Organic inorganic hybridized material for removing agent of heavy metal ions
A technology for heavy metal ions and hybrid materials, applied in the field of organic-inorganic hybrid materials, can solve the problems of low concentration of heavy metal ions, difficulty in post-processing, recovery and reuse of production residues, and achieves a simple preparation process and is suitable for large-scale industrialization. Production, high-sensitivity effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
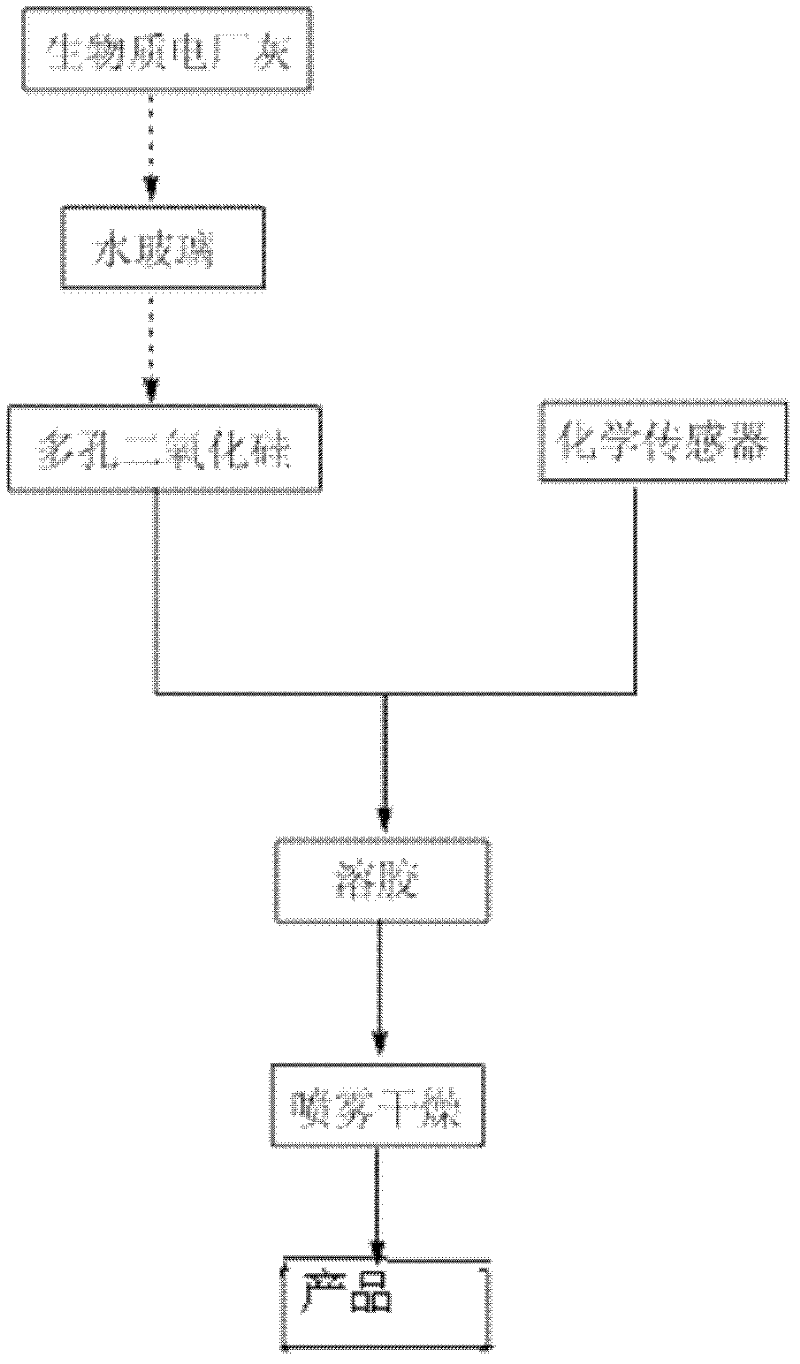
[0029] Porous silica preparation
[0030] At room temperature, 10 mL of ethyl acetate was added dropwise to 100 mL of water glass containing 5 g of cetyl ammonium bromide (CTAB), and the pH value of the solution was adjusted to 9. After stirring at room temperature for 2 hours overnight, the resulting The product was separated by centrifugation, washed with water and ethanol three times respectively, then dried, and finally calcined at 500°C under an air atmosphere to obtain porous silica. For the following examples.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Preparation of Heavy Metal Ion Removal Agent 1
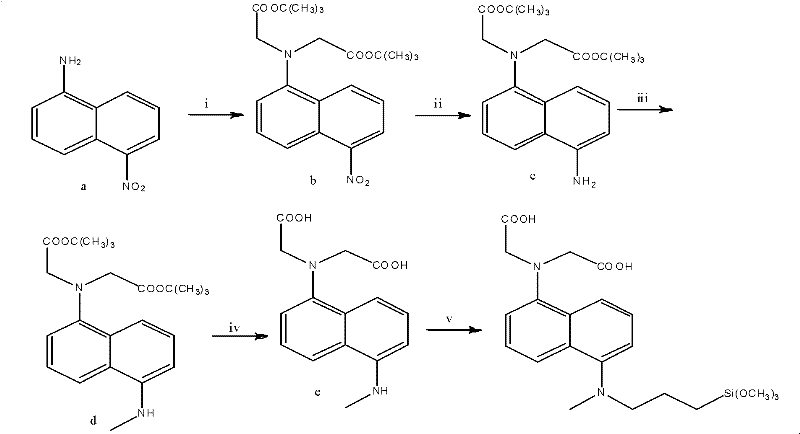
[0033] First, a chemical sensor 1 that selectively recognizes mercury ions is synthesized. The chemical sensor is synthesized by introducing a chelating group iminooxalic acid that has the ability to coordinate to mercury ions into a quinoline derivative of a fluorescent chromophore. The route is as follows, then take 10g of chemical sensor 1 and 20g of porous silica, add 100mL of 95% ethanol by volume, continue to stir for 12h and then spray dry at 100°C to obtain the removal agent 1 for treating heavy metal ions in wastewater.
