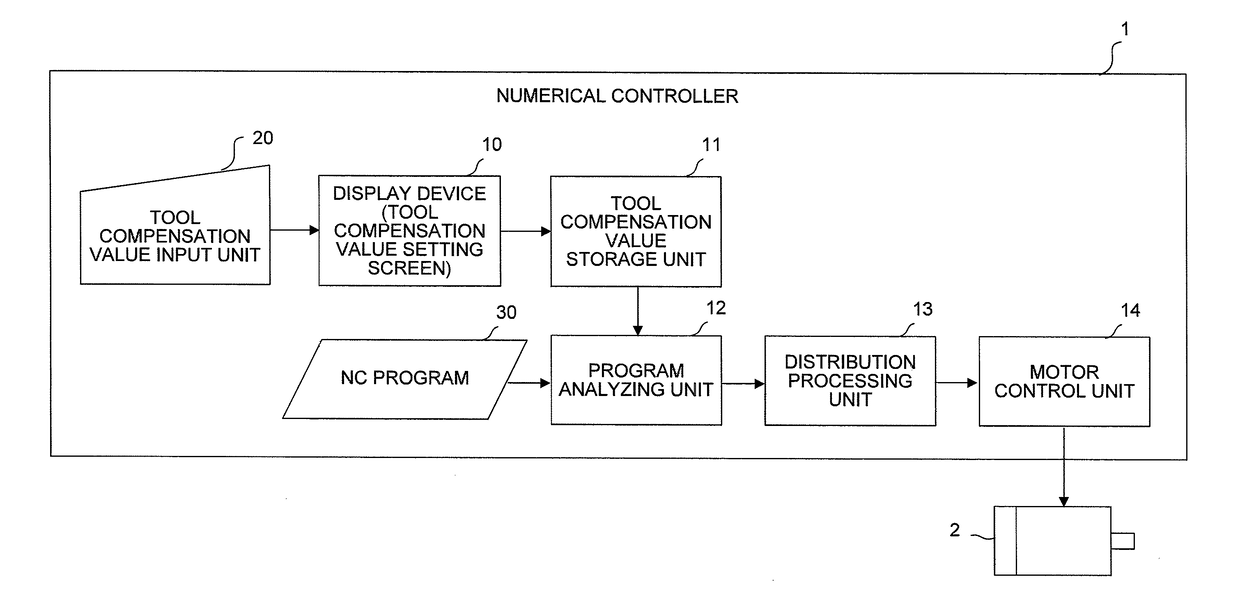
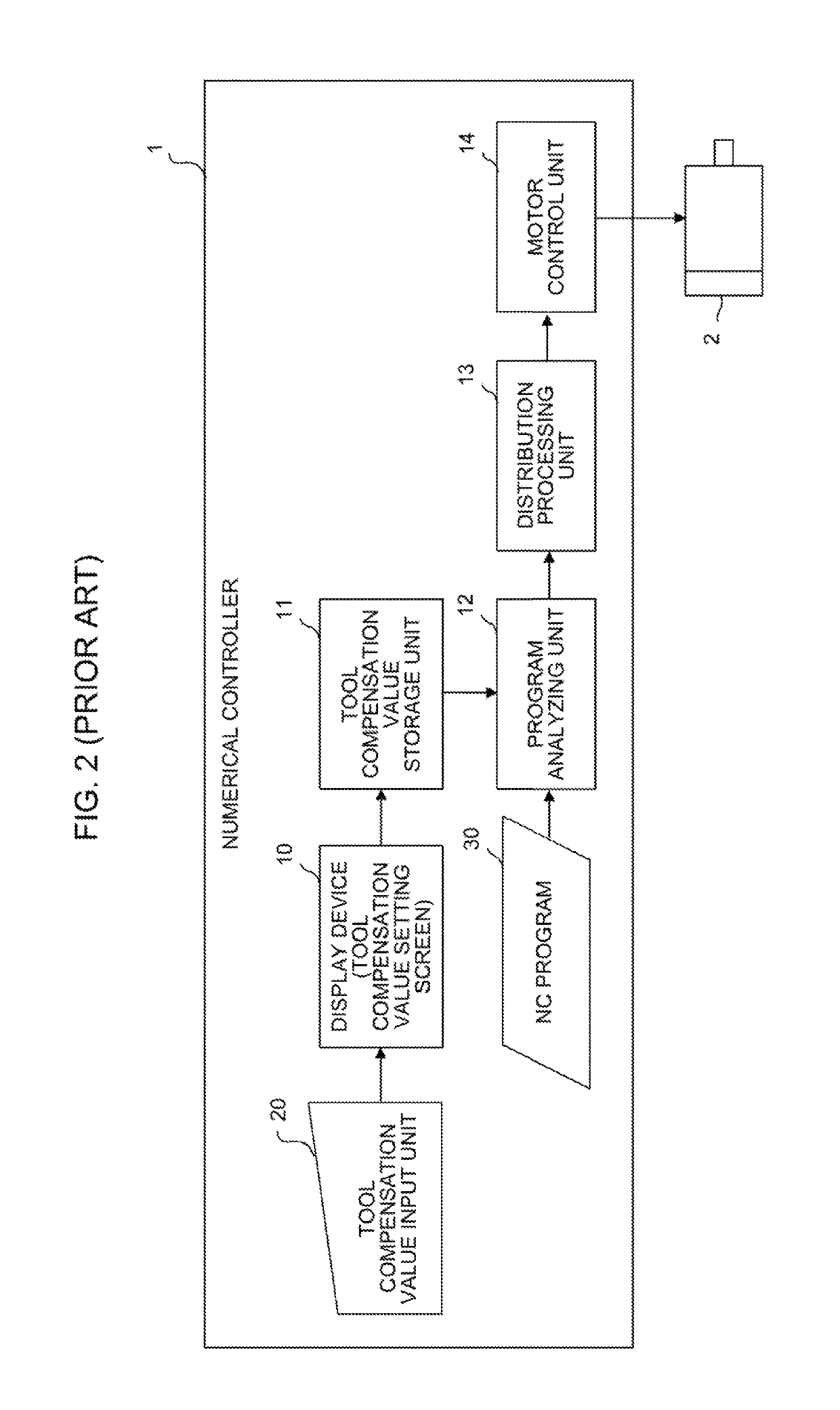
Numerical controller
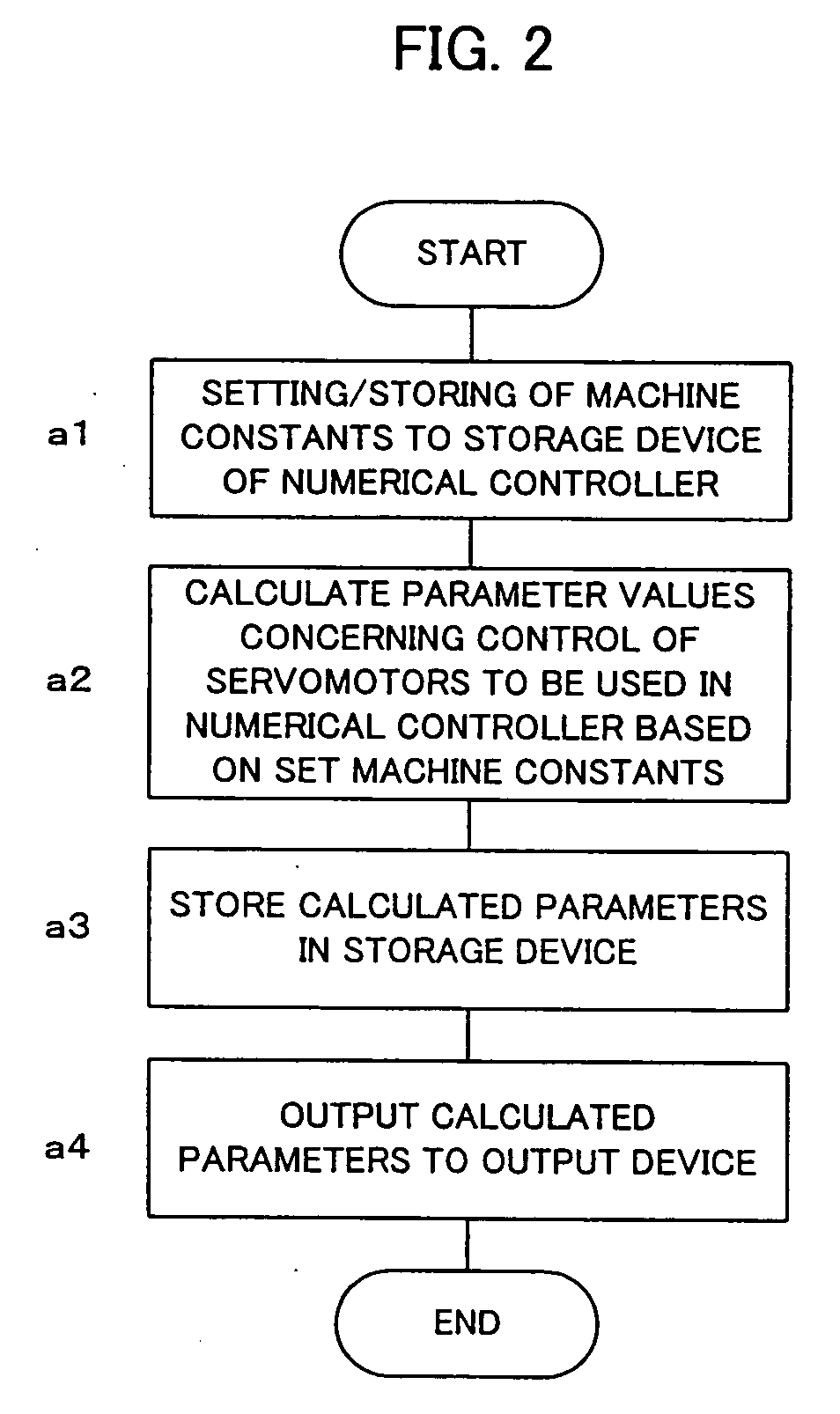
InactiveUS20070038328A1Easy to set upPrevent setting errorsProgramme controlComputer controlDisplay deviceOutput device
A numerical controller that can easily set parameter values related to servo control used within itself. Machine constants are set in the numerical controller. The numerical controller calculates the parameter values related to the servo control used in the numerical controller, from the set machine constants, and stores and sets them in a memory means within the numerical controller. The parameter values calculated are also fed to an output device such as a display device for an operator to check them. When a machine to be controlled by the numerical controller is determined, the machine constants can be easily obtained from the specifications or the like of the machine and set in the numerical controller. Since the numerical controller itself calculates and sets the parameter values related to the servo control, the setting can be easily carried out without full knowledge of the internal elements, structure and operation principle of the machine, the processing performed by the numeric control unit, etc.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Device for detecting broken yarn through shaft frame and method for locating its address
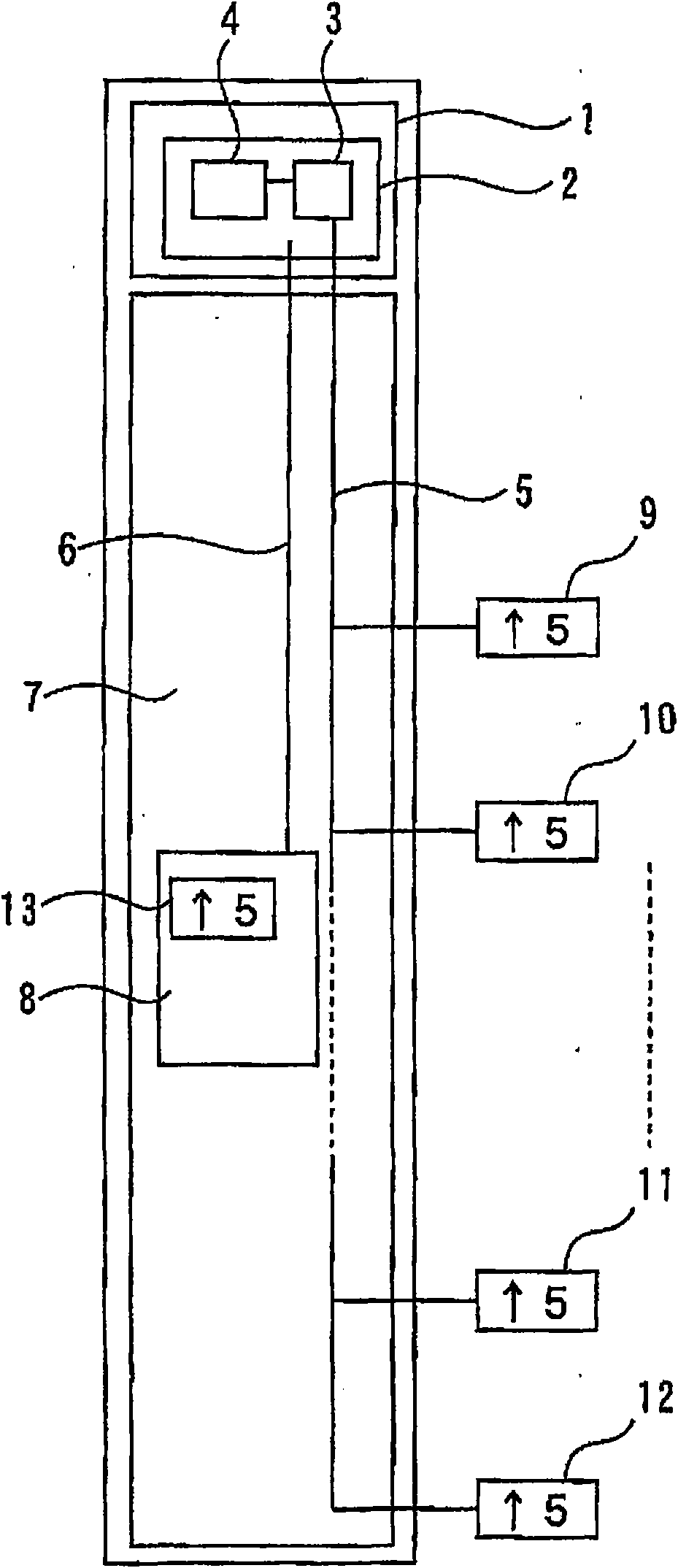
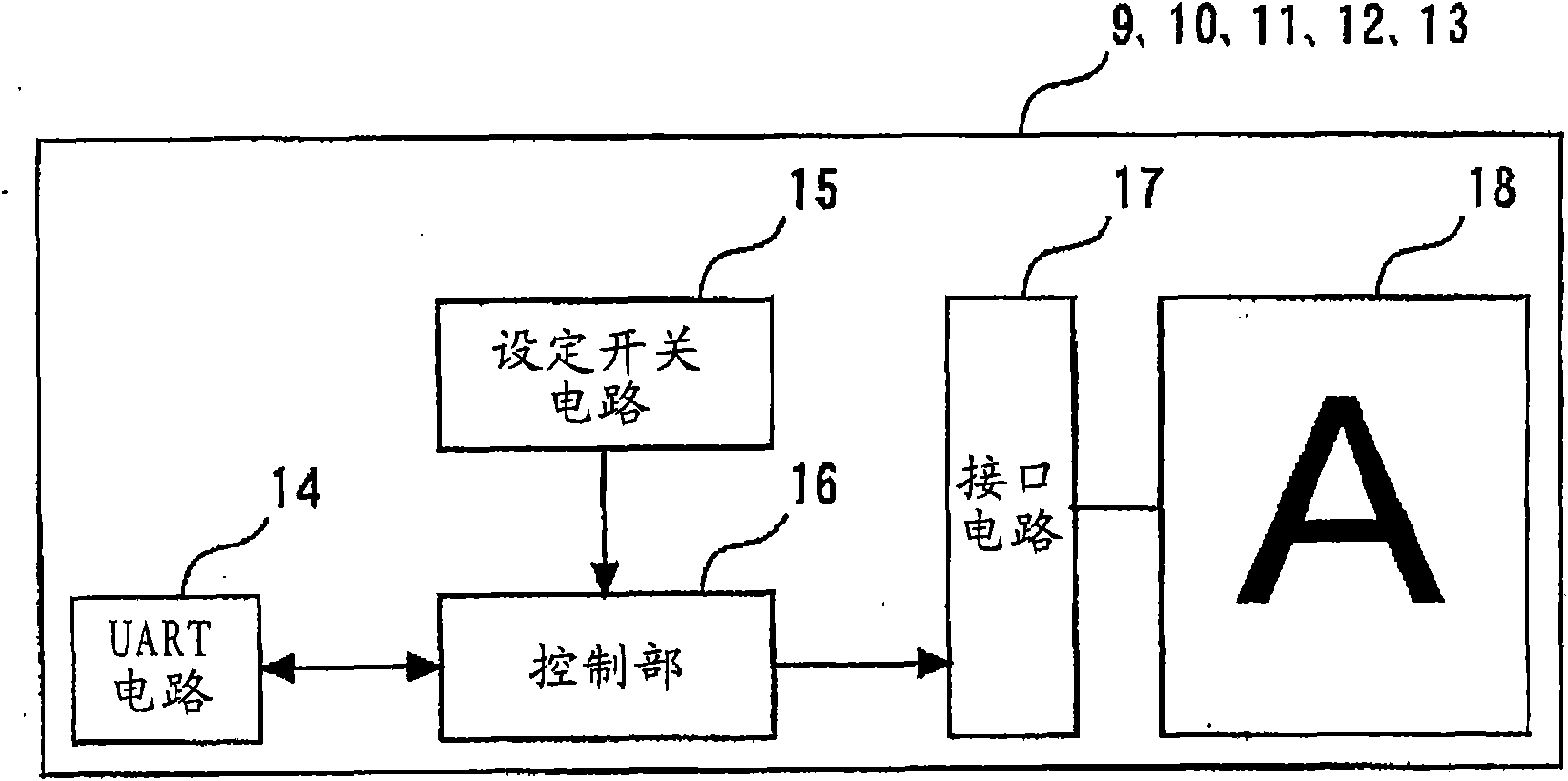
InactiveCN1779006APrevent setting errorsShorten the timeInspecting textilesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsYarnReliability engineering
The invention relates to a method for setting addresses for multiple controllers of a yarn break detection device and a yarn break detection device with address setting function. In this yarn breakage detecting device, a plurality of controllers provided and connected in series corresponding to a plurality of yarn breakage sensors corresponding to the supporting members of each yarn supply body, and a central processing unit for monitoring yarn breakage in the entire creel device are connected in series. connected, the central processing unit outputs a signal including address information to the controller on the most upstream side. The controller on the most upstream side identifies and stores its own address according to the input signal, and at the same time calculates the address information of the subsequent controller on the downstream side according to the information of the input signal according to the prescribed calculation rules, and sends the signal including the address information output to the subsequent controller on the downstream side. In this way, each controller sequentially sets addresses to all subsequent controllers on the downstream side. The address setting of each controller can be automatically set sequentially without installing a hardware address setter such as a DIP switch.
