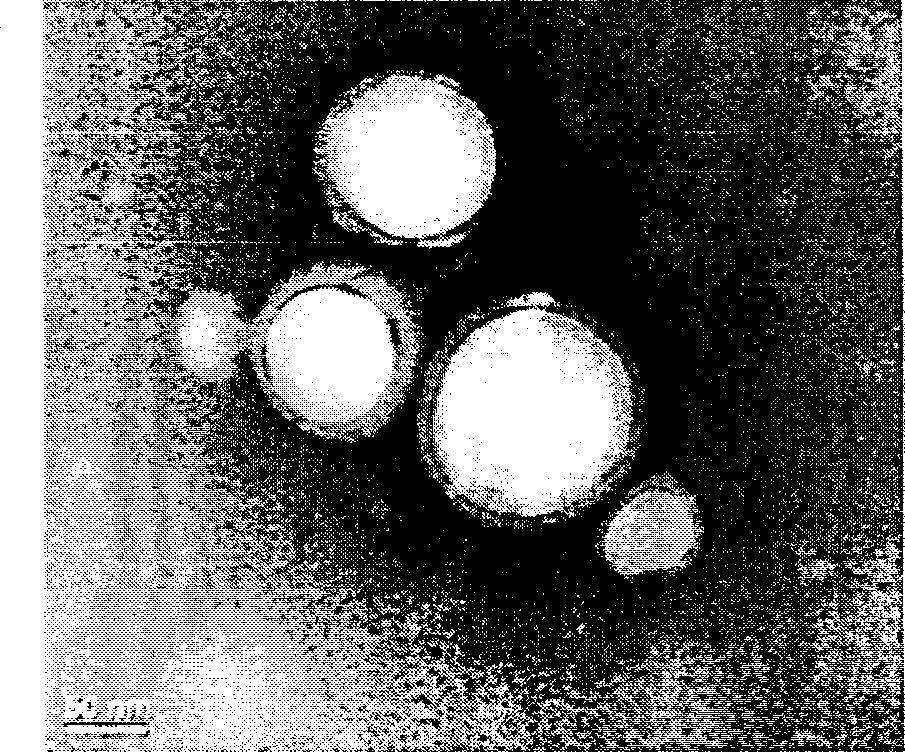Magnetic tumour target polymer nano vesicle and preparation method thereof
A nanovesicle and tumor targeting technology, which is applied in the fields of polymer chemistry and biomedical engineering, can solve the problems of undeveloped research on strong magnetic targeting vesicles, loss of curative effect, toxic and side effects, etc., and improve the characteristics of magnetic resonance imaging , reduce the dosage and side effects, prolong the effect of blood circulation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Preparation of folic acid-modified polymer nanovesicle carrier material folate-PEG-PDLLA
[0038] 1.1 Preparation of allyl-terminated PEG homopolymers:
[0039] The polymer is obtained by the continuous phase anionic ring-opening polymerization of ethylene oxide using potassium alkoxide as an initiator. First, 4 ml of a tetrahydrofuran solution of potassium naphthyl and 1.5 to 2.5 ml of allyl alcohol are uniformly mixed, and then stirred in a dry reaction flask for 15 minutes. Then, 20 ml of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran and 18-crown-6 in tetrahydrofuran (containing 1.5 g of 18-crown-6 and 5 ml of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran) were added under argon protection, and the mixture was cooled in an ice-salt bath after stirring for 15 minutes. , and slowly introduced a certain amount of dry ethylene oxide, and maintained the low temperature for 24 hours to make the polymerization reaction continue. Finally, it was left at room temperature for at least 3 days to facilitate complete...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Preparation of magnetic tumor-targeting polymer nano-drug-loaded vesicles
[0048] 2.1 Preparation of superparamagnetic ferric oxide SPIO nanoparticles
[0049] First, 0.7g of iron acetylacetonate, 2.9g of 1,2-hexadecanediol, 2ml of oleic acid, 2ml of oleylamine and 20ml of dibenzyl ether were mixed uniformly under nitrogen protection, heated at 200°C for two hours, and then heated to Reflux at 300°C for one hour. After the obtained black product was cooled to room temperature, reprecipitated in ethanol, centrifuged to remove excess solvent, dissolved in n-hexane and sealed for storage to obtain a hydrophobic SPIO sample solution.
