Preparation and application of a kind of immobilized protease reagent
An immobilized enzyme and protease technology, applied in the preparation of immobilized protease reagents, can solve the problems of limiting enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency, inevitable enzymatic hydrolysis bias, affecting the identification coverage of proteins and peptides, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0113] Embodiment 1, the synthesis of the carrier material of immobilized protease
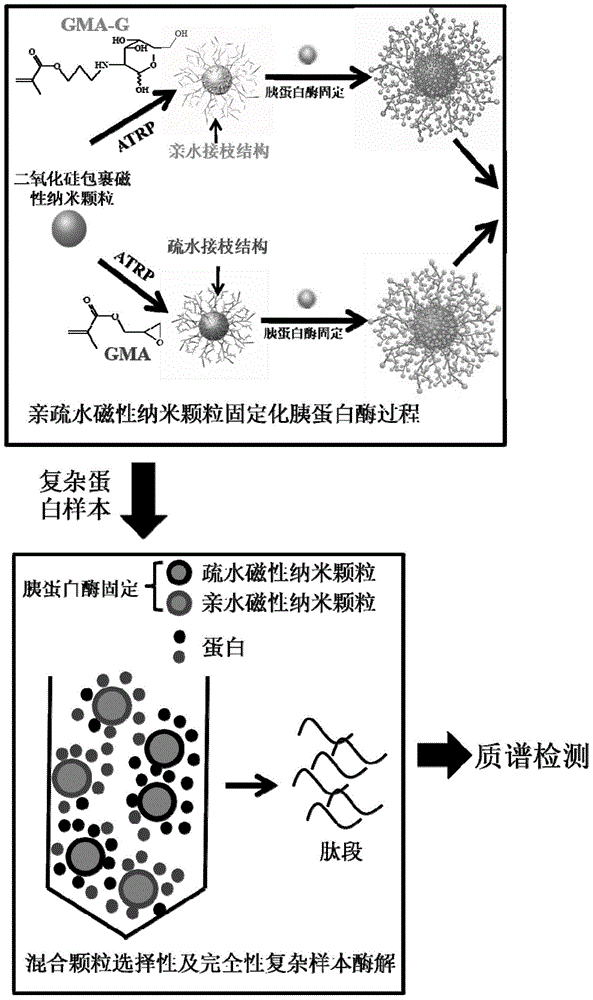
[0114] The technical scheme of preparing trypsin with hydrophilic and hydrophobic dual carriers by SI-ATRP method and the flow chart of enzymatic protein hydrolysis with dual carrier immobilized enzymes are as follows figure 1 shown.
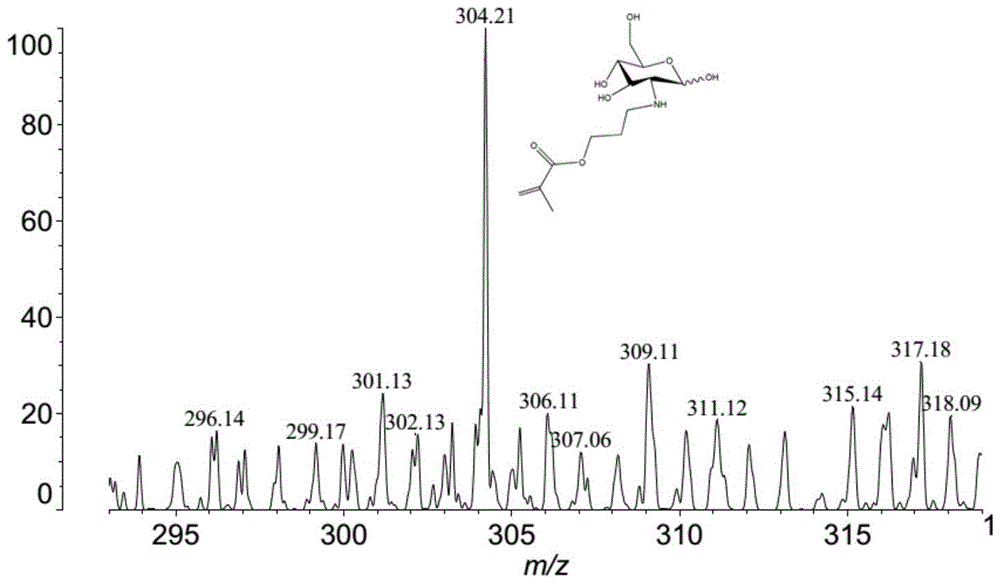
[0115] 1. Synthesis of SI-ATRP initiator
[0116] SI-ATRP initiator was synthesized by reacting 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane with 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide. One end of the initiator was a silane coupling agent bound to the surface of silica-wrapped magnetic nanoparticles, and the other was One end is an ATRP initiator. The specific steps are as follows: add 8mmol 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane and 10mmol triethylamine to 12.5ml tetrahydrofuran, mix and pass through nitrogen to deoxygenate while ice bathing for 30min to obtain a silane coupling agent, then add 10mmol2 -Bromoisobutyryl bromide (ATRP initiator) was slowly added dropwise to the mixture, stirred vig...
