Method for preparing lithium battery electrode materials LiFePO4 and Li4Ti5O12 from vanadium extraction slag
A technology for extracting vanadium waste slag and lithium iron phosphate, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, titanium compounds, etc., can solve the problems of low utilization rate of Ti resources, low added value, hidden dangers of disasters, etc., and achieve added value utilization. High rate, improve electrochemical performance, avoid environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
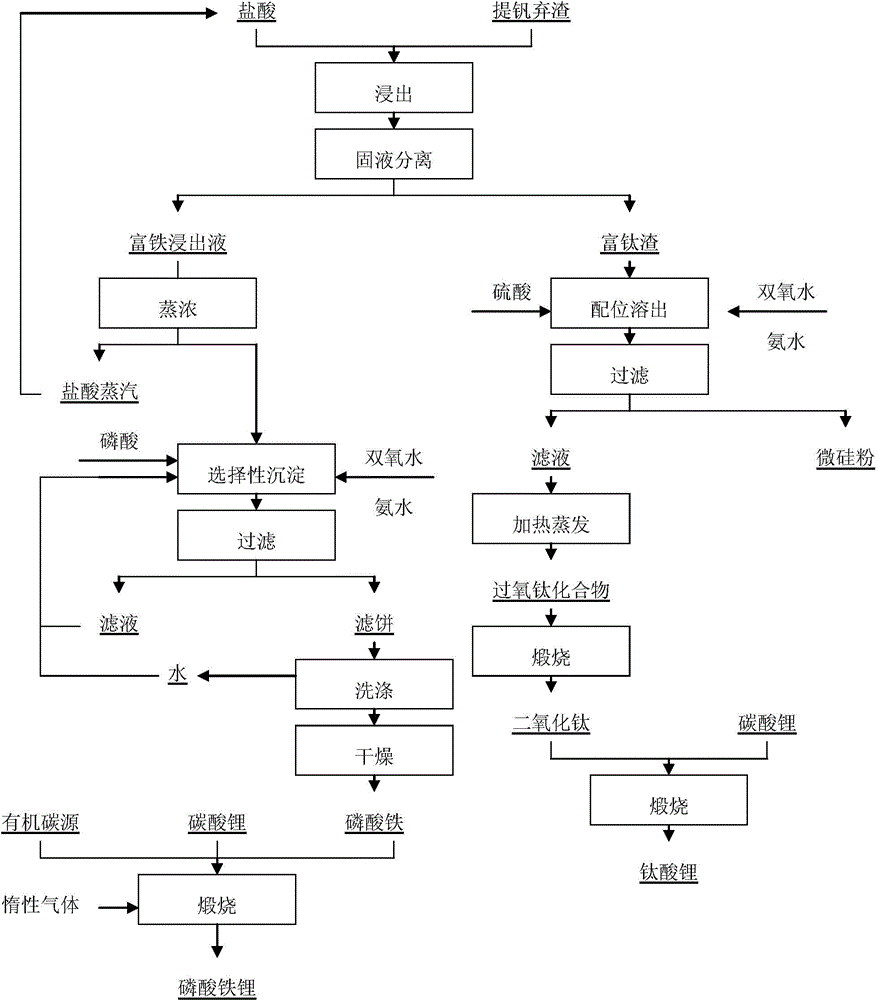
[0057] (2) Preparation of lithium iron phosphate precursor - iron phosphate: using leachate as raw material, using H 3 PO 4 Preparation of ferric phosphate by selective precipitation. A certain molar proportion of H 3 PO 4 Add the solution into the effluent, stir vigorously, add a certain amount of hydrogen peroxide to oxidize Fe(II) to Fe(III), and finally adjust the pH value with ammonia water, react at constant temperature, filter the obtained precipitate, wash and dry, and obtain phosphoric acid Iron powder.