[0050] The n-hexane solution of the hydrophobic SPIO prepared above was mixed with three to five times the dichloromethane solution of tetramethylamine 11-aminodecanoic acid and shaken at room temperature for 24 hours, then separated from the solution with a magnet The precipitate was washed twice with dichloromethane and separated with a ...
Embodiment 3
[0057]Testing of basic properties of magnetic tumor-targeting polymer nano-drug-loaded vesicles
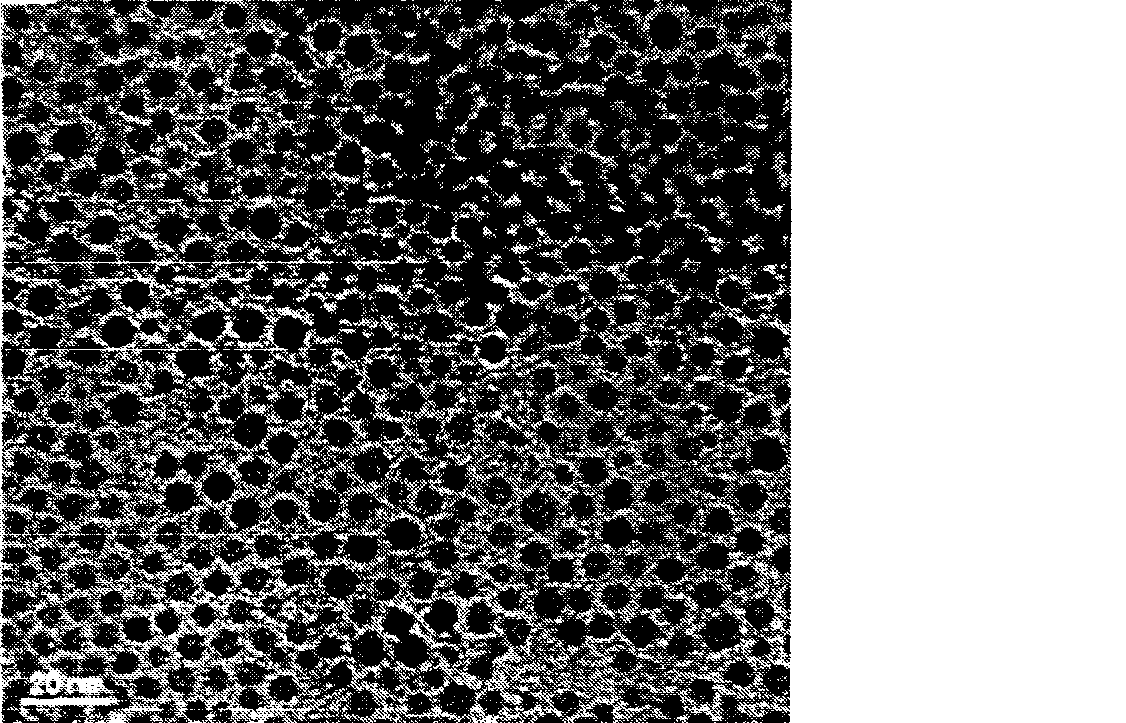
[0058] 3.1 Measurement of size and morphology of magnetic tumor-targeting polymer nano-drug-loaded vesicles
[0059] The particle size of the obtained vesicles was measured by a dynamic light scattering system, and its morphology was observed and determined by transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The test results are shown in Figures 3 to 12 . Image 6 , Figure 7 and Figure 8 are the dynamic light scattering histograms of the corresponding vesicles, in which, it can be clearly seen from the transmission electron microscope pictures that the amphiphilic polymers self-assemble into "hollow spheres" with a central membrane wall in an aqueous solution. The wall is about 20 nm, and the hydrophobic and hydrophilic SPIOs are wrapped in the outer membrane and inner cavity of the vesicles under the interaction of hydrophilic and hydrophobic, respectively...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com