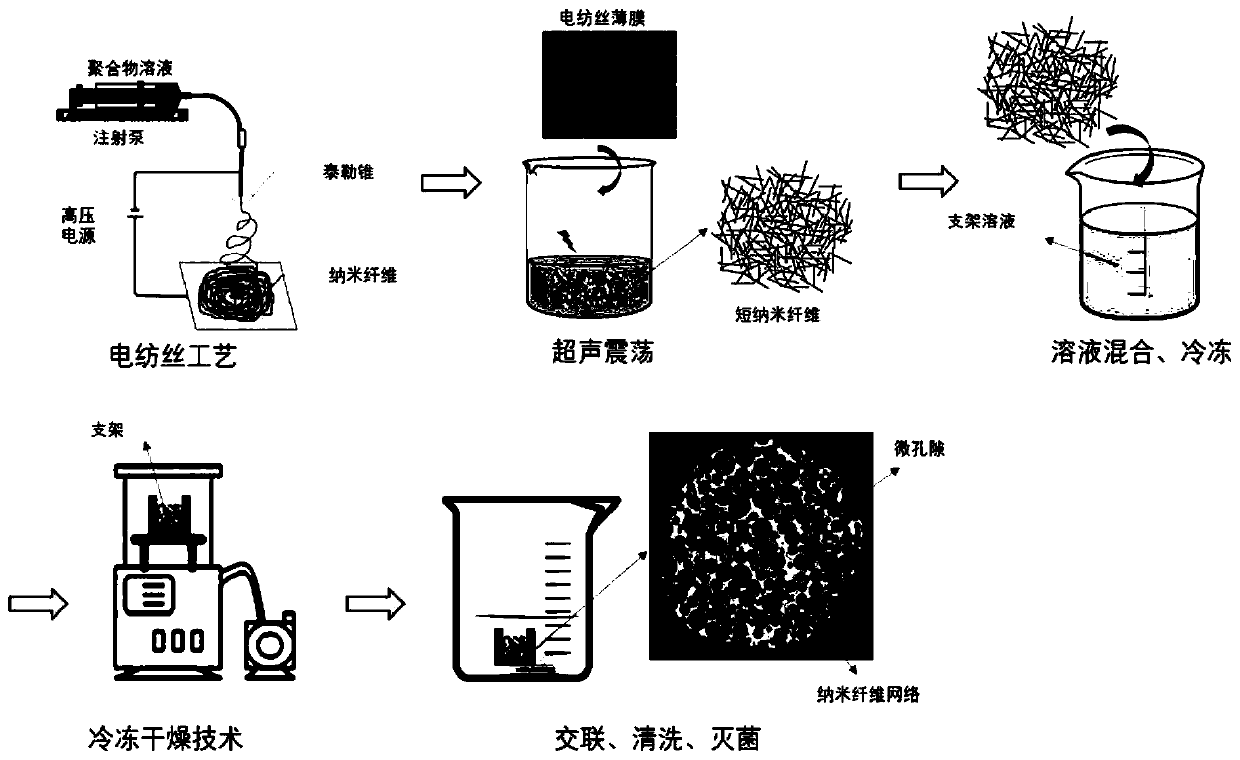
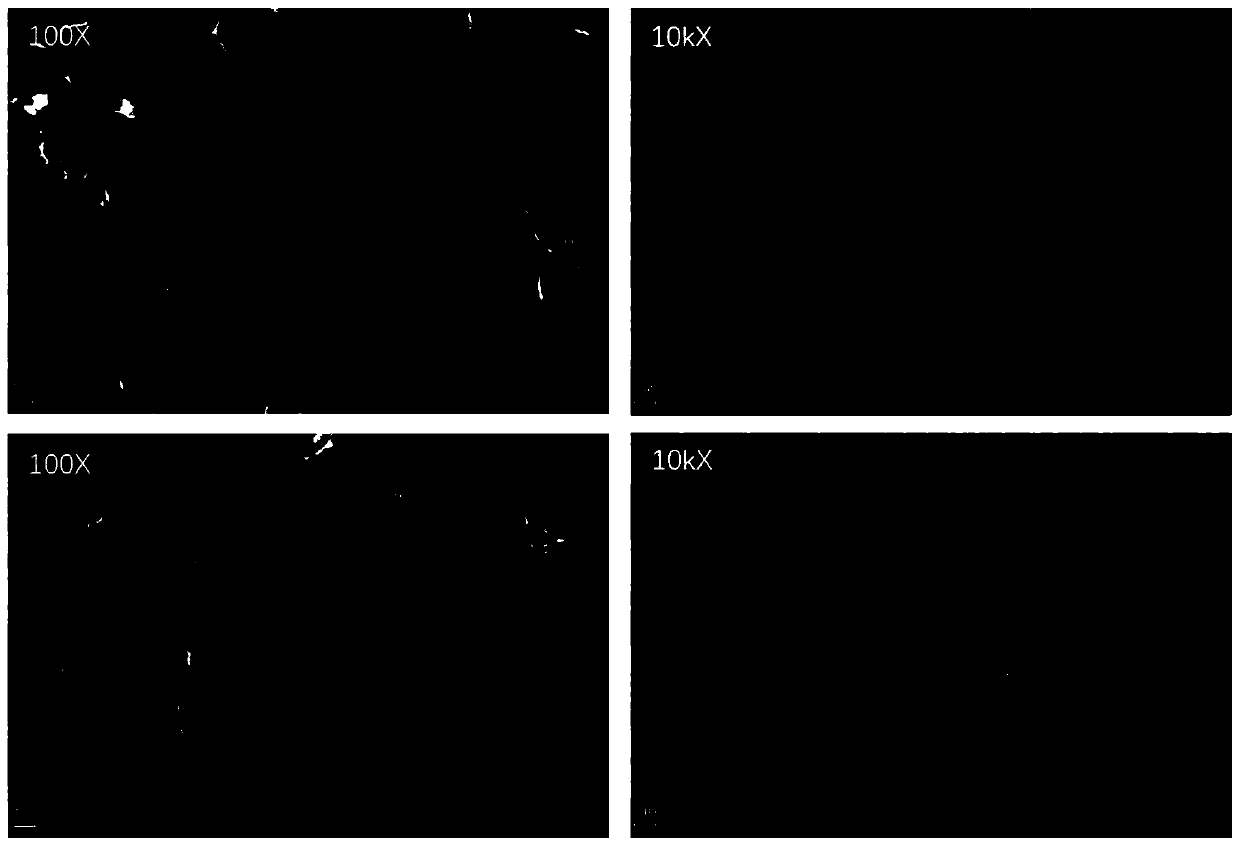
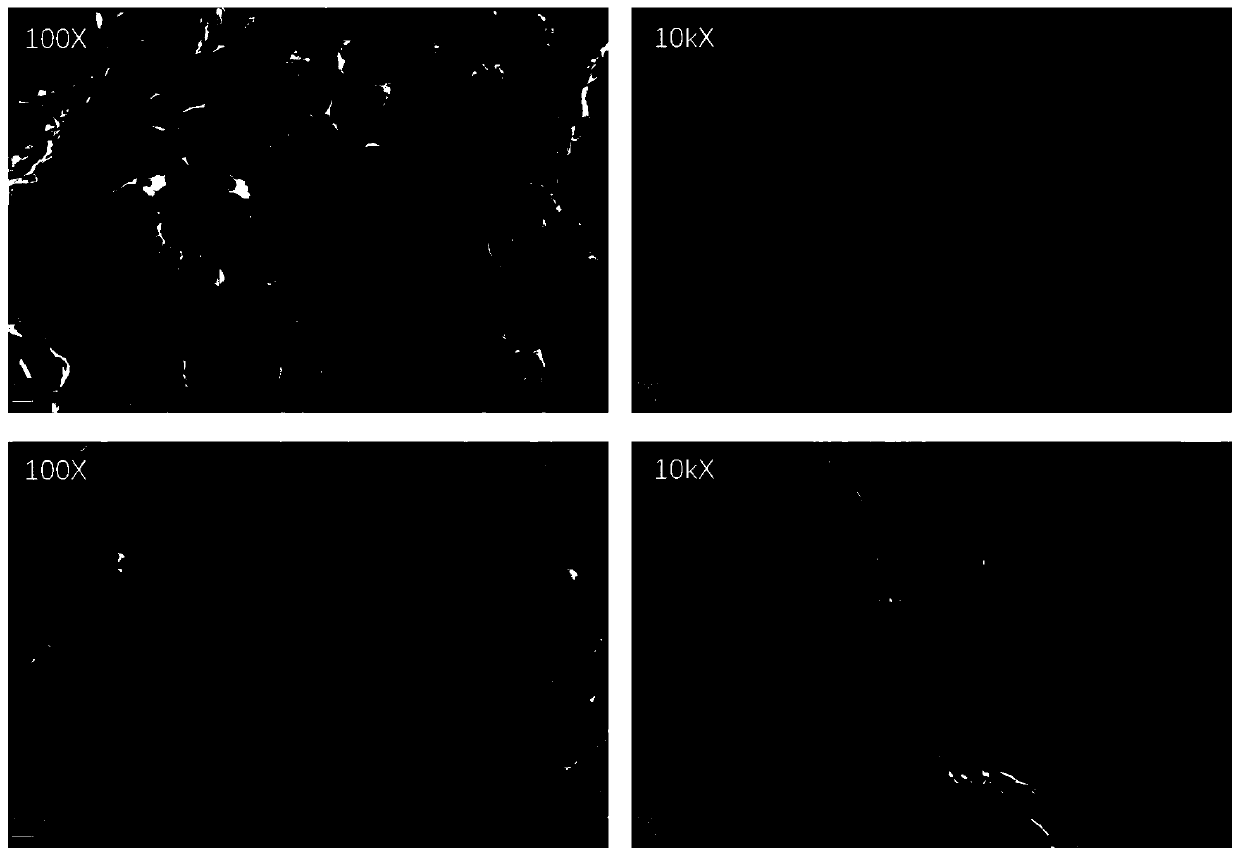
A biomimetic tissue engineering scaffold containing micropores and nanofiber composite structure and preparation method thereof
A technology for tissue engineering scaffolds and nanofibers, which can be used in fiber processing, tissue regeneration, and pharmaceutical formulations. It can solve the problems of small pores, difficult cells, and poor mechanical properties of scaffolds, and achieve the effect of promoting cell adhesion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1: Preparation of biomimetic tissue engineering scaffolds with micropores and nanofiber networks
[0050] Dissolve gelatin (15k~25kDa) in PBS buffer solution to prepare gelatin solution with a concentration of 0.01g / mL; dissolve sodium alginate in PBS buffer solution to prepare alginic acid with a concentration of 0.01g / mL Sodium solution; the above two solutions are prepared into a uniform, bubble-free, precipitation-free mixed solution, that is, a gelatin-sodium alginate mixed solution, the mass ratio of gelatin to sodium alginate is 1:1, and the concentration of gelatin is 0.005g / mL, the concentration of sodium alginate was 0.005g / mL.
