Method of reducing disulfide bond in photo-excitation protein to obtain free sulfydryl
A protein and disulfide bond technology, applied in the field of protein fixation and self-assembly, can solve the problems of destroying protein structure and activity, limiting protein application, complicated steps, etc., and achieving the effect of convenient specific fixation, convenient operation and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
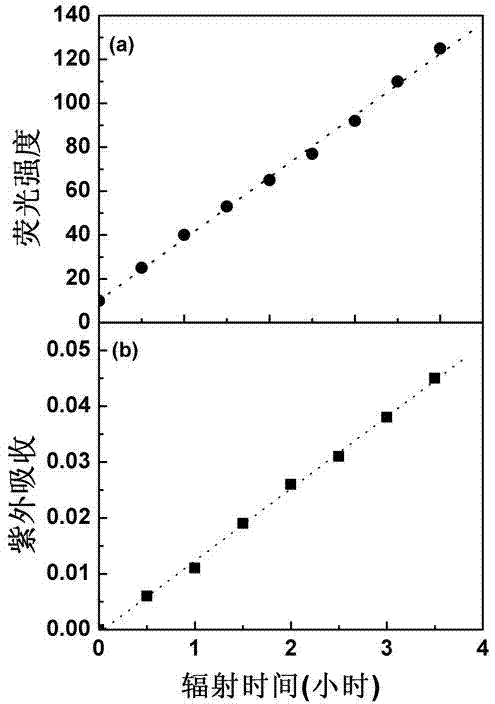
[0022] Photocutinase generates free sulfhydryl groups: Cutinase is a lipolytic enzyme capable of degrading cutin, similar to lipase, which has important industrial uses and can be used to remove oil stains. Prepare 0.1mM cutinase solution, pH 7.5, temperature 25°C, take 2ml and inhale into a quartz cuvette. Use 280-300nm ultraviolet light to irradiate the sample cell of the quartz cuvette, and control the distance of the light so that the light intensity is 0.1W / m 2 , every 30min, detect the strength of the fluorescent signal. Cutinase is a globulin composed of 214 amino acids, of which amino acid No. 69 is tryptophan (Trp69). Such as figure 2(a), In the native state, the fluorescence signal of cutinase tryptophan is quenched. After a certain period of ultraviolet radiation, the fluorescence signal is continuously enhanced. The main reason is that there is a pair of disulfide bonds (Cys31-Cys109) near tryptophan. In the natural state, there is electron and energy tran...
Embodiment 2
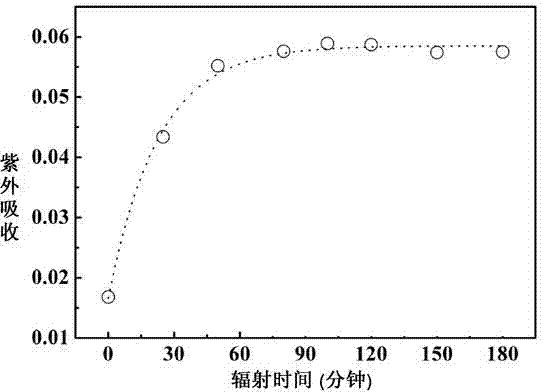
[0024] Illuminating lysozyme to generate free sulfhydryl groups: lysozyme is a glycoside hydrolase that can dissolve the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria, has a strong killing effect on bacteria, and can also be used to prevent food deterioration. Chemicals, baby food and scientific research have a wide range of applications. Prepare 0.01mM lysozyme solution with TrisHCl buffer (pH 7.8, temperature 25°C), take 2ml and inhale into a quartz cuvette. Use 270-300nm ultraviolet light to irradiate the sample cell of the quartz cuvette, control the light intensity, and after a certain period of time, detect whether there is sulfhydryl group generation by Ellman reagent. Such as image 3 As shown, it can be seen that lysozyme has many pairs of disulfide bonds and tryptophan close to each other. After ultraviolet light irradiation, the protein reacts with DTNB, and the product has ultraviolet absorption at 412nm, indicating that there is free sulfhydryl group formation, and with th...
Embodiment 3
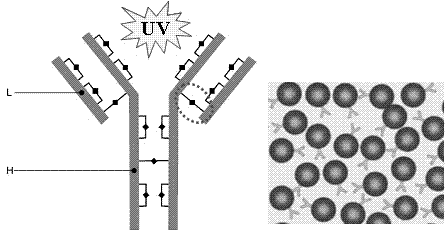
[0026] Combination of immunoglobulin G and gold nanoparticles under illumination: Immunoglobulin G is an important antibody protein, which is often combined with gold nanoparticles for precise positioning of cell surface and intracellular biomacromolecules. It is widely used in immunology, histology, fields of pathology. Such as Figure 4 As shown, the structure of immunoglobulin is a "Y" shape, and the upper "V" is used to recognize the antigen and determine the specificity of the antibody, which is called the Fab segment, and the rest of the carboxyl terminal is the Fc segment. There are more than a dozen pairs of disulfide bonds on immunoglobulins, all of which are close to aromatic amino acids, but most of them are buried inside the structure. Among them, the pair of disulfide bonds marked by a circle has a relatively large solvent exposure, and is prone to reduction when irradiated by ultraviolet light , generating free sulfhydryl groups. At room temperature of 25°C, pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com