Method for producing biodiesel from lignocellulose
A lignocellulose and biodiesel technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of competition with people for food and high cost of biodiesel, and achieve the effect of reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
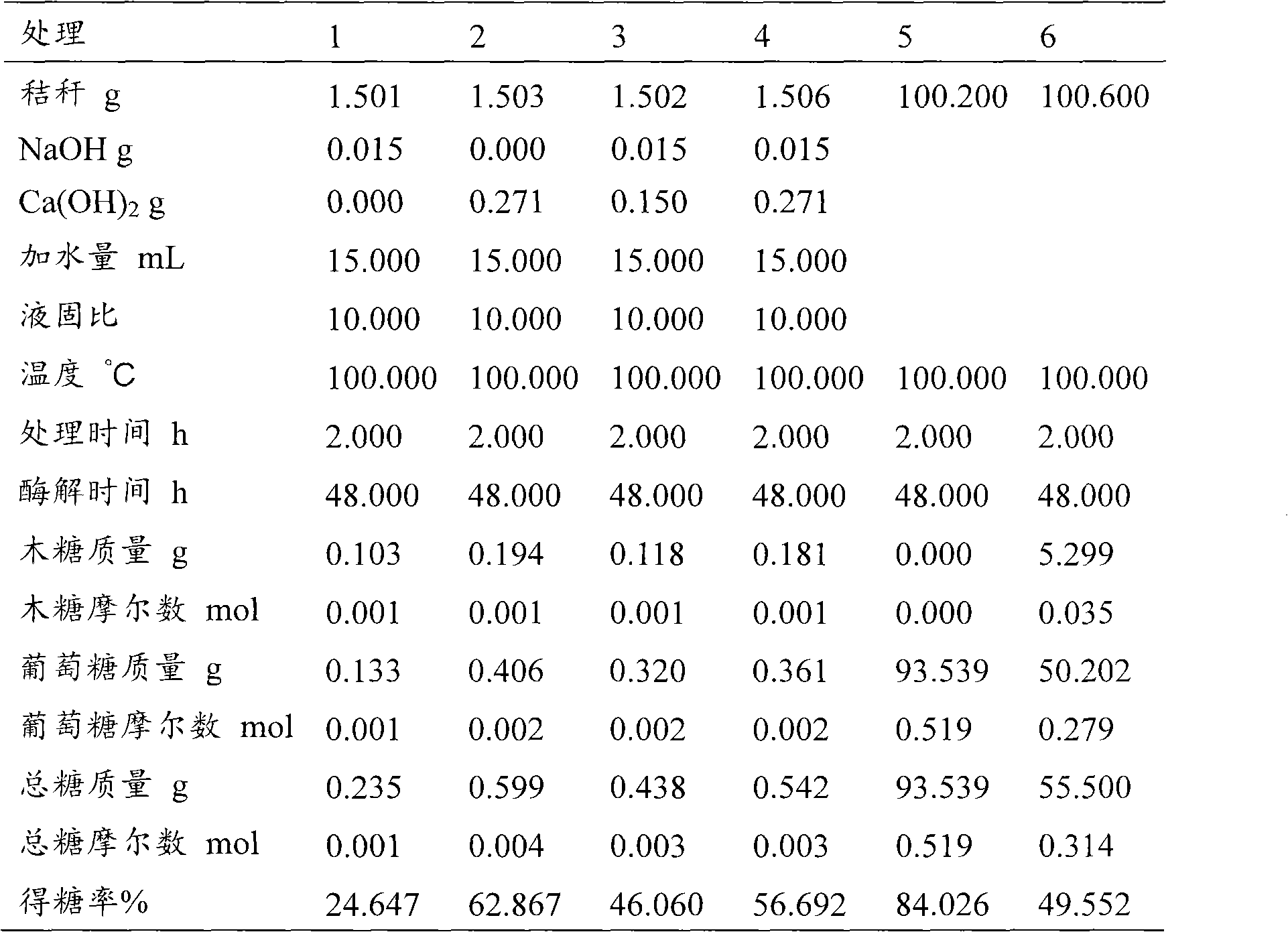
[0030] Embodiment 1: straw pretreatment experiment
[0031] 1. Roll the straw into small pieces and crush it into 40-mesh powder with a pulverizer.
[0032] 2. Weigh 1.5g straw powder into the sealed tube, add NaOH and Ca(OH) in proportion (mass ratio) 2 , and add water according to the solid-to-liquid ratio.
[0033] 3. Treat at 100°C for 2 hours.
[0034] 4. After cooling, adjust the pH to neutral with sulfuric acid, and filter it with a filter dry pan. After suction filtration, wash with water several times and discard the filtrate. Dry the pan and dry the treated straw powder at 80°C until constant weight.
[0035] 5. Weigh 100 mg of the treated straw powder into the enzymatic hydrolysis bottle, and add 2 mL of 0.05mol / L pH=5.47 Citric acid buffer. Add 25 U ctec (cellulase from Novozymes) to 1 g of solid, and enzymatically hydrolyze at 50°C for 24 hours. The blank control is 2mL 0.05mol / L pH=5.47 Citric acid buffer without adding substrate, only adding an equal amoun...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2: 5L fermentor fermentation Clostridium thermocellum
[0043] 1. According to the recipe "KH 2 PO 4 1.0g / L, K 2 HPO 4 (anhydrous) 6g / L, urea 17.8g / L, MgCl 2 ·6H 2 O 2.49g / L, CaCl 2 2H 2 O 135mg / L, FeSO 4 ·6H 2 O 5mg / L, Cysteine hydrochloride 2.0g / L, Resazurin 2.0mg / L, cellobiose 30.0g / L, Yeast extract 12.0g / L, Sodium citrate 2H 2 O 0.752g / L" to prepare fermentation medium (calcium, magnesium, iron salt mother solution added after sterilization), 115 ℃, 15min moist heat sterilization.