Owner:TSUDAKOMA KOGYO KK
Wire electric discharge machining device
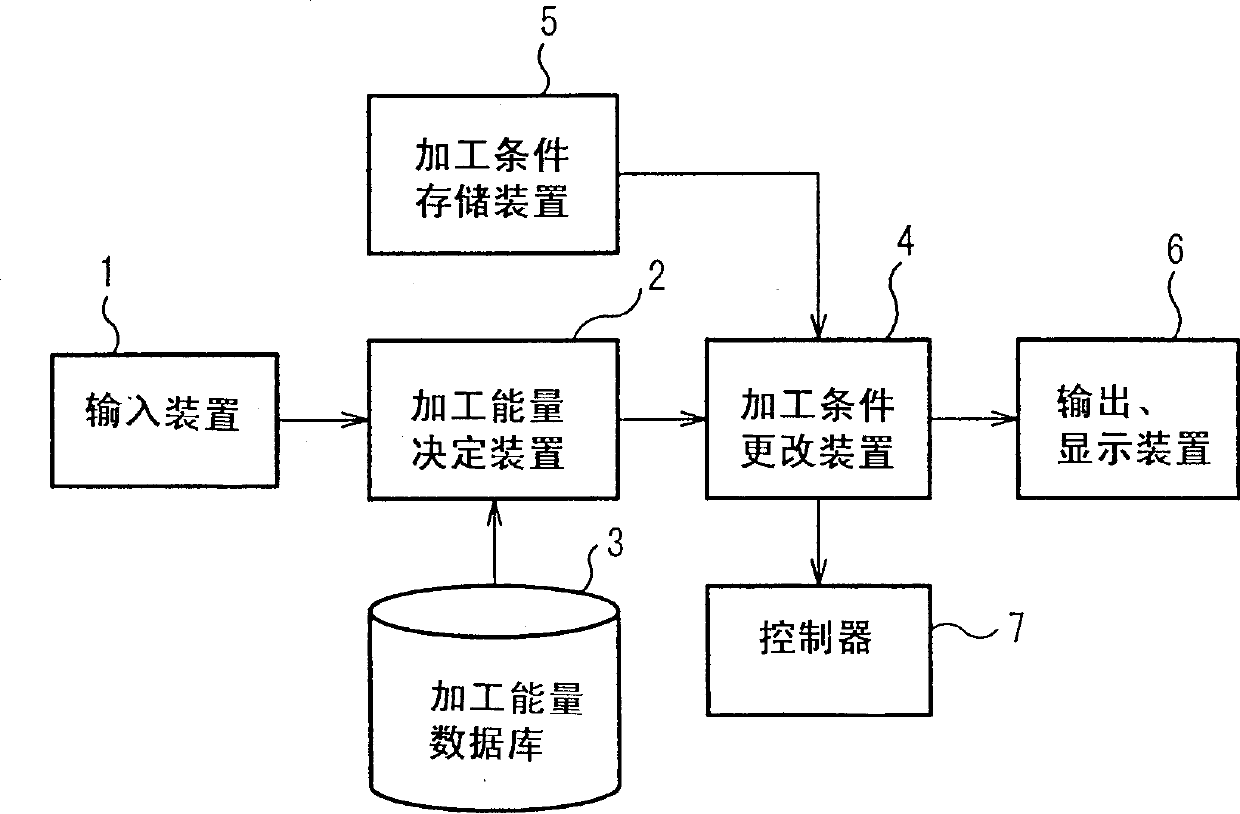
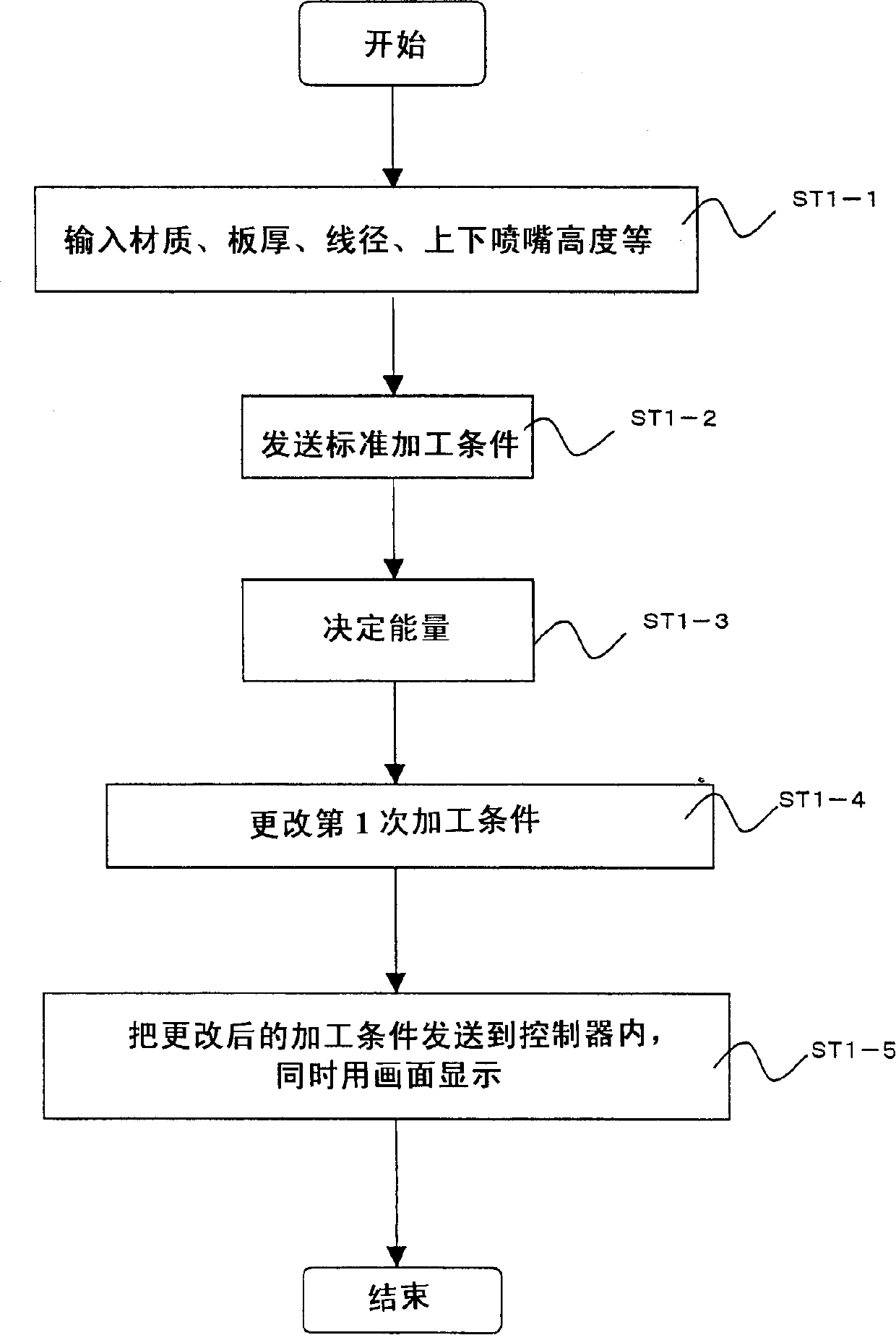
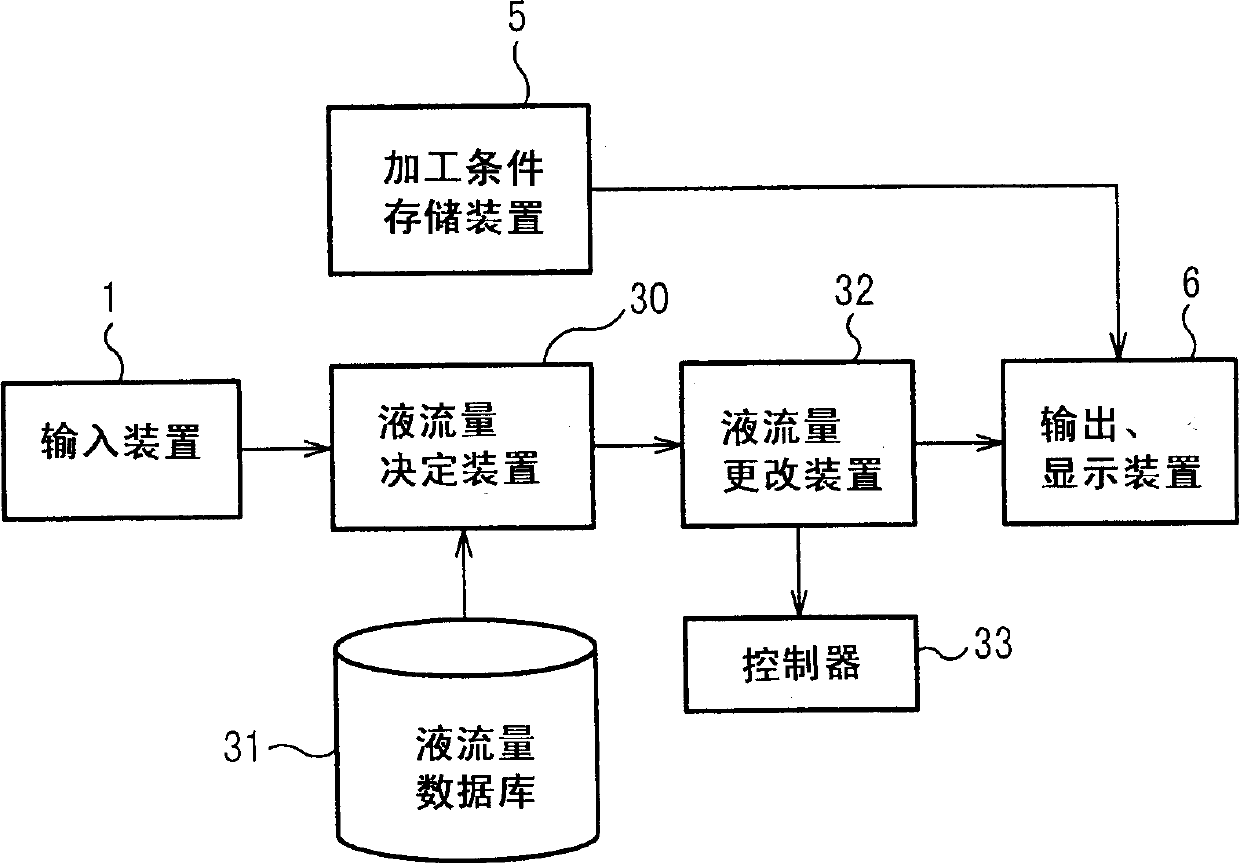
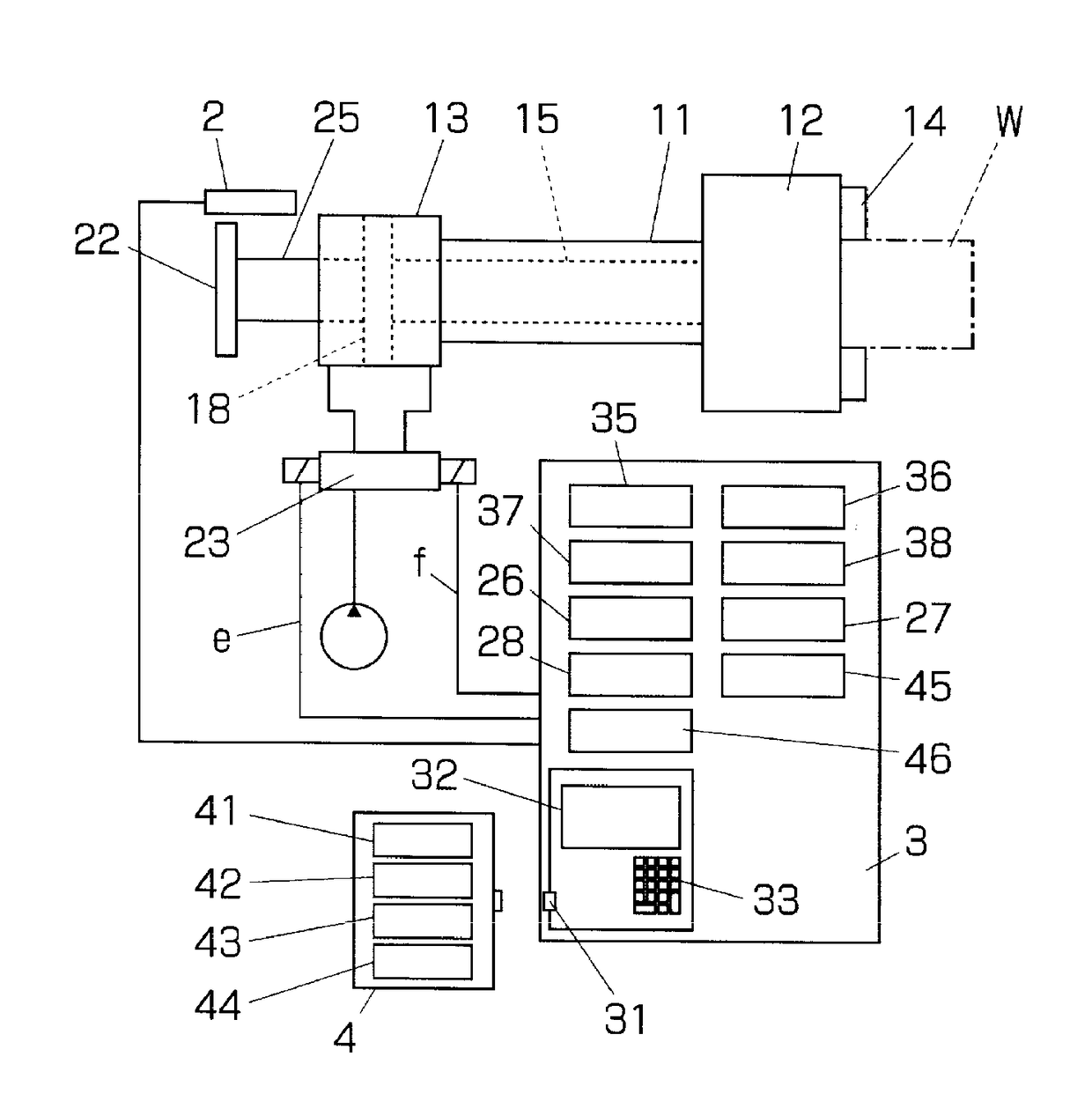
A wire electric discharge machining device capable of machining a work under specified working conditions by using working fluid provided in a clearance between a wire and the work, comprising a machining condition storage means for holding machining conditions, a means for storing the relation between a nozzle height and a machining energy amount, a machining energy determination means for determining, for example, the machining energy amount in a rough machining based on the relation, and a machining condition alteration means for altering the machining conditions according to the machining energy amount, wherein the work is machined under the altered machining conditions, whereby a damage to the wire can be prevented and the accuracy of a machined surface can be increased.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Opening/closing control device of chuck
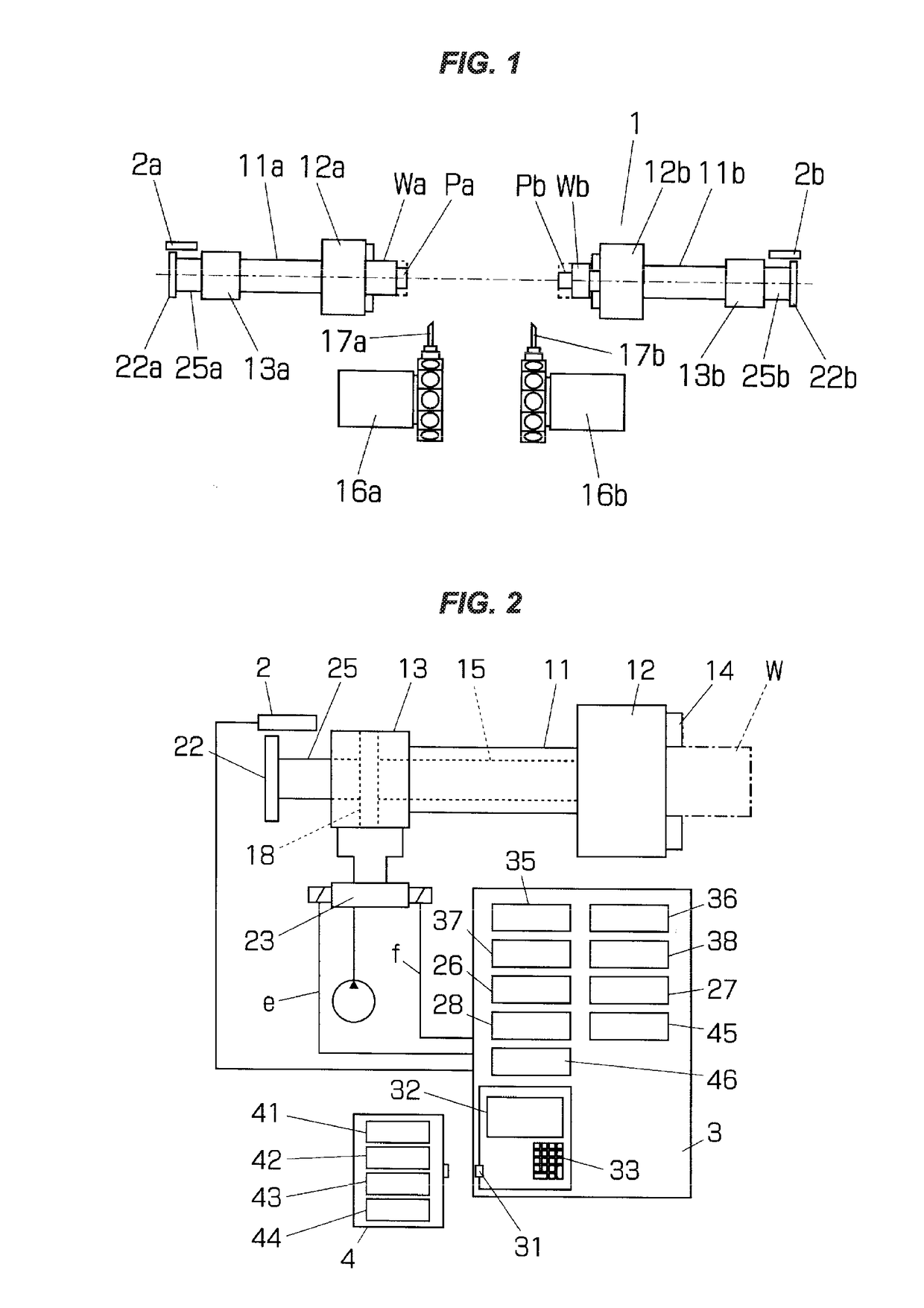