Embodiment 2
[0138] Embodiment 2, the immobilization of trypsin
[0139] 1. Aldehydization of Magnetic Nanoparticles
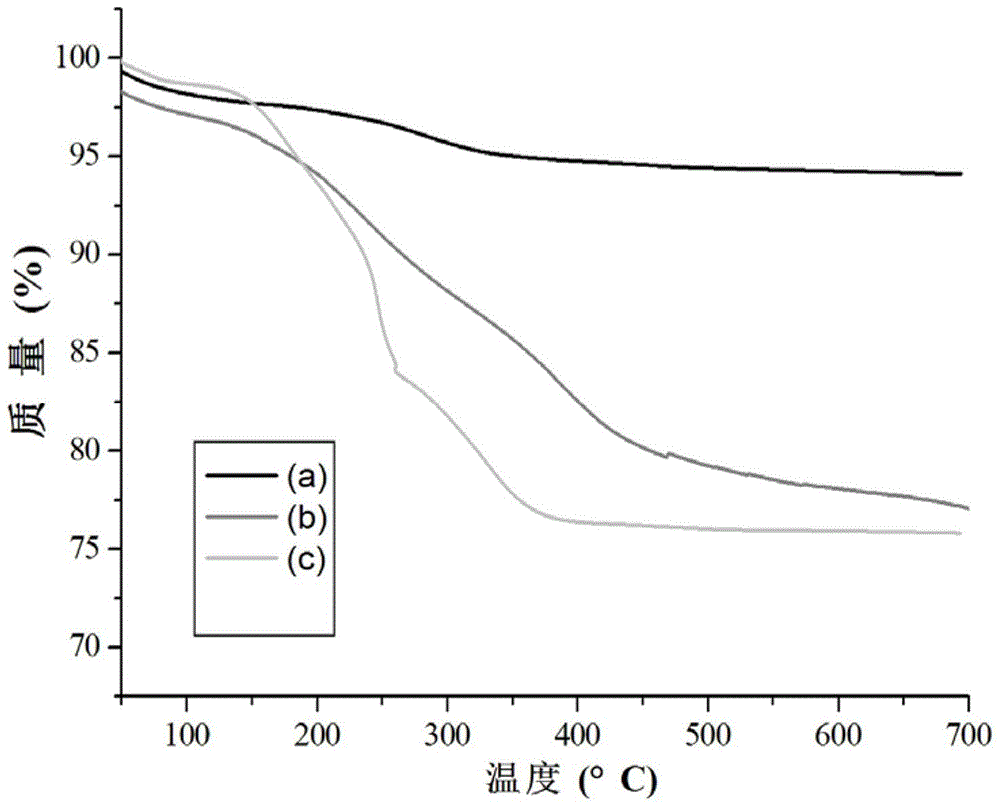
[0140] The aldehyde group functionalization of the polymer side chain of the magnetic nanoparticle modified by GMA-G polymer chain, the specific method is as follows: 10mM sodium periodate aqueous solution is mixed with the magnetic nanoparticle modified by GMA-G polymer chain, at 20 React at -30°C for 2 hours in the dark. After the reaction is completed, use 50% methanol aqueous solution to wash repeatedly to remove the remaining reactants.
[0141] The aldehyde group functionalization of the polymer side chain of the GMA polymer chain-modified magnetic nanoparticles, the specific method is as follows: mix the GMA polymer chain-modified magnetic nanoparticles with 0.2M dilute sulfuric acid, and react at room temperature in the dark for 2 Hour. After the reaction is completed, use 50% methanol aqueous solution to wash repeatedly to remove the remaining reactants.
[01...
Embodiment 3
[0146] Example 3. Functional Analysis of GMA Polymer Chain Modified Magnetic Particle Immobilized Enzyme (GMA-Trypsin) and GMA-G Polymer Chain Modified Magnetic Particle Immobilized Enzyme (GMA-G-Trypsin)
[0147] 1. Extraction of Yeast Whole Protein
[0148] (1) Whole protein extract: 50mM Tris-HCl (pH=8.0), 8M urea, 2mM EDTA.
[0149] (2) Add 10 μl of “cocktail” protease inhibitor (purchased from Roche, Germany) to 500 μl of whole protein extract, mix well, add to a test tube containing yeast, and ultrasonically disrupt the cells. Then centrifuge at 20,000 g for 20 minutes at 4°C to remove unbroken cells and debris, and the solution is yeast whole protein.
[0150] (3) Add 4-5 times the volume of cold acetone solution (pre-cooled at -20°C) to the whole yeast protein solution, place it at -20°C for more than 2 hours, then centrifuge at 12,000g at 4°C for 10 minutes, carefully absorb the supernatant, and keep the precipitate .
[0151] (4) Place the precipitate in a fume ho...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com