Identification method of plasma membrane protein interactions based on chemical cross-linking mass spectrometry analysis
A technology of chemical cross-linking and identification methods, applied in scientific instruments, analytical materials, material analysis by electromagnetic means, etc. and other problems, to achieve the effect of efficient identification, short time-consuming and efficient processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Interaction information identification of HeLa cytoplasmic membrane proteins
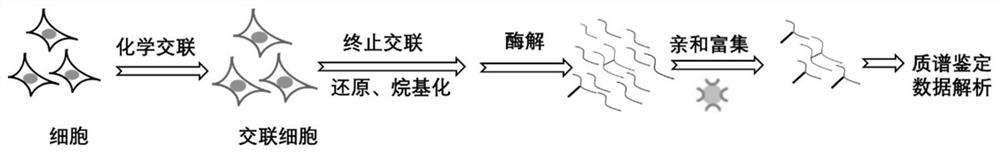
[0031] The experimental procedure is as figure 1 shown:
[0032] (1) Acquisition of cells: The HeLa cells in the culture dish were digested with trypsin at 37°C for 2 min, washed three times with 1х phosphate buffer pre-cooled at 4°C, and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C.
[0033] (2) Chemical cross-linking reaction: count the obtained cells, 1х10 7 Cells were added 1mL 1х phosphate buffer (pH8.0) + 1% lysine-specific enrichment impermeable membrane crosslinker (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide), the initial concentration of crosslinker was 10mM, organic Phase (dimethyl sulfoxide): water phase = 1:99, room temperature, reaction for 1 h. Centrifuge at 3000rpm, 5min, 4°C, and remove the supernatant.
[0034] (3) Reduction and alkylation: Add the same volume of ammonium bicarbonate with a final concentration of 50 mM to terminate the cross-linking, and at the same time, it contains 50...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Interaction-informative identification of Jurkat cytoplasmic membrane proteins
[0044] (1) Acquisition of cells: The cultured Jurkat cells were washed three times with 1х phosphate buffer solution pre-cooled at 4°C, and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C.
[0045] (2) Chemical cross-linking reaction: count the obtained cells, 1х10 8 Cells were added with 1mL 1х phosphate buffer (pH7.4) + 1% lysine-specific membrane-impermeable cross-linking agent (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide), the initial concentration of cross-linking agent was 20 mM, and the organic phase (dimethyl sulfoxide) was added. sulfoxide): water phase volume ratio = 1:99, room temperature, reaction for 1 h. Centrifuge at 3000rpm, 5min, 4°C, and remove the supernatant.
[0046] (3) Reduction and alkylation: Add the same volume of ammonium bicarbonate with a final concentration of 100 mM to terminate the cross-linking, and at the same time, it contains 25 mM tris(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine hydrochlo...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Interaction-informative identification of Escherichia coli plasma membrane proteins
[0054] (1) Acquisition of Escherichia coli: centrifuge 40 mL of Escherichia coli bacteria liquid at 4000 rpm, 4° C., for 6 min. Wash twice with 30mL 1*PBS, centrifuge at 4000rpm, 4°C, 6min.
[0055] (2) Chemical cross-linking reaction: count the obtained Escherichia coli, 1х10 8 Add 1mL 1хphosphate buffer (pH7.8)+1% lysine-specific membrane-impermeable crosslinker (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide), the initial concentration of crosslinker is 20mM, the organic phase (dimethyl sulfoxide) sulfoxide): water phase=1:99, room temperature, reaction for 2h. Centrifuge at 3000rpm, 5min, 4°C, and remove the supernatant.
[0056] (3) Reduction and alkylation: Add the same volume of ammonium bicarbonate with a final concentration of 100 mM to terminate the cross-linking, and at the same time, it contains 25 mM tris(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine hydrochloride. Add iodoacetamide with a final concent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com