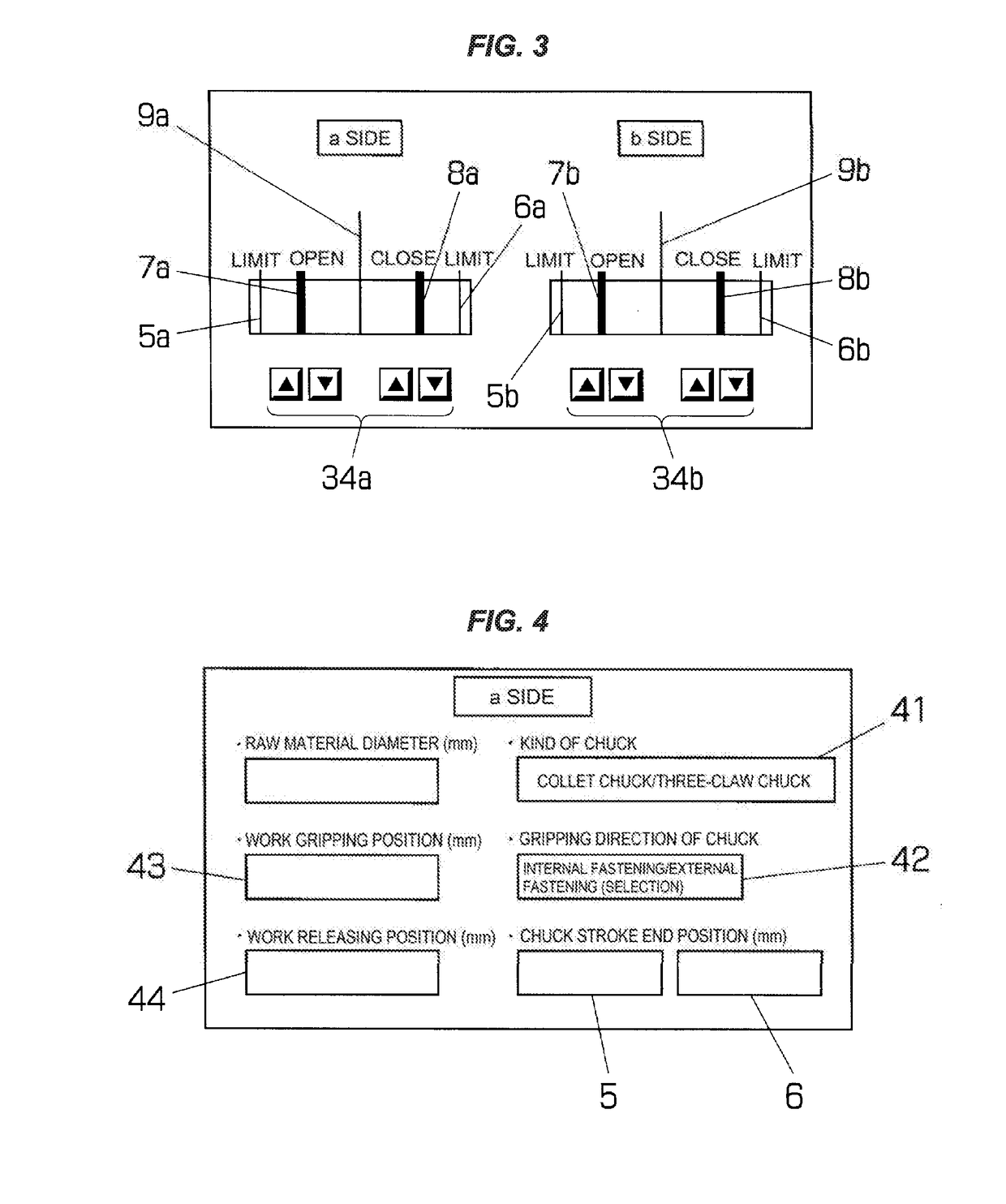
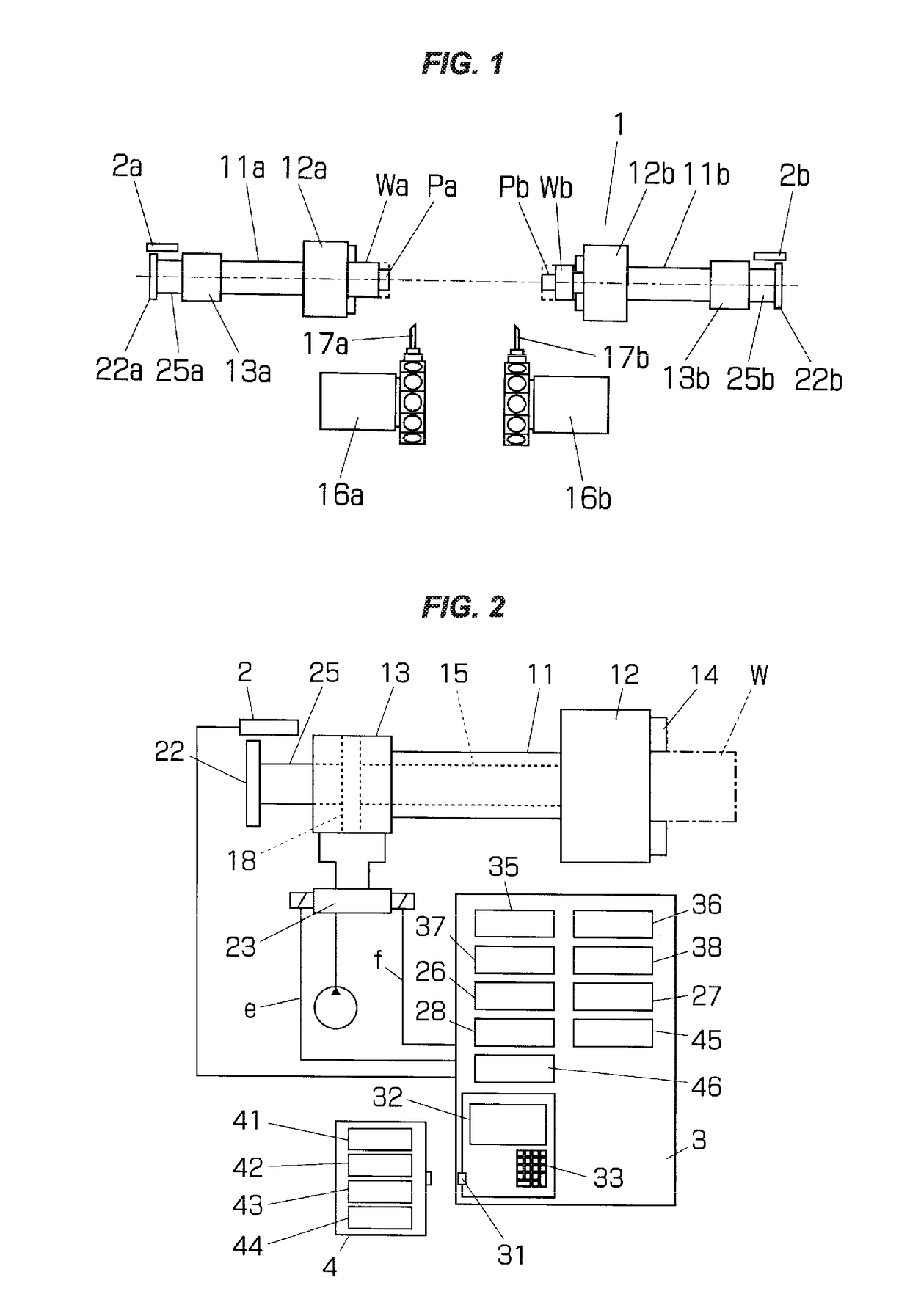
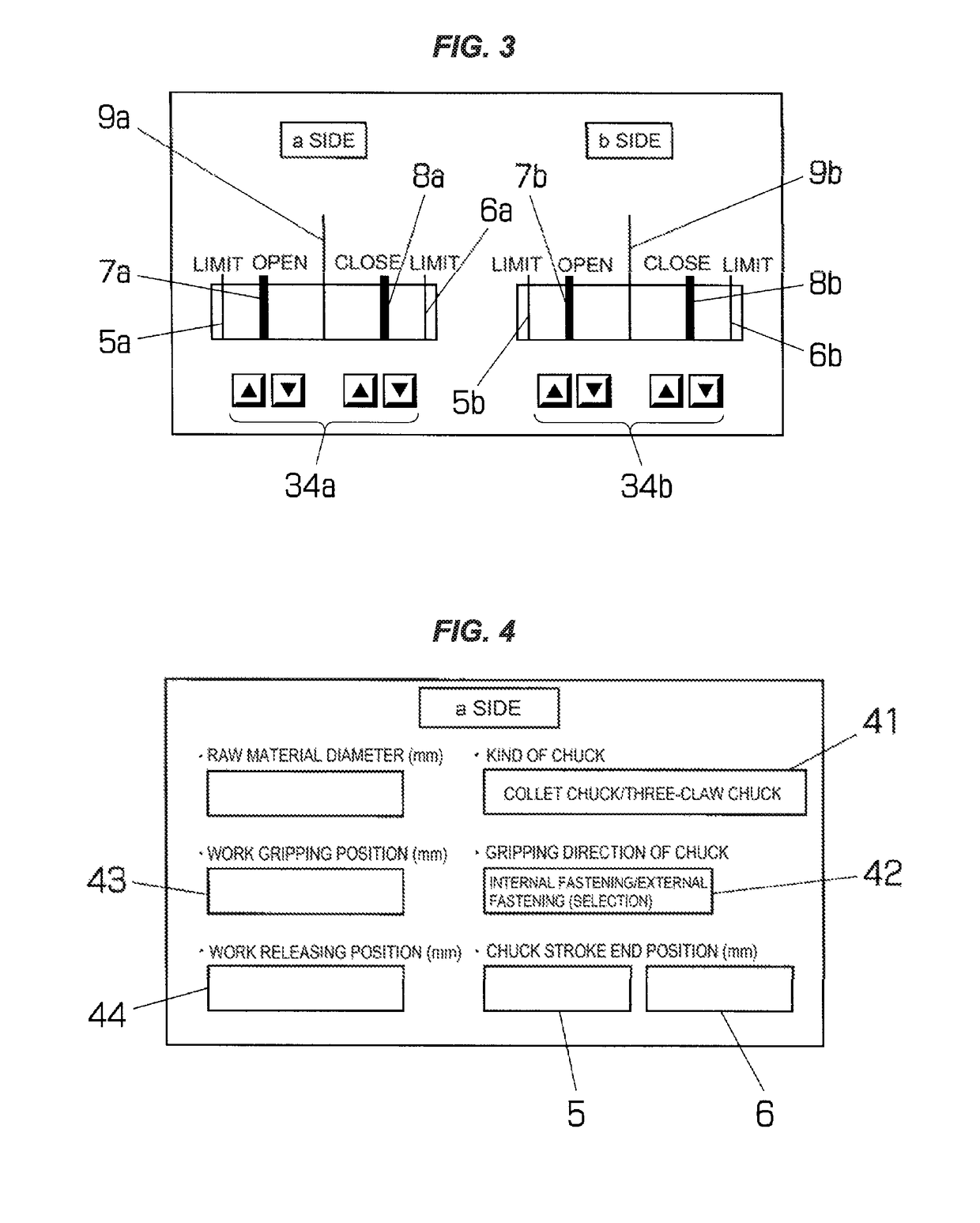
ActiveUS20170209939A1Easily and rapidly carryPrevent set errorSleeve/socket jointsMeasurement/indication equipmentsProduct typeMachine tool
The invention relates to a device controlling a chuck of a machine tool and an auxiliary equipment thereof, thereby facilitating a setup work. Gripping and releasing of a work are confirmed by registering a work gripping position and a work releasing position of a chuck, a kind of a used chuck, and a gripping direction of a work in an external memory device every product type of the work, transferring the work gripping position and the work releasing position in correspondence to the product type to a controller of a machine tool displaying them on a display of an operator control panel, detecting a position of an operation rod opening and closing a claw of the chuck by a stroke sensor, referring to the gripping position of the work, and detecting conformity of the detecting position and set values of the work gripping position and the work releasing position.
