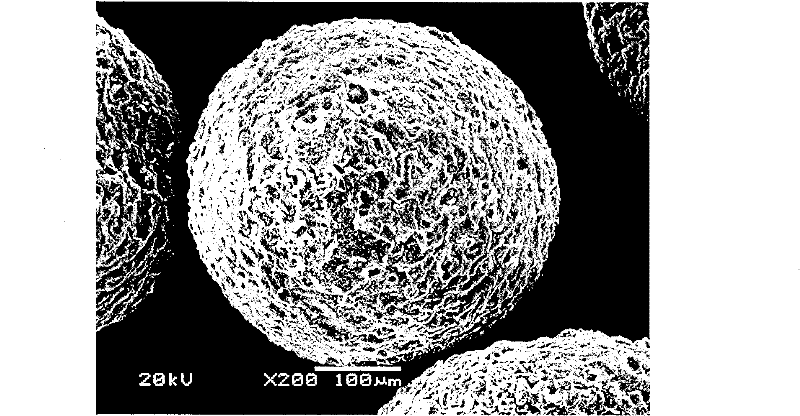
Multi-core adhesive microspheres for loading water soluble low molecular medicament and preparation method thereof
A water-soluble small molecule, drug-loading technology, which is applied in the directions of non-active components of polymer compounds, pharmaceutical formulations, and medical preparations with non-active components, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing the drug-loading capacity and reducing leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
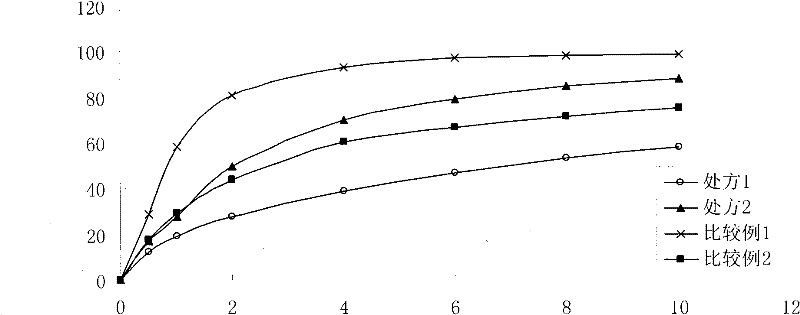
[0059] The influence of embodiment 1 prescription on release rate
[0060] Prescription 1
[0061] Evenly disperse 200mg of berberine hydrochloride and 200mg of aluminum stearate in 10ml of 1% acrylic resin No. II containing 5% water in acetone solution, add this mixture to 80ml of acetone saturated liquid paraffin and stir at a speed of 900rpm Form an oil-in-oil emulsion, stir at room temperature for 5 hours to completely evaporate the internal solvent, centrifuge to obtain acrylic resin core microspheres, wash with n-hexane three times to remove residual liquid paraffin, and dry.
[0062] Add 200mg of the acrylic resin microspheres prepared above to 2% acetic acid solution containing 3% (w / v) chitosan and 3% (w / v) gelatin at 40°C, stir to make it evenly dispersed and let stand Degassing, as the water phase; mix 80ml of liquid paraffin and 0.16g of Span80 as the oil phase; keep both the water phase and the oil phase at 40°C, add the water phase to the oil phase, and stir at ...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2 In Vivo Adhesion Research of Multi-core Adhesive Microspheres
[0072] The experimental conditions are: 200g-250g Wistar rats are fasted for 12 hours, and after anesthesia, a small opening is made in the distal esophagus and proximal duodenum and connected with polyethylene tubes respectively. After flushing away the residual contents in the stomach with normal saline, 100 microspheres and 0.2ml of water were infused. Ten minutes later, the stomach was flushed with artificial gastric juice at a flow rate of 1.5ml / min for 1.5h. Record the number of microspheres cleared from the stomach after washing, and calculate the retention percentage.
[0073] Prescription 2, Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 2 in Example 1 were selected, and the retention rate in the gastric mucosa was investigated in vivo. The higher the retention rate of the microparticles in the gastric mucosa, the better the adhesion performance of the microspheres, and the higher the dru...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Evenly disperse 100mg of amoxicillin and 200mg of magnesium stearate in 10ml of 1% acrylic resin No. III in acetone solution containing 5% of water, add this mixture to 80ml of acetone-saturated liquid paraffin and stir at a speed of 900rpm to form an oil Oil-in-emulsion, stirred at room temperature for 5 hours to completely evaporate the internal solvent, centrifuged to obtain acrylic resin core microspheres, washed three times with petroleum ether to remove residual liquid paraffin, and dried.
[0078] Add 75 mg of the above-mentioned prepared internal acrylate resin microspheres into 2% acetic acid solution containing 3% (w / v) chitosan and 1.5% (w / v) gelatin at 40°C, stir to make it uniformly dispersed and Stand still for defoaming, as the water phase; mix 80ml of liquid paraffin and 0.16g of Span85 as the oil phase; both the water phase and the oil phase are kept at 40°C, add the water phase to the oil phase, and stir at 600 rpm for 20 minutes to obtain an emulsion ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com