Patents
Literature
41results about "Generic and host data combination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
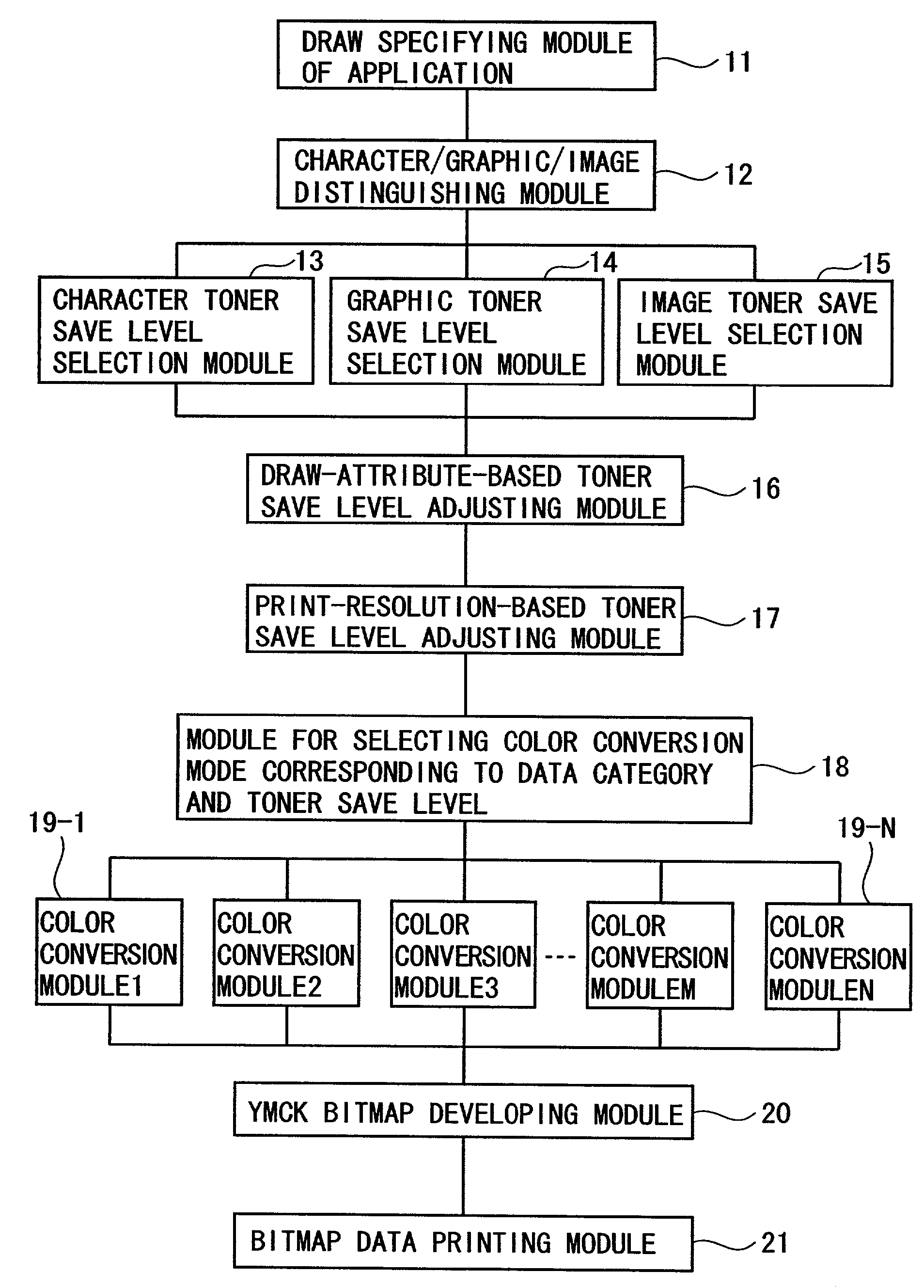
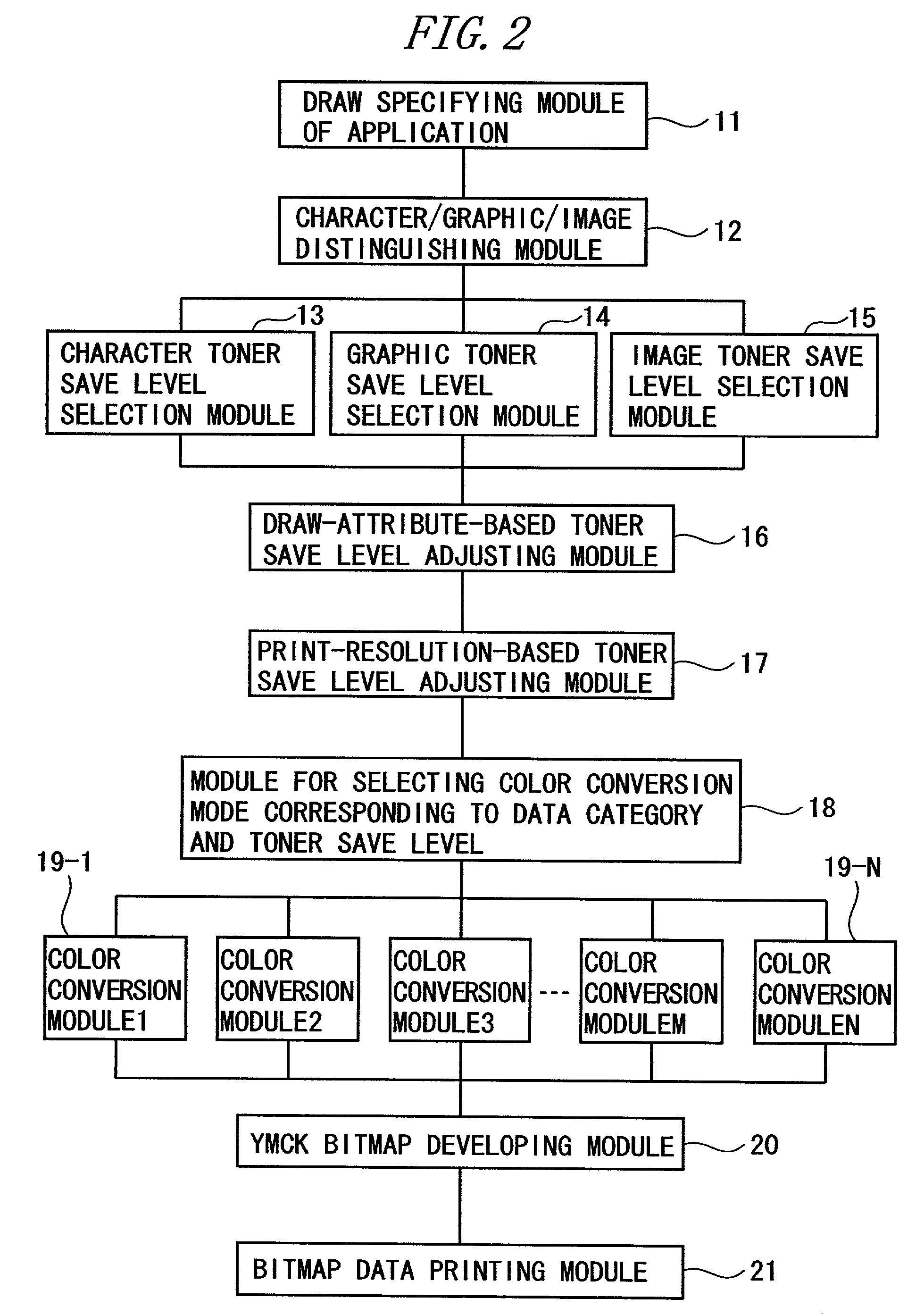
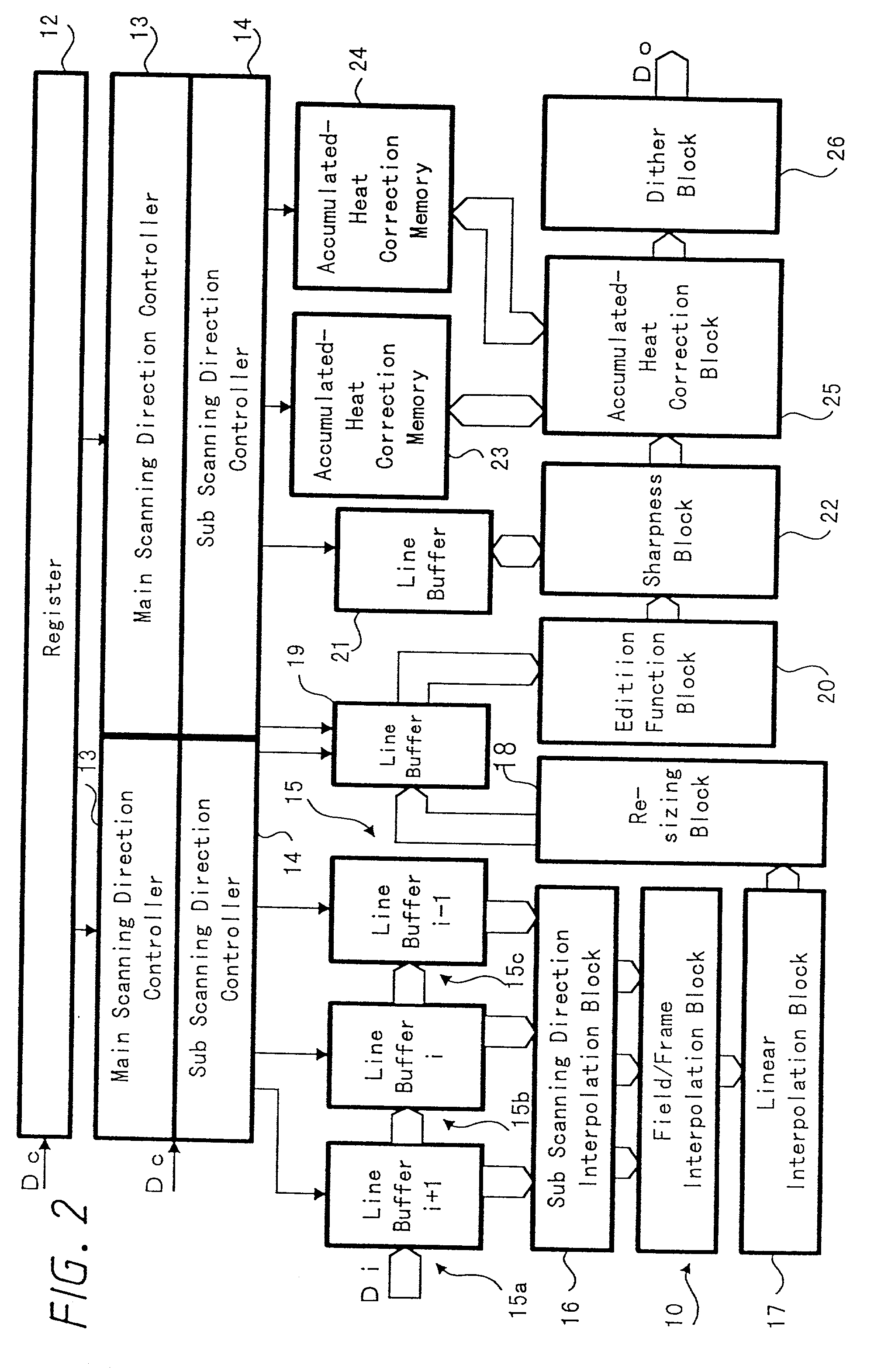
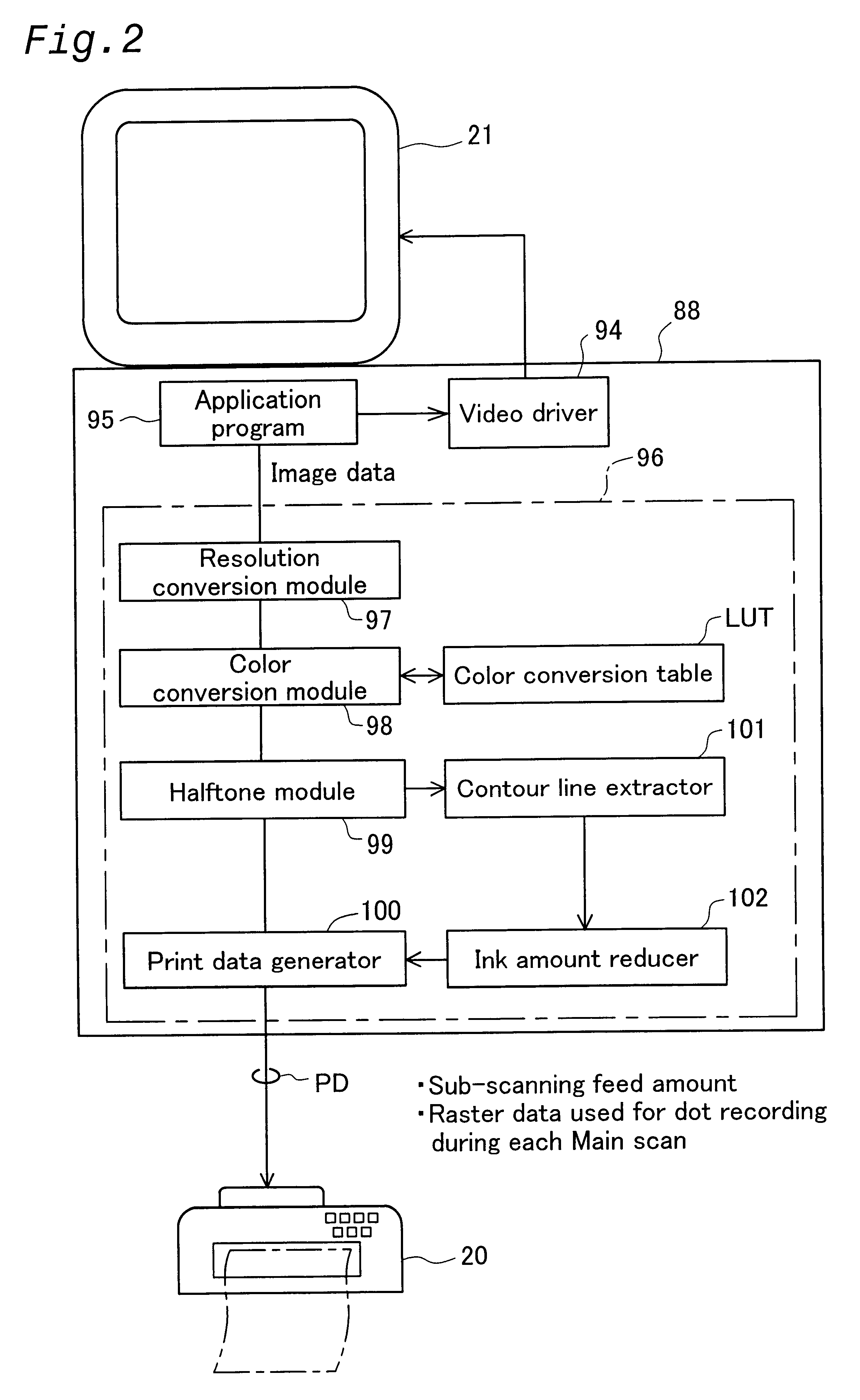
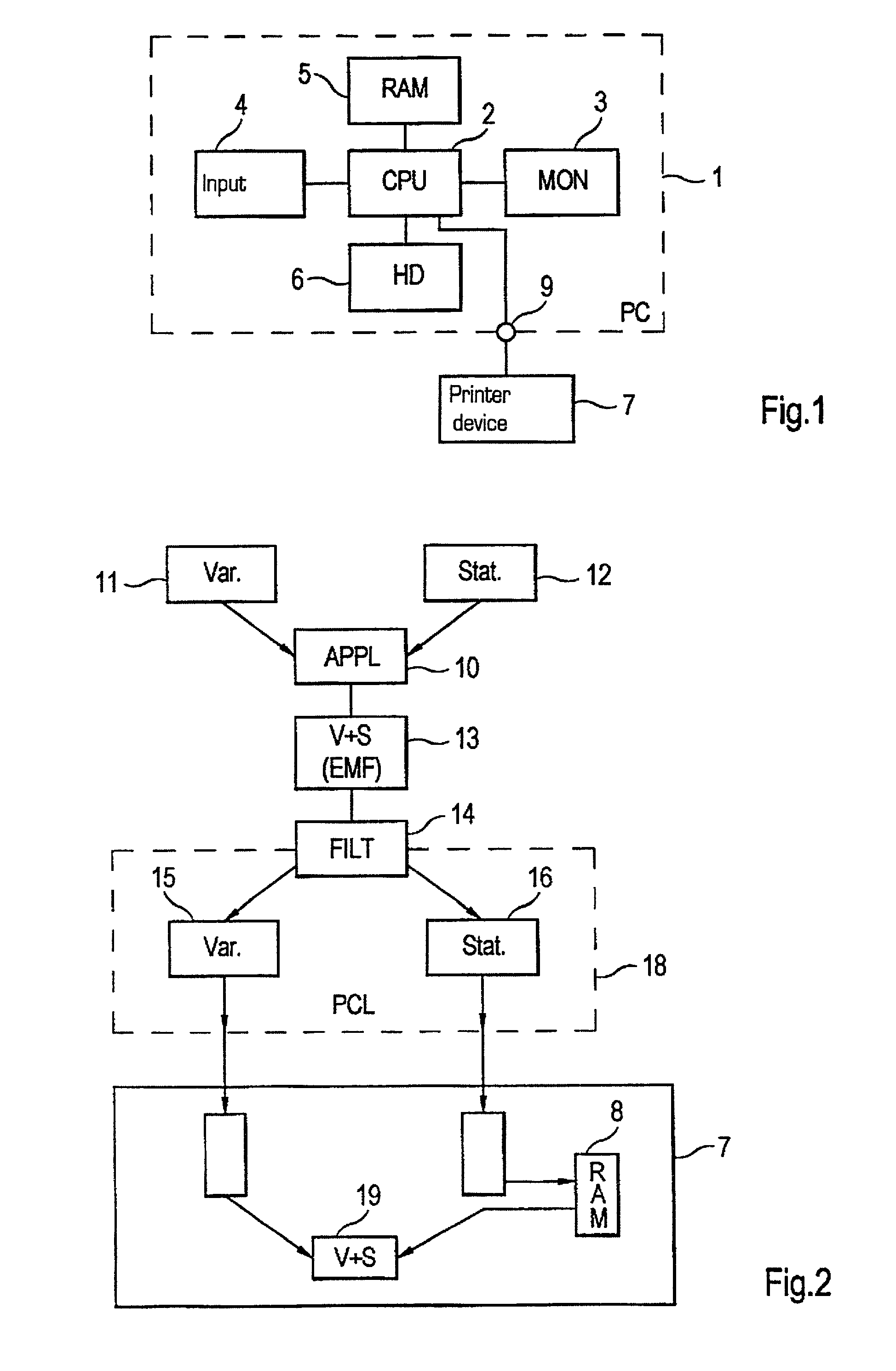
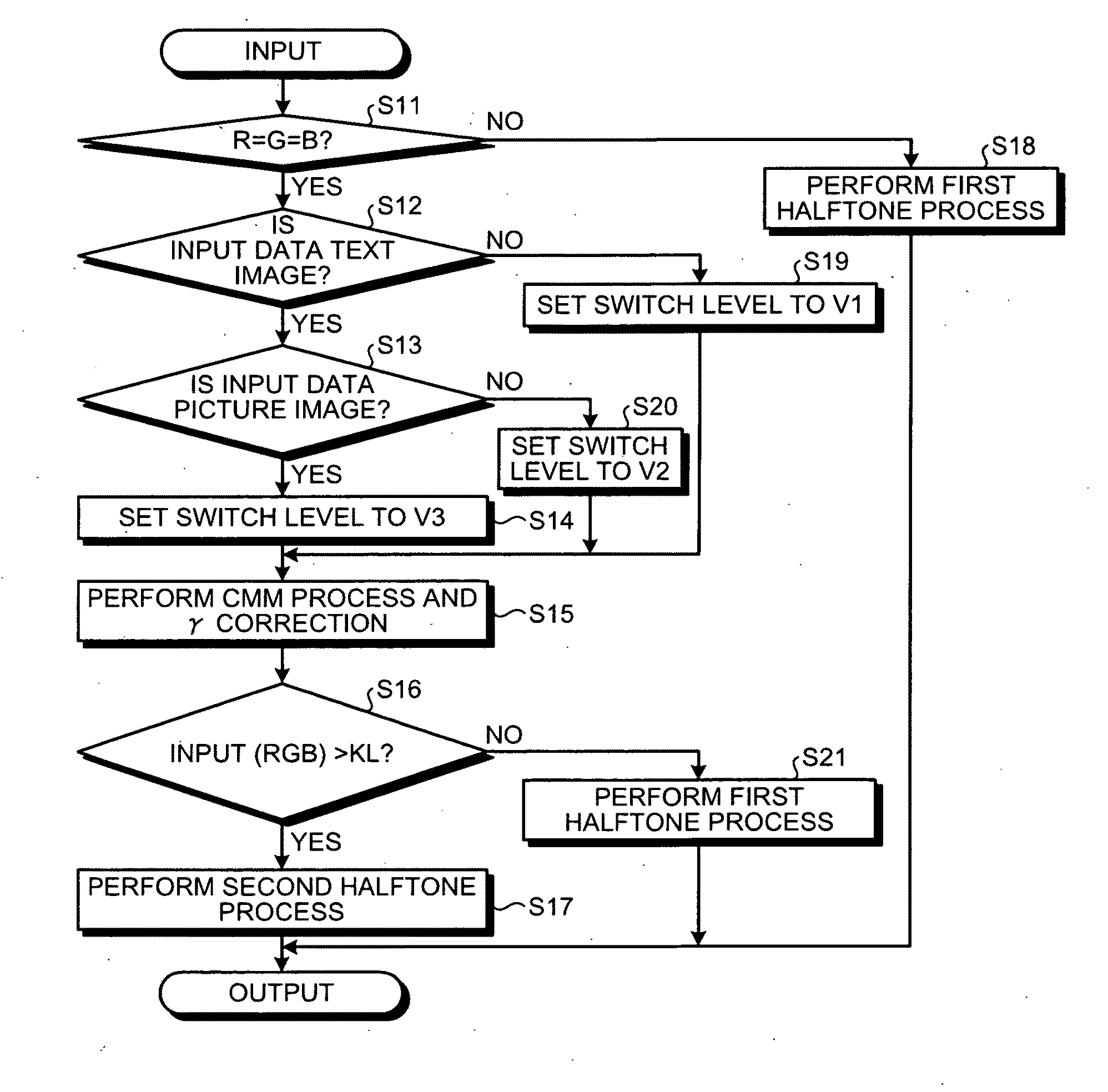
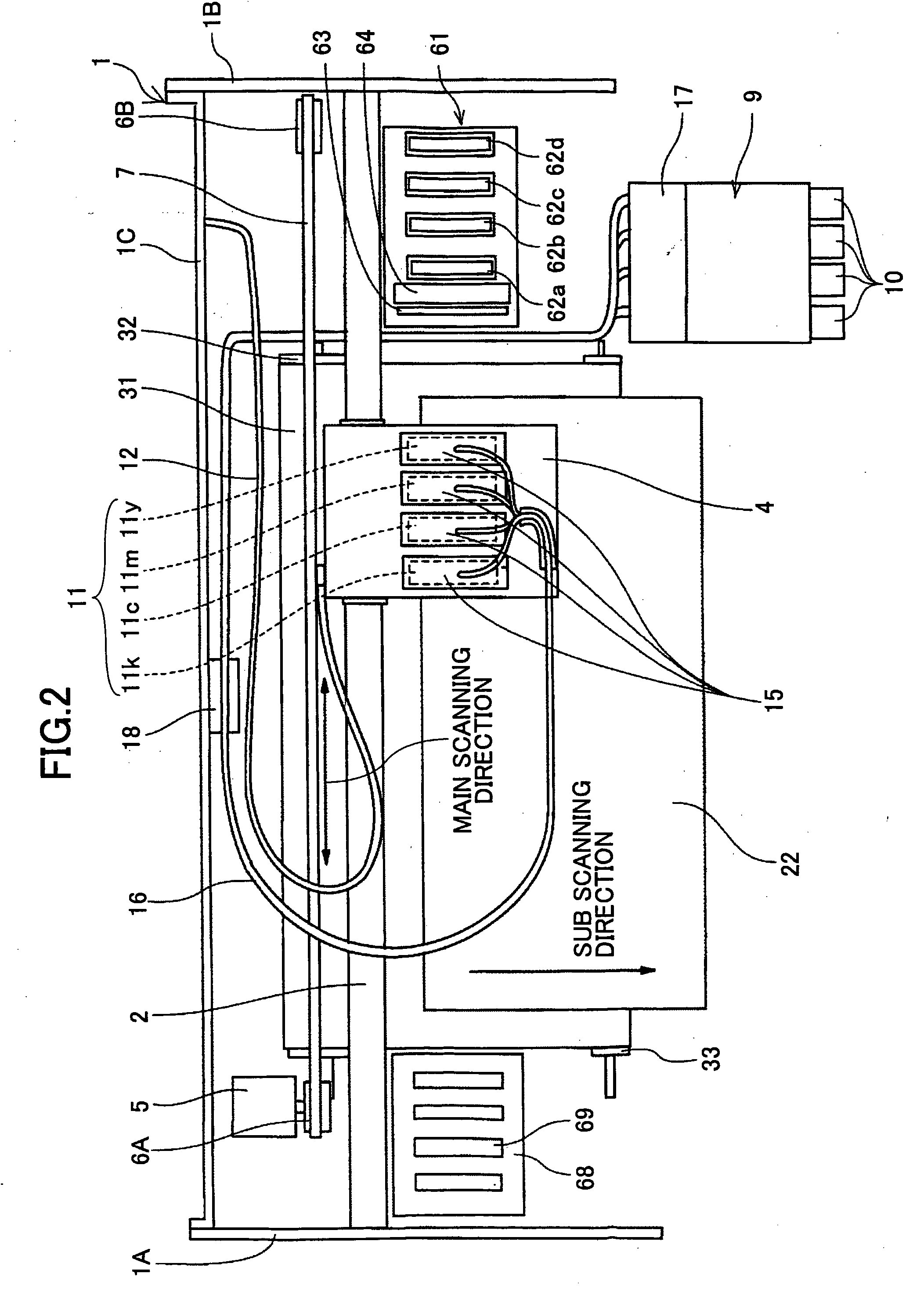
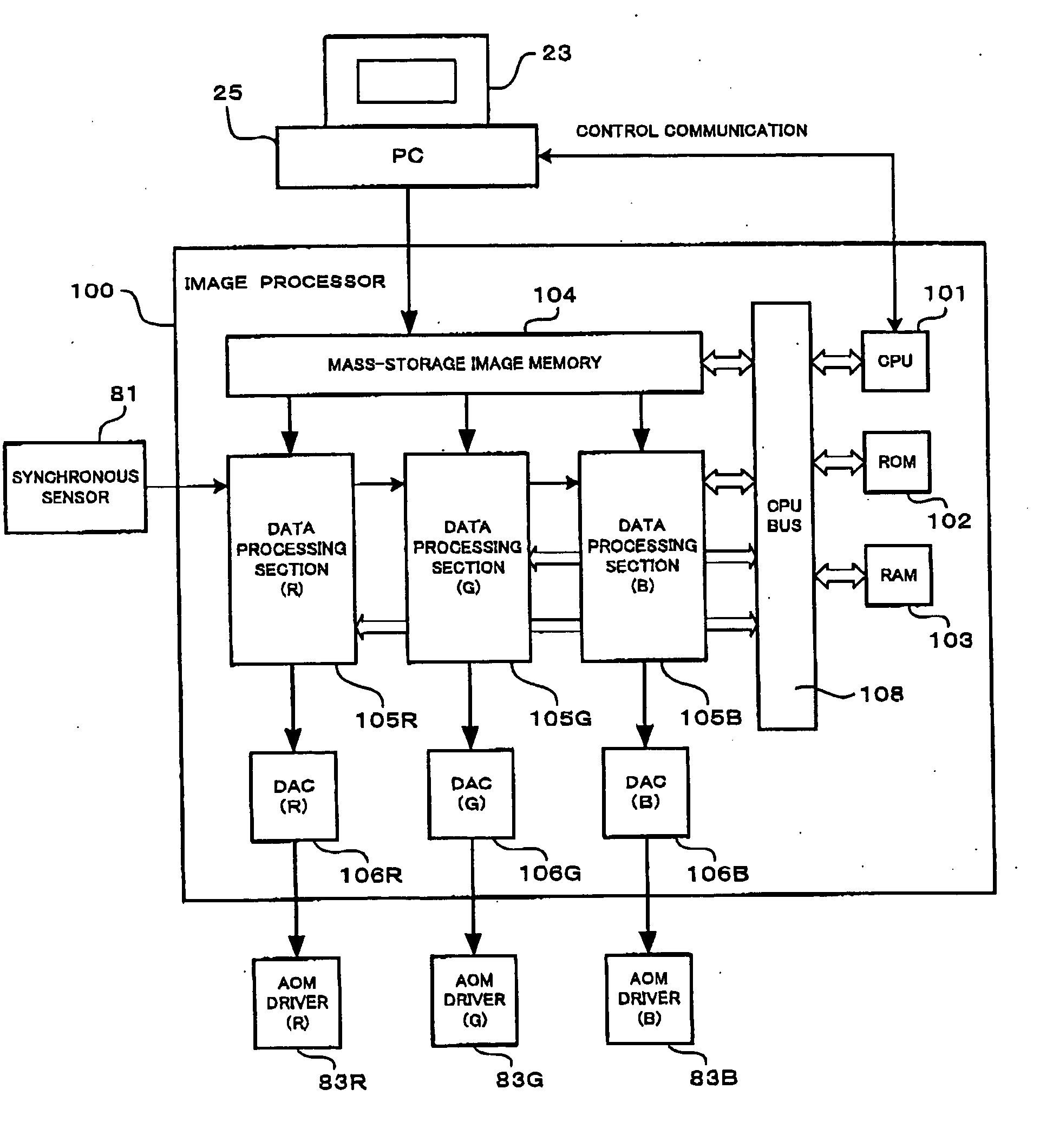
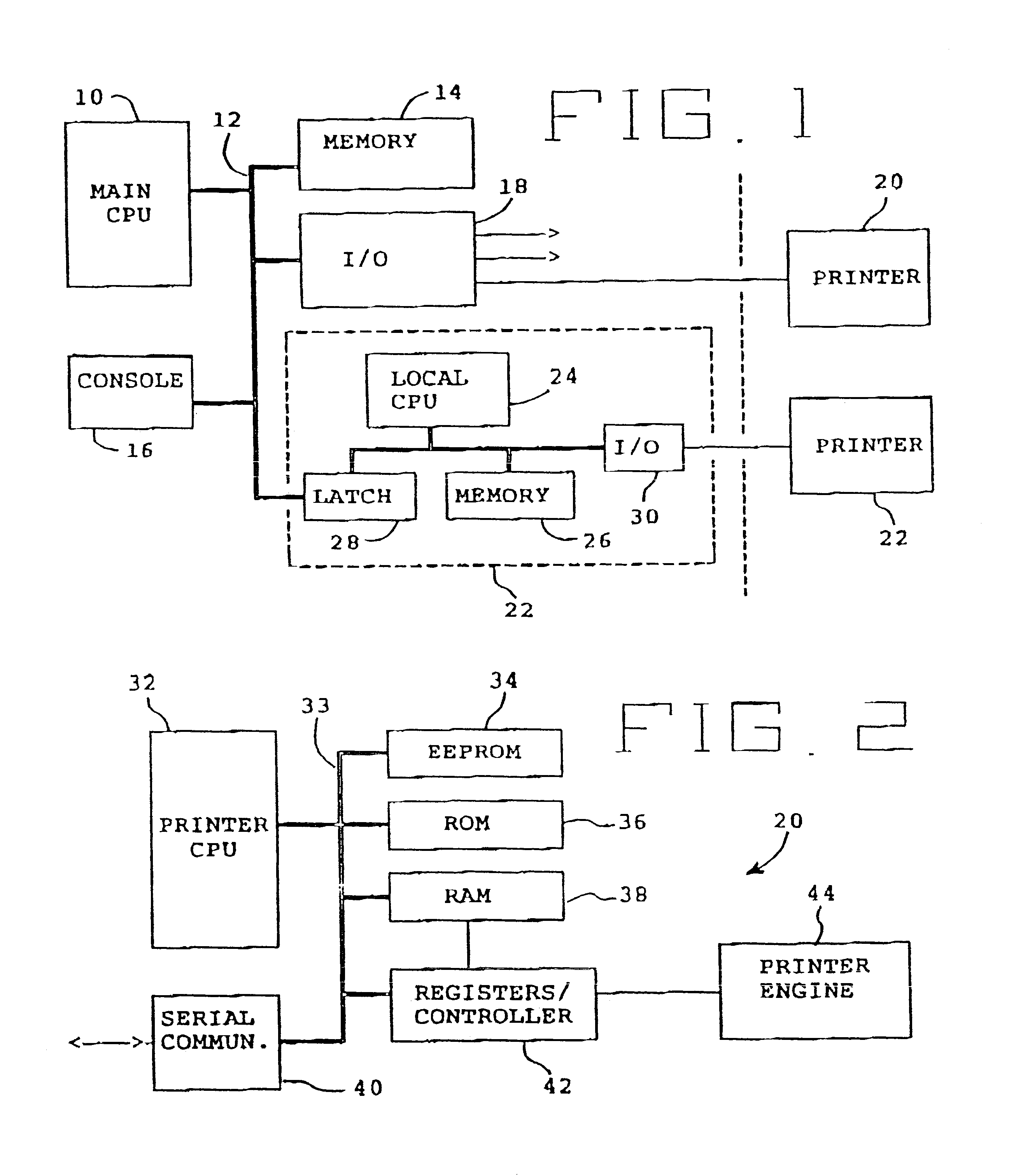
Print control system and medium
InactiveUS7298522B2Minimize consuming quantityDeclineDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsControl systemComputer module
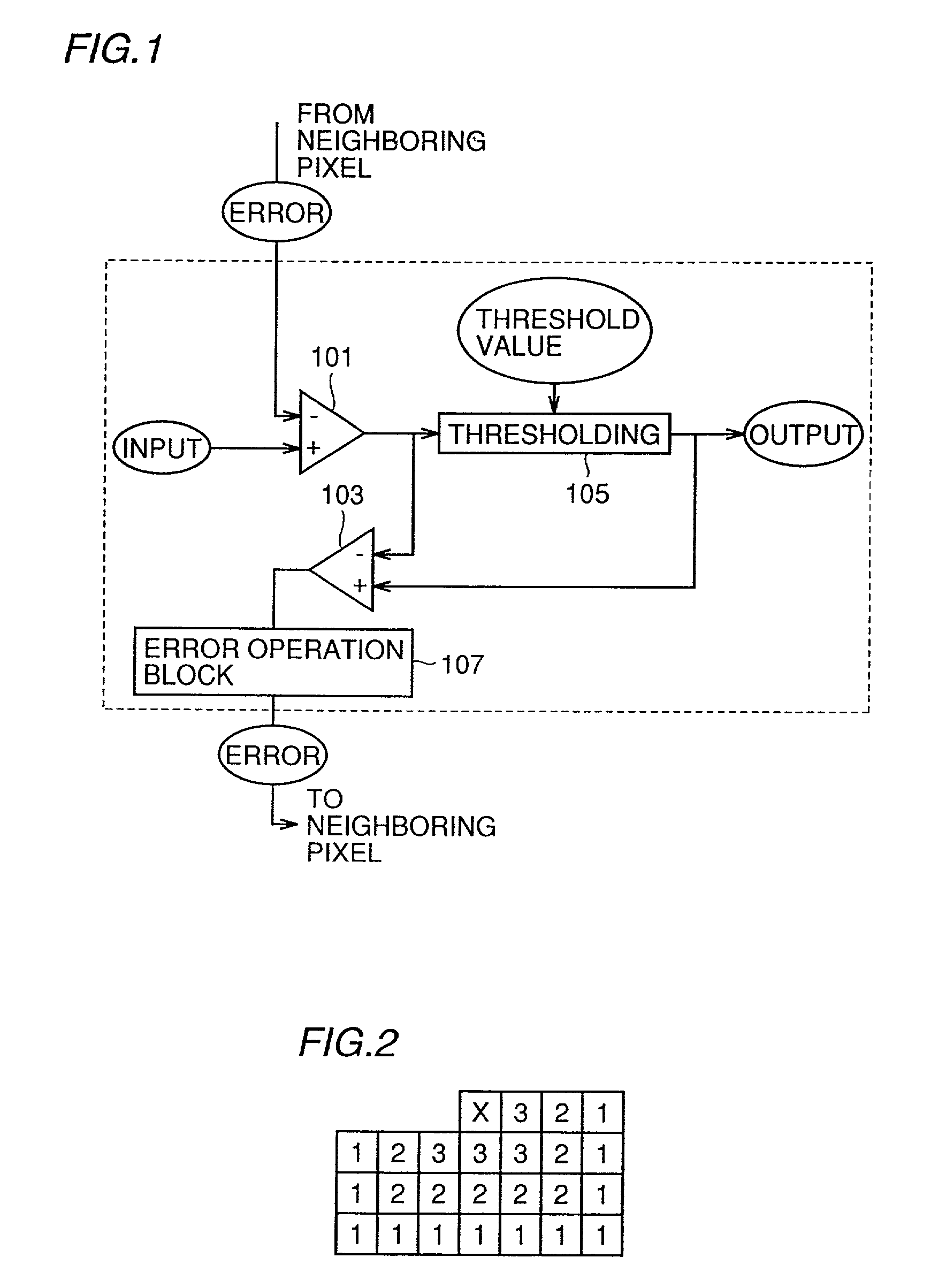
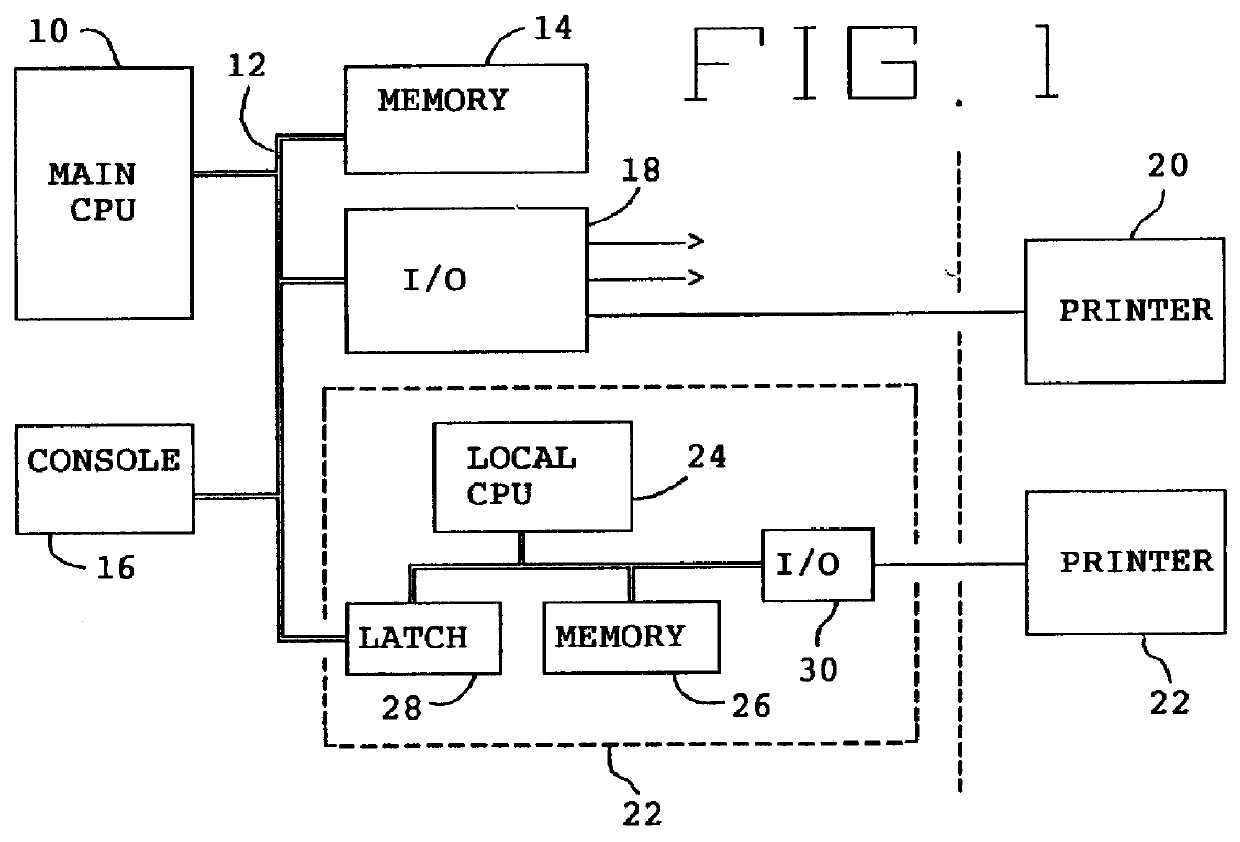
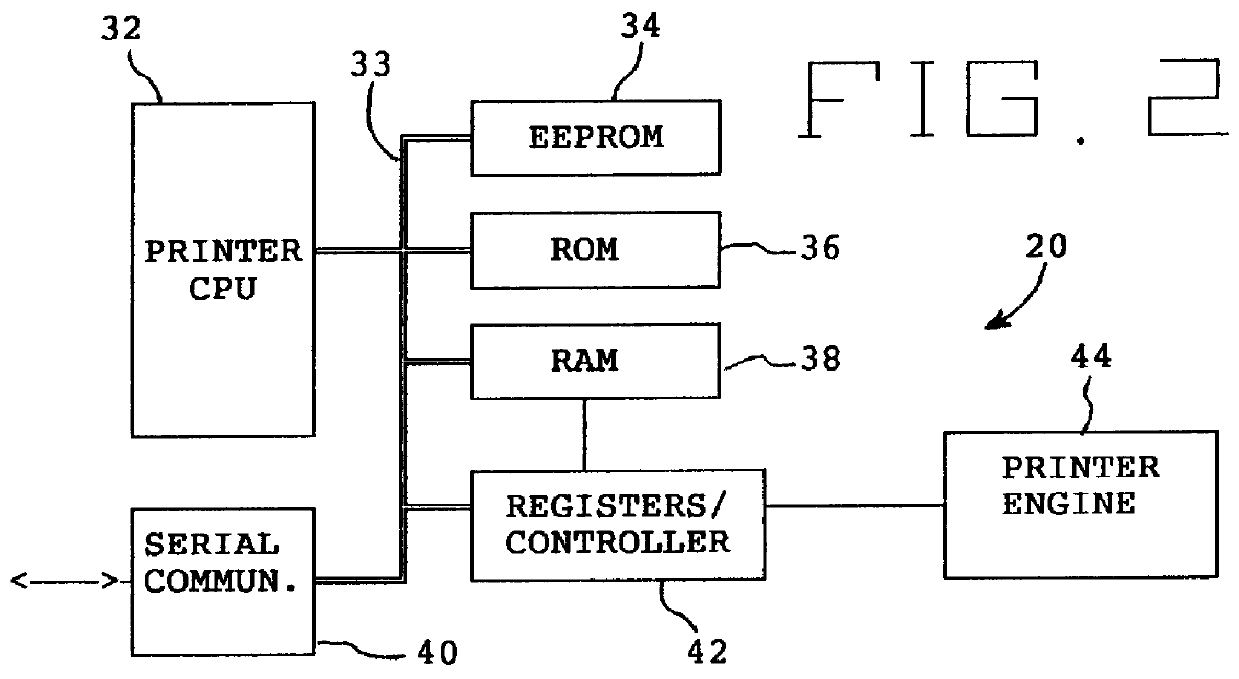
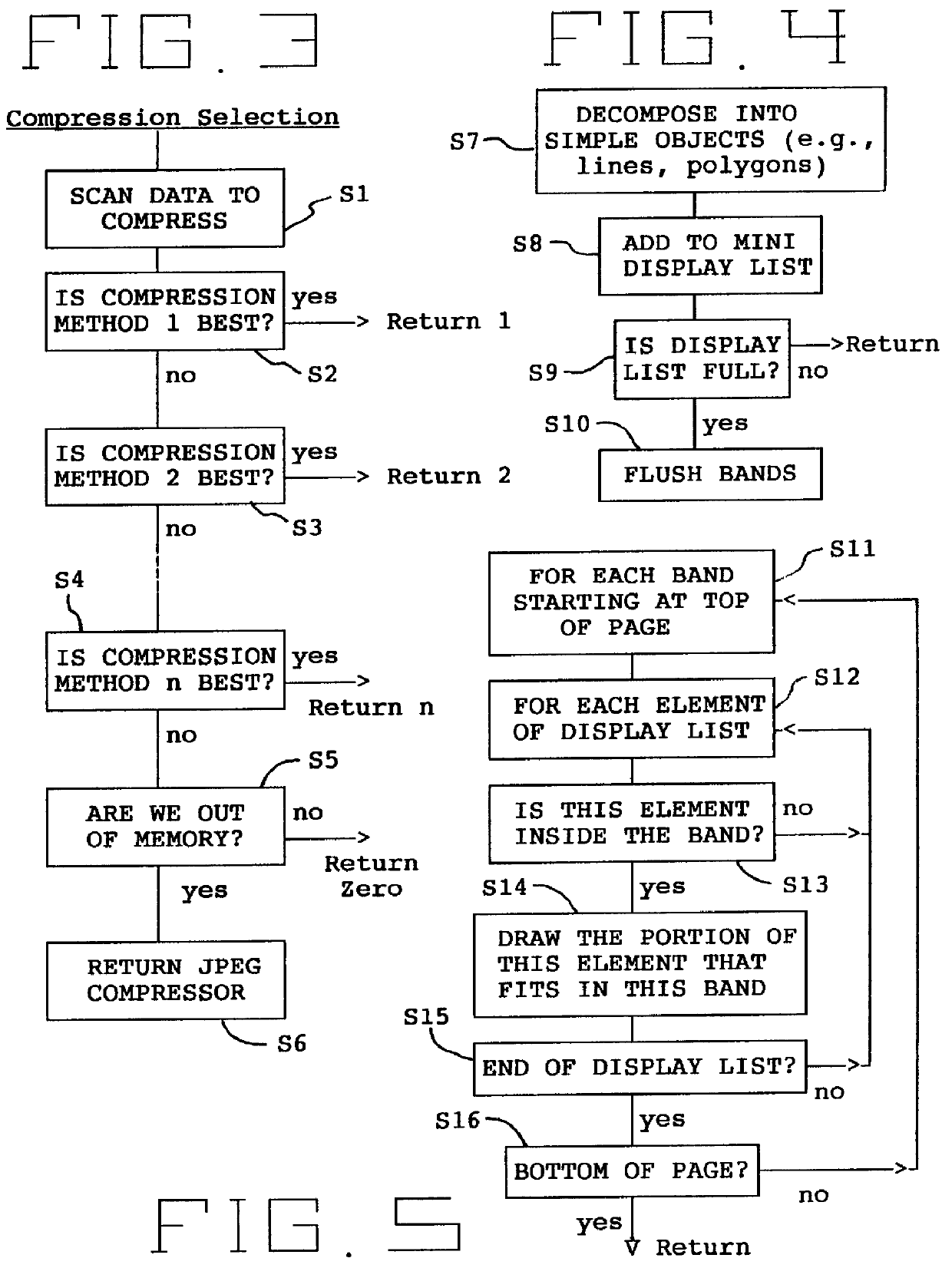
A print control system for controlling a print of print target data containing color specifying information includes a data distinguishing module (12) for distinguishing between pieces of element data contained in the print target data, and a color adjusting module (13, 14, 15, 16, 17) for adjusting a mix of color materials based on the color specifying information according to a category of the element data.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
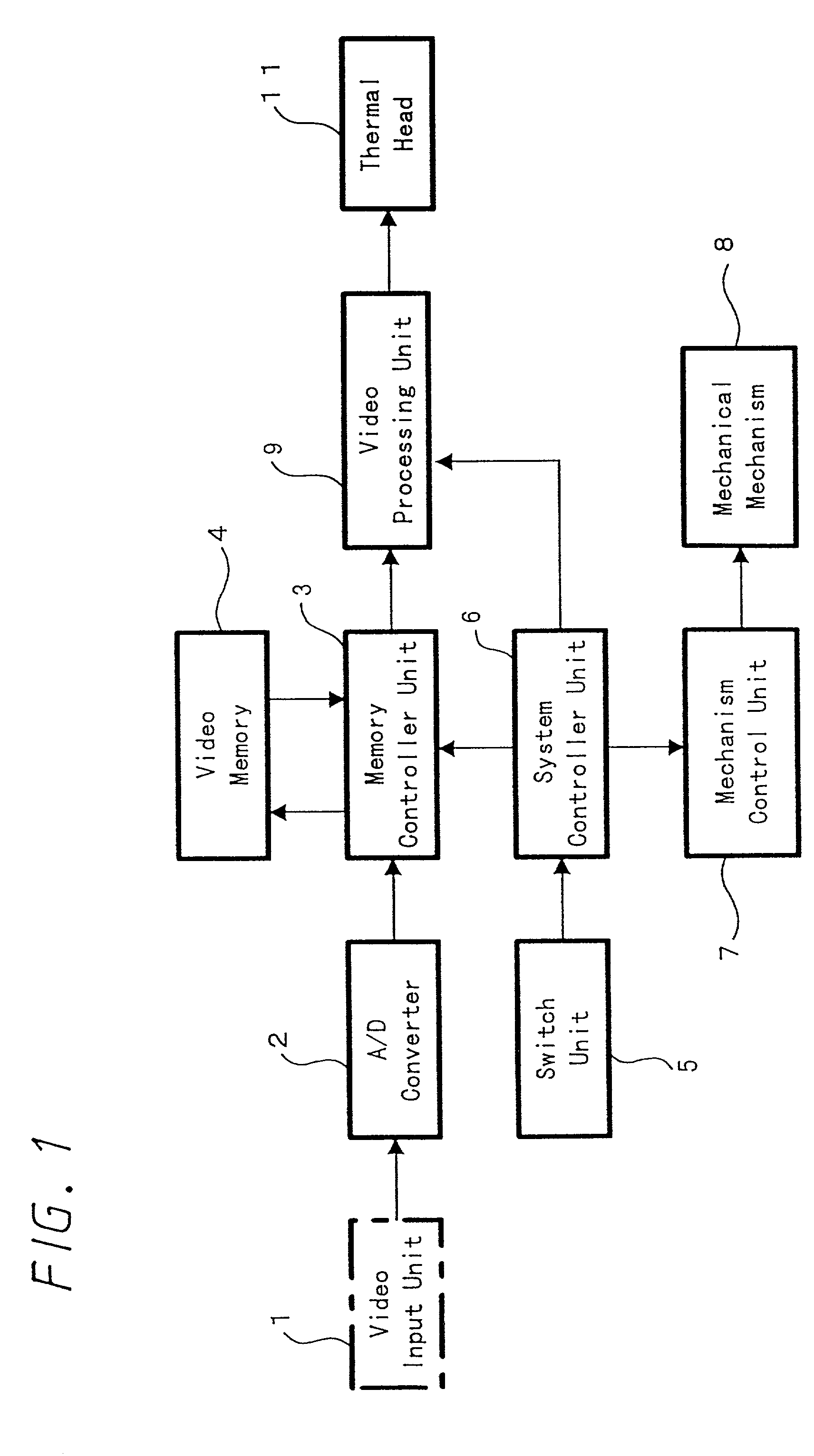
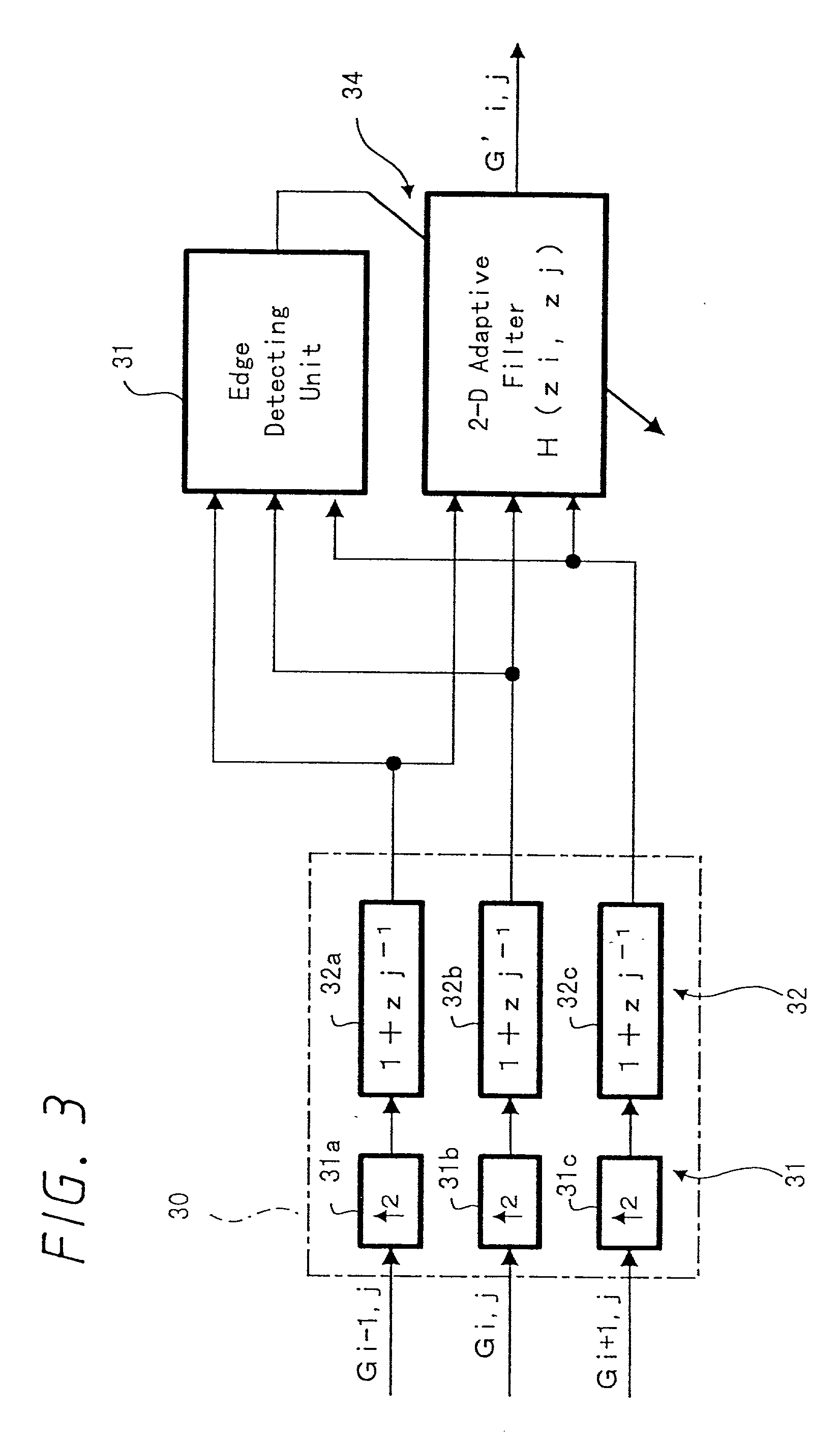
Video processing apparatus for processing pixel for generating high-picture-quality image, method thereof, and video printer to which they are applied
InactiveUS20010035969A1Image can be preventedConvenient ArrangementImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersVideo processingVideo printer
A video processing apparatus according to the present invention includes edge detecting means for detecting an edge direction of an image, coefficient selecting means for selecting a coefficient based on the edge direction detected by the edge detecting means, and filter means for filtering a frequency band by using a frequency characteristic corresponding to the coefficient selected by the coefficient selecting means, wherein the number of pixels of the image is enlarged twice.
Owner:SONY CORP
Printing with reduced outline bleeding
InactiveUS6561610B2Reduce bleedingReduce the amount requiredVisual representation by matrix printersPrintingComputer printingEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Image processing apparatus, image forming apparatus, printer driver, image processing method and computer-readable storage medium
ActiveUS20050200905A1Eliminate the problemSatisfactory picture qualityImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersGraphicsImaging processing
An image forming apparatus forms an image by a plurality of dots, by forming a periphery of a stepped transition portion of a contour portion of at least a character and / or graphics of the image by dots having a smaller size than dots forming portions other than the stepped transition portion, and determining a method of forming the dots having the smaller size depending on an inclination of the contour portion.
