Method for digesting manganese in manganese oxide ore through reduction with nitrosobacteria and dissolution and dilution with dilute acid
A technology of nitrosifying bacteria and manganese dioxide ore, which is applied in photography technology, instruments, photography auxiliary technology, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome purification and impurity removal process of leachate, increased cost, etc., and solve the problem of harmless treatment , Realize recycling and eliminate high iron/sulfur-based impurities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
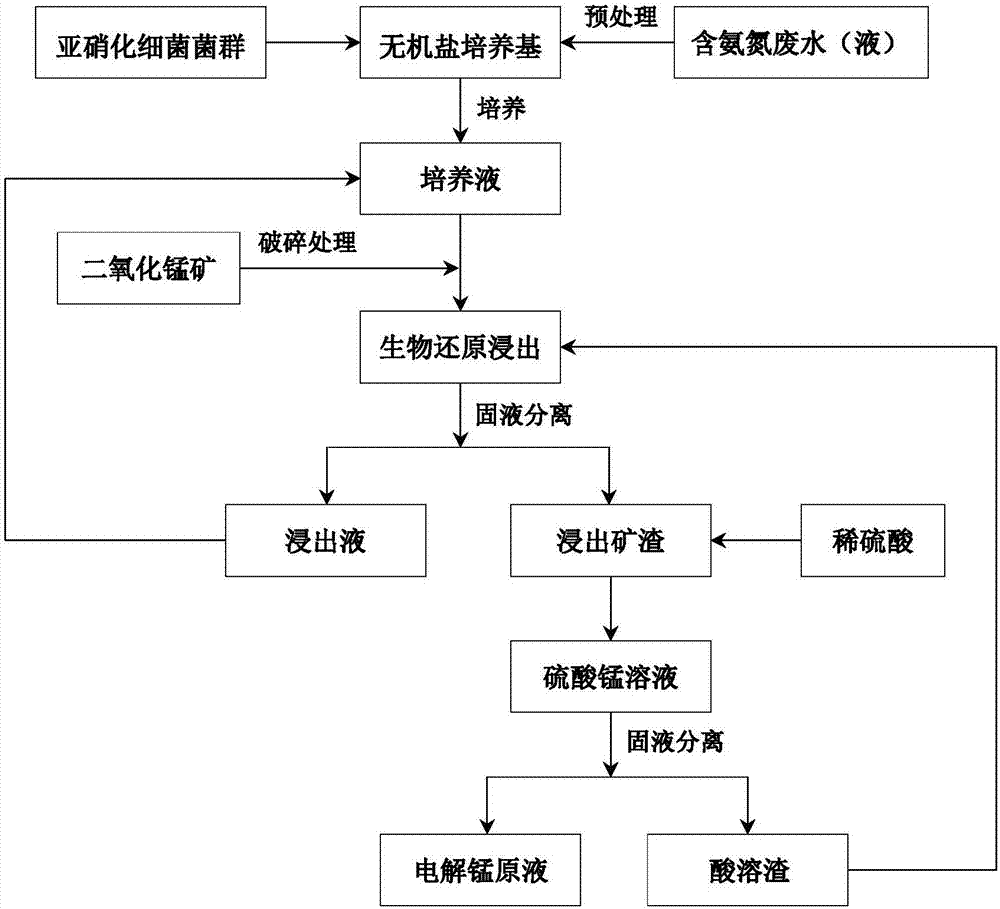
[0022] Nitrosifying Bacteria Biometallurgy Using Waste Electrolyzed Manganese Anolyte as Nitrogen Source and Energy
[0023] (1) Low-grade granular manganese dioxide ore is dried at 105°C, crushed, and ground, and then passed through a 250-mesh sieve to obtain manganese dioxide ore powder with a particle size of less than 58 microns. Collect the spent electrolytic manganese anolyte and let it stand at room temperature for 12 hours, then take the supernatant for later use.
[0024] (2) The cultivation of nitrosative bacteria was carried out in a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask. Based on 100ml of culture medium, 75ml of inorganic salt culture medium (disodium hydrogen phosphate 0.25g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.75g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.03g / L, calcium carbonate 5g / L), 5ml electrolytic manganese waste Anolyte supernatant (ammonia nitrogen 20.38g / L), 20ml nitrosative bacteria flora seed solution. With 2mol / L NaOH solution or H 2 SO 4 The solution adjusted the init...
Embodiment example 2
[0027] Biometallurgy of Nitrosifying Bacteria Using Waste Ammonia as Nitrogen Source and Energy
[0028] (1) Low-grade granular manganese dioxide ore is dried at 105°C, crushed, and ground, and then passed through a 250-mesh sieve to obtain manganese dioxide ore powder with a particle size of less than 58 microns. Collect coking plant waste ammonia water and use 0.5mol / L H 2 SO 4 The pH of the solution was adjusted to 6.0.
[0029] (2) The cultivation of nitrosative bacteria was carried out in a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask. Based on 100ml of culture medium, 70ml of inorganic salt culture medium (disodium hydrogen phosphate 0.25g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.75g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.03g / L, manganese sulfate tetrahydrate 0.01g / L, calcium carbonate 5g / L), 10ml waste ammonia water (ammonia nitrogen concentration 7.0g / L), 20ml nitrosative bacteria flora seed solution. With 2mol / L NaOH solution or H 2 SO 4 The solution adjusted the initial pH of the culture me...
example example 3
[0032] Nitrosifying Bacteria Biometallurgy Using Ammonium Bicarbonate Waste Liquid as Nitrogen Source and Energy
[0033] (1) Low-grade granular manganese dioxide ore is dried at 105°C, crushed, and ground, and then passed through a 250-mesh sieve to obtain manganese dioxide ore powder with a particle size of less than 58 microns. Collect the ammonium bicarbonate waste liquid from the fertilizer plant for future use.
[0034] (2) The cultivation of nitrosative bacteria was carried out in a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask. Based on 100ml of culture medium, 40ml of inorganic salt culture medium (disodium hydrogen phosphate 0.25g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.75g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.03g / L, manganese sulfate tetrahydrate 0.01g / L, calcium carbonate 5g / L), 40ml ammonium bicarbonate waste liquid (ammonia nitrogen concentration 1.2g / L), 20ml nitrosative bacteria flora seed liquid. With 2mol / L NaOH solution or H 2 SO 4 The solution adjusted the initial pH of the cultur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com