Cellulose nanocrystal and preparation method thereof based on oxidation reduction system
A cellulose and nanocrystal technology, applied in the field of nanomaterials and their preparation, can solve the problems of complex and harsh preparation process of Tempo reagent oxidation method, unsuitable for industrialized large-scale production, expensive Tempo reagent, etc., so as to save preparation cost and reduce The effect of preparing energy consumption and shortening the total time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
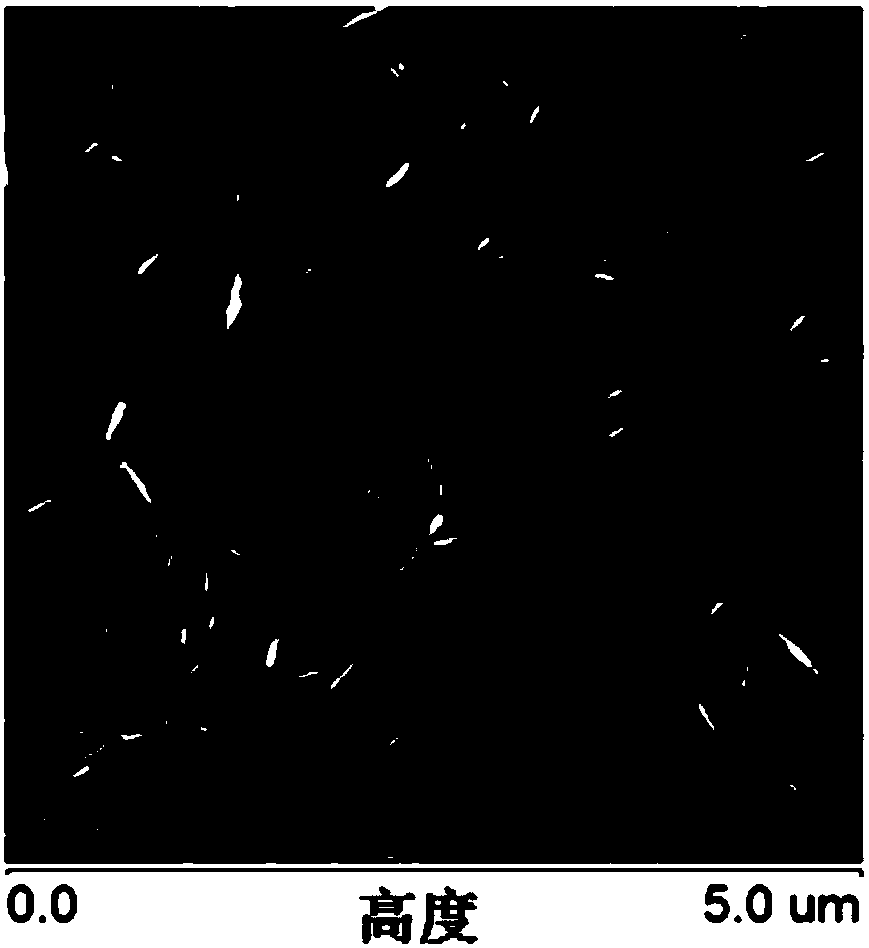
[0048] Soak and swell 5 g of pulp cellulose with 250 mL of 4% sodium hydroxide solution for 24 hours, then crush it into cotton wool with a mixer, wash it with deionized water until the pH of the pulp cellulose is the same as that of deionized water, and then dry it; in this step The sequence of swelling and crushing has no significant effect on the results, it can be swollen first and then crushed, or crushed first and then swelled;
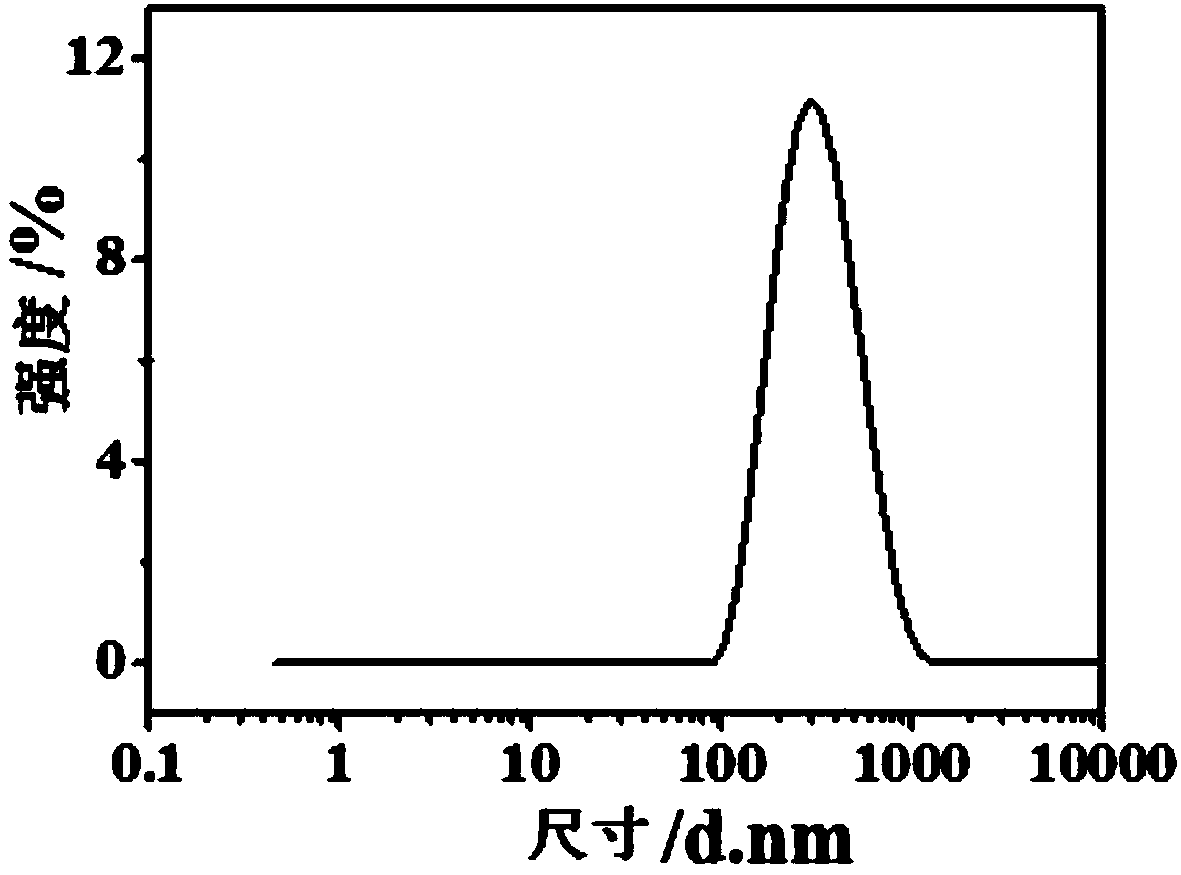
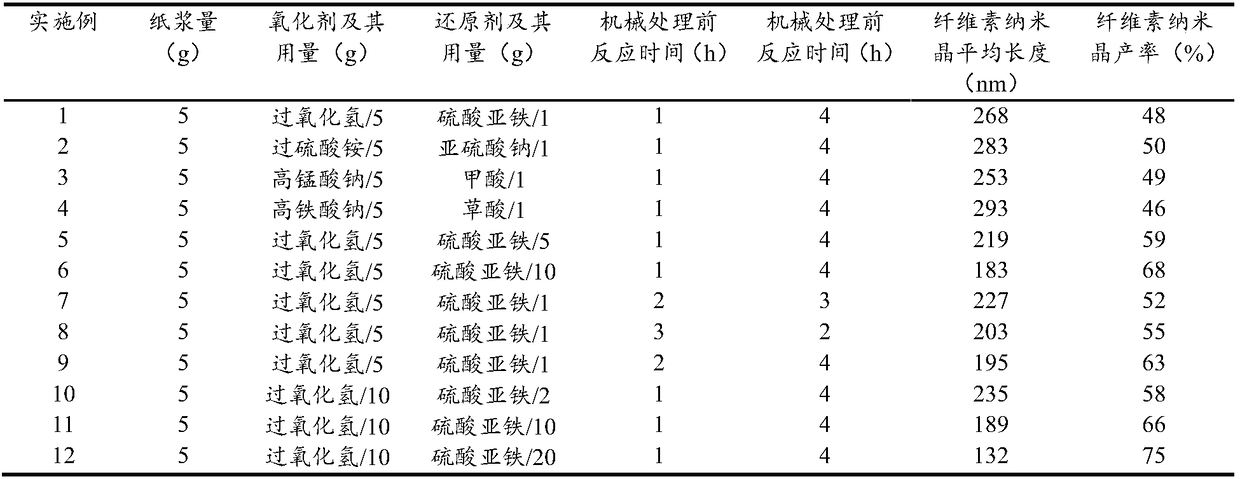
[0049] Disperse the pretreated cellulose raw material in 300mL of deionized water, add 5g of hydrogen peroxide and 1g of ferrous sulfate, stir at 60°C for 1h, then perform mechanical disintegration with a cell crusher at 49% power for 20min, and then Continue to react at 60°C for 4h to stop the reaction, and the total reaction time is 5h. After the reaction, use a high-speed centrifuge to centrifuge the cellulose hydrolyzate at a speed of 8000rpm / min for 10 minutes, then take the precipitate and wash it repeatedly with deionized water and centri...