[0044] 2. After the sterilization is completed, nitrogen gas is continuously fed into the fermenter to remove the oxygen in the medium and the fermenter. After the medium changes from light blue or pink (the color of resazurin) to its own color, adjust the pH of the medium to 7.0, keep the tank temperature at 60°C, and add the required volume of JYT01 primary seed solution at the same time , stop aeration, stir and ferment at 80rpm.
[0045] 3. After about 48 ho...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3: CBP combined with Schizochytrium heterotrophic fermentation to produce biodiesel
[0047] Adopt above embodiment gained Clostridium thermocellum to produce sugar liquid (carbon source content 10%), add yeast extract 3% additionally, vitamin B1, 40mg / L; Vitamin B6, 20mg / L; Vitamin B12, 10mg / L; Sodium (vitamin H) 10mg / L. Fermentation was carried out under the following conditions: temperature 25°C, ventilation volume 1.0L min-1 L-1 (VVM), tank pressure 0.06MPa, stirring speed 200rpm. The pH is controlled to be 6.0, and the fermentation time is 96h.
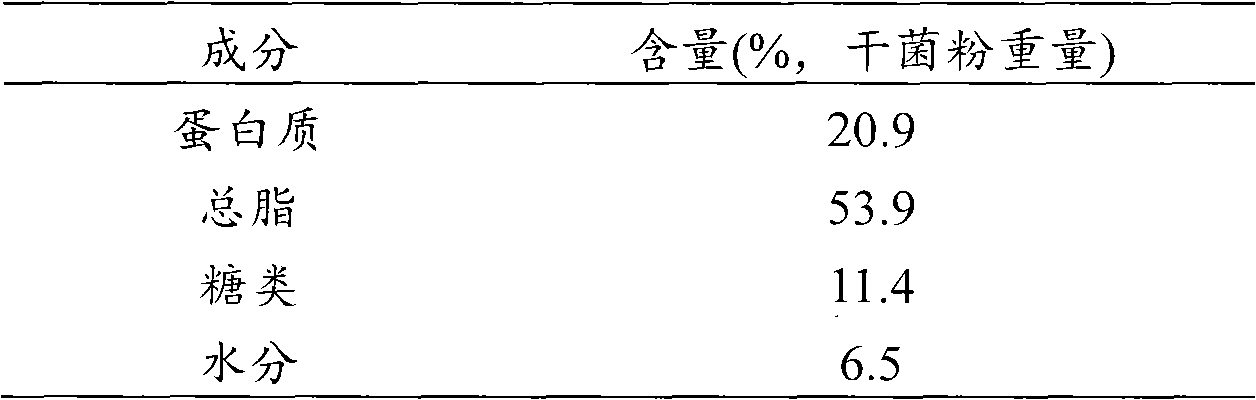
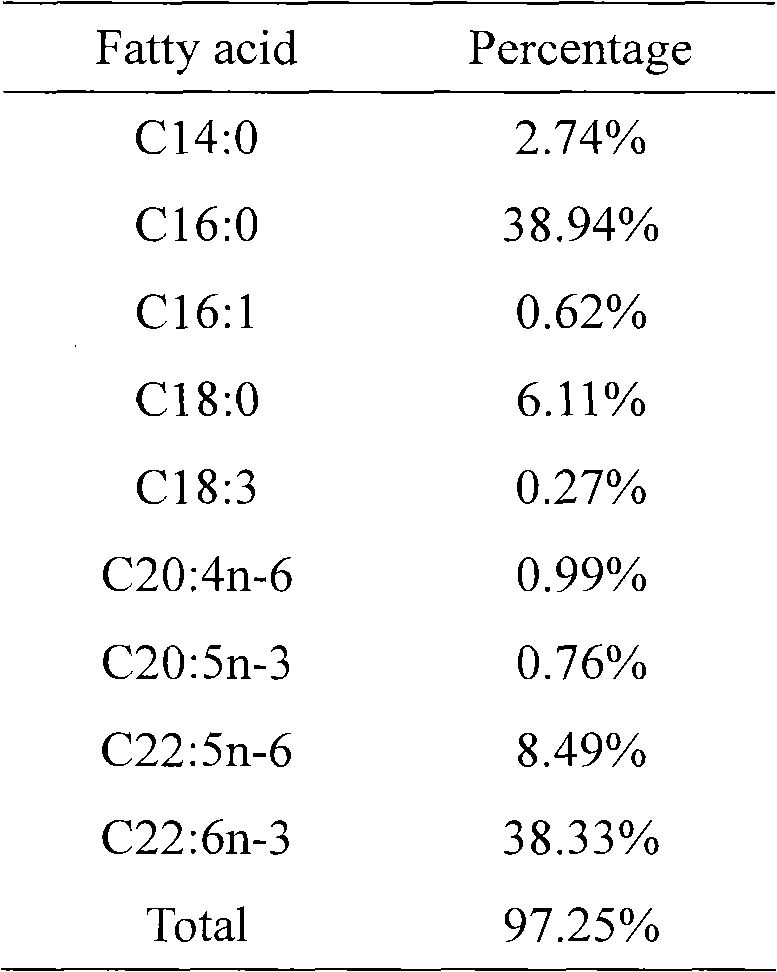
[0048] After the fermentation, the yield of Schizochytrium was 44.15g / L obtained from the 5L fermenter, the bio-oil was 23.8g / L, and the DHA content was 9g / L (Table 2, 3).
[0049] Table 2 Component analysis results of Schizochytrium sp.
[0050]
[0051] Table 3 Fatty acid analysis results of Schizochytrium fermented by CBP
[0052]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com