Aldehyde ketoreductase bacterial strain, aldehyde ketoreductase gene, vector, engineering bacteria and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and reductases, applied in genetic engineering, oxidoreductases, applications, etc., can solve the problems of low product value, difficult boride waste disposal, and high energy consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1 produces aldehyde and ketone reductase microbial screening
[0027] Enrichment medium (bean sprouts juice medium): fresh bean sprouts juice (fresh soybean sprouts, add water at 100g / L and boil for 30 minutes, filter the bean sprouts juice, replenish water to the initial volume) 100mL / L, glucose 50g / L, natural pH, Divide into 250mL shaker flasks, fill 50mL, and sterilize at 115°C for 30 minutes. Add sterile tert-butyl 6-cyano-(5R)-hydroxy-3-oxohexanoate 2 g / L. Solid medium: bean sprout juice medium, add 20g / L agar, natural pH.
[0028] Soil samples collected from all over the country were dispersed with normal saline in a certain proportion and then inoculated into the enrichment medium. Under the conditions of 30°C and 150 rpm, the shaker cultured for 24 hours. The enriched culture solution was diluted step by step, spread on a solid plate medium and cultured at 30°C until an observable single colony was formed. Pick a single colony and transfer it to a ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2 strain identification
[0039] Physiological and biochemical identification and 18S rDNA sequence analysis were performed on the strains with aldehyde and ketone reductase activity screened in Example 1.