Owner:RICOH KK
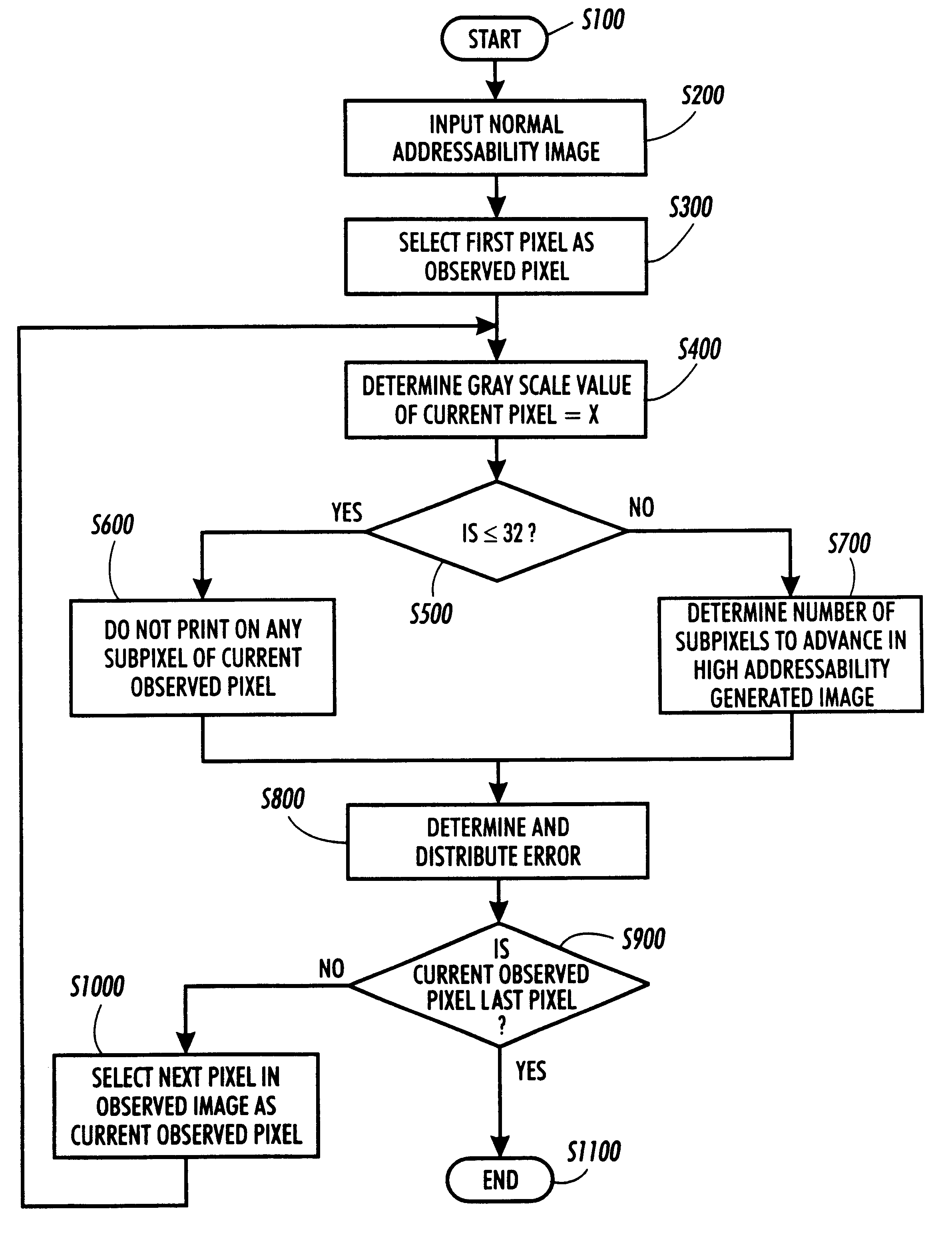
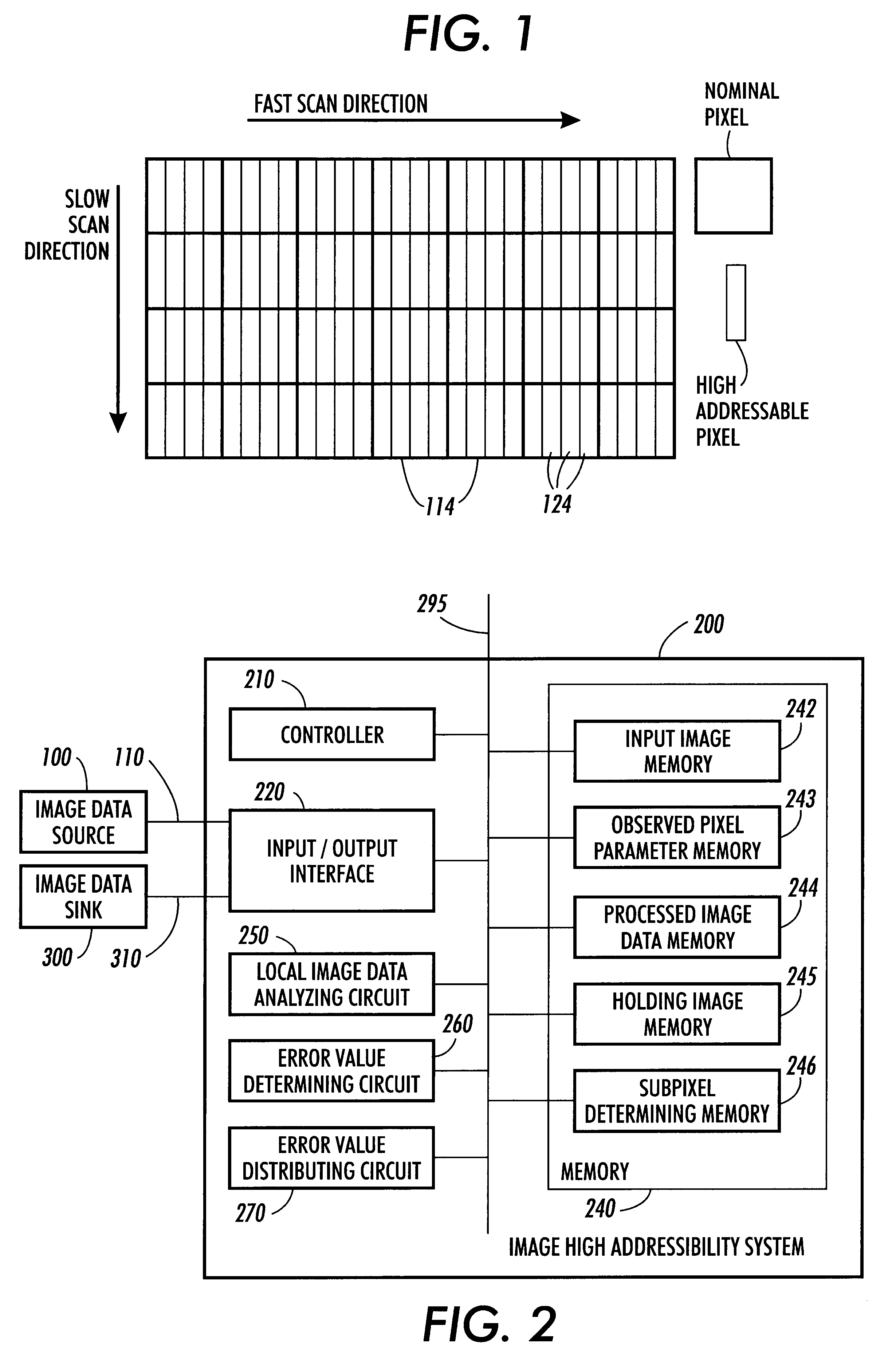
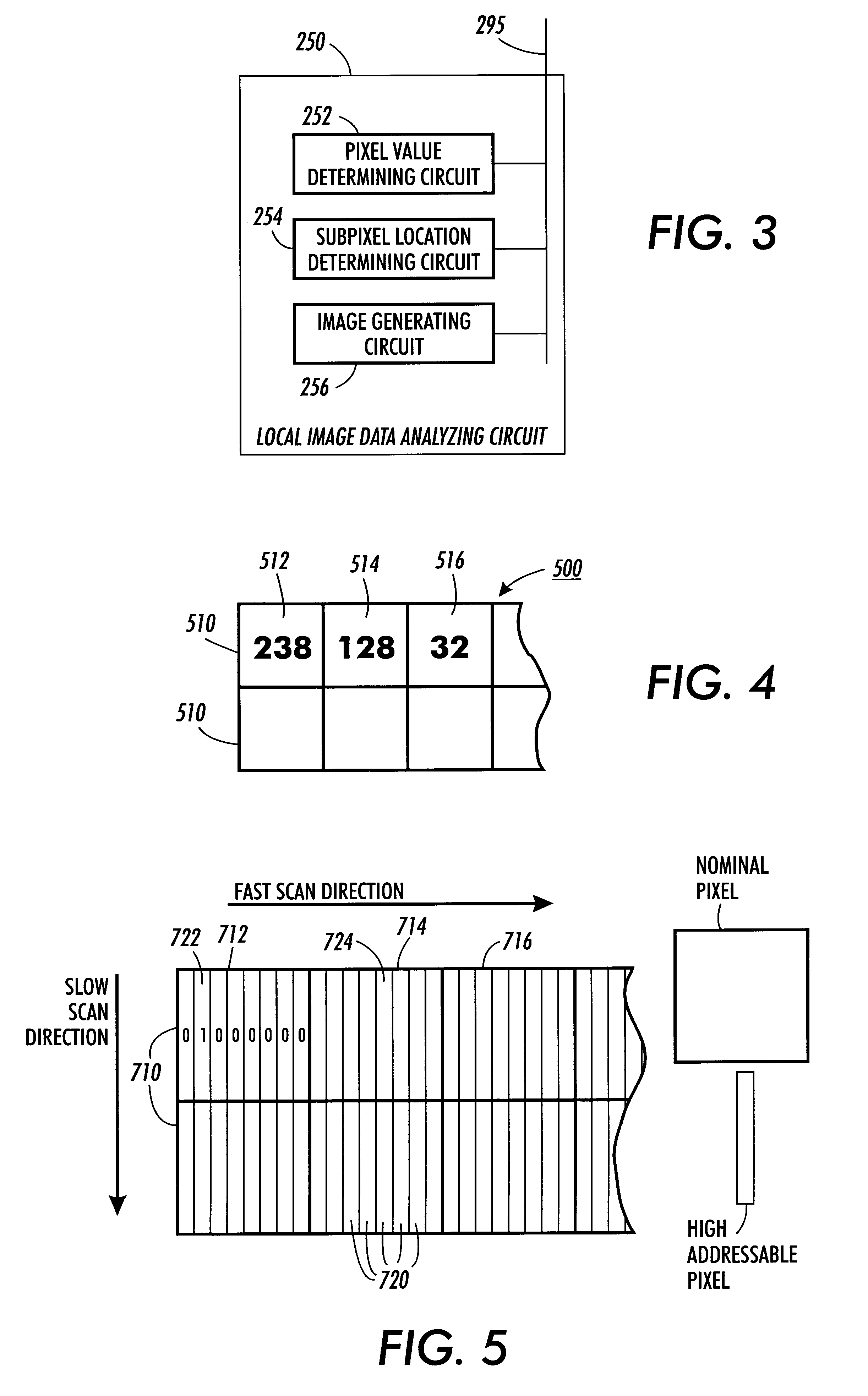
Systems and methods for generating high addressability images
InactiveUS6325487B1Image enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
Image systems and methods generate improved high addressability images. The generated image may be input into a printer for printing. An image is processed so that the location of an ink drop in a high addressability image is determined. The location of a printed subpixel, within a pixel, is determined by the magnitude of the grayscale value of an observed pixel, the magnitude of the error that has been previously accumulated, and a predetermined threshold value. The grayscale value of the observed pixel, accumulated error, and threshold value are used to determine a subpixel value. This subpixel value determines how soon another subpixel is fired after a previously fired subpixel. If the subpixel value is low, then another subpixel will be fired relatively soon after the previously fired subpixel. If the subpixel value is high, then the printer will wait a longer time before firing another subpixel. In other words the lower the subpixel value the sooner another subpixel prints. The image generating process may effectively weight the error on neighboring pixels to effectively generate images having both shadow and highlight regions.
Owner:XEROX CORP
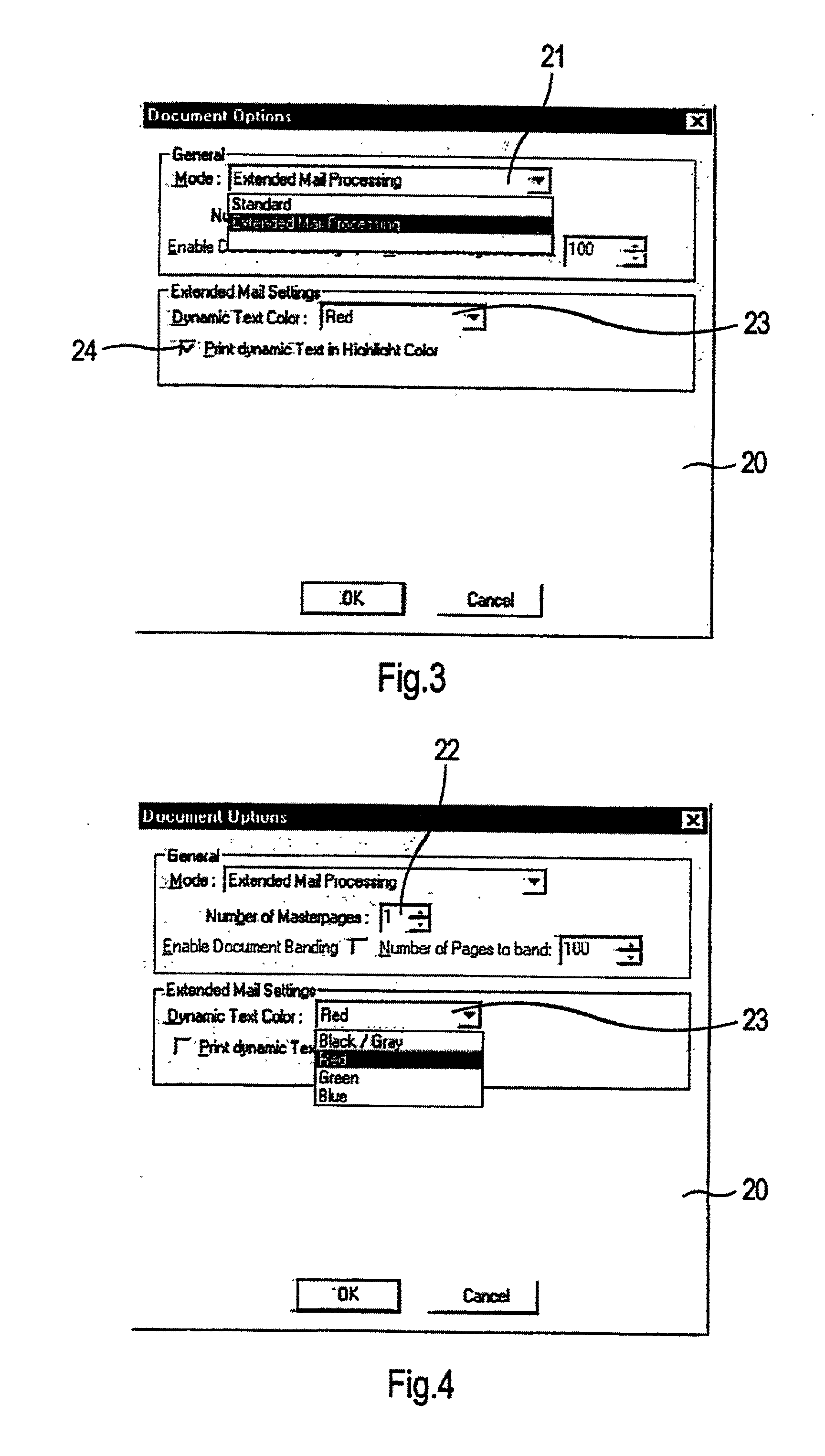
Method, computer program product and system for the transmission of computer data to an output device
InactiveUS7202972B1Reduce data volumeImprove performanceDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsData streamComputer printing
A method and system for outputting data from a computer to an output device, such as a computer, defines a master document in which variable and static data areas are defined. A variable data area is marked and variable data is inserted thereinto to provide a data stream with variable and static data. The marking is used to remove the variable data from the static data. The separated variable and static data is transmitted to the output device such as the printer. The static data is stored at the printer and is not sent to the printer for subsequent documents. The variable data is joined with the static data document by document in the printer.
Owner:OCE PRINTING SYST
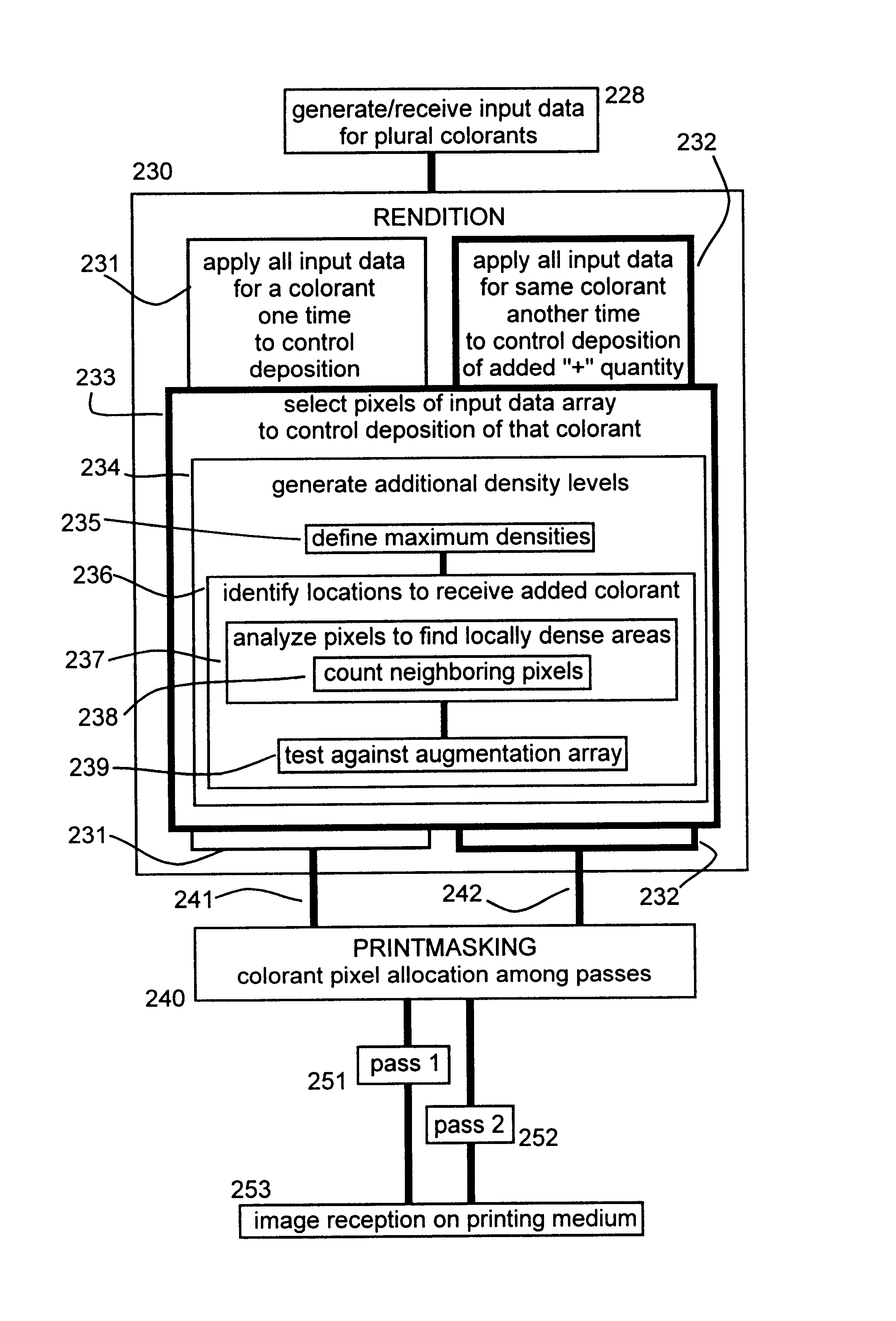
Pixel-density augmentation and adjustment with minimum data, in an incremental printer
InactiveUS6690485B1Extended Density RangeAdd funImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPixel densityAnalysis data
One invention form is a method using all input data for one or preferably plural colorants, one time to control colorant deposition in forming a pixel array on a printing medium, and at least one other time to control deposition of more of the same colorants. At least one "applying" includes choosing data-array pixels to deposit added colorant. The two data-usage times can be associated directly with depositing colorant in respective printer passes; or may be done at (or near) rendition, sending output data to printmasking for pass allocation. Selection preferably includes setting maximum density on the medium-and choosing locations for that density, best by analyzing data to find locally dense areas, e. g. counting neighboring pixels. Selecting also includes defining locations to receive particular density, and creating additional density levels based on densities in the data array. Another method form includes defining an augmentation array and applying it to control part of colorant deposition. Preferably also included is applying the original array to control other deposition of colorant. Applying the augmentation array preferably increases colorant deposition, relative to applying the original array, by less than 100% with non-linear response to data.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Print control apparatus, print control method and memory medium
InactiveUS6922260B2Avoid dischargeDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGraphicsEngineering
There is provided, even in case plural sheet sizes or plural sheet orientations are mixed within a document, a system capable of obtaining an output result close to that of a document not containing such mixed sheet sizes or sheet orientations without causing sheet discharge in the course of printing operation or data overflow from the print area, also providing an enlarging / reducing function to a device lacking such function, and providing a visually agreeable output result, all realized without modification in the conventional printer driver. A host computer is provided with a spool file manager for calculating the relative position of the logic page to the physical page, and a despooler for processing the layout data, obtained by enlarging or reducing the logic page, to a data format matching the graphic engine.
Owner:CANON KK
Image processing method, recording medium, and image processing apparatus
InactiveUS20100309243A1Other printing apparatusGeneric and host data combinationImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
Owner:RICOH KK
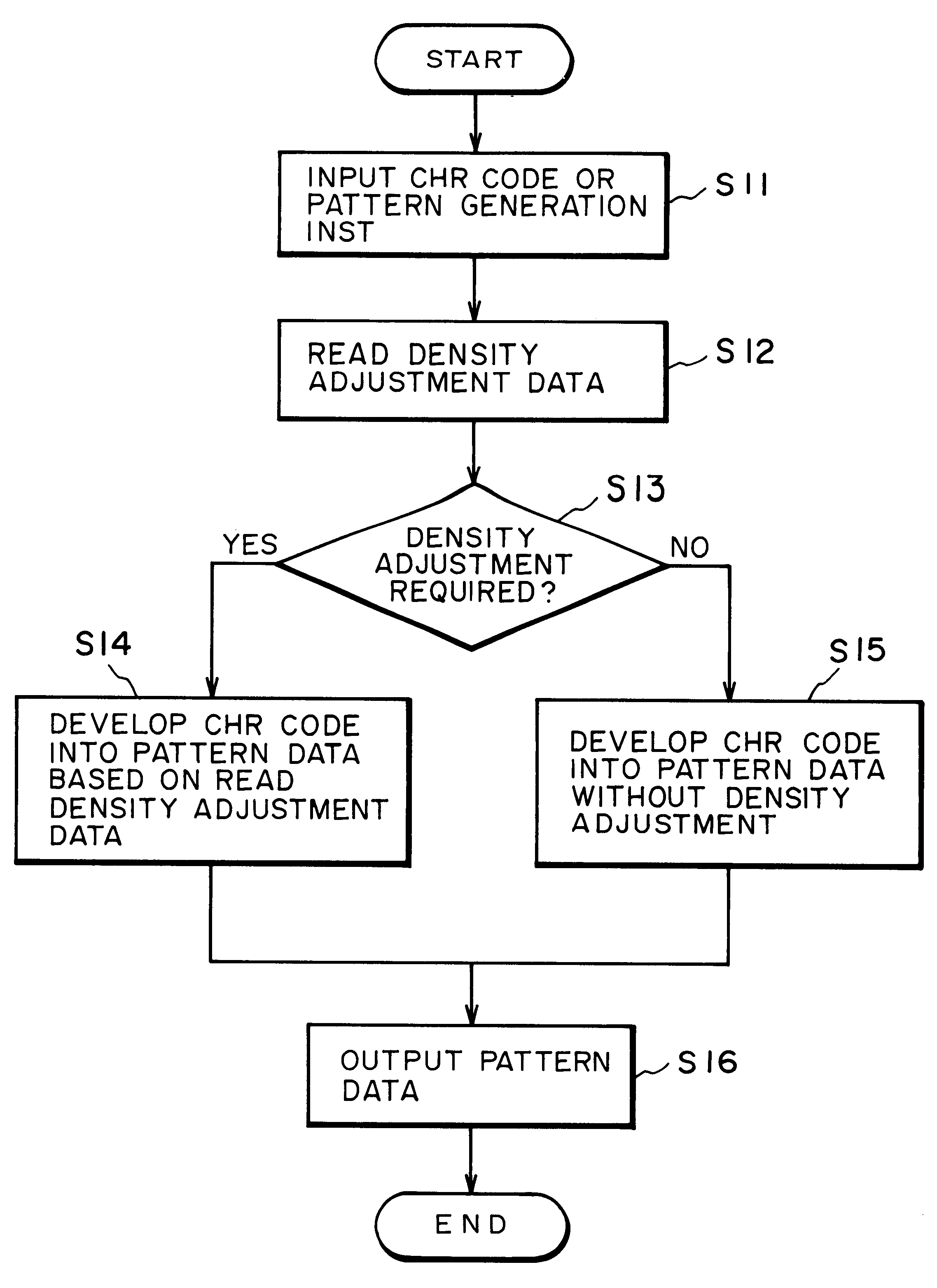
Method and apparatus for generating character pattern
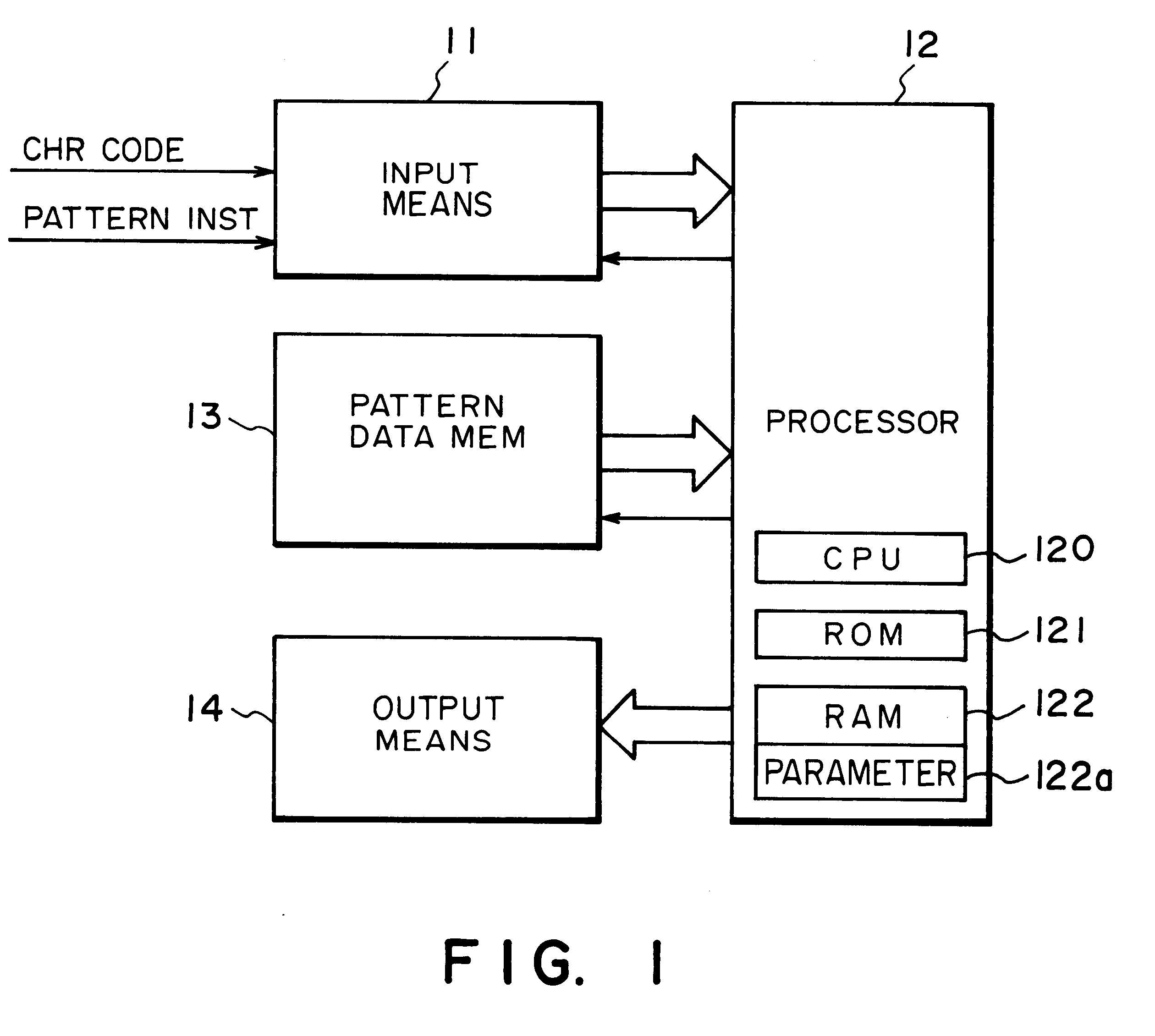
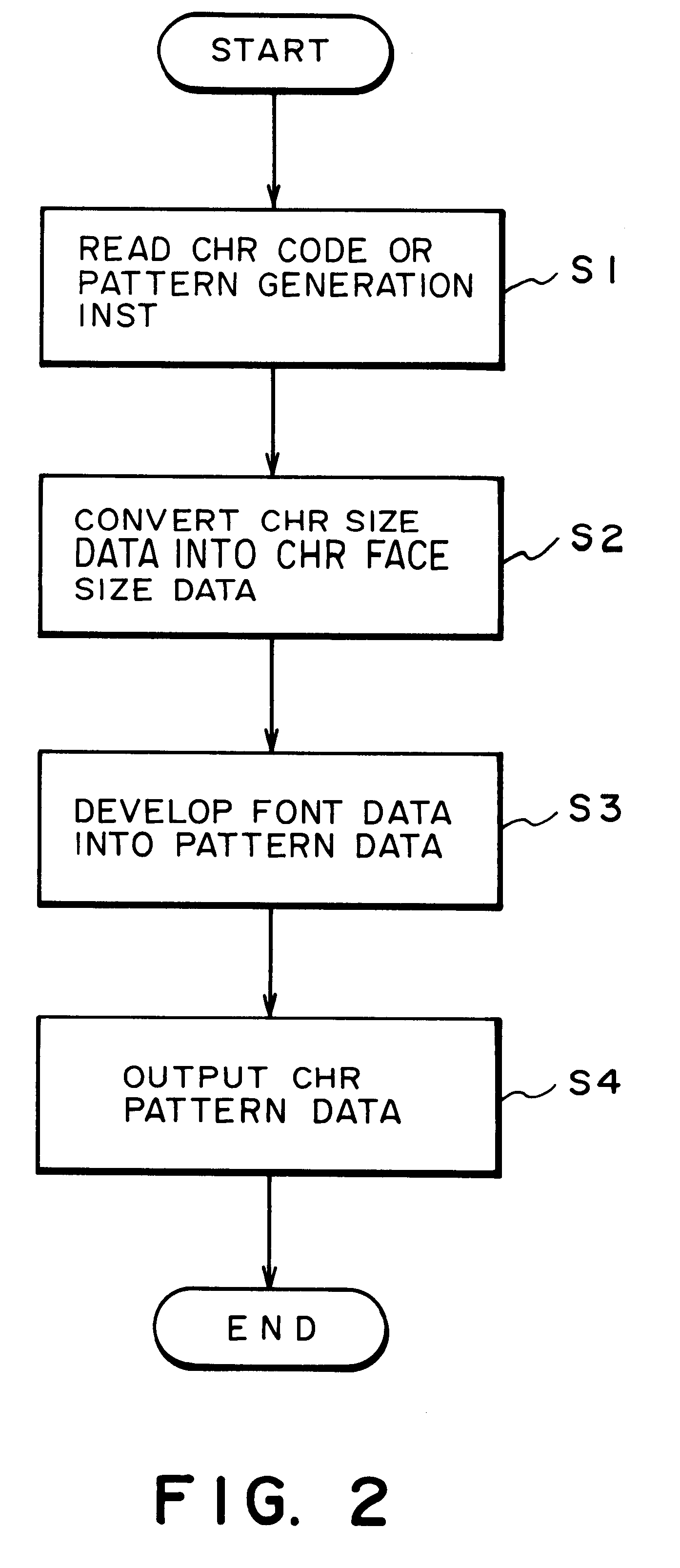
InactiveUS6310624B1Drawing from basic elementsVisual representatino by photographic printingAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
An apparatus for generating a character pattern includes a first memory for storing reference character font data as a coordinate point array, a second memory for storing parameter data in correspondence with at least character size data, and a generator for generating size data of a target character on the basis of the parameter data. Font data corresponding to an input character code is read out from the first memory and is developed into pattern data of a size corresponding to character size data converted by the generator. A method of generating a character pattern for the above apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:CANON KK
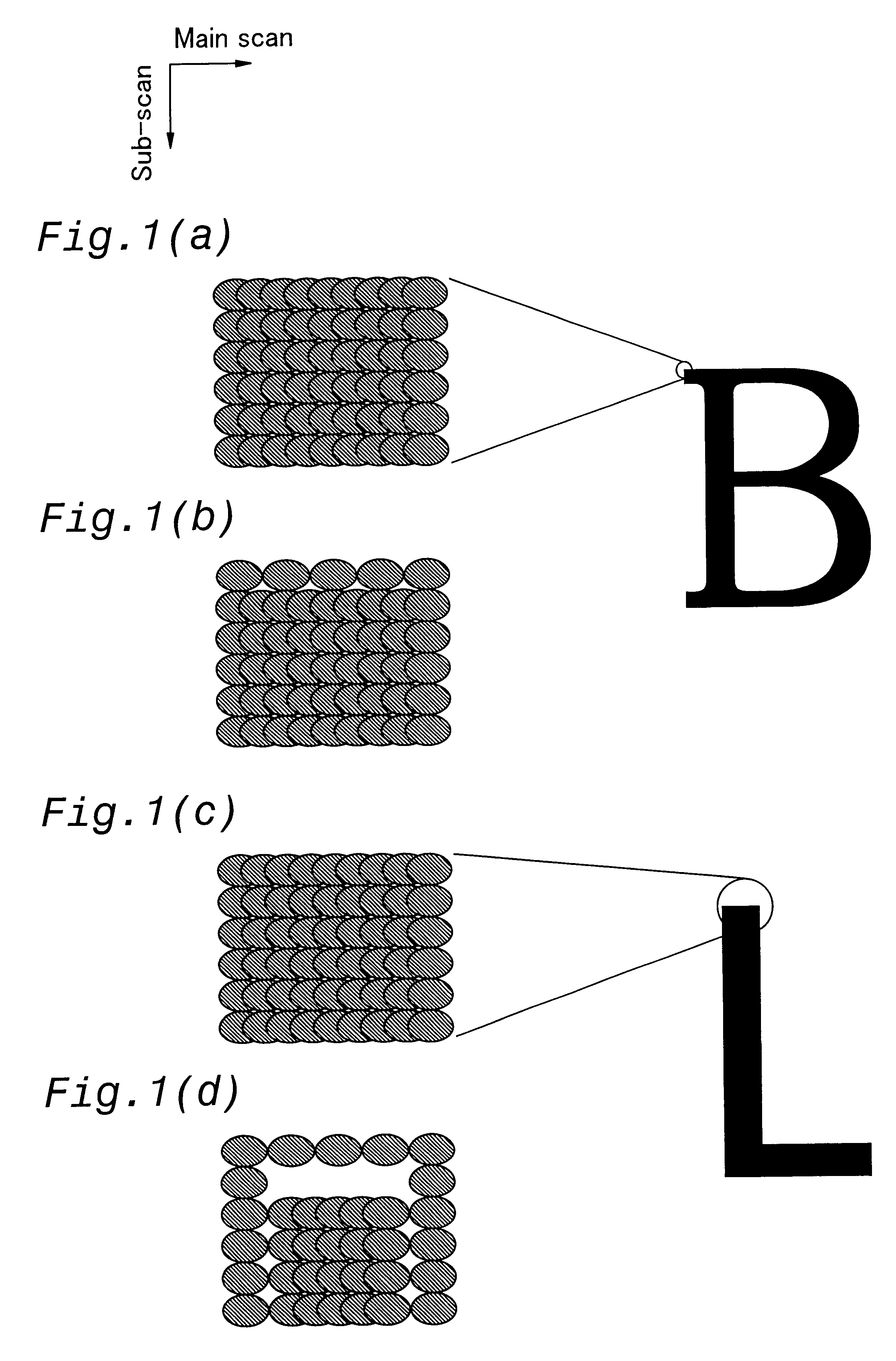
Image Processing Method, Program Thereof, and Image Forming Apparatus
InactiveUS20080304108A1Improve image qualityIncrease printing speedImage enhancementElectrography/magnetographyGraphicsShape change
An image processing method is disclosed. The image processing method includes the steps of detecting one or more dots near a step-shaped changing part of dots of which an outline part of a letter or graphics is composed, by using a reference pattern having a window size of “m×n” dots in which a number of dots “m” corresponds to resolution in the main scanning direction and a number of dots “n” corresponds to resolution in the sub scanning direction, converting the detected one or more dots near the step-shaped changing part that is nearly parallel to the main scanning direction into a dot whose size is smaller than that of dots of the step-shaped changing part, and not converting the detected one or more dots whose part is nearly parallel to the sub scanning direction.