Owner:NAKAMURATOME SEIMITSU IND
Image forming apparatus and display method thereof
InactiveUS8582177B2Prevent setting errorsSetting error can be eliminatedDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsLiquid-crystal displayComputer graphics (images)
An image forming apparatus 100 includes: an image forming part 6, a liquid crystal display part 11, a storage device 92 storing a program for displaying a setting screen at the liquid crystal display part 11; an input part 1 receiving, for example, a setting made for a setting item; and a help key KH for displaying a help screen at the display part. When the help key KH has been pressed in the setting by the called program, the display part 11, before processing is performed for a referenced setting item as the setting item for which the help screen has been referenced, displays a confirmation screen for confirming whether or not the processing may be performed at the current setting for the referenced setting item.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
Recording device
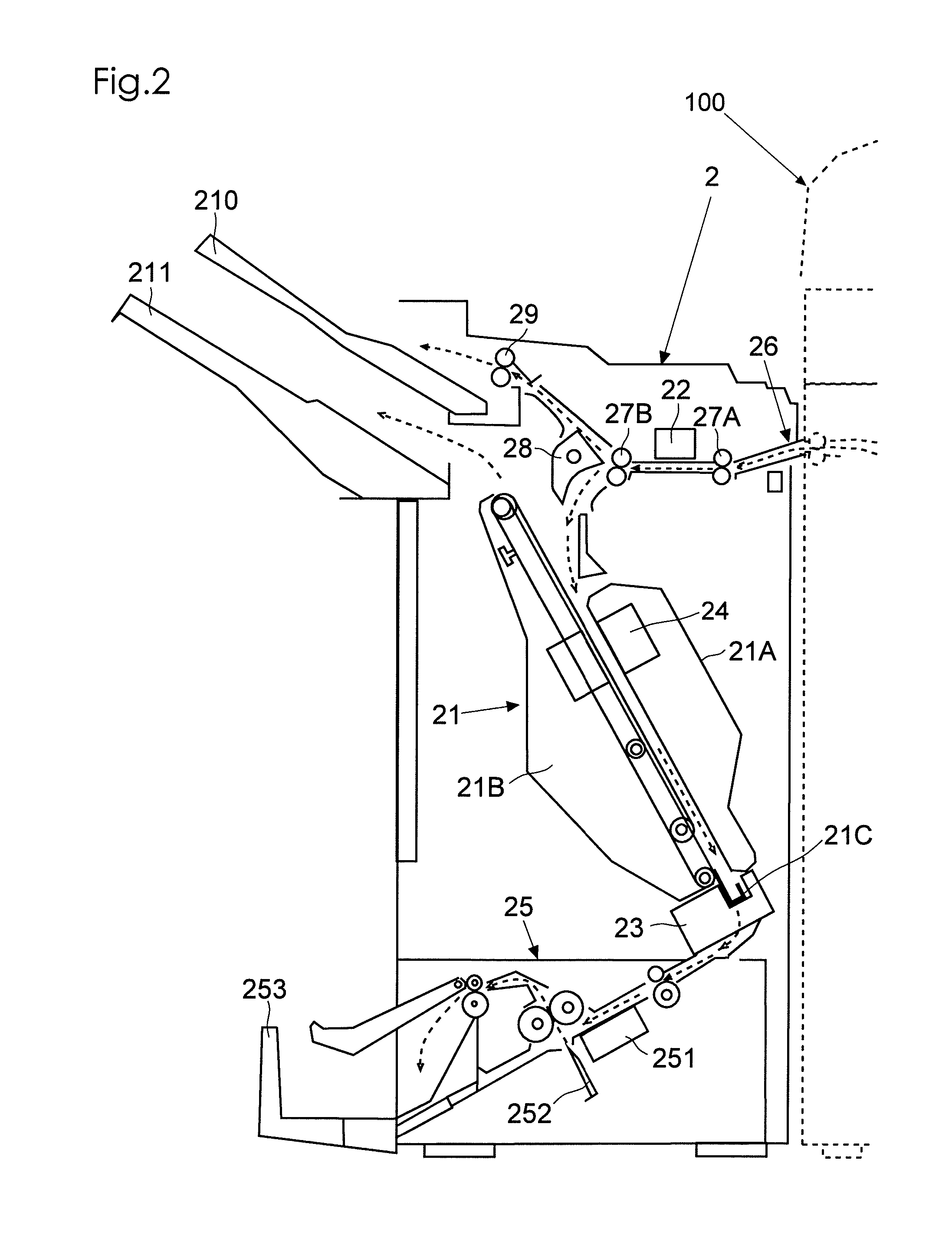
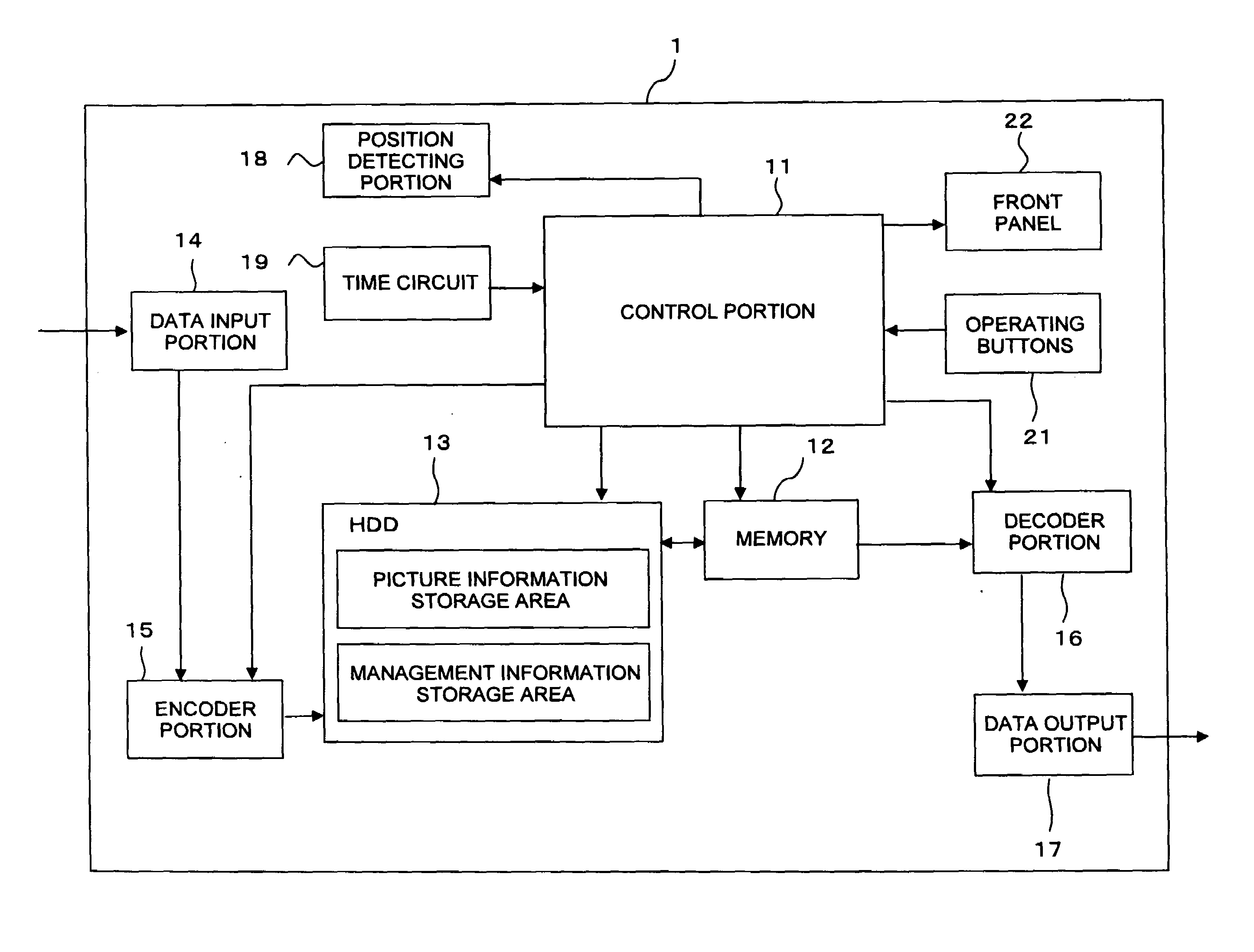
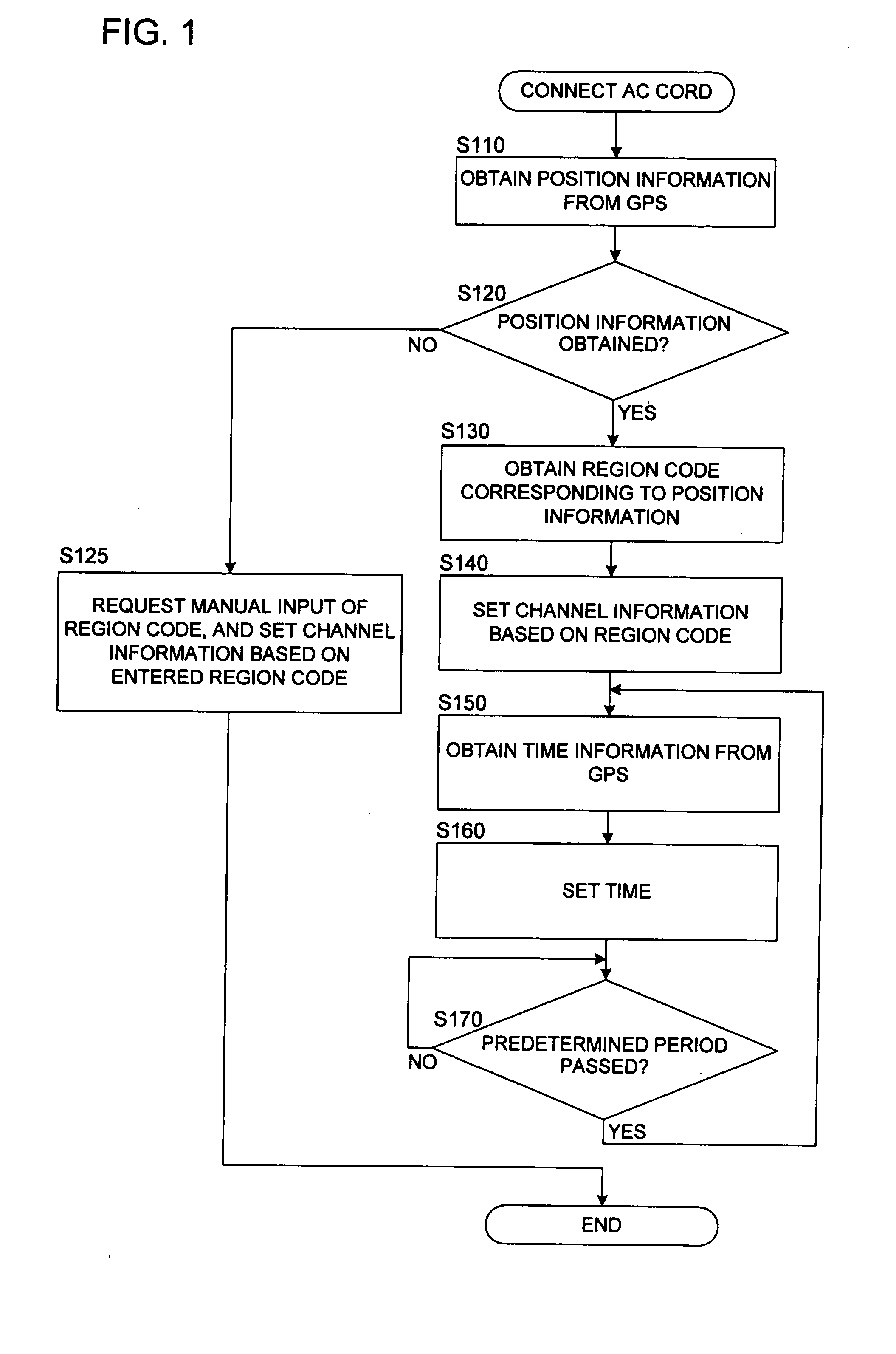
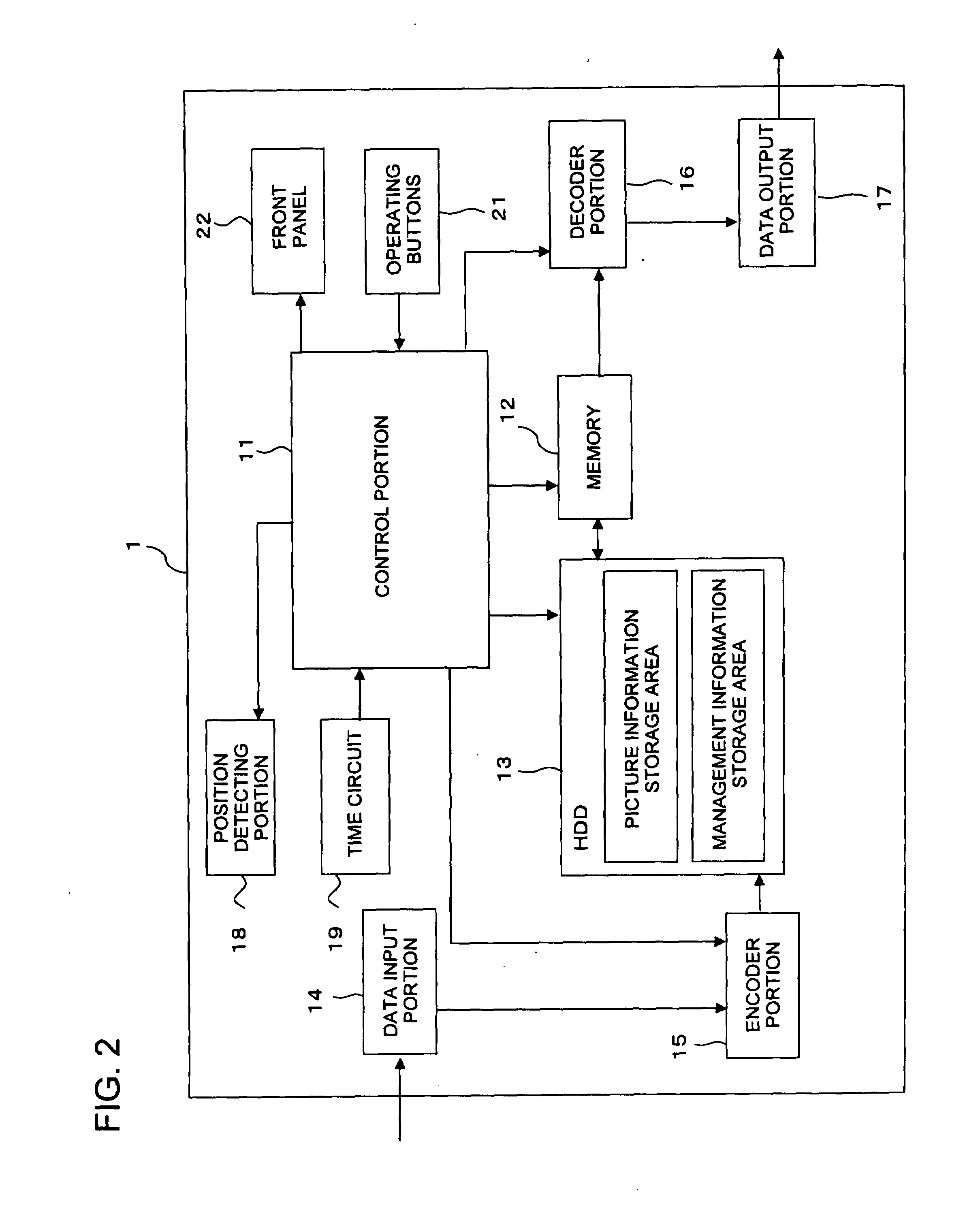
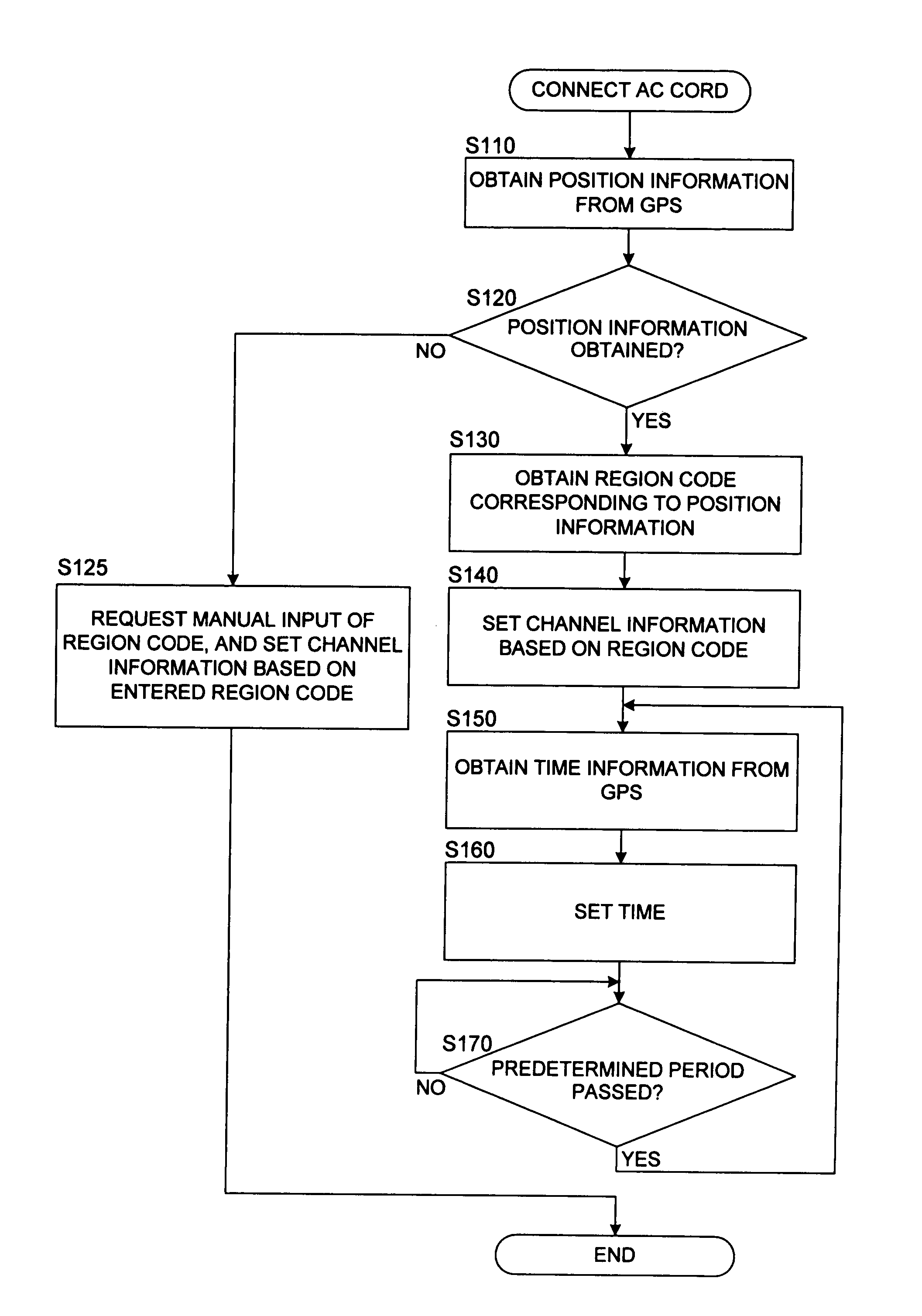
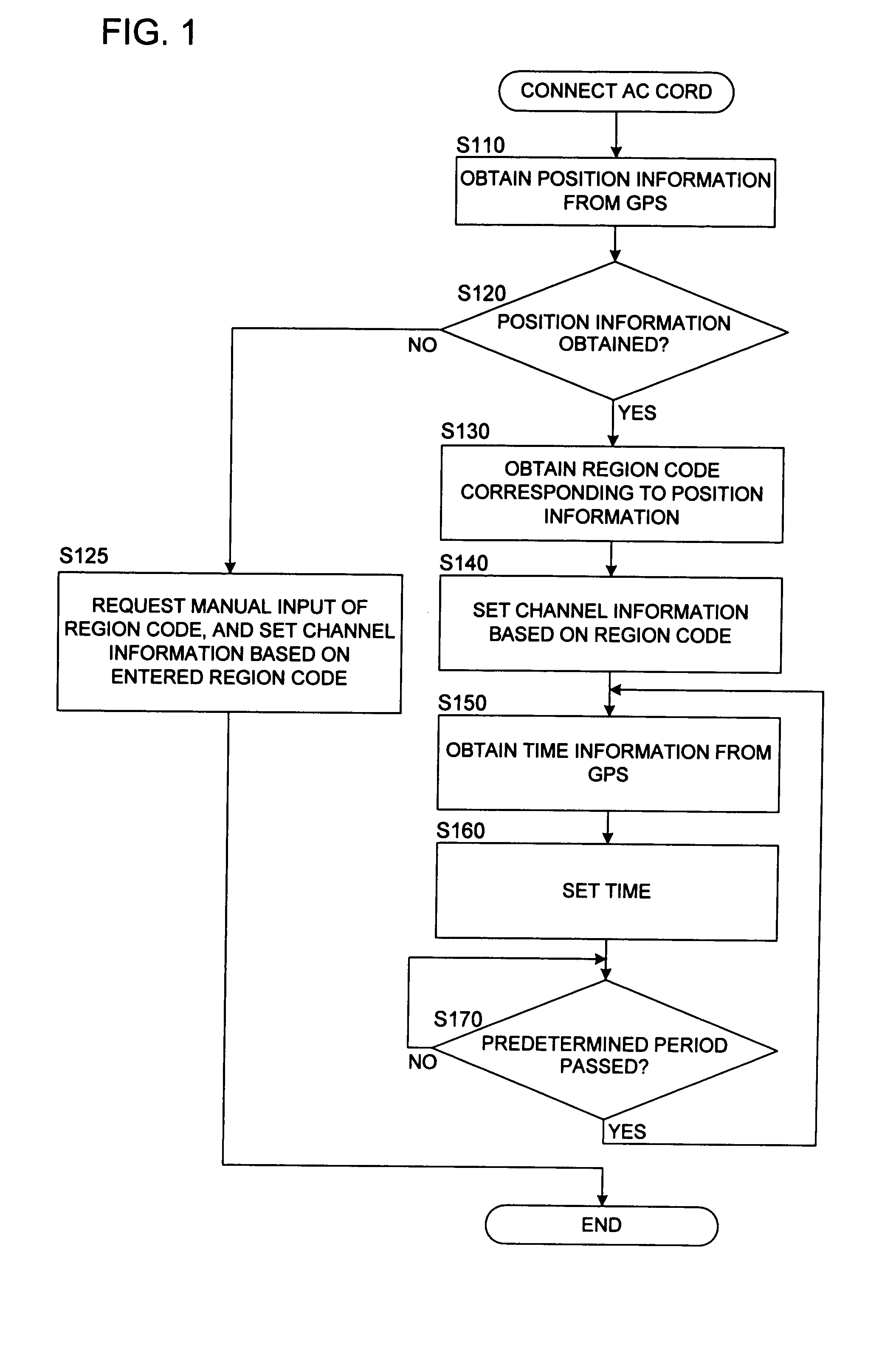
InactiveUS20080025695A1Facilitate performance improvementsReduce workloadTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingComputer scienceSatellite
When a recording device is connected to a power source and a main power is supplied, position information of the recording device is obtained by using GPS satellites. A region where the recording device is installed is decided based on the obtained position information. Channel information appropriate for the decided region is read out from a storage medium such as a memory, and a tuner of the recording device is set automatically using the read channel information thus read. Additionally, when the position information is obtained, it is decided whether or not the position where the recording device is installed is within a predetermined distance from a boundary between regions. If it is adjacent to other region, a plurality of region codes are read out, and a request for selecting one to perform the channel setting is displayed using a display panel or an OSD function so that the selection can be received.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
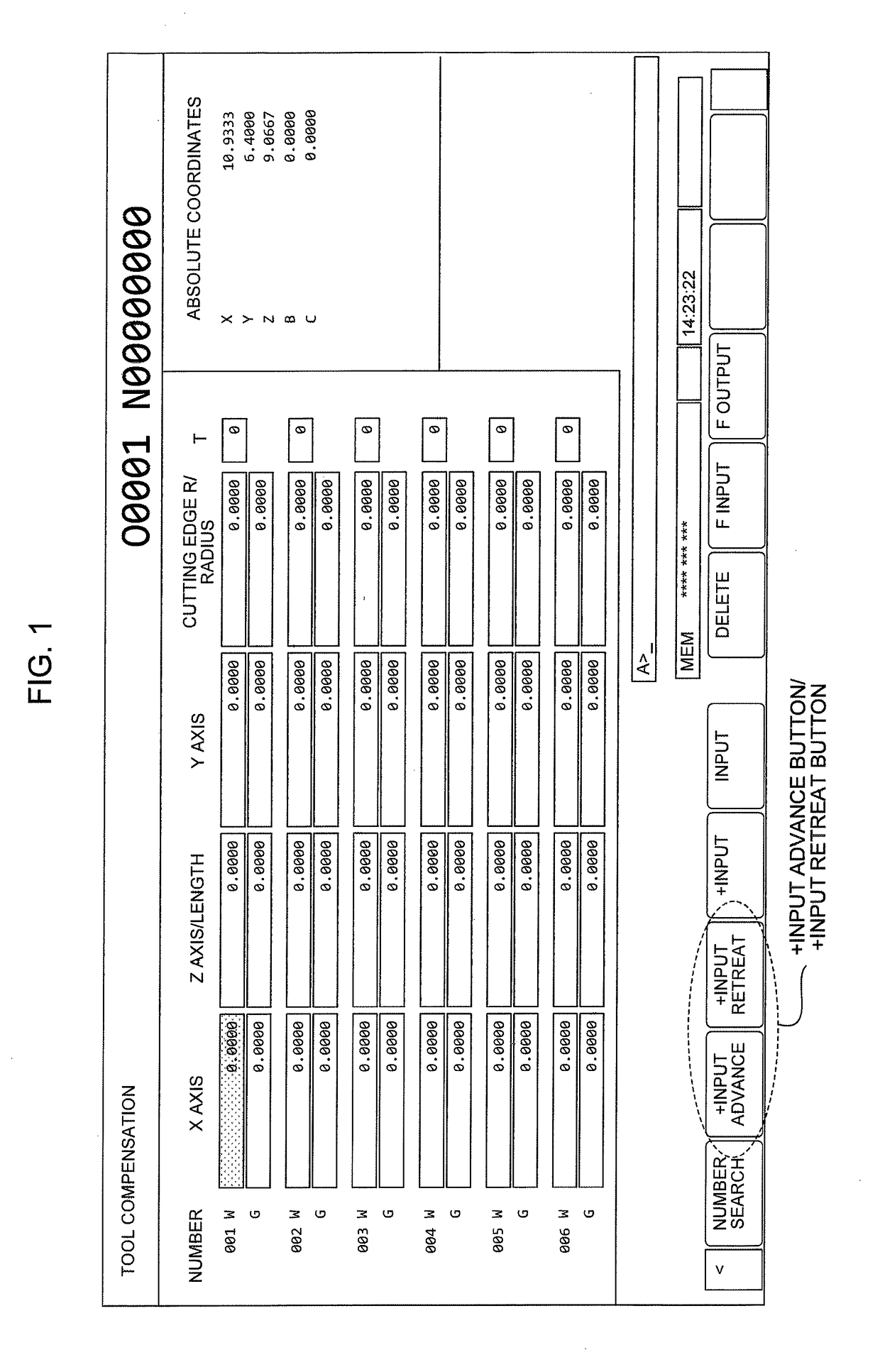
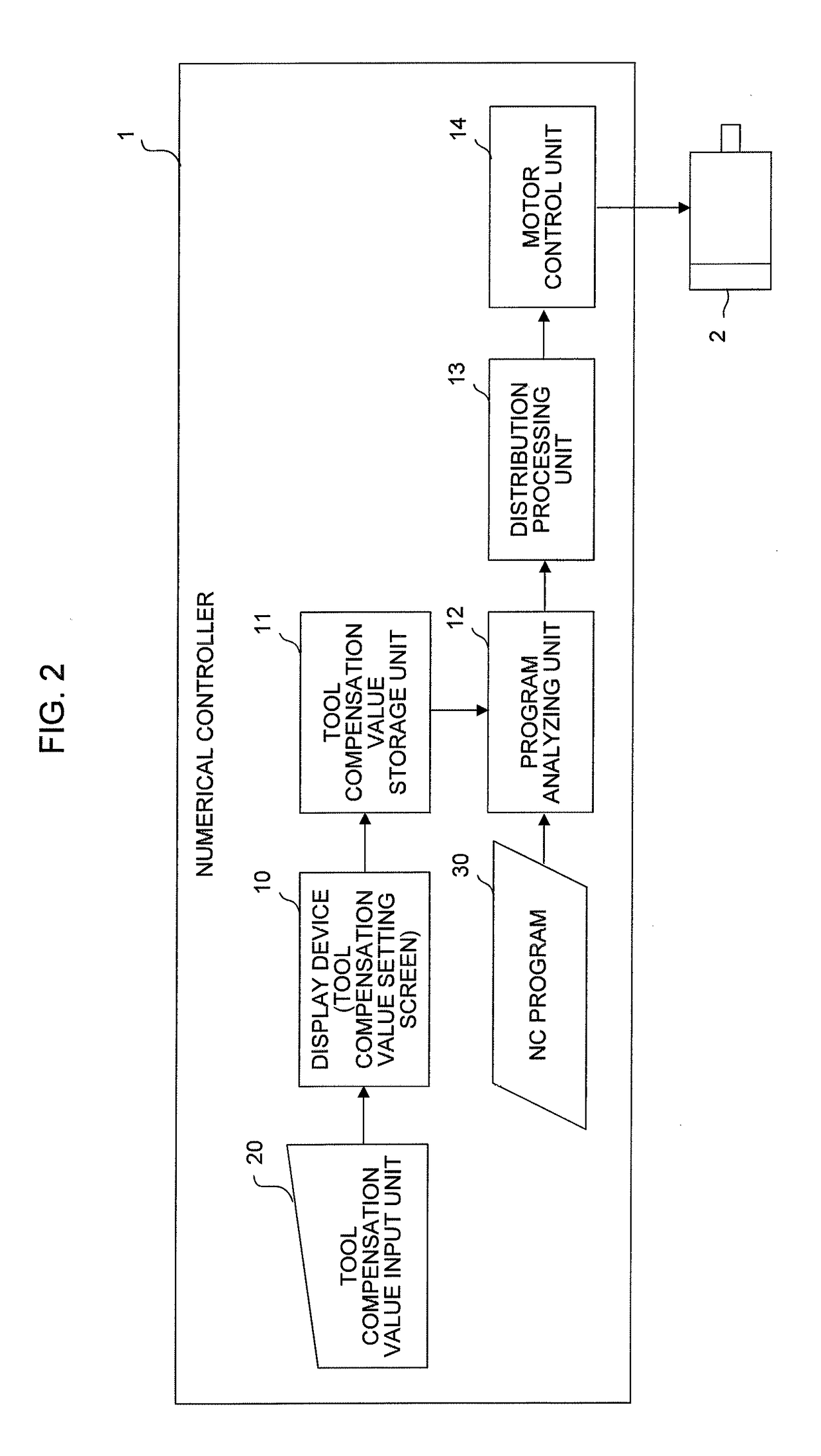
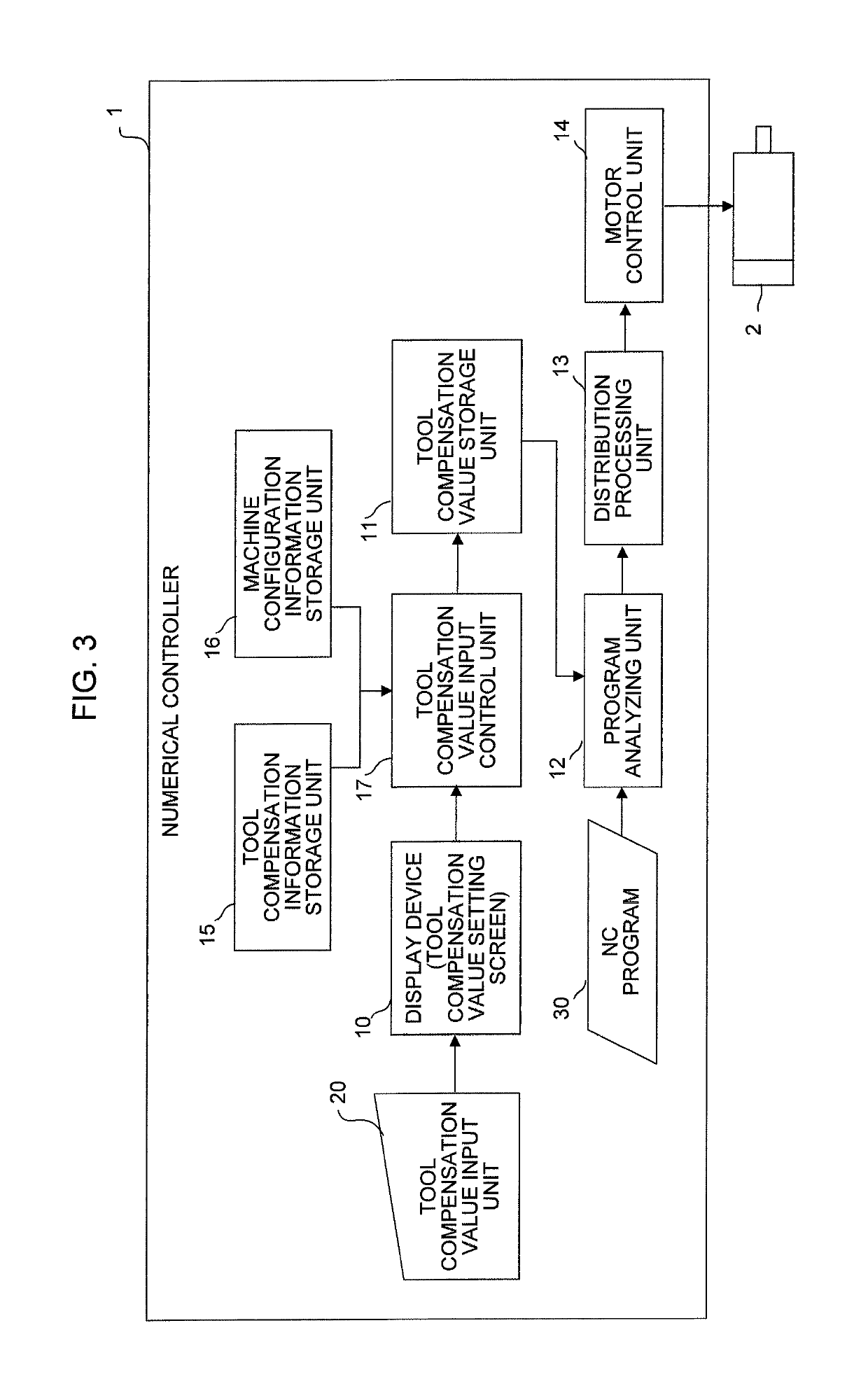
Numerical controller
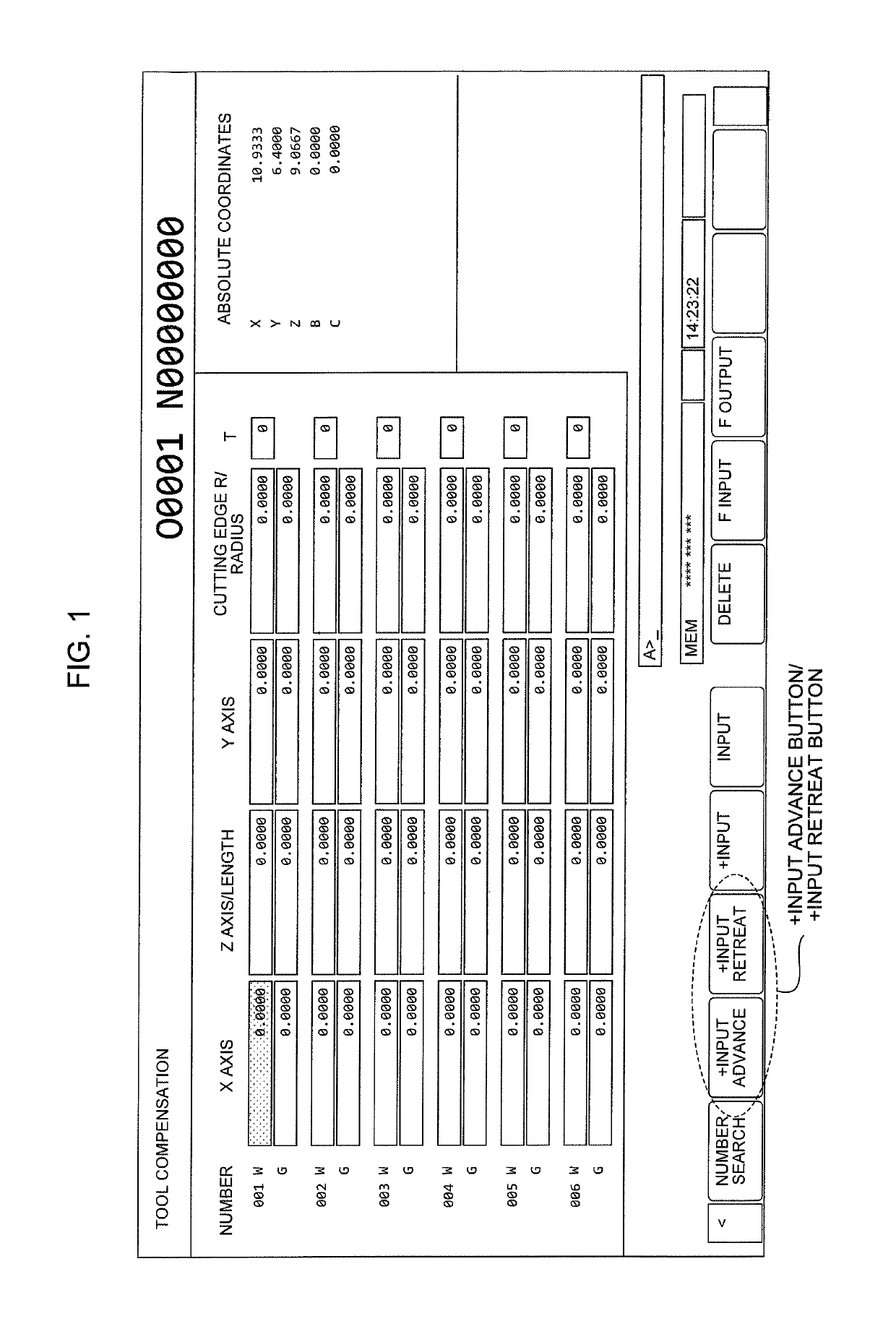
A numerical controller corrects a tool compensation value for a machine tool provided with a tool for machining a workpiece based on an NC machining program. The numerical controller makes it unnecessary for a person in charge of input to be conscious of the sign of the tool compensation value and prevents a tool compensation value input error by providing an input button for bringing a workpiece and a tool cutting edge close to each other by a specified amount (+input advance) and an input button for causing the workpiece and the tool cutting edge to be away from each other by a specified amount (+input retreat) at the time of inputting the tool compensation value.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Opening/closing control device of chuck