[0034]
[0035] In the reaction formula,
[0036] (i) a: triethylamine: tert-butyl bromoacetate=1: 2.2: 2.1 (molar ratio), solvent is acetonitrile, reflux reaction;
[0037] (ii) b: palladium carbon=10: 1 (molar ratio), solvent: methanol;
[0038](iii) methyl iodide: c=1: 1 (molar ratio), dichloromethane is used as solvent, room temperature;
[0039] (iv) trifluoroacetic acid: dichlorometh...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Preparation of Heavy Metal Ion Removal Agent 2
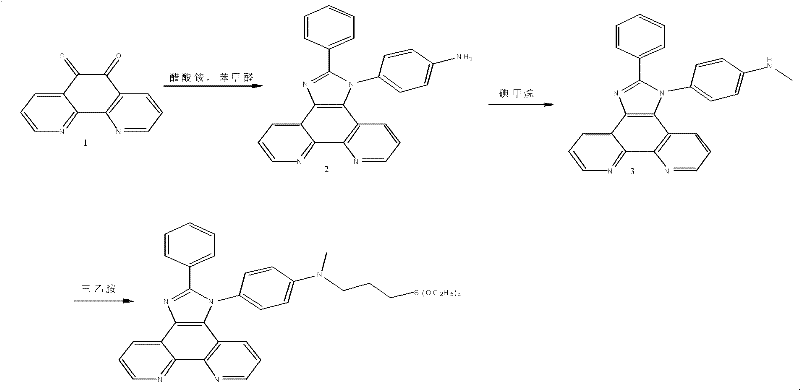
[0043] First, a chemical sensor 2 that can selectively recognize various ions was synthesized. This chemical sensor was synthesized by introducing o-phenanthroline, which has a strong coordination ability to heavy metal ions, into a fluorescent chromophore imidazole derivative. The synthetic route is as follows As shown, then take 10g of chemical sensor 2 and 20g of porous silica, add 100mL of 95% ethanol by volume concentration, continue to stir and react for 12h, and then spray dry at 100°C to obtain remover 2 for treating heavy metal ions in wastewater.
[0044]
[0045] In the reaction formula,
[0046] (1) compound 1: benzaldehyde: p-phenylenediamine: ammonium acetate=1: 1: 1.2: 5 (molar ratio), 120 DEG C of reaction temperature, solvent: glacial acetic acid;
[0047] (2) methyl iodide: 2=1: 1 (molar ratio), dichloromethane is made solvent, room temperature;
[0048] (3) 3: triethylamine: chloropropyl trimethoxy...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com