Owner:RICOH KK
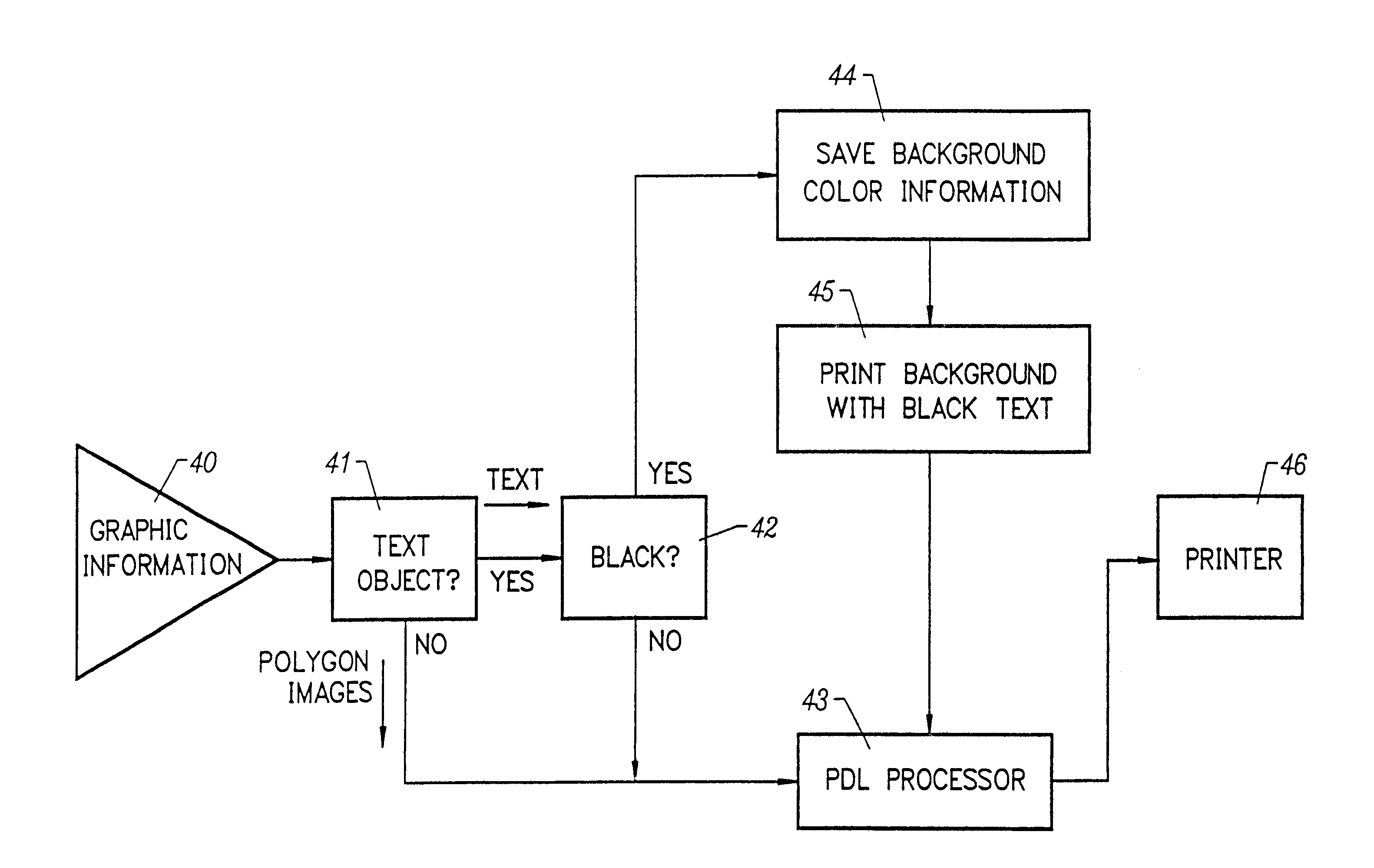
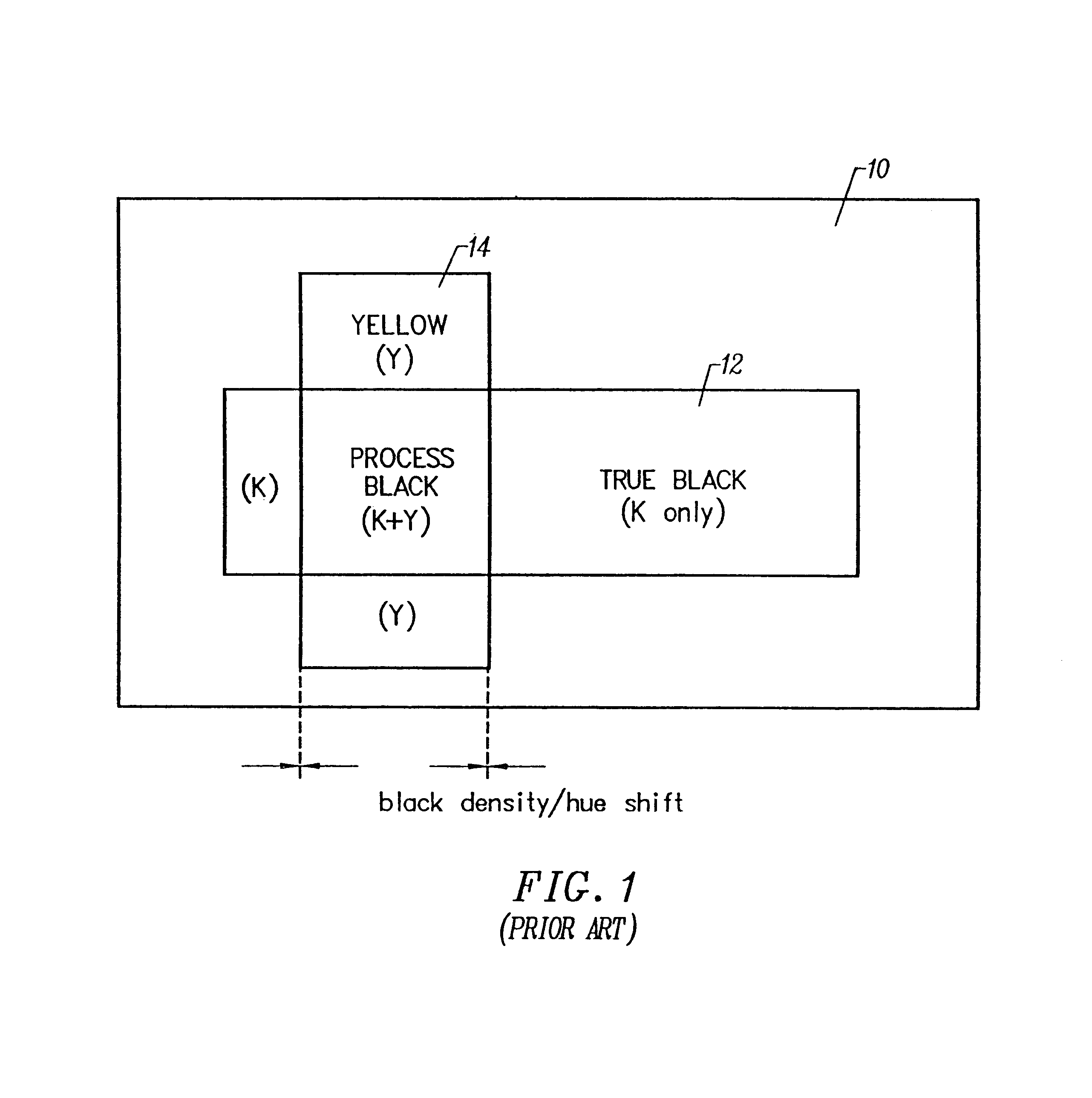
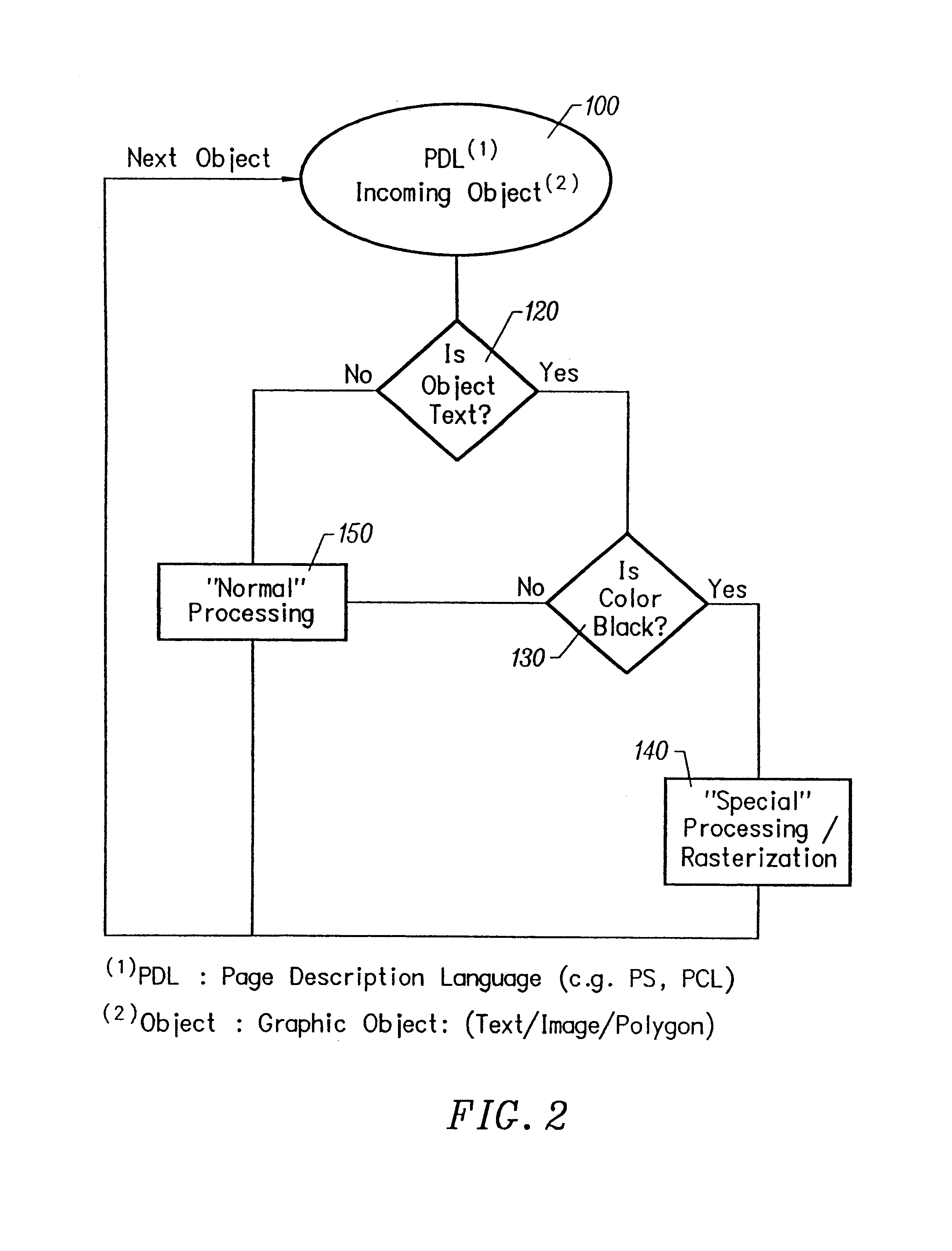
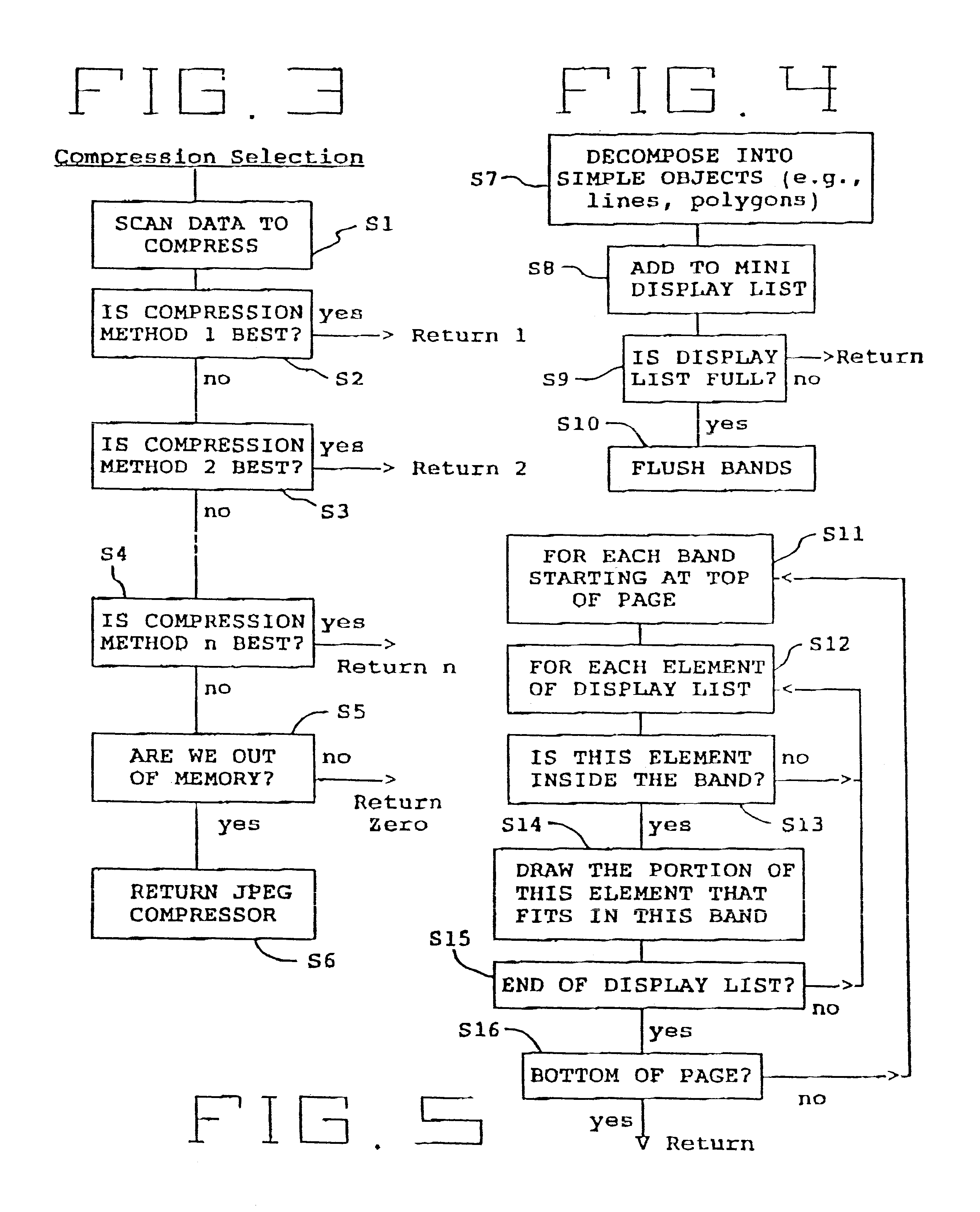
Black text printing from page description languages
A technique for printing black text on a colored background, in which the graphics are broken down into three categories: text, polygons (also referred to as line drawing or vectors), and images (also referred to as bitmaps or raster data) when the incoming graphic information is a Page Description Language (PDL) data file (e.g. Adobe Postscript-PS- or Hewlett-Packard PCL). If the object is not a text object, it is processed in a normal manner. If the object is a text object, a determination is made if the color of the object is black. If the object is not a black text object, it is processed in a normal manner. If the object is a black text object, special processing and rasterization techniques are applied. Thus, the invention exploits to advantage the fact that it is possible in most PDL instances to treat black text differently from other black objects.
Owner:ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING
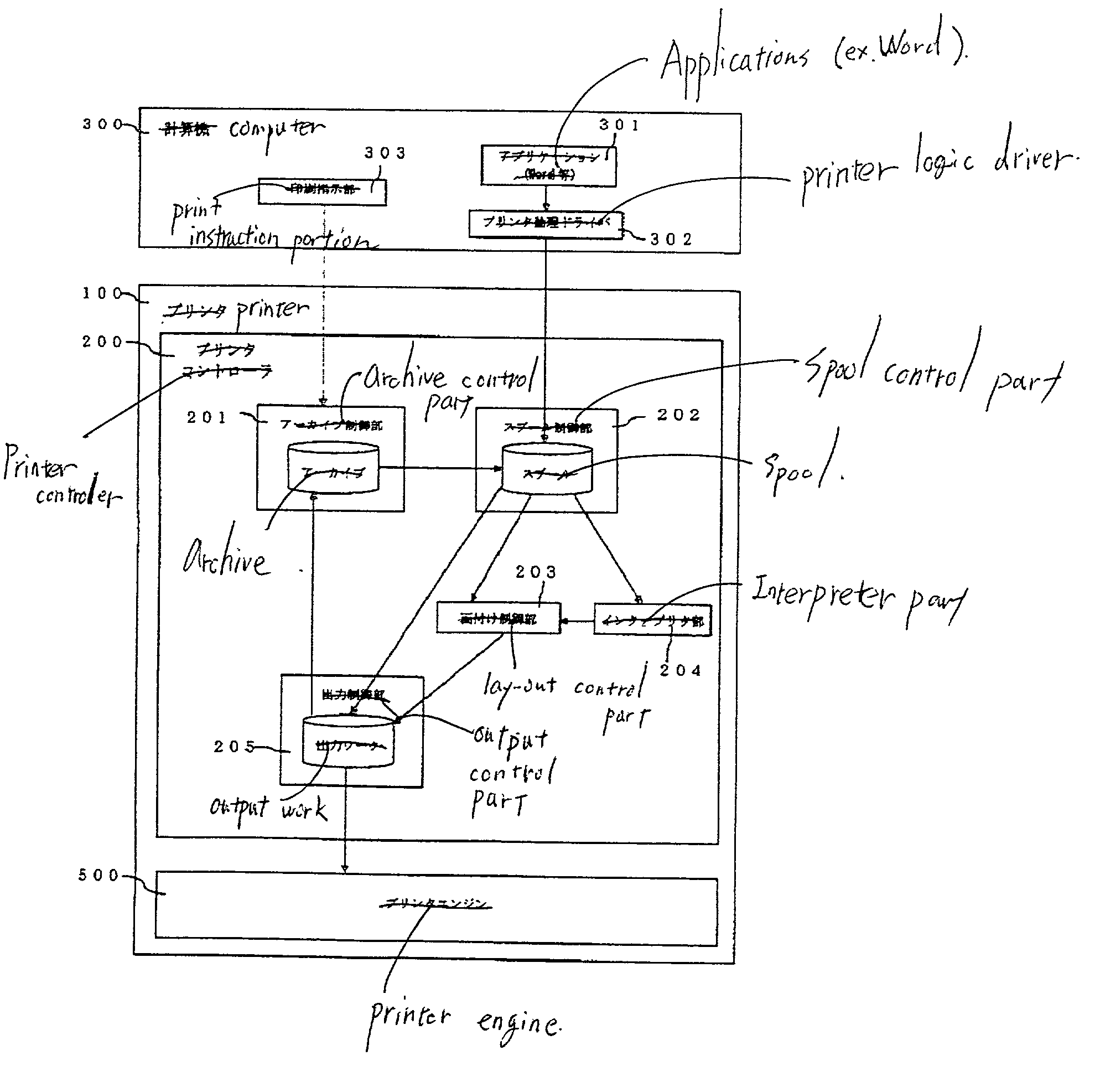
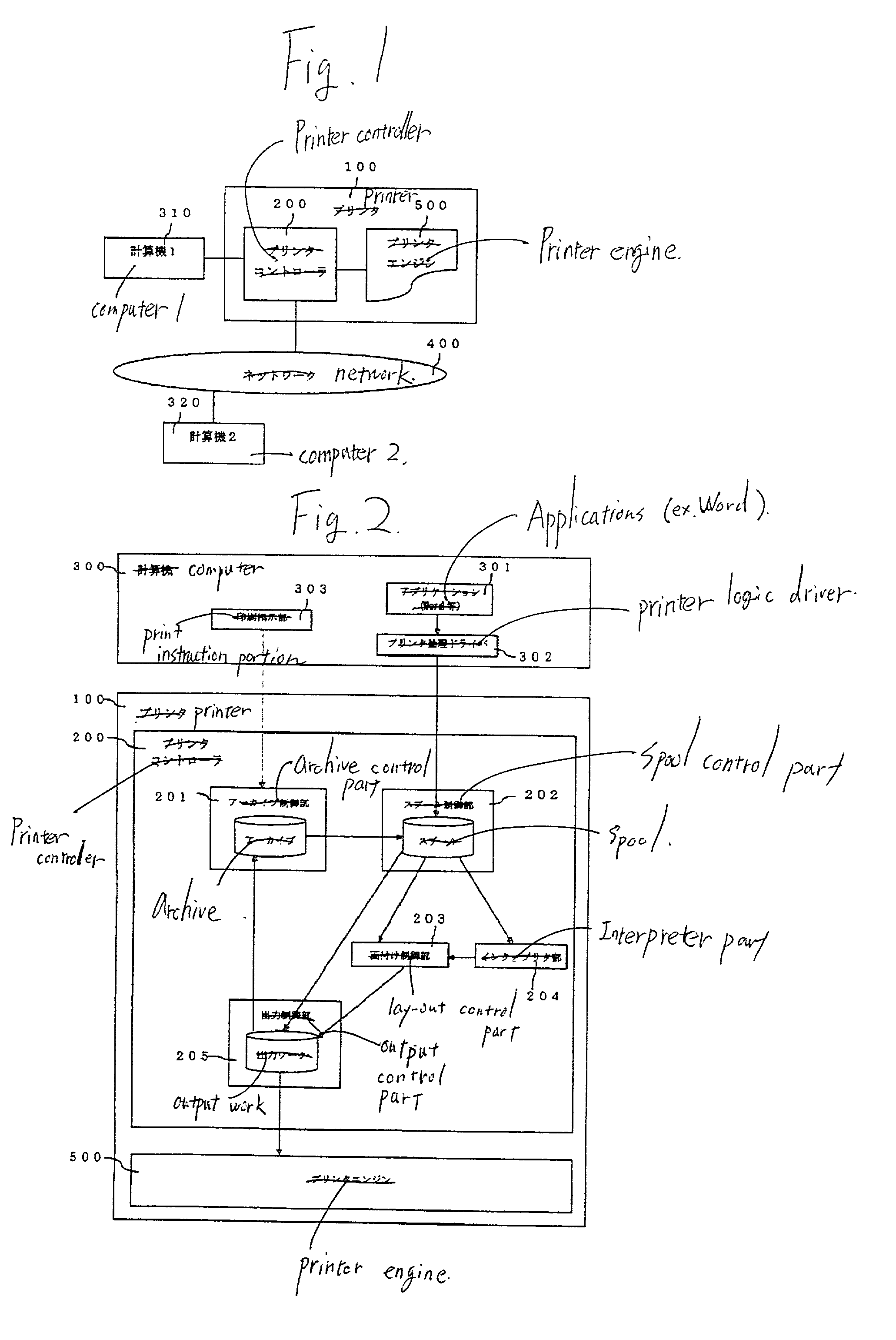
Printer and method of controlling printer
InactiveUS20020051139A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsComputer graphics (images)Documentation
In a printer which interprets a PDL document, develops the PDL document into dot image, and prints the dot image, a PDL document as input is transferred to an interpreter part, the interpreter part interprets the PDL document and develops the PDL document into a dot image whose size is equal to the document size, and transfers the dot image to a laid-out control part, the laid-out control part converts a size of the dot image to a designated sheet size and transfers to an output control part, the output control part transfers the dot image to a printer engine, and the printer engine prints the dot image on a sheet.