ActiveUS10130999B2Easily and rapidly carryPrevent setting errorsSleeve/socket jointsMeasurement/indication equipmentsExternal storageDisplay device
The invention relates to a device controlling a chuck of a machine tool and an auxiliary equipment thereof, thereby facilitating a setup work. Gripping and releasing of a work are confirmed by registering a work gripping position and a work releasing position of a chuck, a kind of a used chuck, and a gripping direction of a work in an external memory device every product type of the work, transferring the work gripping position and the work releasing position in correspondence to the product type to a controller of a machine tool displaying them on a display of an operator control panel, detecting a position of an operation rod opening and closing a claw of the chuck by a stroke sensor, referring to the gripping position of the work, and detecting conformity of the detecting position and set values of the work gripping position and the work releasing position.
Owner:NAKAMURATOME SEIMITSU IND
Recording device
InactiveUS8081859B2Facilitate performance improvementsReduce workloadTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingComputer scienceSatellite
When a recording device is connected to a power source and a main power is supplied, position information of the recording device is obtained by using GPS satellites. A region where the recording device is installed is decided based on the obtained position information. Channel information appropriate for the decided region is read out from a storage medium such as a memory, and a tuner of the recording device is set automatically using the read channel information thus read. Additionally, when the position information is obtained, it is decided whether or not the position where the recording device is installed is within a predetermined distance from a boundary between regions. If it is adjacent to other region, a plurality of region codes are read out, and a request for selecting one to perform the channel setting is displayed using a display panel or an OSD function so that the selection can be received.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Image forming system and control program
InactiveUS20200112651A1Prevent setting errorsPictoral communicationDigital output to print unitsRadiologyImage formation
Provide is an image forming system and a control program capable of preventing a setting error of an output mode by a user when newly generating a correct image. An image forming system includes an image forming unit, an image reading unit, a reference image acquiring unit, and a control unit. The image reading unit reads the image on the sheet formed by the image forming unit. The reference image acquiring unit acquires a reference image as a reference for determining whether the image of the print job formed on the sheet is normal. The control unit prohibits forming of a plurality of copies of the image of the print job by the image forming unit when the reference image acquiring unit newly generates and acquires a reference image by reading the image formed on the sheet by the image forming unit using the image reading unit.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