[0051] Type I rat tail (Collagen, sigma) collagen was dissolved in 1% acetic acid solution to prepare a collagen solution with a concentration of 0.08 g / mL, cross-linked with 0.5 wt% genipin solution, and then dissolved in hexafluoroiso In propanol (HFIP), collagen fibers (265±83 nm in diameter) were prepared by electrospinn...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2: Preparation of biomimetic tissue engineering scaffolds with micropores and nanofiber networks
[0055] Rat tail collagen type I (SIGMA company, product number C7661) was dissolved in 1.0wt% acetic acid solution to prepare a collagen solution with a mass fraction of 0.01 g / mL; chitosan was dissolved in 1.0wt% acetic acid solution to prepare A chitosan solution with a mass fraction of 0.01 g / mL was prepared; the above two solutions were prepared into a uniform, bubble-free, and precipitation-free mixed solution, that is, a collagen-chitosan solution, and the mass ratio of collagen to chitosan was 1 : 1, the concentration of collagen is 0.005g / mL, and the concentration of chitosan is 0.005g / mL.
[0056] Polycaprolactone (PCL) was dissolved in hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) to prepare a PCL solution of 0.1 g / mL, and an electrospinning device was used to prepare PCL fibers (2.0 ± 0.5 μm in diameter), in which the syringe extruded The speed was 0.8 ml / h, the voltage...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3: Preparation of biomimetic tissue engineering scaffolds with micropores and nanofiber networks
[0060] Dissolve silk fibroin (silk fiber) in 1.0wt% acetic acid solution to prepare a silk fibroin solution with a mass fraction of 0.005g / mL; dissolve chitosan in 1.0wt% acetic acid solution to prepare a mass fraction of 0.015g / mL chitosan solution; the above two solutions were prepared into a uniform, bubble-free, and precipitation-free mixed solution, namely silk fibroin-chitosan solution, and the mass ratio of silk fibroin to chitosan was 3 : 1, the concentration of silk fibroin is 0.005g / mL, and the concentration of chitosan is 0.015g / mL.
[0061] Dissolve poly-D,L-lactide (PDLLA) in chloroform to prepare 0.15g / mL PDLLA solution, and use electrospinning equipment to prepare PDLLA fibers (5.0±2.5μm in diameter), in which the syringe extrusion speed It was 1.6ml / h, the voltage was 20kV, and the collecting device was about 15cm away from the needle tip. The col...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com