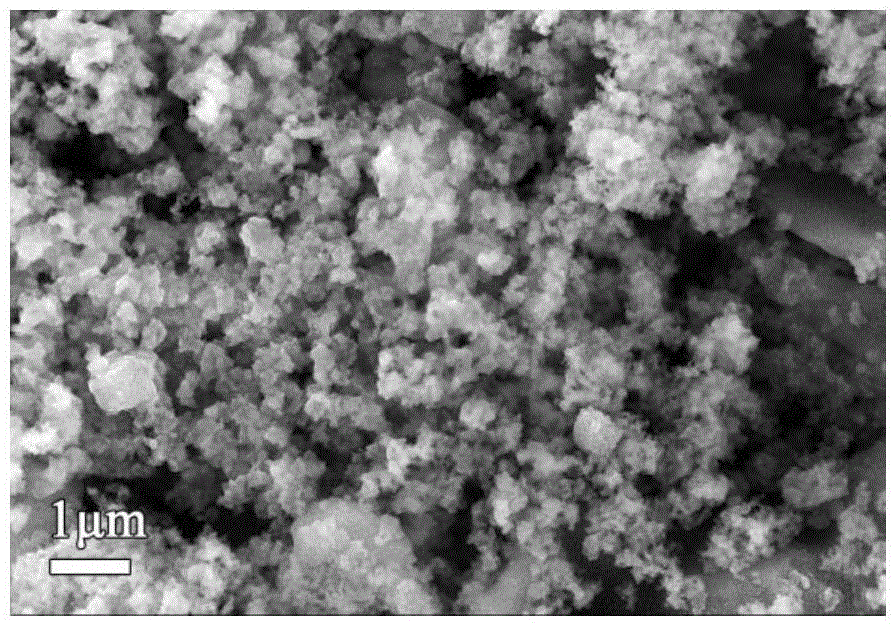
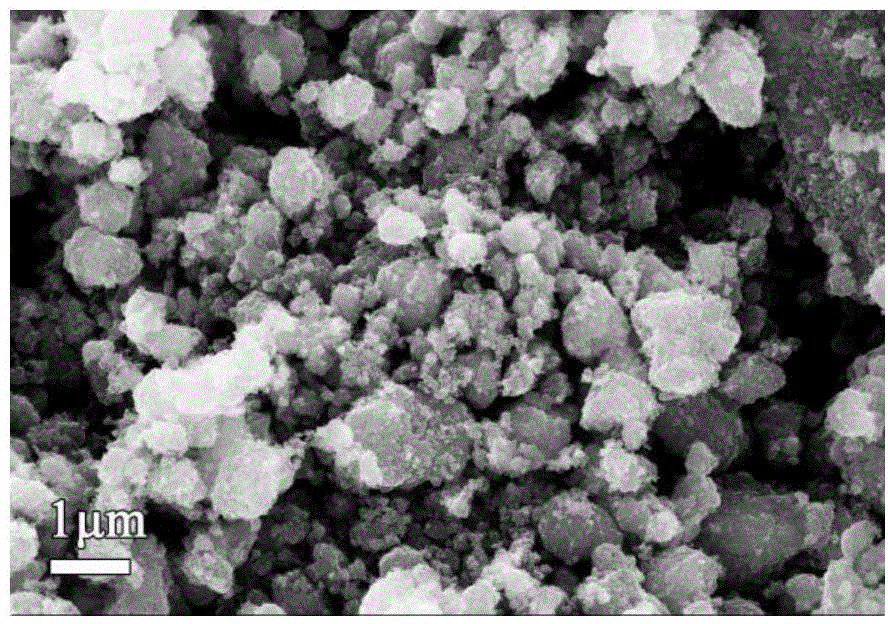
[0058] (3) Preparation of lithium iron phosphate: using iron phosphate as raw material, LiFePO is synthesized by carbothermal reduction method 4 / C Lithium secondary battery cathode material. Weigh Li according to the stoichiometric ratio 2 CO 3 , precursors and organic carbon sources, mixed evenly, calcined under the protection of inert gas in the atmosphere furnace, and taken out after cooling to obtain LiFePO with a small amount of metal doping 4 / C cathod...
Embodiment 1
[0065] (1) Separation of iron and titanium:
[0066] After the vanadium extraction waste slag is mechanically crushed, the vanadium extraction waste slag is leached with hydrochloric acid with a mass concentration of 15% under normal pressure, the mass ratio of hydrochloric acid to vanadium extraction waste slag is 2.125, the leaching temperature is 70°C, and the leaching time is 2h; the leaching is completed Afterwards, the resulting slurry was cooled to room temperature, and filtered to obtain iron-rich leaching filtrate and titanium-rich leaching filter residue.
[0067] (2) Preparation of lithium iron phosphate precursor - iron phosphate:
[0068] The free HCl in the leaching solution obtained in step (1) is subjected to acid steam recovery treatment to obtain a concentrated leaching solution, which is prepared into an iron-rich leaching solution with a molar concentration of 0.265. According to the Fe / P molar ratio of 0.75, phosphoric acid H 3 PO 4 Add it to the iron-r...
Embodiment 2
[0077] (1) Separation of iron and titanium:
[0078] After the vanadium extraction waste slag is mechanically crushed, the vanadium extraction waste slag is leached under normal pressure with hydrochloric acid with a mass concentration of 20%, the mass ratio of hydrochloric acid to vanadium extraction waste slag is 1.75, the leaching temperature is 90°C, and the leaching time is 5h; the leaching is completed Afterwards, the resulting slurry was cooled to room temperature, and filtered to obtain iron-rich leaching filtrate and titanium-rich leaching filter residue.
[0079] (2) Preparation of lithium iron phosphate precursor - iron phosphate:
[0080] The free HCl in the leaching solution obtained in step (1) is subjected to recovery treatment by steaming acid to obtain a concentrated leaching solution, which is prepared into an iron-rich leaching solution with a molar concentration of 0.528. According to the Fe / P molar ratio of 0.87, phosphoric acid H 3 PO 4 Add it to the i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com