On-demand publishing system
ActiveUS8139236B2Improve productivityAvoid it happening againVisual presentationPictoral communicationInformation processingOn demand
According to the present invention an information processing apparatus comprises: a loading unit which loads function information representing a function of the post-printing processing device; an identification unit which identifies a printing function processible by the printing device and a post-processing function processible after printing by the post-printing processing device; a display control unit which displays a setting window for setting the printing function and post-processing function; a data generation unit which generates printing data to be printed by the printing device; a setting information generation unit which generates post-processing setting information subjected to post-printing processing by the post-printing processing device; and wherein the printing data is transmitted to the printing device, and the post-processing setting information is transmitted to the post-printing processing device.
Owner:CANON KK
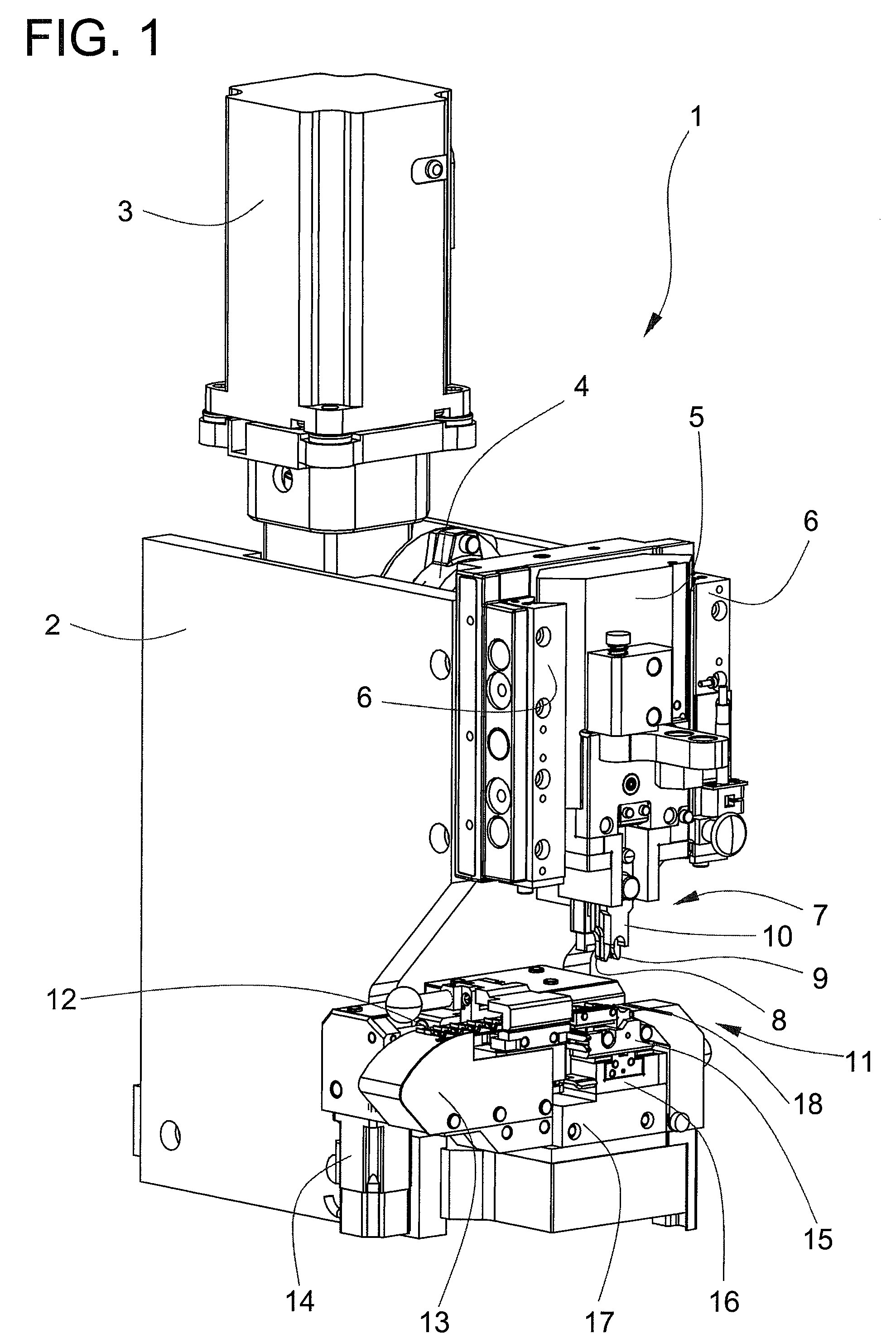
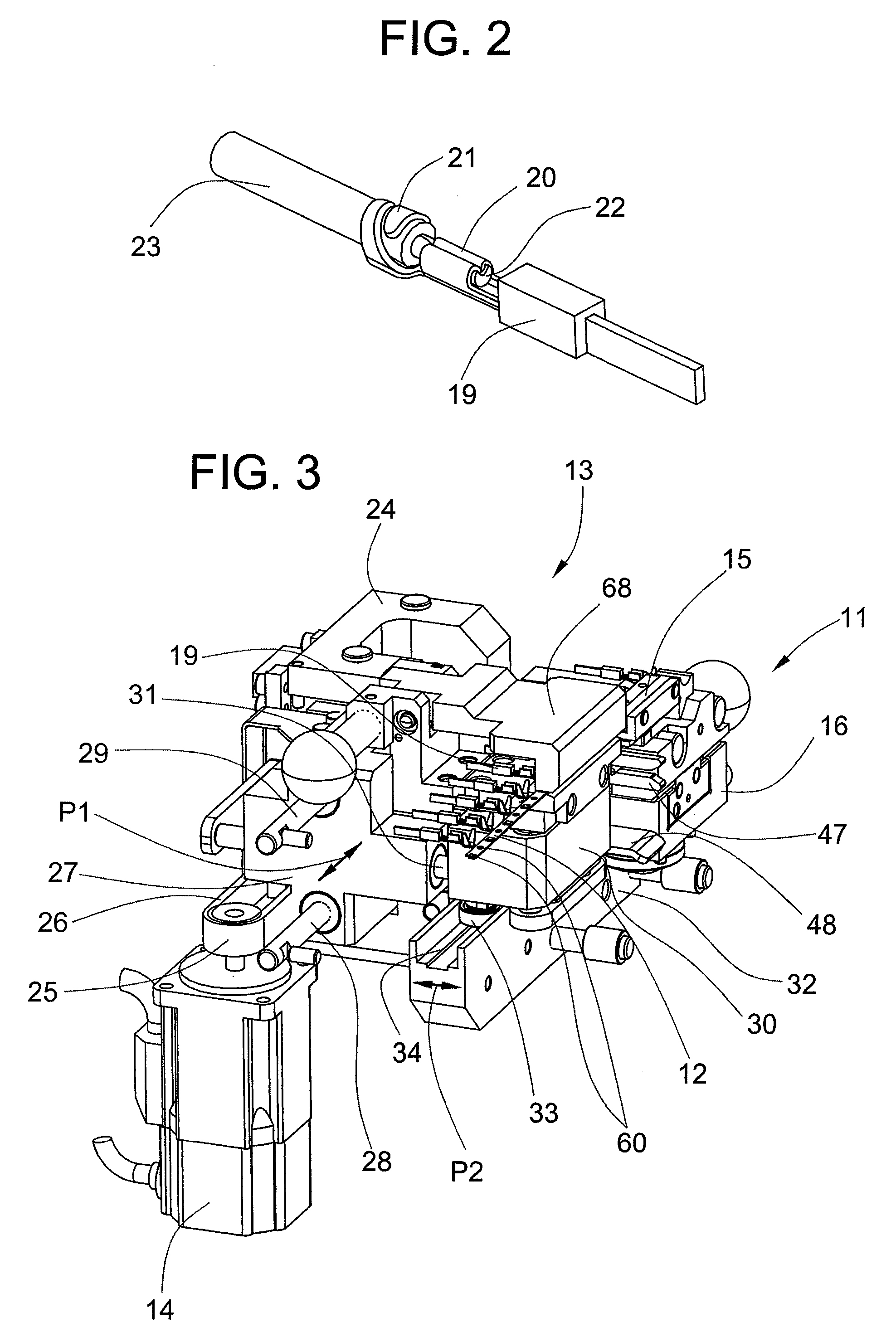
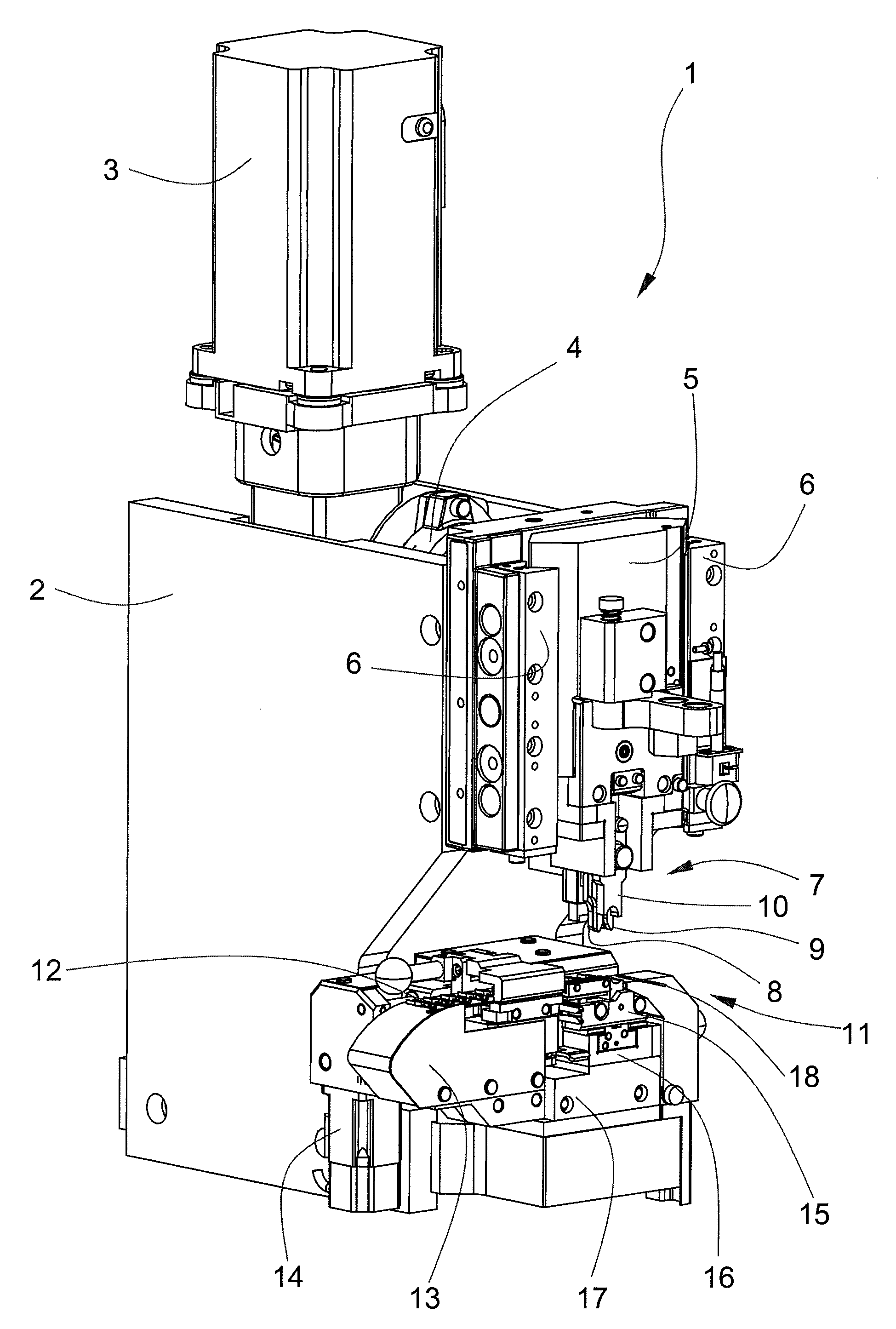
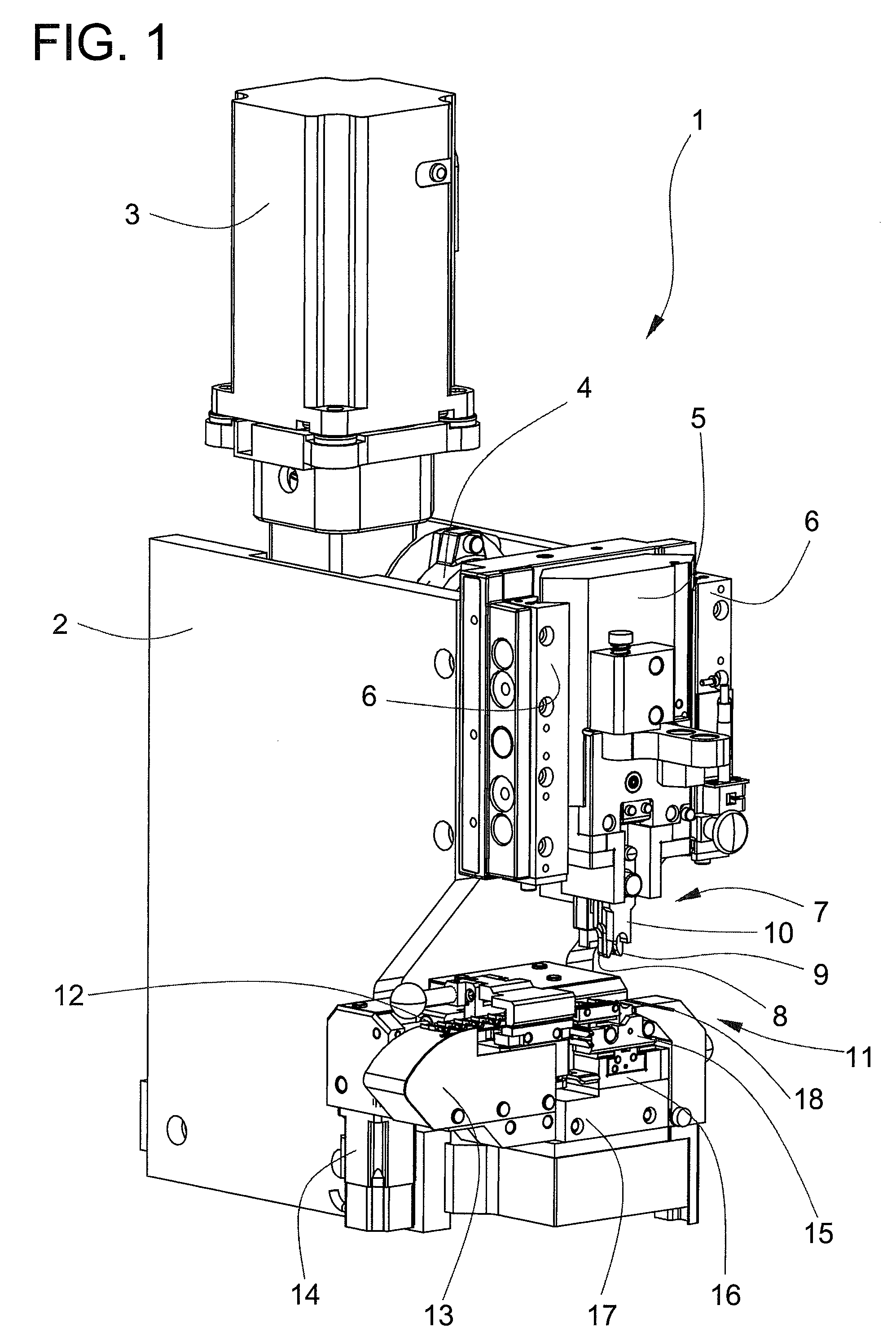
Crimping press
ActiveUS7757386B2Prevent setting errorsEffect on production costMetal-working feeding devicesStripping-off devicesMotor driveEngineering
A crimping device has a contact advancer provided with an exchangeable anvil part. A first pulley, a belt and an advancing motor drive a first carriage. A gripper for advancing the contact belt is guided in a direction crosswise to a direction of the first carriage. The distance between the gripper and the first carriage is determined by a second carriage and a roller of the gripper rolling in a fifth linear guide of the second carriage. The distance from the gripper is predetermined by the exchangeable anvil part and depends on the width of the contact belt. The gripper operates independent of the distance between the transport holes and independent of the width of the contact belt. The anvil part including the belt guide is an exchangeable part and only fits one type of crimp contact and is executed crimp-contact specifically.
Owner:KOMAX HOLDING
Crimping Press
ActiveUS20070062246A1Avoids disadvantagePrevent setting errorsMetal-working feeding devicesStripping-off devicesEngineeringMotor drive