Owner:RICOH PRINTING SYST
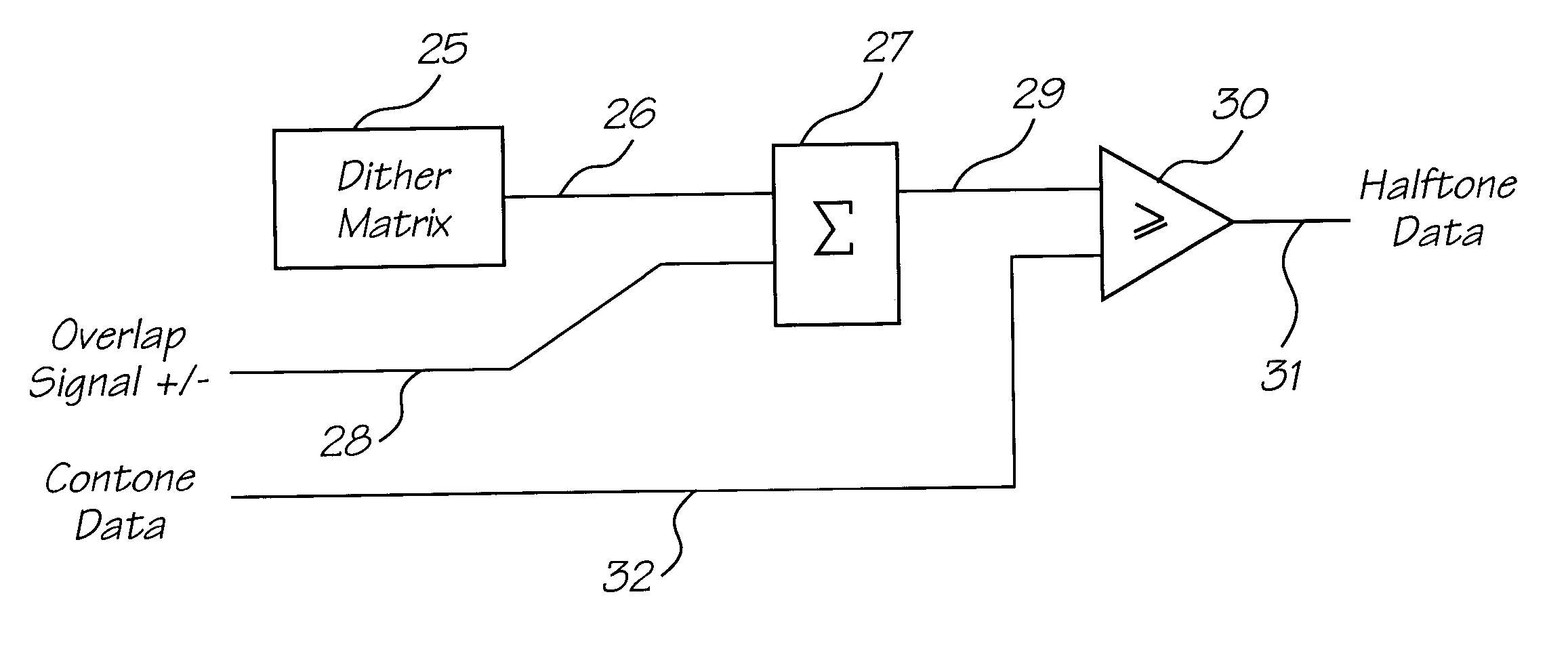
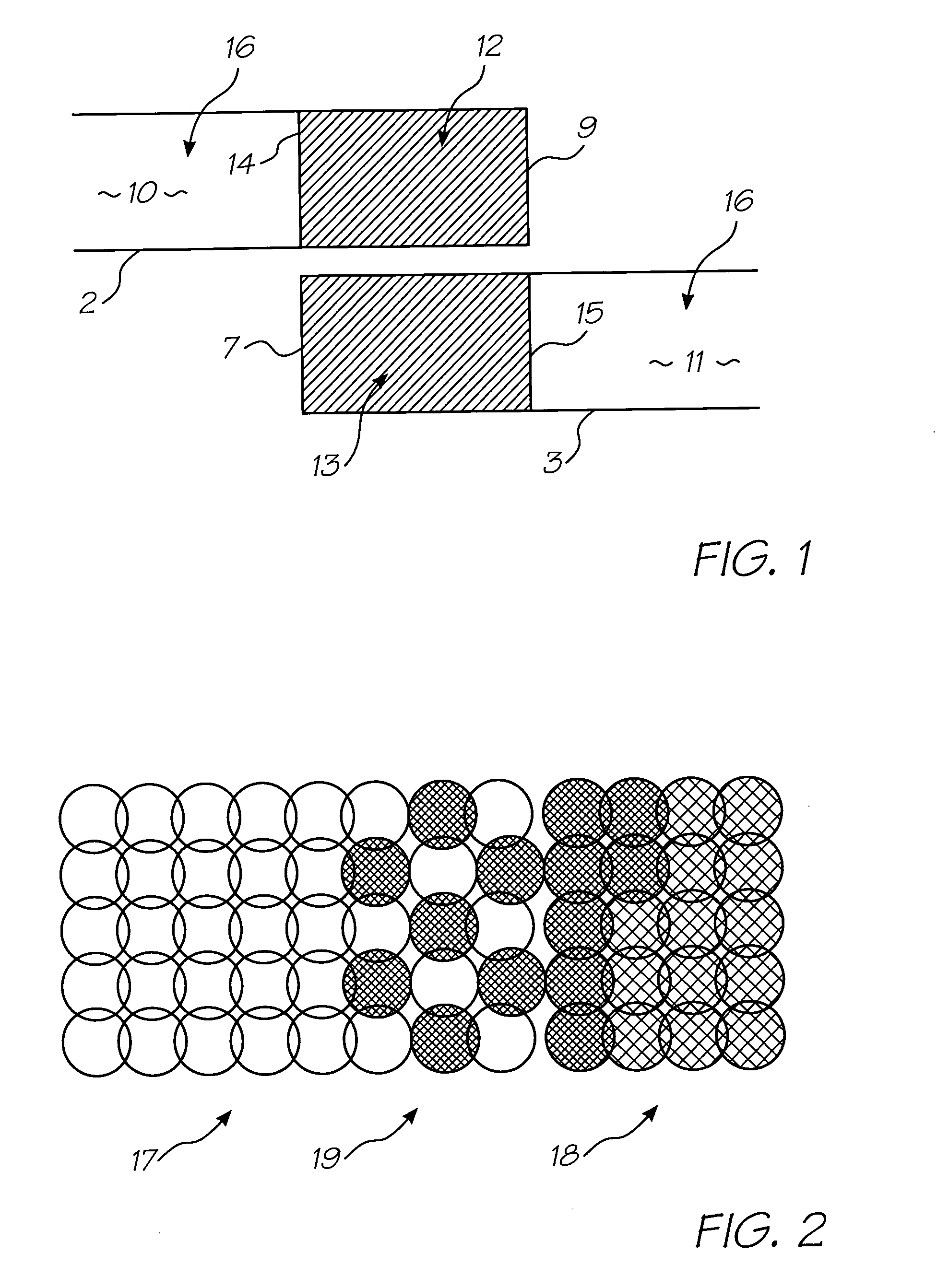
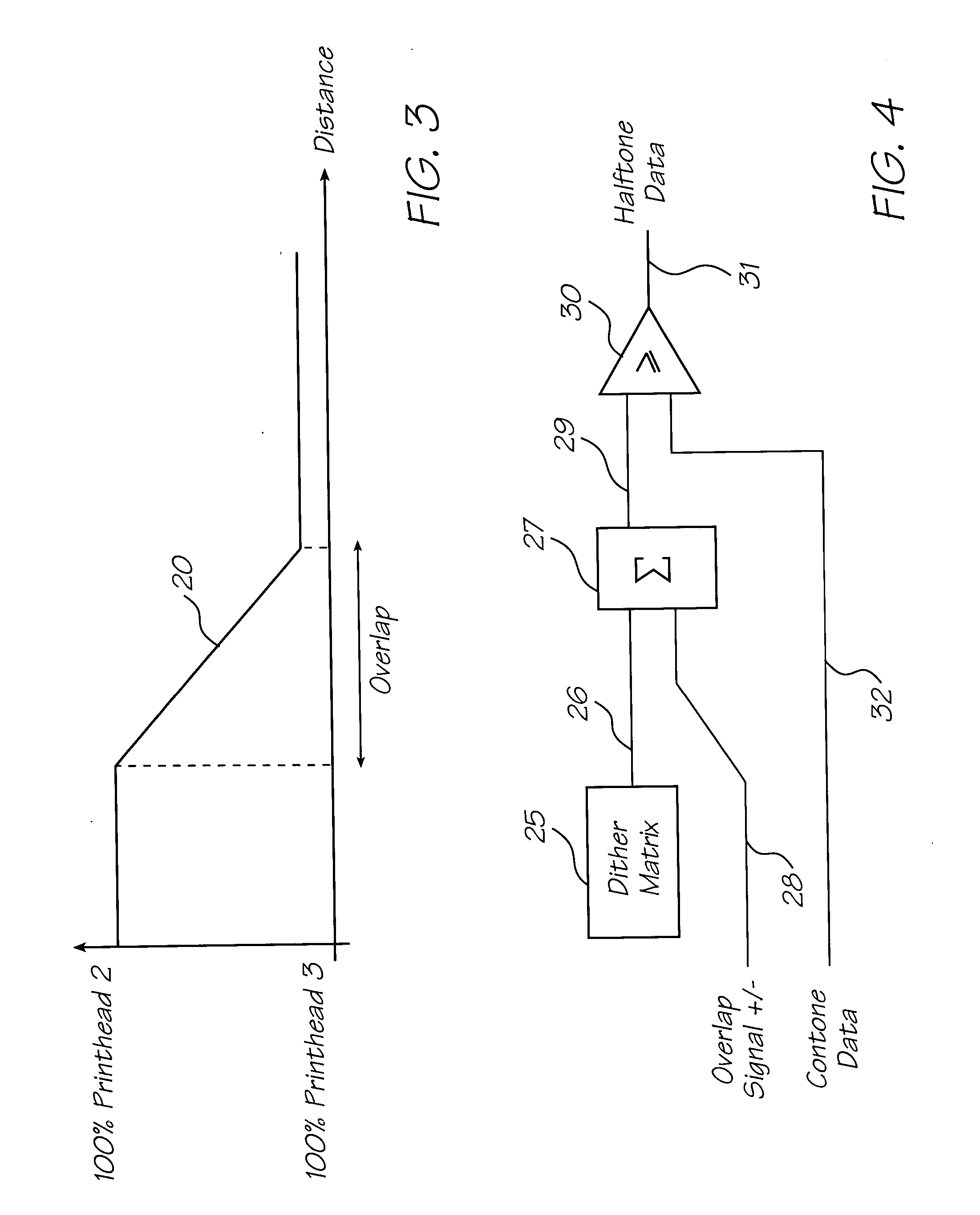
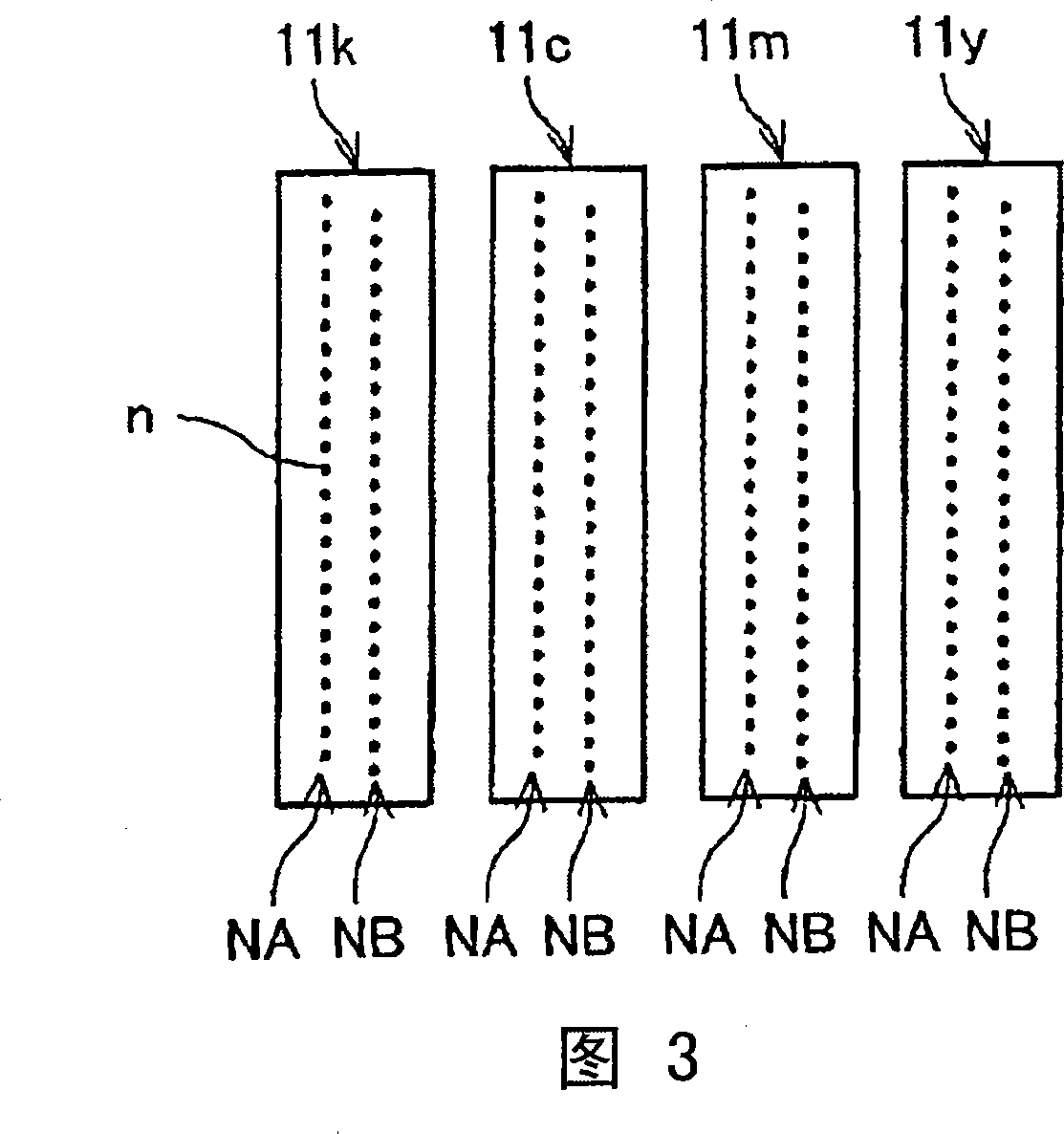
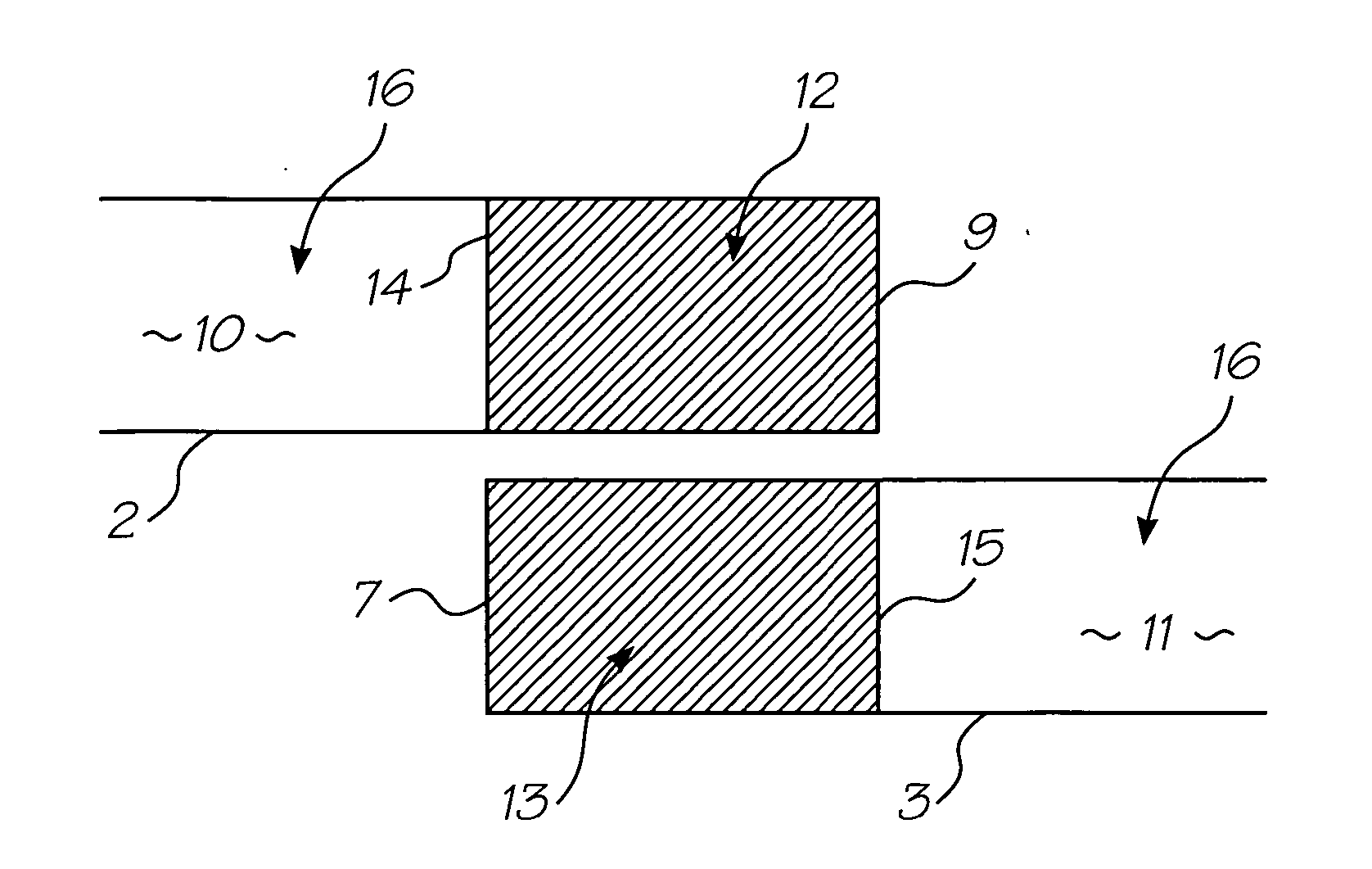
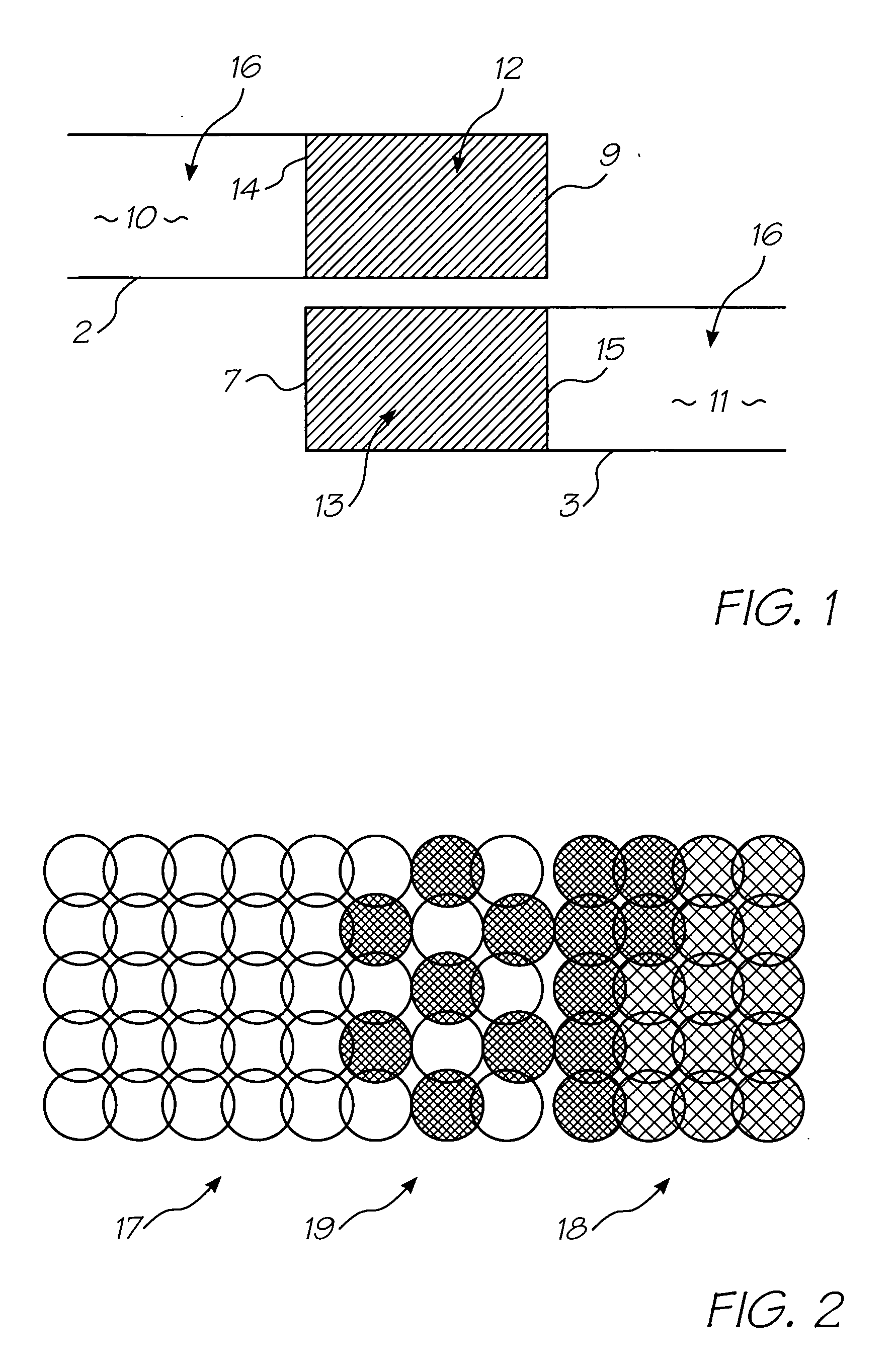
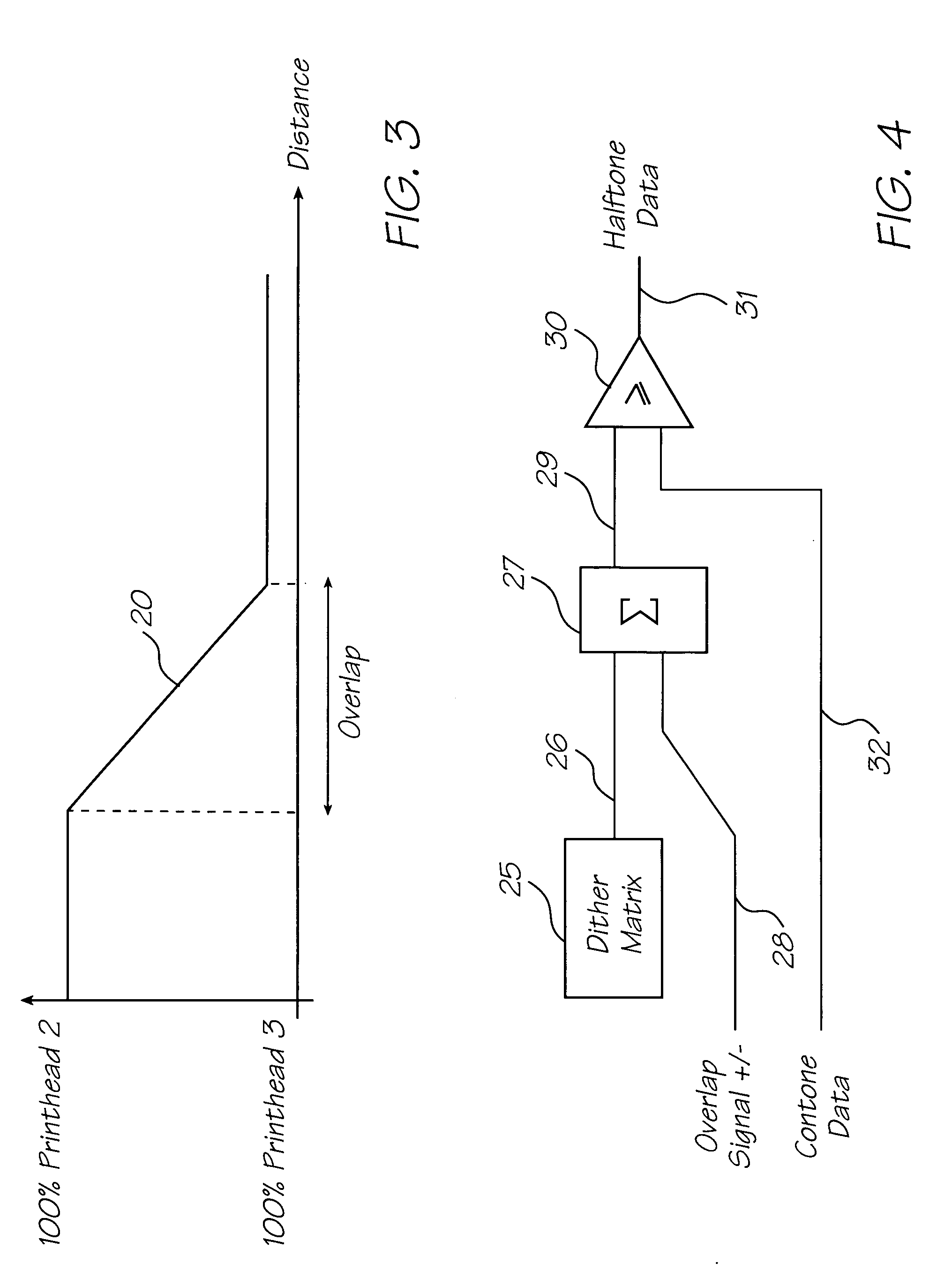
Method of generating halftone print data for overlapping end portions of printhead chips
InactiveUS20050134922A1Effective and convenient mannerProduce some attenuationDigitally marking record carriersVisual representation by matrix printersContinuous toneHue
A method of generating halftone print data for overlapping end portions of a pair of consecutive printhead chips includes the step of generating continuous tone print data for an array of the printhead chips. An initial dither matrix to be applied to the continuous tone print data is generated. Overlap data representing an extent of overlap of the end portions is generated. The overlap data is applied to the initial dither matrix with a summation means to generate an output value. The output value is applied to the continuous tone print data.
Owner:MEMJET TECH LTD +1
Image processing apparatus, image forming apparatus, printer driver, image processing method and computer-readable storage medium
ActiveUS7576886B2Satisfactory picture qualityReduce data transfer timeImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersGraphicsImaging processing
An image forming apparatus forms an image by a plurality of dots, by forming a periphery of a stepped transition portion of a contour portion of at least a character and / or graphics of the image by dots having a smaller size than dots forming portions other than the stepped transition portion, and determining a method of forming the dots having the smaller size depending on an inclination of the contour portion.