[0040] Physiological and biochemical identification: Utilize Vitek 2 microbial automatic identification system to measure bacterial strain XP1461 and bacterial strain XP1462 to the identification result of 46 kinds of identification tests ( as table 1 , Table 2 Shown), through the Vitek 2 reader analysis metabolic fingerprint analysis, it is determined that the bacterial strain XP1461 belongs to the lactis species of the genus Kluyveromyces (kluyveromyces), with a homology of 96%, and the bacterial strain XP1462 belongs to the bailii species of the genus Zygosaccharomyces (Zygosaccharomyces). Origin 98%.
[0041] 18S rDNA sequence analysis: Using the extracted total DNA of strain XP1461 and strain XP1462 as templates, the designed primers: pITS1:5'-TC...
Embodiment 3
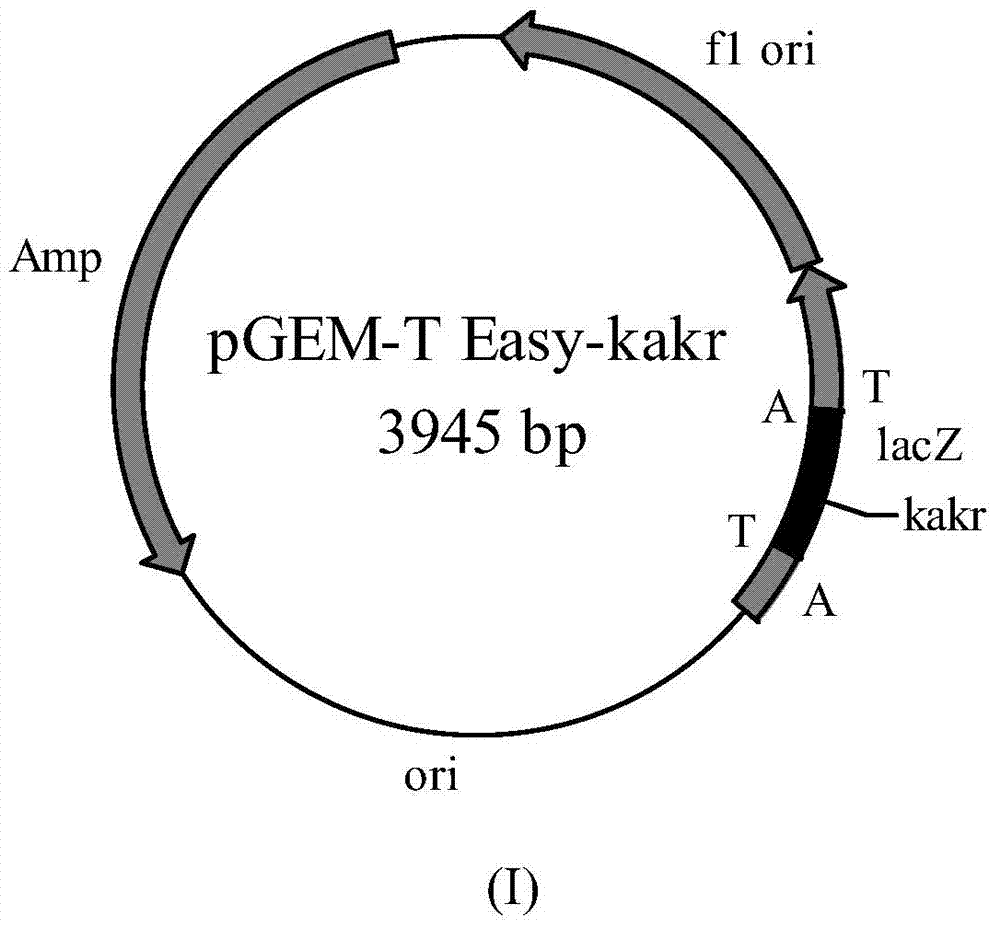
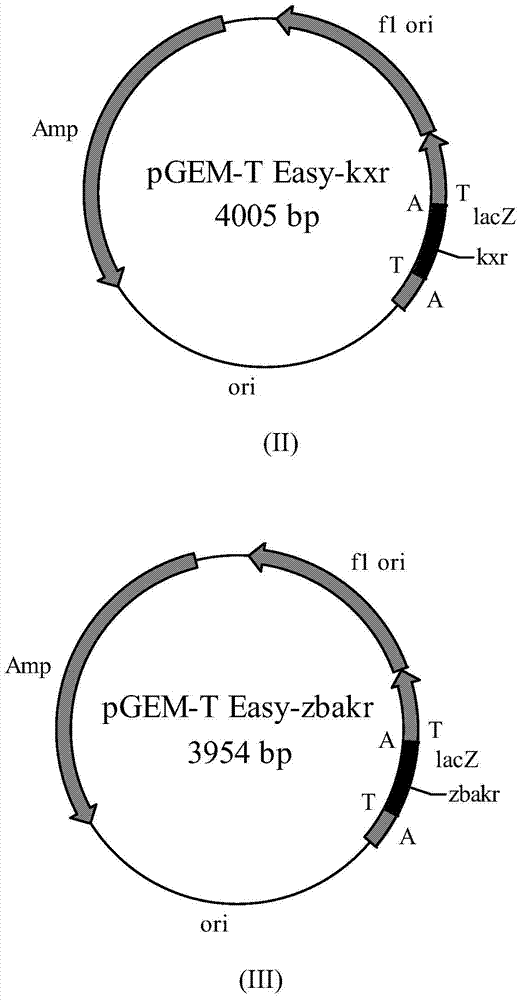
[0043] Example 3: Cloning of aldehyde and ketone reductase gene and construction of recombinant plasmid
[0044] (1) Cloning of the target gene
[0045] Kluyveromyces lactis (Kluyveromyces lactis) XP1461 ( Collection No. CCTCC M 2014380) and Bayer yeast (Zygosaccharomyces bailii) XP1462 ( Collection No. CCTCC M 2014381) total genomic DNA of the bacteria.
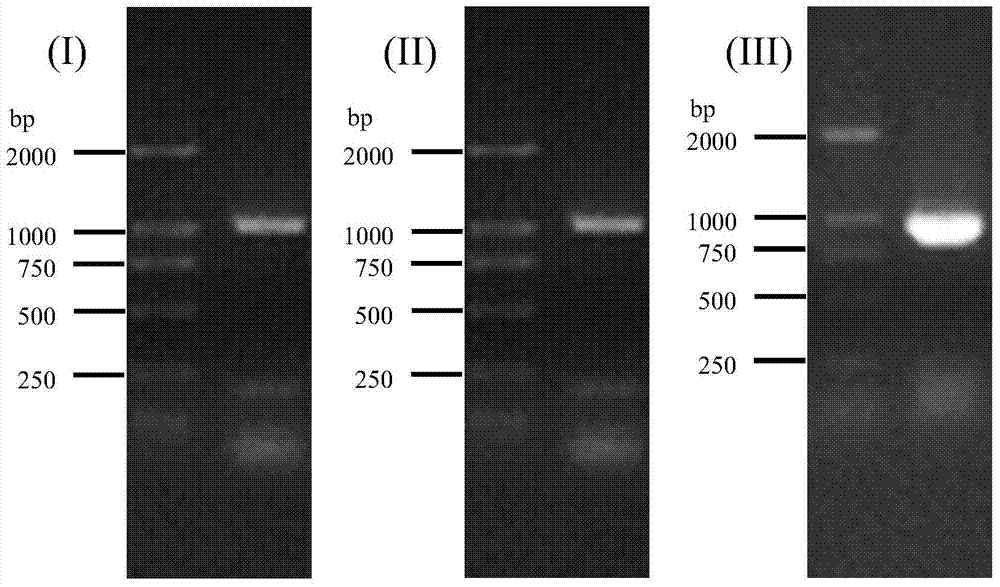
[0046] Using K.lactis M 2014380 genomic DNA as a template, through the upstream primer (primer 1): 5'- CATATG ACTACTCAAAAGTTCTTTACTT-3', downstream primer (primer 2): 5'- GCGGCCGC TCACTTCTGGGATTCAGAAT-3' was amplified by PCR to obtain amplified product 1. Take 10 μL of PCR amplification product 1 and use 0.9% agarose gel electrophoresis to detect, agarose gel electrophoresis picture See picture As shown in (I) in 1, a band appeared at around 1000bp;
[0047] Using K.lactis CCTCC M 2014380 genomic DNA as a template, through the upstream primer (primer 3): 5'- AGATCT ATGACGTACTTAGCAGAAACAG-3', downstream primer ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com