A crimping device has a contact advancer provided with an exchangeable anvil part. A first pulley, a belt and an advancing motor drive a first carriage. A gripper for advancing the contact belt is guided in a direction crosswise to a direction of the first carriage. The distance between the gripper and the first carriage is determined by a second carriage and a roller of the gripper rolling in a fifth linear guide of the second carriage. The distance from the gripper is predetermined by the exchangeable anvil part and depends on the width of the contact belt. The gripper operates independent of the distance between the transport holes and independent of the width of the contact belt. The anvil part including the belt guide is an exchangeable part and only fits one type of crimp contact and is executed crimp-contact specifically.
Owner:KOMAX HOLDING
Method for automatically setting ID in UART ring communication
ActiveUS9678908B2Prevent setting errorsBlocking in networkSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlLoop networksComputer scienceRing type
Owner:LSIS CO LTD
Device for detecting broken yarn through shaft frame and method for locating its address
InactiveCN1779006BPrevent setting errorsShorten the timeInspecting textilesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsYarnEmbedded system
The invention relates to a method for locating address for plural controllers of a yarn breakage detector and the yarn breakage detector with address setting function. The yarn breakage detector is composed of a plurality of serially connected controllers corresponding to a plurality of yarn breakage sensors for each supporting member of a yarn feeding member, and a central processor for monitoring the yarn breakage in the whole creel apparatus and connected to the controllers in series. The central processor outputs a signal containing address information to the controller of the uppermost stream side. The uppermost controller recognizes / memorizes the own address based on the inputted signal, acquires the address information of the following downstream-side controller based on the inputted signal information according to a prescribed operation procedure, and outputs a signal containing the address information to the following downstream-side controller. Each controller successively sets the address to all following downstream controllers. The invention can successively automatically set address for each controller without setting address for other hardware such as DIL switch andso on.
Owner:TSUDAKOMA KOGYO KK
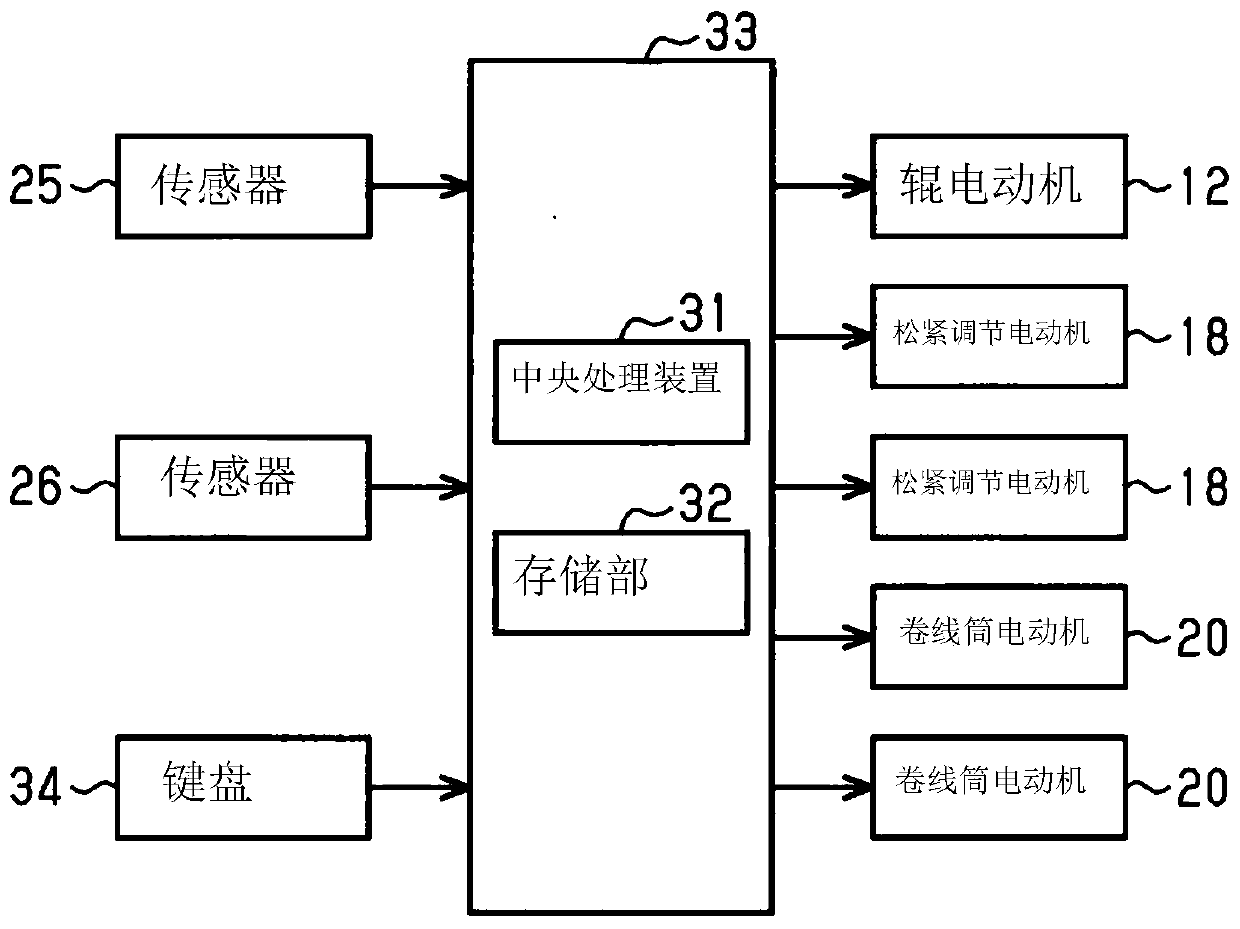
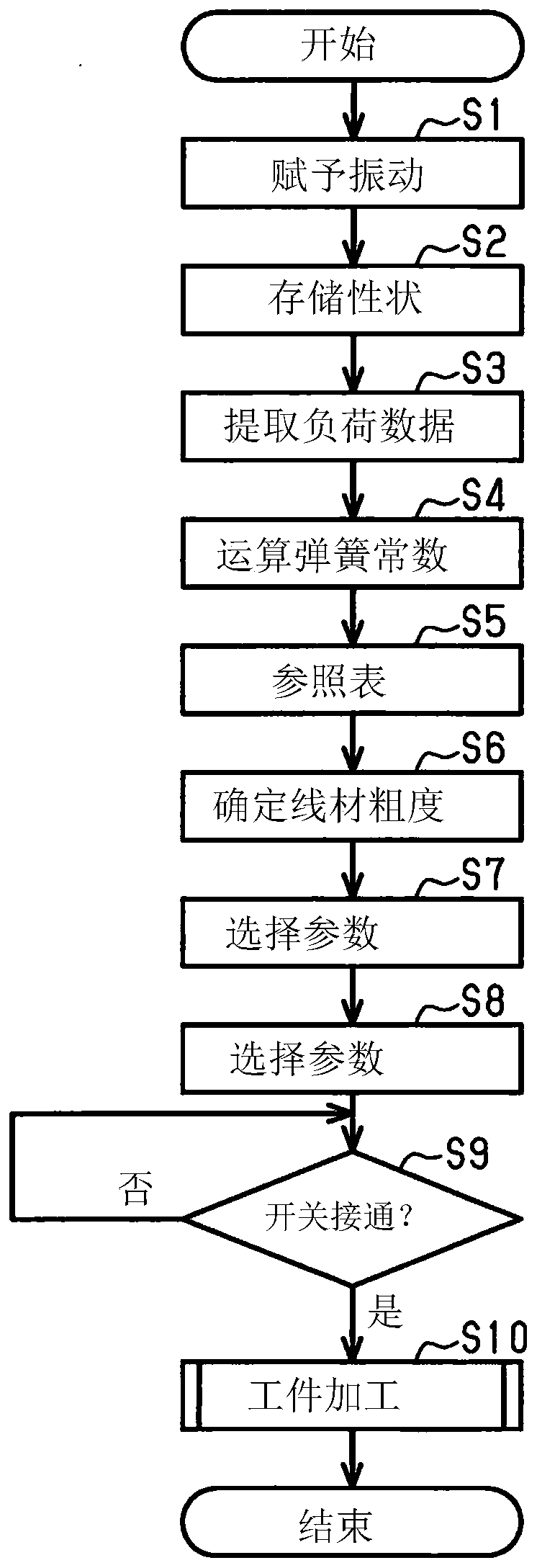
Method for setting operating parameters of wire saw and the wire saw
ActiveCN110497538AReduce machining accuracyAvoid forgettingFine working devicesState variationEngineering
The invention provides a method for setting operating parameters of a wire saw and the wire saw. A wire saw is provided with: a plurality of processing rollers; and a wire rod that travels between theprocessing rollers in a surrounding state. The workpiece is cut by the wire rod by processing the feeding workpiece in a wire rod-based cutting region between the processing rollers. The setting method comprises the steps that before a workpiece is machined, a wire is changed; determining the mechanical characteristics of the wire from the state change of the wire; and setting operating parameters of the wire saw according to the mechanical characteristics.
