Preparation method of lithium iron phosphate/carbon composite material
A carbon composite material, lithium iron phosphate technology, applied in electrical components, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of small tap density, low battery volume specific capacity, and large pollution, and achieve small particle size and capacity retention High efficiency and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
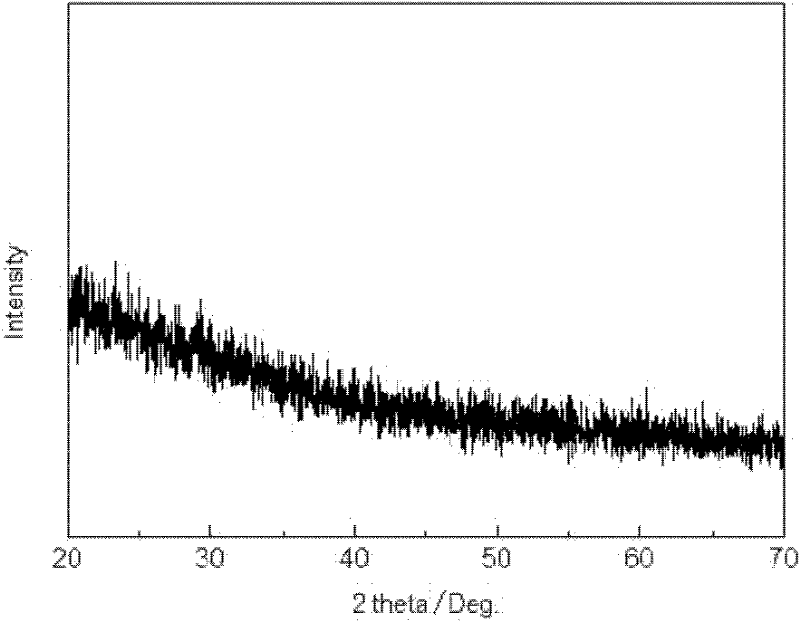
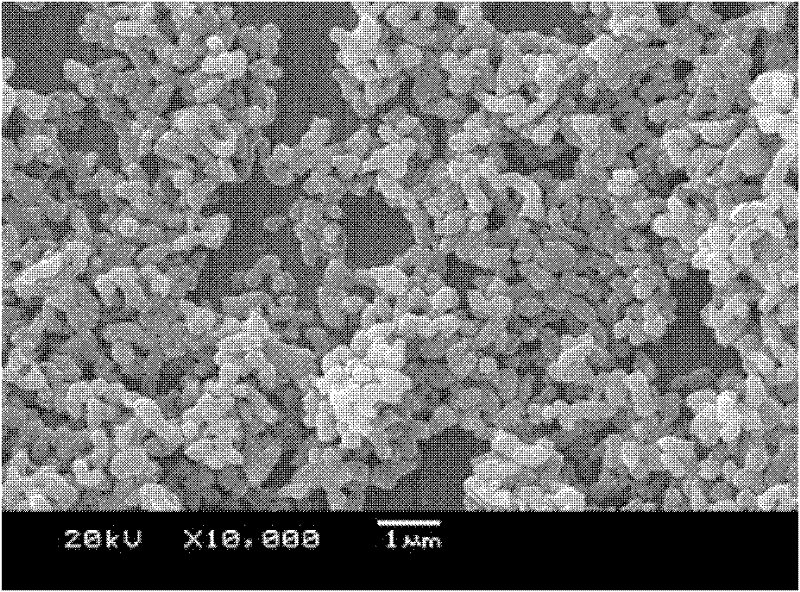
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] 83.40g FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O and 34.80 g H3 PO 4 Add it into 150ml of deionized water, stir until completely dissolved, then add 18.00g of 30wt% H 2 o 2 , stir to make it completely react, add about 321ml of 2M / L ammonia water dropwise to the solution, the pH is about 3.65, continue to stir until the pH value is basically stable. Filtrate, wash the obtained precipitate, and dry at 80°C to obtain the precursor iron phosphate.
[0035] Weigh 12.60g of citric acid and 11.34g of oxalic acid, dissolve them in 90g of deionized water, weigh 15.12g of LiOH·H 2 O was put into the acid solution, and after the reaction was complete, pour 45.26g of synthetic ferric phosphate into it, mix and stir for 15 hours. The reacted slurry was spray-dried to obtain gel particles, which were then calcined at 650°C under a high-purity argon atmosphere, kept for 6 hours, and cooled to room temperature with the furnace to obtain a lithium iron phosphate / carbon composite material.
[0036] The carb...
Embodiment 2
[0039] 13.91gFeSO 4 ·7H 2 O and 5.76g H 3 PO 4 Add it into 25ml of deionized water, stir until completely dissolved, then add 3.00g of 30wt% H 2 o 2 , stir to make it react completely, add 55ml of 2M / L ammonia water dropwise to the solution, the pH is 3.50, continue to stir until the pH value is basically stable. Filtrate, wash the resulting precipitate, and dry at 75°C to obtain the precursor iron phosphate.
[0040] Weigh 5.56g of citric acid and 2.52g of oxalic acid, dissolve them in 30g of deionized water, weigh 5.04g of LiOH·H 2 O was put into the acid solution, after the reaction was complete, pour 22.42g of synthesized ferric phosphate and mechanically stir for 15 hours. The reacted slurry was spray-dried to obtain gel particles, which were then calcined at 650°C under a high-purity argon atmosphere, kept for 6 hours, and cooled to room temperature with the furnace to obtain a lithium iron phosphate / carbon composite material.
[0041] The carbon content in the ma...
Embodiment 3
[0044] 27.80gFeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 11.60gH 3 PO 4 Add 50ml of deionized water, stir until completely dissolved, then add 6.00g of 30wt% H 2 o 2 , Stir to make it completely react, add 107ml of 2M / L ammonia water dropwise to the solution, control the pH to about 3.38, continue to stir until the pH value is basically stable. Filtrate, wash the resulting precipitate, and dry at 75°C to obtain the precursor iron phosphate.
[0045] Weigh 5.04g of citric acid and 3.02g of oxalic acid, dissolve them in 30g of deionized water, weigh 5.04g of LiOH·H 2 O was put into the acid solution, and after the reaction was complete, 22.44 g of synthetic ferric phosphate ball mill was added and mixed for 10 hours. The slurry was spray-dried to obtain gel particles, which were then calcined at 700°C under a high-purity nitrogen atmosphere, kept for 6 hours, and cooled to room temperature with the furnace to obtain a lithium iron phosphate / carbon composite material.
[0046] The carbon content in t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com