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The oxidizing agent used is ammonium persulfate, the reducing agent used is sodium sulfite, and all other conditions (such as: raw material type, dosage and process flow, etc.) are the same as in Example 1 to obtain a stable cellulose nanocrystal suspension. The average crystal length is about 283nm, the average diameter is 19nm, the yield is 50%, and the PDI is 0.3.
[0054] In addition, the oxidizing agent ammonium persulfate in this embodiment can not only be matched with sodium sulfite, but also can be matched with reducing agents such as formic acid, succinic acid, ethanol, methanol, sodium hydride, sodium borohydride, etc. to obtain cellulose nanocrystals. The combination of sodium sulfite works best.
Embodiment 3
[0056] The oxidizing agent used is sodium permanganate, the reducing agent used is formic acid, and all the other conditions (such as: raw material type, consumption and process flow, etc.) are the same as in Example 1 to obtain a stable cellulose nanocrystal suspension. The average length of the nanocrystals is about 253nm, the average diameter is 18nm, the yield is 49%, and the PDI is 0.3.
[0057] In addition, the oxidizing agent sodium permanganate in this example can be matched not only with formic acid, but also with reducing agents such as oxalic acid, succinic acid, ferrous sulfate, methanol, sodium hydride, and sodium borohydride to obtain cellulose nanocrystals. , which works best with formic acid.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com