Owner:RICOH KK
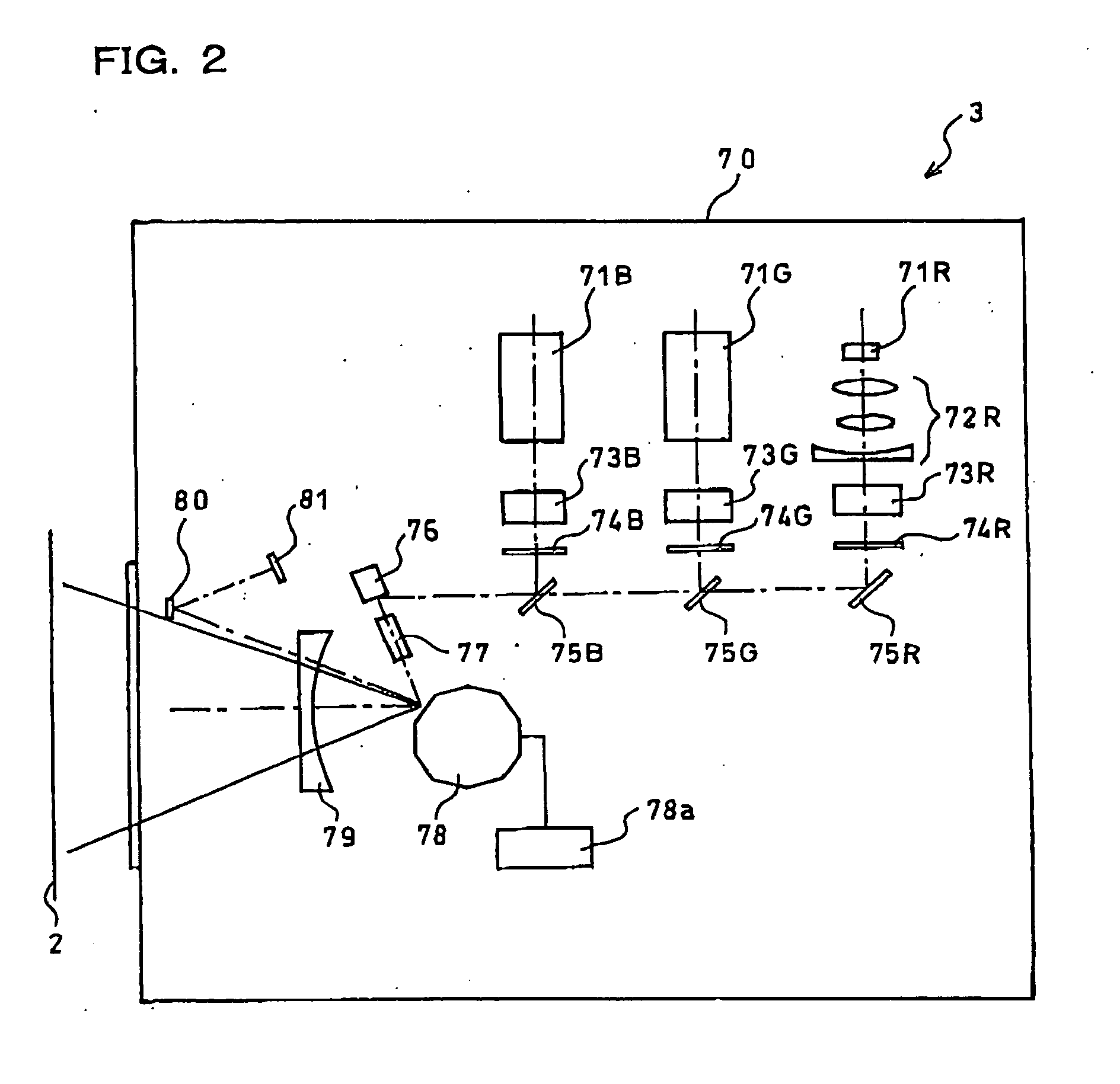
Optical printer with micromirror device
InactiveUS6862108B2Simple structureChange sizeRecording apparatusDigitally marking record carriersColor imageSpatial light modulator
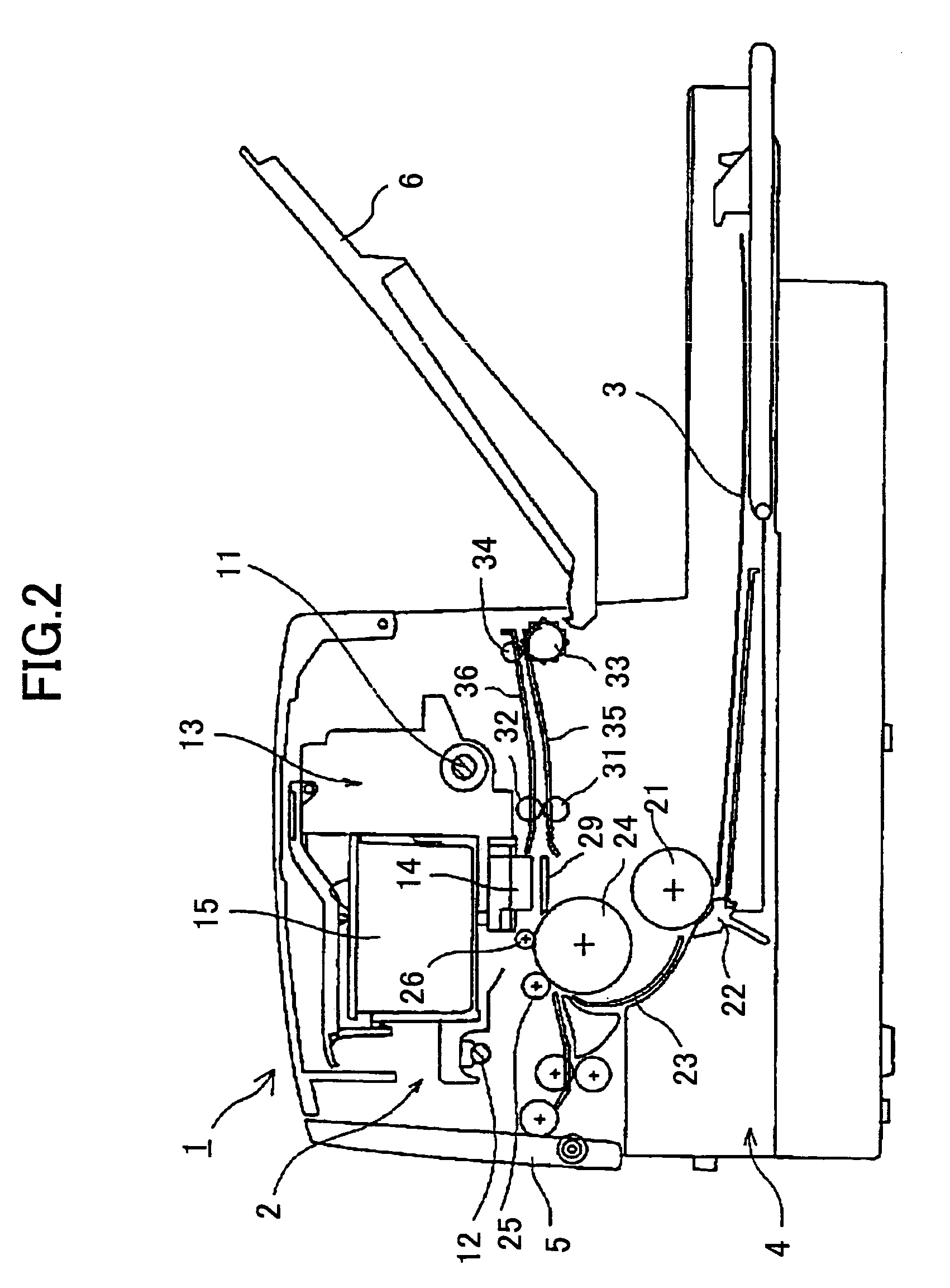
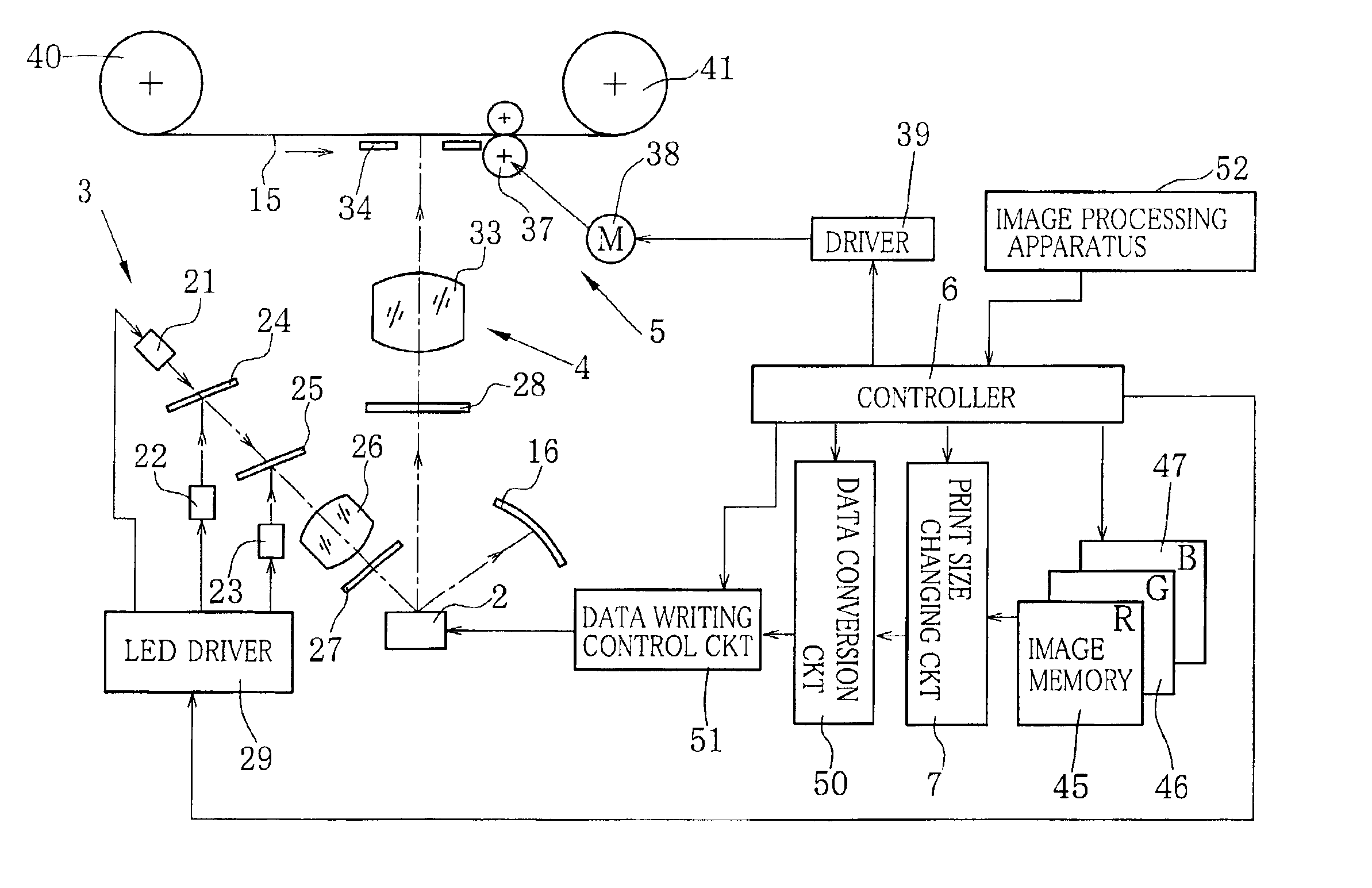
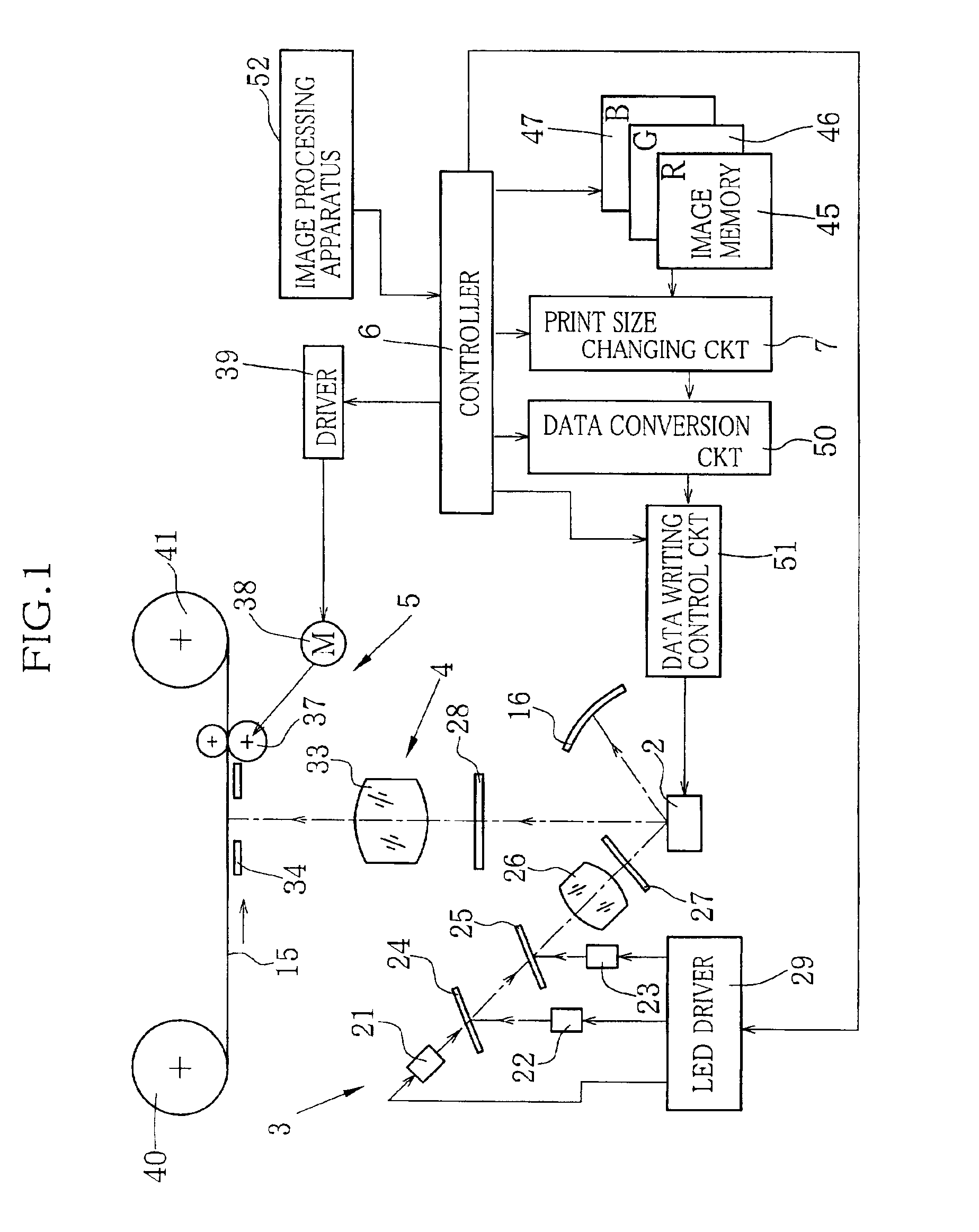
An optical printer has a DMD as a spatial light modulator. An optical image corresponding to a picture frame is projected from the DMD onto a photographic paper in a variable size to print the picture frame in a designated print size. When a maximum print size is designated, image data stored in three color image memories is entirely converted into mirror drive data for driving all micromirrors of the DMD in accordance with the image data. When a smaller print size is designated, the image data is thinned to reduce the image data size in correspondence with the smaller print size. Also a smaller area of the DMD is selected as an active area in which micromirrors are driven in accordance with the thinned image data, to print a picture in the smaller print size.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Exposure device and exposure method
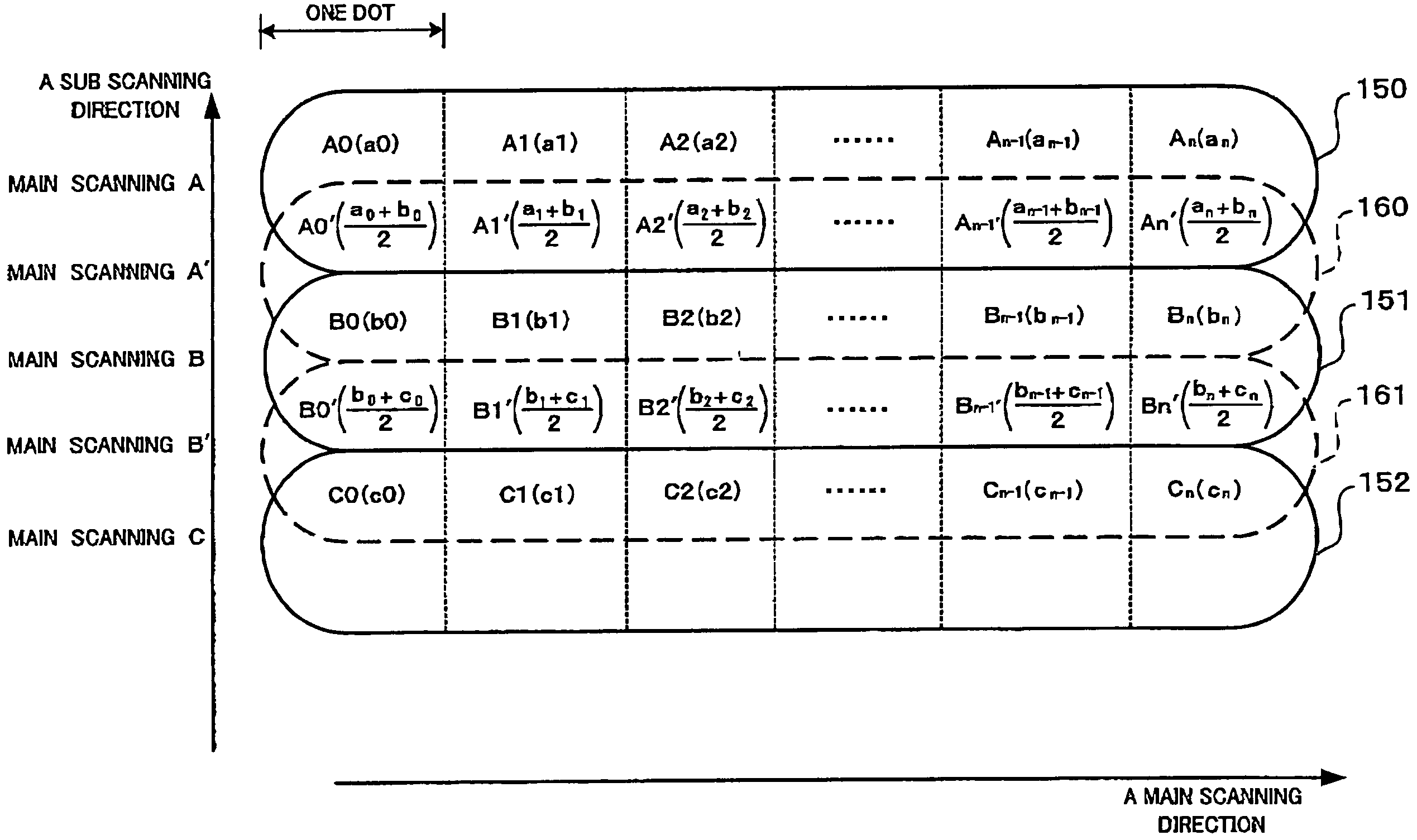
InactiveUS20050219644A1Difference in densityImprove image qualityVisual presentation using printersPrintingPhotographic paperComputer science
In an exposure device according to the present invention, a plurality of exposure bands each containing multiple dots is formed on photographic paper by repeating main scanning in a main scanning direction based on image data that contains multiple pixels and the transfer of the photographic paper in a sub scanning direction. Of the multiple dots contained in each of two continuous exposure bands, the mean value of the pixel levels of two pixels corresponding to two dots with the same positional relationship for the main scanning direction is calculated to derive interpolation data. Thus, the region between the two dots neighboring in the sub scanning direction on the photographic paper is exposed on the basis of the interpolation data.
Owner:NK WORKS CO LTD
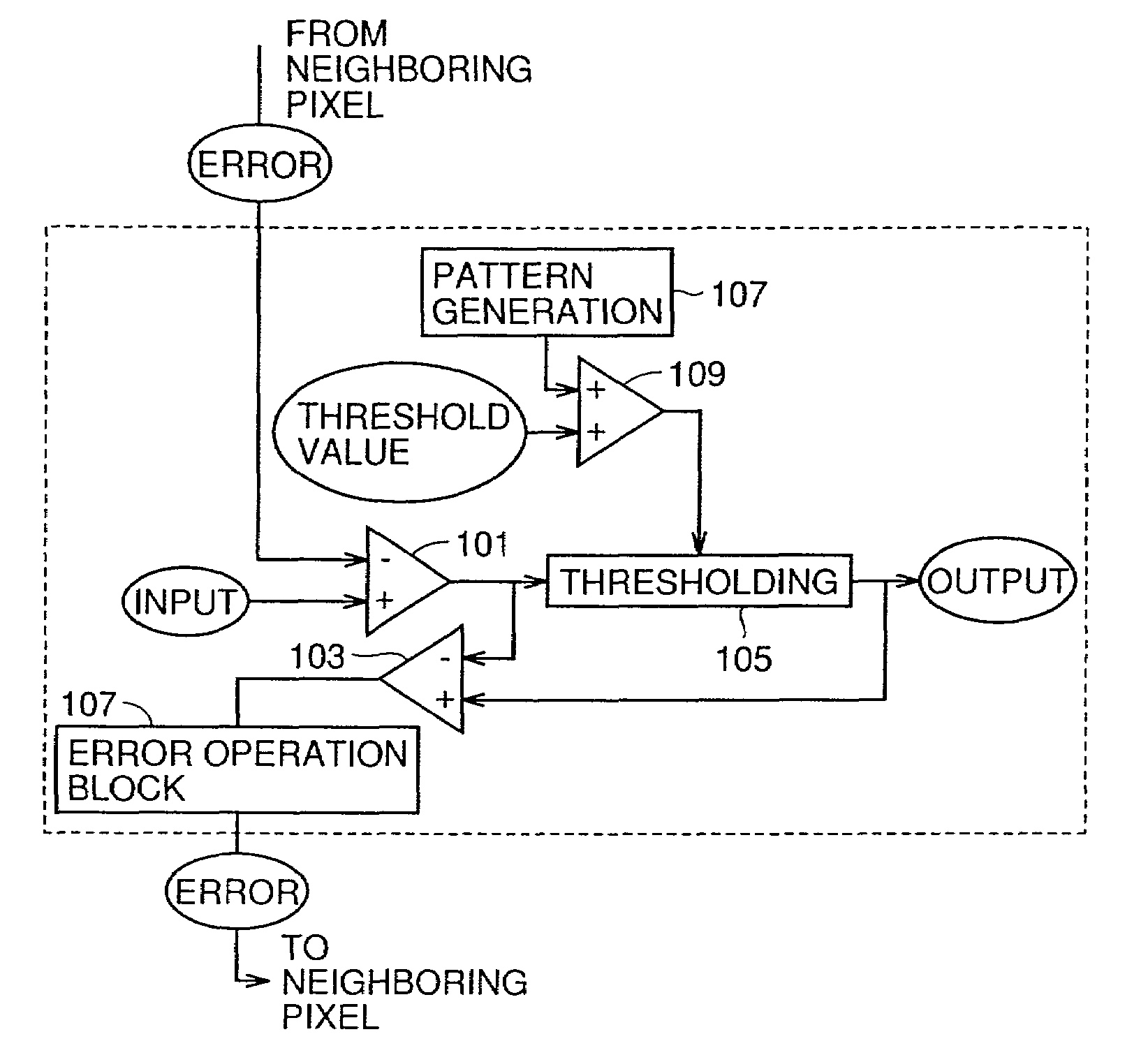
Image processing apparatus and method intensively providing dots in halftone process
InactiveUS7110141B2Solve highHigh levelImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImaging processingDistribution method
There is provided an image processing apparatus, operating as described below, employing an error distribution method to perform a halftone process intensively providing dots to achieve high resolution and a high level of tone representation simultaneously. The image processing apparatus, employing the error distribution method to convert an image represented by multiple values into an image provided in binary representation, employs a distribution weighting coefficient to distribute an error caused at a target pixel to a neighboring pixel. The distribution weighting coefficient simply decreases and ultimately attains zero as the distance from the target pixel increases, and the distance extending to attain zero is also set to vary with direction. Such a distribution weighting coefficient allows a halftone process providing dots intensively.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Ink jet printing
InactiveUS6886932B2Good colorIncreased durabilityMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsEngineeringMagenta
This invention pertains to ink jet printing and more particularly to inkjet printing of wide format substrates such as textiles, and to inks and inks sets suitable for use in such printing, wherein ink set including a first magenta ink; a second magnetic ink; a first cyan ink; a second cyan ink; a yellow ink; an orange ink; a green ink; and black ink.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program
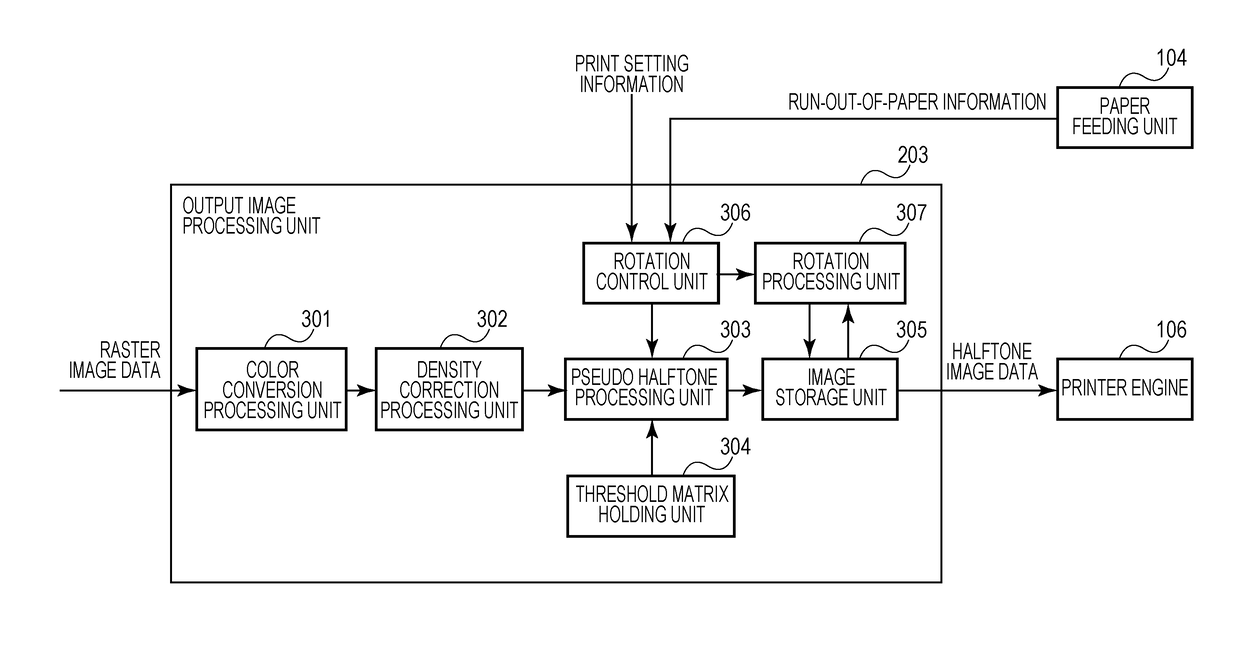
ActiveUS20170150009A1Geometric image transformationGeneric and host data combinationComputational scienceImaging processing
An image processing apparatus which performs image processing for print processing, including: a pseudo halftone processing unit configured to perform pseudo halftone processing by dithering with respect to an input image, and generate a halftone image constituted by plural dots, and a threshold matrix holding unit configured to hold a threshold matrix used for the pseudo halftone processing, wherein in the threshold matrix, thresholds are arranged such that the halftone image has a density region in which dots to be formed depending on a density of the input image are not rotational symmetric on a 90° basis, and orientations of the dots differ from each other in the density region.