Owner:KOMATSU NTC LTD
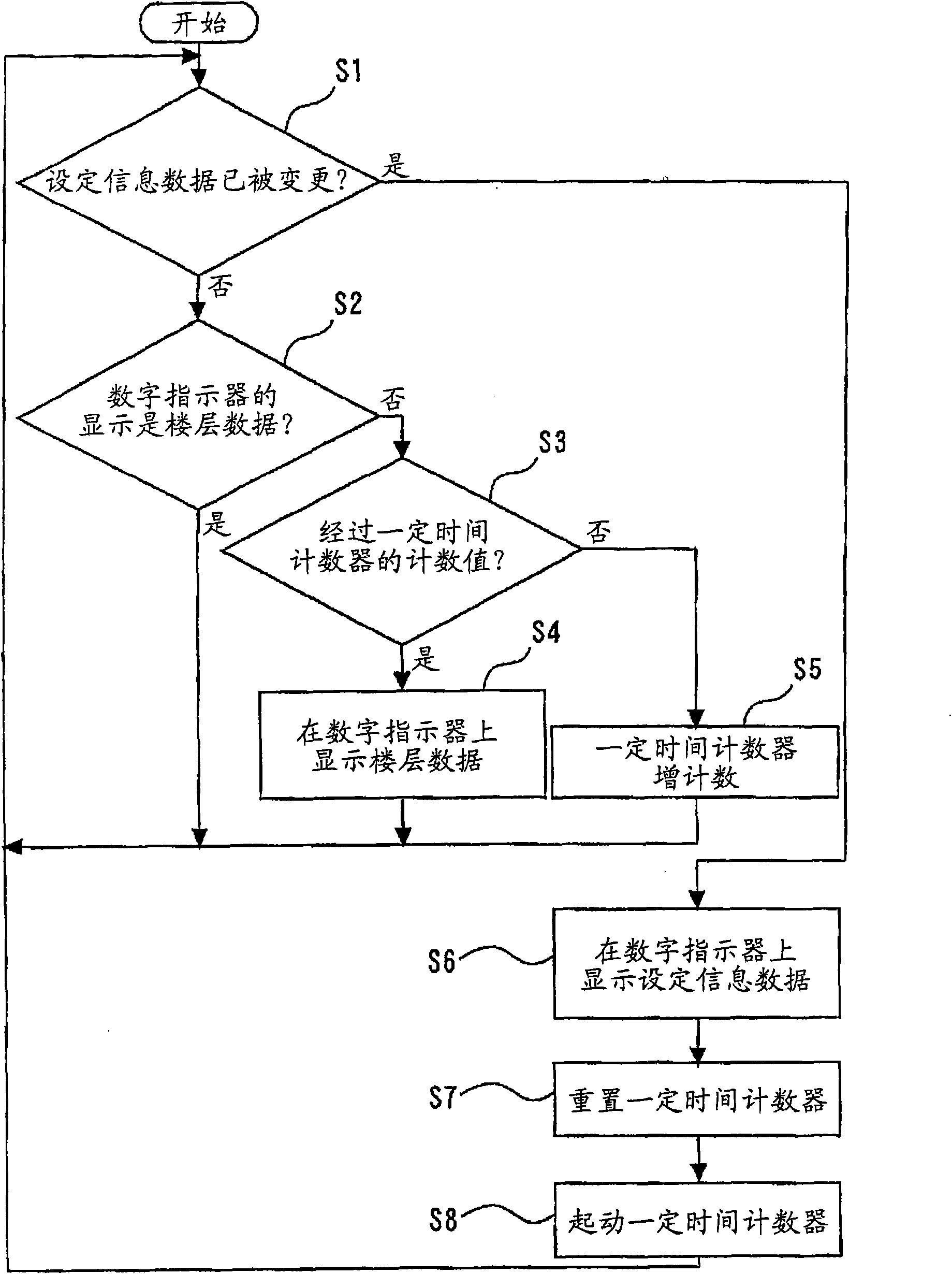
Setting information indicator of elevator operation indicating apparatus
A setting information indicator of an elevator operation indicating apparatus which makes a digital indicator indicate the altered setting information for a predetermined time after a setting alteration moment in time when an installation worker or a maintenance manager altered the setting information data of the elevator operation indicating apparatus. The elevator operation indicating apparatusprovided in the elevator hall or the elevator cage and making the digital indicator indicate the floor data and the setting information data is provided with a control means through which the installation worker or the maintenance manager can perform setting alteration of the setting information data and an indication signal of altered setting information data is outputted to the digital indicator.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Device and method for detecting connection mode of 4-wire or 5-wire resistive touch screen
ActiveCN101957702AImprove compatibilityAvoid judgmentInput/output processes for data processingElectricityEngineering
The invention relates to a device and a method for detecting the connection mode of a 4-wire or 5-wire resistive touch screen. The device comprises five pins and a detector, wherein the detector provides a high potential and a low potential for the two of the five pins at two ends so as to judge whether the 4-wire or 5-wire resistive touch screen is connected in a way of judging whether the pins at the two ends are on or not.
Owner:EGALAX EMPIA TECH INC
Mobile communication system and mobile communication method
InactiveCN1832587ACreate error avoidancePrevent setting errorsWireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork packetMobile communication systems
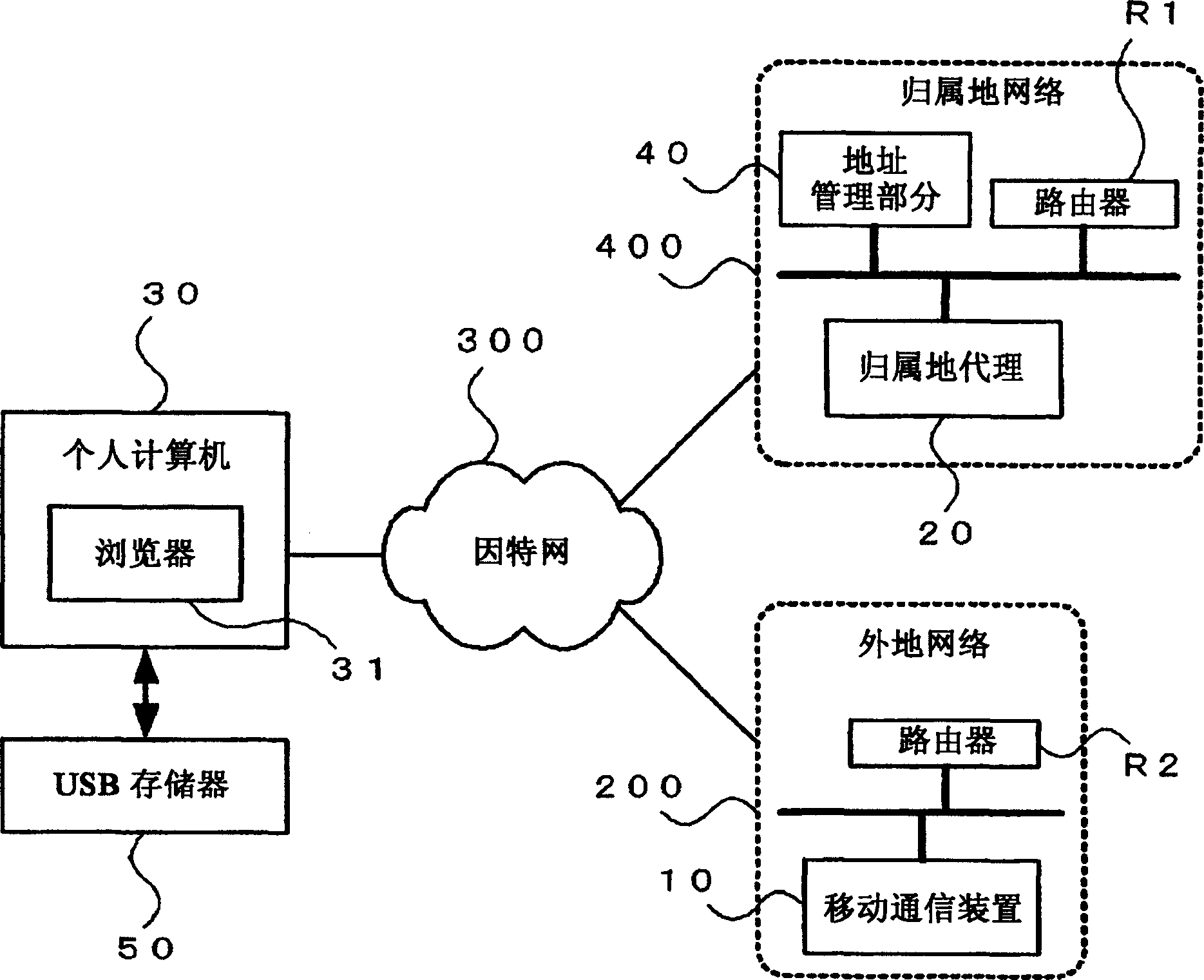
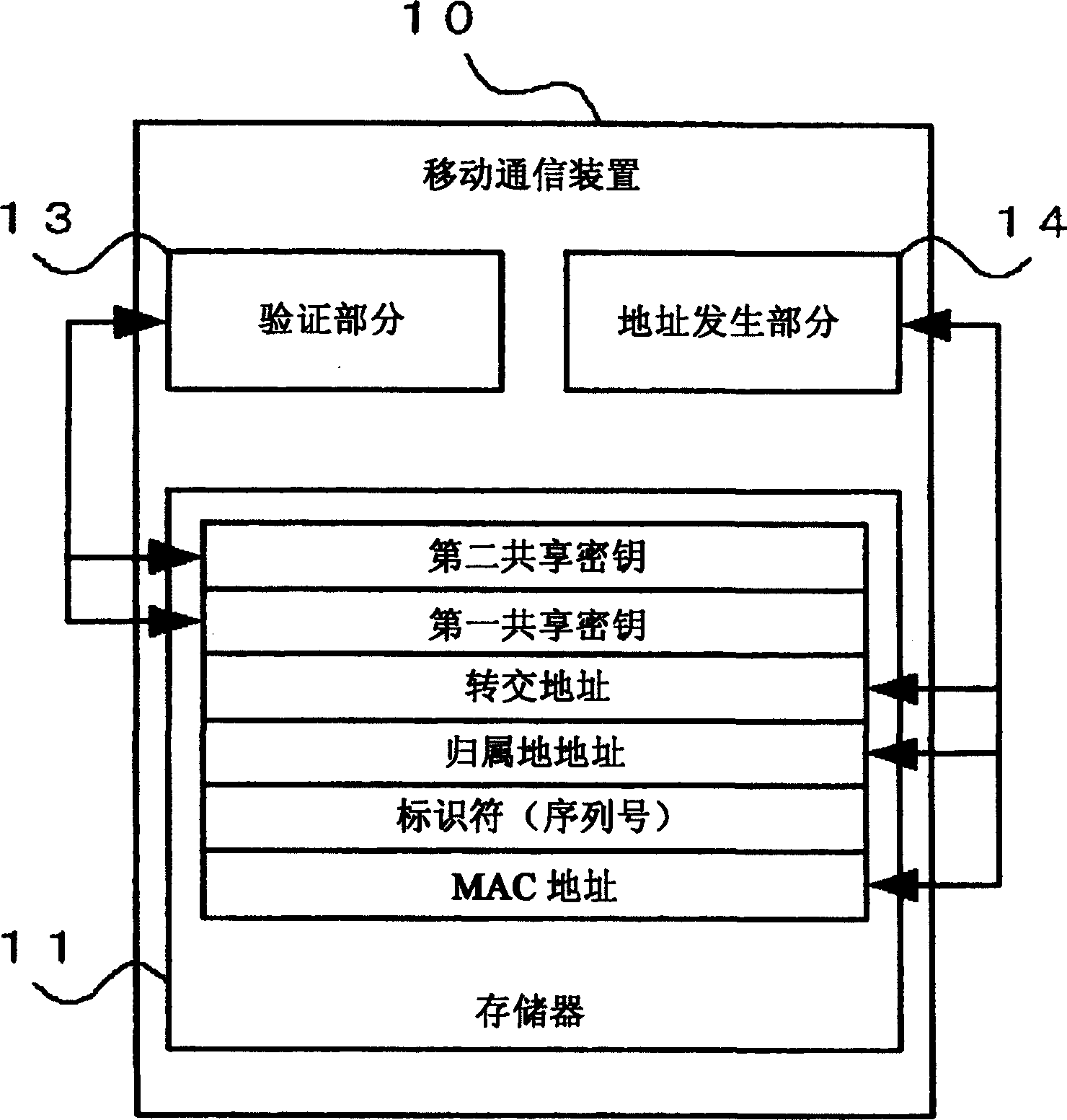
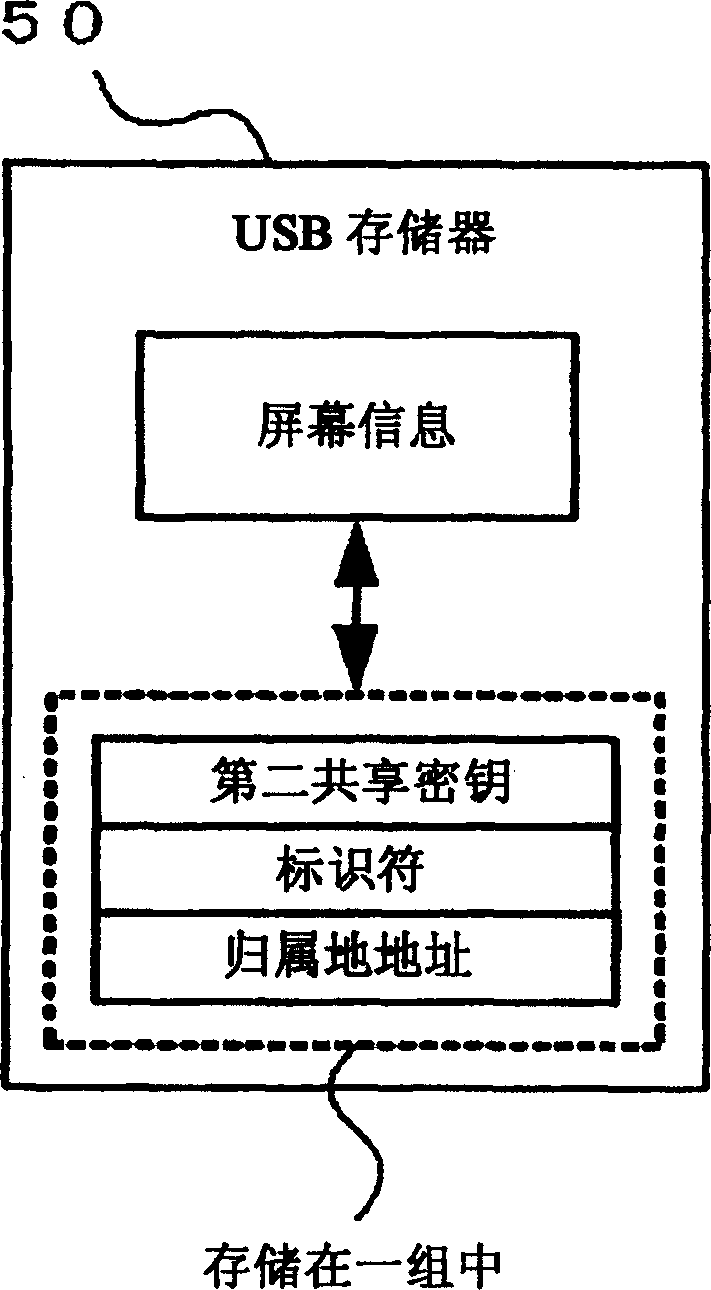
A mobile communication system includes a home agent which transfers a communication packet to a mobile communication device connected to a foreign network, an address management section which manages a plurality of IP addresses, an address generation section which assigns any of the IP addresses managed, by the address management section to the mobile communication device as a home address thereof, a server which stores the home address of the mobile communication device and specific information of the mobile communication device in association with each other, and a source node which connects with the server through a network, and transmits the communication packet to any mobile communication device having the home addresses stored in the server as a destination.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Numerical controller that prevents a tool compensation value setting error
A numerical controller corrects a tool compensation value for a machine tool provided with a tool for machining a workpiece based on an NC machining program. The numerical controller makes it unnecessary for a person in charge of input to be conscious of the sign of the tool compensation value and prevents a tool compensation value input error by providing an input button for bringing a workpiece and a tool cutting edge close to each other by a specified amount (+input advance) and an input button for causing the workpiece and the tool cutting edge to be away from each other by a specified amount (+input retreat) at the time of inputting the tool compensation value.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com