Owner:CANON KK
Color image forming apparatus using inks of plural densities
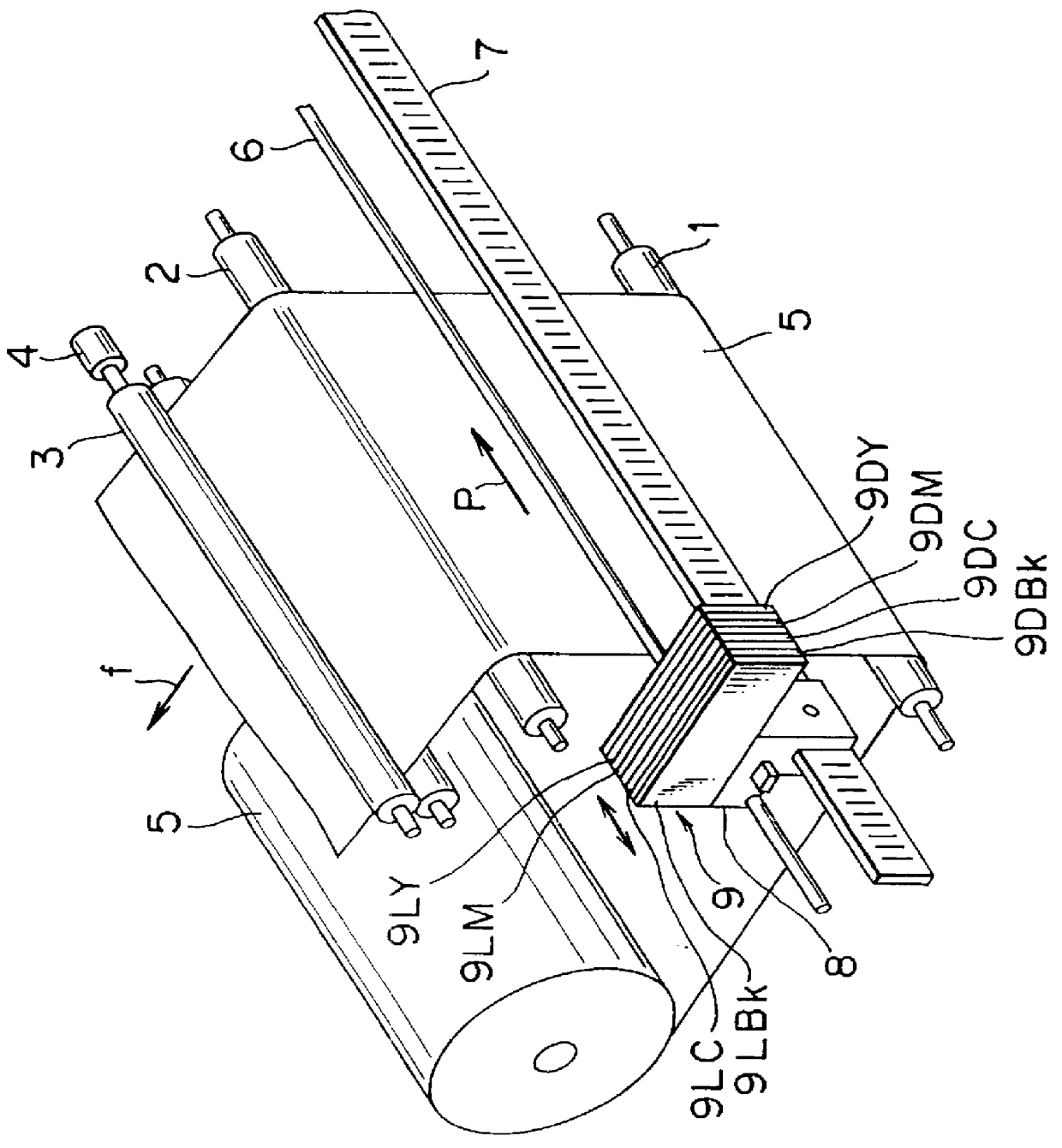
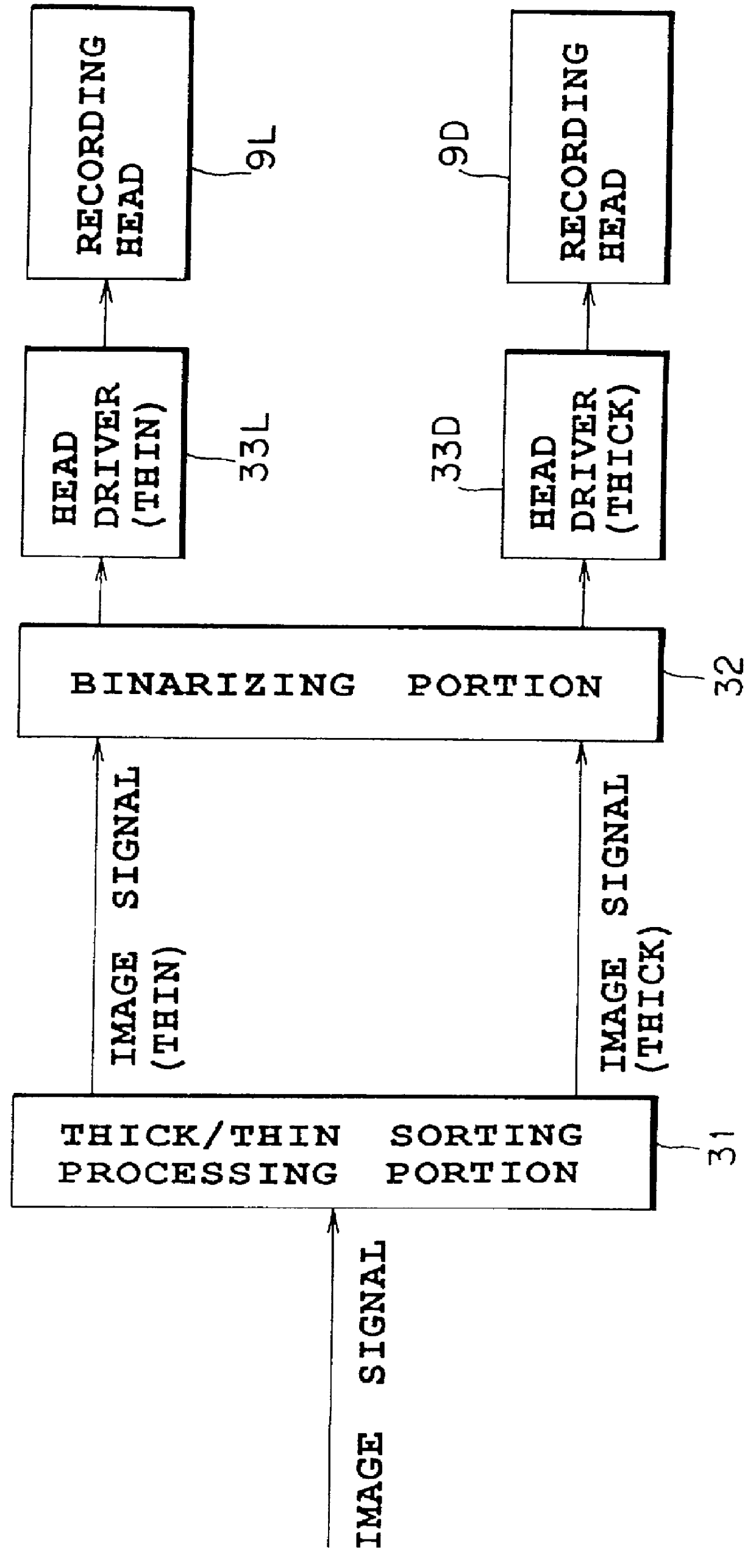
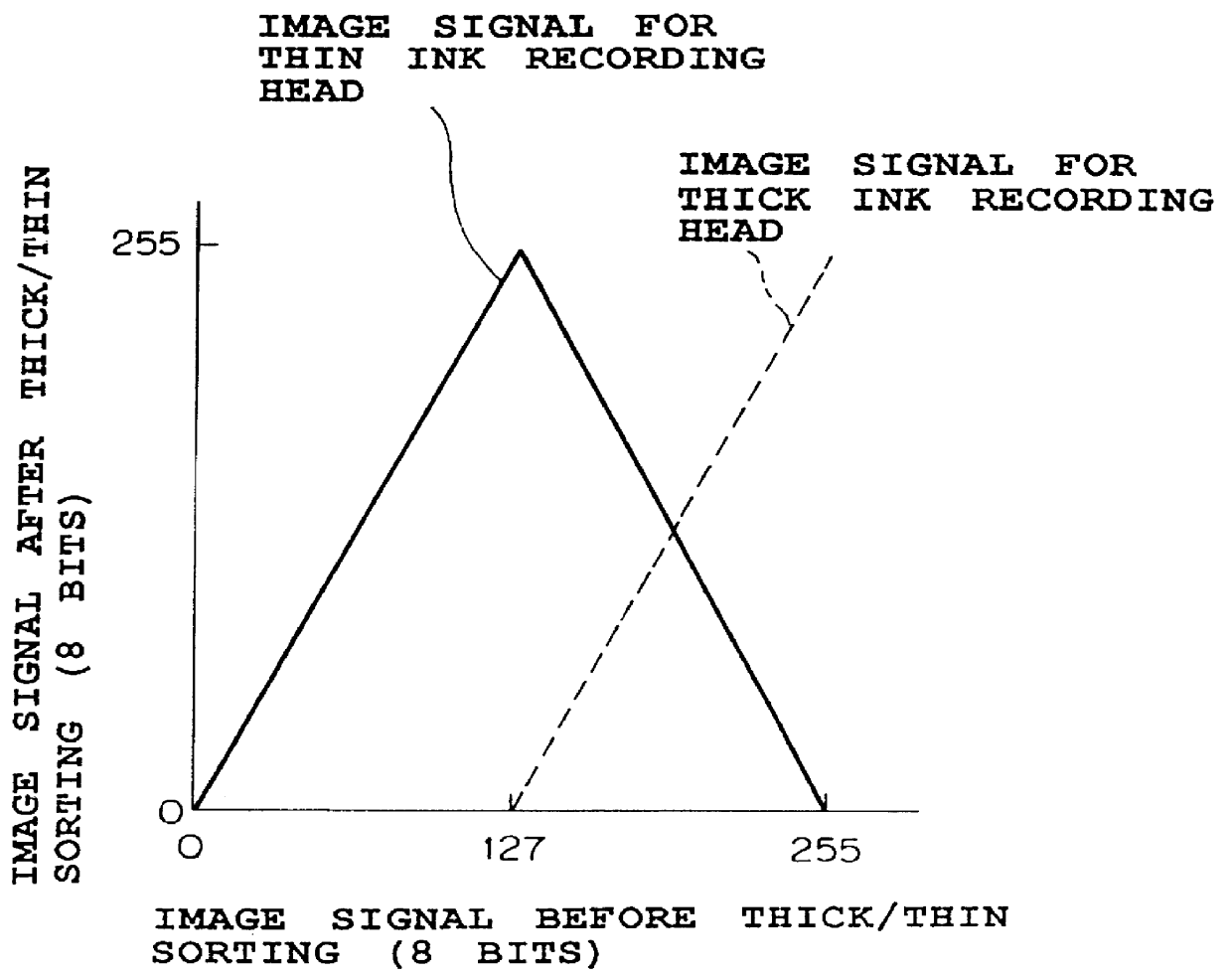
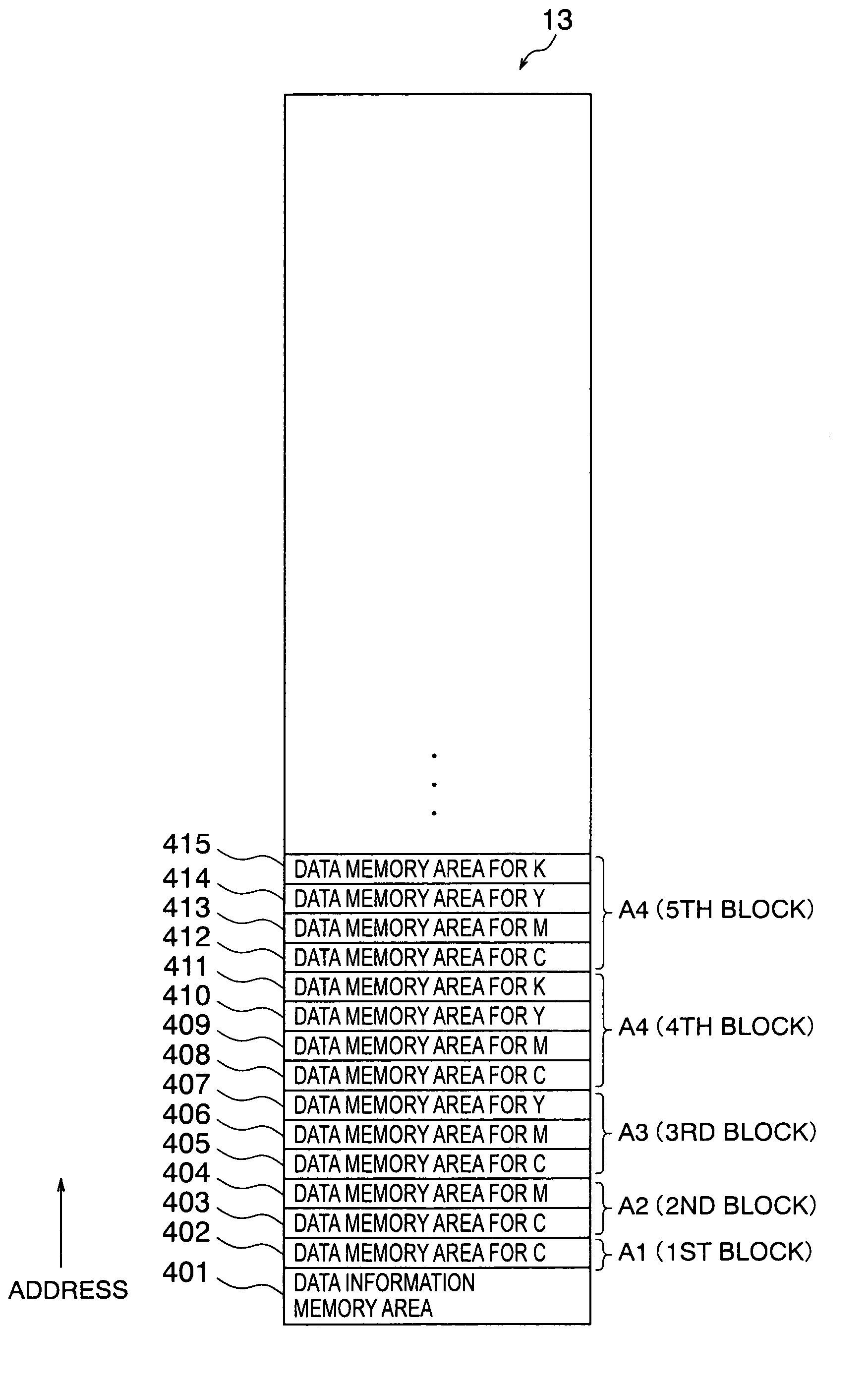
InactiveUS6130686ADuplicating/marking methodsVisual presentation using printersColor imageGeneration process
A color image forming apparatus includes an image signal input portion which supplies three image signals C, M and Y associated with cyan, magenta and yellow; an image signal conversion processing portion which converts the image signals C, M and Y into six image signals associated with thick C and thin C, thick M and thin M, and thick Y and thin Y, respectively, by using a thick / thin sorting table; and a color masking processing portion which performs color masking process, and outputs converted six image signals associated with thick C to thin Y. The converted six image signals undergo a black generation process, a UCR process and a black printing process, and a binarization processing thereafter. This makes it possible to produce color images of high quality with high reproducibility even if the hues of N color materials, which belong to the same color family and have different densities, such as thin cyan and thick cyan, differ from each other to some extent.
Owner:CANON KK
Printing system and method
InactiveUSRE38732E1Easy to handleGeneric and host data combinationRaster outputtingComputer graphics (images)Insertion device
A image is printed from a source of drawing instructions. The image is reducible to pixels arranged in a plurality of ranked image lines. The system employs a storage device having compressed and uncompressed regions. Each region has a designated capacity and each is arranged to store pixels of one or more of the plurality of image lines. A drawing processor is coupled to the storage device and can be coupled to the source of drawing instructions for responding thereto. This drawing processor can store new pixels in the storage device for successively selected ones of the image lines. The drawing processor has a conditional device, a decompression device and an insertion device. The conditional device can compressively encode and move from the uncompressed region to the compressed region, a remote one of the image lines, if: a) the selected one of the image lines is in the compressed region, and b) the uncompressed region has reached its designated capacity. The decompression device can expansively decode the selected one of the image lines, if located in the compressed region. The insertion device can insert one or more new pixels according to the drawing instructions into the selected one of the image lines by storing the selected one in the uncompressed region. The printing system also has a printing engine coupled to the storage device for printing the plurality of image lines in rank order, decompressing compressed ones of the image lines from the compressed region before printing.
Owner:ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING
Image processing method, computer program, recording medium, image processing apparatus, and image forming apparatus
InactiveCN101945770AOther printing apparatusGeneric and host data combinationImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
Owner:RICOH KK
Image correction method and image correcting apparatus
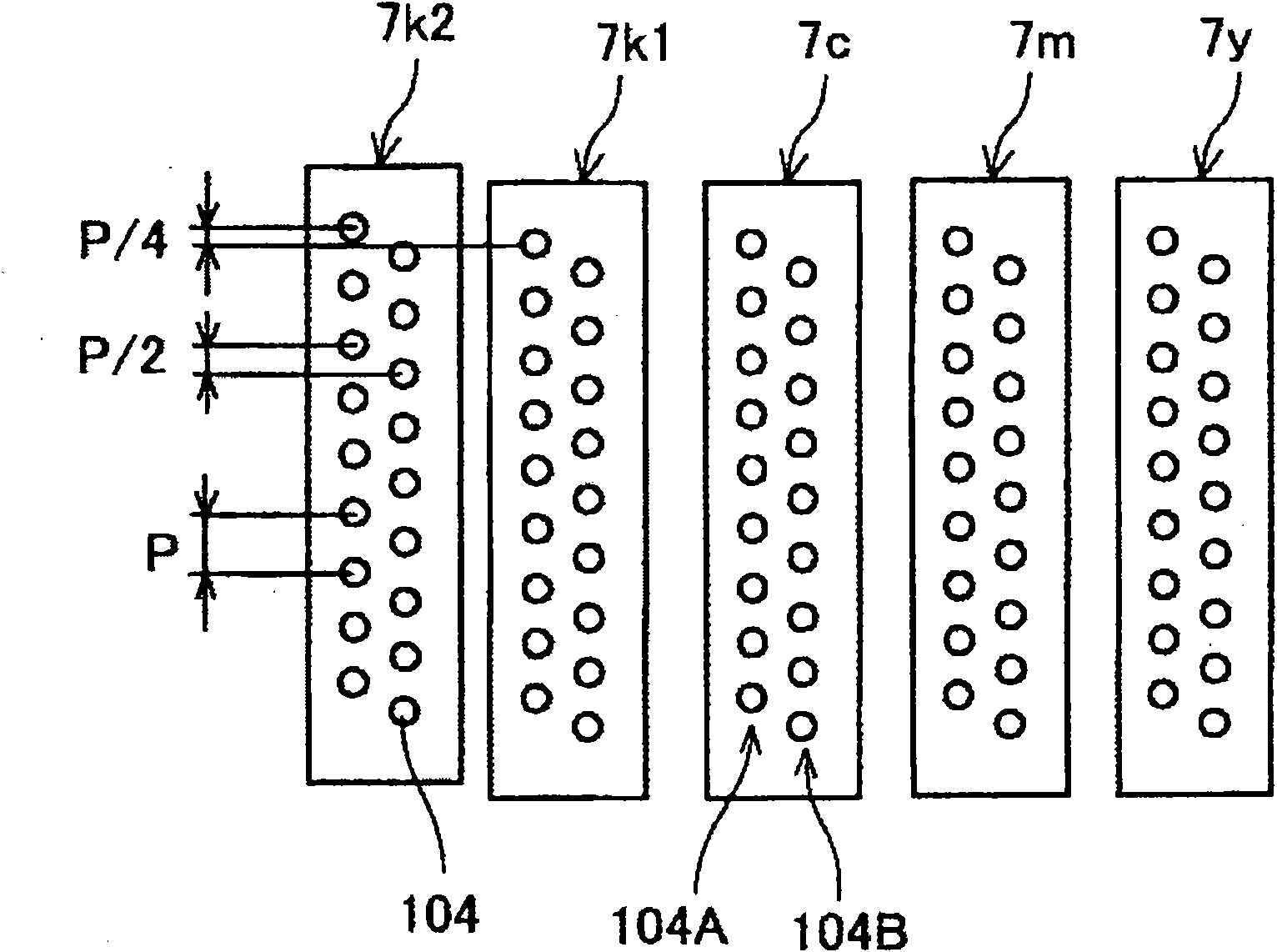
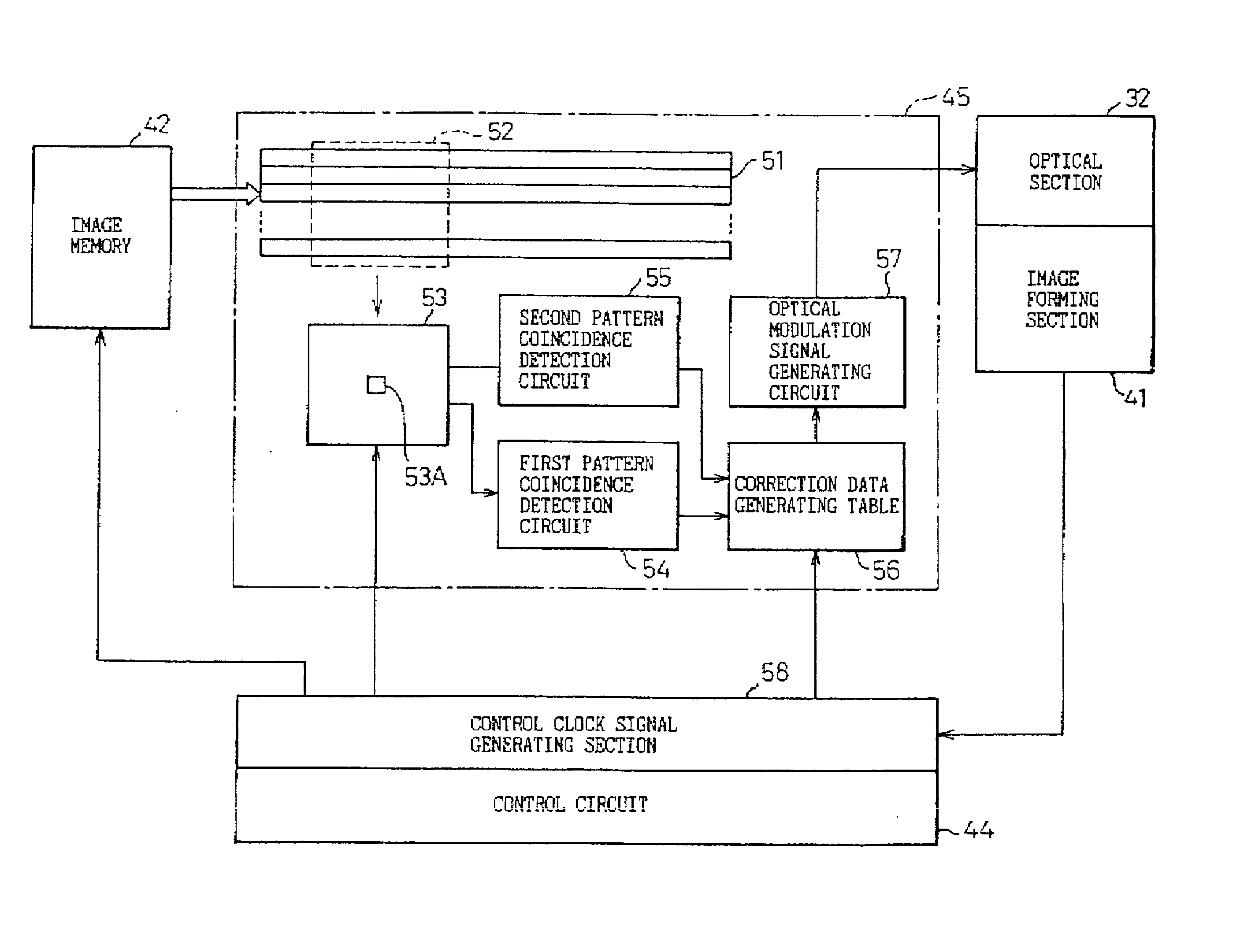
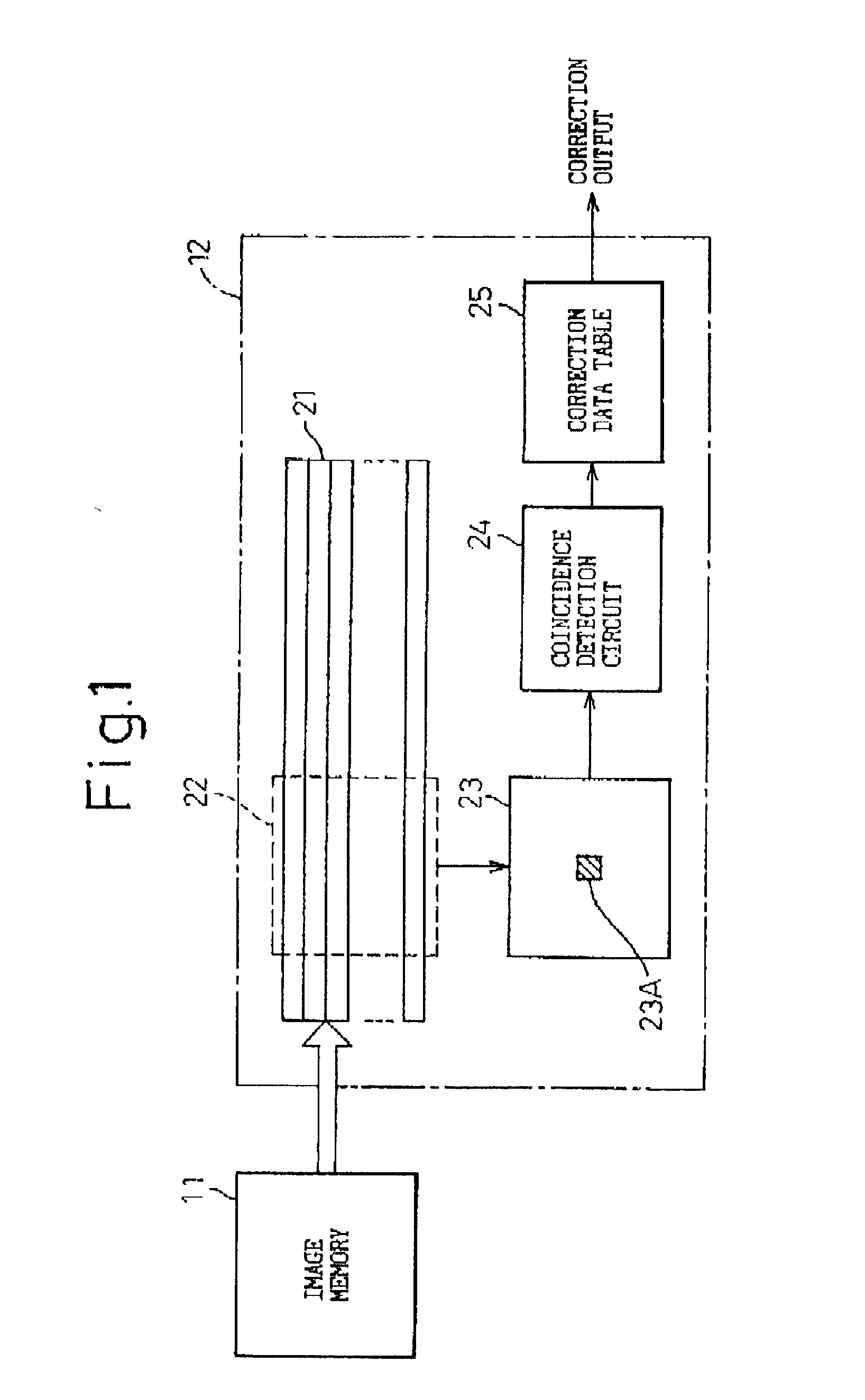
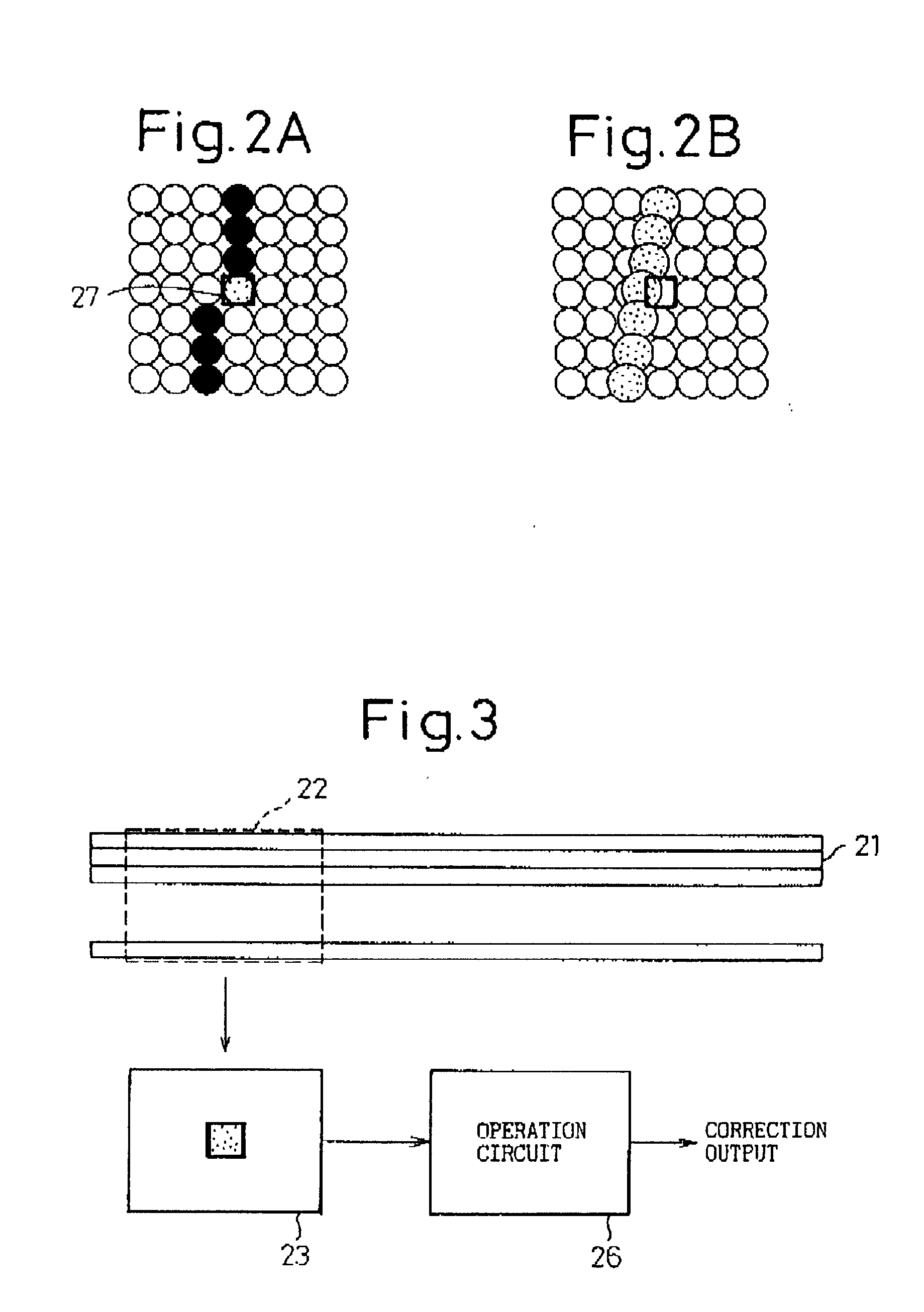
InactiveUS20030007166A1Image enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImage correctionCorrection method
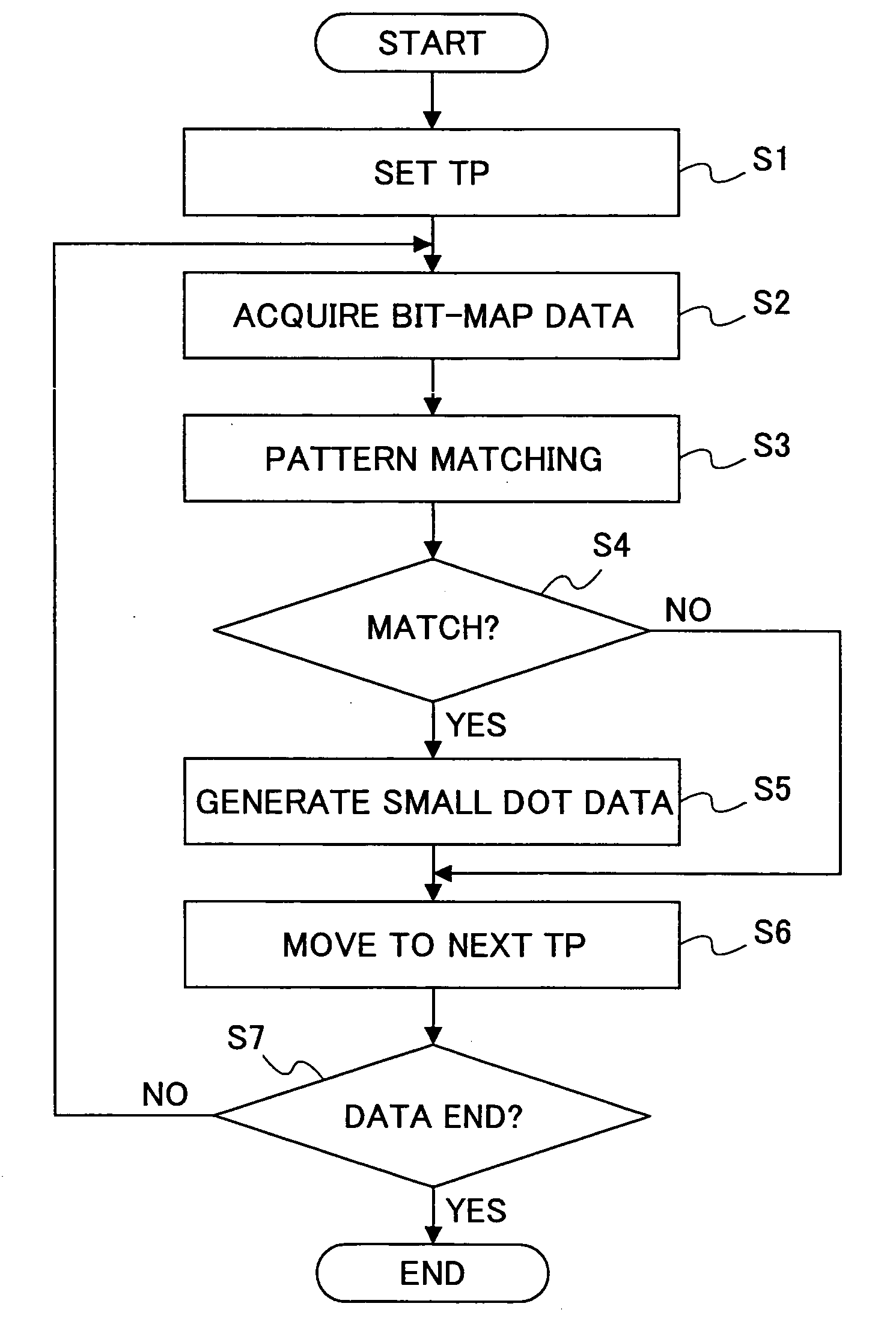
An image correcting method and apparatus is disclosed in which processing other than a smoothing process can be performed in accordance with conditions of a line such as correction of a line width with a small circuit size and at low cost. The disclosed dot image correcting method stores correction data corresponding to a correction dot pattern(s) in a window(s), determines whether or not a dot pattern coincides with a correction dot pattern, and when coincidence is detected, performs correction in accordance with corresponding correction data, characterized in that there are a plurality of windows, and correction data are stored corresponding to a combination of correction dot patterns in various windows, and determination is made as to whether or not dot patterns in a plurality of windows coincide with a combination of correction dot patterns in various windows, and when coincidence is detected, correction is performed in accordance with corresponding correction data.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Printing system and method
InactiveUSRE36947E1Easy to handleDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsComputer graphics (images)Insertion device
A image is printed from a source of drawing instructions. The image is reducible to pixels arranged in a plurality of ranked image lines. The system employs a storage device having compressed and uncompressed regions. Each region has a designated capacity and each is arranged to store pixels of one more of the plurality of image lines. A drawing processor is coupled to the storage device and can be coupled to the source of drawing instructions for responding thereto. This drawing processor can store new pixels in the storage device for successively selected ones of the image lines. The drawing processor has a conditional device, a decompression device and an insertion device. The conditional device can compressively encode and move from the uncompressed region to the compressed region, a remote one of the image lines, if: a) the selected one of the image lines is in the compressed region, and b) the uncompressed region has reached its designated capacity. The decompression device can expansively decode the selected one of the image lines, if located in the compressed region. The insertion device can insert one or more new pixels according to the drawing instructions into the selected one of the image lines by storing the selected one in the uncompressed region. The printing system also has a printing engine coupled to the storage device for printing the plurality of image lines in rank order, decompressing compressed ones of the image lines from the compressed region before printing.
Owner:ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING
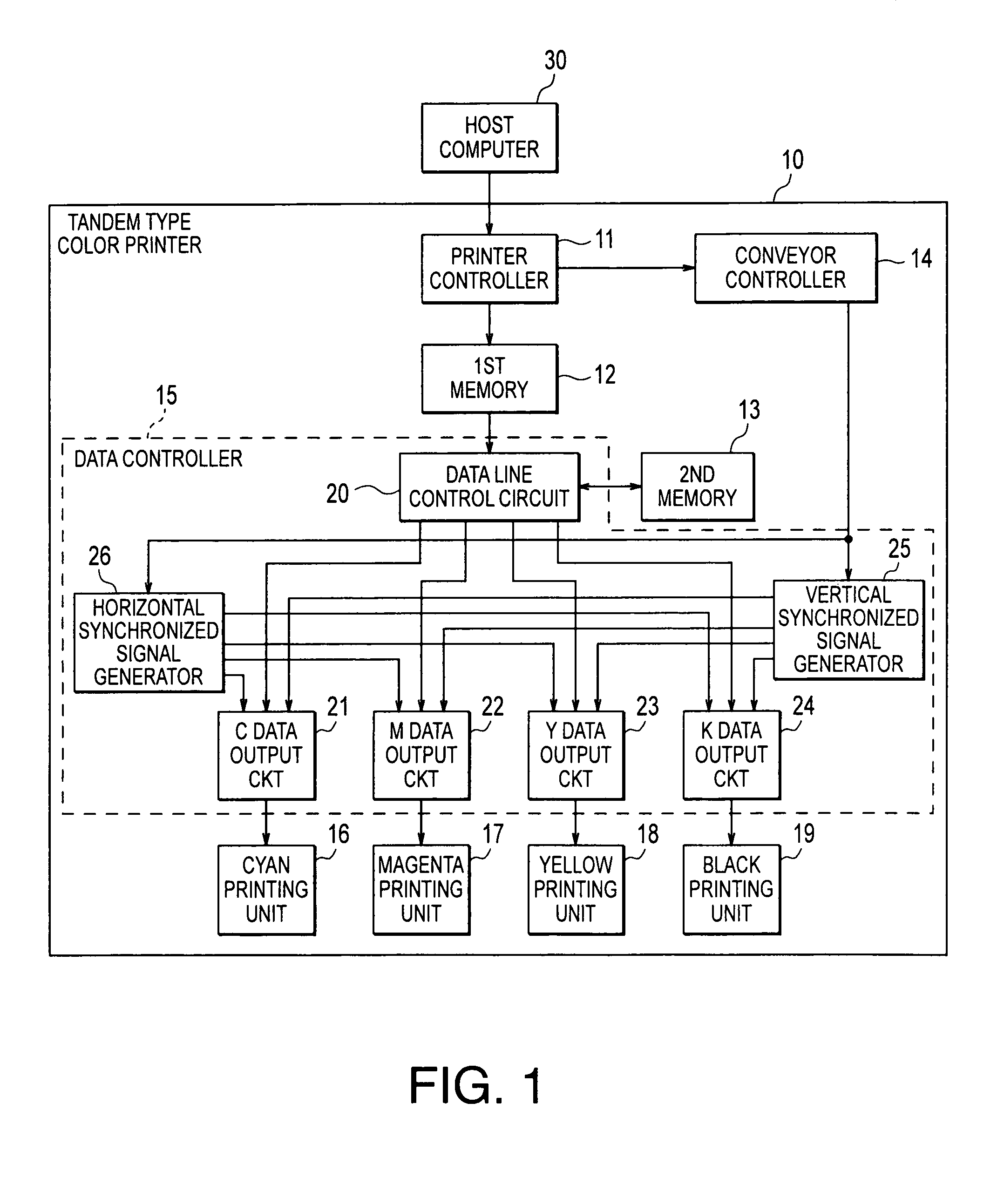
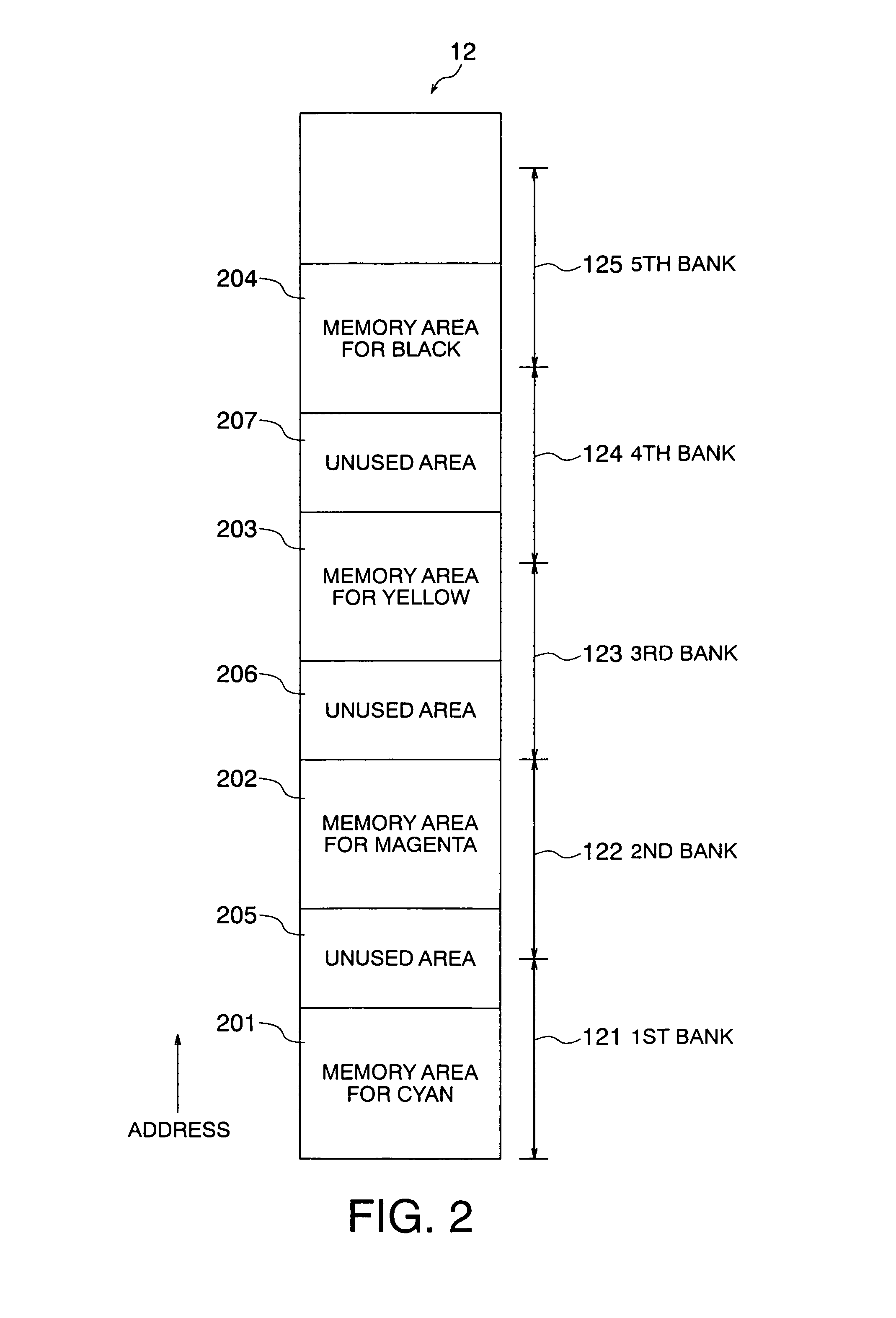
Tandem type color printer capable of making plural copies of printed matter at high speed
InactiveUS6980316B2Shorten the timeVisual presentation using printersElectrographic process apparatusData setControl circuit
In a tandem type color printer, a second memory memorizes bitmap data sets in a second arrangement. In the second arrangement, each of the bitmap data sets is divided into a plurality of data units. In addition, the data units of all of the bitmap data sets are arranged on the basis of predetermined output order regardless of the colors. A first memory separately memorizes the bitmap data sets in a first arrangement different from the second arrangement. A data line control circuit reads out the bitmap data sets from the first memory when a first copy of a printed matter is made by the use of the bitmap data sets. In this time, the data line control circuit stores the bitmap data sets in the second memory with changing its arrangement. When a second or later copy of the printed matter is made, the data line control circuit reads out the bitmap data sets at high speed.
Owner:NEC CORP
Image processing method, image processing program, and image forming apparatus
InactiveCN1993231AIncrease printing speedImprove image qualityElectrography/magnetographyPrintingGraphicsShape change
An image processing method is disclosed. The image processing method includes the steps of detecting one or more dots near a step-shaped changing part of dots of which an outline part of a letter or graphics is composed, by using a reference pattern having a window size of 'm x n' dots in which a number of dots 'm' corresponds to resolution in the main scanning direction and a number of dots 'n' corresponds to resolution in the sub scanning direction, converting the detected one or more dots near the step-shaped changing part that is nearly parallel to the main scanning direction into a dot whose size is smaller than that of dots of the step-shaped changing part, and not converting the detected one or more dots whose part is nearly parallel to the sub scanning direction.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method of generating halftone print data that accommodates overlapping printhead chips
InactiveUS20060012623A1Effective and convenient mannerProduce some attenuationVisual representation by matrix printersOther printing apparatusContinuous toneEngineering
A method of generating halftone print data for overlapping end portions of a pair of consecutive printhead chips in an array of two or more printhead chips where an end portion of a first printhead chip overlaps an end portion of a second printhead chip, each printhead chip including a plurality of ink ejection nozzles, includes generating continuous tone print data for the array of printhead chips, The continuous tone print data for said overlapping end portions is interpolated according to an algorithm such that ink ejection nozzle utilization decreases in each said overlapping end portion towards respective ends of the printhead chips.
Owner:MEMJET TECH LTD +1
Exposure device and exposure method for exposing a photosensitive medium to light on the basis of image data containing multiple pixels
InactiveUS7236184B2Difference in densityImprove image qualityVisual presentation using printersPrintingPhotographic paperComputer science
In an exposure device according to the present invention, a plurality of exposure bands each containing multiple dots is formed on photographic paper by repeating main scanning in a main scanning direction based on image data that contains multiple pixels and the transfer of the photographic paper in a sub scanning direction. Of the multiple dots contained in each of two continuous exposure bands, the mean value of the pixel levels of two pixels corresponding to two dots with the same positional relationship for the main scanning direction is calculated to derive interpolation data. Thus, the region between the two dots neighboring in the sub scanning direction on the photographic paper is exposed on the basis of the interpolation data.
Owner:NK WORKS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for reducing multi-bit image data
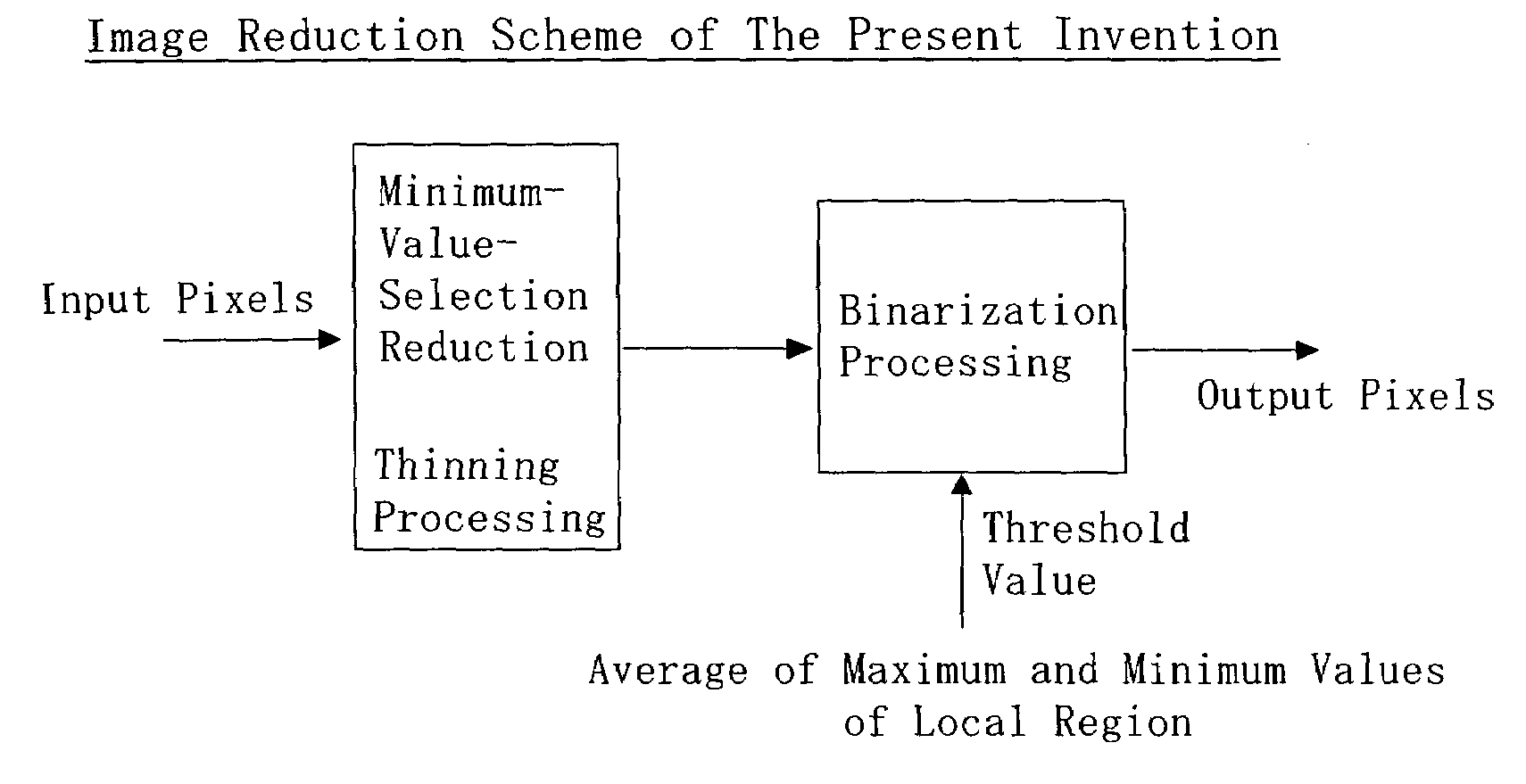
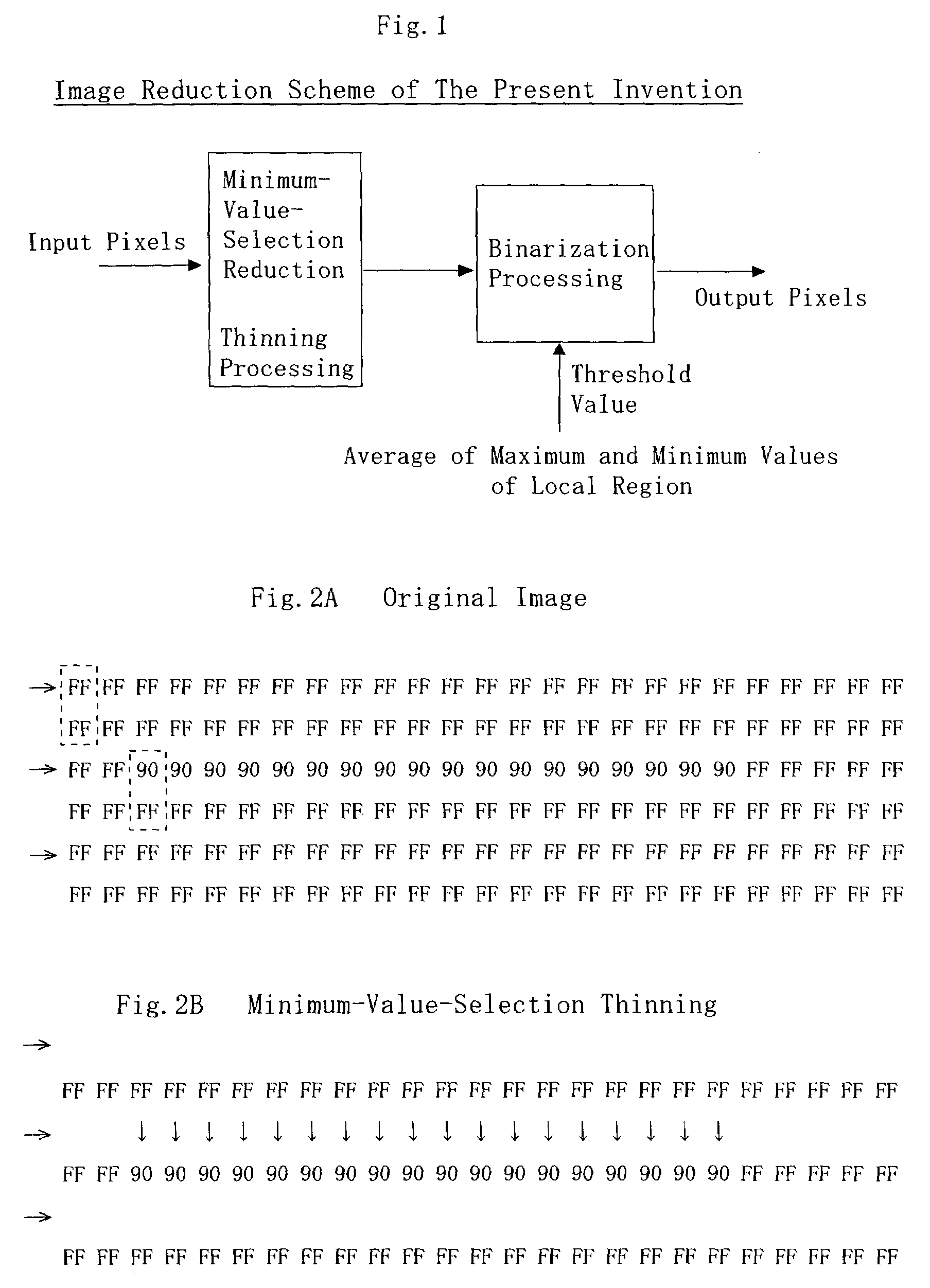
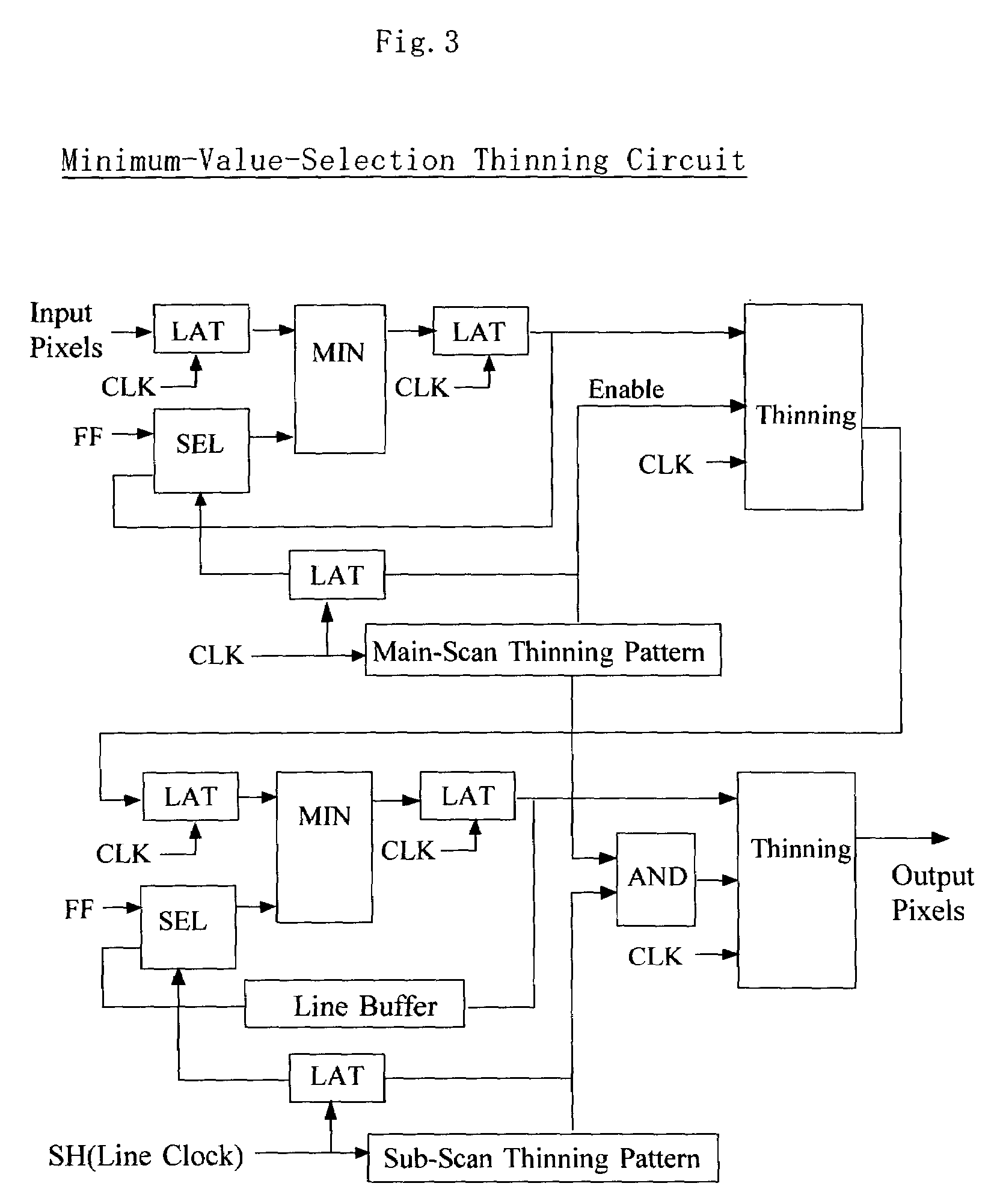
InactiveUS7336390B2Avoid lossFlexible reduction and magnification change processingImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersAlgorithmThinning
Input pixels are input to a thinning processing circuit. When thinning is performed at the thinning processing circuit, minimum values are selected in order to reduce the pixel data, whereby loss of thin lines is prevented. The thinned image data are input to a binarization processing circuit. Although the image having been thinned through selection of minimum values becomes dark as a whole, collapse of characters can be suppressed, because the binarization processing circuit dynamically changes a binarization threshold by employing, as the binarization threshold, the average of maximum and minimum values in each local region. In a density flat portion, the local maximum value and the local minimum value assume the same value. Therefore, when the difference between the local maximum value and the local minimum value is not greater than a predetermined range, binarization is performed by use of a fixed threshold value. Instead of local maximum and minimum values, a local average value may be used as a binarization threshold value.
Owner:PFU LTD
Popular searches
Visual representation by plotters Image data processing details Electric digital data processing Pictoral communication Visual representation by thermal printers Character and pattern recognition Natural language data processing Special data processing applications Digital output to print units Colour-separation/tonal-correction
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com